Business Motivation Model on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Business Motivation Model (BMM) in
The Business Motivation Model (BMM) in
The Business Motivation Model
Business Governance in a Volatile World, Release 1.3, Business Rules Group (2007)
by Birol Berkem, ''Journal of Object Technology'' vol.7, no.8– (2008)
The Business Motivation Model ''Business Governance in a Volatile World'', Release 1.3, September 2007
Business process Enterprise modelling
 The Business Motivation Model (BMM) in
The Business Motivation Model (BMM) in enterprise architecture
Enterprise architecture (EA) is a business function concerned with the structures and behaviours of a business, especially business roles and processes that create and use business data. The international definition according to the Federation of ...
provides a scheme and structure for developing, communicating, and managing business plan
A business plan is a formal written document containing the goals of a business, the methods for attaining those goals, and the time-frame for the achievement of the goals. It also describes the nature of the business, background information on ...
s in an organized manner. Specifically, the Business Motivation Model does all the following:
* identifies factors that motivate the establishing of business plans;
* identifies and defines the elements of business plans; and
* indicates how all these factors and elements inter-relate.
History
Initially developed by the Business Rules Group (BRG), in September 2005, theObject Management Group
The Object Management Group (OMG®) is a computer industry Standards Development Organization (SDO), or Voluntary Consensus Standards Body (VCSB). OMG develops enterprise integration and modeling standards for a range of technologies.
Busin ...
(OMG) voted to accept the Business Motivation Model as the subject of a Request for Comment (RFC). This meant that the OMG was willing to consider the Business Motivation Model as a specification to be adopted by the OMG, subject to comment from any interested parties. Adoption as an OMG specification carries the intention that the Business Motivation Model would, in time, be submitted to the International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ; ; ) is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries.
M ...
(ISO) as a standard.
In August 2008 version 1.0 was released by OMG.
In May 2015, version 1.3 of BMM specification was released and as of May 2015 it is the latest stable release.
Elements
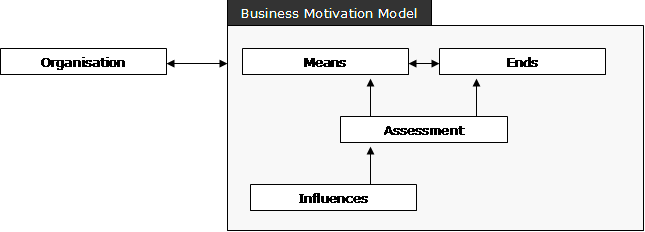
“BMM captures business requirements across different dimensions to rigorously capture and justify why the business wants to do something, what it is aiming to achieve, how it plans to get there, and how it assesses the result.” The main elements of BMM are: * Ends: ''What'' (as opposed to ''how'') the business wants to accomplish * Means: ''How'' the business intends to accomplish its ''ends'' * Directives: The ''rules'' and ''policies'' that ''constrain'' or ''govern'' the available means * Influencers: Can cause changes that affect the organization in its employment of its means or achievement of its ends. Influencers are ''neutral'' by definition. * Assessment: A ''judgment'' of an Influencer that influences the organization's ability to achieve its ends or use its means.Referenced
standards
*Semantics of Business Vocabulary and Business Rules
The Semantics of Business Vocabulary and Business Rules (SBVR) is an adopted standard of the Object Management Group (OMG) intended to be the basis for formal and detailed natural language declarative description of a complex entity, such as a bus ...
(SBVR)
Other related frameworks are:
* POLDAT
* Zachman Framework
The Zachman Framework is a structured tool used in enterprise architecture to organize and understand complex business systems. It acts as an Ontology (information science), ontology, providing a clear and formal way to describe an enterprise th ...
*Business framework
See also
*Business model
A business model describes how a Company, business organization creates, delivers, and captures value creation, value,''Business Model Generation'', Alexander Osterwalder, Yves Pigneur, Alan Smith, and 470 practitioners from 45 countries, self-pub ...
* i*
* Motivation
Motivation is an mental state, internal state that propels individuals to engage in goal-directed behavior. It is often understood as a force that explains why people or animals initiate, continue, or terminate a certain behavior at a particul ...
* Strategy Markup Language
{{primary sources, date=April 2017
Strategy Markup Language (StratML) is an XML-based standard vocabulary and schema for the information commonly contained in strategic and performance plans and reports. StratML Part 1 specifies the elements of st ...
References
Further reading
* * * * *External links
{{Commons categoryThe Business Motivation Model
Business Governance in a Volatile World, Release 1.3, Business Rules Group (2007)
by Birol Berkem, ''Journal of Object Technology'' vol.7, no.8– (2008)
The Business Motivation Model ''Business Governance in a Volatile World'', Release 1.3, September 2007
Business process Enterprise modelling