Buschke–Ollendorff Syndrome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Buschke–Ollendorff syndrome (BOS) is a rare genetic skin disorder associated with
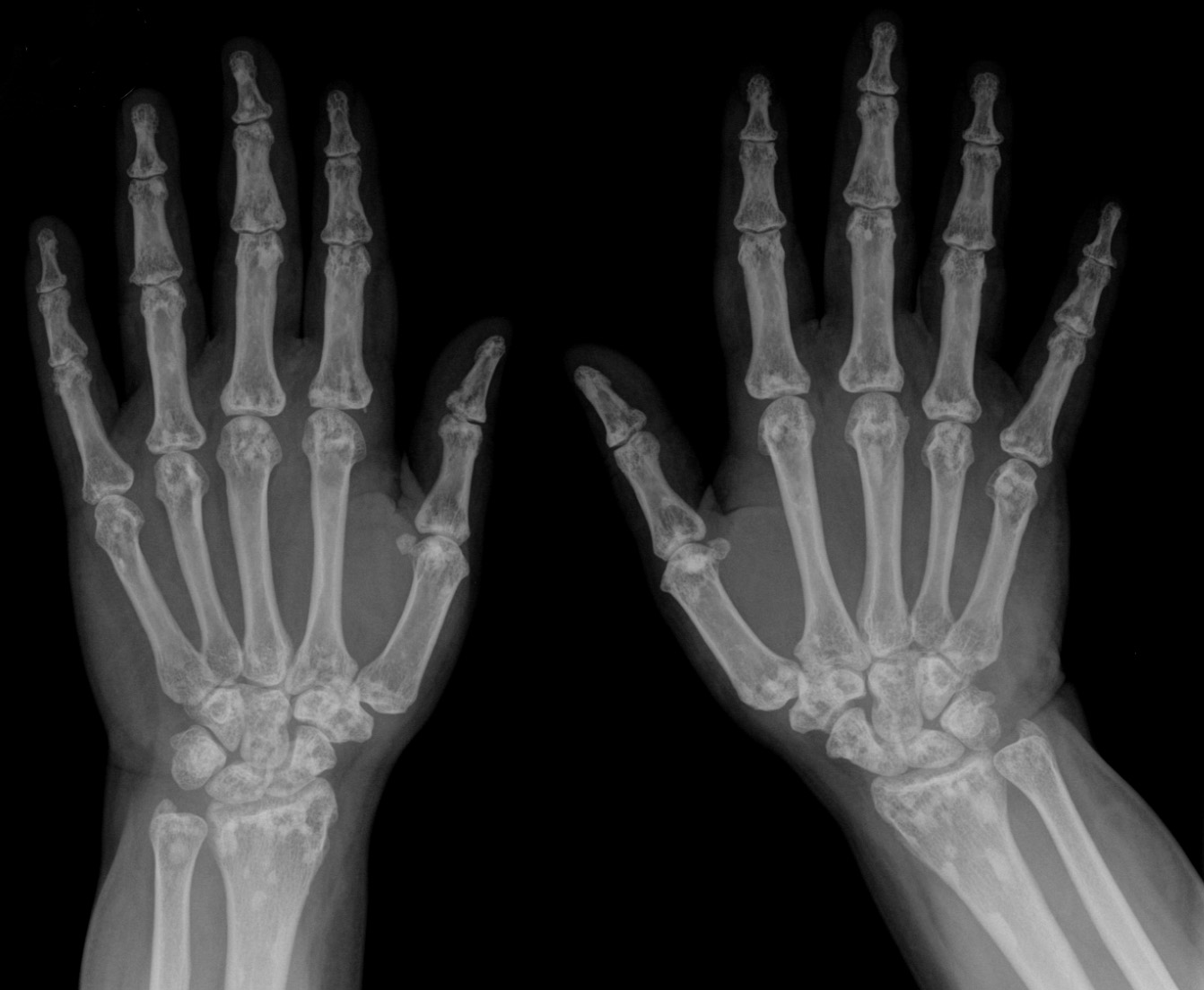 The signs and symptoms of this condition are consistent with the following (possible complications include
The signs and symptoms of this condition are consistent with the following (possible complications include

 The diagnosis of this condition can be ascertained via several techniques one such method is
The diagnosis of this condition can be ascertained via several techniques one such method is
LEMD3
LEM domain-containing protein 3 (LEMD3), also known as MAN1, is an integral protein in the inner nuclear membrane (INM) of the nuclear envelope. It is encoded by the ''LEMD3'' gene and was first identified after it was isolated from the serum of ...
that typically presents with widespread painless papules
A papule is a small, well-defined bump in the skin. It may have a rounded, pointed or flat top, and may have a dip. It can appear with a stalk, be thread-like or look warty. It can be soft or firm and its surface may be rough or smooth. Some ...
.
It is inherited in an autosomal
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosome ...
dominant manner. Conditions that may appear similar include tuberous sclerosis
Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) is a rare multisystem autosomal dominant genetic disease that causes non-cancerous tumours to grow in the brain and on other vital organs such as the kidneys, heart, liver, eyes, lungs and skin. A combinatio ...
, pseudoxanthoma elasticum
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) is a genetic disease that causes mineralization of elastic fibers in some tissues. The most common problems arise in the skin and eyes, and later in blood vessels in the form of premature atherosclerosis. PXE is cau ...
, neurofibroma
A neurofibroma is a benign nerve-sheath tumor in the peripheral nervous system. In 90% of cases, they are found as stand-alone tumors (solitary neurofibroma, solitary nerve sheath tumor or sporadic neurofibroma), while the remainder are found in ...
, and lipoma
A lipoma is a benign tumor made of adipose tissue, fat tissue. They are generally soft to the touch, movable, and painless. They usually occur just under the skin, but occasionally may be deeper. Most are less than in size. Common locations inc ...
, among others.
Its frequency is almost 1 case per every 20,000 people, and it is equally found in both males and females. It is named for Abraham Buschke and Helene Ollendorff Curth
Helene Ollendorff Curth (28 February 1899 – 17 June 1982) was a German-American dermatologist, known for her studies on acanthosis nigricans (AN) and introducing Curth's criteria, a set of characteristics for associating skin signs as markers ...
, who described the condition in one female in 1928.
Signs and symptoms
 The signs and symptoms of this condition are consistent with the following (possible complications include
The signs and symptoms of this condition are consistent with the following (possible complications include aortic stenosis
Aortic stenosis (AS or AoS) is the narrowing of the exit of the left ventricle of the heart (where the aorta begins), such that problems result. It may occur at the aortic valve as well as above and below this level. It typically gets worse o ...
and hearing loss
Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to acquire spo ...
):
:::::::*Osteopoikilosis
Osteopoikilosis is a benign, autosomal dominant, sclerosing (hardening) dysplasia of bone characterized by the presence of numerous bone islands in the skeleton.
Presentation
The radiographic appearance of osteopoikilosis on an X-ray is charact ...
:::::::*Bone pain
:::::::*Connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesod ...
nevi
:::::::*Metaphysis
The metaphysis (: metaphyses) is the neck portion of a long bone between the epiphysis and the diaphysis. It contains the growth plate, the part of the bone that grows during childhood, and as it grows it ossifies near the diaphysis and the ep ...
abnormality
Pathogenesis
Buschke–Ollendorff syndrome is caused by one important factor: mutations in the LEMD3 gene. Among the important aspects of Buschke–Ollendorff syndrome condition, genetically speaking are: * LEMD3 (protein) referred also asMAN1
LEM domain-containing protein 3 (LEMD3), also known as MAN1, is an integral protein in the inner nuclear membrane (INM) of the nuclear envelope. It is encoded by the ''LEMD3'' gene and was first identified after it was isolated from the serum of ...
, is an important protein in inner nuclear membrane
The nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane, is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes that in eukaryotic cells surround the nucleus, which encloses the genetic material.
The nuclear envelope consists of two lipid bilayer membranes ...
.
* LEMD3 gene gives instructions for producing protein that controls signaling for transforming growth factor-beta
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is a multifunctional cytokine belonging to the transforming growth factor superfamily that includes three different mammalian isoforms (TGF-β 1 to 3, HGNC symbols TGFB1, TGFB2, TGFB3) and many other signa ...
.
* LEMD3 gene helps in the bone morphogenic protein
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are a group of growth factors also known as cytokines and as metabologens. Professor Marshall Urist and Professor Hari Reddi discovered their ability to induce the formation of bone and cartilage, BMPs are now ...
pathway
* Both of the above pathways help grow new bone cells
An osteocyte, an oblate-shaped type of bone cell with dendritic processes, is the most commonly found cell in mature bone. It can live as long as the organism itself. The adult human body has about 42 billion of them. Osteocytes do not divide and ...
* BMP and TGF-β pathways controls SMADs proteins, which then bind to DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
* LEMD3 once mutated, causes a reduction of the protein, which in turn causes excess of the above two pathways.
Diagnosis

 The diagnosis of this condition can be ascertained via several techniques one such method is
The diagnosis of this condition can be ascertained via several techniques one such method is genetic testing
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, or ...
, as well as:
* X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
* Ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
* Histological test
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for an individual believed to have Buschke–Ollendorff syndrome is the following: *Melorheostosis
Melorheostosis is a medical developmental disorder and mesenchymal dysplasia in which the bony cortex widens and becomes hyperdense in a sclerotomal distribution. The condition begins in childhood and is characterized by thickening of the bones. ...
* Sclerotic bone metastases
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, ...
.
Treatment
In terms of the treatment of Buschke–Ollendorff syndrome, should the complication ofaortic stenosis
Aortic stenosis (AS or AoS) is the narrowing of the exit of the left ventricle of the heart (where the aorta begins), such that problems result. It may occur at the aortic valve as well as above and below this level. It typically gets worse o ...
occur then surgery may be required.
Treatment for hearing loss may also require surgical intervention.
See also
*List of cutaneous conditions
Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the Human body, body and composed of Human skin, skin, hair, Nail (anatomy), nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function o ...
References
Further reading
* *External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Buschke-Ollendorff syndrome Autosomal dominant disorders Syndromes Dermal and subcutaneous growths Cytoskeletal defects Rare syndromes