Bugatti Type 32 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Bugatti Type 32, commonly called the Tank de Tours, was a streamlined racing car built in 1923. It was built to compete in the
French Grand Prix, which was held on July 2 in Tours on the same year.
The nickname of the car comes from its particular shape, which resembles battle tanks of its era, as well as the location of the Grand Prix. Another Bugatti model that earned the nickname "Tank" for its design and aerodynamics was the 57G Tank from 1936.
 Designed especially for the
Designed especially for the
Schöberbergrennen
Type 32 was replaced by the brand's most successful model in racing, the
Overview
 Designed especially for the
Designed especially for the 1923 French Grand Prix
The 1923 French Grand Prix (formally the XVII Grand Prix de l'Automobile Club de France) was a Grand Prix motor race held at Tours on 2 July 1923. The race was run over 35 laps of the 22.83 km circuit for a total distance of just under 800 ...
in Tours, this original car by Ettore Bugatti
Ettore Arco Isidoro Bugatti (15 September 1881 – 21 August 1947) was an Italian-born French automobile designer and manufacturer. He is remembered as the founder and proprietor of the automobile manufacturing company Automobiles E. Bugatti, wh ...
was designed to be simple and quickly assembled.
The first prototype with an aerodynamic aluminium body was built in six months around the 1,991cc in-line 8-cylinder engine used in prior Bugatti Type 30. The engine rated 90 hp for the competition and weighted for approximately 650 kg.
Design
Compared to the previous competition model, the Type 29. the Type 32 only shared the motorization with the previous model. Type 32 was small in size, with a wheelbase of 1,994m, like theBugatti Type 13
The Bugatti Type 13 was the first true Bugatti car. Production of the Type 13, and later Types 15, 17, 22, and 23, began with the company's founding in 1910 and lasted through 1920, with 435 examples produced. Most road cars used an eight-valve ...
. 5 models of Type 32 were produced. In addition to the prototype, four racing capable cars were made,
Each model came with the 2.0 L (1991 cc/121 in³) straight-8
The straight-eight engine (also referred to as an inline-eight engine; abbreviated I8 or L8) is a piston engine with eight cylinders arranged in a straight line along the crankshaft. The number of cylinders and perfect primary and secondary eng ...
engine based on that in the Type 30.
It was a longitudinal engine with 8 cylinders in line and 5 five bearings with main bearings on the crankshaft. It had 3 valves per cylinder, two intake and one discharge, operated by a single camshaft
Brakes hydraulically actuated at the front and mechanically actuated (metal cable) at the rear.
The Type 32 was the first Bugatti
Automobiles Ettore Bugatti was a German then French manufacturer of high-performance automobiles. The company was founded in 1909 in the then- German city of Molsheim, Alsace, by the Italian-born industrial designer Ettore Bugatti. The ca ...
to be fitted with roller-bearing big ends in order to improve the bottom-end reliability.
The Type 32 also broke new ground (for a racing Bug) by using a three-speed and reverse transaxle unit, the exceptionally short wheelbase and long straight-8 engine making a conventional gearbox difficult to accommodate. It also heralded a hydraulic front brake actuation.
Despite the low center of gravity, its grip on the road was not good. The reason for this was due to its aerodynamics being similar to that of a wing profile, which meant that the vehicle could tend to rise at high speeds. Also, its short wheelbase contributed to the problem.
Specifications
* Track: 41.4 in (1052 mm) * Power: 90 hp (67 kW)Racing and legacy
4 race-capable cars were built for the1923 French Grand Prix
The 1923 French Grand Prix (formally the XVII Grand Prix de l'Automobile Club de France) was a Grand Prix motor race held at Tours on 2 July 1923. The race was run over 35 laps of the 22.83 km circuit for a total distance of just under 800 ...
. The following Type 32 participated at the Tours race:
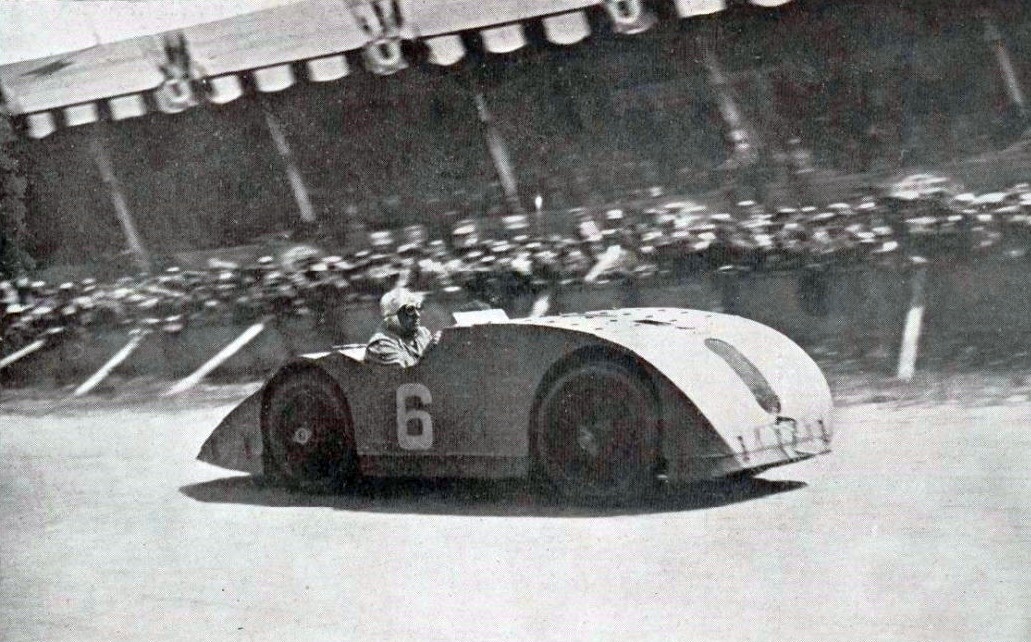
* No. 6, with Ernest Friderich
Ernest Friderich (23 October 1886 Paris – 22 January 1954 Nice) was a French racecar driver
Auto racing (also known as car racing, motor racing, or automobile racing) is a motorsport involving the racing of automobiles for competitio ...
, who finished third at the finish
* No. 18, driven by the Prince of Cystria, retired on lap 12
* No. 11, driven by Pierre de Vizcaya, retired at the start after an accident
* No. 16, driven by Pierre Marco, retired on the third lap3
During the race, the Type 32 reached the top speed of 180 km / h on the main straight. The French GP was Type 32's only GP race. However, for example the No. 6 (chassis No. 4059) was acquired by Mr. Junek from Czechoslovakia, who was racing with the car for the rest of 1923 and won for example the 3rd hill climSchöberbergrennen
Type 32 was replaced by the brand's most successful model in racing, the
Bugatti Type 35
The Bugatti Type 35 was the most successful of the Bugatti racing models. Its version of the Bugatti arch-shaped radiator that had evolved from the more architectural one of the Bugatti Type 13 Brescia, was to become the one that the marque is ...
.
Another tank-bodied Bugatti racer, the 1936 Type 57G, was much more successful.
Notes
References
{{Bugatti road car timeline 32 Grand Prix cars