Bucket-brigade Device on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A bucket brigade or bucket-brigade device (BBD) is a discrete-time analogue delay line, developed in 1969 by F. Sangster and K. Teer of the Philips Research Labs in the 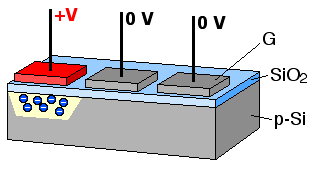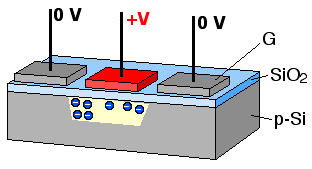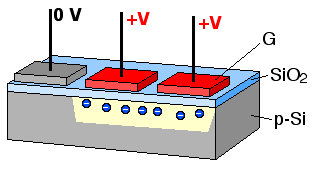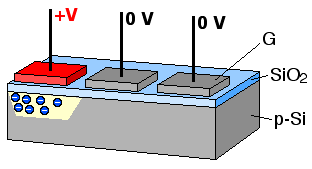 The concept of the bucket-brigade device led to the
The concept of the bucket-brigade device led to the
Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
. It consists of a series of capacitance
Capacitance is the ability of an object to store electric charge. It is measured by the change in charge in response to a difference in electric potential, expressed as the ratio of those quantities. Commonly recognized are two closely related ...
sections C0 to Cn. The stored analogue signal is moved along the line of capacitor
In electrical engineering, a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term st ...
s, one step at each clock cycle
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') is an electronic logic signal (voltage or current) which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and ...
. The name comes from analogy with the term bucket brigade
A bucket brigade or human chain is a method for transporting items where items are passed from one (relatively stationary) person to the next.
The method was important in firefighting before the advent of hand-pumped fire engines, whereby fire ...
, used for a line of people passing buckets of water.
In most signal processing applications, bucket brigades have been replaced by devices that use digital signal processing
Digital signal processing (DSP) is the use of digital processing, such as by computers or more specialized digital signal processors, to perform a wide variety of signal processing operations. The digital signals processed in this manner are a ...
, manipulating samples in digital form. Bucket brigades still see use in specialty applications, such as guitar effects.
A well-known integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
device around 1976, the Reticon SAD-1024 implemented two 512-stage analog delay lines in a 16-pin DIP. It allowed clock frequencies ranging from 1.5 kHz to more than 1.5 MHz. The SAD-512 was a single delay line version. The Philips Semiconductors TDA1022 similarly offered a 512-stage delay line but with a clock rate range of 5–500 kHz. Other common BBD chips include the Panasonic MN3002, MN3005, MN3007, MN3204 and MN3205, with the primary differences being the available delay time. Some examples effects units utilizing Panasonic BBDs are the Boss CE-1 Chorus Ensemble and the Yamaha E1010.
In 2009, the guitar effects pedal manufacturer Visual Sound recommissioned production of the Panasonic-designed MN3102 and MN3207{{Cite web, title =MN3207 1024-Stage Low Voltage Operation Low Noise BBD, url =http://www.synthdiy.com/files/2003/MN3207.pdf, url-status =dead, archiveurl =https://web.archive.org/web/20100821042214/http://www.synthdiy.com/files/2003/MN3207.pdf, archivedate =2010-08-21 BBD chip.
Despite being analog in their representation of individual signal voltage samples, these devices are discrete in the time domain and thus are limited by the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem
The Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem is an essential principle for digital signal processing linking the frequency range of a signal and the sample rate required to avoid a type of distortion called aliasing. The theorem states that the sample r ...
; both the input and output signals are generally low-pass filter
A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The exact frequency response of the filter depends on the filt ...
ed. The input must be low-pass filtered to avoid aliasing
In signal processing and related disciplines, aliasing is a phenomenon that a reconstructed signal from samples of the original signal contains low frequency components that are not present in the original one. This is caused when, in the ori ...
effects, while the output is low-pass filtered for reconstruction. (A low-pass is used as an approximation to the Whittaker–Shannon interpolation formula.)
 The concept of the bucket-brigade device led to the
The concept of the bucket-brigade device led to the charge-coupled device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a ...
(CCD) developed by Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, commonly referred to as ''Bell Labs'', is an American industrial research and development company owned by Finnish technology company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, Murray Hill, New Jersey, the compa ...
for use in digital cameras. The idea of using capacitors to retain a voltage state has older origins and separately led to dynamic random-access memory
Dynamics (from Greek language, Greek δυναμικός ''dynamikos'' "powerful", from δύναμις ''dynamis'' "power (disambiguation), power") or dynamic may refer to:
Physics and engineering
* Dynamics (mechanics), the study of forces and t ...
, where the charges are not propagated, but refreshed, in place.
See also
* Switched capacitorReferences