Brook trout on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The brook trout (''Salvelinus fontinalis'') is a
 The brook trout produces hybrids both with its congeners the
The brook trout produces hybrids both with its congeners the

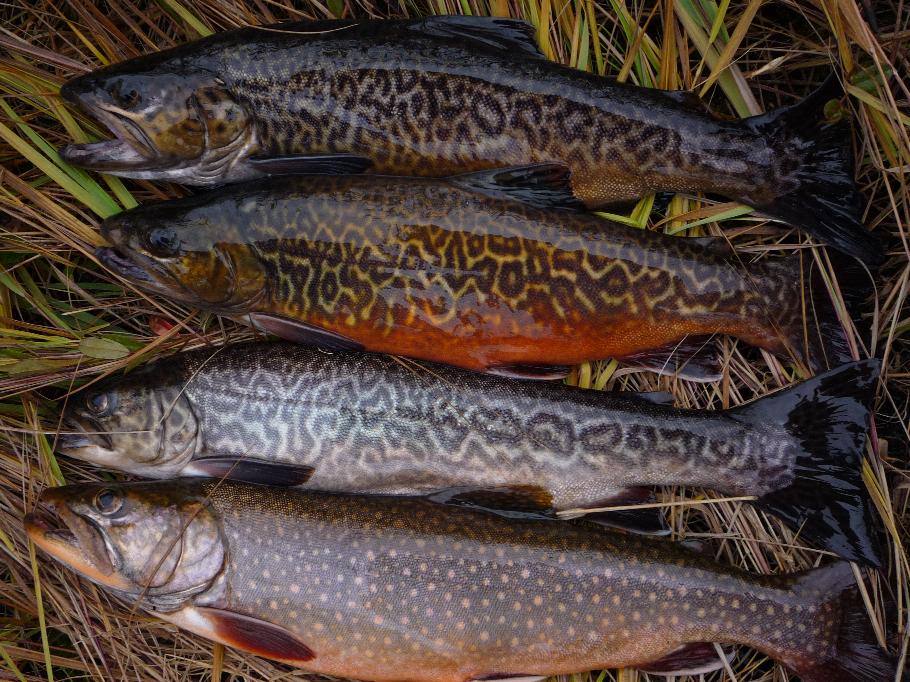
 The brook trout has a dark green to brown color, with a distinctive marbled pattern (called vermiculation) of lighter shades across the flanks and back and extending at least to the
The brook trout has a dark green to brown color, with a distinctive marbled pattern (called vermiculation) of lighter shades across the flanks and back and extending at least to the
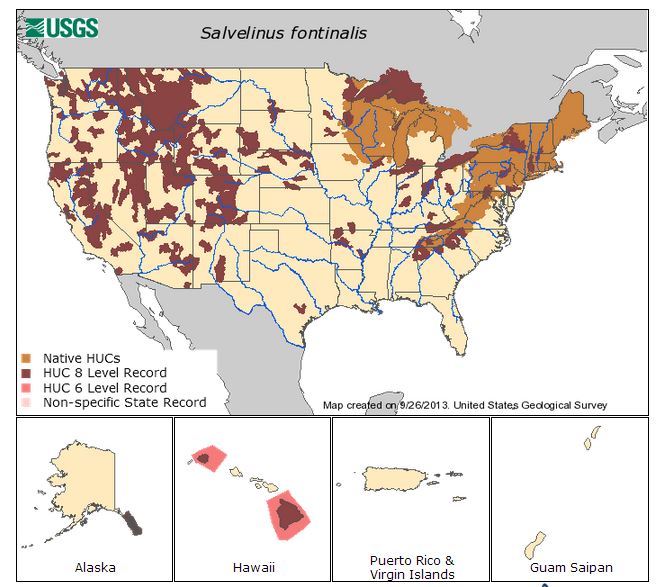
 Brook trout are native to a wide area of Eastern
Brook trout are native to a wide area of Eastern
 The brook trout inhabits large and small
The brook trout inhabits large and small

 Since the 1800s, brook trout populations have been grown by artificial propagation and
Since the 1800s, brook trout populations have been grown by artificial propagation and
species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
of freshwater fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
in the char genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
''Salvelinus
''Salvelinus'' is a genus of Salmonidae, salmonid fish often called char or charr; some species are called "trout". ''Salvelinus'' is a member of the subfamily Salmoninae within the family Salmonidae. The genus has a northern circumpolar distrib ...
'' of the salmon
Salmon (; : salmon) are any of several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the genera ''Salmo'' and ''Oncorhynchus'' of the family (biology), family Salmonidae, native ...
family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
Salmonidae
Salmonidae (, ) is a family (biology), family of ray-finned fish, the only extant member of the suborder Salmonoidei, consisting of 11 extant genera and over 200 species collectively known as "salmonids" or "salmonoids". The family includes salmo ...
native to Eastern North America in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
. Two ecological forms of brook trout have been recognized by the US Forest Service. One ecological form is long-lived potamodromous populations in Lake Superior
Lake Superior is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. Lake Michigan–Huron has a larger combined surface area than Superior, but is normally considered tw ...
known as coaster trout or coasters. The second ecological form is the short-living predaceous anadromous populations which are found in northern lakes and coastal rivers from Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated continental island in southeastern New York (state), New York state, extending into the Atlantic Ocean. It constitutes a significant share of the New York metropolitan area in both population and land are ...
to Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay, sometimes called Hudson's Bay (usually historically), is a large body of Saline water, saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of . It is located north of Ontario, west of Quebec, northeast of Manitoba, and southeast o ...
, which are referred to as salters. In parts of its range, it is also known as the eastern brook trout, speckled trout, brook char (or charr), squaretail, brookie, or mud trout, among others. Adult coaster brook trout are capable of reaching sizes over 2'' ''feet in length and weigh up to 6.8'' ''kg (15'' ''lb), whereas adult salters average between 6 and 15'' ''inches in length and weigh between 0.5 and 2.3'' ''kg (1 and 5'' ''lb). The brook trout is characterized by its distinctive olive-green body with yellow and blue-rimmed red spots, white and black edged orange fins, and dorsal
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ‘back’) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
The fus ...
vermiculation. The diet of the brook trout is restrictive to the season and location of the fish, but will typically consist of terrestrial and aquatic insect
Aquatic insects or water insects live some portion of their life cycle in the water. They feed in the same ways as other insects. Some ''diving'' insects, such as predatory diving beetles, can hunt for food underwater where land-living insects ...
s, fry, crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s, zooplankton, and worm
Worms are many different distantly related bilateria, bilateral animals that typically have a long cylindrical tube-like body, no limb (anatomy), limbs, and usually no eyes.
Worms vary in size from microscopic to over in length for marine ...
s.
Throughout history, non-native brook trout have been transplanted beyond its native borders, where it has spread across North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
and much of the world. These brook trout have been introduced since the 1800s by means of artificial propagation and aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. Nelu ...
in hope of promoting fishery resources. Through this transplantation, brook trout have been observed to affect native populations by outcompeting, preying upon, and hybridizing with many native aquatic species. This invasive nature via human-mediated introductory has led to their classification in the list of the top 100 globally invasive species.
Since the 19th century, isolated native eastern brook trout populations have faced extirpation
Local extinction, also extirpation, is the termination of a species (or other taxon) in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with extinction, global extinctions.
Local extinctions ...
due to stream pollution, habitat destruction
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease ...
, invasive species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native spec ...
, and waterway damming. Although facing these pressures, the brook trout is not listed as an endangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the stat ...
, but native population decline has been observed.
Taxonomy
The scientific name of the brook trout is ''Salvelinus fontinalis''. Initially, the brook trout was scientifically described as ''Salmo fontinalis'' by the naturalist Samuel Latham Mitchill in 1814. The species was later moved to the char genus ''Salvelinus
''Salvelinus'' is a genus of Salmonidae, salmonid fish often called char or charr; some species are called "trout". ''Salvelinus'' is a member of the subfamily Salmoninae within the family Salmonidae. The genus has a northern circumpolar distrib ...
'', which in North America also includes the lake trout
The lake trout (''Salvelinus namaycush'') is a freshwater Salvelinus, char living mainly in lakes in Northern North America. Other names for it include mackinaw, namaycush, lake char (or charr), touladi, togue, laker, and grey trout. In Lake Sup ...
, bull trout, Dolly Varden, and the Arctic char
The Arctic char or Arctic charr (''Salvelinus alpinus'') is a cold-water fish in the family Salmonidae, native to alpine lakes, as well as Arctic and subarctic coastal waters in the Holarctic realm, Holarctic.
Distribution and habitat
It Spaw ...
. The specific epithet "''fontinalis''" comes from the Latin for "of a spring or fountain", in reference to the clear, cold streams and ponds in its native habitat.
Subspecies
There is little recognized systematic substructure in the brook trout, but the two subspecies have been proposed. The aurora trout (''S. f. timagamiensis'') is a subspecies native to two lakes in the Temagami District ofOntario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
, Canada. The silver trout (''S. agassizii'' or ''S. f. agassizii)'' is an extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
trout species or subspecies last seen in Dublin Pond, New Hampshire
New Hampshire ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
, in 1930. It is considered by fisheries biologist Robert J. Behnke as a highly specialized form of brook trout.
Hybrids
 The brook trout produces hybrids both with its congeners the
The brook trout produces hybrids both with its congeners the lake trout
The lake trout (''Salvelinus namaycush'') is a freshwater Salvelinus, char living mainly in lakes in Northern North America. Other names for it include mackinaw, namaycush, lake char (or charr), touladi, togue, laker, and grey trout. In Lake Sup ...
(S.'' namaycush'') and the Arctic char
The Arctic char or Arctic charr (''Salvelinus alpinus'') is a cold-water fish in the family Salmonidae, native to alpine lakes, as well as Arctic and subarctic coastal waters in the Holarctic realm, Holarctic.
Distribution and habitat
It Spaw ...
(''S. alpinus''), and intergeneric hybrids with the brown trout (''Salmo trutta'').
The splake is an intrageneric hybrid between the brook trout and lake trout
The lake trout (''Salvelinus namaycush'') is a freshwater Salvelinus, char living mainly in lakes in Northern North America. Other names for it include mackinaw, namaycush, lake char (or charr), touladi, togue, laker, and grey trout. In Lake Sup ...
(''S. namaycush''). Although uncommon in nature, they are artificially propagated in substantial numbers for stocking into brook trout or lake trout habitats. Although they are fertile, back-crossing in nature is behaviorally problematic and very little natural reproduction occurs. Splake grow more quickly than brook trout, become piscivorous
A piscivore () is a carnivorous animal that primarily eats fish. Fish were the diet of early tetrapod evolution (via water-bound amphibians during the Devonian period); insectivory came next; then in time, the more terrestrially adapted rept ...
sooner, and are more tolerant of competitors than brook trout.
The tiger trout is an intergeneric hybrid between the brook trout and the brown trout. Tiger trout rarely occur naturally but are sometimes artificially propagated. Such crosses are almost always reproductively sterile. They are popular with many fish-stocking programs because they can grow quickly, and may help keep coarse fish (wild non "sport" fish) populations in check due to their highly piscivorous (fish-eating) nature.
The sparctic char is an intrageneric hybrid between the brook trout and the Arctic char.
Ecological forms
The US Forest Service has recognized two ecological forms of brook trout, salters and coasters. The forms express the same general features but vary in size, behavior, and location.Coasters
A potamodromous population of brook trout native to lacustrine regions, which migrate into tributary rivers to spawn, are called "coasters". Coasters tend to be larger than most other populations of brook trout, often reaching 6 to 7 lb (2.7 to 3.2 kg) in size. They also commonly live for longer periods of time and exhibit more predacious behavior than their counterparts. Many coaster populations have been severely reduced byoverfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing Fish stocks, fish stock), resu ...
and habitat loss by the construction of hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energ ...
power dams on Lake Superior tributaries. In Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
, Michigan
Michigan ( ) is a peninsular U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, Upper Midwestern United States. It shares water and land boundaries with Minnesota to the northwest, Wisconsin to the west, ...
, and Minnesota
Minnesota ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Upper Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Manitoba and Ontario to the north and east and by the U.S. states of Wisconsin to the east, Iowa to the so ...
efforts are underway to restore and recover coaster populations.
Salters
When Europeans first settled in Eastern North America, semi- anadromous or sea-run brook trout, commonly called "salters", ranged from southernNew Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
, north throughout the Canadian maritime provinces, and west to Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay, sometimes called Hudson's Bay (usually historically), is a large body of Saline water, saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of . It is located north of Ontario, west of Quebec, northeast of Manitoba, and southeast o ...
. Salters are a short-lived form of brook trout that inhabit smaller bodies of water and exhibit less predacious behavior than coasters. They may spend up to three months at sea feeding on crustaceans, fish, and marine worms in the spring. During this time they won't stray more than a few miles from the river mouth, but then return to freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include non-salty mi ...
tributaries
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream ('' main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which the ...
to spawn in the late summer or autumn. While in saltwater, salters gain a more silvery color, losing much of the distinctive markings seen in freshwater. However, within two weeks of returning to freshwater, they assume typical brook trout color and markings. Salters have faced threats such as habitat destruction
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease ...
, water pollution
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of Body of water, water bodies, with a negative impact on their uses. It is usually a result of human activities. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and ...
, and water way damming that have led to their declining population numbers across the Northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States (also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast) is List of regions of the United States, census regions United States Census Bureau. Located on the East Coast of the United States, ...
.
Description

 The brook trout has a dark green to brown color, with a distinctive marbled pattern (called vermiculation) of lighter shades across the flanks and back and extending at least to the
The brook trout has a dark green to brown color, with a distinctive marbled pattern (called vermiculation) of lighter shades across the flanks and back and extending at least to the dorsal fin
A dorsal fin is a fin on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates. Dorsal fins have evolved independently several times through convergent evolution adapting to marine environments, so the fins are not all homologous. They are found ...
, and often to the tail. A distinctive sprinkling of red dots, surrounded by blue halos, occurs along the flanks. The belly and lower fins are reddish in color, the latter with white leading edges. Often, the belly, particularly of the males, becomes very red or orange when the fish are spawning. Typical lengths of the brook trout vary from , and weights from . The maximum recorded length is and maximum weight . Brook trout can reach at least seven years of age, with reports of 15-year-old specimens observed in California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
habitats to which the species has been introduced. Growth rates are dependent on season, age, water and ambient air temperatures, and flow rates. In general, flow rates affect the rate of change in the relationship between temperature and growth rate. For example, in spring, growth increased with temperature at a faster rate with high flow rates than with low flow rates.
Range and habitat
 Brook trout are native to a wide area of Eastern
Brook trout are native to a wide area of Eastern North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
, but are increasingly confined to higher elevations southward in the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a mountain range in eastern to northeastern North America. The term "Appalachian" refers to several different regions associated with the mountain range, and its surrounding terrain ...
to northern Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
and northwest South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
, Canada from the Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay, sometimes called Hudson's Bay (usually historically), is a large body of Saline water, saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of . It is located north of Ontario, west of Quebec, northeast of Manitoba, and southeast o ...
basin east, the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
–Saint Lawrence
Saint Lawrence or Laurence (; 31 December 225 – 10 August 258) was one of the seven deacons of the city of Rome under Pope Sixtus II who were martyred in the Persecution of Christians, persecution of the Christians that the Roman Empire, Rom ...
system, the Canadian maritime provinces, and the upper Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
drainage as far west as eastern Iowa
Iowa ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the upper Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west; Wisconsin to the northeast, Ill ...
. Their southern historic native range has been drastically reduced, with fish being restricted to higher-elevation, remote streams due to habitat loss and introductions of brown and rainbow trout. As early as 1850, the brook trout's range started to extend west from its native range through introductions. The brook trout was eventually introduced into suitable habitats throughout the western U.S. during the late 19th and early 20th centuries at the behest of the American Acclimatization Society and by private, state, and federal fisheries authorities. Acclimatization movements in Europe, South America, and Oceania resulted in brook trout introductions throughout Europe, in Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
, and New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
. Although not all introductions were successful, a great many established wild, self-sustaining populations of brook trout in non-native waters.
Habitat
 The brook trout inhabits large and small
The brook trout inhabits large and small lake
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from ...
s, river
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of ...
s, stream
A stream is a continuous body of water, body of surface water Current (stream), flowing within the stream bed, bed and bank (geography), banks of a channel (geography), channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a strea ...
s, creeks, and spring pond
A pond is a small, still, land-based body of water formed by pooling inside a depression (geology), depression, either naturally or artificiality, artificially. A pond is smaller than a lake and there are no official criteria distinguishing ...
s in cold temperate climate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (approximately 23.5° to 66.5° N/S of the Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ra ...
s with mild precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
. Clear spring water with adequate cover and moderate flow rates is indicative of strong habitability for brook trout. They exhibit high levels of adaptability when exposed to habitat changes from environmental effects, and have been observed to exhibit more resilience to habitat
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ...
change than other ''Salvelinus
''Salvelinus'' is a genus of Salmonidae, salmonid fish often called char or charr; some species are called "trout". ''Salvelinus'' is a member of the subfamily Salmoninae within the family Salmonidae. The genus has a northern circumpolar distrib ...
'' species. The typical pH range of brook trout waters is 5.0 to 7.5, with pH extremes of 3.5 to 9.8 possible. Water temperatures typically range from . Warm summer temperatures and low flow rates are stressful on brook trout populations—especially larger fish.
Ecology and reproduction
Diet
Brook trout have a diverse diet that includeslarva
A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life stage. Animals with indirect development such as insects, some arachnids, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase ...
l, pupa
A pupa (; : pupae) is the life stage of some insects undergoing transformation between immature and mature stages. Insects that go through a pupal stage are holometabolous: they go through four distinct stages in their life cycle, the stages th ...
l, adult forms of aquatic insects (typically caddisflies, stoneflies, mayflies, and aquatic dipterans), adult forms of terrestrial insects (typically ant
Ants are Eusociality, eusocial insects of the Family (biology), family Formicidae and, along with the related wasps and bees, belong to the Taxonomy (biology), order Hymenoptera. Ants evolved from Vespoidea, vespoid wasp ancestors in the Cre ...
s, beetle
Beetles are insects that form the Taxonomic rank, order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Holometabola. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 40 ...
s, grasshopper
Grasshoppers are a group of insects belonging to the suborder Caelifera. They are amongst what are possibly the most ancient living groups of chewing herbivorous insects, dating back to the early Triassic around 250 million years ago.
Grassh ...
s, and cricket
Cricket is a Bat-and-ball games, bat-and-ball game played between two Sports team, teams of eleven players on a cricket field, field, at the centre of which is a cricket pitch, pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two Bail (cr ...
s) that fall into the water, crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s, frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely semiaquatic group of short-bodied, tailless amphibian vertebrates composing the order (biology), order Anura (coming from the Ancient Greek , literally 'without tail'). Frog species with rough ski ...
s and other amphibians, mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
s, smaller fish, invertebrates, and even small aquatic mammals such as vole
Voles are small rodents that are relatives of lemmings and hamsters, but with a stouter body; a longer, hairy tail; a slightly rounder head; smaller eyes and ears; and differently formed molars (high-crowned with angular cusps instead of lo ...
s and sometimes other young brook trout.
Reproduction
The female constructs a depression in a location in thestream bed
A streambed or stream bed is the bottom of a stream or river and is confined within a Stream channel, channel or the Bank (geography), banks of the waterway. Usually, the bed does not contain terrestrial (land) vegetation and instead supports d ...
, sometimes referred to as a "redd", where groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
percolates upward through the gravel. One or more males approach the female, fertilizing the eggs as the female expresses them. Most spawning involve peripheral males, which directly influences the number of eggs that survive into adulthood. In general, the larger the number of peripheral males present, the more likely the eggs will be cannibalized. The eggs are slightly denser than water. The female then buries the eggs in a small gravel mound where they hatch in 4 to 6 weeks.
Life cycle
Following the deposition of up to 5,000 eggs in gravel beds by the female brook trout, the eggs enter an incubation period from the winter months to early spring. During thisincubation period
Incubation period (also known as the latent period or latency period) is the time elapsed between exposure to a pathogenic organism, a chemical, or ionizing radiation, radiation, and when symptoms and signs are first apparent. In a typical infect ...
, the eggs source oxygen from the stream that passes through the gravel beds and into their gel-like shells. The eggs will then successively hatch into miniature fry that rely upon their yolk
Among animals which produce eggs, the yolk (; also known as the vitellus) is the nutrient-bearing portion of the egg whose primary function is to supply food for the development of the embryo. Some types of egg contain no yolk, for example bec ...
sac for nutrients to compensate for the lack of nutrients provided by the parental trout during the early stages of development. In the ensuing stage of their life cycle, the fry will seek cover from predatory species in rock crevices and inlets. During this period of hiding, the trout will begin to mature into fingerlings by summer and start expressing parr marks to aid in camouflage. At this point, most brook trout will be between 2 and 3 inches in length. Finally, in succeeding months, the trout will fully mature into a trout that is approximately between 10 and 34 inches long and capable of spawning
Spawn is the Egg cell, eggs and Spermatozoa, sperm released or deposited into water by aquatic animals. As a verb, ''to spawn'' refers to the process of freely releasing eggs and sperm into a body of water (fresh or marine); the physical act is ...
in the fall months. These fully developed adult brook trout will express a vibrant olive-green back, cherry red underbelly, black accented fins, and wavy dorsal
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ‘back’) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
The fus ...
patterns. A typical adult brook trout will live to the age of 3 to 4 years old, with occasional brooks living to over the age of 4.
Angling
The brook trout is a popular game fish with anglers, particularly fly fishermen. Until it was displaced by introduced brown trout (1883) andrainbow trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributary, tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in North America and Asia. The steelhead (sometimes called steelhead trout) is an Fish migration#Classification, ...
(1875), the brook trout attracted the most attention of anglers from colonial times through the first 100 years of U.S. history. Sporting writers such as Genio Scott ''Fishing in American Waters'' (1869), Thaddeus Norris ''American Anglers Book'' (1864), Robert Barnwell Roosevelt ''Game Fish of North America'' (1864) and Charles Hallock ''The Fishing Tourist'' (1873) produced guides to the best-known brook trout waters in America. As brook trout populations declined in the mid-19th century near urban areas, anglers flocked to the Adirondacks
The Adirondack Mountains ( ) are a massif of mountains in Northeastern New York (state), New York which form a circular dome approximately wide and covering about . The region contains more than 100 peaks, including Mount Marcy, which is the hi ...
in upstate New York and the Rangeley lakes region in Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
to pursue brook trout. In July 1916 on the Nipigon River in northern Ontario, an Ontario physician, John W. Cook, caught a brook trout, which stands as the IGFA world record.
Today, many anglers practice catch-and-release tactics to preserve remaining populations. Organizations such as Trout Unlimited
Trout Unlimited (TU) is a US non-profit organization dedicated to the conservation of freshwater streams, rivers, and associated upland habitats for trout, salmon, other aquatic species, and people. It is headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. ...
have been at the forefront of efforts to institute air and water quality standards sufficient to protect the brook trout. Revenues derived from the sale of fishing licenses have been used to restore many sections of creeks and streams to brook trout habitat.
Record
The current world angling record brook trout was caught by Dr. W. J. Cook on the Nipigon River, Ontario, in July 1915. The trout weighed only because, at the time of weighing, it was badly decomposed after 21 days in the bush without refrigeration. A brook trout, caught in October 2006 in Manitoba, is not eligible for record status since it was released alive. This trout weighed about based on the accepted formula for calculating weight by measurements, and it currently stands as the record brook trout forManitoba
Manitoba is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population ...
.
Artificial propagation and aquaculture
 Since the 1800s, brook trout populations have been grown by artificial propagation and
Since the 1800s, brook trout populations have been grown by artificial propagation and aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. Nelu ...
. Artificial propagation in fish is the process by which eggs are inseminated, hatched, and grown in a controlled environment that minimizes unfavorable environmental pressures. The fish are then released into the wild when they have reached the appropriate age and size. This process was introduced as a way to counteract the effects of overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing Fish stocks, fish stock), resu ...
and aquatic habitat loss and to reinforce brook trout populations across the Northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States (also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast) is List of regions of the United States, census regions United States Census Bureau. Located on the East Coast of the United States, ...
. Hatchery rearing was also introduced to raise brook trout in large numbers for food production and sale for human consumption.
The process of artificial propagation in brook trout begins by decreasing the temperature of the adult trout's propagation tank to mimic the seasonal changes associated with brook trout spawning season. The acclimated trout are then collected, and the eggs are gently massaged out of the female trout into a collection vessel, and then inseminated with the milt of a male brook. Next, the inseminated eggs are strained of the milt and transferred to a jar for several weeks to develop into viable embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
s. Once the eggs have begun to hatch, the fry are transported into rearing tanks where they will grow and develop before their release into the wild. Their rearing tanks typically consist of large circular tanks with a constant water flow going through them to allow a current to circulate through the tank and keep it clean (some more elaborate systems operate on a re-circulation system where the water is filtered and reused). The fish are typically fed a pelleted food consisting of 40–50% protein and 15% fat made from fish oil, animal protein, plant protein and vitamins and minerals. Finally, once the fish have reached a viable size, around 2 inches in length, they are released into the wild.
This means of brook trout aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. Nelu ...
has sparked controversy due to potential decrease in the fishes fitness, adaptability, and environmental resilience, effectively posing a threat to native brook trout populations. Arguments against artificial propagation of brook trout claim that it can cause a degradation of the overall genetic pool due to the possibility of inbreeding
Inbreeding is the production of offspring from the mating or breeding of individuals or organisms that are closely genetic distance, related genetically. By analogy, the term is used in human reproduction, but more commonly refers to the genet ...
among individuals. This lack of genetic variation
Genetic variation is the difference in DNA among individuals or the differences between populations among the same species. The multiple sources of genetic variation include mutation and genetic recombination. Mutations are the ultimate sources ...
could lead to certain populations of brook trout to become extirpated
Local extinction, also extirpation, is the termination of a species (or other taxon) in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinctions.
Local extinctions mark a chan ...
from their deficiency in adaptability
Adaptability ( "fit to, adjust") is a feature of a system or of a process. This word has been put to use as a specialised term in different disciplines and in business operations. Word definitions of adaptability as a specialised term differ littl ...
.
Conservation status
As early as the late 19th century, native brook trout inNorth America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
became extirpated
Local extinction, also extirpation, is the termination of a species (or other taxon) in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinctions.
Local extinctions mark a chan ...
from many watercourses as land development, forest clear-cutting, and industrialization
Industrialisation (British English, UK) American and British English spelling differences, or industrialization (American English, US) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an i ...
took hold. Streams and creeks that were polluted, dammed, or silted up often became too warm to hold native brook trout, and were colonized by transplanted smallmouth bass and perch or other introduced salmonids such as brown and rainbow trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributary, tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in North America and Asia. The steelhead (sometimes called steelhead trout) is an Fish migration#Classification, ...
. The brown trout, a species not native to North America, has replaced the brook trout in much of the brook trout's native water. If already stressed by overharvesting
Overexploitation, also called overharvesting or ecological overshoot, refers to harvesting a renewable resource to the point of diminishing returns. Continued overexploitation can lead to the destruction of the resource, as it will be unable to ...
or by temperature, brook trout populations are very susceptible to damage by the introduction of exogenous species. Many lacustrine populations of brook trout have been extirpated by the introduction of other species, particularly percids, but sometimes other spiny-rayed fishes.
In addition to chemical pollution and algae growth caused by runoff containing chemicals and fertilizers, air pollution has also been a significant factor in the disappearance of brook trout from their native habitats. In the U.S., acid rain caused by air pollution has resulted in pH levels too low to sustain brook trout in all but the highest headwaters of some Appalachian streams and creeks. Brook trout populations across large parts of eastern Canada have been similarly challenged; a subspecies known as the aurora trout was extirpated from the wild by the effects of acid rain.
Organizations such as Trout Unlimited and Trout Unlimited Canada are partnering with other organizations such as the Southern Appalachian Brook Trout Foundation, the Eastern Brook Trout Joint Venture, and state, provincial, and federal agencies to undertake projects that restore native brook trout habitat and populations.
As an invasive species
Although brook trout populations are under stress in their native range, they are considered aninvasive species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native spec ...
where they have been introduced outside their historic native range. In the northern Rocky Mountains, non-native brook trout are considered a significant contributor to the decline or extirpation of native cutthroat trout (''Oncorhynchus clarki'') in headwater streams. Invasive brook trout populations may provoke territorial competition with the native cutthroat trout that can impede the recovery efforts of cutthroat trout by environmental agencies. Non-native brook trout populations have been subject to eradication programs in efforts to preserve native species. In Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park is a List of national parks of the United States, national park of the United States located in the northwest corner of Wyoming, with small portions extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U ...
, anglers may take an unlimited number of non-native brook trout in some watersheds. In the Lamar River watershed, a mandatory kill regulation for any brook trout caught is in effect. In Europe, introduced brook trout, once established, have had negative impacts on growth rates of native brown trout (''S. trutta'').
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * {{Authority control brook trout Freshwater fish of North America Fish of the Eastern United States Fish of the Great Lakes Ecology of the Appalachian Mountains Symbols of Michigan Symbols of Pennsylvania Symbols of New Hampshire Symbols of New Jersey Symbols of New York (state) Symbols of North Carolina Symbols of Vermont Symbols of Virginia Symbols of West Virginia brook trout brook trout