Bronchial Obstruction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
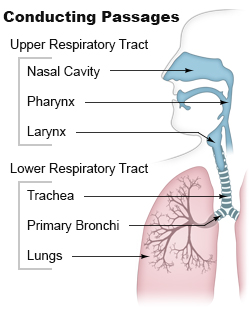 Airway obstruction is a blockage of
Airway obstruction is a blockage of
 With acute upper airway obstruction, respiratory distress can rapidly lead to
With acute upper airway obstruction, respiratory distress can rapidly lead to
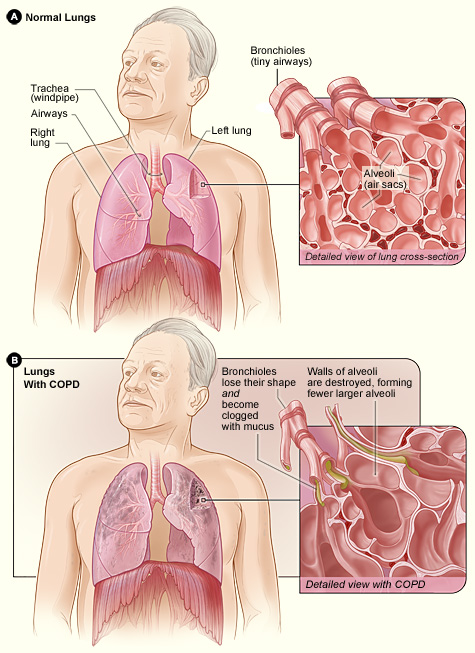 Lower airway obstruction is mainly caused by increased resistance in the
Lower airway obstruction is mainly caused by increased resistance in the
 Airway obstruction is a blockage of
Airway obstruction is a blockage of respiration
Respiration may refer to:
Biology
* Cellular respiration, the process in which nutrients are converted into useful energy in a cell
** Anaerobic respiration, cellular respiration without oxygen
** Maintenance respiration, the amount of cellul ...
in the airway
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of conducting air to the alveoli for the purposes of gas exchange in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory ...
that hinders the free flow of air. Airway obstructions can occur either in the upper airway or lower airway. The upper airway consists of the nose, throat, and larynx. The lower airway comprises the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles.
Airway obstruction is a life-threatening condition and requires urgent attention.
Upper airway obstruction
Causes
The causes of upper airway obstructions can be acute or chronic. Acute causes of upper airway obstruction includeforeign body aspiration
Foreign body aspiration occurs when a foreign body enters the Respiratory tract, airway which can cause difficulty breathing or choking. Objects may reach the respiratory tract and the digestive tract from the mouth and nose, but when an object ent ...
, blunt trauma to the neck, infection, and swelling due to allergies or other inflammatory conditions. In children, viral infections such as croup
Croup ( ), also known as croupy cough, is a type of respiratory infection that is usually caused by a virus. The infection leads to swelling inside the trachea, which interferes with normal breathing and produces the classic symptoms of "bar ...
or epiglottitis
Epiglottitis is the inflammation of the epiglottis—the flap at the base of the tongue that prevents food entering the trachea (windpipe). Symptoms are usually rapid in onset and include trouble swallowing which can result in drooling, changes ...
are frequent causes. Adults are more likely to experience obstruction from enlargement of the tonsils or vocal cord paralysis. Obstructive sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common sleep-related breathing disorder and is characterized by recurrent episodes of complete or partial airway obstruction, obstruction of the respiratory tract#Upper respiratory tract, upper airway lea ...
is the most common chronic cause of upper airway obstruction.
Symptoms
Stridor
Stridor () is an extra-thoracic high-pitched breath sound resulting from turbulent air flow in the larynx or lower in the bronchial tree. It is different from a stertor, which is a noise originating in the pharynx.
Stridor is a physical sig ...
is a high-pitched sound which occurs during breathing and is associated with obstruction at the level of the larynx. Difficulty swallowing and changes in voice are common symptoms. If there is total obstruction, severe respiratory distress
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that c ...
or cyanosis
Cyanosis is the change of Tissue (biology), tissue color to a bluish-purple hue, as a result of decrease in the amount of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the capillary bed. Cyanosis is apparent usually in the Tissue (bi ...
due to hypoxia (lack of oxygen in the blood) can occur.
Diagnosis
respiratory failure
Respiratory failure results from inadequate gas exchange by the respiratory system, meaning that the arterial oxygen, carbon dioxide, or both cannot be kept at normal levels. A drop in the oxygen carried in the blood is known as hypoxemia; a r ...
without appropriate management necessitating urgent and comprehensive assessment of ABCs (airway, breathing, and circulation).
Imaging studies, including x-rays and CT scans, can aid diagnosis and quickly assess the obstruction's extent. For children, ultrasound or MRI are preferred as they do not involve radiation. Flexible laryngoscopy or bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is an endoscopic technique of visualizing the inside of the airways for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. An instrument (bronchoscope) is inserted into the airways, usually through the nose or mouth, or occasionally through a tr ...
can directly visualize the airway.
Management
Treatment depends on how severe the patient's condition is and the cause of the obstruction. If the patient is choking on a foreign body, theHeimlich maneuver
Heimlich maneuver, also known as abdominal thrusts or Heimlich manoeuvre, is a first-aid procedure used to treat upper-airway obstructions (or choking) by foreign objects. American doctor Henry Heimlich is often credited for its discovery. ...
can be used. More invasive methods, such as intubation
Intubation (sometimes entubation) is a medical procedure involving the insertion of a tube into the body. Most commonly, intubation refers to tracheal intubation, a procedure during which an endotracheal tube is inserted into the trachea to supp ...
, may be necessary to secure the airway. In severe cases, intubation may be difficult and a cricothyrotomy
A cricothyrotomy (also called cricothyroidotomy or laryngotomy) is a medical procedure where an opening is created through the cricothyroid membrane to establish a patent airway during emergency airway management. Cricothyrotomy is primarily per ...
or tracheostomy
Tracheotomy (, ), or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision on the front of the neck to open a direct airway to the trachea. The resulting stoma (hole) can serve independently as an airway ...
may be necessary.
Infections typically cause obstruction by swelling and are usually treated with antibiotics or corticosteroids to reduce inflammation. For causes like tumors or abscesses, surgical removal may be required.
Prognosis
With prompt treatment, outcomes are usually favorable. This is especially true for reversible conditions, like foreign body aspiration. Chronic conditions, like vocal cord paralysis and sleep apnea, may need ongoing care. If managed well, they usually have good outcomes.Complications
Untreated or prolonged upper airway obstruction can cause severe, life-threatening complications. * Hypoxia: Low blood oxygen can cause confusion and unconsciousness. It can also lead to cardiac arrest if not treated. *Aspiration pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia is a type of lung infection that is due to a relatively large amount of material from the stomach or mouth entering the lungs. Signs and symptoms often include fever and cough of relatively rapid onset. Complications may incl ...
: Particles entering the lungs can cause infections.
* Structural changes: Repeating obstruction or trauma may scar or narrow the upper airway. This is called subglottic or tracheal stenosis
Laryngotracheal stenosis refers to abnormal narrowing of the central air passageways. This can occur at the level of the larynx, trachea, carina or main bronchi.
In a small number of patients narrowing may be present in more than one anatomical ...
.
* Voice changes: Chronic damage to the vocal cords may cause permanent voice changes or loss.
* Cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest (also known as sudden cardiac arrest CA is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. When the heart stops beating, blood cannot properly Circulatory system, circulate around the body and the blood flow to the ...
: Severe obstruction can cause asphyxiation, leading to heart failure if untreated.
Lower airway obstruction
Causes
 Lower airway obstruction is mainly caused by increased resistance in the
Lower airway obstruction is mainly caused by increased resistance in the bronchioles
The bronchioles ( ) are the smaller branches of the bronchial airways in the lower respiratory tract. They include the terminal bronchioles, and finally the respiratory bronchioles that mark the start of the respiratory zone delivering air to t ...
, usually due to a decreased radius of the bronchioles. This typically occurs due to constriction and inflammation of the bronchioles that reduces the air inhaled in each breath. This restriction is worsened by mucus production and airway remodeling in chronic conditions. Diseases that cause lower airway obstruction are called obstructive lung disease
Obstructive lung disease is a category of respiratory disease characterized by airway obstruction. Many obstructive diseases of the lung result from narrowing (obstruction) of the smaller bronchi and larger bronchioles, often because of excessiv ...
s. Examples include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
, and bronchitis
Bronchitis is inflammation of the bronchi (large and medium-sized airways) in the lungs that causes coughing. Bronchitis usually begins as an infection in the nose, ears, throat, or sinuses. The infection then makes its way down to the bronchi. ...
.
Symptoms
Patients often experiencewheezing
A wheeze is a clinical symptom of a continuous, coarse, whistling sound produced in the respiratory airways during breathing. For wheezes to occur, part of the respiratory tree must be narrowed or obstructed (for example narrowing of the lower ...
, shortness of breath, and a chronic cough. A wheeze is a coarse, whistling sound in the airways during breathing. Worsening symptoms may include increased mucus production and reduced exercise tolerance.
Diagnosis
Spirometry
Spirometry (meaning ''the measuring of breath'') is the most common of the pulmonary function tests (PFTs). It measures lung function, specifically the amount (volume) and/or speed (flow) of air that can be inhaled and exhaled. Spirometry is h ...
that measures the FEV1/FVC ratio, is the gold standard for diagnosing lower airway obstruction. A decreased ratio indicates obstruction.
Chest X-rays can help exclude alternative diagnoses or include other comorbidities. CT images can provide more insight into any possible structural abnormalities.
Management
Treatment of lower airway obstruction includes: *Bronchodilators
A bronchodilator or broncholytic (although the latter occasionally includes secretory inhibition as well) is a substance that dilates the bronchi and bronchioles, decreasing resistance in the respiratory airway and increasing airflow to the lung ...
help relax and widen the airways, which improve the airflow.
* Inhaled corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
s can help decrease airway inflammation.
* Long-term oxygen therapy is usually reserved for more severe chronic cases.
Severe cases may need hospitalization and mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation or assisted ventilation is the Medicine, medical term for using a ventilator, ventilator machine to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, wit ...
to help support breathing by keeping the airways open.
Outcomes
Prognosis depends on the severity and cause of the obstruction. With early diagnosis and treatment, conditions like asthma often have a good outcome. But, chronic diseases like COPD are progressive, requiring ongoing management.Complications
Complications of lower airway obstruction, often from chronic diseases, include: * Chronic hypoxia: Prolonged obstruction reduces oxygen supply. This leads to fatigue, confusion, and eventual organ damage. * ''Cor Pulmonale'': Persistent low oxygen levels can strain the right side of the heart. This can lead to right-sided heart failure. * Frequent infections: There is an increase risk of bacterial infections like pneumonia.See also
*Recurrent airway obstruction
Recurrent airway obstruction, also known as broken wind, heaves, wind-broke horse, or sometimes by the term usually reserved for humans, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or disorder (COPD) – it is a respiratory disease or chronic conditio ...
References
External links
Symptoms and signs: Respiratory system {{DEFAULTSORT:Airway Obstruction