Bosnia Support Committee on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to the north and southwest, with a coast on the Adriatic Sea in the south. Bosnia (region), Bosnia has a moderate continental climate with hot summers and cold, snowy winters. Its geography is largely mountainous, particularly in the central and eastern regions, which are dominated by the Dinaric Alps. Herzegovina, the smaller, southern region, has a Mediterranean climate and is mostly mountainous. Sarajevo is the capital and the largest city.
The area has been inhabited since at least the Upper Paleolithic, with permanent human settlement traced to the Neolithic cultures of Butmir culture, Butmir, Kakanj culture, Kakanj, and Vučedol culture, Vučedol. After the arrival of the first Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-Europeans, the area was populated by several Illyrian and Celts, Celtic civilizations. Most of modern Bosnia was incorporated into the Dalmatia (Roman province), Roman province of Dalmatia by the mid first century BCE. The Early Slavs, ancestors of the modern South Slavic peoples arrived between the sixth and ninth centuries. In the 12th century, the Banate of Bosnia was established as the first independent Bosnian polity. It gradually evolved and expanded into the Kingdom of Bosnia, which became the most powerful state in the western Balkans by the 14th century. The Ottoman Empire Ottoman Bosnia and Herzegovina, annexed the region in 1463 and introduced Islam in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Islam. From the late 19th century until World War I, the country was Austro-Hungarian rule in Bosnia and Herzegovina, annexed into the Austro-Hungarian monarchy. In the interwar period, Bosnia and Herzegovina was part of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. After World War II, it was granted full republic status in the newly formed Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. In 1992, following the breakup of Yugoslavia, 1992 Bosnian independence referendum, the republic proclaimed independence. This was followed by the Bosnian War, which lasted until late 1995 and ended with the signing of the Dayton Agreement.
Bosnia has roughly 3.4 million inhabitants, comprised mostly of ethnic groups in Bosnia and Herzegovina, three main ethnic groups: Bosniaks, who form approximately two-fifths of the population, followed by Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbs at one-third and Croats of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croats at one-fifth; minorities include History of the Jews in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Jews, Romani people in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Roma, National minorities in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Albanians, Montenegrins, Ukrainians and Turks, who are among 17 recognized "national minorities". Bosnia and Herzegovina has a bicameralism, bicameral legislature and a Presidency of Bosnia and Herzegovina, presidency made up of one member from each of the three major ethnic groups. The central government's power is highly limited, as the country is largely decentralized; it comprises two autonomous entities—the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Republika Srpska—and a third unit, the Brčko District, governed by its own local government.
Bosnia and Herzegovina is a developing country. Its economy is dominated by industry and agriculture, followed by tourism and Tertiary sector of the economy, services; tourism has increased significantly in recent years. The country has a social security and universal healthcare system, and primary and secondary education is free. Accession of Bosnia and Herzegovina to the European Union, Bosnia and Herzegovina is an EU candidate country and has also been a candidate for NATO membership since April 2010.
 In the Neretva Delta in the south, there were important Hellenistic period, Hellenistic influences of the Illyrian Daorson, Daors tribe. Their capital was ''Daorson'' in Ošanići near Stolac. Daorson, in the 4th century BCE, was surrounded by megalithic, 5 m high stonewalls (as large as those of Mycenae in Greece), composed of large trapezoid stone blocks. Daors made unique bronze coins and sculptures.
Conflict between the Illyrians and Ancient Rome, Romans started in 229 BCE, but Rome did not complete its annexation of the region until AD 9. It was precisely in modern-day Bosnia and Herzegovina that Rome fought one of the most difficult battles in its history since the Punic Wars, as described by the Roman historian Suetonius. This was the Roman campaign against Illyricum (Roman province), Illyricum, known as . The conflict arose after an attempt to recruit Illyrians, and a revolt spanned for four years (6–9 AD), after which they were subdued. In the Roman period, Latin-speaking settlers from the entire Roman Empire settled among the Illyrians, and Roman soldiers were encouraged to retire in the region.
Following the split of the Empire between 337 and 395 AD, Dalmatia and Pannonia became parts of the Western Roman Empire. The region was conquered by the Ostrogoths in 455 AD. It subsequently changed hands between the Alans and the Huns. By the 6th century, Emperor Justinian I had reconquered the area for the Byzantine Empire. Slavs overwhelmed the Balkans in the 6th and 7th centuries. Illyrian cultural traits were adopted by the South Slavs, as evidenced in certain customs and traditions, and placenames.
In the Neretva Delta in the south, there were important Hellenistic period, Hellenistic influences of the Illyrian Daorson, Daors tribe. Their capital was ''Daorson'' in Ošanići near Stolac. Daorson, in the 4th century BCE, was surrounded by megalithic, 5 m high stonewalls (as large as those of Mycenae in Greece), composed of large trapezoid stone blocks. Daors made unique bronze coins and sculptures.
Conflict between the Illyrians and Ancient Rome, Romans started in 229 BCE, but Rome did not complete its annexation of the region until AD 9. It was precisely in modern-day Bosnia and Herzegovina that Rome fought one of the most difficult battles in its history since the Punic Wars, as described by the Roman historian Suetonius. This was the Roman campaign against Illyricum (Roman province), Illyricum, known as . The conflict arose after an attempt to recruit Illyrians, and a revolt spanned for four years (6–9 AD), after which they were subdued. In the Roman period, Latin-speaking settlers from the entire Roman Empire settled among the Illyrians, and Roman soldiers were encouraged to retire in the region.
Following the split of the Empire between 337 and 395 AD, Dalmatia and Pannonia became parts of the Western Roman Empire. The region was conquered by the Ostrogoths in 455 AD. It subsequently changed hands between the Alans and the Huns. By the 6th century, Emperor Justinian I had reconquered the area for the Byzantine Empire. Slavs overwhelmed the Balkans in the 6th and 7th centuries. Illyrian cultural traits were adopted by the South Slavs, as evidenced in certain customs and traditions, and placenames.

 The Early Slavs raided the Western Balkans, including Bosnia, in the 6th and early 7th century (amid the Migration Period), and were composed of small tribal units drawn from a single Slavic confederation known to the Byzantines as the ''Sclaveni'' (whilst the related ''Antes people, Antes'', roughly speaking, colonized the eastern portions of the Balkans).
Tribes recorded by the ethnonyms of "Serb" and "Croat" are described as a second, later, migration of different people during the second quarter of the 7th century who could not have been particularly numerous; these early "Serb" and "Croat" tribes, whose exact identity is subject to scholarly debate, came to predominate over the Slavs in the neighbouring regions. According to Noel Malcolm, the tribal Croats "settled in an area roughly corresponding to modern Croatia, and probably also including most of Bosnia proper, apart from the eastern strip of the Drina valley" while the tribal Serbs settled an area "corresponding to modern south-western Serbia (later known as Raška (region), Raška), and gradually extended their rule into the territories of Duklja and Zachlumia, Hum". John Van Antwerp Fine Jr., on the other hand, describes the settling of the tribal Croats to involve Croatia, Dalmatia and Western Bosnia, with the rest of Bosnia seemingly being a territory between early Serb and Croat rule.
Bosnia is also believed to be first mentioned ''as a land (horion Bosona)'' in Byzantine Emperor Constantine Porphyrogenitus' ''De Administrando Imperio'' in the mid 10th century, at the end of a chapter entitled ''Of the Serbs and the country in which they now dwell''. This has been scholarly interpreted in several ways and used especially by the Serb national ideologists to prove Bosnia as originally a "Serb" land. Other scholars have asserted the inclusion of Bosnia in the chapter to merely be the result of Serbian Grand Duke Časlav of Serbia, Časlav's temporary rule over Bosnia at the time, while also pointing out Porphyrogenitus does not say anywhere explicitly that Bosnia is a "Serb land". In fact, the very translation of the critical sentence where the word ''Bosona'' (Bosnia) appears is subject to varying interpretation. In time, Bosnia formed a unit under its own Kulin Ban, ruler, who called himself Bosnian. Bosnia, along with other territories, became part of Duklja in the 11th century, although it retained its own nobility and institutions.
The Early Slavs raided the Western Balkans, including Bosnia, in the 6th and early 7th century (amid the Migration Period), and were composed of small tribal units drawn from a single Slavic confederation known to the Byzantines as the ''Sclaveni'' (whilst the related ''Antes people, Antes'', roughly speaking, colonized the eastern portions of the Balkans).
Tribes recorded by the ethnonyms of "Serb" and "Croat" are described as a second, later, migration of different people during the second quarter of the 7th century who could not have been particularly numerous; these early "Serb" and "Croat" tribes, whose exact identity is subject to scholarly debate, came to predominate over the Slavs in the neighbouring regions. According to Noel Malcolm, the tribal Croats "settled in an area roughly corresponding to modern Croatia, and probably also including most of Bosnia proper, apart from the eastern strip of the Drina valley" while the tribal Serbs settled an area "corresponding to modern south-western Serbia (later known as Raška (region), Raška), and gradually extended their rule into the territories of Duklja and Zachlumia, Hum". John Van Antwerp Fine Jr., on the other hand, describes the settling of the tribal Croats to involve Croatia, Dalmatia and Western Bosnia, with the rest of Bosnia seemingly being a territory between early Serb and Croat rule.
Bosnia is also believed to be first mentioned ''as a land (horion Bosona)'' in Byzantine Emperor Constantine Porphyrogenitus' ''De Administrando Imperio'' in the mid 10th century, at the end of a chapter entitled ''Of the Serbs and the country in which they now dwell''. This has been scholarly interpreted in several ways and used especially by the Serb national ideologists to prove Bosnia as originally a "Serb" land. Other scholars have asserted the inclusion of Bosnia in the chapter to merely be the result of Serbian Grand Duke Časlav of Serbia, Časlav's temporary rule over Bosnia at the time, while also pointing out Porphyrogenitus does not say anywhere explicitly that Bosnia is a "Serb land". In fact, the very translation of the critical sentence where the word ''Bosona'' (Bosnia) appears is subject to varying interpretation. In time, Bosnia formed a unit under its own Kulin Ban, ruler, who called himself Bosnian. Bosnia, along with other territories, became part of Duklja in the 11th century, although it retained its own nobility and institutions.
 In the High Middle Ages, political circumstance led to the area being contested between the Kingdom of Hungary and the Byzantine Empire. Following another shift of power between the two in the early 12th century, Bosnia found itself outside the control of both and emerged as the Banate of Bosnia (under the rule of local ''Ban (title), bans''). The first Bosnian ban known by name was Ban Borić. The second was Ban Kulin, whose rule marked the start of a controversy involving the Bosnian Church – considered heretical by the Roman Catholic Church. In response to Hungarian attempts to use church politics regarding the issue as a way to reclaim sovereignty over Bosnia, Kulin held a council of local church leaders to renounce the heresy and embraced Catholicism in 1203. Despite this, Hungarian ambitions remained unchanged long after Kulin's death in 1204, waning only after an unsuccessful invasion in 1254. During this time, the population was called ''Dobri Bošnjani'' ("Good Bosnians"). The names Serb and Croat, though occasionally appearing in peripheral areas, were not used in Bosnia proper.
Bosnian history from then until the early 14th century was marked by a power struggle between the Šubić family, Šubić and Kotromanić dynasty, Kotromanić families. This conflict came to an end in 1322, when Stephen II, Ban of Bosnia, Stephen II Kotromanić became ''Ban''. By the time of his death in 1353, he was successful in annexing territories to the north and west, as well as Zahumlje and parts of Dalmatia. He was succeeded by his ambitious nephew Tvrtko I of Bosnia, Tvrtko who, following a prolonged struggle with nobility and inter-family strife, gained full control of the country in 1367. By the year 1377, Bosnia was elevated into a kingdom with the coronation of Tvrtko as the first List of rulers of Bosnia, Bosnian King in Mile near Visoko during the Middle Ages, Visoko in the Bosnian heartland.Anđelić Pavao, Krunidbena i grobna crkva bosanskih vladara u Milima (Arnautovićima) kod Visokog. Glasnik Zemaljskog muzeja XXXIV/1979., Zemaljski muzej Bosne i Hercegovine, Sarajevo, 1980,183–247
Following his death in 1391, however, Bosnia fell into a long period of decline. The Ottoman Empire had started its Ottoman wars in Europe, conquest of Europe and posed a major threat to the Balkans throughout the first half of the 15th century. Finally, after decades of political and social instability, the Kingdom of Bosnia ceased to exist in 1463 after its conquest by the Ottoman Empire.
There was a general awareness in medieval Bosnia, at least amongst the nobles, that they shared a joint state with Serbia and that they belonged to the same ethnic group. That awareness diminished over time, due to differences in political and social development, but it was kept in Herzegovina and parts of Bosnia which were a part of Serbian state.
In the High Middle Ages, political circumstance led to the area being contested between the Kingdom of Hungary and the Byzantine Empire. Following another shift of power between the two in the early 12th century, Bosnia found itself outside the control of both and emerged as the Banate of Bosnia (under the rule of local ''Ban (title), bans''). The first Bosnian ban known by name was Ban Borić. The second was Ban Kulin, whose rule marked the start of a controversy involving the Bosnian Church – considered heretical by the Roman Catholic Church. In response to Hungarian attempts to use church politics regarding the issue as a way to reclaim sovereignty over Bosnia, Kulin held a council of local church leaders to renounce the heresy and embraced Catholicism in 1203. Despite this, Hungarian ambitions remained unchanged long after Kulin's death in 1204, waning only after an unsuccessful invasion in 1254. During this time, the population was called ''Dobri Bošnjani'' ("Good Bosnians"). The names Serb and Croat, though occasionally appearing in peripheral areas, were not used in Bosnia proper.
Bosnian history from then until the early 14th century was marked by a power struggle between the Šubić family, Šubić and Kotromanić dynasty, Kotromanić families. This conflict came to an end in 1322, when Stephen II, Ban of Bosnia, Stephen II Kotromanić became ''Ban''. By the time of his death in 1353, he was successful in annexing territories to the north and west, as well as Zahumlje and parts of Dalmatia. He was succeeded by his ambitious nephew Tvrtko I of Bosnia, Tvrtko who, following a prolonged struggle with nobility and inter-family strife, gained full control of the country in 1367. By the year 1377, Bosnia was elevated into a kingdom with the coronation of Tvrtko as the first List of rulers of Bosnia, Bosnian King in Mile near Visoko during the Middle Ages, Visoko in the Bosnian heartland.Anđelić Pavao, Krunidbena i grobna crkva bosanskih vladara u Milima (Arnautovićima) kod Visokog. Glasnik Zemaljskog muzeja XXXIV/1979., Zemaljski muzej Bosne i Hercegovine, Sarajevo, 1980,183–247
Following his death in 1391, however, Bosnia fell into a long period of decline. The Ottoman Empire had started its Ottoman wars in Europe, conquest of Europe and posed a major threat to the Balkans throughout the first half of the 15th century. Finally, after decades of political and social instability, the Kingdom of Bosnia ceased to exist in 1463 after its conquest by the Ottoman Empire.
There was a general awareness in medieval Bosnia, at least amongst the nobles, that they shared a joint state with Serbia and that they belonged to the same ethnic group. That awareness diminished over time, due to differences in political and social development, but it was kept in Herzegovina and parts of Bosnia which were a part of Serbian state.
 Furthermore, several Bosnian Muslims played influential roles in the Ottoman Empire's cultural and political history during this time.Riedlmayer, Andras (1993)
Furthermore, several Bosnian Muslims played influential roles in the Ottoman Empire's cultural and political history during this time.Riedlmayer, Andras (1993)
A Brief History of Bosnia–Herzegovina
. The Bosnian Manuscript Ingathering Project. Bosnian recruits formed a large component of the Ottoman ranks in the battles of Battle of Mohács, Mohács and Battle of Krbava Field, Krbava field, while numerous other Bosnians rose through the ranks of the Ottoman military to occupy the highest positions of power in the Empire, including admirals such as Matrakçı Nasuh; generals such as Isa Bey Ishaković, Isa-Beg Ishaković, Gazi Husrev Bey, Gazi Husrev-beg, Telli Hasan Pasha and Sarı Süleyman Pasha; administrators such as Ferhad Pasha Sokolović and Osman Gradaščević; and Grand Viziers such as the influential Sokollu Mehmed Pasha and Damat Ibrahim Pasha. Some Bosnians emerged as Sufism, Sufi mystics, scholars such as Muhamed Hevaji Uskufi Bosnevi, Ali Džabić; and poets in the Turkish language, Turkish, Albanian language, Albanian, Arabic, and Persian languages.Imamović, Mustafa (1996). Historija Bošnjaka. Sarajevo: BZK Preporod; However, by the late 17th century the Empire's military misfortunes caught up with the country, and the end of the Great Turkish War with the treaty of Karlowitz in 1699 again made Bosnia the Empire's westernmost province. The 18th century was marked by further military failures, numerous revolts within Bosnia, and several outbreaks of plague. The Porte's efforts at modernizing the Ottoman state were met with distrust growing to hostility in Bosnia, where local aristocrats stood to lose much through the proposed Tanzimat reforms. This, combined with frustrations over territorial, political concessions in the north-east, and the plight of Slavs, Slavic Muslims, Muslim refugees arriving from the Sanjak of Smederevo into Bosnia Eyalet, culminated in a partially unsuccessful revolt by Husein Gradaščević, who endorsed a Bosnia Eyalet autonomous from the authoritarian rule of the Ottoman Sultan Mahmud II, who persecuted, executed and abolished the Janissary, Janissaries and reduced the role of autonomous Pashas in Rumelia. Mahmud II sent his Grand vizier to subdue Bosnia Eyalet and succeeded only with the reluctant assistance of Ali Pasha Rizvanbegović. Related rebellions were extinguished by 1850, but the situation continued to deteriorate. New nationalist movements appeared in Bosnia by the middle of the 19th century. Shortly after Serbia's breakaway from the Ottoman Empire in the early 19th century, Serbian and Croatian nationalism rose up in Bosnia, and such nationalists made irredentist claims to Bosnia's territory. This trend continued to grow in the rest of the 19th and 20th centuries. Agrarian unrest eventually sparked the Herzegovina uprising (1875–1877), Herzegovinian rebellion, a widespread peasant uprising, in 1875. The conflict rapidly spread and came to involve several Balkan states and Great Powers, a situation that led to the Congress of Berlin and the Treaty of Berlin (1878), Treaty of Berlin in 1878.
 At the Congress of Berlin in 1878, the Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarian Foreign Minister Gyula Andrássy obtained the occupation and administration of Bosnia and Herzegovina, and he also obtained the right to station garrisons in the Sanjak of Novi Pazar, which would remain under Ottoman Empire, Ottoman administration until 1908, when the Austro-Hungarian troops withdrew from the Sanjak.
Although Austro-Hungarian officials quickly came to an agreement with the Bosnians, tensions remained and a mass emigration of Bosnians occurred. However, a state of relative stability was reached soon enough and Austro-Hungarian authorities were able to embark on a number of social and administrative reforms they intended would make Bosnia and Herzegovina into a "model" colony.
Habsburg Monarchy, Habsburg rule had several key concerns in Bosnia. It tried to dissipate the South Slav nationalism by disputing the earlier Serb and Croat claims to Bosnia and encouraging identification of Bosnian or Bosniaks, Bosniak identity. Habsburg rule also tried to provide for modernisation by codifying laws, introducing new political institutions, establishing and expanding industries.
Austria–Hungary began to plan the annexation of Bosnia, but due to international disputes the issue was not resolved until the Bosnian Crisis, annexation crisis of 1908. Several external matters affected the status of Bosnia and its relationship with Austria–Hungary. May Coup (Serbia), A bloody coup occurred in Serbia in 1903, which brought a radical anti-Austrian government into power in Belgrade. Then in 1908, the revolt in the Ottoman Empire raised concerns that the Istanbul government might seek the outright return of Bosnia and Herzegovina. These factors caused the Austro-Hungarian government to seek a permanent resolution of the Bosnian question sooner, rather than later.
Taking advantage of the turmoil in the Ottoman Empire, Austro-Hungarian diplomacy tried to obtain provisional Russian approval for changes over the status of Bosnia and Herzegovina and published the annexation proclamation on 6 October 1908. Despite international objections to the Austro-Hungarian annexation, Russians and their client state, Serbia, were compelled to accept the Austro-Hungarian annexation of Bosnia and Herzegovina in March 1909.
In 1910, Habsburg Emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria, Franz Joseph proclaimed the first constitution in Bosnia, which led to relaxation of earlier laws, elections and formation of the Diet of Bosnia, Bosnian parliament and growth of new political life.
At the Congress of Berlin in 1878, the Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarian Foreign Minister Gyula Andrássy obtained the occupation and administration of Bosnia and Herzegovina, and he also obtained the right to station garrisons in the Sanjak of Novi Pazar, which would remain under Ottoman Empire, Ottoman administration until 1908, when the Austro-Hungarian troops withdrew from the Sanjak.
Although Austro-Hungarian officials quickly came to an agreement with the Bosnians, tensions remained and a mass emigration of Bosnians occurred. However, a state of relative stability was reached soon enough and Austro-Hungarian authorities were able to embark on a number of social and administrative reforms they intended would make Bosnia and Herzegovina into a "model" colony.
Habsburg Monarchy, Habsburg rule had several key concerns in Bosnia. It tried to dissipate the South Slav nationalism by disputing the earlier Serb and Croat claims to Bosnia and encouraging identification of Bosnian or Bosniaks, Bosniak identity. Habsburg rule also tried to provide for modernisation by codifying laws, introducing new political institutions, establishing and expanding industries.
Austria–Hungary began to plan the annexation of Bosnia, but due to international disputes the issue was not resolved until the Bosnian Crisis, annexation crisis of 1908. Several external matters affected the status of Bosnia and its relationship with Austria–Hungary. May Coup (Serbia), A bloody coup occurred in Serbia in 1903, which brought a radical anti-Austrian government into power in Belgrade. Then in 1908, the revolt in the Ottoman Empire raised concerns that the Istanbul government might seek the outright return of Bosnia and Herzegovina. These factors caused the Austro-Hungarian government to seek a permanent resolution of the Bosnian question sooner, rather than later.
Taking advantage of the turmoil in the Ottoman Empire, Austro-Hungarian diplomacy tried to obtain provisional Russian approval for changes over the status of Bosnia and Herzegovina and published the annexation proclamation on 6 October 1908. Despite international objections to the Austro-Hungarian annexation, Russians and their client state, Serbia, were compelled to accept the Austro-Hungarian annexation of Bosnia and Herzegovina in March 1909.
In 1910, Habsburg Emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria, Franz Joseph proclaimed the first constitution in Bosnia, which led to relaxation of earlier laws, elections and formation of the Diet of Bosnia, Bosnian parliament and growth of new political life.
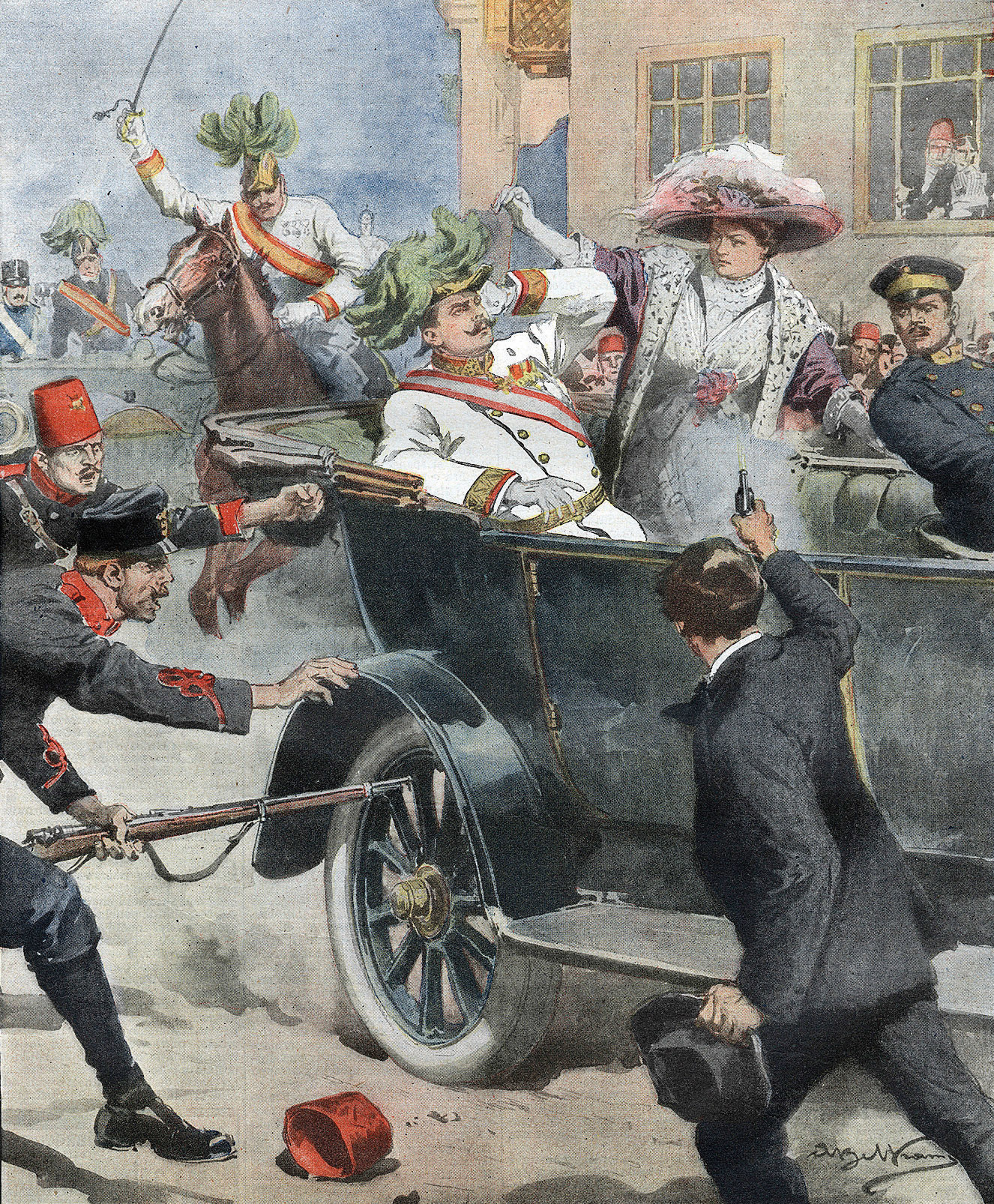 On 28 June 1914, Gavrilo Princip, a Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnian Serb member of the revolutionary movement Young Bosnia, Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, assassinated the heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria, Archduke Franz Ferdinand, in Sarajevo—an event that was the spark that set off World War I. At the end of the war, the Bosnian Muslims had lost more men per capita than any other ethnic group in the Habsburg Empire whilst serving in the Bosnian-Herzegovinian Infantry of the Austro-Hungarian Army. Nonetheless, Bosnia and Herzegovina as a whole managed to escape the conflict relatively unscathed.
The Austro-Hungarian authorities established an auxiliary militia known as the Schutzkorps with a moot role in the empire's policy of Anti-Serb sentiment, anti-Serb repression. Schutzkorps, predominantly recruited among the Bosnian Muslim population, were tasked with hunting down rebel Serbs (the ''Chetniks'' and ''Komitadji'') and became known for their persecution of Serbs particularly in Serb populated areas of eastern Bosnia, where they partly retaliated against Serbian Chetniks who in fall 1914 had carried out attacks against the Muslim population in the area. The proceedings of the Austro-Hungarian authorities led to around 5,500 citizens of Serb ethnicity in Bosnia and Herzegovina being arrested, and between 700 and 2,200 died in prison while 460 were executed. Around 5,200 Serb families were forcibly expelled from Bosnia and Herzegovina.
On 28 June 1914, Gavrilo Princip, a Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnian Serb member of the revolutionary movement Young Bosnia, Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, assassinated the heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria, Archduke Franz Ferdinand, in Sarajevo—an event that was the spark that set off World War I. At the end of the war, the Bosnian Muslims had lost more men per capita than any other ethnic group in the Habsburg Empire whilst serving in the Bosnian-Herzegovinian Infantry of the Austro-Hungarian Army. Nonetheless, Bosnia and Herzegovina as a whole managed to escape the conflict relatively unscathed.
The Austro-Hungarian authorities established an auxiliary militia known as the Schutzkorps with a moot role in the empire's policy of Anti-Serb sentiment, anti-Serb repression. Schutzkorps, predominantly recruited among the Bosnian Muslim population, were tasked with hunting down rebel Serbs (the ''Chetniks'' and ''Komitadji'') and became known for their persecution of Serbs particularly in Serb populated areas of eastern Bosnia, where they partly retaliated against Serbian Chetniks who in fall 1914 had carried out attacks against the Muslim population in the area. The proceedings of the Austro-Hungarian authorities led to around 5,500 citizens of Serb ethnicity in Bosnia and Herzegovina being arrested, and between 700 and 2,200 died in prison while 460 were executed. Around 5,200 Serb families were forcibly expelled from Bosnia and Herzegovina.
 Once the Kingdom of Yugoslavia was conquered by German forces in World War II, all of Bosnia and Herzegovina was ceded to the Nazi puppet regime, the Independent State of Croatia (NDH) led by the Ustaše. The NDH leaders embarked on a Genocide of Serbs in the Independent State of Croatia, campaign of extermination of Serbs, Jews, Romani people, Romani as well as dissident Croats, and, later, Josip Broz Tito's Yugoslav Partisans, Partisans by setting up a number of Jasenovac concentration camp, death camps. The regime systematically and brutally massacred Serbs in villages in the countryside, using a variety of tools. The scale of the violence meant that approximately every sixth Serb living in Bosnia and Herzegovina was the victim of a massacre and virtually every Serb had a family member that was killed in the war, mostly by the Ustaše. The experience had a profound impact in the collective memory of Serbs in Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina. An estimated 209,000 Serbs or 16.9% of its Bosnia population were killed on the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina during the war.
The Ustaše recognized both Catholicism and Islam as the national religions, but held the position Eastern Orthodox Church, as a symbol of Serb identity, was their greatest foe.Ramet (2006), pgg. 118. Although Croats were by far the largest ethnic group to constitute the Ustaše, the Vice President of the NDH and leader of the Yugoslav Muslim Organization Džafer Kulenović was a Muslim, and Muslims in total constituted nearly 12% of the Ustaše military and civil service authority.
Many Serbs themselves took up arms and joined the Chetniks, a Serb nationalist movement with the aim of establishing an ethnically homogeneous 'Greater Serbian' state within the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. The Chetniks, in turn, pursued a Chetnik war crimes in World War II, genocidal campaign against ethnic Muslims and Croats, as well as persecuting a large number of Communism, communist Serbs and other Communist sympathizers, with the Muslim populations of Bosnia, Herzegovina and Sandžak being a primary target. Once captured, Muslim villagers were systematically massacred by the Chetniks. Of the 75,000 Muslims who died in Bosnia and Herzegovina during the war, approximately 30,000 (mostly civilians) were killed by the Chetniks. Massacres against Croats were smaller in scale but similar in action. Between 64,000 and 79,000 Bosnian Croats were killed between April 1941 to May 1945. Of these, about 18,000 were killed by the Chetniks.
A percentage of Muslims served in Nazi 13th Waffen Mountain Division of the SS Handschar (1st Croatian), ''Waffen-SS'' units. These units were responsible for massacres of Serbs in northwest and eastern Bosnia, most notably in Vlasenica. On 12 October 1941, a group of 108 prominent Sarajevan Muslims signed the Resolution of Sarajevo Muslims by which they condemned the persecution of Serbs organized by the Ustaše, made distinction between Muslims who participated in such persecutions and the Muslim population as a whole, presented information about the persecutions of Muslims by Serbs, and requested security for all citizens of the country, regardless of their identity.
Starting in 1941, Yugoslav communists under the leadership of Josip Broz Tito organized their own multi-ethnic resistance group, the Partisans, who fought against both Axis powers, Axis and Chetnik forces. On 29 November 1943, the Anti-Fascist Council for the National Liberation of Yugoslavia (AVNOJ) with Tito at its helm held a founding conference in Jajce where Bosnia and Herzegovina was reestablished as a republic within the Yugoslav federation in its Habsburg borders. During the entire course of World War II in Yugoslavia, 64.1% of all Bosnian Partisans were Serbs, 23% were Muslims and 8.8% Croats.
Military success eventually prompted the Allies of World War II, Allies to support the Partisans, resulting in the successful Maclean Mission, but Tito declined their offer to help and relied on his own forces instead. All the major military offensives by the antifascist movement of Yugoslavia against Nazis and their local supporters were conducted in Bosnia and Herzegovina and its peoples bore the brunt of the fighting. More than 300,000 people died in Bosnia and Herzegovina in World War II, or more than 10% of the population. At the end of the war, the establishment of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, with the 1946 Yugoslav Constitution, constitution of 1946, officially made Bosnia and Herzegovina one of six constituent republics in the new state.
Once the Kingdom of Yugoslavia was conquered by German forces in World War II, all of Bosnia and Herzegovina was ceded to the Nazi puppet regime, the Independent State of Croatia (NDH) led by the Ustaše. The NDH leaders embarked on a Genocide of Serbs in the Independent State of Croatia, campaign of extermination of Serbs, Jews, Romani people, Romani as well as dissident Croats, and, later, Josip Broz Tito's Yugoslav Partisans, Partisans by setting up a number of Jasenovac concentration camp, death camps. The regime systematically and brutally massacred Serbs in villages in the countryside, using a variety of tools. The scale of the violence meant that approximately every sixth Serb living in Bosnia and Herzegovina was the victim of a massacre and virtually every Serb had a family member that was killed in the war, mostly by the Ustaše. The experience had a profound impact in the collective memory of Serbs in Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina. An estimated 209,000 Serbs or 16.9% of its Bosnia population were killed on the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina during the war.
The Ustaše recognized both Catholicism and Islam as the national religions, but held the position Eastern Orthodox Church, as a symbol of Serb identity, was their greatest foe.Ramet (2006), pgg. 118. Although Croats were by far the largest ethnic group to constitute the Ustaše, the Vice President of the NDH and leader of the Yugoslav Muslim Organization Džafer Kulenović was a Muslim, and Muslims in total constituted nearly 12% of the Ustaše military and civil service authority.
Many Serbs themselves took up arms and joined the Chetniks, a Serb nationalist movement with the aim of establishing an ethnically homogeneous 'Greater Serbian' state within the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. The Chetniks, in turn, pursued a Chetnik war crimes in World War II, genocidal campaign against ethnic Muslims and Croats, as well as persecuting a large number of Communism, communist Serbs and other Communist sympathizers, with the Muslim populations of Bosnia, Herzegovina and Sandžak being a primary target. Once captured, Muslim villagers were systematically massacred by the Chetniks. Of the 75,000 Muslims who died in Bosnia and Herzegovina during the war, approximately 30,000 (mostly civilians) were killed by the Chetniks. Massacres against Croats were smaller in scale but similar in action. Between 64,000 and 79,000 Bosnian Croats were killed between April 1941 to May 1945. Of these, about 18,000 were killed by the Chetniks.
A percentage of Muslims served in Nazi 13th Waffen Mountain Division of the SS Handschar (1st Croatian), ''Waffen-SS'' units. These units were responsible for massacres of Serbs in northwest and eastern Bosnia, most notably in Vlasenica. On 12 October 1941, a group of 108 prominent Sarajevan Muslims signed the Resolution of Sarajevo Muslims by which they condemned the persecution of Serbs organized by the Ustaše, made distinction between Muslims who participated in such persecutions and the Muslim population as a whole, presented information about the persecutions of Muslims by Serbs, and requested security for all citizens of the country, regardless of their identity.
Starting in 1941, Yugoslav communists under the leadership of Josip Broz Tito organized their own multi-ethnic resistance group, the Partisans, who fought against both Axis powers, Axis and Chetnik forces. On 29 November 1943, the Anti-Fascist Council for the National Liberation of Yugoslavia (AVNOJ) with Tito at its helm held a founding conference in Jajce where Bosnia and Herzegovina was reestablished as a republic within the Yugoslav federation in its Habsburg borders. During the entire course of World War II in Yugoslavia, 64.1% of all Bosnian Partisans were Serbs, 23% were Muslims and 8.8% Croats.
Military success eventually prompted the Allies of World War II, Allies to support the Partisans, resulting in the successful Maclean Mission, but Tito declined their offer to help and relied on his own forces instead. All the major military offensives by the antifascist movement of Yugoslavia against Nazis and their local supporters were conducted in Bosnia and Herzegovina and its peoples bore the brunt of the fighting. More than 300,000 people died in Bosnia and Herzegovina in World War II, or more than 10% of the population. At the end of the war, the establishment of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, with the 1946 Yugoslav Constitution, constitution of 1946, officially made Bosnia and Herzegovina one of six constituent republics in the new state.
Branko Mikulic – socialist emperor manqué
. Dani (magazine), BH Dani Their efforts proved key during the turbulent period following Tito's death in 1980, and are today considered some of the early steps towards Independence Day (Bosnia and Herzegovina), Bosnian independence. However, the republic did not escape the increasingly nationalistic climate of the time. With the fall of communism and the start of the breakup of Yugoslavia, doctrine of tolerance began to lose its potency, creating an opportunity for nationalist elements in the society to spread their influence.
 On 18 November 1990, 1990 Bosnian general election, multi-party parliamentary elections were held throughout Bosnia and Herzegovina. A second round followed on 25 November, resulting in a Parliamentary Assembly of Bosnia and Herzegovina, national assembly where communist power was replaced by a coalition of three ethnically based parties. Following Slovenia and Croatia's declarations of independence from Yugoslavia, a significant split developed among the residents of Bosnia and Herzegovina on the issue of whether to remain within Yugoslavia (overwhelmingly favored by Serbs) or seek independence (overwhelmingly favored by Muslims (ethnic group), Muslims and Croats).
The Serb members of parliament, consisting mainly of the Serb Democratic Party (Bosnia and Herzegovina), Serb Democratic Party members, abandoned the central parliament in Sarajevo, and formed the National Assembly (Republika Srpska), Assembly of the Serb People of Bosnia and Herzegovina on 24 October 1991, which marked the end of the three-ethnic coalition that governed after the elections in 1990. This Assembly established the Serbian Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina in part of the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina on 9 January 1992. It was renamed Republika Srpska (1992–1995), Republika Srpska in August 1992. On 18 November 1991, the party branch in Bosnia and Herzegovina of the ruling party in the Republic of Croatia, the Croatian Democratic Union (HDZ), proclaimed the existence of the Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia, Croatian Community of Herzeg-Bosnia in a separate part of the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina with the Croatian Defence Council (HVO) as its military branch. It went unrecognized by the Council of Ministers of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Government of Bosnia and Herzegovina, which declared it illegal.
On 18 November 1990, 1990 Bosnian general election, multi-party parliamentary elections were held throughout Bosnia and Herzegovina. A second round followed on 25 November, resulting in a Parliamentary Assembly of Bosnia and Herzegovina, national assembly where communist power was replaced by a coalition of three ethnically based parties. Following Slovenia and Croatia's declarations of independence from Yugoslavia, a significant split developed among the residents of Bosnia and Herzegovina on the issue of whether to remain within Yugoslavia (overwhelmingly favored by Serbs) or seek independence (overwhelmingly favored by Muslims (ethnic group), Muslims and Croats).
The Serb members of parliament, consisting mainly of the Serb Democratic Party (Bosnia and Herzegovina), Serb Democratic Party members, abandoned the central parliament in Sarajevo, and formed the National Assembly (Republika Srpska), Assembly of the Serb People of Bosnia and Herzegovina on 24 October 1991, which marked the end of the three-ethnic coalition that governed after the elections in 1990. This Assembly established the Serbian Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina in part of the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina on 9 January 1992. It was renamed Republika Srpska (1992–1995), Republika Srpska in August 1992. On 18 November 1991, the party branch in Bosnia and Herzegovina of the ruling party in the Republic of Croatia, the Croatian Democratic Union (HDZ), proclaimed the existence of the Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia, Croatian Community of Herzeg-Bosnia in a separate part of the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina with the Croatian Defence Council (HVO) as its military branch. It went unrecognized by the Council of Ministers of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Government of Bosnia and Herzegovina, which declared it illegal.
 A declaration of the sovereignty of Bosnia and Herzegovina on 15 October 1991 was followed by a 1992 Bosnian independence referendum, referendum for independence on 29 February and 1 March 1992, which was boycotted by the great majority of Serbs. The turnout in the independence referendum was 63.4 per cent and 99.7 per cent of voters voted for independence. Bosnia and Herzegovina declared independence on 3 March 1992 and received international recognition the following month on 6 April 1992. The Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina was admitted as a member state of the United Nations on 22 May 1992. Serbian leader Slobodan Milošević and Croatian leader Franjo Tuđman are believed to have agreed on a partition of Bosnia and Herzegovina in March 1991, with the aim of establishing Greater Serbia and Greater Croatia.
Following Bosnia and Herzegovina's declaration of independence, Bosnian Serb militias mobilized in different parts of the country. Government forces were poorly equipped and unprepared for the war. International recognition of Bosnia and Herzegovina increased diplomatic pressure for the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) to withdraw from the republic's territory, which they officially did in June 1992. The Bosnian Serb members of the JNA simply changed insignia, formed the Army of Republika Srpska (VRS), and continued fighting. Armed and equipped from JNA stockpiles in Bosnia, supported by volunteers and various paramilitary forces from Serbia, and receiving extensive humanitarian, logistical and financial support from the Serbia and Montenegro, Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Republika Srpska's offensives in 1992 managed to place much of the country under its control. The Bosnian Serb advance was accompanied by the ethnic cleansing of Bosniaks and Bosnian Croats from VRS-controlled areas. Dozens of concentration camps were established in which inmates were subjected to violence and abuse, including rape. The ethnic cleansing culminated in the Srebrenica massacre of more than 8,000 Bosniak men and boys in July 1995, which was ruled to have been a genocide by the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY). Bosniak and Bosnian Croat forces also committed war crimes against civilians from different ethnic groups, though on a smaller scale. Most of the Bosniak and Croat atrocities were committed during the Croat–Bosniak War, a sub-conflict of the Bosnian War that pitted the Army of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) against the HVO. The Bosniak-Croat conflict ended in March 1994, with the signing of the Washington Agreement (1994), Washington Agreement, leading to the creation of a joint Bosniak-Croat Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, which amalgamated HVO-held territory with that held by the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH).
A declaration of the sovereignty of Bosnia and Herzegovina on 15 October 1991 was followed by a 1992 Bosnian independence referendum, referendum for independence on 29 February and 1 March 1992, which was boycotted by the great majority of Serbs. The turnout in the independence referendum was 63.4 per cent and 99.7 per cent of voters voted for independence. Bosnia and Herzegovina declared independence on 3 March 1992 and received international recognition the following month on 6 April 1992. The Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina was admitted as a member state of the United Nations on 22 May 1992. Serbian leader Slobodan Milošević and Croatian leader Franjo Tuđman are believed to have agreed on a partition of Bosnia and Herzegovina in March 1991, with the aim of establishing Greater Serbia and Greater Croatia.
Following Bosnia and Herzegovina's declaration of independence, Bosnian Serb militias mobilized in different parts of the country. Government forces were poorly equipped and unprepared for the war. International recognition of Bosnia and Herzegovina increased diplomatic pressure for the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) to withdraw from the republic's territory, which they officially did in June 1992. The Bosnian Serb members of the JNA simply changed insignia, formed the Army of Republika Srpska (VRS), and continued fighting. Armed and equipped from JNA stockpiles in Bosnia, supported by volunteers and various paramilitary forces from Serbia, and receiving extensive humanitarian, logistical and financial support from the Serbia and Montenegro, Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Republika Srpska's offensives in 1992 managed to place much of the country under its control. The Bosnian Serb advance was accompanied by the ethnic cleansing of Bosniaks and Bosnian Croats from VRS-controlled areas. Dozens of concentration camps were established in which inmates were subjected to violence and abuse, including rape. The ethnic cleansing culminated in the Srebrenica massacre of more than 8,000 Bosniak men and boys in July 1995, which was ruled to have been a genocide by the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY). Bosniak and Bosnian Croat forces also committed war crimes against civilians from different ethnic groups, though on a smaller scale. Most of the Bosniak and Croat atrocities were committed during the Croat–Bosniak War, a sub-conflict of the Bosnian War that pitted the Army of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) against the HVO. The Bosniak-Croat conflict ended in March 1994, with the signing of the Washington Agreement (1994), Washington Agreement, leading to the creation of a joint Bosniak-Croat Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, which amalgamated HVO-held territory with that held by the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH).
 On 4 February 2014, the 2014 unrest in Bosnia and Herzegovina, protests against the Government of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, one of the country's two entities, dubbed the Bosnian Spring, the name being taken from the Arab Spring, began in the northern town of Tuzla. Workers from several factories that had been privatised and gone bankrupt assembled to demand action over jobs, unpaid salaries and pensions. Soon protests spread to the rest of the Federation, with violent clashes reported in close to 20 towns, the biggest of which were Sarajevo, Zenica, Mostar, Bihać, Brčko and Tuzla. The Bosnian news media reported that hundreds of people had been injured during the protests, including dozens of police officers, with bursts of violence in Sarajevo, in the northern city of Tuzla, in Mostar in the south, and in Zenica in central Bosnia. The same level of unrest or activism did not occur in Republika Srpska, but hundreds of people also gathered in support of protests in the city of Banja Luka against its separate government.
The protests marked the largest outbreak of public anger over high unemployment and two decades of political inertia in the country since the end of the Bosnian War in 1995. According to a report made by Christian Schmidt of the High Representative for Bosnia and Herzegovina, Office of High Representative in late 2021, Bosnia and Herzegovina has been experiencing intensified political and ethnic tensions, which could potentially break the country apart and slide it back into war once again. The European Union fears this will lead to further Balkanization in the region.
On 15 December 2022, Bosnia and Herzegovina was recognised by the European Union as a candidate country for Accession of Bosnia and Herzegovina to the European Union, accession following the decision of the European Council.
On 4 February 2014, the 2014 unrest in Bosnia and Herzegovina, protests against the Government of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, one of the country's two entities, dubbed the Bosnian Spring, the name being taken from the Arab Spring, began in the northern town of Tuzla. Workers from several factories that had been privatised and gone bankrupt assembled to demand action over jobs, unpaid salaries and pensions. Soon protests spread to the rest of the Federation, with violent clashes reported in close to 20 towns, the biggest of which were Sarajevo, Zenica, Mostar, Bihać, Brčko and Tuzla. The Bosnian news media reported that hundreds of people had been injured during the protests, including dozens of police officers, with bursts of violence in Sarajevo, in the northern city of Tuzla, in Mostar in the south, and in Zenica in central Bosnia. The same level of unrest or activism did not occur in Republika Srpska, but hundreds of people also gathered in support of protests in the city of Banja Luka against its separate government.
The protests marked the largest outbreak of public anger over high unemployment and two decades of political inertia in the country since the end of the Bosnian War in 1995. According to a report made by Christian Schmidt of the High Representative for Bosnia and Herzegovina, Office of High Representative in late 2021, Bosnia and Herzegovina has been experiencing intensified political and ethnic tensions, which could potentially break the country apart and slide it back into war once again. The European Union fears this will lead to further Balkanization in the region.
On 15 December 2022, Bosnia and Herzegovina was recognised by the European Union as a candidate country for Accession of Bosnia and Herzegovina to the European Union, accession following the decision of the European Council.
, ''The World Factbook'', 22 August 2006 It lies between latitudes 42nd parallel north, 42° and 46th parallel north, 46° N, and longitudes 15th meridian east, 15° and 20th meridian east, 20° E. The country's name comes from the two alleged regions Bosnia (region), Bosnia and Herzegovina, whose border was never defined. Historically, Bosnia's official name never included any of its many regions until the Austro-Hungarian occupation. The country is mostly mountainous, encompassing the central Dinaric Alps. The northeastern parts reach into the Pannonian Basin, while in the south it borders the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic. The Dinaric Alps generally run in a southeast–northwest direction, and get higher towards the south. The highest point of the country is the peak of Maglić (mountain), Maglić at , on the Montenegrin border. Other major mountains include Volujak (mountain), Volujak, Zelengora, Lelija, Lebršnik, Orjen, Kozara, Grmeč, Čvrsnica, Prenj, Vran, Vranica, Velež (Bosnia and Herzegovina), Velež, Vlašić (Bosnian mountain), Vlašić, Cincar, Romanija, Jahorina, Bjelašnica, Treskavica and Trebević. The geological composition of the Dinaric chain of mountains in Bosnia consists primarily of limestone (including Mesozoic limestone), with deposits of iron, coal, zinc, manganese, bauxite, lead, and salt present in some areas, especially in central and northern Bosnia. Overall, nearly 50% of Bosnia and Herzegovina is forested. Most forest areas are in the centre, east and west parts of Bosnia. Herzegovina has a drier Mediterranean climate, with dominant karst topography. Northern Bosnia (Posavina) contains very fertile agricultural land along the Sava river and the corresponding area is heavily farmed. This farmland is a part of the Pannonian Plain stretching into neighboring Croatia and Serbia. The country has only of coastline,Bosnia-and-Herzegovina Neum britannica.com
, ''britannica.com'', 9 September 2015 around the town of Neum in the Herzegovina-Neretva Canton. Although the city is surrounded by Croatian peninsulas, by international law, Bosnia and Herzegovina has a right of passage to the outer sea. Sarajevo is the capital and largest city. Other major cities include Banja Luka and Prijedor in the northwest region known as Bosanska Krajina, Tuzla, Bijeljina, Doboj and Brčko in the northeast, Zenica in the central part of the country, and Mostar, the largest city in the southern region of Herzegovina. There are seven major rivers in Bosnia and Herzegovina:
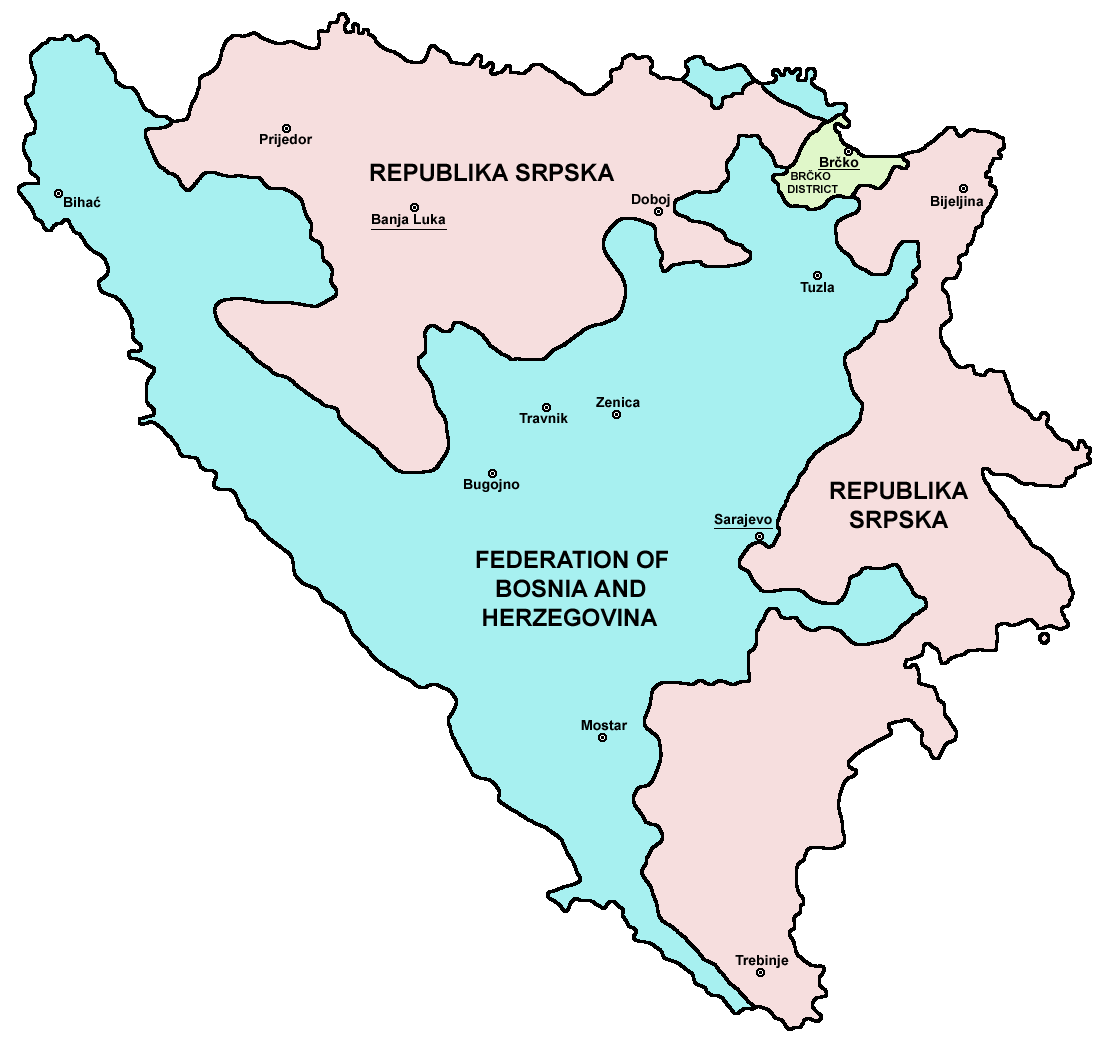 As a result of the Dayton Agreement, the civilian peace implementation is supervised by the High Representative for Bosnia and Herzegovina selected by the Peace Implementation Council (PIC). The High Representative is the highest political authority in the country. The High Representative has many governmental and legislative powers, including the dismissal of elected and non-elected officials. Due to the vast powers of the High Representative over Politics of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnian politics and essential veto powers, the position has also been compared to that of a viceroy.
Politics take place in a framework of a parliamentary system, parliamentary representative democracy, whereby Executive (government), executive power is exercised by the Council of Ministers of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Legislature, Legislative power is vested in both the Council of Ministers and the Parliamentary Assembly of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Members of the Parliamentary Assembly are chosen according to a proportional representation (PR) system.
Bosnia and Herzegovina is a liberal democracy. It has several levels of political structuring, according to the Dayton Agreement. The most important of these levels is the division of the country into two entities: the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Republika Srpska. The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina covers 51% of Bosnia and Herzegovina's total area, while Republika Srpska covers 49%. The entities, based largely on the territories held by the two warring sides at the time, were formally established by the Dayton Agreement in 1995 because of the tremendous changes in Bosnia and Herzegovina's ethnic structure. At the national level, there exists only a finite set of exclusive or joint competencies, whereas the majority of authority rests within the entities. Sumantra Bose describes Bosnia and Herzegovina as a consociational confederation.
The Brčko District in the north of the country was created in 2000, out of land from both entities. It officially belongs to both, but is governed by neither, and functions under a decentralized system of local government. For election purposes, Brčko District voters can choose to participate in either the Federation or Republika Srpska elections. The Brčko District has been praised for maintaining a multiethnic population and a level of prosperity significantly above the national average.OHR Bulletin 66 (3 February 1998)
As a result of the Dayton Agreement, the civilian peace implementation is supervised by the High Representative for Bosnia and Herzegovina selected by the Peace Implementation Council (PIC). The High Representative is the highest political authority in the country. The High Representative has many governmental and legislative powers, including the dismissal of elected and non-elected officials. Due to the vast powers of the High Representative over Politics of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnian politics and essential veto powers, the position has also been compared to that of a viceroy.
Politics take place in a framework of a parliamentary system, parliamentary representative democracy, whereby Executive (government), executive power is exercised by the Council of Ministers of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Legislature, Legislative power is vested in both the Council of Ministers and the Parliamentary Assembly of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Members of the Parliamentary Assembly are chosen according to a proportional representation (PR) system.
Bosnia and Herzegovina is a liberal democracy. It has several levels of political structuring, according to the Dayton Agreement. The most important of these levels is the division of the country into two entities: the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Republika Srpska. The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina covers 51% of Bosnia and Herzegovina's total area, while Republika Srpska covers 49%. The entities, based largely on the territories held by the two warring sides at the time, were formally established by the Dayton Agreement in 1995 because of the tremendous changes in Bosnia and Herzegovina's ethnic structure. At the national level, there exists only a finite set of exclusive or joint competencies, whereas the majority of authority rests within the entities. Sumantra Bose describes Bosnia and Herzegovina as a consociational confederation.
The Brčko District in the north of the country was created in 2000, out of land from both entities. It officially belongs to both, but is governed by neither, and functions under a decentralized system of local government. For election purposes, Brčko District voters can choose to participate in either the Federation or Republika Srpska elections. The Brčko District has been praised for maintaining a multiethnic population and a level of prosperity significantly above the national average.OHR Bulletin 66 (3 February 1998)
Final hearing of the Arbitration Tribunal in Vienna
. OHR. The third level of Bosnia and Herzegovina's political subdivision is manifested in Cantons of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, cantons. They are unique to the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina entity, which consists of ten of them. Each has a cantonal government, which is under the law of the Federation as a whole. Some cantons are ethnically mixed and have special laws to ensure the equality of all constituent people. The fourth level of political division in Bosnia and Herzegovina are the Municipalities of Bosnia and Herzegovina, municipalities. The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina is divided into 79 municipalities, and Republika Srpska into 64. Municipalities also have their own local government, and are typically based on the most significant city or place in their territory. As such, many municipalities have a long tradition and history with their present boundaries. Some others, however, were only created following the recent war after traditional municipalities were split by the Inter-Entity Boundary Line. Each canton in the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina consists of several municipalities, which are divided into local communities. Besides entities, cantons, and municipalities, Bosnia and Herzegovina also has four "official" cities. These are: Banja Luka, Mostar, Sarajevo and Istočno Sarajevo, East Sarajevo. The territory and government of the cities of Banja Luka and Mostar corresponds to the municipalities of the same name, while the cities of Sarajevo and East Sarajevo officially consist of several municipalities. Cities have their own city government whose power is in between that of the municipalities and cantons (or the entity, in the case of Republika Srpska). More recently, several central institutions have been established (such as a defence minister, defense ministry, security ministry, state court, indirect taxation service and so on) in the process of transferring part of the jurisdiction from the entities to the state. The representation of the government of Bosnia and Herzegovina is by elites who represent the country's three major groups, with each having a guaranteed share of power. The Chairman of the Presidency of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Chair of the Presidency of Bosnia and Herzegovina rotates among three members (Bosniaks, Bosniak, Serbs, Serb, Croats, Croat), each elected as the chair for an eight-month term within their four-year term as a member. The three members of the Presidency are elected directly by the people, with Federation voters voting for the Bosniak and the Croat and the Republika Srpska voters voting for the Serb. The Chairman of the Council of Ministers of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Chair of the Council of Ministers is nominated by the Presidency and approved by the parliamentary House of Representatives of Bosnia and Herzegovina, House of Representatives. The Chair of the Council of Ministers is then responsible for appointing a Foreign Minister, Minister of Foreign Trade and others as appropriate. The Parliamentary Assembly is the lawmaking body in Bosnia and Herzegovina. It consists of two houses: the House of Peoples of Bosnia and Herzegovina, House of Peoples and the House of Representatives. The House of Peoples has 15 delegates chosen by parliaments of the entities, two-thirds of which come from the Federation (5 Bosniaks and 5 Croats) and one-third from the Republika Srpska (5 Serbs). The House of Representatives is composed of 42 Members elected by the people under a form of proportional representation, two-thirds elected from the Federation and one-third elected from Republika Srpska. The Constitutional Court of Bosnia and Herzegovina is the supreme, final arbiter of legal matters. It is composed of nine members: four members are selected by the House of Representatives of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Federal House of Representatives, two by the National Assembly (Republika Srpska), National Assembly of Republika Srpska and three by the President of the European Court of Human Rights after consultation with the Presidency, who cannot be Bosnian citizens. However, the highest political authority in the country is the High Representative for Bosnia and Herzegovina, the chief executive officer for the international civilian presence in the country and is selected by the European Union. Since 1995, the High Representative has been able to bypass the elected parliamentary assembly, and since 1997 has been able to remove elected officials. The methods selected by the High Representative have been criticized as undemocratic. International supervision High Representative for Bosnia and Herzegovina#Conditions for closure of the Office of the High Representative, is to end when the country is deemed politically and democratically stable and self-sustaining.
 Bosnia and Herzegovina is home to three ethnic "Ethnic groups in Bosnia and Herzegovina, constituent peoples", namely Bosniaks, Serbs and Croats, plus a number of smaller groups including History of the Jews in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Jews and Romani people in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Roma. According to data from the 2013 census published by the Statistical system of Bosnia and Herzegovina#The Agency for Statistics of Bosnia and Herzegovina (BHAS), Agency for Statistics of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosniaks constitute 50.1% of the population, Serbs 30.8%, Croats 15.5% and others 2.7%, with the remaining respondents not declaring their ethnicity or not answering. The census results are contested by the Republika Srpska statistical office and by Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnian Serb politicians. The dispute over the census concerns the inclusion of non-permanent Bosnian residents in the figures, which Republika Srpska officials oppose. The European Union's statistics office, Eurostat, concluded in May 2016 that the census methodology used by the Bosnian statistical agency is in line with international recommendations.
Bosnia and Herzegovina is home to three ethnic "Ethnic groups in Bosnia and Herzegovina, constituent peoples", namely Bosniaks, Serbs and Croats, plus a number of smaller groups including History of the Jews in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Jews and Romani people in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Roma. According to data from the 2013 census published by the Statistical system of Bosnia and Herzegovina#The Agency for Statistics of Bosnia and Herzegovina (BHAS), Agency for Statistics of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosniaks constitute 50.1% of the population, Serbs 30.8%, Croats 15.5% and others 2.7%, with the remaining respondents not declaring their ethnicity or not answering. The census results are contested by the Republika Srpska statistical office and by Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnian Serb politicians. The dispute over the census concerns the inclusion of non-permanent Bosnian residents in the figures, which Republika Srpska officials oppose. The European Union's statistics office, Eurostat, concluded in May 2016 that the census methodology used by the Bosnian statistical agency is in line with international recommendations.
 During the Bosnian War, the economy suffered €200 billion in material damages, roughly €326.38 billion in 2022 (inflation adjusted). Bosnia and Herzegovina faces the dual-problem of rebuilding a war-torn country and introducing transitional liberal market reforms to its formerly mixed economy. One legacy of the previous era is a strong industry; under former republic president Džemal Bijedić and Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslav President Josip Broz Tito, metal industries were promoted in the republic, resulting in the development of a large share of Yugoslavia's plants; Socialist Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina, SR Bosnia and Herzegovina had a very strong industrial export oriented economy in the 1970s and 1980s, with large scale exports worth millions of USD, US$.
For most of Bosnia's history, agriculture has been conducted on privately owned farms; Fresh food has traditionally been exported from the republic.
The war in the 1990s, caused a dramatic change in the Bosnian economy. GDP fell by 60% and the destruction of physical infrastructure devastated the economy. With much of the production capacity unrestored, the Bosnian economy still faces considerable difficulties. Figures show GDP and per capita income increased 10% from 2003 to 2004; this and Bosnia's shrinking Government debt, national debt being negative trends, and high unemployment 38.7% and a large Balance of trade, trade deficit remain cause for concern.
The national currency is the (Euro-pegged) Bosnia and Herzegovina convertible mark, convertible mark (KM), controlled by the currency board. Annual inflation is the lowest relative to other countries in the region at 1.9% in 2004. The international debt was $5.1 billion (as of 31 December 2014). Gross domestic product, Real GDP growth rate was 5% for 2004 according to the Central Bank of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Statistical Office of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Bosnia and Herzegovina has displayed positive progress in the previous years, which decisively moved its place from the lowest income equality rank of List of countries by income equality, income equality rankings fourteen out of 193 nations.
According to Eurostat data, Bosnia and Herzegovina's PPS GDP per capita stood at 29 per cent of the EU average in 2010.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) announced a loan to Bosnia worth US$500 million to be delivered by IMF Stand-By Arrangement, Stand-By Arrangement. This was scheduled to be approved in September 2012.
The Embassy of the United States, Sarajevo, United States Embassy in Sarajevo produces the Country Commercial Guide – an annual report that delivers a comprehensive look at Bosnia and Herzegovina's commercial and economic environment, using economic, political, and market analysis.
By some estimates, Informal economy, grey economy is 25.5% of GDP.
In 2017, exports grew by 17% when compared to the previous year, totaling €5.65 billion. The total volume of International trade, foreign trade in 2017 amounted to €14.97 billion and increased by 14% compared to the previous year. Imports of goods increased by 12% and amounted to €9.32 billion. The balance of trade, coverage of imports by exports increased by 3% compared to the previous year and now it is 61 percent. In 2017, Bosnia and Herzegovina mostly exported car seats, electricity, wood processing, processed wood, aluminium and furniture. In the same year, it mostly imported Petroleum, crude oil, Car, automobiles, motor oil, coal and briquettes.
The unemployment rate in 2017 was 20.5%, but The Vienna Institute for International Economic Studies is predicting falling unemployment rate for the next few years. In 2018, the unemployment should be 19.4% and it should further fall to 18.8% in 2019. In 2020, the unemployment rate should go down to 18.3%.
On 31 December 2017, the Council of Ministers of Bosnia and Herzegovina issued the report on public debt of Bosnia and Herzegovina, stating the public debt was reduced by €389.97 million, or by more than 6% when compared to 31 December 2016. By the end of 2017, public debt was €5.92 billion, which amounted to 35.6 percent of GDP.
, there were 32,292 registered companies in the country, which together had revenues of €33.572 billion that same year.
In 2017, the country received €397.35 million in foreign direct investment, which equals to 2.5% of the GDP.
In 2017, Bosnia and Herzegovina ranked third in the world in terms of the number of new jobs created by foreign investment, relative to the number of inhabitants.
In 2018, Bosnia and Herzegovina exported goods worth 11.9 billion KM (€6.07 billion), which is 7.43% higher than in the same period in 2017, while imports amounted to 19.27 billion KM (€9.83 billion), which is 5.47% higher.
The average price of new apartments sold in the country in the first six months of 2018 is 1,639 km (€886.31) per square metre. This represents a jump of 3.5% from the previous year.
On 30 June 2018, public debt of Bosnia and Herzegovina amounted to about €6.04 billion, of which external debt is 70.56 percent, while the internal debt is 29.4 percent of total public indebtedness. The share of public debt in gross domestic product is 34.92 percent.
In the first 7 months of 2018, 811,660 tourists visited the country, a 12.2% jump when compared to the first 7 months of 2017. In the first 11 months of 2018, 1,378,542 tourists visited Bosnia-Herzegovina, an increase of 12.6%, and had 2,871,004 overnight hotel stays, a 13.8% increase from the previous year. Also, 71.8% of the tourists came from foreign countries. In the first seven months of 2019, 906,788 tourists visited the country, an 11.7% jump from the previous year.
In 2018, the total value of mergers and acquisitions in Bosnia and Herzegovina amounted to €404.6 million.
In 2018, 99.5 percent of enterprises in Bosnia and Herzegovina used computers in their business, while 99.3 percent had internet connections, according to a survey conducted by the Bosnia and Herzegovina Statistics Agency.
In 2018, Bosnia and Herzegovina received 783.4 million KM (€400.64 million) in direct foreign investment, which was equivalent to 2.3% of GDP.
In 2018, the Central Bank of Bosnia and Herzegovina made a profit of 8,430,875 km (€4,306,347).
The World Bank predicted that the economy would grow 3.4% in 2019.
Bosnia and Herzegovina was placed 83rd on the Index of Economic Freedom for 2019. The total rating for Bosnia and Herzegovina is 61.9. This position represents some progress relative to the 91st place in 2018. This result is below the regional level, but still above the global average, making Bosnia and Herzegovina a "moderately free" country.
On 31 January 2019, total deposits in Bosnian banks were KM 21.9 billion (€11.20 billion), which represents 61.15% of nominal GDP.
In the second quarter of 2019, the average price of new apartments sold in Bosnia and Herzegovina was 1,606 km (€821.47) per square metre.
In the first six months of 2019, exports amounted to 5.829 billion KM (€2.98 billion), which is 0.1% less than in the same period of 2018, while imports amounted to 9.779 billion KM (€5.00 billion), which is by 4.5% more than in the same period of the previous year.
In the first six months of 2019, foreign direct investment amounted to 650.1 million KM (€332.34 million).
Bosnia and Herzegovina was ranked 80th in the Global Innovation Index in 2024.
As of 30 November 2023, Bosnia and Herzegovina had 1.3 million registered motor vehicles.
During the Bosnian War, the economy suffered €200 billion in material damages, roughly €326.38 billion in 2022 (inflation adjusted). Bosnia and Herzegovina faces the dual-problem of rebuilding a war-torn country and introducing transitional liberal market reforms to its formerly mixed economy. One legacy of the previous era is a strong industry; under former republic president Džemal Bijedić and Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslav President Josip Broz Tito, metal industries were promoted in the republic, resulting in the development of a large share of Yugoslavia's plants; Socialist Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina, SR Bosnia and Herzegovina had a very strong industrial export oriented economy in the 1970s and 1980s, with large scale exports worth millions of USD, US$.
For most of Bosnia's history, agriculture has been conducted on privately owned farms; Fresh food has traditionally been exported from the republic.
The war in the 1990s, caused a dramatic change in the Bosnian economy. GDP fell by 60% and the destruction of physical infrastructure devastated the economy. With much of the production capacity unrestored, the Bosnian economy still faces considerable difficulties. Figures show GDP and per capita income increased 10% from 2003 to 2004; this and Bosnia's shrinking Government debt, national debt being negative trends, and high unemployment 38.7% and a large Balance of trade, trade deficit remain cause for concern.
The national currency is the (Euro-pegged) Bosnia and Herzegovina convertible mark, convertible mark (KM), controlled by the currency board. Annual inflation is the lowest relative to other countries in the region at 1.9% in 2004. The international debt was $5.1 billion (as of 31 December 2014). Gross domestic product, Real GDP growth rate was 5% for 2004 according to the Central Bank of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Statistical Office of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Bosnia and Herzegovina has displayed positive progress in the previous years, which decisively moved its place from the lowest income equality rank of List of countries by income equality, income equality rankings fourteen out of 193 nations.
According to Eurostat data, Bosnia and Herzegovina's PPS GDP per capita stood at 29 per cent of the EU average in 2010.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) announced a loan to Bosnia worth US$500 million to be delivered by IMF Stand-By Arrangement, Stand-By Arrangement. This was scheduled to be approved in September 2012.
The Embassy of the United States, Sarajevo, United States Embassy in Sarajevo produces the Country Commercial Guide – an annual report that delivers a comprehensive look at Bosnia and Herzegovina's commercial and economic environment, using economic, political, and market analysis.
By some estimates, Informal economy, grey economy is 25.5% of GDP.
In 2017, exports grew by 17% when compared to the previous year, totaling €5.65 billion. The total volume of International trade, foreign trade in 2017 amounted to €14.97 billion and increased by 14% compared to the previous year. Imports of goods increased by 12% and amounted to €9.32 billion. The balance of trade, coverage of imports by exports increased by 3% compared to the previous year and now it is 61 percent. In 2017, Bosnia and Herzegovina mostly exported car seats, electricity, wood processing, processed wood, aluminium and furniture. In the same year, it mostly imported Petroleum, crude oil, Car, automobiles, motor oil, coal and briquettes.
The unemployment rate in 2017 was 20.5%, but The Vienna Institute for International Economic Studies is predicting falling unemployment rate for the next few years. In 2018, the unemployment should be 19.4% and it should further fall to 18.8% in 2019. In 2020, the unemployment rate should go down to 18.3%.
On 31 December 2017, the Council of Ministers of Bosnia and Herzegovina issued the report on public debt of Bosnia and Herzegovina, stating the public debt was reduced by €389.97 million, or by more than 6% when compared to 31 December 2016. By the end of 2017, public debt was €5.92 billion, which amounted to 35.6 percent of GDP.
, there were 32,292 registered companies in the country, which together had revenues of €33.572 billion that same year.
In 2017, the country received €397.35 million in foreign direct investment, which equals to 2.5% of the GDP.
In 2017, Bosnia and Herzegovina ranked third in the world in terms of the number of new jobs created by foreign investment, relative to the number of inhabitants.
In 2018, Bosnia and Herzegovina exported goods worth 11.9 billion KM (€6.07 billion), which is 7.43% higher than in the same period in 2017, while imports amounted to 19.27 billion KM (€9.83 billion), which is 5.47% higher.
The average price of new apartments sold in the country in the first six months of 2018 is 1,639 km (€886.31) per square metre. This represents a jump of 3.5% from the previous year.
On 30 June 2018, public debt of Bosnia and Herzegovina amounted to about €6.04 billion, of which external debt is 70.56 percent, while the internal debt is 29.4 percent of total public indebtedness. The share of public debt in gross domestic product is 34.92 percent.
In the first 7 months of 2018, 811,660 tourists visited the country, a 12.2% jump when compared to the first 7 months of 2017. In the first 11 months of 2018, 1,378,542 tourists visited Bosnia-Herzegovina, an increase of 12.6%, and had 2,871,004 overnight hotel stays, a 13.8% increase from the previous year. Also, 71.8% of the tourists came from foreign countries. In the first seven months of 2019, 906,788 tourists visited the country, an 11.7% jump from the previous year.
In 2018, the total value of mergers and acquisitions in Bosnia and Herzegovina amounted to €404.6 million.
In 2018, 99.5 percent of enterprises in Bosnia and Herzegovina used computers in their business, while 99.3 percent had internet connections, according to a survey conducted by the Bosnia and Herzegovina Statistics Agency.
In 2018, Bosnia and Herzegovina received 783.4 million KM (€400.64 million) in direct foreign investment, which was equivalent to 2.3% of GDP.
In 2018, the Central Bank of Bosnia and Herzegovina made a profit of 8,430,875 km (€4,306,347).
The World Bank predicted that the economy would grow 3.4% in 2019.
Bosnia and Herzegovina was placed 83rd on the Index of Economic Freedom for 2019. The total rating for Bosnia and Herzegovina is 61.9. This position represents some progress relative to the 91st place in 2018. This result is below the regional level, but still above the global average, making Bosnia and Herzegovina a "moderately free" country.
On 31 January 2019, total deposits in Bosnian banks were KM 21.9 billion (€11.20 billion), which represents 61.15% of nominal GDP.
In the second quarter of 2019, the average price of new apartments sold in Bosnia and Herzegovina was 1,606 km (€821.47) per square metre.
In the first six months of 2019, exports amounted to 5.829 billion KM (€2.98 billion), which is 0.1% less than in the same period of 2018, while imports amounted to 9.779 billion KM (€5.00 billion), which is by 4.5% more than in the same period of the previous year.
In the first six months of 2019, foreign direct investment amounted to 650.1 million KM (€332.34 million).
Bosnia and Herzegovina was ranked 80th in the Global Innovation Index in 2024.
As of 30 November 2023, Bosnia and Herzegovina had 1.3 million registered motor vehicles.
, Reuters.com; retrieved 17 March 2010. Since 2019, pilgrimages to Međugorje have been officially authorized and organized by the Holy See, Vatican. Bosnia has also become an increasingly popular skiing and Ecotourism destination. The mountains that hosted the winter olympic games of Bjelašnica, Jahorina and Igman are the most visited skiing mountains in Bosnia-Herzegovina. Bosnia and Herzegovina remains one of the last undiscovered natural regions of the southern area of the Alps, with vast tracts of wild and untouched nature attracting adventurers and nature lovers. ''National Geographic'' named Bosnia and Herzegovina as the best mountain biking adventure destination for 2012.
, The central Dinaric Alps, Bosnian Dinaric Alps are favored by hikers and mountaineers, as they contain both Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean and Alpine climate, Alpine climates. Rafting, Whitewater rafting has become somewhat of a national sport, national pastime in Bosnia and Herzegovina. The primary rivers used for whitewater rafting in the country include the Vrbas (river), Vrbas, Tara (Drina), Tara, Drina, Neretva and Una (Sava), Una. Meanwhile, the most prominent rivers are the Vrbas and Tara, as they both hosted International Rafting Federation, The 2009 World Rafting Championship. The reason the Tara river is immensely popular for whitewater rafting is because it contains the deepest canyon, river canyon in Europe, the Tara River Canyon. Most recently, the ''HuffPost, Huffington Post'' named Bosnia and Herzegovina the "9th Greatest Adventure in the World for 2013", adding that the country boasts "the cleanest water and air in Europe; the greatest untouched forests; and the most wildlife. The best way to experience is the three rivers trip, which purls through the best the Balkans have to offer."
 Sarajevo International Airport, also known as Butmir Airport, is the main international airport in Bosnia and Herzegovina, located southwest of the Sarajevo main railway station in the city of Sarajevo in the suburb of Butmir.
Railway operations in Bosnia and Herzegovina are successors of the Yugoslav Railways within the country boundaries following independence from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, former Yugoslavia in 1992. Today, they are operated by the Railways of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ŽFBiH) in the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and by Republika Srpska Railways (ŽRS) in Republika Srpska.
Sarajevo International Airport, also known as Butmir Airport, is the main international airport in Bosnia and Herzegovina, located southwest of the Sarajevo main railway station in the city of Sarajevo in the suburb of Butmir.
Railway operations in Bosnia and Herzegovina are successors of the Yugoslav Railways within the country boundaries following independence from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, former Yugoslavia in 1992. Today, they are operated by the Railways of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ŽFBiH) in the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and by Republika Srpska Railways (ŽRS) in Republika Srpska.
 Primary schooling lasts for nine years. Secondary education is provided by general and technical secondary schools (typically Gymnasium (school), Gymnasiums) where studies typically last for four years. All forms of secondary schooling include an element of vocational education, vocational training. Pupils graduating from general secondary schools obtain the ''Matura'' and can enroll in any tertiary educational institution or academy by passing a qualification examination prescribed by the governing body or institution. Students graduating technical subjects obtain a Diploma.
The first bespoke higher-education institution was a school of Sufism, Sufi philosophy established by Gazi Husrev Bey, Gazi Husrev-beg in 1531. Numerous other religious schools then followed. In 1887, under the Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarian Empire, a Sharia law school began a five-year program.
In the 1940s, the University of Sarajevo became the city's first secular higher education institute. In the 1950s, post-baccalaurate graduate degrees became available. Severely damaged during the Bosnian War, war, it was recently rebuilt in partnership with more than 40 other universities. There are various other institutions of higher education, including: University Džemal Bijedić of Mostar, University of Banja Luka, University of Mostar, University of East Sarajevo, University of Tuzla, American University in Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Academy of Sciences and Arts of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Also, Bosnia and Herzegovina is home to several private and international higher education institutions, some of which are:
*Sarajevo School of Science and Technology
*International University of Sarajevo
*American University in Bosnia and Herzegovina
*Sarajevo Graduate School of Business
*International Burch University
*United World College in Mostar
Primary schooling lasts for nine years. Secondary education is provided by general and technical secondary schools (typically Gymnasium (school), Gymnasiums) where studies typically last for four years. All forms of secondary schooling include an element of vocational education, vocational training. Pupils graduating from general secondary schools obtain the ''Matura'' and can enroll in any tertiary educational institution or academy by passing a qualification examination prescribed by the governing body or institution. Students graduating technical subjects obtain a Diploma.
The first bespoke higher-education institution was a school of Sufism, Sufi philosophy established by Gazi Husrev Bey, Gazi Husrev-beg in 1531. Numerous other religious schools then followed. In 1887, under the Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarian Empire, a Sharia law school began a five-year program.
In the 1940s, the University of Sarajevo became the city's first secular higher education institute. In the 1950s, post-baccalaurate graduate degrees became available. Severely damaged during the Bosnian War, war, it was recently rebuilt in partnership with more than 40 other universities. There are various other institutions of higher education, including: University Džemal Bijedić of Mostar, University of Banja Luka, University of Mostar, University of East Sarajevo, University of Tuzla, American University in Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Academy of Sciences and Arts of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Also, Bosnia and Herzegovina is home to several private and international higher education institutions, some of which are:
*Sarajevo School of Science and Technology
*International University of Sarajevo
*American University in Bosnia and Herzegovina
*Sarajevo Graduate School of Business
*International Burch University
*United World College in Mostar
Bosnia and Herzegovina
", EJC Media Landscapes Post-war developments included the establishment of an independent Communication Regulatory Agency, the adoption of a Press Code, the establishment of the Press Council, the decriminalization of libel and defamation, the introduction of a rather advanced Freedom of Access to Information Law, and the creation of a Public Service Broadcasting System from the formerly state-owned broadcaster. Yet, internationally backed positive developments have been often obstructed by domestic elites, and the professionalisation of media and journalists has proceeded only slowly. High levels of partisanship and linkages between the media and the political systems hinder the adherence to professional code of conducts.
 The Bosnia and Herzegovina art, art of Bosnia and Herzegovina was always evolving and ranged from the original medieval tombstones called Stećak, Stećci to paintings in Kotromanić dynasty, Kotromanić court. Twenty stećak necropolis sites in Bosnia and Herzegovina were added on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 2006. However, only with the arrival of Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarians did the painting renaissance in Bosnia really begin to flourish. The first educated artists from European academies appeared with the beginning of the 20th century. Among those are: Gabrijel Jurkić, Petar Šain, Roman Petrović and Lazar Drljača.
After World War II, artists like Mersad Berber and Safet Zec rose in popularity.
In 2007, Ars Aevi, a museum of contemporary art that includes works by renowned world artists, was founded in Sarajevo.
The Bosnia and Herzegovina art, art of Bosnia and Herzegovina was always evolving and ranged from the original medieval tombstones called Stećak, Stećci to paintings in Kotromanić dynasty, Kotromanić court. Twenty stećak necropolis sites in Bosnia and Herzegovina were added on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 2006. However, only with the arrival of Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarians did the painting renaissance in Bosnia really begin to flourish. The first educated artists from European academies appeared with the beginning of the 20th century. Among those are: Gabrijel Jurkić, Petar Šain, Roman Petrović and Lazar Drljača.
After World War II, artists like Mersad Berber and Safet Zec rose in popularity.
In 2007, Ars Aevi, a museum of contemporary art that includes works by renowned world artists, was founded in Sarajevo.
 Bosnian cuisine uses many spices, in moderate quantities. Most dishes are light, as they are boiled; the sauces are fully natural, consisting of little more than the natural juices of the vegetables in the dish. Typical ingredients include tomatoes, potatoes, onions, garlic, Capsicum, peppers, cucumbers, carrots, cabbage, mushrooms, spinach, zucchini, bean, dried beans, fresh beans, plums, milk, paprika and cream called Smetana (dairy product), pavlaka. Bosnian cuisine is balanced between Western culture, Western and Eastern world, Eastern influences. As a result of the Turkish cuisine, Ottoman administration for almost 500 years, Bosnian food is closely related to Turkish, Greek cuisine, Greek and other former Ottoman and Mediterranean cuisine, Mediterranean cuisines. However, because of years of Austrian rule, there are many influences from Central European cuisine, Central Europe. Typical meat dishes include primarily beef and Lamb and mutton, lamb. Some local specialties are ćevapi, Börek, burek, dolma, Sarma (food), sarma, Pilaf, pilav, goulash, ajvar and a whole range of Eastern sweets. Ćevapi is a grilled dish of minced meat, a type of kebab, popular in former Yugoslavia and considered a national dish in Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia. Local wines come from Herzegovina where the climate is suitable for growing grapes. Herzegovinian ''loza'' (similar to Italian Grappa but less sweet) is very popular. Plum (''rakija'') or apple (''jabukovača'') alcohol beverages are produced in the north. In the south, distilleries used to produce vast quantities of brandy and supply all of ex-Yugoslav alcohol factories (brandy is the base of most alcoholic drinks).
Coffeehouses, where Turkish coffee, Bosnian coffee is served in Cezve, džezva with Turkish delight, rahat lokum and Cube sugar, sugar cubes, are common in Sarajevo and every city in the country. Coffee drinking is a favorite Bosnian pastime and part of the culture. Bosnia and Herzegovina is the ninth country in the entire world by per capita coffee consumption.
Bosnian cuisine uses many spices, in moderate quantities. Most dishes are light, as they are boiled; the sauces are fully natural, consisting of little more than the natural juices of the vegetables in the dish. Typical ingredients include tomatoes, potatoes, onions, garlic, Capsicum, peppers, cucumbers, carrots, cabbage, mushrooms, spinach, zucchini, bean, dried beans, fresh beans, plums, milk, paprika and cream called Smetana (dairy product), pavlaka. Bosnian cuisine is balanced between Western culture, Western and Eastern world, Eastern influences. As a result of the Turkish cuisine, Ottoman administration for almost 500 years, Bosnian food is closely related to Turkish, Greek cuisine, Greek and other former Ottoman and Mediterranean cuisine, Mediterranean cuisines. However, because of years of Austrian rule, there are many influences from Central European cuisine, Central Europe. Typical meat dishes include primarily beef and Lamb and mutton, lamb. Some local specialties are ćevapi, Börek, burek, dolma, Sarma (food), sarma, Pilaf, pilav, goulash, ajvar and a whole range of Eastern sweets. Ćevapi is a grilled dish of minced meat, a type of kebab, popular in former Yugoslavia and considered a national dish in Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia. Local wines come from Herzegovina where the climate is suitable for growing grapes. Herzegovinian ''loza'' (similar to Italian Grappa but less sweet) is very popular. Plum (''rakija'') or apple (''jabukovača'') alcohol beverages are produced in the north. In the south, distilleries used to produce vast quantities of brandy and supply all of ex-Yugoslav alcohol factories (brandy is the base of most alcoholic drinks).
Coffeehouses, where Turkish coffee, Bosnian coffee is served in Cezve, džezva with Turkish delight, rahat lokum and Cube sugar, sugar cubes, are common in Sarajevo and every city in the country. Coffee drinking is a favorite Bosnian pastime and part of the culture. Bosnia and Herzegovina is the ninth country in the entire world by per capita coffee consumption.
 Association football is the most popular sport in Bosnia and Herzegovina. It dates from 1903, but its popularity grew significantly after World War I. Bosnian clubs FK Sarajevo and FK Željezničar Sarajevo, Željezničar won the Yugoslav First League, Yugoslav Championship, while the Yugoslavia national football team, Yugoslav national football team included Bosnian players of all ethnic backgrounds and generations, such as Safet Sušić, Zlatko Vujović, Mehmed Baždarević, Davor Jozić, Faruk Hadžibegić, Predrag Pašić, Blaž Slišković, Vahid Halilhodžić, Dušan Bajević, Ivica Osim, Josip Katalinski, Tomislav Knez, Velimir Sombolac and numerous others. The Bosnia and Herzegovina national football team played at the 2014 FIFA World Cup, its first major tournament. Players on the team again includes notable players of all country's ethnic background, such as then and now captains Emir Spahić, Zvjezdan Misimović and Edin Džeko, defenders like Ognjen Vranješ, Sead Kolašinac and Toni Šunjić, midfielders like Miralem Pjanić and Senad Lulić, striker Vedad Ibišević, etc. Former Bosnian footballers include Hasan Salihamidžić, who became only the second Bosnian to ever win a UEFA Champions League trophy, after Elvir Baljić. He made 234 appearances and scored 31 goals for German club FC Bayern Munich. Sergej Barbarez, who played for several clubs in the German Bundesliga. including Borussia Dortmund, Hamburger SV and Bayer 04 Leverkusen, Bayer Leverkusen was joint-top scorer in the 2000–01 Bundesliga season with 22 goals. Meho Kodro spent most of his career playing in Spain, most notably with Real Sociedad and FC Barcelona. Elvir Rahimić made 302 appearances for Russian club PFC CSKA Moscow, CSKA Moscow with whom he won the UEFA Europa League, UEFA Cup in 2005 UEFA Cup Final, 2005.
Milena Nikolić, member of the Bosnia and Herzegovina women's national football team, women's national team, was the 2013–14 UEFA Women's Champions League UEFA Women's Champions League#Top scorers by tournament, top scorer.
Bosnia and Herzegovina was the world champion of volleyball at the 2004 Summer Paralympics and volleyball at the 2012 Summer Paralympics. Many among those on the team lost their legs in the Bosnian War. Its Bosnia and Herzegovina national sitting volleyball team, national sitting volleyball team is one of the dominant forces in Sitting volleyball, the sport worldwide, winning nine European Championships, three World Championships and two Volleyball at the Summer Paralympics, Paralympic gold medals.
Tennis is also gaining a lot of popularity after the recent successes of Damir Džumhur and Mirza Bašić at Grand Slam (tennis), Grand Slam level. Other notable tennis players who have represented Bosnia and Herzegovina are Tomislav Brkić, Amer Delić and Mervana Jugić-Salkić.
Association football is the most popular sport in Bosnia and Herzegovina. It dates from 1903, but its popularity grew significantly after World War I. Bosnian clubs FK Sarajevo and FK Željezničar Sarajevo, Željezničar won the Yugoslav First League, Yugoslav Championship, while the Yugoslavia national football team, Yugoslav national football team included Bosnian players of all ethnic backgrounds and generations, such as Safet Sušić, Zlatko Vujović, Mehmed Baždarević, Davor Jozić, Faruk Hadžibegić, Predrag Pašić, Blaž Slišković, Vahid Halilhodžić, Dušan Bajević, Ivica Osim, Josip Katalinski, Tomislav Knez, Velimir Sombolac and numerous others. The Bosnia and Herzegovina national football team played at the 2014 FIFA World Cup, its first major tournament. Players on the team again includes notable players of all country's ethnic background, such as then and now captains Emir Spahić, Zvjezdan Misimović and Edin Džeko, defenders like Ognjen Vranješ, Sead Kolašinac and Toni Šunjić, midfielders like Miralem Pjanić and Senad Lulić, striker Vedad Ibišević, etc. Former Bosnian footballers include Hasan Salihamidžić, who became only the second Bosnian to ever win a UEFA Champions League trophy, after Elvir Baljić. He made 234 appearances and scored 31 goals for German club FC Bayern Munich. Sergej Barbarez, who played for several clubs in the German Bundesliga. including Borussia Dortmund, Hamburger SV and Bayer 04 Leverkusen, Bayer Leverkusen was joint-top scorer in the 2000–01 Bundesliga season with 22 goals. Meho Kodro spent most of his career playing in Spain, most notably with Real Sociedad and FC Barcelona. Elvir Rahimić made 302 appearances for Russian club PFC CSKA Moscow, CSKA Moscow with whom he won the UEFA Europa League, UEFA Cup in 2005 UEFA Cup Final, 2005.
Milena Nikolić, member of the Bosnia and Herzegovina women's national football team, women's national team, was the 2013–14 UEFA Women's Champions League UEFA Women's Champions League#Top scorers by tournament, top scorer.
Bosnia and Herzegovina was the world champion of volleyball at the 2004 Summer Paralympics and volleyball at the 2012 Summer Paralympics. Many among those on the team lost their legs in the Bosnian War. Its Bosnia and Herzegovina national sitting volleyball team, national sitting volleyball team is one of the dominant forces in Sitting volleyball, the sport worldwide, winning nine European Championships, three World Championships and two Volleyball at the Summer Paralympics, Paralympic gold medals.
Tennis is also gaining a lot of popularity after the recent successes of Damir Džumhur and Mirza Bašić at Grand Slam (tennis), Grand Slam level. Other notable tennis players who have represented Bosnia and Herzegovina are Tomislav Brkić, Amer Delić and Mervana Jugić-Salkić.
Project Gutenberg
* * * * * * Okey, Robin. ''Taming Balkan Nationalism: The Habsburg 'Civilizing' Mission in Bosnia, 1878–1914'' (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2007) * Phillips, Douglas A. ''Bosnia and Herzegovina'' (Philadelphia: Chelsea House, 2004).
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' (archived 3 July 2008) * {{Authority control Bosnia and Herzegovina, Balkan countries Federal republics Member states of the Council of Europe Member states of the Union for the Mediterranean Member states of the United Nations States and territories established in 1992 Countries in Europe Observer states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
Etymology
The first preserved widely acknowledged mention of a form of the name "Bosnia (region), Bosnia" is in , a politico-geographical handbook written by the List of Byzantine emperors, Byzantine emperor Constantine VII in the mid-10th century (between 948 and 952) describing the "small land" () in Greek language, Greek of "Bosona" (). The name of the land is believed to derive from the name of the river Bosna (river), Bosna that courses through the Bosnian heartland. According to Philology, philologist Anton Mayer, the name ''Bosna'' could derive from Illyrian language, Illyrian *"Bass-an-as", which in turn could derive from the Proto-Indo-European root ''wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/bʰegʷ-, bʰegʷ-'', meaning "the running water". The name ''Herzegovina'' means "herzog's [land]", and "herzog" derives from the German word for "duke". It originates from the title of a 15th-century Bosnian magnate, Stjepan Vukčić Kosača, who was "Herceg [Herzog] of Hum and the Coast" (1448). Hum (formerly called Zachlumia) was an early medieval principality that had been conquered by the Bosnian Banate in the first half of the 14th century. When the Ottomans took over administration of the region, they called it the Sanjak of Herzegovina (''Hersek''). It was included within the Bosnia Eyalet until the formation of the short-lived Herzegovina Eyalet in the 1830s, which reemerged in the 1850s, after which the administrative region became commonly known as ''Bosnia and Herzegovina''. On initial 1992 Bosnian independence referendum, proclamation of independence in 1992, the country's official name was the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina, but following the 1995 Dayton Agreement and the new Constitution of Bosnia and Herzegovina, constitution that accompanied it, the official name was changed to Bosnia and Herzegovina.History
Early history
Bosnia has been inhabited since at least the Paleolithic, Paleolithic era. Notably, the Badanj Cave near Stolac features one of the oldest known cave engravings, depicting an animal figure believed to be a horse, dating back to approximately 13,000 to 12,000 BC. During the Neolithic, Neolithic period, significant cultures such as the Butmir and Kakanj emerged along the Bosna (river), Bosna River. The Butmir culture, flourishing around 5100 to 4500 BC, is renowned for its distinctive ceramics and anthropomorphic figurines. Excavations near Sarajevo have uncovered intricately decorated pottery and realistic human figurines from this culture. From the 8th century BCE, Illyrian tribes evolved into kingdoms. The most notable Illyrian kingdoms and dynasties were those of Bardylis, Bardylis of the Dardani and of Agron of Illyria, Agron of the Ardiaei who created the last and best-known Illyrian kingdom. Agron ruled over the Ardiaei and had extended his rule to other tribes as well. From the 7th century BCE, bronze was replaced by iron, after which only jewelry and art objects were still made out of bronze. Illyrian tribes, under the influence of Hallstatt cultures to the north, formed regional centers that were slightly different. Parts of Central Bosnia were inhabited by the Daesitiates tribe. The Iron Age Glasinac-Mati culture is associated with the Autariatae tribe. A very important role in their life was the cult of the dead, which is seen in their careful burials and burial ceremonies, as well as the richness of their burial sites. In northern parts, there was a long tradition of cremation and burial in shallow graves, while in the south the dead were buried in large stone or earth Tumulus, tumuli (natively called ''gromile'') that in Herzegovina were reaching monumental sizes, more than 50 m wide and 5 m high. ''Japodian tribes'' had an affinity to decoration (heavy, oversized necklaces out of yellow, blue or white glass paste, and large bronze Fibula (brooch), fibulas, as well as spiral bracelets, diadems and helmets out of bronze foil). In the 4th century BCE, the first invasion of Celts is recorded. They brought the technique of the Potter's wheel, pottery wheel, new types of fibulas and different bronze and iron belts. They only passed on their way to Greece, so their influence in Bosnia and Herzegovina is negligible. Celtic migrations displaced many List of ancient tribes in Illyria, Illyrian tribes from their former lands, but some Celtic and Illyrian tribes mixed. Concrete historical evidence for this period is scarce, but overall it appears the region was populated by a number of different peoples speaking distinct languages. In the Neretva Delta in the south, there were important Hellenistic period, Hellenistic influences of the Illyrian Daorson, Daors tribe. Their capital was ''Daorson'' in Ošanići near Stolac. Daorson, in the 4th century BCE, was surrounded by megalithic, 5 m high stonewalls (as large as those of Mycenae in Greece), composed of large trapezoid stone blocks. Daors made unique bronze coins and sculptures.
Conflict between the Illyrians and Ancient Rome, Romans started in 229 BCE, but Rome did not complete its annexation of the region until AD 9. It was precisely in modern-day Bosnia and Herzegovina that Rome fought one of the most difficult battles in its history since the Punic Wars, as described by the Roman historian Suetonius. This was the Roman campaign against Illyricum (Roman province), Illyricum, known as . The conflict arose after an attempt to recruit Illyrians, and a revolt spanned for four years (6–9 AD), after which they were subdued. In the Roman period, Latin-speaking settlers from the entire Roman Empire settled among the Illyrians, and Roman soldiers were encouraged to retire in the region.
Following the split of the Empire between 337 and 395 AD, Dalmatia and Pannonia became parts of the Western Roman Empire. The region was conquered by the Ostrogoths in 455 AD. It subsequently changed hands between the Alans and the Huns. By the 6th century, Emperor Justinian I had reconquered the area for the Byzantine Empire. Slavs overwhelmed the Balkans in the 6th and 7th centuries. Illyrian cultural traits were adopted by the South Slavs, as evidenced in certain customs and traditions, and placenames.
In the Neretva Delta in the south, there were important Hellenistic period, Hellenistic influences of the Illyrian Daorson, Daors tribe. Their capital was ''Daorson'' in Ošanići near Stolac. Daorson, in the 4th century BCE, was surrounded by megalithic, 5 m high stonewalls (as large as those of Mycenae in Greece), composed of large trapezoid stone blocks. Daors made unique bronze coins and sculptures.
Conflict between the Illyrians and Ancient Rome, Romans started in 229 BCE, but Rome did not complete its annexation of the region until AD 9. It was precisely in modern-day Bosnia and Herzegovina that Rome fought one of the most difficult battles in its history since the Punic Wars, as described by the Roman historian Suetonius. This was the Roman campaign against Illyricum (Roman province), Illyricum, known as . The conflict arose after an attempt to recruit Illyrians, and a revolt spanned for four years (6–9 AD), after which they were subdued. In the Roman period, Latin-speaking settlers from the entire Roman Empire settled among the Illyrians, and Roman soldiers were encouraged to retire in the region.
Following the split of the Empire between 337 and 395 AD, Dalmatia and Pannonia became parts of the Western Roman Empire. The region was conquered by the Ostrogoths in 455 AD. It subsequently changed hands between the Alans and the Huns. By the 6th century, Emperor Justinian I had reconquered the area for the Byzantine Empire. Slavs overwhelmed the Balkans in the 6th and 7th centuries. Illyrian cultural traits were adopted by the South Slavs, as evidenced in certain customs and traditions, and placenames.
Middle Ages

 The Early Slavs raided the Western Balkans, including Bosnia, in the 6th and early 7th century (amid the Migration Period), and were composed of small tribal units drawn from a single Slavic confederation known to the Byzantines as the ''Sclaveni'' (whilst the related ''Antes people, Antes'', roughly speaking, colonized the eastern portions of the Balkans).
Tribes recorded by the ethnonyms of "Serb" and "Croat" are described as a second, later, migration of different people during the second quarter of the 7th century who could not have been particularly numerous; these early "Serb" and "Croat" tribes, whose exact identity is subject to scholarly debate, came to predominate over the Slavs in the neighbouring regions. According to Noel Malcolm, the tribal Croats "settled in an area roughly corresponding to modern Croatia, and probably also including most of Bosnia proper, apart from the eastern strip of the Drina valley" while the tribal Serbs settled an area "corresponding to modern south-western Serbia (later known as Raška (region), Raška), and gradually extended their rule into the territories of Duklja and Zachlumia, Hum". John Van Antwerp Fine Jr., on the other hand, describes the settling of the tribal Croats to involve Croatia, Dalmatia and Western Bosnia, with the rest of Bosnia seemingly being a territory between early Serb and Croat rule.
Bosnia is also believed to be first mentioned ''as a land (horion Bosona)'' in Byzantine Emperor Constantine Porphyrogenitus' ''De Administrando Imperio'' in the mid 10th century, at the end of a chapter entitled ''Of the Serbs and the country in which they now dwell''. This has been scholarly interpreted in several ways and used especially by the Serb national ideologists to prove Bosnia as originally a "Serb" land. Other scholars have asserted the inclusion of Bosnia in the chapter to merely be the result of Serbian Grand Duke Časlav of Serbia, Časlav's temporary rule over Bosnia at the time, while also pointing out Porphyrogenitus does not say anywhere explicitly that Bosnia is a "Serb land". In fact, the very translation of the critical sentence where the word ''Bosona'' (Bosnia) appears is subject to varying interpretation. In time, Bosnia formed a unit under its own Kulin Ban, ruler, who called himself Bosnian. Bosnia, along with other territories, became part of Duklja in the 11th century, although it retained its own nobility and institutions.
The Early Slavs raided the Western Balkans, including Bosnia, in the 6th and early 7th century (amid the Migration Period), and were composed of small tribal units drawn from a single Slavic confederation known to the Byzantines as the ''Sclaveni'' (whilst the related ''Antes people, Antes'', roughly speaking, colonized the eastern portions of the Balkans).
Tribes recorded by the ethnonyms of "Serb" and "Croat" are described as a second, later, migration of different people during the second quarter of the 7th century who could not have been particularly numerous; these early "Serb" and "Croat" tribes, whose exact identity is subject to scholarly debate, came to predominate over the Slavs in the neighbouring regions. According to Noel Malcolm, the tribal Croats "settled in an area roughly corresponding to modern Croatia, and probably also including most of Bosnia proper, apart from the eastern strip of the Drina valley" while the tribal Serbs settled an area "corresponding to modern south-western Serbia (later known as Raška (region), Raška), and gradually extended their rule into the territories of Duklja and Zachlumia, Hum". John Van Antwerp Fine Jr., on the other hand, describes the settling of the tribal Croats to involve Croatia, Dalmatia and Western Bosnia, with the rest of Bosnia seemingly being a territory between early Serb and Croat rule.
Bosnia is also believed to be first mentioned ''as a land (horion Bosona)'' in Byzantine Emperor Constantine Porphyrogenitus' ''De Administrando Imperio'' in the mid 10th century, at the end of a chapter entitled ''Of the Serbs and the country in which they now dwell''. This has been scholarly interpreted in several ways and used especially by the Serb national ideologists to prove Bosnia as originally a "Serb" land. Other scholars have asserted the inclusion of Bosnia in the chapter to merely be the result of Serbian Grand Duke Časlav of Serbia, Časlav's temporary rule over Bosnia at the time, while also pointing out Porphyrogenitus does not say anywhere explicitly that Bosnia is a "Serb land". In fact, the very translation of the critical sentence where the word ''Bosona'' (Bosnia) appears is subject to varying interpretation. In time, Bosnia formed a unit under its own Kulin Ban, ruler, who called himself Bosnian. Bosnia, along with other territories, became part of Duklja in the 11th century, although it retained its own nobility and institutions.
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman conquest of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Ottoman conquest of Bosnia marked a new era in the country's history and introduced drastic changes in the political and cultural landscape. The Ottomans incorporated Bosnia as an integral province of the Ottoman Empire with its historical name and territorial integrity. Within Bosnia, the Ottomans introduced a number of key changes in the territory's socio-political administration; including a new landholding system, a reorganization of administrative units, and a complex system of social differentiation by class and religious affiliation. Following Ottoman occupation, there was a steady flow of people out of Bosnia and a large number of abandoned villages in Bosnia are mentioned in the Ottoman registers,Bosnia: A Short History , Chapter: Islamicization of Bosnia while those who stayed eventually became Muslims. Many Catholics in Bosnia fled to neighboring Catholic lands in the early Ottoman occupation. The evidence indicates that the early Muslim conversions in Ottoman Bosnia in the 15th–16th century were among the locals who stayed rather than mass Muslim settlements from outside Bosnia. In Herzegovina, many Eastern Orthodoxy, Orthodox people had also embraced Islam. By the late 16th and early 17th century, Muslims are considered to have become an absolute majority in Bosnia and Herzegovina. The Albanian Catholic priest Pjetër Mazreku reported in 1624 that there were 450,000 Muslims, 150,000 Catholics and 75,000 Eastern Orthodox in Bosnia and Herzegovina. There was a lack of Serbian Orthodox Church, Orthodox Church activity in Bosnia proper in the pre-Ottoman period. An Orthodox Christian population in Bosnia was introduced as a direct result of Ottoman policy.Bosnia: A Short History p. 55 From the 15th century and onwards, Orthodox Christians (Orthodox Vlachs and non-Vlach Orthodox Serbs) from Serbia and other regions settled in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Favored by the Ottomans over the Catholics, many Orthodox churches were allowed to be built in Bosnia by the Ottomans. Quite a few Vlachs also became Islamized in Bosnia, and some (mainly in Croatia) became Catholics. The four centuries of Ottoman rule also had a drastic impact on Bosnia's population make-up, which changed several times as a result of the empire's conquests, frequent wars with European powers, forced and economic migrations, and epidemics. A native Slavic-speaking Muslim community emerged and eventually became the largest of the ethno-religious groups due to a lack of strong Christian church organizations and continuous rivalry between the Orthodox and Catholic churches, while the indigenous Bosnian Church disappeared altogether (ostensibly by conversion of its members to Islam). The Ottomans referred to them as ''kristianlar'' while the Orthodox and Catholics were called ''gebir'' or ''kafir'', meaning "unbeliever". The Bosnian Franciscans (and the Catholic population as a whole) were protected by official imperial decrees and in accordance and the full extent of Ottoman laws; however, in effect, these often merely affected arbitrary rule and behavior of powerful local elite. As the Ottoman Empire continued its rule in the Balkans (Rumelia), Bosnia was somewhat relieved of the pressures of being a frontier province and experienced a period of general welfare. A number of cities, such as Sarajevo and Mostar, were established and grew into regional centers of trade and urban culture and were then visited by Ottoman traveler Evliya Çelebi in 1648. Within these cities, various Ottoman Sultans financed the construction of many works of Architecture of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnian architecture such as the country's first library in Sarajevo, Madrasa, madrassas, a school of Sufi philosophy, and a clock tower (''Sahat Kula''), bridges such as the Stari Most, the Emperor's Mosque and the Gazi Husrev-beg Mosque.A Brief History of Bosnia–Herzegovina
. The Bosnian Manuscript Ingathering Project. Bosnian recruits formed a large component of the Ottoman ranks in the battles of Battle of Mohács, Mohács and Battle of Krbava Field, Krbava field, while numerous other Bosnians rose through the ranks of the Ottoman military to occupy the highest positions of power in the Empire, including admirals such as Matrakçı Nasuh; generals such as Isa Bey Ishaković, Isa-Beg Ishaković, Gazi Husrev Bey, Gazi Husrev-beg, Telli Hasan Pasha and Sarı Süleyman Pasha; administrators such as Ferhad Pasha Sokolović and Osman Gradaščević; and Grand Viziers such as the influential Sokollu Mehmed Pasha and Damat Ibrahim Pasha. Some Bosnians emerged as Sufism, Sufi mystics, scholars such as Muhamed Hevaji Uskufi Bosnevi, Ali Džabić; and poets in the Turkish language, Turkish, Albanian language, Albanian, Arabic, and Persian languages.Imamović, Mustafa (1996). Historija Bošnjaka. Sarajevo: BZK Preporod; However, by the late 17th century the Empire's military misfortunes caught up with the country, and the end of the Great Turkish War with the treaty of Karlowitz in 1699 again made Bosnia the Empire's westernmost province. The 18th century was marked by further military failures, numerous revolts within Bosnia, and several outbreaks of plague. The Porte's efforts at modernizing the Ottoman state were met with distrust growing to hostility in Bosnia, where local aristocrats stood to lose much through the proposed Tanzimat reforms. This, combined with frustrations over territorial, political concessions in the north-east, and the plight of Slavs, Slavic Muslims, Muslim refugees arriving from the Sanjak of Smederevo into Bosnia Eyalet, culminated in a partially unsuccessful revolt by Husein Gradaščević, who endorsed a Bosnia Eyalet autonomous from the authoritarian rule of the Ottoman Sultan Mahmud II, who persecuted, executed and abolished the Janissary, Janissaries and reduced the role of autonomous Pashas in Rumelia. Mahmud II sent his Grand vizier to subdue Bosnia Eyalet and succeeded only with the reluctant assistance of Ali Pasha Rizvanbegović. Related rebellions were extinguished by 1850, but the situation continued to deteriorate. New nationalist movements appeared in Bosnia by the middle of the 19th century. Shortly after Serbia's breakaway from the Ottoman Empire in the early 19th century, Serbian and Croatian nationalism rose up in Bosnia, and such nationalists made irredentist claims to Bosnia's territory. This trend continued to grow in the rest of the 19th and 20th centuries. Agrarian unrest eventually sparked the Herzegovina uprising (1875–1877), Herzegovinian rebellion, a widespread peasant uprising, in 1875. The conflict rapidly spread and came to involve several Balkan states and Great Powers, a situation that led to the Congress of Berlin and the Treaty of Berlin (1878), Treaty of Berlin in 1878.
Austria-Hungary
 At the Congress of Berlin in 1878, the Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarian Foreign Minister Gyula Andrássy obtained the occupation and administration of Bosnia and Herzegovina, and he also obtained the right to station garrisons in the Sanjak of Novi Pazar, which would remain under Ottoman Empire, Ottoman administration until 1908, when the Austro-Hungarian troops withdrew from the Sanjak.
Although Austro-Hungarian officials quickly came to an agreement with the Bosnians, tensions remained and a mass emigration of Bosnians occurred. However, a state of relative stability was reached soon enough and Austro-Hungarian authorities were able to embark on a number of social and administrative reforms they intended would make Bosnia and Herzegovina into a "model" colony.
Habsburg Monarchy, Habsburg rule had several key concerns in Bosnia. It tried to dissipate the South Slav nationalism by disputing the earlier Serb and Croat claims to Bosnia and encouraging identification of Bosnian or Bosniaks, Bosniak identity. Habsburg rule also tried to provide for modernisation by codifying laws, introducing new political institutions, establishing and expanding industries.
Austria–Hungary began to plan the annexation of Bosnia, but due to international disputes the issue was not resolved until the Bosnian Crisis, annexation crisis of 1908. Several external matters affected the status of Bosnia and its relationship with Austria–Hungary. May Coup (Serbia), A bloody coup occurred in Serbia in 1903, which brought a radical anti-Austrian government into power in Belgrade. Then in 1908, the revolt in the Ottoman Empire raised concerns that the Istanbul government might seek the outright return of Bosnia and Herzegovina. These factors caused the Austro-Hungarian government to seek a permanent resolution of the Bosnian question sooner, rather than later.
Taking advantage of the turmoil in the Ottoman Empire, Austro-Hungarian diplomacy tried to obtain provisional Russian approval for changes over the status of Bosnia and Herzegovina and published the annexation proclamation on 6 October 1908. Despite international objections to the Austro-Hungarian annexation, Russians and their client state, Serbia, were compelled to accept the Austro-Hungarian annexation of Bosnia and Herzegovina in March 1909.
In 1910, Habsburg Emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria, Franz Joseph proclaimed the first constitution in Bosnia, which led to relaxation of earlier laws, elections and formation of the Diet of Bosnia, Bosnian parliament and growth of new political life.
At the Congress of Berlin in 1878, the Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarian Foreign Minister Gyula Andrássy obtained the occupation and administration of Bosnia and Herzegovina, and he also obtained the right to station garrisons in the Sanjak of Novi Pazar, which would remain under Ottoman Empire, Ottoman administration until 1908, when the Austro-Hungarian troops withdrew from the Sanjak.
Although Austro-Hungarian officials quickly came to an agreement with the Bosnians, tensions remained and a mass emigration of Bosnians occurred. However, a state of relative stability was reached soon enough and Austro-Hungarian authorities were able to embark on a number of social and administrative reforms they intended would make Bosnia and Herzegovina into a "model" colony.
Habsburg Monarchy, Habsburg rule had several key concerns in Bosnia. It tried to dissipate the South Slav nationalism by disputing the earlier Serb and Croat claims to Bosnia and encouraging identification of Bosnian or Bosniaks, Bosniak identity. Habsburg rule also tried to provide for modernisation by codifying laws, introducing new political institutions, establishing and expanding industries.
Austria–Hungary began to plan the annexation of Bosnia, but due to international disputes the issue was not resolved until the Bosnian Crisis, annexation crisis of 1908. Several external matters affected the status of Bosnia and its relationship with Austria–Hungary. May Coup (Serbia), A bloody coup occurred in Serbia in 1903, which brought a radical anti-Austrian government into power in Belgrade. Then in 1908, the revolt in the Ottoman Empire raised concerns that the Istanbul government might seek the outright return of Bosnia and Herzegovina. These factors caused the Austro-Hungarian government to seek a permanent resolution of the Bosnian question sooner, rather than later.
Taking advantage of the turmoil in the Ottoman Empire, Austro-Hungarian diplomacy tried to obtain provisional Russian approval for changes over the status of Bosnia and Herzegovina and published the annexation proclamation on 6 October 1908. Despite international objections to the Austro-Hungarian annexation, Russians and their client state, Serbia, were compelled to accept the Austro-Hungarian annexation of Bosnia and Herzegovina in March 1909.
In 1910, Habsburg Emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria, Franz Joseph proclaimed the first constitution in Bosnia, which led to relaxation of earlier laws, elections and formation of the Diet of Bosnia, Bosnian parliament and growth of new political life.
 On 28 June 1914, Gavrilo Princip, a Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnian Serb member of the revolutionary movement Young Bosnia, Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, assassinated the heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria, Archduke Franz Ferdinand, in Sarajevo—an event that was the spark that set off World War I. At the end of the war, the Bosnian Muslims had lost more men per capita than any other ethnic group in the Habsburg Empire whilst serving in the Bosnian-Herzegovinian Infantry of the Austro-Hungarian Army. Nonetheless, Bosnia and Herzegovina as a whole managed to escape the conflict relatively unscathed.
The Austro-Hungarian authorities established an auxiliary militia known as the Schutzkorps with a moot role in the empire's policy of Anti-Serb sentiment, anti-Serb repression. Schutzkorps, predominantly recruited among the Bosnian Muslim population, were tasked with hunting down rebel Serbs (the ''Chetniks'' and ''Komitadji'') and became known for their persecution of Serbs particularly in Serb populated areas of eastern Bosnia, where they partly retaliated against Serbian Chetniks who in fall 1914 had carried out attacks against the Muslim population in the area. The proceedings of the Austro-Hungarian authorities led to around 5,500 citizens of Serb ethnicity in Bosnia and Herzegovina being arrested, and between 700 and 2,200 died in prison while 460 were executed. Around 5,200 Serb families were forcibly expelled from Bosnia and Herzegovina.
On 28 June 1914, Gavrilo Princip, a Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnian Serb member of the revolutionary movement Young Bosnia, Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, assassinated the heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria, Archduke Franz Ferdinand, in Sarajevo—an event that was the spark that set off World War I. At the end of the war, the Bosnian Muslims had lost more men per capita than any other ethnic group in the Habsburg Empire whilst serving in the Bosnian-Herzegovinian Infantry of the Austro-Hungarian Army. Nonetheless, Bosnia and Herzegovina as a whole managed to escape the conflict relatively unscathed.
The Austro-Hungarian authorities established an auxiliary militia known as the Schutzkorps with a moot role in the empire's policy of Anti-Serb sentiment, anti-Serb repression. Schutzkorps, predominantly recruited among the Bosnian Muslim population, were tasked with hunting down rebel Serbs (the ''Chetniks'' and ''Komitadji'') and became known for their persecution of Serbs particularly in Serb populated areas of eastern Bosnia, where they partly retaliated against Serbian Chetniks who in fall 1914 had carried out attacks against the Muslim population in the area. The proceedings of the Austro-Hungarian authorities led to around 5,500 citizens of Serb ethnicity in Bosnia and Herzegovina being arrested, and between 700 and 2,200 died in prison while 460 were executed. Around 5,200 Serb families were forcibly expelled from Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Kingdom of Yugoslavia
Following World War I, Bosnia and Herzegovina joined the South Slav Kingdom of Yugoslavia, Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (soon renamed Yugoslavia). Political life in Bosnia and Herzegovina at this time was marked by two major trends: social and economic unrest over Distribution (economics), property redistribution and the formation of several political parties that frequently changed coalitions and alliances with parties in other Yugoslav regions. The dominant ideological conflict of the Yugoslav state, between Croatian regionalism and Serbian centralization, was approached differently by Bosnia and Herzegovina's major ethnic groups and was dependent on the overall political atmosphere. The political reforms brought about in the newly established Yugoslav kingdom saw few benefits for the Bosnian Muslims; according to the 1910 final census of land ownership and population according to religious affiliation conducted in Austria-Hungary, Muslims owned 91.1%, Orthodox Serbs owned 6.0%, Croat Catholics owned 2.6% and others, 0.3% of the property. Following the reforms, Bosnian Muslims were dispossessed of a total of 1,175,305 hectares of agricultural and forest land. Although the initial split of the country into 33 oblasts erased the presence of traditional geographic entities from the map, the efforts of Bosnian politicians, such as Mehmed Spaho, ensured the six oblasts carved up from Bosnia and Herzegovina corresponded to the six sanjaks from Ottoman times and, thus, matched the country's traditional boundary as a whole. The establishment of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1929, however, brought the redrawing of administrative regions into Kingdom of Yugoslavia#Subdivisions, banates or ''Banovina (region), banovinas'' that purposely avoided all historical and ethnic lines, removing any trace of a Bosnian entity. Serbo-Croat tensions over the structuring of the Yugoslav state continued, with the concept of a separate Bosnian division receiving little or no consideration. The Cvetković–Maček Agreement, Cvetković-Maček Agreement that created the Banovina of Croatia, Croatian banate in 1939 encouraged what was essentially a partition of Bosnia and Herzegovina between Croatia and Serbia. However the rising threat of Adolf Hitler's Nazi Germany forced Yugoslav politicians to shift their attention. Following a period that saw attempts at appeasement, the signing of the Tripartite Pact, Tripartite Treaty, and a Yugoslav coup d'état, coup d'état, Yugoslavia was finally invaded by Germany on 6 April 1941.World War II (1941–45)
 Once the Kingdom of Yugoslavia was conquered by German forces in World War II, all of Bosnia and Herzegovina was ceded to the Nazi puppet regime, the Independent State of Croatia (NDH) led by the Ustaše. The NDH leaders embarked on a Genocide of Serbs in the Independent State of Croatia, campaign of extermination of Serbs, Jews, Romani people, Romani as well as dissident Croats, and, later, Josip Broz Tito's Yugoslav Partisans, Partisans by setting up a number of Jasenovac concentration camp, death camps. The regime systematically and brutally massacred Serbs in villages in the countryside, using a variety of tools. The scale of the violence meant that approximately every sixth Serb living in Bosnia and Herzegovina was the victim of a massacre and virtually every Serb had a family member that was killed in the war, mostly by the Ustaše. The experience had a profound impact in the collective memory of Serbs in Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina. An estimated 209,000 Serbs or 16.9% of its Bosnia population were killed on the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina during the war.
The Ustaše recognized both Catholicism and Islam as the national religions, but held the position Eastern Orthodox Church, as a symbol of Serb identity, was their greatest foe.Ramet (2006), pgg. 118. Although Croats were by far the largest ethnic group to constitute the Ustaše, the Vice President of the NDH and leader of the Yugoslav Muslim Organization Džafer Kulenović was a Muslim, and Muslims in total constituted nearly 12% of the Ustaše military and civil service authority.
Many Serbs themselves took up arms and joined the Chetniks, a Serb nationalist movement with the aim of establishing an ethnically homogeneous 'Greater Serbian' state within the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. The Chetniks, in turn, pursued a Chetnik war crimes in World War II, genocidal campaign against ethnic Muslims and Croats, as well as persecuting a large number of Communism, communist Serbs and other Communist sympathizers, with the Muslim populations of Bosnia, Herzegovina and Sandžak being a primary target. Once captured, Muslim villagers were systematically massacred by the Chetniks. Of the 75,000 Muslims who died in Bosnia and Herzegovina during the war, approximately 30,000 (mostly civilians) were killed by the Chetniks. Massacres against Croats were smaller in scale but similar in action. Between 64,000 and 79,000 Bosnian Croats were killed between April 1941 to May 1945. Of these, about 18,000 were killed by the Chetniks.
A percentage of Muslims served in Nazi 13th Waffen Mountain Division of the SS Handschar (1st Croatian), ''Waffen-SS'' units. These units were responsible for massacres of Serbs in northwest and eastern Bosnia, most notably in Vlasenica. On 12 October 1941, a group of 108 prominent Sarajevan Muslims signed the Resolution of Sarajevo Muslims by which they condemned the persecution of Serbs organized by the Ustaše, made distinction between Muslims who participated in such persecutions and the Muslim population as a whole, presented information about the persecutions of Muslims by Serbs, and requested security for all citizens of the country, regardless of their identity.
Starting in 1941, Yugoslav communists under the leadership of Josip Broz Tito organized their own multi-ethnic resistance group, the Partisans, who fought against both Axis powers, Axis and Chetnik forces. On 29 November 1943, the Anti-Fascist Council for the National Liberation of Yugoslavia (AVNOJ) with Tito at its helm held a founding conference in Jajce where Bosnia and Herzegovina was reestablished as a republic within the Yugoslav federation in its Habsburg borders. During the entire course of World War II in Yugoslavia, 64.1% of all Bosnian Partisans were Serbs, 23% were Muslims and 8.8% Croats.
Military success eventually prompted the Allies of World War II, Allies to support the Partisans, resulting in the successful Maclean Mission, but Tito declined their offer to help and relied on his own forces instead. All the major military offensives by the antifascist movement of Yugoslavia against Nazis and their local supporters were conducted in Bosnia and Herzegovina and its peoples bore the brunt of the fighting. More than 300,000 people died in Bosnia and Herzegovina in World War II, or more than 10% of the population. At the end of the war, the establishment of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, with the 1946 Yugoslav Constitution, constitution of 1946, officially made Bosnia and Herzegovina one of six constituent republics in the new state.
Once the Kingdom of Yugoslavia was conquered by German forces in World War II, all of Bosnia and Herzegovina was ceded to the Nazi puppet regime, the Independent State of Croatia (NDH) led by the Ustaše. The NDH leaders embarked on a Genocide of Serbs in the Independent State of Croatia, campaign of extermination of Serbs, Jews, Romani people, Romani as well as dissident Croats, and, later, Josip Broz Tito's Yugoslav Partisans, Partisans by setting up a number of Jasenovac concentration camp, death camps. The regime systematically and brutally massacred Serbs in villages in the countryside, using a variety of tools. The scale of the violence meant that approximately every sixth Serb living in Bosnia and Herzegovina was the victim of a massacre and virtually every Serb had a family member that was killed in the war, mostly by the Ustaše. The experience had a profound impact in the collective memory of Serbs in Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina. An estimated 209,000 Serbs or 16.9% of its Bosnia population were killed on the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina during the war.
The Ustaše recognized both Catholicism and Islam as the national religions, but held the position Eastern Orthodox Church, as a symbol of Serb identity, was their greatest foe.Ramet (2006), pgg. 118. Although Croats were by far the largest ethnic group to constitute the Ustaše, the Vice President of the NDH and leader of the Yugoslav Muslim Organization Džafer Kulenović was a Muslim, and Muslims in total constituted nearly 12% of the Ustaše military and civil service authority.
Many Serbs themselves took up arms and joined the Chetniks, a Serb nationalist movement with the aim of establishing an ethnically homogeneous 'Greater Serbian' state within the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. The Chetniks, in turn, pursued a Chetnik war crimes in World War II, genocidal campaign against ethnic Muslims and Croats, as well as persecuting a large number of Communism, communist Serbs and other Communist sympathizers, with the Muslim populations of Bosnia, Herzegovina and Sandžak being a primary target. Once captured, Muslim villagers were systematically massacred by the Chetniks. Of the 75,000 Muslims who died in Bosnia and Herzegovina during the war, approximately 30,000 (mostly civilians) were killed by the Chetniks. Massacres against Croats were smaller in scale but similar in action. Between 64,000 and 79,000 Bosnian Croats were killed between April 1941 to May 1945. Of these, about 18,000 were killed by the Chetniks.
A percentage of Muslims served in Nazi 13th Waffen Mountain Division of the SS Handschar (1st Croatian), ''Waffen-SS'' units. These units were responsible for massacres of Serbs in northwest and eastern Bosnia, most notably in Vlasenica. On 12 October 1941, a group of 108 prominent Sarajevan Muslims signed the Resolution of Sarajevo Muslims by which they condemned the persecution of Serbs organized by the Ustaše, made distinction between Muslims who participated in such persecutions and the Muslim population as a whole, presented information about the persecutions of Muslims by Serbs, and requested security for all citizens of the country, regardless of their identity.
Starting in 1941, Yugoslav communists under the leadership of Josip Broz Tito organized their own multi-ethnic resistance group, the Partisans, who fought against both Axis powers, Axis and Chetnik forces. On 29 November 1943, the Anti-Fascist Council for the National Liberation of Yugoslavia (AVNOJ) with Tito at its helm held a founding conference in Jajce where Bosnia and Herzegovina was reestablished as a republic within the Yugoslav federation in its Habsburg borders. During the entire course of World War II in Yugoslavia, 64.1% of all Bosnian Partisans were Serbs, 23% were Muslims and 8.8% Croats.
Military success eventually prompted the Allies of World War II, Allies to support the Partisans, resulting in the successful Maclean Mission, but Tito declined their offer to help and relied on his own forces instead. All the major military offensives by the antifascist movement of Yugoslavia against Nazis and their local supporters were conducted in Bosnia and Herzegovina and its peoples bore the brunt of the fighting. More than 300,000 people died in Bosnia and Herzegovina in World War II, or more than 10% of the population. At the end of the war, the establishment of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, with the 1946 Yugoslav Constitution, constitution of 1946, officially made Bosnia and Herzegovina one of six constituent republics in the new state.
Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (1945–1992)
Due to its central geographic position within the Yugoslav federation, post-war Bosnia was selected as a base for the development of the military defense industry. This contributed to a large concentration of arms and military personnel in Bosnia; a significant factor in Bosnian War, the war that followed the break-up of Yugoslavia in the 1990s. However, Bosnia's existence within Yugoslavia, for the large part, was relatively peaceful and very prosperous, with high employment, a strong industrial and export oriented economy, a good education system and social and medical security for every citizen of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Several international corporations operated in Bosnia—Volkswagen as part of TAS (car factory in Sarajevo, from 1972), Coca-Cola (from 1975), SKF Sweden (from 1967), Marlboro (cigarette), Marlboro (a tobacco factory in Sarajevo), and Holiday Inn hotels. Sarajevo was the site of the 1984 Winter Olympics. During the 1950s and 1960s, Bosnia was a political backwater of Yugoslavia. In the 1970s, a strong Bosnian political elite arose, fueled in part by Tito's leadership in the Non-Aligned Movement and Bosnians serving in Yugoslavia's diplomatic corps. While working within the Socialist system, politicians such as Džemal Bijedić, Branko Mikulić and Hamdija Pozderac reinforced and protected the sovereignty of Bosnia and Herzegovina.Stojic, Mile (2005)Branko Mikulic – socialist emperor manqué
. Dani (magazine), BH Dani Their efforts proved key during the turbulent period following Tito's death in 1980, and are today considered some of the early steps towards Independence Day (Bosnia and Herzegovina), Bosnian independence. However, the republic did not escape the increasingly nationalistic climate of the time. With the fall of communism and the start of the breakup of Yugoslavia, doctrine of tolerance began to lose its potency, creating an opportunity for nationalist elements in the society to spread their influence.
Bosnian War (1992–1995)
 On 18 November 1990, 1990 Bosnian general election, multi-party parliamentary elections were held throughout Bosnia and Herzegovina. A second round followed on 25 November, resulting in a Parliamentary Assembly of Bosnia and Herzegovina, national assembly where communist power was replaced by a coalition of three ethnically based parties. Following Slovenia and Croatia's declarations of independence from Yugoslavia, a significant split developed among the residents of Bosnia and Herzegovina on the issue of whether to remain within Yugoslavia (overwhelmingly favored by Serbs) or seek independence (overwhelmingly favored by Muslims (ethnic group), Muslims and Croats).
The Serb members of parliament, consisting mainly of the Serb Democratic Party (Bosnia and Herzegovina), Serb Democratic Party members, abandoned the central parliament in Sarajevo, and formed the National Assembly (Republika Srpska), Assembly of the Serb People of Bosnia and Herzegovina on 24 October 1991, which marked the end of the three-ethnic coalition that governed after the elections in 1990. This Assembly established the Serbian Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina in part of the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina on 9 January 1992. It was renamed Republika Srpska (1992–1995), Republika Srpska in August 1992. On 18 November 1991, the party branch in Bosnia and Herzegovina of the ruling party in the Republic of Croatia, the Croatian Democratic Union (HDZ), proclaimed the existence of the Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia, Croatian Community of Herzeg-Bosnia in a separate part of the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina with the Croatian Defence Council (HVO) as its military branch. It went unrecognized by the Council of Ministers of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Government of Bosnia and Herzegovina, which declared it illegal.
On 18 November 1990, 1990 Bosnian general election, multi-party parliamentary elections were held throughout Bosnia and Herzegovina. A second round followed on 25 November, resulting in a Parliamentary Assembly of Bosnia and Herzegovina, national assembly where communist power was replaced by a coalition of three ethnically based parties. Following Slovenia and Croatia's declarations of independence from Yugoslavia, a significant split developed among the residents of Bosnia and Herzegovina on the issue of whether to remain within Yugoslavia (overwhelmingly favored by Serbs) or seek independence (overwhelmingly favored by Muslims (ethnic group), Muslims and Croats).
The Serb members of parliament, consisting mainly of the Serb Democratic Party (Bosnia and Herzegovina), Serb Democratic Party members, abandoned the central parliament in Sarajevo, and formed the National Assembly (Republika Srpska), Assembly of the Serb People of Bosnia and Herzegovina on 24 October 1991, which marked the end of the three-ethnic coalition that governed after the elections in 1990. This Assembly established the Serbian Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina in part of the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina on 9 January 1992. It was renamed Republika Srpska (1992–1995), Republika Srpska in August 1992. On 18 November 1991, the party branch in Bosnia and Herzegovina of the ruling party in the Republic of Croatia, the Croatian Democratic Union (HDZ), proclaimed the existence of the Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia, Croatian Community of Herzeg-Bosnia in a separate part of the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina with the Croatian Defence Council (HVO) as its military branch. It went unrecognized by the Council of Ministers of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Government of Bosnia and Herzegovina, which declared it illegal.
 A declaration of the sovereignty of Bosnia and Herzegovina on 15 October 1991 was followed by a 1992 Bosnian independence referendum, referendum for independence on 29 February and 1 March 1992, which was boycotted by the great majority of Serbs. The turnout in the independence referendum was 63.4 per cent and 99.7 per cent of voters voted for independence. Bosnia and Herzegovina declared independence on 3 March 1992 and received international recognition the following month on 6 April 1992. The Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina was admitted as a member state of the United Nations on 22 May 1992. Serbian leader Slobodan Milošević and Croatian leader Franjo Tuđman are believed to have agreed on a partition of Bosnia and Herzegovina in March 1991, with the aim of establishing Greater Serbia and Greater Croatia.
Following Bosnia and Herzegovina's declaration of independence, Bosnian Serb militias mobilized in different parts of the country. Government forces were poorly equipped and unprepared for the war. International recognition of Bosnia and Herzegovina increased diplomatic pressure for the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) to withdraw from the republic's territory, which they officially did in June 1992. The Bosnian Serb members of the JNA simply changed insignia, formed the Army of Republika Srpska (VRS), and continued fighting. Armed and equipped from JNA stockpiles in Bosnia, supported by volunteers and various paramilitary forces from Serbia, and receiving extensive humanitarian, logistical and financial support from the Serbia and Montenegro, Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Republika Srpska's offensives in 1992 managed to place much of the country under its control. The Bosnian Serb advance was accompanied by the ethnic cleansing of Bosniaks and Bosnian Croats from VRS-controlled areas. Dozens of concentration camps were established in which inmates were subjected to violence and abuse, including rape. The ethnic cleansing culminated in the Srebrenica massacre of more than 8,000 Bosniak men and boys in July 1995, which was ruled to have been a genocide by the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY). Bosniak and Bosnian Croat forces also committed war crimes against civilians from different ethnic groups, though on a smaller scale. Most of the Bosniak and Croat atrocities were committed during the Croat–Bosniak War, a sub-conflict of the Bosnian War that pitted the Army of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) against the HVO. The Bosniak-Croat conflict ended in March 1994, with the signing of the Washington Agreement (1994), Washington Agreement, leading to the creation of a joint Bosniak-Croat Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, which amalgamated HVO-held territory with that held by the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH).
A declaration of the sovereignty of Bosnia and Herzegovina on 15 October 1991 was followed by a 1992 Bosnian independence referendum, referendum for independence on 29 February and 1 March 1992, which was boycotted by the great majority of Serbs. The turnout in the independence referendum was 63.4 per cent and 99.7 per cent of voters voted for independence. Bosnia and Herzegovina declared independence on 3 March 1992 and received international recognition the following month on 6 April 1992. The Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina was admitted as a member state of the United Nations on 22 May 1992. Serbian leader Slobodan Milošević and Croatian leader Franjo Tuđman are believed to have agreed on a partition of Bosnia and Herzegovina in March 1991, with the aim of establishing Greater Serbia and Greater Croatia.
Following Bosnia and Herzegovina's declaration of independence, Bosnian Serb militias mobilized in different parts of the country. Government forces were poorly equipped and unprepared for the war. International recognition of Bosnia and Herzegovina increased diplomatic pressure for the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) to withdraw from the republic's territory, which they officially did in June 1992. The Bosnian Serb members of the JNA simply changed insignia, formed the Army of Republika Srpska (VRS), and continued fighting. Armed and equipped from JNA stockpiles in Bosnia, supported by volunteers and various paramilitary forces from Serbia, and receiving extensive humanitarian, logistical and financial support from the Serbia and Montenegro, Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Republika Srpska's offensives in 1992 managed to place much of the country under its control. The Bosnian Serb advance was accompanied by the ethnic cleansing of Bosniaks and Bosnian Croats from VRS-controlled areas. Dozens of concentration camps were established in which inmates were subjected to violence and abuse, including rape. The ethnic cleansing culminated in the Srebrenica massacre of more than 8,000 Bosniak men and boys in July 1995, which was ruled to have been a genocide by the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY). Bosniak and Bosnian Croat forces also committed war crimes against civilians from different ethnic groups, though on a smaller scale. Most of the Bosniak and Croat atrocities were committed during the Croat–Bosniak War, a sub-conflict of the Bosnian War that pitted the Army of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH) against the HVO. The Bosniak-Croat conflict ended in March 1994, with the signing of the Washington Agreement (1994), Washington Agreement, leading to the creation of a joint Bosniak-Croat Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, which amalgamated HVO-held territory with that held by the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ARBiH).
Recent history
 On 4 February 2014, the 2014 unrest in Bosnia and Herzegovina, protests against the Government of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, one of the country's two entities, dubbed the Bosnian Spring, the name being taken from the Arab Spring, began in the northern town of Tuzla. Workers from several factories that had been privatised and gone bankrupt assembled to demand action over jobs, unpaid salaries and pensions. Soon protests spread to the rest of the Federation, with violent clashes reported in close to 20 towns, the biggest of which were Sarajevo, Zenica, Mostar, Bihać, Brčko and Tuzla. The Bosnian news media reported that hundreds of people had been injured during the protests, including dozens of police officers, with bursts of violence in Sarajevo, in the northern city of Tuzla, in Mostar in the south, and in Zenica in central Bosnia. The same level of unrest or activism did not occur in Republika Srpska, but hundreds of people also gathered in support of protests in the city of Banja Luka against its separate government.
The protests marked the largest outbreak of public anger over high unemployment and two decades of political inertia in the country since the end of the Bosnian War in 1995. According to a report made by Christian Schmidt of the High Representative for Bosnia and Herzegovina, Office of High Representative in late 2021, Bosnia and Herzegovina has been experiencing intensified political and ethnic tensions, which could potentially break the country apart and slide it back into war once again. The European Union fears this will lead to further Balkanization in the region.
On 15 December 2022, Bosnia and Herzegovina was recognised by the European Union as a candidate country for Accession of Bosnia and Herzegovina to the European Union, accession following the decision of the European Council.
On 4 February 2014, the 2014 unrest in Bosnia and Herzegovina, protests against the Government of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, one of the country's two entities, dubbed the Bosnian Spring, the name being taken from the Arab Spring, began in the northern town of Tuzla. Workers from several factories that had been privatised and gone bankrupt assembled to demand action over jobs, unpaid salaries and pensions. Soon protests spread to the rest of the Federation, with violent clashes reported in close to 20 towns, the biggest of which were Sarajevo, Zenica, Mostar, Bihać, Brčko and Tuzla. The Bosnian news media reported that hundreds of people had been injured during the protests, including dozens of police officers, with bursts of violence in Sarajevo, in the northern city of Tuzla, in Mostar in the south, and in Zenica in central Bosnia. The same level of unrest or activism did not occur in Republika Srpska, but hundreds of people also gathered in support of protests in the city of Banja Luka against its separate government.
The protests marked the largest outbreak of public anger over high unemployment and two decades of political inertia in the country since the end of the Bosnian War in 1995. According to a report made by Christian Schmidt of the High Representative for Bosnia and Herzegovina, Office of High Representative in late 2021, Bosnia and Herzegovina has been experiencing intensified political and ethnic tensions, which could potentially break the country apart and slide it back into war once again. The European Union fears this will lead to further Balkanization in the region.
On 15 December 2022, Bosnia and Herzegovina was recognised by the European Union as a candidate country for Accession of Bosnia and Herzegovina to the European Union, accession following the decision of the European Council.
Geography
Bosnia and Herzegovina is in the western Balkans, bordering Croatia () to the north and west, Serbia () to the east, and Montenegro () to the southeast. It has a coastline about long surrounding the town of Neum.Field Listing – Coastline, ''The World Factbook'', 22 August 2006 It lies between latitudes 42nd parallel north, 42° and 46th parallel north, 46° N, and longitudes 15th meridian east, 15° and 20th meridian east, 20° E. The country's name comes from the two alleged regions Bosnia (region), Bosnia and Herzegovina, whose border was never defined. Historically, Bosnia's official name never included any of its many regions until the Austro-Hungarian occupation. The country is mostly mountainous, encompassing the central Dinaric Alps. The northeastern parts reach into the Pannonian Basin, while in the south it borders the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic. The Dinaric Alps generally run in a southeast–northwest direction, and get higher towards the south. The highest point of the country is the peak of Maglić (mountain), Maglić at , on the Montenegrin border. Other major mountains include Volujak (mountain), Volujak, Zelengora, Lelija, Lebršnik, Orjen, Kozara, Grmeč, Čvrsnica, Prenj, Vran, Vranica, Velež (Bosnia and Herzegovina), Velež, Vlašić (Bosnian mountain), Vlašić, Cincar, Romanija, Jahorina, Bjelašnica, Treskavica and Trebević. The geological composition of the Dinaric chain of mountains in Bosnia consists primarily of limestone (including Mesozoic limestone), with deposits of iron, coal, zinc, manganese, bauxite, lead, and salt present in some areas, especially in central and northern Bosnia. Overall, nearly 50% of Bosnia and Herzegovina is forested. Most forest areas are in the centre, east and west parts of Bosnia. Herzegovina has a drier Mediterranean climate, with dominant karst topography. Northern Bosnia (Posavina) contains very fertile agricultural land along the Sava river and the corresponding area is heavily farmed. This farmland is a part of the Pannonian Plain stretching into neighboring Croatia and Serbia. The country has only of coastline,Bosnia-and-Herzegovina Neum britannica.com
, ''britannica.com'', 9 September 2015 around the town of Neum in the Herzegovina-Neretva Canton. Although the city is surrounded by Croatian peninsulas, by international law, Bosnia and Herzegovina has a right of passage to the outer sea. Sarajevo is the capital and largest city. Other major cities include Banja Luka and Prijedor in the northwest region known as Bosanska Krajina, Tuzla, Bijeljina, Doboj and Brčko in the northeast, Zenica in the central part of the country, and Mostar, the largest city in the southern region of Herzegovina. There are seven major rivers in Bosnia and Herzegovina:
Biodiversity
Phytogeography, Phytogeographically, Bosnia and Herzegovina belongs to the Boreal Kingdom and is shared between the Illyrian province of the Circumboreal Region and Adriatic province of the Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean Region. According to the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina can be subdivided into four ecoregions: Balkan mixed forests, Dinaric Mountains mixed forests, Pannonian mixed forests and Illyrian deciduous forests. The country had a 2018 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 5.99/10, ranking it 89th globally out of 172 countries. In Bosnia and Herzegovina forest cover is around 43% of the total land area, equivalent to 2,187,910 hectares (ha) of forest in 2020, down from 2,210,000 hectares (ha) in 1990. For the year 2015, 74% of the forest area was reported to be under State ownership, public ownership and 26% Private property, private ownership.Politics
Government
 As a result of the Dayton Agreement, the civilian peace implementation is supervised by the High Representative for Bosnia and Herzegovina selected by the Peace Implementation Council (PIC). The High Representative is the highest political authority in the country. The High Representative has many governmental and legislative powers, including the dismissal of elected and non-elected officials. Due to the vast powers of the High Representative over Politics of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnian politics and essential veto powers, the position has also been compared to that of a viceroy.
Politics take place in a framework of a parliamentary system, parliamentary representative democracy, whereby Executive (government), executive power is exercised by the Council of Ministers of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Legislature, Legislative power is vested in both the Council of Ministers and the Parliamentary Assembly of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Members of the Parliamentary Assembly are chosen according to a proportional representation (PR) system.
Bosnia and Herzegovina is a liberal democracy. It has several levels of political structuring, according to the Dayton Agreement. The most important of these levels is the division of the country into two entities: the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Republika Srpska. The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina covers 51% of Bosnia and Herzegovina's total area, while Republika Srpska covers 49%. The entities, based largely on the territories held by the two warring sides at the time, were formally established by the Dayton Agreement in 1995 because of the tremendous changes in Bosnia and Herzegovina's ethnic structure. At the national level, there exists only a finite set of exclusive or joint competencies, whereas the majority of authority rests within the entities. Sumantra Bose describes Bosnia and Herzegovina as a consociational confederation.
The Brčko District in the north of the country was created in 2000, out of land from both entities. It officially belongs to both, but is governed by neither, and functions under a decentralized system of local government. For election purposes, Brčko District voters can choose to participate in either the Federation or Republika Srpska elections. The Brčko District has been praised for maintaining a multiethnic population and a level of prosperity significantly above the national average.OHR Bulletin 66 (3 February 1998)
As a result of the Dayton Agreement, the civilian peace implementation is supervised by the High Representative for Bosnia and Herzegovina selected by the Peace Implementation Council (PIC). The High Representative is the highest political authority in the country. The High Representative has many governmental and legislative powers, including the dismissal of elected and non-elected officials. Due to the vast powers of the High Representative over Politics of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnian politics and essential veto powers, the position has also been compared to that of a viceroy.
Politics take place in a framework of a parliamentary system, parliamentary representative democracy, whereby Executive (government), executive power is exercised by the Council of Ministers of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Legislature, Legislative power is vested in both the Council of Ministers and the Parliamentary Assembly of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Members of the Parliamentary Assembly are chosen according to a proportional representation (PR) system.
Bosnia and Herzegovina is a liberal democracy. It has several levels of political structuring, according to the Dayton Agreement. The most important of these levels is the division of the country into two entities: the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Republika Srpska. The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina covers 51% of Bosnia and Herzegovina's total area, while Republika Srpska covers 49%. The entities, based largely on the territories held by the two warring sides at the time, were formally established by the Dayton Agreement in 1995 because of the tremendous changes in Bosnia and Herzegovina's ethnic structure. At the national level, there exists only a finite set of exclusive or joint competencies, whereas the majority of authority rests within the entities. Sumantra Bose describes Bosnia and Herzegovina as a consociational confederation.
The Brčko District in the north of the country was created in 2000, out of land from both entities. It officially belongs to both, but is governed by neither, and functions under a decentralized system of local government. For election purposes, Brčko District voters can choose to participate in either the Federation or Republika Srpska elections. The Brčko District has been praised for maintaining a multiethnic population and a level of prosperity significantly above the national average.OHR Bulletin 66 (3 February 1998)Final hearing of the Arbitration Tribunal in Vienna
. OHR. The third level of Bosnia and Herzegovina's political subdivision is manifested in Cantons of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, cantons. They are unique to the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina entity, which consists of ten of them. Each has a cantonal government, which is under the law of the Federation as a whole. Some cantons are ethnically mixed and have special laws to ensure the equality of all constituent people. The fourth level of political division in Bosnia and Herzegovina are the Municipalities of Bosnia and Herzegovina, municipalities. The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina is divided into 79 municipalities, and Republika Srpska into 64. Municipalities also have their own local government, and are typically based on the most significant city or place in their territory. As such, many municipalities have a long tradition and history with their present boundaries. Some others, however, were only created following the recent war after traditional municipalities were split by the Inter-Entity Boundary Line. Each canton in the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina consists of several municipalities, which are divided into local communities. Besides entities, cantons, and municipalities, Bosnia and Herzegovina also has four "official" cities. These are: Banja Luka, Mostar, Sarajevo and Istočno Sarajevo, East Sarajevo. The territory and government of the cities of Banja Luka and Mostar corresponds to the municipalities of the same name, while the cities of Sarajevo and East Sarajevo officially consist of several municipalities. Cities have their own city government whose power is in between that of the municipalities and cantons (or the entity, in the case of Republika Srpska). More recently, several central institutions have been established (such as a defence minister, defense ministry, security ministry, state court, indirect taxation service and so on) in the process of transferring part of the jurisdiction from the entities to the state. The representation of the government of Bosnia and Herzegovina is by elites who represent the country's three major groups, with each having a guaranteed share of power. The Chairman of the Presidency of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Chair of the Presidency of Bosnia and Herzegovina rotates among three members (Bosniaks, Bosniak, Serbs, Serb, Croats, Croat), each elected as the chair for an eight-month term within their four-year term as a member. The three members of the Presidency are elected directly by the people, with Federation voters voting for the Bosniak and the Croat and the Republika Srpska voters voting for the Serb. The Chairman of the Council of Ministers of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Chair of the Council of Ministers is nominated by the Presidency and approved by the parliamentary House of Representatives of Bosnia and Herzegovina, House of Representatives. The Chair of the Council of Ministers is then responsible for appointing a Foreign Minister, Minister of Foreign Trade and others as appropriate. The Parliamentary Assembly is the lawmaking body in Bosnia and Herzegovina. It consists of two houses: the House of Peoples of Bosnia and Herzegovina, House of Peoples and the House of Representatives. The House of Peoples has 15 delegates chosen by parliaments of the entities, two-thirds of which come from the Federation (5 Bosniaks and 5 Croats) and one-third from the Republika Srpska (5 Serbs). The House of Representatives is composed of 42 Members elected by the people under a form of proportional representation, two-thirds elected from the Federation and one-third elected from Republika Srpska. The Constitutional Court of Bosnia and Herzegovina is the supreme, final arbiter of legal matters. It is composed of nine members: four members are selected by the House of Representatives of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Federal House of Representatives, two by the National Assembly (Republika Srpska), National Assembly of Republika Srpska and three by the President of the European Court of Human Rights after consultation with the Presidency, who cannot be Bosnian citizens. However, the highest political authority in the country is the High Representative for Bosnia and Herzegovina, the chief executive officer for the international civilian presence in the country and is selected by the European Union. Since 1995, the High Representative has been able to bypass the elected parliamentary assembly, and since 1997 has been able to remove elected officials. The methods selected by the High Representative have been criticized as undemocratic. International supervision High Representative for Bosnia and Herzegovina#Conditions for closure of the Office of the High Representative, is to end when the country is deemed politically and democratically stable and self-sustaining.
Military
The Armed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina (OSBiH) were unified into a single entity in 2005, with the merger of the Army of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Army of Republika Srpska, which had defended their respective regions. The Ministry of Defence (Bosnia and Herzegovina), Ministry of Defence was formed in 2004. The Bosnian military consists of the Armed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnian Ground Forces and Air Force and Anti-Aircraft Defence of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Air Force and Air Defense. The Ground Forces number 7,200 active and 5,000 reserve personnel. They are armed with a mix of American, Yugoslav, Soviet, and European-made weaponry, vehicles, and military equipment. The Air Force and Air Defense Forces have 1,500 personnel and about 62 aircraft. The Air Defense Forces operate Man-portable air-defense system, MANPADS hand-held missiles, surface-to-air missile (SAM) batteries, anti-aircraft cannons, and radar. The Army has recently adopted remodeled MARPAT uniforms, used by Bosnian soldiers serving with the International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) in Afghanistan. A domestic production program is now underway to ensure that army units are equipped with the correct ammunition. Beginning in 2007, the Ministry of Defence undertook the army's first ever international assistance mission, enlisting the military to serve with ISAF peace missions to Afghanistan, Iraq and the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 2007. Five officers, acting as officers/advisors, served in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. 45 soldiers, mostly acting as base security and medical assistants, served in Afghanistan. 85 Bosnian soldiers served as base security in Iraq, occasionally conducting infantry patrols there as well. All three deployed groups have been commended by their respective international forces as well as the Ministry of Defence of Bosnia and Herzegovina. The international assistance operations are still ongoing. The Air Force and Anti-Aircraft Defence of Bosnia and Herzegovina was formed when elements of the Army of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Republika Srpska Air Force were merged in 2006. The Air Force has seen improvements in the last few years with added funds for aircraft repairs and improved cooperation with the Army, Ground Forces as well as to the citizens of the country. The Ministry of Defence is pursuing the acquisition of new aircraft including helicopters and perhaps even fighter jets.Foreign relations
Accession of Bosnia and Herzegovina to the European Union, European Union integration is one of the main political objectives of Bosnia and Herzegovina; it initiated the Stabilisation and Association Process in 2007. Countries participating in the SAP have been offered the possibility to become, once they fulfill the necessary conditions, Member States of the EU. Bosnia and Herzegovina has been a candidate country for EU accession since December 2022. Accession talks are set to begin following the impeding of more reforms. The implementation of the Dayton Agreement in 1995 has focused the efforts of policymakers in Bosnia and Herzegovina, as well as the international community, on regional stabilization in the countries-successors of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, former Yugoslavia. Within Bosnia and Herzegovina, relations with its neighbors of Croatia, Serbia and Montenegro have been fairly stable since the signing of the Dayton Agreement. On 23 April 2010, Bosnia and Herzegovina received the Enlargement of NATO#Membership Action Plan, Membership Action Plan from NATO, which is the last step before full membership in the alliance. Full membership was initially expected in 2014 or 2015, depending on the progress of reforms. In December 2018, NATO approved a Bosnian Membership Action Plan. Bosnia and Herzegovina is the 61st most peaceful country in the world, according to the 2024 Global Peace Index.Demography
According to the 1991 population census in Bosnia and Herzegovina, 1991 census, Bosnia and Herzegovina had a population of 4,369,319, while the 1996 World Bank Group census showed a decrease to 3,764,425. Large population migrations during the Yugoslav Wars in the 1990s have caused demographic shifts in the country. Between 1991 and 2013, political disagreements made it impossible to organize a census. A census had been planned for 2011, and then for 2012, but was delayed until October 2013. The 2013 population census in Bosnia and Herzegovina, 2013 census found a total population of 3,531,159 people, a drop of approximately 20% since 1991. The 2013 census figures include non-permanent Bosnian residents and for this reason are contested by Republika Srpska officials and Serb politicians (see Ethnic groups below).Largest cities
Ethnic groups
 Bosnia and Herzegovina is home to three ethnic "Ethnic groups in Bosnia and Herzegovina, constituent peoples", namely Bosniaks, Serbs and Croats, plus a number of smaller groups including History of the Jews in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Jews and Romani people in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Roma. According to data from the 2013 census published by the Statistical system of Bosnia and Herzegovina#The Agency for Statistics of Bosnia and Herzegovina (BHAS), Agency for Statistics of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosniaks constitute 50.1% of the population, Serbs 30.8%, Croats 15.5% and others 2.7%, with the remaining respondents not declaring their ethnicity or not answering. The census results are contested by the Republika Srpska statistical office and by Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnian Serb politicians. The dispute over the census concerns the inclusion of non-permanent Bosnian residents in the figures, which Republika Srpska officials oppose. The European Union's statistics office, Eurostat, concluded in May 2016 that the census methodology used by the Bosnian statistical agency is in line with international recommendations.
Bosnia and Herzegovina is home to three ethnic "Ethnic groups in Bosnia and Herzegovina, constituent peoples", namely Bosniaks, Serbs and Croats, plus a number of smaller groups including History of the Jews in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Jews and Romani people in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Roma. According to data from the 2013 census published by the Statistical system of Bosnia and Herzegovina#The Agency for Statistics of Bosnia and Herzegovina (BHAS), Agency for Statistics of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosniaks constitute 50.1% of the population, Serbs 30.8%, Croats 15.5% and others 2.7%, with the remaining respondents not declaring their ethnicity or not answering. The census results are contested by the Republika Srpska statistical office and by Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnian Serb politicians. The dispute over the census concerns the inclusion of non-permanent Bosnian residents in the figures, which Republika Srpska officials oppose. The European Union's statistics office, Eurostat, concluded in May 2016 that the census methodology used by the Bosnian statistical agency is in line with international recommendations.
Languages
Bosnia's constitution does not specify any official languages. However, academics Hilary Footitt and Michael Kelly note the Dayton Agreement states it is "done in Bosnian language, Bosnian, Croatian language, Croatian, English and Serbian language, Serbian", and they describe this as the "de facto recognition of three official languages" at the state level. The equal status of Bosnian, Serbian and Croatian was verified by the Constitutional Court of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Constitutional Court in 2000. It ruled the provisions of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Federation and Republika Srpska constitutions on language were incompatible with the state constitution, since they only recognised Bosnian and Croatian (in the case of the Federation) and Serbian (in the case of Republika Srpska) as official languages at the entity level. As a result, the wording of the entity constitutions was changed and all three languages were made official in both entities. The three standard languages are fully Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible and are known collectively under the appellation of Serbo-Croatian, despite this term not being formally recognized in the country. Use of one of the three languages has become a marker of ethnic identity. Michael Kelly and Catherine Baker argue: "The three official languages of today's Bosnian state...represent the symbolic assertion of national identity over the pragmatism of mutual intelligibility". According to the 1992 European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages (ECRML), Bosnia and Herzegovina recognizes the following minority languages: Albanian language, Albanian, Montenegrin language, Montenegrin, Czech language, Czech, Italian language, Italian, Hungarian language, Hungarian, Macedonian language, Macedonian, German language, German, Polish language, Polish, Romani language, Romani, Romanian language, Romanian, Rusyn language, Rusyn, Slovak language, Slovak, Slovene language, Slovene, Turkish language, Turkish, Ukrainian language, Ukrainian and Jewish (Yiddish and Judaeo-Spanish, Ladino). The German minority in Bosnia and Herzegovina are mostly remnants of Danube Swabians, who settled in the area after the Austrian Empire, Habsburg monarchy claimed the Balkans from the Ottoman Empire. Due to Flight and expulsion of Germans (1944–1950), expulsions and Persecution of Germans, (forced) assimilation after the two World wars, the number of ethnic Germans in Bosnia and Herzegovina was drastically diminished. In the 2013 census, 52.86% of the population consider their mother tongue Bosnian, 30.76% Serbian, 14.6% Croatian and 1.57% another language, with 0.21% not giving an answer.Religion
Bosnia and Herzegovina is a religiously diverse country. According to the 2013 census, Muslims comprised 50.7% of the population, while Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Christians made 30.7%, Catholic Church, Catholic Christians 15.2%, 1.2% other and 1.1% Atheism, atheist or Agnosticism, agnostic, with the remainder not declaring or not answering the question. A 2012 survey found 54% of Bosnia's Muslims were non-denominational Muslim, non-denominational, while 38% followed Sunni Islam, Sunnism.Urban areas
Sarajevo is home to 419,957 inhabitants in its urban area which comprises the Sarajevo#Municipalities and city government, City of Sarajevo as well as the municipalities of Ilidža, Vogošća, Istočna Ilidža, Istočno Novo Sarajevo and Istočni Stari Grad. The Sarajevo metropolitan area, metro area has a population of 555,210 and includes Sarajevo Canton, Istočno Sarajevo, East Sarajevo and the municipalities of Breza, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Breza, Kiseljak, Kreševo and Visoko.Healthcare
According to the 2024 Global Hunger Index (GHI), Bosnia and Herzegovina has a low level of hunger, with a GHI score of less than 5.Economy
Tourism
According to projections by the World Tourism Organization, Bosnia and Herzegovina had the third highest tourism growth rate in the world between 1995 and 2020. In 2017, 1,307,319 tourists visited Bosnia and Herzegovina, an increase of 13.7%, and had 2,677,125 overnight hotel stays, a 12.3% increase from the previous year. 71.5% of the tourists came from foreign countries. In 2018, 1.883.772 tourists visited Bosnia and Herzegovina, an increase of 44,1%, and had 3.843.484 overnight hotel stays, a 43.5% increase from the previous year. Also, 71.2% of the tourists came from foreign countries. In 2006, when ranking the best cities in the world, Lonely Planet placed Sarajevo, the Capital city, national capital and host of the 1984 Winter Olympics, as #43 on the list. Tourism in Sarajevo is chiefly focused on historical, religious, and cultural aspects. In 2010, Lonely Planet's "Best in Travel" nominated it as one of the top ten cities to visit that year. Sarajevo also won travel blog Foxnomad's "Best City to Visit" competition in 2012, beating more than one hundred other cities around the entire world. Medjugorje, Međugorje has become one of the most popular pilgrimage sites for Catholics from around the world and has turned into Europe's third most important religious place, where each year more than 1 million people visit. It has been estimated that 30 million pilgrims have come to Međugorje since the reputed apparitions began in 1981.Vatican Probes Claims of Apparitions at Medugorje, Reuters.com; retrieved 17 March 2010. Since 2019, pilgrimages to Međugorje have been officially authorized and organized by the Holy See, Vatican. Bosnia has also become an increasingly popular skiing and Ecotourism destination. The mountains that hosted the winter olympic games of Bjelašnica, Jahorina and Igman are the most visited skiing mountains in Bosnia-Herzegovina. Bosnia and Herzegovina remains one of the last undiscovered natural regions of the southern area of the Alps, with vast tracts of wild and untouched nature attracting adventurers and nature lovers. ''National Geographic'' named Bosnia and Herzegovina as the best mountain biking adventure destination for 2012.
, The central Dinaric Alps, Bosnian Dinaric Alps are favored by hikers and mountaineers, as they contain both Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean and Alpine climate, Alpine climates. Rafting, Whitewater rafting has become somewhat of a national sport, national pastime in Bosnia and Herzegovina. The primary rivers used for whitewater rafting in the country include the Vrbas (river), Vrbas, Tara (Drina), Tara, Drina, Neretva and Una (Sava), Una. Meanwhile, the most prominent rivers are the Vrbas and Tara, as they both hosted International Rafting Federation, The 2009 World Rafting Championship. The reason the Tara river is immensely popular for whitewater rafting is because it contains the deepest canyon, river canyon in Europe, the Tara River Canyon. Most recently, the ''HuffPost, Huffington Post'' named Bosnia and Herzegovina the "9th Greatest Adventure in the World for 2013", adding that the country boasts "the cleanest water and air in Europe; the greatest untouched forests; and the most wildlife. The best way to experience is the three rivers trip, which purls through the best the Balkans have to offer."
Infrastructure
Transport
 Sarajevo International Airport, also known as Butmir Airport, is the main international airport in Bosnia and Herzegovina, located southwest of the Sarajevo main railway station in the city of Sarajevo in the suburb of Butmir.
Railway operations in Bosnia and Herzegovina are successors of the Yugoslav Railways within the country boundaries following independence from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, former Yugoslavia in 1992. Today, they are operated by the Railways of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ŽFBiH) in the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and by Republika Srpska Railways (ŽRS) in Republika Srpska.
Sarajevo International Airport, also known as Butmir Airport, is the main international airport in Bosnia and Herzegovina, located southwest of the Sarajevo main railway station in the city of Sarajevo in the suburb of Butmir.
Railway operations in Bosnia and Herzegovina are successors of the Yugoslav Railways within the country boundaries following independence from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, former Yugoslavia in 1992. Today, they are operated by the Railways of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ŽFBiH) in the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and by Republika Srpska Railways (ŽRS) in Republika Srpska.
Telecommunications
The Bosnian communications market was fully Economic liberalization, liberalised in January 2006. The three landline telephone operators predominantly provide services in their operating areas but have nationwide licenses for domestic and international calls. Mobile data services are also available, including high-speed Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution, EDGE, 3G and 4G services. ''Oslobođenje'' (Liberation), founded in 1943, is one of the country's longest running continuously circulating newspapers. There are many national publications, including the ''Dnevni avaz'' (Daily Voice), founded in 1995, and ''Jutarnje Novine'' (Morning News), to name but a few in circulation in Sarajevo. Other local periodicals include the Croatian ''Hrvatska riječ'' newspaper and Bosnian ''Start (Bosnian magazine), Start'' magazine, as well as ''Slobodna Bosna'' (''Free Bosnia'') and ''BH Dani'' (''BH Days'') weekly newspapers. ''Novi Plamen'', a monthly magazine, was the most left-wing publication. International news station Al Jazeera Media Network, Al Jazeera maintains a sister channel catering to the Balkans, Balkan region, Al Jazeera Balkans, broadcasting out of and based in Sarajevo. Since 2014, the N1 (TV channel), N1 platform has broadcast as an affiliate of CNN International, with offices in Sarajevo, Zagreb and Belgrade. As of 2021, Bosnia and Herzegovina ranked second highest in freedom of the press, press freedom in the region, after Croatia, and is placed 58th internationally. , there are 3,374,094 internet users in the country, or 95.55% of the entire population.Education
 Primary schooling lasts for nine years. Secondary education is provided by general and technical secondary schools (typically Gymnasium (school), Gymnasiums) where studies typically last for four years. All forms of secondary schooling include an element of vocational education, vocational training. Pupils graduating from general secondary schools obtain the ''Matura'' and can enroll in any tertiary educational institution or academy by passing a qualification examination prescribed by the governing body or institution. Students graduating technical subjects obtain a Diploma.
The first bespoke higher-education institution was a school of Sufism, Sufi philosophy established by Gazi Husrev Bey, Gazi Husrev-beg in 1531. Numerous other religious schools then followed. In 1887, under the Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarian Empire, a Sharia law school began a five-year program.
In the 1940s, the University of Sarajevo became the city's first secular higher education institute. In the 1950s, post-baccalaurate graduate degrees became available. Severely damaged during the Bosnian War, war, it was recently rebuilt in partnership with more than 40 other universities. There are various other institutions of higher education, including: University Džemal Bijedić of Mostar, University of Banja Luka, University of Mostar, University of East Sarajevo, University of Tuzla, American University in Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Academy of Sciences and Arts of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Also, Bosnia and Herzegovina is home to several private and international higher education institutions, some of which are:
*Sarajevo School of Science and Technology
*International University of Sarajevo
*American University in Bosnia and Herzegovina
*Sarajevo Graduate School of Business
*International Burch University
*United World College in Mostar
Primary schooling lasts for nine years. Secondary education is provided by general and technical secondary schools (typically Gymnasium (school), Gymnasiums) where studies typically last for four years. All forms of secondary schooling include an element of vocational education, vocational training. Pupils graduating from general secondary schools obtain the ''Matura'' and can enroll in any tertiary educational institution or academy by passing a qualification examination prescribed by the governing body or institution. Students graduating technical subjects obtain a Diploma.
The first bespoke higher-education institution was a school of Sufism, Sufi philosophy established by Gazi Husrev Bey, Gazi Husrev-beg in 1531. Numerous other religious schools then followed. In 1887, under the Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarian Empire, a Sharia law school began a five-year program.
In the 1940s, the University of Sarajevo became the city's first secular higher education institute. In the 1950s, post-baccalaurate graduate degrees became available. Severely damaged during the Bosnian War, war, it was recently rebuilt in partnership with more than 40 other universities. There are various other institutions of higher education, including: University Džemal Bijedić of Mostar, University of Banja Luka, University of Mostar, University of East Sarajevo, University of Tuzla, American University in Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Academy of Sciences and Arts of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Also, Bosnia and Herzegovina is home to several private and international higher education institutions, some of which are:
*Sarajevo School of Science and Technology
*International University of Sarajevo
*American University in Bosnia and Herzegovina
*Sarajevo Graduate School of Business
*International Burch University
*United World College in Mostar
Culture
Architecture
The architecture of Bosnia and Herzegovina is largely influenced by four major periods where political and social changes influenced the creation of distinct cultural and architectural habits of the population. Each period made its influence felt and contributed to a greater diversity of cultures and architectural language in this region.Media
Some television, magazines, and newspapers in Bosnia and Herzegovina are state-owned, and some are for-profit corporations funded by advertising, Subscription business model, subscription, and other sales-related revenues. The Constitution of Bosnia and Herzegovina guarantees freedom of speech. As a Transition economy, country in transition with a post-war legacy and a politics of Bosnia and Herzegovina, complex domestic political structure, Bosnia and Herzegovina's media system is under transformation. In the early post-war period (1995–2005), media development was guided mainly by international donors and cooperation agencies, who invested to help reconstruct, diversify, democratize and professionalize media outlets.Tarik Jusić,Bosnia and Herzegovina
", EJC Media Landscapes Post-war developments included the establishment of an independent Communication Regulatory Agency, the adoption of a Press Code, the establishment of the Press Council, the decriminalization of libel and defamation, the introduction of a rather advanced Freedom of Access to Information Law, and the creation of a Public Service Broadcasting System from the formerly state-owned broadcaster. Yet, internationally backed positive developments have been often obstructed by domestic elites, and the professionalisation of media and journalists has proceeded only slowly. High levels of partisanship and linkages between the media and the political systems hinder the adherence to professional code of conducts.
Literature
Bosnia and Herzegovina has a rich literature, including the Nobel Prize winner Ivo Andrić and poets such as Antun Branko Šimić, Aleksa Šantić, Jovan Dučić and Mak Dizdar, writers such as Zlatko Topčić, Meša Selimović, Semezdin Mehmedinović, Miljenko Jergović, Isak Samokovlija, Safvet-beg Bašagić, Abdulah Sidran, Petar Kočić, Aleksandar Hemon and Nedžad Ibrišimović. The Sarajevo National Theatre, National Theater was founded in 1919 in Sarajevo and its first director was dramatist Branislav Nušić. Magazines such as ''Novi Plamen'' or ''Sarajevske sveske'' are some of the more prominent publications covering cultural and literary themes. By the late 1950s, Ivo Andrić's works had been translated into a number of languages. In 1958, the Association of Writers of Yugoslavia nominated Andrić as its first ever candidate for the Nobel Prize in LiteratureArt
 The Bosnia and Herzegovina art, art of Bosnia and Herzegovina was always evolving and ranged from the original medieval tombstones called Stećak, Stećci to paintings in Kotromanić dynasty, Kotromanić court. Twenty stećak necropolis sites in Bosnia and Herzegovina were added on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 2006. However, only with the arrival of Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarians did the painting renaissance in Bosnia really begin to flourish. The first educated artists from European academies appeared with the beginning of the 20th century. Among those are: Gabrijel Jurkić, Petar Šain, Roman Petrović and Lazar Drljača.
After World War II, artists like Mersad Berber and Safet Zec rose in popularity.
In 2007, Ars Aevi, a museum of contemporary art that includes works by renowned world artists, was founded in Sarajevo.
The Bosnia and Herzegovina art, art of Bosnia and Herzegovina was always evolving and ranged from the original medieval tombstones called Stećak, Stećci to paintings in Kotromanić dynasty, Kotromanić court. Twenty stećak necropolis sites in Bosnia and Herzegovina were added on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 2006. However, only with the arrival of Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarians did the painting renaissance in Bosnia really begin to flourish. The first educated artists from European academies appeared with the beginning of the 20th century. Among those are: Gabrijel Jurkić, Petar Šain, Roman Petrović and Lazar Drljača.
After World War II, artists like Mersad Berber and Safet Zec rose in popularity.
In 2007, Ars Aevi, a museum of contemporary art that includes works by renowned world artists, was founded in Sarajevo.
Music
Typical Bosnian songs are ''Ganga (music), ganga, rera'', and the traditional Slavic music for the folk dances such as ''Kolo (dance), kolo'', while from the Ottoman era the most popular is Sevdalinka. Pop and Rock music has a tradition here as well, with the more famous musicians including Dino Zonić, Goran Bregović, Davorin Popović, Kemal Monteno, Zdravko Čolić, Elvir Laković Laka, Edo Maajka, Hari Varešanović, Dino Merlin, Mladen Vojičić Tifa, Željko Bebek, etc. Other composers such as Đorđe Novković, Al' Dino, Haris Džinović, Kornelije Kovač, and many Musical ensemble#Rock and pop bands, rock and pop bands, for example, Bijelo Dugme, Crvena jabuka, Divlje jagode, Indexi, Plavi orkestar, Zabranjeno Pušenje, Ambasadori, Dubioza kolektiv, who were among the leading ones in the former Yugoslavia. Bosnia is home to the composer Dušan Šestić, the creator of the National Anthem of Bosnia and Herzegovina and father of singer Marija Šestić, to the jazz musician, educator and Bosnian jazz ambassador Sinan Alimanović, composer Saša Lošić and pianist Saša Toperić. In the villages, especially in Herzegovina, Bosniaks, Serbs and Croats play the ancient gusle. The gusle is used mainly to recite epic poems in a usually dramatic tone. Probably the most distinctive and identifiably "Bosnian" of music, Sevdalinka is a kind of emotional, melancholic folk song that often describes sad subjects such as love and loss, the death of a dear person or heartbreak. Sevdalinkas were traditionally performed with a Bağlama, saz, a Turkish string instrument, which was later replaced by the accordion. However the more modern arrangement is typically a vocalist accompanied by the accordion along with snare drums, upright bass, guitars, clarinets and violins. Rural folk traditions in Bosnia and Herzegovina include the shouted, polyphony, polyphonic ganga and "ravne pjesme" (''flat song'') styles, as well as instruments like a droneless Bagpipes, bagpipe, wooden flute and šargija. The gusle, an instrument found throughout the Balkans, is also used to accompany ancient Slavs, Slavic epic poetry, epic Poetry, poems. There are also Bosnian folk songs in the Judaeo-Spanish, Ladino language, derived from the area's Jewish population. ''Bosnian roots music'' came from Central Bosnia, Posavina, the Drina valley and Kalesija. It is usually performed by singers with two violinists and a šargija player. These bands first appeared around World War I and became popular in the 1960s. This is the third oldest music after the Sevdalinka and Nasheed, ilahija. Self-taught people, mostly in two or three members of the different choices of old instruments, mostly in the violin, sacking, saz, drums, flutes () or wooden flute, as others have already called, the original performers of Bosnian music that can not be written notes, transmitted by ear from generation to generation, family is usually hereditary. It is thought to be brought from Persia-Kalesi tribe that settled in the area of the present Sprečanski valleys and hence probably the name Kalesija. In this part of Bosnia, it is the most common. This kind of music was enjoyed by all three peoples in Bosnia, Bosniaks, Serbs and Croats, and it contributed a lot to reconcile people socializing, entertainment and other organizations through festivals. In Kalesija, it is maintained each year with the Original Bosnian Festival music.Cinema and theatre
Sarajevo is internationally renowned for its eclectic and diverse selection of festivals. The Sarajevo Film Festival was established in 1995, during the Bosnian War and has become the premier and largest film festival in the Balkans and Southeast Europe. Bosnia has a rich cinematic and film heritage, dating back to the Kingdom of Yugoslavia; many Bosnian filmmakers have achieved international prominence and some have won international awards ranging from the Academy Awards to multiple Palme d'Ors and Golden Bears. Some notable Bosnian screenwriters, directors and producers are Danis Tanović (known for the Academy Award and Golden Globe Awards, Golden Globe Award winning 2001 film ''No Man's Land (2001 film), No Man's Land'' and Silver Bear Grand Jury Prize winning 2016 film ''Death in Sarajevo''), Jasmila Žbanić (won Golden Bear, Academy Award and British Academy Film Awards, BAFTA nominated 2020 film ''Quo Vadis, Aida?''), Emir Kusturica (won two Palme d'Ors at Cannes Film Festival, Cannes), Zlatko Topčić, Ademir Kenović, Ahmed Imamović, Pjer Žalica, Aida Begić, etc.Cuisine
Sports
Bosnia and Herzegovina has produced many athletes. The most important international Sport, sporting event in the history of Bosnia and Herzegovina were the 1984 Winter Olympics, 14th Winter Olympics, held in Sarajevo from 7 to 19 February 1984. The RK Borac Banja Luka, Borac handball club has won seven Yugoslav Handball Championships, as well as the EHF Champions League, European Cup in 1975–76 European Cup (handball), 1976 and the EHF European League, International Handball Federation Cup in 1991. Amel Mekić, Bosnian judoka, became 2011 European Judo Championships, European champion in 2011. Track and field athlete Amel Tuka won bronze and silver medals in 800 metres at the 2015 World Championships in Athletics, 2015 and 2019 IAAF World Athletics Championships and Hamza Alić won the silver medal in 2013 European Athletics Indoor Championships – Men's shot put, shot put at the 2013 European Athletics Indoor Championships, 2013 European Indoor Championships. The KK Bosna Royal, Bosna Royal basketball club from Sarajevo were Euroleague Basketball, European Champions in 1978–79 FIBA European Champions Cup, 1979. The Yugoslavia men's national basketball team, which won medals in every world championship from 1963 through 1990, included Bosnian players such as FIBA Hall of Famers Dražen Dalipagić and Mirza Delibašić. Bosnia and Herzegovina regularly qualifies for the EuroBasket, European Championship in Basketball, with players including Mirza Teletović, Nihad Đedović and Jusuf Nurkić. The Bosnia and Herzegovina men's national under-16 and under-17 basketball team, Bosnia and Herzegovina national under-16 team won two gold medals in 2015, winning both Basketball at the 2015 European Youth Summer Olympic Festival, 2015 European Youth Summer Olympic Festival as well as the 2015 FIBA Europe Under-16 Championship. Women's basketball club ŽKK Jedinstvo Tuzla, Jedinstvo Aida from Tuzla won the EuroLeague Women, Women's European Club Championship in 1989 and Ronchetti Cup final in 1990, led by Razija Mujanović, three times best female European basketball player, and Mara Lakić The Bosnian chess team was Yugoslav Chess Championship, Champion of Yugoslavia seven times, in addition to club ŠK Bosna winning four European Chess Club Cups. Chess grandmaster Borki Predojević has also won two European Championships. The most impressive success of Bosnian Chess was a runner-up position at the 31st Chess Olympiad in 1994 in Moscow, featuring Grandmasters Predrag Nikolić, Ivan Sokolov (chess player), Ivan Sokolov and Bojan Kurajica. Middle-weight Boxing, boxer Marijan Beneš has won several Championships of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Yugoslav Championships and the European Amateur Boxing Championships, European Championship. In 1978, he won the World Title against Elisha Obed from The Bahamas. Association football is the most popular sport in Bosnia and Herzegovina. It dates from 1903, but its popularity grew significantly after World War I. Bosnian clubs FK Sarajevo and FK Željezničar Sarajevo, Željezničar won the Yugoslav First League, Yugoslav Championship, while the Yugoslavia national football team, Yugoslav national football team included Bosnian players of all ethnic backgrounds and generations, such as Safet Sušić, Zlatko Vujović, Mehmed Baždarević, Davor Jozić, Faruk Hadžibegić, Predrag Pašić, Blaž Slišković, Vahid Halilhodžić, Dušan Bajević, Ivica Osim, Josip Katalinski, Tomislav Knez, Velimir Sombolac and numerous others. The Bosnia and Herzegovina national football team played at the 2014 FIFA World Cup, its first major tournament. Players on the team again includes notable players of all country's ethnic background, such as then and now captains Emir Spahić, Zvjezdan Misimović and Edin Džeko, defenders like Ognjen Vranješ, Sead Kolašinac and Toni Šunjić, midfielders like Miralem Pjanić and Senad Lulić, striker Vedad Ibišević, etc. Former Bosnian footballers include Hasan Salihamidžić, who became only the second Bosnian to ever win a UEFA Champions League trophy, after Elvir Baljić. He made 234 appearances and scored 31 goals for German club FC Bayern Munich. Sergej Barbarez, who played for several clubs in the German Bundesliga. including Borussia Dortmund, Hamburger SV and Bayer 04 Leverkusen, Bayer Leverkusen was joint-top scorer in the 2000–01 Bundesliga season with 22 goals. Meho Kodro spent most of his career playing in Spain, most notably with Real Sociedad and FC Barcelona. Elvir Rahimić made 302 appearances for Russian club PFC CSKA Moscow, CSKA Moscow with whom he won the UEFA Europa League, UEFA Cup in 2005 UEFA Cup Final, 2005.
Milena Nikolić, member of the Bosnia and Herzegovina women's national football team, women's national team, was the 2013–14 UEFA Women's Champions League UEFA Women's Champions League#Top scorers by tournament, top scorer.
Bosnia and Herzegovina was the world champion of volleyball at the 2004 Summer Paralympics and volleyball at the 2012 Summer Paralympics. Many among those on the team lost their legs in the Bosnian War. Its Bosnia and Herzegovina national sitting volleyball team, national sitting volleyball team is one of the dominant forces in Sitting volleyball, the sport worldwide, winning nine European Championships, three World Championships and two Volleyball at the Summer Paralympics, Paralympic gold medals.
Tennis is also gaining a lot of popularity after the recent successes of Damir Džumhur and Mirza Bašić at Grand Slam (tennis), Grand Slam level. Other notable tennis players who have represented Bosnia and Herzegovina are Tomislav Brkić, Amer Delić and Mervana Jugić-Salkić.
Association football is the most popular sport in Bosnia and Herzegovina. It dates from 1903, but its popularity grew significantly after World War I. Bosnian clubs FK Sarajevo and FK Željezničar Sarajevo, Željezničar won the Yugoslav First League, Yugoslav Championship, while the Yugoslavia national football team, Yugoslav national football team included Bosnian players of all ethnic backgrounds and generations, such as Safet Sušić, Zlatko Vujović, Mehmed Baždarević, Davor Jozić, Faruk Hadžibegić, Predrag Pašić, Blaž Slišković, Vahid Halilhodžić, Dušan Bajević, Ivica Osim, Josip Katalinski, Tomislav Knez, Velimir Sombolac and numerous others. The Bosnia and Herzegovina national football team played at the 2014 FIFA World Cup, its first major tournament. Players on the team again includes notable players of all country's ethnic background, such as then and now captains Emir Spahić, Zvjezdan Misimović and Edin Džeko, defenders like Ognjen Vranješ, Sead Kolašinac and Toni Šunjić, midfielders like Miralem Pjanić and Senad Lulić, striker Vedad Ibišević, etc. Former Bosnian footballers include Hasan Salihamidžić, who became only the second Bosnian to ever win a UEFA Champions League trophy, after Elvir Baljić. He made 234 appearances and scored 31 goals for German club FC Bayern Munich. Sergej Barbarez, who played for several clubs in the German Bundesliga. including Borussia Dortmund, Hamburger SV and Bayer 04 Leverkusen, Bayer Leverkusen was joint-top scorer in the 2000–01 Bundesliga season with 22 goals. Meho Kodro spent most of his career playing in Spain, most notably with Real Sociedad and FC Barcelona. Elvir Rahimić made 302 appearances for Russian club PFC CSKA Moscow, CSKA Moscow with whom he won the UEFA Europa League, UEFA Cup in 2005 UEFA Cup Final, 2005.
Milena Nikolić, member of the Bosnia and Herzegovina women's national football team, women's national team, was the 2013–14 UEFA Women's Champions League UEFA Women's Champions League#Top scorers by tournament, top scorer.
Bosnia and Herzegovina was the world champion of volleyball at the 2004 Summer Paralympics and volleyball at the 2012 Summer Paralympics. Many among those on the team lost their legs in the Bosnian War. Its Bosnia and Herzegovina national sitting volleyball team, national sitting volleyball team is one of the dominant forces in Sitting volleyball, the sport worldwide, winning nine European Championships, three World Championships and two Volleyball at the Summer Paralympics, Paralympic gold medals.
Tennis is also gaining a lot of popularity after the recent successes of Damir Džumhur and Mirza Bašić at Grand Slam (tennis), Grand Slam level. Other notable tennis players who have represented Bosnia and Herzegovina are Tomislav Brkić, Amer Delić and Mervana Jugić-Salkić.
See also
* Outline of Bosnia and HerzegovinaNotes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Allcock, John B., Marko Milivojevic, et al. ''Conflict in the Former Yugoslavia: An Encyclopedia'' (1998) * * * (Also aProject Gutenberg
* * * * * * Okey, Robin. ''Taming Balkan Nationalism: The Habsburg 'Civilizing' Mission in Bosnia, 1878–1914'' (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2007) * Phillips, Douglas A. ''Bosnia and Herzegovina'' (Philadelphia: Chelsea House, 2004).
External links
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' (archived 3 July 2008) * {{Authority control Bosnia and Herzegovina, Balkan countries Federal republics Member states of the Council of Europe Member states of the Union for the Mediterranean Member states of the United Nations States and territories established in 1992 Countries in Europe Observer states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation