Biting Flies on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Many species of
 Most arthropod bites and stings cause
Most arthropod bites and stings cause

 Most arthropod bites and stings do not require a specific diagnosis since they typically improve with supportive management alone. Certain bites and stings present with characteristic appearances and distributions. In general, however, dermoscopic findings of bitten or stung skin rarely aid in diagnosis. Rather, patient history (recent travel to endemic areas, outdoor activities, and other risk factors) primarily guides the diagnostic approach, which can raise clinical suspicion for more serious complications like vector-borne diseases.
Most arthropod bites and stings do not require a specific diagnosis since they typically improve with supportive management alone. Certain bites and stings present with characteristic appearances and distributions. In general, however, dermoscopic findings of bitten or stung skin rarely aid in diagnosis. Rather, patient history (recent travel to endemic areas, outdoor activities, and other risk factors) primarily guides the diagnostic approach, which can raise clinical suspicion for more serious complications like vector-borne diseases.
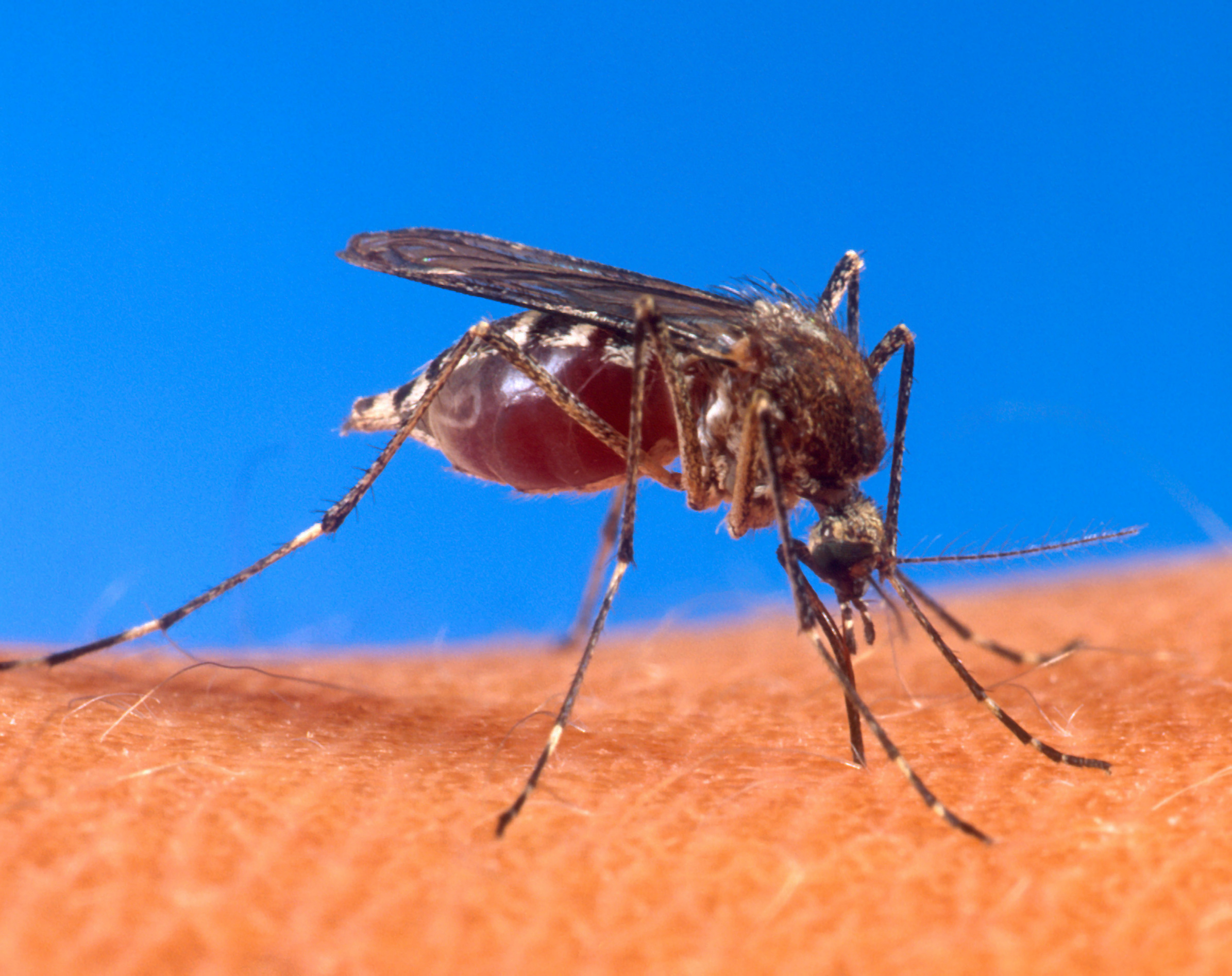 A bite is defined as coming from the mouthparts of the arthropod. The bite consists of both the bite wound and the
A bite is defined as coming from the mouthparts of the arthropod. The bite consists of both the bite wound and the



Identifying insect bites and stings
Diagnosing Mysterious "Bug Bites"
{{DEFAULTSORT:Arthropod Bites And Stings Lists of animals Medical lists Arthropods and humans Parasitic infestations, stings, and bites of the skin Arthropod attacks
arthropods
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
(insects, arachnids, millipedes and centipedes) can bite or sting human beings. These bites and stings generally occur as a defense mechanism or during normal arthropod feeding. While most cases cause self-limited irritation, medically relevant complications include envenomation
Envenomation is the process by which venom is injected by the bite or sting of a venomous animal.
Many kinds of animals, including mammals (e.g., the northern short-tailed shrew, ''Blarina brevicauda''), reptiles (e.g., many snakes), spiders, i ...
, allergic reactions
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic dermatitis, alle ...
, and transmission of vector-borne diseases
In epidemiology, a disease vector is any living agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen such as a parasite or microbe, to another living organism. Agents regarded as vectors are mostly blood-sucking (hematophagous) arthropods such ...
.
Signs and symptoms
 Most arthropod bites and stings cause
Most arthropod bites and stings cause self-limited
Self-limiting may refer to:
*Self-limiting (biology), describing an organism or colony of organisms which limits its own growth
*Governor (device), used to control the speed of mechanical equipment to prevent it from operating at unsafe speeds
*E ...
redness, itch
An itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes a strong desire or reflex to scratch. Itches have resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itches have many similarities to pain, and while both ...
iness and/or pain around the site. Less commonly (around 10% of Hymenoptera
Hymenoptera is a large order of insects, comprising the sawflies, wasps, bees, and ants. Over 150,000 living species of Hymenoptera have been described, in addition to over 2,000 extinct ones. Many of the species are parasitic.
Females typi ...
sting reactions), a large local reaction occurs when the area of swelling is greater than . Rarely (1-3% of Hymenoptera sting reactions), systemic reactions can affect multiple organs and pose a medical emergency, as in the case of anaphylactic shock
Anaphylaxis (Greek: 'up' + 'guarding') is a serious, potentially fatal allergic reaction and medical emergency that is rapid in onset and requires immediate medical attention regardless of the use of emergency medication on site. It typically ...
.
Defensive and predatory bites and stings
Many arthropods bite or sting in order to immobilize their prey or deter potential predators as adefense
Defense or defence may refer to:
Tactical, martial, and political acts or groups
* Defense (military), forces primarily intended for warfare
* Civil defense, the organizing of civilians to deal with emergencies or enemy attacks
* Defense industr ...
mechanism. Stings containing venom are more likely to be painful. Less frequently, venomous spider bites are also associated with morbidity
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are asso ...
and mortality in humans.
Most arthropod stings involve ''Hymenoptera
Hymenoptera is a large order of insects, comprising the sawflies, wasps, bees, and ants. Over 150,000 living species of Hymenoptera have been described, in addition to over 2,000 extinct ones. Many of the species are parasitic.
Females typi ...
'' (ants, wasps, and bees). While the majority of Hymenoptera stings are locally painful, their associated venom rarely cause toxic reactions unless victims receive many stings at once. The low mortality (around 60 deaths per year in the US out of unreported millions of stings nationwide) associated with Hymenoptera is mostly due to anaphylaxis from venom hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) is an abnormal physiological condition in which there is an undesirable and adverse immune response to an antigen. It is an abnormality in the immune system that causes Imm ...
.
Most scorpion sting
A scorpion sting is an injury caused by the stinger of a scorpion resulting in the medical condition known as scorpionism, which may vary in severity. The anatomical part of the scorpion that delivers the sting is called a "telson". In typical cas ...
s also cause self-limited pain or paresthesia
Paresthesia is a sensation of the skin that may feel like numbness (''hypoesthesia''), tingling, pricking, chilling, or burning. It can be temporary or Chronic condition, chronic and has many possible underlying causes. Paresthesia is usually p ...
s. Only certain species (from family ''Buthidae
The Buthidae are the largest family of scorpions, containing about 100 genera and 1339 species as of 2022. A few very large genera ('' Ananteris'', '' Centruroides'', '' Compsobuthus'', or '' Tityus'') are known, but a high number of species-poor ...
'') inject neurotoxic
Neurotoxicity is a form of toxicity in which a biological, chemical, or physical agent produces an adverse effect on the structure or function of the central and/or peripheral nervous system. It occurs when exposure to a substance – specifical ...
venom, responsible for most morbidity and mortality. Severe toxic reactions can occur resulting in progressive hemodynamic
Hemodynamics or haemodynamics are the dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. The hemodynamic response continuously ...
instability, neuromuscular dysfunction, cardiogenic shock
Cardiogenic shock is a medical emergency resulting from inadequate blood flow to the body's organs due to the dysfunction of the heart. Signs of inadequate blood flow include low urine production (<30 mL/hour), cool arms and legs, and decreased ...
, pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema (British English: oedema), also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive fluid accumulation in the tissue or air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. This leads to impaired gas exchange, most often leading to shortness ...
, multi-organ failure, and death. Although robust epidemiological data is unavailable, global estimates of scorpion stings exceed 1.2 million resulting in more than 3000 deaths annually.
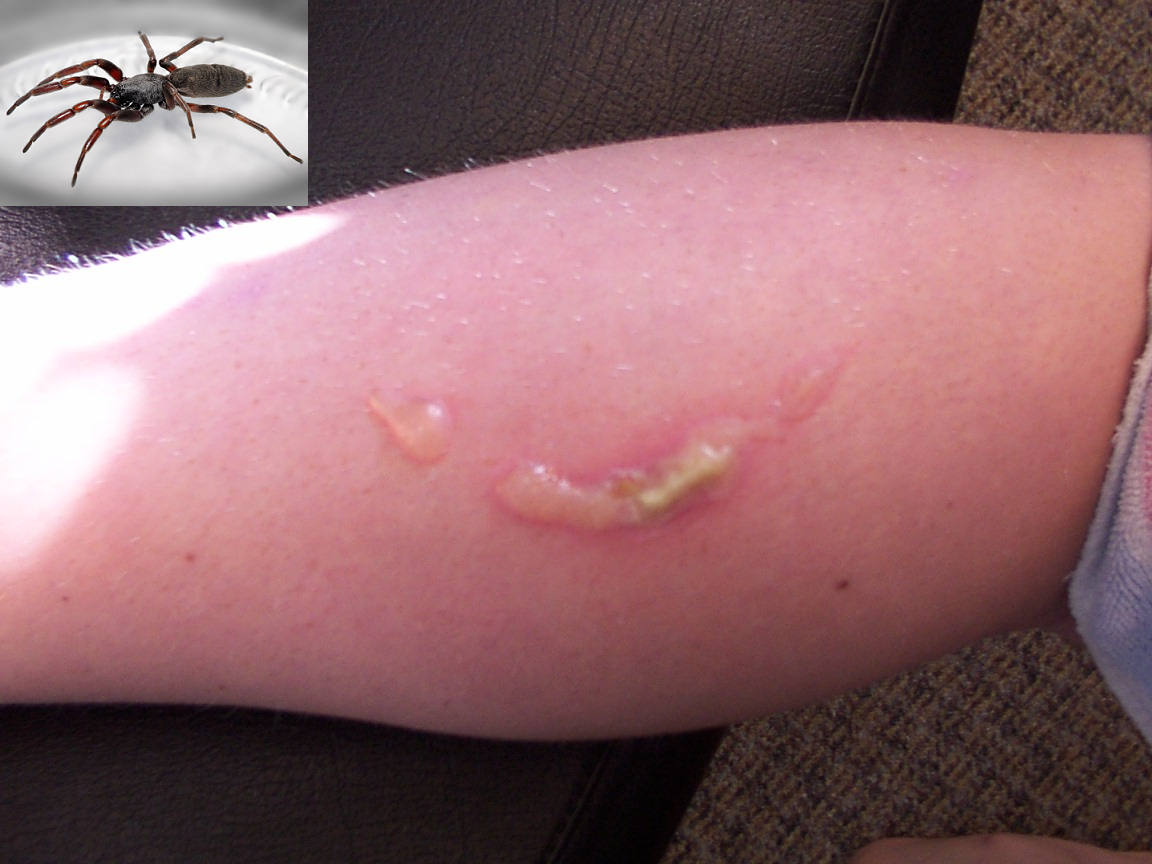
Spider bite
A spider bite, also known as arachnidism, is an injury resulting from the bite of a spider. The effects of most bites are not serious. Most bites result in mild symptoms around the area of the bite. Rarely they may produce a necrotic skin woun ...
s most often cause minor symptoms and resolve without intervention. Medically significant spider bites involve substantial envenomation
Envenomation is the process by which venom is injected by the bite or sting of a venomous animal.
Many kinds of animals, including mammals (e.g., the northern short-tailed shrew, ''Blarina brevicauda''), reptiles (e.g., many snakes), spiders, i ...
from only certain species such as widow spiders and recluse spider
The recluse spiders (''Loxosceles'' (), also known as brown spiders, fiddle-backs, violin spiders, and reapers, are a genus of spiders that were first described by R. T. Lowe in 1832. They are venomous spiders known for their bite, which sometime ...
s. Symptoms of latrodectism
Latrodectism () is the illness caused by the bite of ''Latrodectus'' spiders (the black widow spider and related species). Pain, muscle rigidity, vomiting, and sweating are the symptoms of latrodectism.
There are several spider species all named ...
(from widow spiders) may include pain at the bite or involve the chest and abdomen, sweating, muscle cramps and vomiting among others. By comparison, loxoscelism
Loxoscelism () is a condition occasionally produced by the bite of the recluse spiders (genus ''Loxosceles''). The area becomes dusky and a shallow open sore forms as the skin around the bite dies (necrosis). It is the only proven type of necrotic ...
(from recluse spiders) can present with local necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. The term "necrosis" came about in the mid-19th century and is commonly attributed to German pathologist Rudolf Virchow, who i ...
of the surrounding skin and widespread breakdown of red blood cells. Headaches, vomiting and a mild fever may also occur.
Feeding bites
Feeding bites have characteristic patterns and symptoms that reflect feeding habits of the offending pest and the chemistry of its saliva. Feeding bites are less likely to be felt at the time of the bite, although there are some exceptions. Since feeding requires longer attachment to prey than envenomation, feeding bites are more often associated with vector transmission of disease.Herness J, Snyder MJ, Newman RS. Arthropod bites and stings. American family physician. 2022 Aug;106(2):137-47.As vectors of disease
In addition to stings and bites causing discomfort in of themselves, bites can also spread secondary infections if the arthropod is carrying a virus, bacteria, or parasite. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that 17% of all infectious diseases worldwide were transmitted by arthropod vectors, resulting in over 700,000 deaths annually.Global vector control response 2017–2030. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. The table below lists common arthropod vectors and their associated diseases. The figure below representsendemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
areas of common vector-borne disease
In epidemiology, a disease vector is any living agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen such as a parasite or microbe, to another living organism. Agents regarded as vectors are mostly blood-sucking ( hematophagous) arthropods such ...
s.
*Estimated global number of cases annually according to WHO in 2017. If a vector transmits multiple diseases, aggregate case numbers are listed. Rough estimates are only meant to provide a sense of scale. Unknown disease burden is listed as NA for not available.

Diagnosis
 Most arthropod bites and stings do not require a specific diagnosis since they typically improve with supportive management alone. Certain bites and stings present with characteristic appearances and distributions. In general, however, dermoscopic findings of bitten or stung skin rarely aid in diagnosis. Rather, patient history (recent travel to endemic areas, outdoor activities, and other risk factors) primarily guides the diagnostic approach, which can raise clinical suspicion for more serious complications like vector-borne diseases.
Most arthropod bites and stings do not require a specific diagnosis since they typically improve with supportive management alone. Certain bites and stings present with characteristic appearances and distributions. In general, however, dermoscopic findings of bitten or stung skin rarely aid in diagnosis. Rather, patient history (recent travel to endemic areas, outdoor activities, and other risk factors) primarily guides the diagnostic approach, which can raise clinical suspicion for more serious complications like vector-borne diseases.
Microscopic appearance
Skinbiopsies
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, an interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves the extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of ...
are not indicated for bites or stings, since the histomorphologic appearance is non-specific
Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition.
Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences.
A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature ...
. Bites and stings as well as other conditions (e.g. drug reactions, urticarial reactions, and early bullous pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid (a type of pemphigoid) is an autoimmune pruritic skin disease that typically occurs in people aged over 60, that may involve the formation of blisters ( bullae) in the space between the epidermal and dermal skin layers. It is ...
) can cause microscopic changes such as a wedge
A wedge is a triangle, triangular shaped tool, a portable inclined plane, and one of the six simple machines. It can be used to separate two objects or portions of an object, lift up an object, or hold an object in place. It functions by conver ...
-shaped superficial dermal
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided i ...
perivascular infiltrate consisting of abundant lymphocytes
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), and ...
and scattered eosinophils
Eosinophils, sometimes called eosinophiles or, less commonly, acidophils, are a variety of white blood cells and one of the immune system components responsible for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections in vertebrates. Along wi ...
, as shown in the adjacent figure:
Prevention
Prevention strategies against arthropod bites and stings comprise measures for personal protection, travel advisories, public health and environmental concerns.Personal protection
Travelers should seek to minimize outdoor activity during peak activity times and avoid high risk areas such as regions with known outbreaks orepidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of hosts in a given population within a short period of time. For example, in meningococcal infection ...
s. Standing water and dense vegetation also commonly attract arthropods. Clothes covering most exposed skin can also provide a measure of physical protection, which may be augmented when the fabric is treated with pesticides such as Permethrin
Permethrin is a medication and an insecticide. As a medication, it is used to treat scabies and lice. It is applied to the skin as a cream or lotion. As an insecticide, it can be sprayed onto outer clothing or mosquito nets to kill the insects ...
. Topical repellants such as N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide (DEET
''N'',''N''-Diethyl-''meta''-toluamide, also called diethyltoluamide or DEET (, from DET, the initials of di- + ethyl + toluamide), is the oldest, one of the most effective, and most common active ingredients in commercial insect repellents. ...
) is supported by a large body of evidence.
Vaccines may also help prevent vector-borne diseases for eligible patients. For example, Japanese encephalitis
Japanese encephalitis (JE) is an infection of the brain caused by the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV). While most infections result in little or no symptoms, occasional inflammation of the brain occurs. In these cases, symptoms may include he ...
, Yellow fever, and Dengue fever
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne disease caused by dengue virus, prevalent in tropical and subtropical areas. Asymptomatic infections are uncommon, mild cases happen frequently; if symptoms appear, they typically begin 3 to 14 days after i ...
have FDA-approved vaccines available. Since they are relatively new vaccines, however, they are not standard of care as of 2023. Additionally, patients traveling to Malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
endemic regions are routinely prescribed Malaria chemoprophylaxis.
Patients with a history of venom hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) is an abnormal physiological condition in which there is an undesirable and adverse immune response to an antigen. It is an abnormality in the immune system that causes Imm ...
may benefit from venom immunotherapy
Immunotherapy or biological therapy is the treatment of disease by activating or suppressing the immune system. Immunotherapies designed to elicit or amplify an immune response are classified as ''activation immunotherapies,'' while immunotherap ...
(VIT). Patients eligibile for VIT include those with a prior anaphylactic reaction to a venomous sting and who have IgE
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is a type of antibody (or immunoglobulin (Ig) " isoform") that has been found only in mammals. IgE is synthesised by plasma cells. Monomers of IgE consist of two heavy chains (ε chain) and two light chains, with the ε ...
to venom allergens. VIT can help prevent future severe systemic reactions in select patients.
Global health
International organizations such as WHO aim to reducedisease burden
Disease burden is the impact of a health problem as measured by financial cost, mortality, morbidity, or other indicators. It is often quantified in terms of quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) or disability-adjusted life years (DALYs). Both ...
s of neglected tropical diseases, many of which are vector borne. Such campaigns must incorporate multipronged approaches to consider global inequality, access to resources, and climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
.
Management
Most arthropod bites and stings require only supportive care. However, complications such as envenomation and severe allergic reactions can present as medical emergencies.Supportive care
Local reactions to bites and stings are treated symptomatically. If a stinger is still embedded, manual removal can reduce further irritation. Washing the affected area with soap and water can help reduce risk of contamination. Oralantihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides ...
s, calamine
Calamine, also known as calamine lotion, is a medication made from powdered calamine (mineral), calamine mineral that is used to treat mild itchiness. Conditions treated include sunburn, insect bites, Toxicodendron radicans, poison ivy, poiso ...
lotion, topical corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
s and cold compresses are common over the counter remedies to reduce itchiness and local inflammation. In more severe cases, such as large local reactions, systemic glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebra ...
s are sometimes prescribed, although limited evidence supports their effectiveness. There are limited data to support one treatment over another.
Medical emergencies
Systemic reactions from venom hypersensitivity can rapidly progress to a medical emergency. The mainstay of anaphylactic shock management is intramuscularly injectedepinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
. The patient should be stabilized and transferred to an intensive care unit.
Toxic reactions to envenomation are similarly managed with medical stabilization and symptomatic treatment. Tetanus prophylaxis
Tetanus (), also known as lockjaw, is a bacterial infection caused by ''Clostridium tetani'' and characterized by muscle spasms. In the most common type, the spasms begin in the jaw and then progress to the rest of the body. Each spasm usually l ...
should be up to date but antibiotics are typically unnecessary unless a bacterial superinfection
A superinfection is a second infection superimposed on an earlier one, especially by a different microbial agent of exogenous or endogenous origin, that is resistant to the treatment being used against the first infection. Examples of this in bact ...
is suspected. Antivenom drugs have been created for certain species such as ''Centruroides
''Centruroides'' is a genus of scorpions of the family Buthidae. Several North American species are known by the common vernacular name bark scorpion. Numerous species are extensively found throughout the southern United States, Mexico, Centra ...
'' scorpion stings, but these drugs are not yet widely available and so typically reserved for severe systemic toxicity.
Several vector-borne diseases can present emergently.
Treatment of vector-borne diseases
After confirmation of diagnosis, antimicrobials are prescribed according to standard of care.Biting and stinging arthropods
 A bite is defined as coming from the mouthparts of the arthropod. The bite consists of both the bite wound and the
A bite is defined as coming from the mouthparts of the arthropod. The bite consists of both the bite wound and the saliva
Saliva (commonly referred as spit or drool) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which ...
. The saliva of the arthropod may contain anticoagulant
An anticoagulant, commonly known as a blood thinner, is a chemical substance that prevents or reduces the coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some occur naturally in blood-eating animals, such as leeches and mosquitoes, which ...
s, as in insects and arachnids which feed from blood. Feeding bites may also contain anaesthetic
An anesthetic (American English) or anaesthetic (British English; see spelling differences) is a drug used to induce anesthesia — in other words, to result in a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. They may be divided into t ...
, to prevent the bite from being felt. Feeding bites may also contain digestive enzyme
Digestive enzymes take part in the chemical process of digestion, which follows the mechanical process of digestion. Food consists of macromolecules of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats that need to be broken down chemically by digestive enzymes ...
s, as in spider
Spiders (order (biology), order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight limbs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude spider silk, silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and ran ...
s; spider bites have primarily evolved to paralyse and then digest prey. A sting comes from the abdomen; in most insects (which are all largely hymenoptera
Hymenoptera is a large order of insects, comprising the sawflies, wasps, bees, and ants. Over 150,000 living species of Hymenoptera have been described, in addition to over 2,000 extinct ones. Many of the species are parasitic.
Females typi ...
ns), the stinger is a modified ovipositor
The ovipositor is a tube-like organ used by some animals, especially insects, for the laying of eggs. In insects, an ovipositor consists of a maximum of three pairs of appendages. The details and morphology of the ovipositor vary, but typica ...
, which protrudes from the abdomen. The sting consists of an insertion wound, and venom. The venom is evolved to cause pain to a predator, paralyse a prey item, or both. Because insect stingers evolved from ovipositors, in most hymenopterans only the female can sting. However, there are a few orders of wasp where the male has evolved a "pseudo sting" - the male genitalia has evolved two sharp protrusions which can deliver an insertion wound. However, they do not contain venom, so they are not considered a true sting. In ant
Ants are Eusociality, eusocial insects of the Family (biology), family Formicidae and, along with the related wasps and bees, belong to the Taxonomy (biology), order Hymenoptera. Ants evolved from Vespoidea, vespoid wasp ancestors in the Cre ...
s that bite instead of sting, such as the Formicinae
The Formicinae are a subfamily within the Formicidae containing ants of moderate evolutionary development.
Formicines retain some primitive features, such as the presence of cocoons around pupae, the presence of ocelli in workers, and littl ...
, the bite causes the wound, but during the bite the abdomen bends forward to spray formic acid
Formic acid (), systematically named methanoic acid, is the simplest carboxylic acid. It has the chemical formula HCOOH and structure . This acid is an important intermediate in chemical synthesis and occurs naturally, most notably in some an ...
into the wound, causing additional pain. In arachnids that sting (all largely scorpions
Scorpions are predatory arachnids of the Order (biology), order Scorpiones. They have eight legs and are easily recognized by a pair of Chela (organ), grasping pincers and a narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward cur ...
), the stinger is not a modified ovipositor, but instead a metasoma
The metasoma is the posterior part of the body, or tagma (biology), tagma, of arthropods whose body is composed of three parts, the other two being the prosoma and the mesosoma. In insects, it contains most of the digestive tract, respiratory sy ...
that bears a telson. (Scorpions lack an ovipositor entirely and give birth to live young
In animals, viviparity is development of the embryo inside the body of the mother, with the maternal circulation providing for the metabolic needs of the embryo's development, until the mother gives birth to a fully or partially developed juven ...
.)
Insects
Diptera (True flies)
*Black flies
A black fly or blackfly (sometimes called a buffalo gnat, turkey gnat, or white socks) is any member of the family Simuliidae of the Culicomorpha infraorder. It is related to the Ceratopogonidae, Chironomidae, and Thaumaleidae. Over 2,200 speci ...
(Simuliidae)
* Horse-flies
Horse flies and deer flies are true flies in the family Tabanidae in the insect order Diptera. The adults are often large and agile in flight. Only females bite land vertebrates, including humans, to obtain blood. They prefer to fly in sunli ...
(Tabanidae)
** Deer flies
Chrysopsinae is an insect subfamily in the family Tabanidae commonly known as deer flies or sheep flies and are bloodsucking insects considered pests to humans and cattle. They are large flies with large brightly-coloured compound eyes, and larg ...
/Yellow flies (Chrysops)
* Tsetse flies
Tsetse ( , or ) (sometimes spelled tzetze; also known as tik-tik flies) are large, biting flies that inhabit much of tropical Africa. Tsetse flies include all the species in the genus ''Glossina'', which are placed in their own family, Glos ...
(Glossinidae)
* Stable flies
''Stomoxys calcitrans'' is known by the common names stable fly, barn fly, biting house fly, dog fly, and power mower fly. Unlike most members of the family Muscidae, ''Stomoxys calcitrans'' ('sharp mouth' + 'kicking') and others of its genus s ...
(Muscidae)
* Biting midge
Ceratopogonidae is a family of flies commonly known as no-see-ums, sand flies or biting midges, generally in length. The family includes more than 5,000 species, distributed worldwide, apart from the Antarctic and the Arctic. A 2025 study from ...
s or No see-ums (Ceratopogonidae)
** Highland midge
The highland midge (scientific name: ''Culicoides impunctatus''; ; ) is a species of biting midge found across the Palearctic (throughout Britain, Ireland, Scandinavia, other regions of Northern Europe, Russia and Northern China) in upland and l ...
* Mosquito
Mosquitoes, the Culicidae, are a Family (biology), family of small Diptera, flies consisting of 3,600 species. The word ''mosquito'' (formed by ''Musca (fly), mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish and Portuguese for ''little fly''. Mos ...
s (Culicidae)
* Botflies
Botflies, also known as warble flies, heel flies, and gadflies, are flies of the family Oestridae. Their larvae are internal parasites of mammals, some species growing in the host's flesh and others within the gut. ''Dermatobia hominis'' is t ...
(as larvae, Oestridae)
* Sandflies
Sandfly or sand fly is a colloquial name for any species or genus of flying, biting, blood-sucking dipteran (fly) encountered in sandy areas. In the United States, ''sandfly'' may refer to certain horse flies that are also known as "greenhead ...
(Phlebotomidae)
** Lutzomyia
''Lutzomyia'' is a genus of Phlebotominae, phlebotomine Sandfly, sand flies consisting of nearly 400 species, at least 33 of which have medical importance as Vector (epidemiology), vectors of human disease. Species of the genus ''Lutzomyia'' are ...
** Phlebotomus
''Phlebotomus'' is a genus of " sand flies" in the Diptera family Psychodidae. In the past, they have sometimes been considered to belong in a separate family, Phlebotomidae, but this alternative classification has not gained wide acceptance.
E ...
* Blow-flies
The Calliphoridae (commonly known as blowflies, blow flies, blow-flies, carrion flies, bluebottles, or greenbottles) are a family of insects in the order Diptera, with almost 1,900 known species. The maggot larvae, often used as fishing bait, ...
(as larvae, Calliphoridae)
* Screw-worm flies (as larvae, Calliphoridae)
* Hippoboscidae
__NOTOC__
Hippoboscidae, the louse flies or keds, are obligate parasites of mammals and birds. In this family, the winged species can fly at least reasonably well, though others with vestigial or no wings are flightless and highly apomorphic. As ...
(Keds)

Hymenoptera (ants, bees and wasps)
*Ants
Ants are eusocial insects of the family Formicidae and, along with the related wasps and bees, belong to the order Hymenoptera. Ants evolved from vespoid wasp ancestors in the Cretaceous period. More than 13,800 of an estimated total of ...
** Bull ants (sting)
** Fire ants
Fire ants are several species of ants in the genus ''Solenopsis'', which includes over 200 species. ''Solenopsis'' are stinging ants, and most of their common names reflect this, for example, ginger ants and tropical fire ants. Many of the nam ...
(both bite and sting)
** Bullet ant
A bullet is a kinetic projectile, a component of firearm ammunition that is shot from a gun barrel. They are made of a variety of materials, such as copper, lead, steel, polymer, rubber and even wax; and are made in various shapes and constru ...
s (sting)
* Bees
Bees are winged insects closely related to wasps and ants, known for their roles in pollination and, in the case of the best-known bee species, the western honey bee, for producing honey. Bees are a monophyletic lineage within the superfamil ...
** Honeybees
A honey bee (also spelled honeybee) is a eusocial flying insect within the genus ''Apis'' of the bee clade, all native to mainland Afro-Eurasia. After bees spread naturally throughout Africa and Eurasia, humans became responsible for the cur ...
(sting)
** Stingless bees
Stingless bees (SB), sometimes called stingless honey bees or simply meliponines, are a large group of bees (from about 462 to 552 described species), comprising the tribe Meliponini (or subtribe Meliponina according to other authors). They belon ...
(bite)
** Bumblebees
A bumblebee (or bumble bee, bumble-bee, or humble-bee) is any of over 250 species in the genus ''Bombus'', part of Apidae, one of the bee families. This genus is the only Extant taxon, extant group in the tribe Bombini, though a few extinct r ...
(sting)
* Wasps
A wasp is any insect of the narrow-waisted suborder Apocrita of the order Hymenoptera which is neither a bee nor an ant; this excludes the broad-waisted sawflies (Symphyta), which look somewhat like wasps, but are in a separate suborder. Th ...
(sting)
** Hornets
Hornets (insects in the genus ''Vespa'') are the largest of the eusocial wasps, and are similar in appearance to yellowjackets, their close relatives. Some species can reach up to in length. They are distinguished from other vespine wasps by ...
(sting)
** Yellow Jackets
Yellowjacket or yellowjacket is the common name in North America for predatory social wasps of the genera ''Vespula'' and ''Dolichovespula''. Members of these genera are known simply as "wasps" in other English-speaking countries. Most of these ...
(sting)
** Paper wasp
Paper wasps are a type of Eusociality, social vespid wasps. The term is typically used to refer to members of the Vespidae, vespid subfamily Polistinae, though it often colloquially includes members of the subfamilies Vespinae (hornets and yel ...
s (sting)
Siphonaptera (Fleas)
*Fleas
Flea, the common name for the order Siphonaptera, includes 2,500 species of small flightless insects that live as external parasites of mammals and birds. Fleas live by ingesting the blood of their hosts. Adult fleas grow to about long, ar ...
(bite)
** Human flea
The human flea (''Pulex irritans'') – once also called the house flea – is a cosmopolitan flea species that has, in spite of the common name, a wide host spectrum. It is one of six species in the genus '' Pulex''; the other five are all conf ...
''Pulex irritans''
** Chigoe flea ''Tunga penetrans
''Tunga penetrans'' is a species of flea also known as the jigger, jigger flea, chigoe, chigo, chigoe flea, chigo flea, nigua, sand flea, or burrowing flea. It is a parasitic insect found in most tropical and sub-tropical climates. In its parasi ...
''

Phthiraptera (Lice)
*Lice
Louse (: lice) is the common name for any member of the infraorder Phthiraptera, which contains nearly 5,000 species of wingless parasitic insects. Phthiraptera was previously recognized as an order, until a 2021 genetic study determined th ...
(bite)
** Head lice
The head louse (''Pediculus humanus capitis'') is an obligate ectoparasite of humans. Head lice are wingless insects that spend their entire lives on the human scalp and feed exclusively on human blood. Humans are the only known hosts of this s ...
** Body lice
The body louse (''Pediculus humanus humanus'', also known as ''Pediculus humanus corporis'') or the cootie is a hematophagic ectoparasite louse that infests humans. It is one of three lice which infest humans, the other two being the head lou ...
** Crab lice
The crab louse or pubic louse (''Pthirus pubis'') is an insect that is an obligate ectoparasite of humans, feeding exclusively on blood. The crab louse usually is found in the person's pubic hair. Although the louse cannot jump, it can also liv ...
Other insects
*Assassin bug
The Reduviidae is a large cosmopolitan family of the suborder Heteroptera of the order Hemiptera (true bugs). Among the Hemiptera and together with the Nabidae almost all species are terrestrial ambush predators; most other predatory Hemiptera ...
/Kissing bug
* Bedbugs
* Conenose bug
The members of the Triatominae , a subfamily of the Reduviidae, are also known as conenose bugs, kissing bugs (so-called from their habit of feeding from around the mouths of people), or vampire bugs. Other local names for them used in the Ameri ...
Arachnids

Spiders
Mites
*Chiggers
''Trombicula'', known as chiggers, red bugs, scrub-itch mites, or berry bugs, are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods) in the Trombiculidae family. In their larval stage, they attach to various animals and humans, then feed on skin, often ...
* Red Poultry Mite
* Spiny rat mite
* House mouse mite
* Northern fowl mite
* Tropical fowl mite
* Mange mite
Mange () is a type of skin disease caused by parasitic mites. Because various species of mites also infect plants, birds and reptiles, the term "mange", or colloquially "the mange", suggesting poor condition of the skin and fur due to the infecti ...
* Scabies
Scabies (; also sometimes known as the seven-year itch) is a contagious human skin infestation by the tiny (0.2–0.45 mm) mite ''Sarcoptes scabiei'', variety ''hominis''. The word is from . The most common symptoms are severe itchiness a ...
* Ticks
Ticks are parasitic arachnids of the order Ixodida. They are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, and species, but can become larger when engorged. Ticks a ...
Scorpions
* All species stingMyriapoda
*Centipedes
Centipedes (from Neo-Latin , "hundred", and Latin language, Latin , "foot") are predatory arthropods belonging to the class Chilopoda (Ancient Greek , ''kheilos'', "lip", and Neo-Latin suffix , "foot", describing the forcipules) of the subphyl ...
References
External links
Identifying insect bites and stings
Diagnosing Mysterious "Bug Bites"
{{DEFAULTSORT:Arthropod Bites And Stings Lists of animals Medical lists Arthropods and humans Parasitic infestations, stings, and bites of the skin Arthropod attacks