Birth Rate Decline on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Population decline, also known as depopulation, is a reduction in a human
population
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region or area. Governments conduct a census to quantify the resident population size within a given jurisdiction. The term is also applied to non-human animals, microorganisms, and pl ...
size. Throughout history, Earth's total
human population
In world demographics, the world population is the total number of humans currently alive. It was estimated by the United Nations to have exceeded eight billion in mid-November 2022. It took around 300,000 years of human prehistory and histor ...
has
continued to grow but projections suggest this long-term trend may be coming to an end.
From antiquity until the beginning of the
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
, the global population grew very slowly, at about
0.04% per year. After about 1800, the growth rate accelerated to a peak of 2.1% annually during the 1962–1968 period, but since then, due to the worldwide collapse of the
total fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were t ...
, it has slowed to 0.9% as of 2023.
The global growth rate in absolute numbers accelerated to a peak of 92.8 million in 1990, but has since slowed to 70.4 million in 2023.
Long-term projections indicate that the growth rate of the human population of the planet will continue to slow and that before the end of the 21st century, it will reach
zero
0 (zero) is a number representing an empty quantity. Adding (or subtracting) 0 to any number leaves that number unchanged; in mathematical terminology, 0 is the additive identity of the integers, rational numbers, real numbers, and compl ...
.
Examples of this emerging trend are
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
, whose population is currently (2023) declining at the rate of 0.5% per year,
and
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, whose population has peaked and is currently (2023) declining at the rate of about 0.2% per year.
By 2050, Europe's population is projected to be declining at the rate of 0.3% per year.
Population growth has declined mainly due to the abrupt decline in the global total fertility rate, from 5.3 in 1963 to 2.2 in 2023.
The decline in the total fertility rate has occurred in every region of the world and is a result of a process known as
demographic transition
In demography, demographic transition is a phenomenon and theory in the Social science, social sciences referring to the historical shift from high birth rates and high Mortality rate, death rates to low birth rates and low death rates as societi ...
. To maintain its population, ignoring migration, a country on average requires a minimum fertility rate of 2.2 children per woman of childbearing age (the number is slightly greater than two because not all children live to adulthood). However, most societies experience a
drop in fertility to well below two as they grow more wealthy.
The tendency of women in wealthier countries to have fewer children is attributed to a
variety of reasons, such as lower
infant mortality
Infant mortality is the death of an infant before the infant's first birthday. The occurrence of infant mortality in a population can be described by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the number of deaths of infants under one year of age ...
and a reduced need for children as a source of family labor or retirement welfare, both of which reduce the incentive to have many children. Better access to education for young women, which broadens their job prospects, is also often cited.
Possible consequences of long-term national population decline can be net negative or positive. If a country can increase its
workforce
In macroeconomics, the workforce or labour force is the sum of people either working (i.e., the employed) or looking for work (i.e., the unemployed):
\text = \text + \text
Those neither working in the marketplace nor looking for work are out ...
productivity
Productivity is the efficiency of production of goods or services expressed by some measure. Measurements of productivity are often expressed as a ratio of an aggregate output to a single input or an aggregate input used in a production proce ...
faster than its population is declining, the results, in terms of its economy, the quality of life of its citizens, and the environment, can be net positive. If it cannot increase workforce productivity faster than its population's decline, the results can be negative.
National efforts to confront a declining population to date have been focused on the possible negative economic consequences and have been centered on increasing the size and productivity of the workforce.
Causes
A reduction over time in a region's population can be caused by sudden adverse events such as outbursts of infectious
disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function (biology), function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical condi ...
,
famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food caused by several possible factors, including, but not limited to war, natural disasters, crop failure, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenom ...
, and
war
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or between such organi ...
or by long-term trends, for example,
sub-replacement fertility
Sub-replacement fertility is a total fertility rate (TFR) that (if sustained) leads to each new generation being less populous than the older, previous one in a given area. The United Nations Population Division defines sub-replacement fertilit ...
, persistently low
birth rate
Birth rate, also known as natality, is the total number of live childbirth, human births per 1,000 population for a given period divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registr ...
s, high
mortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular Statistical population, population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically ...
s, and continued
emigration
Emigration is the act of leaving a resident country or place of residence with the intent to settle elsewhere (to permanently leave a country). Conversely, immigration describes the movement of people into one country from another (to permanentl ...
.
Short-term population shocks
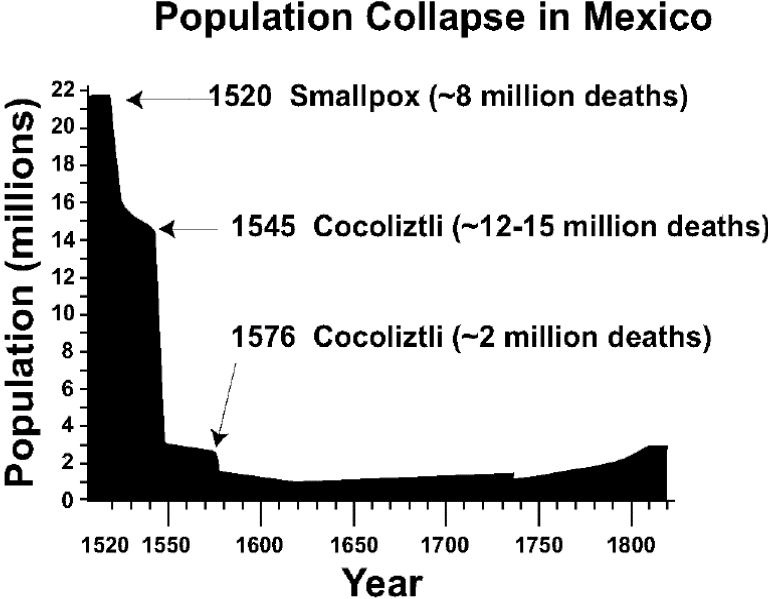
Historical episodes of short-term human population decline have been common and have been caused by several factors.
High mortality rates caused by:
*
Disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function (biology), function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical condi ...
, for example, the
Black Death
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic that occurred in Europe from 1346 to 1353. It was one of the list of epidemics, most fatal pandemics in human history; as many as people perished, perhaps 50% of Europe's 14th century population. ...
that devastated Europe in the 14th and 17th centuries, the arrival of
Old World diseases in the Americas during European colonization, and the
Spanish flu
The 1918–1920 flu pandemic, also known as the Great Influenza epidemic or by the common misnomer Spanish flu, was an exceptionally deadly global influenza pandemic caused by the H1N1 subtype of the influenza A virus. The earliest docum ...
pandemic after World War I,
*
Famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food caused by several possible factors, including, but not limited to war, natural disasters, crop failure, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenom ...
, for example, the
Great Irish Famine
The Great Famine, also known as the Great Hunger ( ), the Famine and the Irish Potato Famine, was a period of mass starvation and disease in Ireland lasting from 1845 to 1852 that constituted a historical social crisis and had a major impact o ...
of the 19th century, and the
Great Chinese Famine caused by the
Great Leap Forward
The Great Leap Forward was an industrialization campaign within China from 1958 to 1962, led by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). Party Chairman Mao Zedong launched the campaign to transform the country from an agrarian society into an indu ...
which caused tens of millions of deaths,
*
War
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or between such organi ...
, for example, the
Mongol invasion of Europe
From the 1220s to the 1240s, the Mongol Empire, Mongols conquered the Turkic peoples, Turkic states of Volga Bulgaria, Cumania and Iranian peoples, Iranian state of Alania, and various principalities in Eastern Europe. Following this, they began ...
in the 13th century, which may have reduced the population of Hungary by 20–40%,
* Civil unrest, for example, the
forced migration of the population of Syria because of the Syrian Civil War.
* A combination of these. The first half of the 20th century in
Imperial Russia
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor/empress, or imperialism.
Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to:
Places
United States
* Imperial, California
* Imperial, Missouri
* Imperial, Nebraska
* Imperial, Pennsylvania
* ...
and the
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
was marked by a succession of major wars,
famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food caused by several possible factors, including, but not limited to war, natural disasters, crop failure, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenom ...
s and other disasters which caused large-scale population losses (approximately 60 million excess deaths).
Less frequently, short-term population declines are caused by
genocide
Genocide is violence that targets individuals because of their membership of a group and aims at the destruction of a people. Raphael Lemkin, who first coined the term, defined genocide as "the destruction of a nation or of an ethnic group" by ...
or mass
execution
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence ordering that an offender be punished in ...
. For example, it has been estimated that the
Armenian genocide
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenians, Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was implemented primarily t ...
caused 1.5 million deaths, the
Jewish Holocaust
The Holocaust (), known in Hebrew language, Hebrew as the (), was the genocide of History of the Jews in Europe, European Jews during World War II. From 1941 to 1945, Nazi Germany and Collaboration with Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy ...
about 6 million, and, during the period 1975 - 1979, the population of
Cambodia
Cambodia, officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. It is bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the north, and Vietnam to the east, and has a coastline ...
declined 26% because of wide-scale
executions by the Khmer Rouge.
In modern times, the
AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
pandemic
A pandemic ( ) is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has a sudden increase in cases and spreads across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. Widespread endemic (epi ...
and the
COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
have caused short-term drops in fertility and significant
excess mortality
In epidemiology, the excess deaths or excess mortality is a measure of the increase in the number of deaths during a time period and/or in a certain group, as compared to the expected value or statistical trend during a reference period (typicall ...
in a number of countries.
Some population declines result from indeterminate causes, for example, the
Bronze Age Collapse
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a period of societal collapse in the Mediterranean basin during the 12th century BC. It is thought to have affected much of the Eastern Mediterranean and Near East, in particular Egypt, Anatolia, the Aege ...
, which has been described as the worst disaster in ancient history.
Long-term historic trends in world population growth
In spite of these short-term population shocks, world population has continued to grow. From around 10,000 BC to the beginning of the
Early modern period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
(generally 1500 – 1800), world population grew very slowly, around
0.04% per year. During that period, population growth was governed by conditions now labeled the “
Malthusian Trap
Malthusianism is a theory that population growth is potentially exponential, according to the Malthusian growth model, while the growth of the food supply or other resources is linear, which eventually reduces living standards to the point of tri ...
”.
After 1700, driven by increases in human productivity due to the
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
, particularly the increase in
agricultural productivity
Agricultural productivity is measured as the ratio of Agriculture, agricultural outputs to inputs. While individual products are usually measured by weight, which is known as crop yield, varying products make measuring overall agricultural out ...
,
population growth
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. The World population, global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to 8.2 billion in 2025. Actual global human population growth amounts to aroun ...
accelerated to around 0.6% per year, a rate that was over ten times the rate of population growth of the previous 12,000 years. This rapid increase in global population caused
Malthus
Thomas Robert Malthus (; 13/14 February 1766 – 29 December 1834) was an English economist, cleric, and scholar influential in the fields of political economy and demography.
In his 1798 book ''An Essay on the Principle of Population'', Mal ...
and others to raise the first concerns about
overpopulation
Overpopulation or overabundance is a state in which the population of a species is larger than the carrying capacity of its environment. This may be caused by increased birth rates, lowered mortality rates, reduced predation or large scale migr ...
.
After
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
birth rates in the United States and many European countries fell below replacement level. This prompted concern about population decline.
The recovery of the birth rate in most western countries around 1940 that produced the "baby boom", with annual growth rates in the 1.0 – 1.5% range, and which peaked during the period 1962–1968 at 2.1% per year,
temporarily dispelled prior concerns about population decline, and the world was once again fearful of
overpopulation
Overpopulation or overabundance is a state in which the population of a species is larger than the carrying capacity of its environment. This may be caused by increased birth rates, lowered mortality rates, reduced predation or large scale migr ...
.

But after 1968 the global population growth rate started a long decline, and the United Nations Population Division (UN) has reported that in the year 2023 it had dropped to about 0.9%,
less than half of its peak during the period 1962 – 1968. Although
still growing, the UN predicts that global population will level out around 2084,
and some sources predict the start of a decline before then.
The principal cause of this phenomenon is the abrupt decline in the global
total fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were t ...
, from 5.3 in 1963 to 2.2 in 2023, as the world continues to move through the stages of the
Demographic Transition
In demography, demographic transition is a phenomenon and theory in the Social science, social sciences referring to the historical shift from high birth rates and high Mortality rate, death rates to low birth rates and low death rates as societi ...
.
The decline in the total fertility rate has occurred in every region of the world and has brought renewed concern from some for population decline.
The era of rapid global population increase, and concomitant concern about a population explosion, has been short compared with the span of human history. It began roughly at the beginning of the industrial revolution and appears to be now drawing to a close.
Possible consequences
Predictions of the ''net'' economic (and other) effects from a slow and continuous population decline (e.g. due to low fertility rates) are mainly theoretical since such a phenomenon is a relatively new and unprecedented one. The results of many of these studies show that the estimated impact of population growth on economic growth is generally small and can be positive, negative, or nonexistent. A recent meta-study found no relationship between population growth and economic growth.
Possible positive effects
The effects of a declining population can be positive. The single best gauge of economic success is the growth of GDP per person, not total GDP.
GDP per person (also known as GDP per capita or per capita GDP) is a rough proxy for average living standards. A country can both increase its average living standard and grow its total GDP even though its population growth is low or even negative. The economies of both
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
and
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
went into recovery around the time their populations began to decline (2003–2006). In other words, both the total and per capita GDP in both countries grew more rapidly after 2005 than before.
Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
's economy also began to grow rapidly from 1999 onward, even though its population had been shrinking since 1992–93. Many Eastern European countries have been experiencing similar effects to Russia. Such renewed growth calls into question the conventional wisdom that economic growth requires population growth, or that economic growth is impossible during a population decline.
More recently (2009–2017) Japan has experienced a higher growth of GDP per capita than the United States, even though its population declined over that period.
In the United States, the relationship between population growth and growth of GDP per capita has been found to be empirically insignificant. This evidence shows that individual prosperity can grow during periods of population decline.
Attempting to better understand the economic impact of these pluses and minuses, Lee et al. analyzed data from 40 countries. They found that typically fertility well above replacement and population growth would be most beneficial for government budgets. Fertility near replacement and population stability, however, would be most beneficial for standards of living when the analysis includes the effects of age structure on families as well as governments. Fertility moderately below replacement and population decline would maximize per capita consumption when the cost of providing capital for a growing labor force is taken into account.
A focus on
productivity
Productivity is the efficiency of production of goods or services expressed by some measure. Measurements of productivity are often expressed as a ratio of an aggregate output to a single input or an aggregate input used in a production proce ...
growth that leads to an increase in both per capita GDP and total GDP can bring other
benefits to:
*the workforce through higher wages, benefits and better working conditions
*customers through lower prices
*owners and shareholders through higher profits
*the environment through more money for investment in more stringent environmental protection
*governments through higher tax proceeds to fund government activities
Another approach to possible positive effects of population decline is to consider Earth's
human carrying capacity. Global population decline would begin to counteract the negative effects of
human overpopulation
Human overpopulation (or human population overshoot) is the idea that human populations may become too large to be sustainability, sustained by their environment or resources in the long term. The topic is usually discussed in the context of wor ...
. There have been many estimates of Earth's carrying capacity, each generally predicting a high-low range of maximum human population possible. The lowest low estimate is less than one billion, the highest high estimate is over one trillion.
A statistical analysis of these historical estimates revealed that the median of high estimates of all of the ranges would be 12 billion, and the median of low estimates would be about 8 billion.
According to this analysis, this planet may be entering a zone where its human carrying capacity could be exceeded.
However, the large variance in these studies’ estimates diminishes our confidence in them, as such estimates are very difficult to make with current data and methods.
Possible negative effects
The effects of a declining population can also be negative. As a country's population declines, GDP growth may grow even more slowly or may even decline. If the decline in total population is not matched by an equal or greater increase in productivity (GDP/capita), and if that condition continues from one calendar quarter to the next, it follows that a country would experience a decline in GDP, known as an
economic recession
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is ...
. If these conditions become permanent, the country could find itself in a permanent recession.
Other possible negative impacts of a declining population are:
* A rise in the
dependency ratio
The dependency ratio is an age-population ratio of those typically not in the labor force (the ''dependent'' part ages 0 to 14 and 65+) and those typically in the labor force (the ''productive'' part ages 15 to 64). It is used to measure the press ...
which would increase the economic pressure on the workforce
* A loss of culture and the diminishment of trust among citizens
* A crisis in end-of-life care for the elderly because there are insufficient caregivers for them
* Difficulties in funding entitlement programs because there are
fewer workers relative to retirees
* A decline in military strength
* A decline in innovation since change comes from the young
* A strain on mental health caused by permanent recession
* Deflation caused by the aging population
All these negative effects could be summarized under the heading of "Underpopulation". Underpopulation is usually defined as a state in which a country's population has declined too much to support its current economic system.
Population decline can cause internal population pressures that then lead to secondary effects such as ethnic conflict, forced refugee flows, and
hyper-nationalism.
This is particularly true in regions where different ethnic or racial groups have different growth rates.
Low fertility rates that cause long-term population decline can also lead to
population aging
Population ageing is an overall change in the ages of a population. This can typically be summarised in a single parameter as an increase in the median age. Causes are a long-term decline in fertility rates and a decline in mortality rates. Most ...
, an imbalance in the population age structure. Population aging in Europe due to low fertility rates has given rise to concerns about its impact on social cohesion.
A smaller national population can also have geo-strategic effects, but the correlation between population and
power
Power may refer to:
Common meanings
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power, a type of energy
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
Math ...
is a tenuous one. Technology and resources often play more significant roles. Since
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the "static" theory saw a population's absolute size as being one of the components of a country's national power.
More recently, the "human capital" theory has emerged. This view holds that the quality and skill level of a labor force and the technology and resources available to it are more important than simply a nation's population size.
While there were in the past advantages to high fertility rates, that "
demographic dividend
Demographic dividend, as defined by the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), is "the economic growth potential that can result from shifts in a population’s age structure, mainly when the share of the working-age population (15 to 64) is large ...
" has now largely disappeared.
Contemporary decline by country
The table below shows the countries that have been affected by population decline between 2010 and 2020. The term "population" used here is based on the ''de facto'' definition of population, which counts all residents regardless of legal status or citizenship, except for refugees not permanently settled in the country of asylum, who are generally considered part of the population of the country of origin. This means that population growth in this table includes net changes from immigration and emigration. For a table of natural population changes, see the
list of countries by natural increase.
[Figure includes ]Abkhazia
Abkhazia, officially the Republic of Abkhazia, is a List of states with limited recognition, partially recognised state in the South Caucasus, on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, at the intersection of Eastern Europe and West Asia. It cover ...
and South Ossetia
Ossetia ( , ; or , or , ) is an Ethnolinguistics, ethnolinguistic region on both sides of the Greater Caucasus Mountains, largely inhabited by the Ossetians. The Ossetian language is part of the Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian b ...
.
[Includes the ]Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic
Transnistria, officially known as the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic and locally as Pridnestrovie, is a landlocked breakaway state internationally recognized as part of Moldova. It controls most of the narrow strip of land between the Dni ...
.
East Asia
China
China's population peaked at 1.41 billion in 2021 and began declining in 2022.
China recorded more deaths than births for the first time in 2022 with a net decrease of 850,000 and this trend continued in 2023 when deaths overnumbered births by a margin of more than 2 million and in 2024 with deaths overnumbering births by 1.4 million.
The UN's Population Division, assuming that China's total fertility rate will rise from 1 in 2022 to 1.34 by 2100, projects its population to be 633 million by 2100, a decline of about 56%.
Japan

Though Japan's
natural increase
In demography and population dynamics, the rate of natural increase (RNI), also known as natural population change, is defined as the birth rate minus the death rate of a particular population, over a particular time period. It is typically expre ...
turned negative as early as 2005, the 2010 census result figure was slightly higher, at just above 128 million, than the 2005 census. Factors implicated in the puzzling figures were more Japanese returnees than expected as well as changes in the methodology of data collection. However, the official count put the population as of October 1, 2015, at 127.1 million, down by 947,000 or 0.7% from the previous quinquennial census. The gender ratio is increasingly skewed; some 106 women per 100 men live in Japan. In 2019, Japan's population fell by a record-breaking 276,000; if immigration is excluded from the figures, the drop would have been 487,000. Given the population boom of the 1950s and 1960s, the total population is still 52% above 1950 levels.
The UN's Population Division, assuming that Japan's total fertility rate will rise from 1.2 in 2023 to 1.47 by 2100, projects its population to fall to 77 million by 2100, a decline of about 38%.
South Korea
South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
's total fertility rate has been consistently lower than that of Japan, breaking below 1 in 2018, and fell to 0.778 in 2022. As a result, its population fell in 2020 for the first time in the country's history from 51.8 million in 2020 to 51.6 in 2022.
The UN's Population Division, assuming that South Korea's total fertility rate will rise from 0.72 in 2023 to 1.3 by 2100, projects its population to fall to nearly 22 million by 2100, a decline of about 58%.
Taiwan
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
recorded more deaths than births for the first time in 2020, despite recording virtually no
COVID-19 deaths, thus starting an era of demographic decline for the foreseeable future. Taiwan's population fell from 23.6 million in 2020 to 23.4 in 2023, while the total fertility rate decreased from 1.05 in 2020 to 0.85 in 2023.
The UN's Population Division, assuming that Taiwan's total fertility rate will rise from 0.87 in 2023 to 1.33 by 2100, projects its population to fall to 10 million by 2100, a decline of about 57%.
Thailand
Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
's total fertility rate has been consistently lower than the
replacement rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were t ...
of 2.1 since the beginning of the 1990s and reached a new low in 2022, at 1. Thailand 's population decline started in 2020 and Thailand for the first time recorded more deaths than births in 2021. This negative natural population change amplified in 2022 and 2023 and, in the absence of substantial immigration, this trend will continue in the coming years due to the very low fertility rate.
Eastern Europe and former Soviet republics
Population in the
ex-USSR and
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
is rapidly shrinking due to low birth rates, very high death rates (linked to
alcoholism
Alcoholism is the continued drinking of alcohol despite it causing problems. Some definitions require evidence of dependence and withdrawal. Problematic use of alcohol has been mentioned in the earliest historical records. The World He ...
and high rates of infectious diseases such as
AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
and
TB), as well as high emigration rates. In Russia and the former communist bloc,
birth rates fell abruptly after
the fall of the Soviet Union, and death rates generally rose sharply. In addition, in the 25 years after 1989, some 20 million people from Eastern Europe are estimated to have migrated to Western Europe or the United States.
Belarus
Belarus's population peaked at 10,151,806 in the 1989 Census and declined to 9,480,868 as of 2015 as estimated by the state statistical service. This represents a 7.1% decline since the peak census figure.
Estonia
In the last Soviet census of 1989, it had a population of 1,565,662, which was close to its peak population.
The state statistics reported an estimate of 1,314,370 for 2016.
This represents a 19.2% decline since the peak census figure.
Georgia
In the last Soviet census of 1989, it had a population of 5,400,841, which was close to its
peak population.
The state statistics reported an estimate of 4,010,000 for the 2014 Census, which includes estimated numbers for quasi-independent
Abkhazia
Abkhazia, officially the Republic of Abkhazia, is a List of states with limited recognition, partially recognised state in the South Caucasus, on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, at the intersection of Eastern Europe and West Asia. It cover ...
and
South Ossetia
South Ossetia, officially the Republic of South Ossetia or the State of Alania, is a landlocked country in the South Caucasus with International recognition of Abkhazia and South Ossetia, partial diplomatic recognition. It has an offici ...
.
This represents a 25.7% decline since the peak census figure, but nevertheless somewhat higher than the 1950 population.
Latvia
When Latvia split from the Soviet Union, it had a population of 2,666,567, which was very close to its peak population.
The latest census recorded a population of 2,067,887 in 2011, while the state statistics reported an estimate of 1,986,086 for 2015.
This represents a 25.5% decline since the peak census figure, with only one of two nations worldwide falling below 1950 levels. The decline is caused by both a negative natural population growth (more deaths than births) and a negative
net migration rate
The net migration rate is the difference between the number of immigrants (people coming into an area) and the number of emigrants (people leaving an area) per year divided by the population. When the number of immigrants is larger than the num ...
. As of 1 May 2024,
Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to t ...
had a total population of 1,862,700.
Lithuania
When Lithuania split from the Soviet Union, it had a population of 3.7 million, which was close to its peak population.
The latest census recorded a population of 3.05 million in 2011, down from 3.4 million in 2001,
further falling to 2,988,000 on September 1, 2012.
This represents a 23.8% decline since the peak census figure, and some 13.7% since 2001.
Ukraine
Ukraine census in 1989 resulted in 51,452,034 people. Ukraine's own estimates show a peak of 52,244,000 people in 1993; however, this number has plummeted to 45,439,822 as of December 1, 2013. Having
lost Crimean territory to Russia in early 2014 and subsequently experiencing war, the population dropped to 42,981,850 as of August 2014. This represents a 19.7% decrease in total population since the peak figure, but 16.8% above the 1950 population even without Crimea.
Its absolute total decline (9,263,000) since its peak population is the highest of all nations; this includes loss of territory and heavy net emigration. Eastern Ukraine may yet lose many Russian-speaking citizens due to the new Russian citizenship law. An editorial projects significant gender and age imbalance in the population in Ukraine as a substantial problem if most refugees, as in other cases, do not return over time. Approximately 3.8 million more people have left the country during the
2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thou ...
,
and thousands have died in the conflict.
The Russian invasion of Ukraine considerably deepened the country's demographic crisis. The
birth rate
Birth rate, also known as natality, is the total number of live childbirth, human births per 1,000 population for a given period divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registr ...
in Ukraine was 28% lower in the first six months of 2023 compared to the same period in 2021. A July 2023 study by the
Vienna Institute for International Economic Studies stated that "
gardless of how long the war lasts and whether or not there is further military escalation, Ukraine is unlikely to recover demographically from the consequences of the war. Even in 2040 it will have only about 35 million inhabitants, around 20% fewer than before the war (2021: 42.8 million) and the decline in the working-age population is likely to be the most severe and far-reaching."
Hungary
Hungary's population peaked in 1980, at 10,709,000, and has continued its decline to under 10 million as of August 2010. This represents a decline of 7.1% since its peak; however, compared to neighbors situated to the East, Hungary peaked almost a decade earlier yet the rate has been far more modest, averaging −0.23% a year over the period.
Balkans
Albania
Albania's population in 1989 recorded 3,182,417 people, the largest for any census. Since then, its population declined to an estimated 2,893,005 in January 2015. The decline has since accelerated with a 1.3% drop in population reported in 2021 leaving a total population of 2.79 million. This represents a decrease of 12% in total population since the peak census figure.
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina's population peaked at 4,377,033 in the 1991 Census, shortly before the
Yugoslav wars
The Yugoslav Wars were a series of separate but related#Naimark, Naimark (2003), p. xvii. ethnic conflicts, wars of independence, and Insurgency, insurgencies that took place from 1991 to 2001 in what had been the Socialist Federal Republic of ...
that produced tens of thousands of civilian victims and refugees. The latest census of 2016 reported a population of 3,511,372. This represents a 19.8% decline since the peak census figure.
Bulgaria
Bulgaria's population declined from a peak of 9,009,018 in 1989 and since 2001, has lost yet another 600,000 people, according to 2011 census preliminary figures to no more than 7.3 million, further down to 7,245,000. This represents a 24.3% decrease in total population since the peak and a −0.82% annual rate in the last 10 years.
The Bulgarian population has fallen by more than 844,000 people, or 11.5 percent, in the last decade, the National Institute of Statistics in Sofia said during a presentation of the results so far of the 2021 census, the first since 2011.
The country currently employs just over 6.5 million people, compared to 7.3 million in the previous workforce.
Croatia
Croatia's population declined from 4,784,265
in 1991 to 4,456,096 (by the old statistical method) of which 4,284,889
are permanent residents (by the new statistical method), in 2011, a decline of 8% (11.5% by the new definition of permanent residency in 2011 census). The main reasons for the decline since 1991 are: low birth rates, emigration and
war in Croatia
The Croatian War of Independence) and (rarely) "War in Krajina" ( sr-Cyrl-Latn, Рат у Крајини, Rat u Krajini) are used. was an armed conflict fought in Croatia from 1991 to 1995 between Croats, Croat forces loyal to the Governmen ...
. From 2001 and 2011 main reason for the drop in population is due to a difference in the definition of permanent residency used in censuses till 2001 (censuses of 1948, 1953, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991 and 2001) and the one used in 2011.
[Croatian Bureau of Statistic]
Notes on methodology (Census 2011)
, retrieved 7 July 2013 By 2021 the population dropped to 3,888,529, a 9.25% decrease from 2011 numbers.
Greece
Greece's population declined by about half a million people between its 2011 and 2021 censuses. The main drivers are increased emigration rates and lower birth rates following the
2008 financial crisis
The 2008 financial crisis, also known as the global financial crisis (GFC), was a major worldwide financial crisis centered in the United States. The causes of the 2008 crisis included excessive speculation on housing values by both homeowners ...
.
Romania
Romania's 1991 census showed 23,185,084 people, and the October 2011 census recorded 20,121,641 people, while the state statistical estimate for 2014 is 19,947,311. This represents a decrease of 16.2% since the historical peak in 1991.
Serbia
Serbia recorded a peak census population of 7,822,795 in 1991 in the Yugoslav era, falling to 7,186,862 in the 2011 census. That represents a decline of 5.1% since its peak census figure.
Other
Italy
Although Italy had recorded more deaths than births continuously since 1993, the country's population only peaked in 2015 at 60,796,000 due to substantial immigration. The Italian population fell by a record amount in 2020, and in 2021, it recorded the lowest number of births since its unification in 1861 at only 399,431, with its population being projected to shrink to 47.2 million in 2070, a decline of nearly 20 percent.
As of April 2024, Italian population stands at 58,968,501 inhabitants. The UN's Population Division, assuming that Italy's total fertility rate will rise from 1.2 in 2024 to 1.5 by 2100, projects its population to be 35.5 million by 2100, a decline of about 40%.
Uruguay
Uruguay's fertility rate had been consistently low in Latin America since the 20th century at 3 children per women, with the fertility rates in Latin American countries converging at 2 children beginning in the 1990s, but Uruguay's fertility rate declined sharply from 2 in 2015 to 1.28 in 2022, largely due to decreased births to women under 20. Uruguay recorded more deaths than births for the first time in 2021 and the population decline has been only offset slightly by immigration.
Venezuela
In spite of a positive
natural increase
In demography and population dynamics, the rate of natural increase (RNI), also known as natural population change, is defined as the birth rate minus the death rate of a particular population, over a particular time period. It is typically expre ...
of almost 1% per year, Venezuela's population has declined during the 2015-20 period due to emigration caused by threats of violence as well as shortages of
basic needs
The basic needs approach is one of the major approaches to the measurement of absolute poverty in developing countries globally. It works to define the absolute minimum resources necessary for long-term physical well-being, usually in terms of Co ...
.
Resumed declines
Russia

The decline in Russia's total population is among the largest in numbers, but not in percentage. After having peaked at 148,689,000 in 1991, the population then decreased, falling to 142,737,196 by 2008. This represents a 4.0% decrease in total population since the peak census figure. However, the Russian population then rose to 146,870,000 in 2018. This recent trend can be attributed to a lower death rate, higher birth rate, the annexation of Crimea and continued immigration, mostly from Ukraine and Armenia. It is some 40% above the 1950 population.
Russia has become increasingly reliant on immigration to maintain its population; 2021 had the highest net immigration since 1994, despite which there was a small overall decline from 146.1 million to 145.4 million in 2021, the largest decline in over a decade.
The natural death rate in January 2020, 2021, and 2022 have each been nearly double the natural birth rate.
In March 2023, ''The Economist'' reported that "Over the past three years the country has lost around 2 million more people than it would ordinarily have done, as a result of war
in Ukraine">Russo-Ukrainian_War.html" ;"title="nowiki/>Russo-Ukrainian War">in Ukraine disease and exodus."
According to Russian economist Alexander Isakov, "Russia’s population has been declining and the war will reduce it further. Reasons?
Emigration
Emigration is the act of leaving a resident country or place of residence with the intent to settle elsewhere (to permanently leave a country). Conversely, immigration describes the movement of people into one country from another (to permanentl ...
, lower fertility and Casualties of the Russo-Ukrainian War">war-related casualties."
According to the analysis of economists
Oleg Itskhoki and
Maxim Mironov, Russia may lose more than 10% of men aged 20–29 as a result of losses in the war and emigration. In June 2024, it was estimated that approximately 2% of all Russian men between the ages of 20 and 50 may have been killed or seriously wounded in Ukraine since February 2022.
The UN is projecting that the decline that started in 2021 will continue, and if current demographic conditions persist, Russia's population would be 120 million in fifty years, a decline of about 17%.
The UN's 2024 scenarios project Russia's population to be between 74 million and 112 million in 2100, a decline of 25 to 50%.
Portugal
Between 2011 and 2021, Portugal's population declined from 10.56 to 10.34 million people. The fertility rate has been consistently below 2 since the early 1980s, and the gap is increasingly being made up by immigrants.
Purportedly halted declines
Armenia
Armenia's population peaked at 3,604,000 in 1991 and declined to a post-Soviet low of 2,961,500 at the beginning of 2020, in spite of a continuous natural population increase. This represented a 17.2% decrease in the total population since the peak census figure. Armenia's population began to increase again to 2,962,300 in 2021; 2,969,200 in 2022 and 2,990,900 in 2023. As of the beginning of 2024 the population had rebounded to 3,015,400 at 1978 levels.
Germany
In Germany, a continuously low birth rate has been offset by waves of immigration. From 2002 to 2011 the population declined by 2 million, the most since the Cold War.
The 2011 national census recorded a population of 80.2 million people, following which official estimates showed an increase of 3 million over the next decade. The official estimate for 2020 was a slight decrease from 2019.
Third-party estimates show a slight increase, instead.
Ireland
In the current area of the
Republic of Ireland
Ireland ( ), also known as the Republic of Ireland (), is a country in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 Counties of Ireland, counties of the island of Ireland, with a population of about 5.4 million. ...
, the population has fluctuated dramatically. The population of Ireland was 8 million in 1841, but it dropped due to the
Irish famine
The Great Famine, also known as the Great Hunger ( ), the Famine and the Irish Potato Famine, was a period of mass starvation and disease in Ireland lasting from 1845 to 1852 that constituted a historical social crisis and had a major impact ...
and later emigration. The population of the Republic of Ireland hit a bottom at 2.8 million in the 1961 census, but it then rose and in 2011 it was 4.58 million. As of 2020, it is estimated to be just under 5 million according to the country's Central Statistics Office.
Poland
The population of Poland in the last 20 years has caused many years of recorded growth and decline with the population. The recorded population of Poland between 2002 and 2006 had shown a decreasing trend while between 2007 and 2012 the population had an increasing trend. Though since 2020, COVID-19 has started to cause the population to decline rapidly, with over 117,000 people reportedly dying from COVID-19 in Poland by October 2022. However, Poland also saw a large number of Ukrainian Refugees move into Poland, with over 7.8 million people having crossed the border by October 2022 between Poland and Ukraine since the war began, of which 1.4 million have stayed in Poland.
Syria
Syria's population declined during the period 2012 - 2018 due to an ongoing
civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
. During that period many Syrians emigrated to other
Middle eastern
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
countries. The civil war makes an accurate count of the
Syrian population difficult, but the UN estimates that it peaked in 2012 at 22.9 million and dropped to 18.9 million in 2018, a decline of 17%.
Since then Syria's population has resumed growing, and the UN projects that by 2025 it will have reached 24.9 million.
Declines within regions or ethnic groups of a country
United States
In spite of a growing population at a national level, some formerly large American municipalities have dramatically shrunk after the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, and in particular during the 1950s–1970s, due to
suburbanization
Suburbanization (American English), also spelled suburbanisation (British English), is a population shift from historic core cities or rural areas into suburbs. Most suburbs are built in a formation of (sub)urban sprawl. As a consequence ...
,
urban decay
Urban decay (also known as urban rot, urban death or urban blight) is the sociological process by which a previously functioning city, or part of a city, falls into disrepair and decrepitude. There is no single process that leads to urban decay. ...
,
race riots
This is a list of ethnic riots by country, and includes riots based on ethnic, sectarian, xenophobic, and racial conflict. Some of these riots can also be classified as pogroms.
Africa
Americas
United States
Nativist period: 1700s� ...
,
high crime rates,
deindustrialization
Deindustrialization is a process of social and economic change caused by the removal or reduction of industrial capacity or activity in a country or region, especially of heavy industry or manufacturing industry.
There are different interpr ...
and emigration from the
Rust Belt
The Rust Belt, formerly the Steel Belt or Factory Belt, is an area of the United States that underwent substantial Deindustrialization, industrial decline in the late 20th century. The region is centered in the Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic (Uni ...
to the
Sun Belt
The Sun Belt is a region of the United States generally considered stretching across the Southeast and Southwest. Another rough definition of the region is the area south of the Parallel 36°30′ north. Several climates can be found in the re ...
. For instance,
Detroit
Detroit ( , ) is the List of municipalities in Michigan, most populous city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is situated on the bank of the Detroit River across from Windsor, Ontario. It had a population of 639,111 at the 2020 United State ...
's population peaked at almost 2 million in 1953, and then declined to less than 700,000 by 2020. Other cities whose populations have dramatically shrunk since the 1950s include
Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-large ...
,
Buffalo,
Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ; colloquially nicknamed Cincy) is a city in Hamilton County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. Settled in 1788, the city is located on the northern side of the confluence of the Licking River (Kentucky), Licking and Ohio Ri ...
,
Cleveland
Cleveland is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located along the southern shore of Lake Erie, it is situated across the Canada–U.S. maritime border and approximately west of the Ohio-Pennsylvania st ...
,
Flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Historically, flint was widely used to make stone tools and start ...
,
Gary,
New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
,
St. Louis
St. Louis ( , sometimes referred to as St. Louis City, Saint Louis or STL) is an independent city in the U.S. state of Missouri. It lies near the confluence of the Mississippi and the Missouri rivers. In 2020, the city proper had a populatio ...
,
Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, second-most populous city in Pennsylvania (after Philadelphia) and the List of Un ...
,
Scranton
Scranton is a city in and the county seat of Lackawanna County, Pennsylvania, United States. With a population of 76,328 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, Scranton is the most populous city in Northeastern Pennsylvania and the ...
,
Youngstown
Youngstown is a city in Mahoning County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of municipalities in Ohio, 11th-most populous city in Ohio with a population of 60,068 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The Mahoning ...
and
Wilmington (Delaware). In addition, the
depopulation of the Great Plains, caused by a very high rate of
rural flight
Rural flight (also known as rural-to-urban migration, rural depopulation, or rural exodus) is the Human migration, migratory pattern of people from rural areas into urban areas. It is urbanization seen from the rural perspective.
In Industriali ...
from isolated agricultural counties, has been going on since the 1930s.
In addition, starting from the 1950s, the United States has witnessed the phenomenon of the
white flight
The white flight, also known as white exodus, is the sudden or gradual large-scale migration of white people from areas becoming more racially or ethnoculturally diverse. Starting in the 1950s and 1960s, the terms became popular in the Racism ...
or white exodus, the large-scale migration of
people of various European ancestries from racially mixed urban regions to more racially homogeneous
suburb
A suburb (more broadly suburban area) is an area within a metropolitan area. They are oftentimes where most of a metropolitan areas jobs are located with some being predominantly residential. They can either be denser or less densely populated ...
an or
exurban
An exurb (or alternately: exurban area) is an area outside the typically denser inner suburban area, at the edge of a metropolitan area, which has some economic and commuting connection to the metro area, low housing-density,
and relatively hi ...
regions. The term has more recently been applied to other migrations by
whites
White is a racial classification of people generally used for those of predominantly European ancestry. It is also a skin color specifier, although the definition can vary depending on context, nationality, ethnicity and point of view.
De ...
, from older, inner suburbs to rural areas, as well as from the U.S.
Northeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A '' compass rose'' is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—eac ...
and
Midwest
The Midwestern United States (also referred to as the Midwest, the Heartland or the American Midwest) is one of the four census regions defined by the United States Census Bureau. It occupies the northern central part of the United States. It ...
to the warmer climate in the
Southeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, Radius, radially arrayed compass directions (or Azimuth#In navigation, azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A ''compass rose'' is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, ...
and
Southwest
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A '' compass rose'' is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west— ...
. Migration of middle-class white populations was observed during the
Civil rights movement in the 1950s and 1960s out of cities such as
Cleveland
Cleveland is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located along the southern shore of Lake Erie, it is situated across the Canada–U.S. maritime border and approximately west of the Ohio-Pennsylvania st ...
,
Detroit
Detroit ( , ) is the List of municipalities in Michigan, most populous city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is situated on the bank of the Detroit River across from Windsor, Ontario. It had a population of 639,111 at the 2020 United State ...
,
Kansas City
The Kansas City metropolitan area is a bi-state metropolitan area anchored by Kansas City, Missouri. Its 14 counties straddle the border between the U.S. states of Missouri (9 counties) and Kansas (5 counties). With and a population of more t ...
and
Oakland
Oakland is a city in the East Bay region of the San Francisco Bay Area in the U.S. state of California. It is the county seat and most populous city in Alameda County, with a population of 440,646 in 2020. A major West Coast port, Oakland is ...
, although racial segregation of public schools had ended there long before the
Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all Federal tribunals in the United States, U.S. federal court cases, and over Stat ...
' decision ''
Brown v. Board of Education
''Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka'', 347 U.S. 483 (1954), was a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court that ruled that U.S. state laws establishing racial segregation in public schools are unconstitutional, even if the ...
'' in 1954. In the 1970s, attempts to achieve effective
desegregation
Racial integration, or simply integration, includes desegregation (the process of ending systematic racial segregation), leveling barriers to association, creating equal opportunity regardless of race, and the development of a culture that draws ...
(or "integration") using forced
busing
Desegregation busing (also known as integrated busing, forced busing, or simply busing) was an attempt to diversify the racial make-up of schools in the United States by transporting students to more distant schools with less diverse student pop ...
in some areas led to more families moving out of former areas. More recently, as of 2018,
California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
had the largest ethnic/racial
minority population in the United States;
Non-Hispanic whites
Non-Hispanic Whites, also referred to as White Anglo Americans or Non-Latino Whites, are White Americans who are classified by the United States census as "White" and not of Hispanic or Latino origin. According to annual estimates from the Unit ...
decreased from about 76.3 – 78% of the state's population in 1970 to 36.6%% in 2018 and 39.3% of the total population was
Hispanic-Latino (of any race).
A combination of long-term trends, housing affordability, falling birthrates and rising death rates from the COVID-19 pandemic have caused as many as 16 US states to start declining in population.
The Commonwealth of
Puerto Rico's population peaked in 2000 at 3.8 million and has since declined to 3.3 million in 2020, due to a negative
natural change, and
emigration
Emigration is the act of leaving a resident country or place of residence with the intent to settle elsewhere (to permanently leave a country). Conversely, immigration describes the movement of people into one country from another (to permanentl ...
, due to natural disasters and economic difficulties.
France
The term '
Empty diagonal' is used for
French departments
In the administrative divisions of France, the department (, ) is one of the three levels of government under the national level ("territorial collectivity, territorial collectivities"), between the Regions of France, administrative regions a ...
that have low or declining populations. Due to continued emigration, many departments in
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
are seeing declines in population, including:
Aisne
Aisne ( , ; ; ) is a French departments of France, department in the Hauts-de-France region of northern France. It is named after the river Aisne (river), Aisne. In 2020, it had a population of 529,374.
Geography
The department borders No ...
,
Allier
Allier ( , , ; ) is a Departments of France, department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes Regions of France, region that borders Cher (department), Cher to the west, Nièvre to the north, Saône-et-Loire and Loire (department), Loire to the east, Pu ...
,
Ardennes
The Ardennes ( ; ; ; ; ), also known as the Ardennes Forest or Forest of Ardennes, is a region of extensive forests, rough terrain, rolling hills and ridges primarily in Belgium and Luxembourg, extending into Germany and France.
Geological ...
,
Cantal
Cantal (; or ) is a rural Departments of France, department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes Regions of France, region of France, with its Prefectures in France, prefecture in Aurillac. Its other principal towns are Saint-Flour, Cantal, Saint-Flou ...
,
Charente
Charente (; Saintongese: ''Chérente''; ) is a department in the administrative region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine, southwestern France. It is named after the river Charente, the most important and longest river in the department, and also the r ...
,
Cher
Cher ( ; born Cheryl Sarkisian, May 20, 1946) is an American singer, actress and television personality. Dubbed the "Honorific nicknames in popular music, Goddess of Pop", she is known for her Androgyny, androgynous contralto voice, Music an ...
,
Corrèze
Corrèze (; ) is a département in France, named after the river Corrèze which runs through it. Although its prefecture is Tulle, its most populated city is Brive-la-Gaillarde. Corrèze is located in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, on the bo ...
,
Creuse
Creuse (; or ) is a department in central France named after the river Creuse. After Lozère, it is the second least populated department in France. It is bordered by Indre and Cher to the north, Allier and Puy-de-Dôme to the east, Cor ...
,
Dordogne
Dordogne ( , or ; ; ) is a large rural departments of France, department in south west France, with its Prefectures in France, prefecture in Périgueux. Located in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region roughly half-way between the Loire Valley and ...
,
Eure
Eure ( ; ; or ) is a department in the administrative region of Normandy, northwestern France, named after the river Eure. Its prefecture is Évreux. In 2021, Eure had a population of 598,934.[Eure-et-Loir
Eure-et-Loir (, locally: ) is a French department, named after the Eure and Loir rivers. It is located in the region of Centre-Val de Loire. In 2019, Eure-et-Loir had a population of 431,575.][Haute-Marne
Haute-Marne (; English: Upper Marne) is a department in the Grand Est region of Northeastern France. Named after the river Marne, its prefecture is Chaumont. In 2019, it had a population of 172,512.][Haute-Saône
Haute-Saône (; Frainc-Comtou: ''Hâte-Saône''; English: Upper Saône) is a department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region of northeastern France. Named after the river Saône, it had a population of 235,313 in 2019.] ,
Haute-Vienne
Haute-Vienne (; , ; Upper Vienne) is a département in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region in southwest-central France. Named after the Vienne River, it is one of the twelve départements that together constitute Nouvelle-Aquitaine. The prefecture an ...
,
Indre
Indre (); is a department in central France named after the river Indre. The inhabitants of the department are known as the ''Indriens'' (masculine; ) and ''Indriennes'' (feminine; ). Indre is part of the current administrative region of Cent ...
,
Jura,
Loir-et-Cher
Loir-et-Cher (, ) is a Departments of France, department in the Centre-Val de Loire Regions of France, region of France. It is named after two rivers which run through it, the Loir in its northern part and the Cher (river), Cher in its southern p ...
,
Lot-et-Garonne
Lot-et-Garonne (, ) is a department in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region of Southwestern France. Named after the rivers Lot and Garonne, it had a population of 331,271 in 2019.[Lozère
Lozère (; ) is a landlocked Departments of France, department in the Regions of France, region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie in Southern France, located near the Massif Central, bounded to the northeast by Haute-Loire, to the ...]
,
Manche
Manche (, ; Norman language, Norman: ) is a coastal Departments of France, French ''département'' in Normandy (administrative region), Normandy on the English Channel, which is known as , literally "the sleeve", in French. Manche is bordered by ...
,
Marne,
Mayenne
Mayenne ( ) is a landlocked department in northwest France named after the river Mayenne. Mayenne is part of the administrative region of Pays de la Loire and is surrounded by the departments of Manche, Orne, Sarthe, Maine-et-Loire, and Il ...
,
Meuse
The Meuse or Maas is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a total length of .
History
From 1301, the upper ...
,
Moselle
The Moselle ( , ; ; ) is a river that rises in the Vosges mountains and flows through north-eastern France and Luxembourg to western Germany. It is a bank (geography), left bank tributary of the Rhine, which it joins at Koblenz. A sm ...
,
Nièvre
Nièvre () is a department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region, central-east France. Named after the river Nièvre, it had a population of 204,452 in 2019.[Orne
Orne (; or ) is a département in the northwest of France, named after the river Orne. It had a population of 279,942 in 2019.][Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...]
,
Sarthe
Sarthe () is a department of the French region of Pays de la Loire, and the province of Maine, situated in the '' Grand-Ouest'' of the country. It is named after the river Sarthe, which flows from east of Le Mans to just north of Angers. It ha ...
,
Somme __NOTOC__
Somme or The Somme may refer to: Places
*Somme (department), a department of France
* Somme, Queensland, Australia
* Canal de la Somme, a canal in France
*Somme (river), a river in France
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Somme'' (book), ...
,
Territoire de Belfort
The Territoire de Belfort (; "Territory of Belfort") is a department in the northeastern French region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté. In 2020 it had a population of 140,120.[Vosges
The Vosges ( , ; ; Franconian and ) is a range of medium mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a single geomorphological unit and ...]
and
Yonne
Yonne (, in Burgundian: ''Ghienne'') is a department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in France. It is named after the river Yonne, which flows through it, in the country's north-central part. One of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté's eight con ...
. For more information, see the
List of French departments by population
This table lists the 101 French departments in descending order of population, area and population density.
Data description
The figures include:
* population without double counting for 1999;
* ''municipal population'' (legal population in 20 ...
.
South Africa
The term 'white flight' has also been used for large-scale
post-colonial emigration of
whites from Africa, or parts of that continent,
driven by levels of violent crime and anti-colonial state policies.
In recent decades, there has been a steady and proportional decline in
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
's white community, due to higher birth rates among other South African ethnic groups, as well as a high rate of emigration. In 1977, there were 4.3 million
White South Africans
White South Africans are South Africans of European descent. In linguistic, cultural, and historical terms, they are generally divided into the Afrikaans-speaking descendants of the Dutch East India Company's original colonists, known as Afr ...
, constituting 16.4% of the population at the time. An estimated 800,000 emigrated between 1995 and 2016,
[White flight from South Africa , Between staying and going](_blank)
, The Economist, 25 September 2008 citing
crime
In ordinary language, a crime is an unlawful act punishable by a State (polity), state or other authority. The term ''crime'' does not, in modern criminal law, have any simple and universally accepted definition,Farmer, Lindsay: "Crime, definiti ...
and a
lack of employment opportunities. It may also be noted that in recent times, a large proportion of white South African emigrants have chosen to return home. For instance, in May 2014, Homecoming Revolution estimated that around 340,000 white South Africans had returned to South Africa in the preceding decade.
Furthermore, immigration from Europe has also supplemented the white population. The 2011 census found that 63,479 white people living in South Africa were born in Europe; of these, 28,653 had moved to South Africa since 2001.
India
The
Parsis
The Parsis or Parsees () are a Zoroastrian ethnic group in the Indian subcontinent. They are descended from Persian refugees who migrated to the Indian subcontinent during and after the Arab-Islamic conquest of Iran in the 7th century, w ...
of India have one of the lowest fertility rates in the world (0.8 children per woman in 2017); this coupled with emigration has resulted in population decline at least since the 1940s. Their population has more than halved from its peak.
Lebanon
Lebanon has recorded major waves of emigration from the late 19th century to early 20th century and during the
Lebanese Civil War
The Lebanese Civil War ( ) was a multifaceted armed conflict that took place from 1975 to 1990. It resulted in an estimated 150,000 fatalities and led to the exodus of almost one million people from Lebanon.
The religious diversity of the ...
which led to the exodus of almost one million people from Lebanon. Due to the
Syrian refugee crisis, according to the UN's population division, Lebanon's population increased massively from 5.05 million in 2011 to 6.5 million in 2015, but the population began declining again in 2016, with a total population of 6.26 million, 6.11 million in 2017, 5.95 million in 2018, and 5.76 million in 2019.
Between 2018 and 2023, the decline in the number of Lebanese accelerated from 25,000 per year to 78,000 due to massive emigration caused by the
Lebanese liquidity crisis
The Lebanese liquidity crisis is an ongoing financial crisis affecting Lebanon, that became fully apparent in August 2019, and was further exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic in Lebanon (which began in February 2020), the 2020 Beirut port ex ...
.
However, the number of births to refugees has been increasing and the country hosts a large population of unregistered refugees, other illegal residents, and other people without legal documentation, making it difficult to count the population of Lebanon. Dr. Ali Faour, a population affairs researcher, estimates the Lebanese population including undocumented migrants to be 8 million. Regardless, the population of Lebanese nationality continues to age and decline as financial struggles increase emigration and decrease marriages. Consequentially, the share of Lebanese nationals in Lebanon may have decreased to between 45 and 50 percent, a sharp decline from 80 percent in 2004, although a 2024 report estimated the share at 65 to 69 percent of the resident population.
Regionally, the mountainous and Christian-majority areas have low fertility rates comparable to European nations, with most of the population increase being concentrated in northern Lebanon.
National efforts to confront declining populations
A country with a declining population will struggle to fund public services such as health care, old age benefits, defense, education, water and sewage infrastructure, etc.
To maintain some level of economic growth and continue to improve its citizens’ quality of life, national efforts to confront declining populations will tend to focus on the threat of a declining GDP. Because a country's GDP is dependent on the size and productivity of its workforce, a country confronted with a declining population, will focus on increasing the size and productivity of that workforce.
Increase the size of the workforce
A country's
workforce
In macroeconomics, the workforce or labour force is the sum of people either working (i.e., the employed) or looking for work (i.e., the unemployed):
\text = \text + \text
Those neither working in the marketplace nor looking for work are out ...
is that segment of its working-age population that is employed. Working age population is generally defined as those people aged 15–64.
Policies that could increase the size of the workforce include:
* Natalism
Natalism
Natalism (also called pronatalism or the pro-birth position) is a policy paradigm or personal value that promotes the reproduction of human life as an important objective of humanity and therefore advocates a high birthrate.
Cf.:
According to t ...
is a set of government policies and cultural changes that promote parenthood and encourage women to bear more children. These generally fall into three broad categories:
# Financial incentives. These may include child benefits and other public transfers that help families cover the cost of children.
# Support for parents to combine family and work. This includes maternity-leave policies, parental-leave policies that grant (by law) leaves of absence from work to care for their children, and childcare services.
# Broad social change that encourages children and parenting
For example, Sweden built up an extensive
welfare state
A welfare state is a form of government in which the State (polity), state (or a well-established network of social institutions) protects and promotes the economic and social well-being of its citizens, based upon the principles of equal oppor ...
from the 1930s and onward, partly as a consequence of the debate following "
Crisis in the Population Question", published in 1934. Today, (2017) Sweden has extensive parental leave that allows parents to share 16 months of paid leave per child, the cost divided between both employer and State.
Other examples include
Romania's natalist policy during the 1967–90 period and Poland's 500+ program.
* Encourage more women to join the workforce.
Encouraging those women in the working-age population who are not working to find jobs would increase the size of the workforce.
Female
participation in the workforce currently (2018) lags men's in all but three countries worldwide.
Among developed countries, the workforce participation gap between men and women can be especially wide. For example, currently (2018), in South Korea 59% of women work compared with 79% of men,
and currently (2023) in India, only 33% of women are working.
However, even assuming that more women would want to join the workforce, increasing their participation would give these countries only a short-term increase in their workforce, because at some point a participation ceiling is reached, further increases are not possible, and the impact on GDP growth ceases.
* Stop the decline of men in the workforce.
In the United States, the labor force participation of men has been falling since the late 1960s.
The
labor force participation rate
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is the proportion of people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work dur ...
is the ratio between the size of the workforce and the size of the working-age population. In 1969 the labor force participation rate of men in their prime years of 25–54 was 96% and in 2023 was 89%.
* Raise the retirement age.
Raising the retirement age has the effect of increasing the working-age population,
but raising the retirement age requires other policy and cultural changes if it is to have any impact on the size of the workforce:
# Pension reform. Many retirement policies encourage early retirement. For example, in 2018 less than 10% of Europeans between ages 64–74 were employed.
Instead of encouraging work after retirement, many public pension plans restrict earnings or hours of work.
# Workplace cultural reform. Employer attitudes towards older workers must change. Extending working lives will require investment in training and working conditions to maintain the productivity of older workers.
One study estimated that increasing the retirement age by 2–3 years per decade between 2010 and 2050 would offset declining working-age populations faced by "old" countries such as Germany and Japan.
* Increase
immigration
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not usual residents or where they do not possess nationality in order to settle as Permanent residency, permanent residents. Commuting, Commuter ...
.
A country can increase the size of its workforce by importing more migrants into their working age population.
Even if the indigenous workforce is declining, qualified immigrants can reduce or even reverse this decline. However, this policy can only work if the immigrants can join the workforce and if the indigenous population accepts them.
For example, starting in 2019 Japan, a country with a declining workforce, will allow five-year visas for 250,000 unskilled guest workers. Under the new measure, between 260,000 and 345,000 five-year visas will be made available for workers in 14 sectors suffering severe labor shortages, including caregiving, construction, agriculture and shipbuilding.
* Reduce
emigration
Emigration is the act of leaving a resident country or place of residence with the intent to settle elsewhere (to permanently leave a country). Conversely, immigration describes the movement of people into one country from another (to permanentl ...
.
The table above shows that long-term persistent emigration, often caused by what is called "
Brain Drain", is often one of the major causes of a county's population decline. However,
research
Research is creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge. It involves the collection, organization, and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to ...
has also found that emigration can have net positive effects on sending countries, so this would argue against any attempts to reduce it.
Increase the productivity of the workforce
Development economists would call increasing the size of the workforce "extensive growth". They would call increasing the
productivity
Productivity is the efficiency of production of goods or services expressed by some measure. Measurements of productivity are often expressed as a ratio of an aggregate output to a single input or an aggregate input used in a production proce ...
of that workforce "intensive growth". In this case, GDP growth is driven by increased output per worker, and by extension, increased GDP/capita.
In the context of a stable or declining population, increasing workforce productivity is better than mostly short-term efforts to increase the size of the workforce. Economic theory predicts that in the long term, most growth will be attributable to intensive growth, that is, new
technology
Technology is the application of Conceptual model, conceptual knowledge to achieve practical goals, especially in a reproducible way. The word ''technology'' can also mean the products resulting from such efforts, including both tangible too ...
and new and better ways of doing things plus the addition of
capital
Capital and its variations may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** Capital region, a metropolitan region containing the capital
** List of national capitals
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter
Econom ...
and
education
Education is the transmission of knowledge and skills and the development of character traits. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, such as public schools, following a curriculum. Non-formal education als ...
to spread them to the workforce.
Increasing workforce productivity through intensive growth can only succeed if workers who become unemployed through the introduction of new technology can be retrained so that they can keep their skills current and not be left behind. Otherwise, the result is
technological unemployment
The term technological unemployment is used to describe the loss of jobs caused by technological change. It is a key type of structural unemployment. Technological change typically includes the introduction of labour-saving "mechanical-muscle" ...
. Funding for worker retraining could come from a
robot tax
A robot tax is a legislative strategy to disincentivize the replacement of workers by machines and bolster the social safety net for those who are displaced. While the automation of manual labour has been contemplated since before the Industrial R ...
, although the idea is controversial.
Long-term future trends
A long-term population decline is typically caused by
sub-replacement fertility
Sub-replacement fertility is a total fertility rate (TFR) that (if sustained) leads to each new generation being less populous than the older, previous one in a given area. The United Nations Population Division defines sub-replacement fertilit ...
, coupled with a net immigration rate that fails to compensate for the excess of deaths over births.
A long-term decline is accompanied by
population aging
Population ageing is an overall change in the ages of a population. This can typically be summarised in a single parameter as an increase in the median age. Causes are a long-term decline in fertility rates and a decline in mortality rates. Most ...
and creates an increase in the ratio of
retirees
A pensioner is a person who receives a pension, most commonly because of retirement from the workforce. This is a term typically used in the United Kingdom (along with OAP, initialism of old-age pensioner), Ireland and Australia where someone of p ...
to workers and children.
When a sub-replacement fertility rate remains constant, population decline accelerates over the long term.
Because of the global decline in the fertility rate, projections of future global population show a marked slowing of population growth and the possibility of long-term decline.
The table below summarizes the United Nations projections for future population growth. Any such long-term projections are necessarily highly speculative. The UN divides the world into six regions. Under their projections, during the period 2045–2050, Europe's population will be in decline and all other regions will experience significant reductions in growth; then, by the end of the 21st century (the period 2095–2100) three of these regions will be showing population decline and global population will have peaked and started to decline.
Note: the UN's methods for generating these numbers are explained at this reference.
The table shows UN predictions of long-term decline of population growth rates in every region; however, short-term baby booms and healthcare improvements, among other factors, can cause reversals of trends. Population declines in Russia (1994–2008), Germany (1974–1984), and Ireland (1850–1961) have seen long-term reversals.
The UK, having seen almost zero growth during the period 1975–1985, is now (2015–2020) growing at 0.6% per year.
Some scholars believe there exists a form of "cultural selection" that will significantly affect future demographics due to significant differences in fertility rates between cultures, such as within certain religious groups, that cannot be explained by factors such as income. In the book ''Shall the Religious Inherit the Earth?'',
Eric Kaufmann
Eric Peter Kaufmann (born 11 May 1970) is a Canadians, Canadian professor of politics at the University of Buckingham. He was appointed in October 2023, following his resignation from his post at Birkbeck, University of London, after two decades ...
argues that demographic trends point to religious fundamentalists greatly increasing as a share of the population over the next century. From the perspective of
evolutionary psychology
Evolutionary psychology is a theoretical approach in psychology that examines cognition and behavior from a modern evolutionary perspective. It seeks to identify human psychological adaptations with regard to the ancestral problems they evolved ...
, it is expected that selection pressure should occur for whatever psychological or cultural traits maximize fertility.
[Can we be sure the world's population will stop rising?]
BBC News, 13 October 2012
See also
*
Antinatalism
Antinatalism or anti-natalism is the philosophical value judgment that procreation is unethical or unjustifiable. Antinatalists thus argue that humans should abstain from making children. Some antinatalists consider coming into existence to alw ...
*
Birth dearth
Birth dearth was coined by Ben J. Wattenberg in his 1987 book ''Birth Dearth''. This term refers to the declining fertility rates observed in many modern industrialized nations. It is often cited as a response to overpopulation. Countries and ge ...
*
Climate crisis
''Climate crisis'' is a term that is used to describe global warming and climate change and their effects. This term and the term ''climate emergency'' have been used to emphasize the threat of global warming to Earth's natural environment an ...
*
Ghost town
A ghost town, deserted city, extinct town, or abandoned city is an abandoned settlement, usually one that contains substantial visible remaining buildings and infrastructure such as roads. A town often becomes a ghost town because the economi ...
*
History of Easter Island#Destruction of society and population
*
Holocene extinction
The Holocene extinction, also referred to as the Anthropocene extinction or the sixth mass extinction, is an ongoing extinction event caused exclusively by human activities during the Holocene epoch. This extinction event spans numerous families ...
*
Human extinction
Human extinction or omnicide is the hypothetical end of the human species, either by population decline due to extraneous natural causes, such as an asteroid impact or large-scale volcanism, or via anthropogenic destruction (self-extinction ...
*
Human overpopulation
Human overpopulation (or human population overshoot) is the idea that human populations may become too large to be sustainability, sustained by their environment or resources in the long term. The topic is usually discussed in the context of wor ...
*
Human population planning
Human population planning is the practice of managing the growth rate of a human population. The practice, traditionally referred to as population control, had historically been implemented mainly with the goal of increasing population growth, ...
*
Negative Population Growth
Negative Population Growth is a non-profit organization in the United States, founded in 1972. It is named after the organization Zero Population Growth, which founder Don Mann believed wasn't going far enough to address his concerns about overpo ...
*
Political demography
Political demography is the study of the relationship between politics and population change. Population change is driven by classic Demographics, demographic mechanisms – birth, death, age structure, and Human migration, migration.
However, in ...
*
Population ageing
Population ageing is an overall change in the ages of a population. This can typically be summarised in a single parameter as an increase in the median age. Causes are a long-term decline in fertility rates and a decline in mortality rates. Most ...
*
Population cycle
A population cycle in zoology is a phenomenon where populations rise and fall over a predictable period of time. There are some species where population numbers have reasonably predictable patterns of change although the full reasons for populati ...
*
Population growth
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. The World population, global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to 8.2 billion in 2025. Actual global human population growth amounts to aroun ...
*
Rural flight
Rural flight (also known as rural-to-urban migration, rural depopulation, or rural exodus) is the Human migration, migratory pattern of people from rural areas into urban areas. It is urbanization seen from the rural perspective.
In Industriali ...
*
Societal collapse
Societal collapse (also known as civilizational collapse or systems collapse) is the fall of a complex human society characterized by the loss of cultural identity and of social complexity as an Complex adaptive system, adaptive system, the downf ...
*
Steady-state economy
A steady-state economy is an economy made up of a constant stock of physical wealth (capital) and a constant population size. In effect, such an economy does not grow in the course of time. The term usually refers to the economy, national eco ...
*
Sub-replacement fertility
Sub-replacement fertility is a total fertility rate (TFR) that (if sustained) leads to each new generation being less populous than the older, previous one in a given area. The United Nations Population Division defines sub-replacement fertilit ...
*
Total fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were t ...
*
Zero population growth
Zero population growth, sometimes abbreviated ZPG, is a condition of demography, demographic balance where the number of people in a specified population neither population growth, grows nor population decline, declines; that is, the number of bi ...
Case studies:
*
Aging of Europe
The ageing of Europe, also known as the greying of Europe, is a demographic phenomenon in Europe characterised by a decrease in fertility, a decrease in mortality rate, and a higher life expectancy among European populations. Low birth rates an ...
*
Aging of Japan
*
Aging of South Korea
In demographic terms, aging refers to an increase in the proportion of senior citizens to the total population. The term "senior citizen" encompasses those aged 65 or older. In 2045, South Korea is projected to become the world's most aged popula ...
*
Aging of the United States
*
Empty diagonal
*
*
Russian Cross
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Population Decline
Aftermath of war
Ageing
Control of demographics
Social impact of the COVID-19 pandemic
Urban decay
Demographic economic problems
 Historical episodes of short-term human population decline have been common and have been caused by several factors.
High mortality rates caused by:
*
Historical episodes of short-term human population decline have been common and have been caused by several factors.
High mortality rates caused by:
*  Though Japan's
Though Japan's  The decline in Russia's total population is among the largest in numbers, but not in percentage. After having peaked at 148,689,000 in 1991, the population then decreased, falling to 142,737,196 by 2008. This represents a 4.0% decrease in total population since the peak census figure. However, the Russian population then rose to 146,870,000 in 2018. This recent trend can be attributed to a lower death rate, higher birth rate, the annexation of Crimea and continued immigration, mostly from Ukraine and Armenia. It is some 40% above the 1950 population.
Russia has become increasingly reliant on immigration to maintain its population; 2021 had the highest net immigration since 1994, despite which there was a small overall decline from 146.1 million to 145.4 million in 2021, the largest decline in over a decade. The natural death rate in January 2020, 2021, and 2022 have each been nearly double the natural birth rate.
In March 2023, ''The Economist'' reported that "Over the past three years the country has lost around 2 million more people than it would ordinarily have done, as a result of war in Ukraine">Russo-Ukrainian_War.html" ;"title="nowiki/>Russo-Ukrainian War">in Ukraine disease and exodus." According to Russian economist Alexander Isakov, "Russia’s population has been declining and the war will reduce it further. Reasons? Emigration
Emigration is the act of leaving a resident country or place of residence with the intent to settle elsewhere (to permanently leave a country). Conversely, immigration describes the movement of people into one country from another (to permanentl ...
The decline in Russia's total population is among the largest in numbers, but not in percentage. After having peaked at 148,689,000 in 1991, the population then decreased, falling to 142,737,196 by 2008. This represents a 4.0% decrease in total population since the peak census figure. However, the Russian population then rose to 146,870,000 in 2018. This recent trend can be attributed to a lower death rate, higher birth rate, the annexation of Crimea and continued immigration, mostly from Ukraine and Armenia. It is some 40% above the 1950 population.
Russia has become increasingly reliant on immigration to maintain its population; 2021 had the highest net immigration since 1994, despite which there was a small overall decline from 146.1 million to 145.4 million in 2021, the largest decline in over a decade. The natural death rate in January 2020, 2021, and 2022 have each been nearly double the natural birth rate.
In March 2023, ''The Economist'' reported that "Over the past three years the country has lost around 2 million more people than it would ordinarily have done, as a result of war in Ukraine">Russo-Ukrainian_War.html" ;"title="nowiki/>Russo-Ukrainian War">in Ukraine disease and exodus." According to Russian economist Alexander Isakov, "Russia’s population has been declining and the war will reduce it further. Reasons? Emigration
Emigration is the act of leaving a resident country or place of residence with the intent to settle elsewhere (to permanently leave a country). Conversely, immigration describes the movement of people into one country from another (to permanentl ...