Birklands on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sherwood Forest is the remnants of an ancient
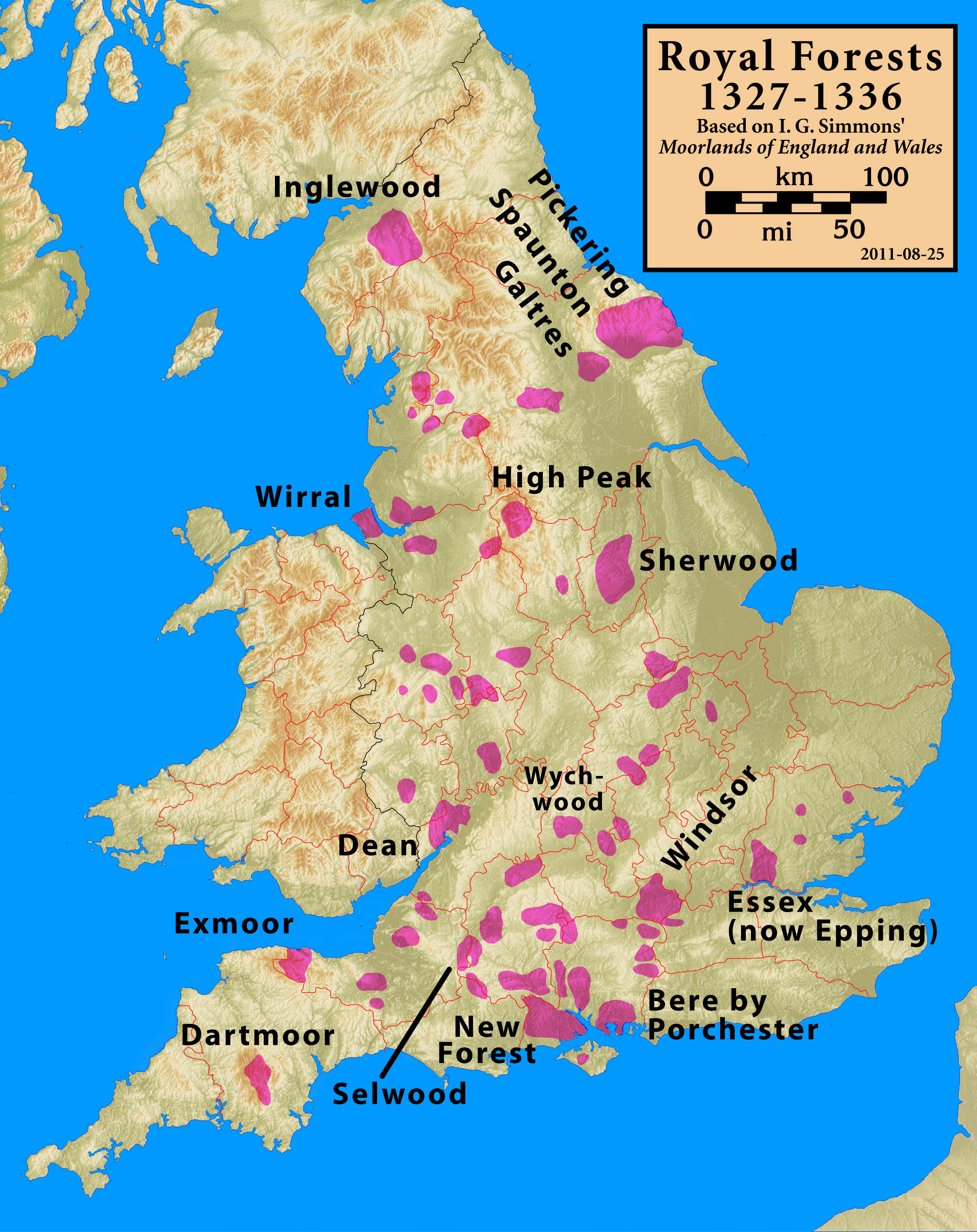 After the dissolution of the monasteries by
After the dissolution of the monasteries by
 During the
During the  Part of the forest was opened to the public as a
Part of the forest was opened to the public as a

Forestry EnglandThe News, History, and Archaeology of The Real Sherwood ForestNottinghamshire County Council's Official Sherwood Forest Page
Sherwood Forest Regeneration PlansSherwood Forest Trust Official WebsiteThe Living Legend
details current plans for the forest.
Official tourism website for Nottinghamshire and Sherwood ForestAccording to Ancient Custom: Research on the possible Origins and Purpose of Thynghowe Sherwood Forest
{{Authority control Country parks in Nottinghamshire English royal forests Forests and woodlands of Nottinghamshire Nature reserves in Nottinghamshire Protected areas established in 1969 Protected areas established in 2002 Protected areas established in 2007 Tourist attractions in Nottinghamshire Edwinstowe
Royal Forest
A royal forest, occasionally known as a kingswood (), is an area of land with different definitions in England, Wales, Scotland and Ireland. The term ''forest'' in the ordinary modern understanding refers to an area of wooded land; however, the ...
in Nottinghamshire
Nottinghamshire (; abbreviated ''Notts.'') is a ceremonial county in the East Midlands of England. The county is bordered by South Yorkshire to the north-west, Lincolnshire to the east, Leicestershire to the south, and Derbyshire to the west. Th ...
, within the East Midlands
The East Midlands is one of nine official regions of England. It comprises the eastern half of the area traditionally known as the Midlands. It consists of Derbyshire, Leicestershire, Lincolnshire (except for North Lincolnshire and North East ...
region in England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
. It has association with the legend
A legend is a genre of folklore that consists of a narrative featuring human actions, believed or perceived to have taken place in human history. Narratives in this genre may demonstrate human values, and possess certain qualities that give the ...
of Robin Hood
Robin Hood is a legendary noble outlaw, heroic outlaw originally depicted in English folklore and subsequently featured in literature, theatre, and cinema. According to legend, he was a highly skilled archer and swordsman. In some versions o ...
. The forest was proclaimed by William the Conqueror
William the Conqueror (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), sometimes called William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England (as William I), reigning from 1066 until his death. A descendant of Rollo, he was D ...
and mentioned in the Domesday Book
Domesday Book ( ; the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book") is a manuscript record of the Great Survey of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 at the behest of William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by ...
in 1086. The reserve has the highest concentration of ancient trees in Europe.UK Government, Natural England, Nottinghamshire's National Nature Reserve Corporate Report 2014, retrieved on 9 April 2025
Today, Sherwood Forest National Nature Reserve encompasses , surrounding the village of Edwinstowe
Edwinstowe is a village and civil parish in the Newark and Sherwood district of Nottinghamshire, England, on the edge of Sherwood Forest and the Dukeries. It is associated with the legends of Robin Hood and Maid Marian, and to a lesser extent ...
and the site of Thoresby Hall
Thoresby Hall is a 19th-century country house and park in Budby, Nottinghamshire, some 2 miles (4 km) north of Ollerton. It is one of four neighbouring country houses and estates in the Dukeries in north Nottinghamshire all occupied by duk ...
. The reserve contains more than a thousand ancient oaks which are known to be more than 500 years old, with the Major Oak
The Major Oak is a large English oak (''Quercus robur'') near the village of Edwinstowe in the midst of Sherwood Forest, Nottinghamshire, England. According to local folklore, it was Robin Hood's shelter where he and his Merry Men slept. It we ...
being twice that age. Sherwood Forest is within an area which used to be called ‘Birch Lund’ which is Viking
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9� ...
in origin, now known as Birklands. The oak trees from Sherwood Forest were used to build the roof of St Paul’s Cathedral
St Paul's Cathedral, formally the Cathedral Church of St Paul the Apostle, is an Anglican cathedral in London, England, the seat of the Bishop of London. The cathedral serves as the mother church of the Diocese of London in the Church of Engl ...
in London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
and 1st Viscount Nelson naval fleet.
Etymology
Sherwood originally was named Sciryuda in 958AD, meaning the ‘woodland belonging to the shire’. Its name is derived from its status as the ''shire
Shire () is a traditional term for an administrative division of land in Great Britain and some other English-speaking countries. It is generally synonymous with county (such as Cheshire and Worcestershire). British counties are among the oldes ...
(or sher) wood'' of Nottinghamshire, which extended into several neighbouring counties (shires), bordered to the west by the River Erewash
The River Erewash is a river in England, a tributary of the River Trent that flows roughly southwards through Derbyshire and Nottinghamshire, forming the boundary between the two counties for much of its length. It rises near Kirkby-in-Ashf ...
and the Forest of East Derbyshire
The Forest of East Derbyshire was, in the Middle Ages, an area of wooded heath between the rivers Derwent and the Erewash in Derbyshire.
Unlike the Forest of High Peak and Duffield Frith it was not taken over by William I, but became a royal ...
.
Prehistory
The area has been wooded since the end of the Last Glacial Period (as attested by pollen sampling cores). This is about 10000 years ago. Evidence of flint tools have shown use in Sherwood Forest by prehistoric hunter gatherers. During the Iron Age and Roman periods human habitation and farming was common. In the 9th century farming made an impact on Sherwood’s landscape.History
DuringRoman Britain
Roman Britain was the territory that became the Roman province of ''Britannia'' after the Roman conquest of Britain, consisting of a large part of the island of Great Britain. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410.
Julius Caes ...
various camps were discovered in parts of Sherwood Forest. It is to this that two remains of Roman Villas
A Roman villa was typically a farmhouse or country house in the territory of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, sometimes reaching extravagant proportions.
Nevertheless, the term "Roman villa" generally covers buildings with the common ...
were identified in nearby Mansfield Woodhouse
Mansfield Woodhouse is a town and civil parish in the Mansfield District, Mansfield district of Nottinghamshire, England. It is about north of Mansfield, along the main A60 road in a wide, low valley between the Rivers River Maun, Maun and Rive ...
by Major Hayman Rooke in 1787.
Sherwood Forest was first recorded as being named Sciryuda in 958AD.
King Edwin of Northumbria
Edwin (; c. 586 – 12 October 632/633), also known as Eadwine or Æduinus, was the King of Deira and Bernicia – which later became known as Northumbria – from around 616 until his death. He was the second monarch to rule bo ...
in 633AD was killed at Hatfield Chase
Hatfield Chase is a low-lying area in South Yorkshire and North Lincolnshire, England, which was often flooded. It was a royal hunting ground until Charles I of England, Charles I appointed the Dutch engineer Cornelius Vermuyden to drain it in 1 ...
in a battle against his Mercian rival King Penda of Mercia
Penda (died 15 November 655)Manuscript A of the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' gives the year as 655. Bede also gives the year as 655 and specifies a date, 15 November. R. L. Poole (''Studies in Chronology and History'', 1934) put forward the theor ...
and his body was carried into the forest and buried/hidden in St Mary's Church, Edwinstowe
St Mary's Church is a parish church in the Church of England in Edwinstowe. The church was mentioned in the Doomsday Book of 1086, given by William II of England, William II to Lincoln Cathedral. The Church of England: The diocese of Southwell ...
. His head was later buried in York
York is a cathedral city in North Yorkshire, England, with Roman Britain, Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers River Ouse, Yorkshire, Ouse and River Foss, Foss. It has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a Yor ...
and his body in Whitby
Whitby is a seaside town, port and civil parish in North Yorkshire, England. It is on the Yorkshire Coast at the mouth of the River Esk, North Yorkshire, River Esk and has a maritime, mineral and tourist economy.
From the Middle Ages, Whitby ...
. The village of Edwinstowe
Edwinstowe is a village and civil parish in the Newark and Sherwood district of Nottinghamshire, England, on the edge of Sherwood Forest and the Dukeries. It is associated with the legends of Robin Hood and Maid Marian, and to a lesser extent ...
takes its name from King Edwin of Northumbria
Edwin (; c. 586 – 12 October 632/633), also known as Eadwine or Æduinus, was the King of Deira and Bernicia – which later became known as Northumbria – from around 616 until his death. He was the second monarch to rule bo ...
.
In 1066, in the invasion of England, William the Conqueror
William the Conqueror (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), sometimes called William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England (as William I), reigning from 1066 until his death. A descendant of Rollo, he was D ...
made Sherwood Forest a Royal Hunting Forest.Robert White,The Dukery, and Sherwood Forest, (1875) retrieved in the 8th April 2023 When the Domesday Book
Domesday Book ( ; the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book") is a manuscript record of the Great Survey of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 at the behest of William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by ...
was compiled in 1086, the forest covered perhaps a quarter of Nottinghamshire (approximately 19,000 acres or 7,800 hectares) in woodland and heath subject to the forest laws.
The earliest notice of the forest at Sherwood was at the time of Henry II
Henry II may refer to:
Kings
* Saint Henry II, Holy Roman Emperor (972–1024), crowned King of Germany in 1002, of Italy in 1004 and Emperor in 1014
*Henry II of England (1133–89), reigned from 1154
*Henry II of Jerusalem and Cyprus (1271–1 ...
when William Peverel the Younger
William "the Younger" Peverel ( or – after 1155) was the son of William Peverel. He married Avicia de Lancaster (1088 – ) in La Marche, Normandy, France. She was possibly the daughter of William de Lancaster I and Countess Gundred de Warenn ...
answered the plea of the forest, to which he profited and controlled the area.
During the 12th and 13th centuries Christian Monastic Orders had established large estates within Sherwood Forest. Three Abbeys were founded Rufford Abbey
Rufford Abbey is a country estate in Rufford, Nottinghamshire, England, two miles (4 km) south of Ollerton. Originally a Cistercian abbey, it was converted to a country house in the 16th century after Henry VIII’s dissolution of the ...
, Newstead Abbey
Newstead Abbey, in Nottinghamshire, England, was formerly an Augustinian priory. Converted to a domestic home following the Dissolution of the Monasteries, it is now best known as the ancestral home of Lord Byron. The Abbey is on the national ...
and Thurgarton Priory.
Sherwood Forest was frequently visited by the Mercian Kings
The Mercia, Kingdom of Mercia was a state in the English Midlands from the 6th century to the 10th century. For some two hundred years from the mid-7th century onwards it was the dominant member of the Heptarchy and consequently the most powerful ...
. The forest became popular with King John and Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots (Latin: Malleus Scotorum), was King of England from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he was Lord of Ireland, and from 125 ...
. The remains of a hunting lodge can be found at Kings Clipstone
Kings Clipstone is a settlement and civil parish, in the Newark and Sherwood district, in the county of Nottinghamshire, England. The parish lies in the west of the county, and north west within the district. It is 122 miles north of London, 1 ...
named King John's Palace.cite web Nottinghamshire County Council, History of Sherwood Forest, Robin Hood and Major Oak, 2023 retrieved on the 8th April 2023 Prior to King John reluctantly signing the Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter"), sometimes spelled Magna Charta, is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the Archbishop of Canterbury, Cardin ...
at Runnymede
Runnymede is a water-meadow alongside the River Thames in the English county of Surrey, bordering Berkshire and just over west of central London. It is notable for its association with the sealing of Magna Carta, and as a consequence is, with ...
in 1215, the Forest Laws came with much displeasure to the ruling classes of the forest.
 After the dissolution of the monasteries by
After the dissolution of the monasteries by Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
in 1536, the land of Sherwood was sold and granted into private ownership which was converted into house estates. James I James I may refer to:
People
*James I of Aragon (1208–1276)
* James I of Sicily or James II of Aragon (1267–1327)
* James I, Count of La Marche (1319–1362), Count of Ponthieu
* James I, Count of Urgell (1321–1347)
*James I of Cyprus (1334� ...
in the 1600s visited the forest, as did Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
and Charles II brought back under control the management of Sherwood Forest.
Sherwood Forest in 1623 had a narrow escape from a fire which broke out. The only record of this occurrence is written in a letter which is preserved in the British Museum
The British Museum is a Museum, public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is the largest in the world. It documents the story of human cu ...
.
In the 17th and 18th century’s Charles II and then Queen Anne sold large areas of Sherwood Crown Land to private owners who built the estates of Thoresby Hall
Thoresby Hall is a 19th-century country house and park in Budby, Nottinghamshire, some 2 miles (4 km) north of Ollerton. It is one of four neighbouring country houses and estates in the Dukeries in north Nottinghamshire all occupied by duk ...
, The former Clumber House, Welbeck Abbey
Welbeck Abbey is an English country house near the village of Welbeck in the Bassetlaw District of Nottinghamshire. It was the site of a monastery belonging to the Premonstratensian order, and after the Dissolution of the Monasteries a residen ...
and Worksop Manor
Worksop Manor is an 18th-century country house in Bassetlaw, Nottinghamshire. It stands in one of the four contiguous estates in the Dukeries area of Nottinghamshire. Traditionally, the Lord of the Manor of Worksop may assist a British mona ...
. These estates became known as the Dukeries
The Dukeries is an area of the county of Nottinghamshire so called because it contained four ducal seats. It is south of Worksop, which has been called its "gateway". The area was included within the ancient Sherwood Forest
Sherwood Fo ...
. Newstead Abbey
Newstead Abbey, in Nottinghamshire, England, was formerly an Augustinian priory. Converted to a domestic home following the Dissolution of the Monasteries, it is now best known as the ancestral home of Lord Byron. The Abbey is on the national ...
was converted into a country House and Rufford Abbey
Rufford Abbey is a country estate in Rufford, Nottinghamshire, England, two miles (4 km) south of Ollerton. Originally a Cistercian abbey, it was converted to a country house in the 16th century after Henry VIII’s dissolution of the ...
was partially demolished and converted into a country House.
250px, King John's Palace, Kings Clipstone
Mansfield
Mansfield is a market town and the administrative centre of the Mansfield District in Nottinghamshire, England. It is the largest town in the wider Mansfield Urban Area and the second largest settlement in Nottinghamshire (following the city ...
anciently became the pre-eminent in importance among the towns of the forest.William Horner Groves, The History of Mansfield, (1894) retrieved on the 8th April 2023
Geology
Sherwood Forest is established over an area underlain by thePermian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years, from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.902 Mya. It is the s ...
and Triassic
The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is t ...
age New Red Sandstone
The New Red Sandstone, chiefly in United Kingdom, British geology, is composed of beds of red sandstone and associated rocks laid down throughout the Permian (300 million years ago) to the end of the Triassic (about 200 million years a ...
. The larger part of the Forest is found across the outcrop of pebbly sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
s known as the Chester Formation. The regional dip is a gentle one to the east, hence younger rocks are found in that direction and older ones exposed to the west. The local stratigraphy
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers (strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks.
Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithost ...
is (uppermost/youngest at top):
*Mercia Mudstone Group
The Mercia Mudstone Group is an early Triassic lithostratigraphy, lithostratigraphic group (stratigraphy), group (a sequence of rock strata) which is widespread in Britain, especially in the English Midlands—the name is derived from the ancient ...
**Tarporley Siltstone Formation (siltstone
Siltstone, also known as aleurolite, is a clastic sedimentary rock that is composed mostly of silt. It is a form of mudrock with a low clay mineral content, which can be distinguished from shale by its lack of fissility.
Although its permeabil ...
s, mudstone
Mudstone, a type of mudrock, is a fine-grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Mudstone is distinguished from ''shale'' by its lack of fissility.Blatt, H., and R.J. Tracy, 1996, ''Petrology.'' New York, New York, ...
s and sandstones)
***including Retford Member (mudstones)
*Sherwood Sandstone Group
The Sherwood Sandstone Group is a Triassic lithostratigraphic group (a sequence of rock strata) which is widespread in Britain, especially in the English Midlands. The name is derived from Sherwood Forest in Nottinghamshire which is underlain by ...
**Chester Formation (pebbly sandstones)
**Lenton Sandstone Formation
**Edlington Formation (mudstones and sandstones)
The sandstone is an aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing material, consisting of permeability (Earth sciences), permeable or fractured rock, or of unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Aquifers vary greatly in their characteristics. The s ...
providing a local water supply. Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), as well as the current and most recent of the twelve periods of the ...
deposits include river sands and gravels, river terrace deposits and some scattered mid-Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
glacial till
image:Geschiebemergel.JPG, Closeup of glacial till. Note that the larger grains (pebbles and gravel) in the till are completely surrounded by the matrix of finer material (silt and sand), and this characteristic, known as ''matrix support'', is d ...
. There are 41 local geodiversity sites within the Sherwood NCA; these are largely quarries and river sections.
Management and conservation
The Sherwood Forest Trust is a smallcharity
Charity may refer to:
Common meanings
* Charitable organization or charity, a non-profit organization whose primary objectives are philanthropy and social well-being of persons
* Charity (practice), the practice of being benevolent, giving and sha ...
that covers the ancient royal boundary and current national character area
A National Character Area (NCA) is a natural subdivision of England based on a combination of landscape, biodiversity, geodiversity and economic activity. There are 159 National Character Areas and they follow natural, rather than administrative, b ...
of Sherwood Forest. Its aims are based on conservation, heritage and communities but also include tourism and the economy.
Nottinghamshire County Council and Forestry England
Forestry England is a division of the Forestry Commission, responsible for managing and promoting publicly owned forests in England.
Forest Enterprise, the precursor to Forestry England, was originally formed as a Great Britain-wide organizati ...
jointly manage the ancient remnant of forest north of the village of Edwinstowe, providing walks, footpaths and a host of other activities.
This central core of ancient Sherwood is a Site of Special Scientific Interest
A Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) in Great Britain, or an Area of Special Scientific Interest (ASSI) in the Isle of Man and Northern Ireland, is a conservation designation denoting a protected area in the United Kingdom and Isle ...
(SSSI) called Birklands and Bilhaugh, NNR and Special Area of Conservation
A special area of conservation (SAC) is defined in the European Union's Habitats Directive (92/43/EEC), also known as the ''Directive on the Conservation of Natural Habitats and of Wild Fauna and Flora''. They are to protect the 220 habitats and ap ...
(SAC). It is a very important site for ancient oaks, wood pasture, invertebrates and fungi, as well as being linked to the legends of Robin Hood.
 During the
During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
parts of Sherwood Forest were used extensively by the military for ammunition stores, POW camp
A prisoner-of-war camp (often abbreviated as POW camp) is a site for the containment of enemy fighters captured as prisoners of war by a belligerent power in time of war.
There are significant differences among POW camps, internment camps, an ...
s and training areas. Oil was produced at Eakring
Eakring is a village and civil parish in the Newark and Sherwood district of Nottinghamshire, England. Its population at the 2011 census was 419, and this increased to 440 residents for the 2021 census. There was sizeable oil production there i ...
. After the war large ammunition dumps were abandoned in the forest and were not cleared until 1952, with at least 46,000 tons of ammunition in them.
 Part of the forest was opened to the public as a
Part of the forest was opened to the public as a country park
A country park is a natural area designated for people to visit and enjoy recreation in a countryside environment.
United Kingdom
History
In the United Kingdom, the term ''country park'' has a specific meaning. There are around 250 designated c ...
in 1969 by Nottinghamshire County Council, which manages a small part of the forest under lease from the Thoresby Estate. In 2002 a portion of Sherwood Forest was designated a national nature reserve by English Nature
English Nature was the Executive agency, United Kingdom government agency that promoted the Conservation (ethic), conservation of wildlife, geology and wild places throughout England between 1990 and 2006. It was a non-departmental public body ...
. In 2007 Natural England
Natural England is a non-departmental public body in the United Kingdom sponsored by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. It is responsible for ensuring that England's natural environment, including its land, flora and fauna, ...
officially incorporated the Budby South Forest, Nottinghamshire's largest area of dry lowland heath, into the Nature Reserve, nearly doubling its size from .
A new Sherwood Forest Visitor Centre was authorised in 2015. In August 2018 the RSPB
The Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB) is a Charitable_organization#United_Kingdom, charitable organisation registered in Charity Commission for England and Wales, England and Wales and in Office of the Scottish Charity Regulator, ...
opened the new development with a shop and café, having been granted permission to manage the woods in 2015. Part of an agreement with Natural England was that the land where the existing 1970s visitor centre was located would be restored to wood pasture.
Some portions of the forest retain many very old oaks, especially in the portion known as the Dukeries
The Dukeries is an area of the county of Nottinghamshire so called because it contained four ducal seats. It is south of Worksop, which has been called its "gateway". The area was included within the ancient Sherwood Forest.
History
In the 17 ...
, south of the town of Worksop
Worksop ( ) is a market town in the Bassetlaw District in Nottinghamshire, England. It is located south of Doncaster, south-east of Sheffield and north of Nottingham. Located close to Nottinghamshire's borders with South Yorkshire and Derbys ...
, which was so called because it used to contain four ducal residences, as well as a number of other country estates.
The River Idle
The River Idle is a river in Nottinghamshire, England, formed by the confluence of the River Maun and the River Meden near Markham Moor. It flows north from its source through Retford and Bawtry before joining the River Trent at West Stockwi ...
, a tributary of the Trent, is formed in Sherwood Forest from the confluence of several minor streams.
Tourism
Sherwood attracts around 350,000 tourists annually, many from other countries. Each August the nature reserve hosts a week-long Robin Hood Festival. This event recreates a medieval atmosphere and features the major characters from the Robin Hood legend. The week's entertainment includesjoust
Jousting is a medieval and renaissance martial game or hastilude between two combatants either on horse or on foot. The joust became an iconic characteristic of the knight in Romantic medievalism.
The term is derived from Old French , ultim ...
ers and strolling players dressed in medieval attire, in addition to a medieval encampment complete with jester
A jester, also known as joker, court jester, or fool, was a member of the household of a nobleman or a monarch kept to entertain guests at the royal court. Jesters were also travelling performers who entertained common folk at fairs and town ma ...
s, musicians, rat-catcher
A rat-catcher is a person who kills or captures rats as a professional form of pest control. Keeping the rat population under control was practiced in Europe to prevent the spread of diseases, most notoriously the Black Death, and to prevent dam ...
s, alchemists
Alchemy (from the Arabic word , ) is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practised in China, India, the Muslim world, and Europe. In its Western form, alchemy is first ...
and fire eater
Fire eating is the act of putting a flaming object into the mouth and extinguishing it. A fire eater can be an entertainer, a street performer, part of a sideshow or a circus act but has also been part of spiritual tradition in India.
Physi ...
s. 200px, Sherwood Forest Art and Craft Centre
The Sherwood Forest Art and Craft Centre is in the former coach house and stables of Edwinstowe Hall. The centre contains art studios and a cafe and hosts special events, including craft demonstrations and exhibitions.
Other tourist destinations nearby
Thoresby Hall
Thoresby Hall is a 19th-century country house and park in Budby, Nottinghamshire, some 2 miles (4 km) north of Ollerton. It is one of four neighbouring country houses and estates in the Dukeries in north Nottinghamshire all occupied by duk ...
, and park
200px, Thoresby Hall
Rufford Abbey
Rufford Abbey is a country estate in Rufford, Nottinghamshire, England, two miles (4 km) south of Ollerton. Originally a Cistercian abbey, it was converted to a country house in the 16th century after Henry VIII’s dissolution of the ...
country park. Rufford Abbey is owned by English Heritage
English Heritage (officially the English Heritage Trust) is a charity that manages over 400 historic monuments, buildings and places. These include prehistoric sites, a battlefield, medieval castles, Roman forts, historic industrial sites, Lis ...
with the park managed by Parkwood Outdoors.
left, 200px, Rufford Abbey
Clumber Park
Clumber Park is a country park in The Dukeries near Worksop in the civil parish of Clumber and Hardwick, Nottinghamshire, England. The estate, which was the seat of the Earl of Lincoln, Pelham-Clintons, Dukes of Newcastle, was purchased by the Na ...
is a former estate of Clumber House. The park is owned by the National Trust
The National Trust () is a heritage and nature conservation charity and membership organisation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland.
The Trust was founded in 1895 by Octavia Hill, Sir Robert Hunter and Hardwicke Rawnsley to "promote the ...
.
200px, Clumber Park
Sherwood Pines Forest Park
Sherwood Pines Forest Park is a forest park located near the village of Kings Clipstone, Nottinghamshire, England. Originally called Clipstone Heath, it was acquired by Forestry England in 1925 and planted with trees in response to a wood shortag ...
which also houses a Go Ape
Go Ape! is an outdoor adventure company which runs tree top ropes courses under the names Tree Top Challenge, Tree Top Adventure and Zip Trekking, as well as ground-based Forest Segway Safaris, at locations across the United Kingdom and the United ...
site. Adjacent is Center Parcs UK and Ireland
Center Parcs UK and Ireland (formerly Center Parcs UK) is a short-break holiday company that operates six holiday villages in the United Kingdom and Republic of Ireland, with each covering about of woodland. The company's first village opened ...
Sherwood Forest.
Nearest towns/cities to Sherwood Forest
Worksop
Worksop ( ) is a market town in the Bassetlaw District in Nottinghamshire, England. It is located south of Doncaster, south-east of Sheffield and north of Nottingham. Located close to Nottinghamshire's borders with South Yorkshire and Derbys ...
Southwell, Nottinghamshire
Southwell ( , ) is a minster (church), minster and market town, and a civil parish, in the district of Newark and Sherwood in Nottinghamshire, England. It is home to the Listed building, grade-I listed Southwell Minster, the cathedral of the An ...
200px, Southwell Minster
Mansfield
Mansfield is a market town and the administrative centre of the Mansfield District in Nottinghamshire, England. It is the largest town in the wider Mansfield Urban Area and the second largest settlement in Nottinghamshire (following the city ...
Southwell
Newark on Trent
Newark-on-Trent () or Newark is a market town and civil parish in the Newark and Sherwood district in Nottinghamshire, England. It is on the River Trent, and was historically a major inland port. The A1 road (Great Britain), A1 road bypasses th ...
Nottingham
Nottingham ( , East Midlands English, locally ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area in Nottinghamshire, East Midlands, England. It is located south-east of Sheffield and nor ...
Major Oak
Sherwood Forest is home to theMajor Oak
The Major Oak is a large English oak (''Quercus robur'') near the village of Edwinstowe in the midst of Sherwood Forest, Nottinghamshire, England. According to local folklore, it was Robin Hood's shelter where he and his Merry Men slept. It we ...
, an oak
An oak is a hardwood tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' of the beech family. They have spirally arranged leaves, often with lobed edges, and a nut called an acorn, borne within a cup. The genus is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisp ...
tree between 800 and 1,000 years old, and since the Victorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the reign of Queen Victoria, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. Slightly different definitions are sometimes used. The era followed the ...
, its limbs have been partially supported by scaffolding. The Major Oak was identified by Major Hayman Rooke
Major Hayman Rooke (1723–1806) was an English antiquarian and British Army soldier who discovered the Major Oak tree in Sherwood Forest and two Roman Villas near Mansfield Woodhouse, Nottinghamshire. The Major Oak is named after him.
Bio ...
in 1790. It is believed that the Major Oak took the name of Major Hayman Rooke
Major Hayman Rooke (1723–1806) was an English antiquarian and British Army soldier who discovered the Major Oak tree in Sherwood Forest and two Roman Villas near Mansfield Woodhouse, Nottinghamshire. The Major Oak is named after him.
Bio ...
. The Major Oak used to be named the Cockpen Tree, after the cockfighting that once took place beneath it.
Samplings of the Major Oak have been planted in the US Ambassadors Winfield House
Winfield House is an English townhouse in Regent's Park, central London and the official residence of the United States Ambassador to the United Kingdom (formally, ambassador to the Court of St. James's). The grounds are , the second largest ...
in London.
The Major Oak was featured on the 2005 BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) is a British public service broadcaster headquartered at Broadcasting House in London, England. Originally established in 1922 as the British Broadcasting Company, it evolved into its current sta ...
TV programme ''Seven Natural Wonders
''Seven Natural Wonders'' is a television series that was broadcast on BBC Two
BBC Two is a British free-to-air Public service broadcasting in the United Kingdom, public broadcast television channel owned and operated by the BBC. It is t ...
'' as one of the natural wonders of the Midlands
The Midlands is the central region of England, to the south of Northern England, to the north of southern England, to the east of Wales, and to the west of the North Sea. The Midlands comprises the ceremonial counties of Derbyshire, Herefor ...
.
Parliament Oak
TheParliament Oak
The Parliament Oak is a veteran tree in Sherwood Forest. It is reputed to have been the site for Wikt:impromptu, impromptu-parliaments held by John of England, King John and Edward I. In the 19th century the tree was propped-up by William Benti ...
is situated in Sherwood Forest near Market Warsop
Market Warsop is a town within the civil parish of Warsop in Mansfield District, Nottinghamshire, England, on the outskirts of the remnants of Sherwood Forest.OS Explorer Map 270: Sherwood Forest: (1:25 000): The adjacent villages in the parish ...
.
It is reputed that King John in 1212 and King Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots (Latin: Malleus Scotorum), was King of England from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he was Lord of Ireland, and from 1254 ...
in 1290 had impromptu parliaments at the tree.

Thynghowe
Thynghowe
Thynghowe was an important Viking Age open-air assembly place or , located at Sherwood Forest, in Nottinghamshire, England. It was lost to history until its rediscovery in 2005 by the husband and wife team of Stuart Reddish and Lynda Mallett, lo ...
, an important Danelaw
The Danelaw (, ; ; ) was the part of History of Anglo-Saxon England, England between the late ninth century and the Norman Conquest under Anglo-Saxon rule in which Danes (tribe), Danish laws applied. The Danelaw originated in the conquest and oc ...
meeting place where people came to resolve disputes and settle issues, was lost to history until its rediscovery in 2005–06 by local history enthusiasts amidst the old oaks of an area known as the Birklands. Experts believe it may also yield clues about the boundary of the ancient Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced t ...
kingdoms of Mercia
Mercia (, was one of the principal kingdoms founded at the end of Sub-Roman Britain; the area was settled by Anglo-Saxons in an era called the Heptarchy. It was centred on the River Trent and its tributaries, in a region now known as the Midlan ...
and Northumbria
Northumbria () was an early medieval Heptarchy, kingdom in what is now Northern England and Scottish Lowlands, South Scotland.
The name derives from the Old English meaning "the people or province north of the Humber", as opposed to the Sout ...
.
English Heritage
English Heritage (officially the English Heritage Trust) is a charity that manages over 400 historic monuments, buildings and places. These include prehistoric sites, a battlefield, medieval castles, Roman forts, historic industrial sites, Lis ...
inspected the site, confirming that it was known as ‘Thynghowe’ in 1334 and 1609.
Politics
The forest gives its name to theParliamentary constituency
An electoral (congressional, legislative, etc.) district, sometimes called a constituency, riding, or ward, is a geographical portion of a political unit, such as a country, state or province, city, or administrative region, created to provi ...
of Sherwood Forest
Sherwood Forest is the remnants of an ancient royal forest, Royal Forest in Nottinghamshire, within the East Midlands region in England. It has association with the legend of Robin Hood. The forest was proclaimed by William the Conqueror and ...
(formerly Sherwood before the 2023 Periodic Review of Westminster constituencies
The 2023 review of Westminster constituencies was the most recent cycle of the process to redraw the Constituencies of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, constituency map for the House of Commons of the United Kingdom. The new constituency b ...
). This is current represented by one member of parliament.
See also
* List of forests in the United Kingdom * List of ancient woods in England *Sherwood Foresters
The Sherwood Foresters (Nottinghamshire and Derbyshire Regiment) was a line infantry regiment of the British Army in existence for just under 90 years, from 1881 to 1970. In 1970, the regiment was amalgamated with the Worcestershire Regiment to ...
, a British Army
The British Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of the United Kingdom. the British Army comprises 73,847 regular full-time personnel, 4,127 Brigade of Gurkhas, Gurkhas, 25,742 Army Reserve (United Kingdom), volunteer reserve perso ...
regiment associated with Nottinghamshire
Nottinghamshire (; abbreviated ''Notts.'') is a ceremonial county in the East Midlands of England. The county is bordered by South Yorkshire to the north-west, Lincolnshire to the east, Leicestershire to the south, and Derbyshire to the west. Th ...
References
Further reading
*Bankes, Richard. ''Sherwood Forest in 1609: A Crown Survey'' ( Thoroton Society record series) *Conduit, Brian. ''Exploring Sherwood Forest'' *Fletcher, John. ''Ornament of Sherwood Forest from Ducal Estate to Public Park'' *Gray, Adrian. ''Sherwood Forest and the Dukeries'' (Phillimore) 2008 *Innes-Smith, Robert. ''The Dukeries & Sherwood Forest'' *''Sherwood Forest and the East Midlands Walks'' (Jarrold Pathfinder Guides) *Ottewell, David. ''Sherwood Forest in Old Photographs'' (Britain in Old Photographs) *Woodward, Guy H. and Woodward, Grace Steele. ''The Secrets of Sherwood Forest: Oil Production in England During World War II''. University of Oklahoma Press, 1973.External links
*Forestry England
Sherwood Forest Regeneration Plans
details current plans for the forest.
Official tourism website for Nottinghamshire and Sherwood Forest
{{Authority control Country parks in Nottinghamshire English royal forests Forests and woodlands of Nottinghamshire Nature reserves in Nottinghamshire Protected areas established in 1969 Protected areas established in 2002 Protected areas established in 2007 Tourist attractions in Nottinghamshire Edwinstowe