Bioimage informatics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bioimage informatics is a subfield of


 Subcellular location analysis was one of the initial problems in this field. In its supervised mode, the problem is to learn a classifier that can recognize images from the major cell
Subcellular location analysis was one of the initial problems in this field. In its supervised mode, the problem is to learn a classifier that can recognize images from the major cell
 High throughput screens using automated imaging technology (sometimes called
High throughput screens using automated imaging technology (sometimes called
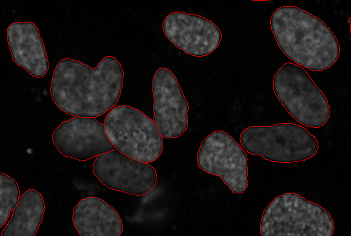 Segmentation of cells is an important sub-problem in many of the fields below (and sometimes useful on its own if the goal is only to obtain a cell count in a
Segmentation of cells is an important sub-problem in many of the fields below (and sometimes useful on its own if the goal is only to obtain a cell count in a
BrainAligner
is a software that has been used to automate the 3D deformable and nonlinear registration process using a reliable-landmark-matching strategy. It has been primarily used to generate more than 50,000 3D standardized fruitfly brain images at Janelia Farm of HHMI, with other applications including dragonfly and mice.
BMC Bioinformatics
has a section devoted to bioimage analysis, visualization and related applications. Other computational biology and bioinformatics journals also regularly publish bioimage informatics work. A European Union Cost action called NEUBIAS (network of european bioimage analysts) has been organizing annual conferences as well as bioimage analyst training schools and taggathons since 2017.
chunkflow
o
Icy
Visualization and analysis platforms such a
Vaa3D
have appeared in recent years and have been used in both large scale projects especially for neuroscience and desktop applications. Other researchers develop their own methods, typically based on a programming language with good computer vision support such as Python, C++, or
Mahotas
library for Python is one popular example. Although, examples of researcher developed methods in programming languages with less computer vision support as R exist (e.g. trackdem ).
Vaa3D: High-performance multi-dimensional image visualization and analysis
Bioformats
The Image file IO engine that supports dozens of formats
bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, in particular when the data sets are large and complex. As an interdisciplinary field of science, bioinformatics combin ...
and computational biology
Computational biology refers to the use of data analysis, mathematical modeling and computational simulations to understand biological systems and relationships. An intersection of computer science, biology, and big data, the field also has fo ...
. It focuses on the use of computational techniques to analyze bioimages, especially cellular and molecular images, at large scale and high throughput. The goal is to obtain useful knowledge out of complicated and heterogeneous image and related metadata.
Automated microscopes are able to collect large numbers of images with minimal intervention. This has led to a data explosion, which absolutely requires automatic processing. Additionally, and surprisingly, for several of these tasks, there is evidence that automated systems can perform better than humans. In addition, automated systems are unbiased, unlike human based analysis whose evaluation may (even unconsciously) be influenced by the desired outcome.
There has been an increasing focus on developing novel image processing
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimension ...
, computer vision
Computer vision is an Interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary scientific field that deals with how computers can gain high-level understanding from digital images or videos. From the perspective of engineering, it seeks to understand and automate t ...
, data mining, database and visualization techniques to extract, compare, search and manage the biological knowledge in these data-intensive problems.
Data Modalities
Several data collection systems and platforms are used, which require different methods to be handled optimally.Fluorescent Microscopy

Fluorescent microscopy
A fluorescence microscope is an optical microscope that uses fluorescence instead of, or in addition to, scattering, reflection, and attenuation or absorption, to study the properties of organic or inorganic substances. "Fluorescence micr ...
allows the direct visualization of molecules at the subcellular level, in both live and fixed cells. Molecules of interest are marked with either green fluorescent protein
The green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a protein that exhibits bright green fluorescence when exposed to light in the blue to ultraviolet range. The label ''GFP'' traditionally refers to the protein first isolated from the jellyfish '' Aeq ...
(GFP), another fluorescent protein, or a fluorescently-labeled antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and Viral disease, viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique m ...
. Several types of microscope are regularly used: widefield, confocal In geometry, confocal means having the same foci: confocal conic sections.
* For an optical cavity consisting of two mirrors, confocal means that they share their foci. If they are identical mirrors, their radius of curvature, ''R''mirror, equals ' ...
, or two-photon. Most microscopy system will also support the collection of time-series (movies).
In general, filters are used so that each dye is imaged separately (for example, a blue filter is used to image Hoechst, then rapidly switched to a green filter to image GFP). For consumption, the images are often displayed in false color
False color (or pseudo color) refers to a group of color Signal processing, rendering methods used to display images in color which were recorded in the visible spectrum, visible or non-visible parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. A false-c ...
by showing each channel in a different color, but these may not even be related to the original wavelengths used. In some cases, the original image could even have been acquired in non-visible wavelengths (infrared is common).
The choices at the image acquisition stage will influence the analysis and often require special processing. Confocal stacks will require 3D processing and widefield pseudo-stacks will often benefit from digital deconvolution to remove the out-of-focus light.
The advent of automated microscopes that can acquire many images automatically is one of the reasons why analysis cannot be done by eye (otherwise, annotation would rapidly become the research bottleneck). Using automated microscopes means that some images might be out-of-focus (automated focus finding systems may sometimes be incorrect), contain a small number of cells, or be filled with debris. Therefore, the images generated will be harder to analyse than images acquired by an operator as they would have chosen other locations to image and focus correctly. On the other hand, the operator might introduce an unconscious bias in his selection by choosing only the cells whose phenotype is most like the one expected before the experiment.
Histology

Histology
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures vi ...
is a microscopy application where tissue slices are stained and observed under the microscope (typically light microscope, but electron microscopy is also used).
When using a light microscope, unlike the case of fluorescent imaging, images are typically acquired using standard color camera-systems. This reflects partially the history of the field, where humans were often interpreting the images, but also the fact that the sample can be illuminated with white light and all light collected rather than having to excite fluorophores. When more than one dye is used, a necessary preprocessing step is to unmix the channels and recover an estimate of the pure dye-specific intensities.
It has been shown that the subcellular location of stained proteins can be identified from histology images.
If the goal is a medical diagnostic, then histology applications will often fall into the realm of digital pathology
Digital pathology is a sub-field of pathology that focuses on data management based on information generated from digitized specimen slides. Through the use of computer-based technology, digital pathology utilizes virtual microscopy. Glass slides ...
or automated tissue image analysis
Automated tissue image analysis or histopathology image analysis (HIMA) is a process by which computer-controlled automatic test equipment is used to evaluate tissue samples, using computations to derive quantitative measurements from an image to ...
, which are sister fields of bioimage informatics. The same computational techniques are often applicable, but the goals are medically- rather than research-oriented.
Important Problems
Subcellular Location Analysis
 Subcellular location analysis was one of the initial problems in this field. In its supervised mode, the problem is to learn a classifier that can recognize images from the major cell
Subcellular location analysis was one of the initial problems in this field. In its supervised mode, the problem is to learn a classifier that can recognize images from the major cell organelles
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' th ...
based on images.
Methods used are based on machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence.
Machine ...
, building a discriminative classifier based on numeric features computed from the image. Features are either generic features from computer vision
Computer vision is an Interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary scientific field that deals with how computers can gain high-level understanding from digital images or videos. From the perspective of engineering, it seeks to understand and automate t ...
, such as Haralick texture features or features specially designed to capture biological factors (e.g., co-localization with a nuclear marker being a typical example).
For the basic problem of identifying organelles, very high accuracy values can be obtained, including better than ? results. These methods are useful in basic cell biology research, but have also been applied to the discovery of proteins whose location changes in cancer cells.
However, classification into organelles is a limited form of the problem as many proteins will localize to multiple locations simultaneously (mixed patterns) and many patterns can be distinguished even though they are not different membrane-bound components. There are several unsolved problems in this area and research is ongoing.
High-Content Screening
 High throughput screens using automated imaging technology (sometimes called
High throughput screens using automated imaging technology (sometimes called high-content screening High-content screening (HCS), also known as high-content analysis (HCA) or cellomics, is a method that is used in biological research and drug discovery to identify substances such as small molecules, peptides, or RNAi that alter the phenotype of ...
) have become a standard method for both drug discovery and basic biological research. Using multi-well plates, robotics, and automated microscopy, the same assay can be applied to a large library of possible reagents (typically either small molecules
Within the fields of molecular biology and pharmacology, a small molecule or micromolecule is a low molecular weight (≤ 1000 daltons) organic compound that may regulate a biological process, with a size on the order of 1 nm. Many drugs are ...
or RNAi
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules are involved in sequence-specific suppression of gene expression by double-stranded RNA, through translational or transcriptional repression. Historically, RNAi was known by o ...
) very rapidly, obtaining thousands of images in a short amount of time. Due to the high volume of data generated, automatic image analysis is a necessity.
When positive and negative controls are available, the problem can be approached as a classification problem and the same techniques of feature computation and classification that are used for subcellular location analysis can be applied.
Segmentation
 Segmentation of cells is an important sub-problem in many of the fields below (and sometimes useful on its own if the goal is only to obtain a cell count in a
Segmentation of cells is an important sub-problem in many of the fields below (and sometimes useful on its own if the goal is only to obtain a cell count in a viability assay
A viability assay is an assay that is created to determine the ability of organs, cells or tissues to maintain or recover a state of survival. Viability can be distinguished from the all-or-nothing states of life and death by the use of a quan ...
). The goal is to identify the boundaries of cells in a multi-cell image. This allows for processing each cell individually to measure parameters. In 3D data, segmentation must be performed in 3D space.
As the imaging of a nuclear marker is common across many images, a widely used protocol is to segment the nuclei. This can be useful by itself if nuclear measurements are needed or it can serve to seed a watershed which extends the segmentation to the whole image.
All major segmentation methods have been reported on cell images, from simple thresholding to level set methods. Because there are multiple image modalities and different cell types, each of which implies different tradeoffs, there is no single accepted solution for this problem.
Cell image segmentation as an important procedure is often used to study gene expression and colocalization relationship etc. of individual cells. In such cases of single-cell analysis it is often needed to uniquely determine the identities of cells while segmenting the cells. Such a recognition task is often non-trivial computationally. For model organisms such as C. elegans that have well-defined cell lineages, it is possible to explicitly recognize the cell identities via image analysis, by combining both image segmentation and pattern recognition methods. Simultaneous segmentation and recognition of cells has also been proposed as a more accurate solution for this problem when an "atlas" or other prior information of cells is available. Since gene expression at single cell resolution can be obtained using these types of imaging based approaches, it is possible to combine these methods with other single cell gene expression quantification methods such as RNAseq.
Tracking
Tracking is another traditional image processing problem which appears in bioimage informatics. The problem is to relate objects that appear in subsequent frames of a film. As with segmentation, the problem can be posed in both two- and three-dimensional forms. In the case of fluorescent imaging, tracking must often be performed on very low contrast images. As obtaining high contrast is done by shining more light which damages the sample and destroys the dye, illumination is kept at a minimum. It is often useful to think of a photon budget: the number of photons that can be used for imaging before the damage to the sample is so great that data can no longer be trusted. Therefore, if high contrast images are to be obtained, then only a few frames can be used; while for long movies, each frame will be of very low contrast.Registration
When image data samples of different natures, such as those corresponding to different labeling methods, different individuals, samples at different time points, etc. are considered, images often need to be registered for better comparison. One example is as time-course data is collected, images in subsequent frames must often beregistered
Registered may refer to:
* Registered mail, letters, packets or other postal documents considered valuable and in need of a chain of custody
* Registered trademark symbol, symbol ® that provides notice that the preceding is a trademark or service ...
so that minor shifts in the camera position can be corrected for. Another example is that when many images of a model animal (e.g. C. elegans
''Caenorhabditis elegans'' () is a free-living transparent nematode about 1 mm in length that lives in temperate soil environments. It is the type species of its genus. The name is a blend of the Greek ''caeno-'' (recent), ''rhabditis'' ( ...
or Drosophila brain or a mouse brain
The mouse brain refers to the brain of Mus musculus. Various brain atlases exist.
For reasons of reproducibility, genetically characterized, stable strains like C57BL/6 were chosen to produce high-resolution images and databases. Well known onl ...
) are collected, there is often a substantial need to register these images to compare their patterns (e.g. those correspond to the same or different neuron population, those share or differ in the gene expression, etc.).
Medical image registration software packages were early attempts to be used for the microscopic image registration applications. However, due to the often much larger image file size and a much bigger number of specimens in the experiments, in many cases it is needed to develop new 3D image registration software. ThBrainAligner
is a software that has been used to automate the 3D deformable and nonlinear registration process using a reliable-landmark-matching strategy. It has been primarily used to generate more than 50,000 3D standardized fruitfly brain images at Janelia Farm of HHMI, with other applications including dragonfly and mice.
Important Venues
A consortium of scientists from universities and research institutes have organized annual meetings on bioimage informatics since 2005. TheISMB
Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology (ISMB) is an annual academic conference on the subjects of bioinformatics and computational biology organised by the International Society for Computational Biology (ISCB). The principal focus of the co ...
conference has had a ''Bioimaging & Data Visualization'' track since 2010. The journal Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, in particular when the data sets are large and complex. As an interdisciplinary field of science, bioinformatics combin ...
also introduced a ''Bioimage Informatics'' track in 2012. The OpenAccess journaBMC Bioinformatics
has a section devoted to bioimage analysis, visualization and related applications. Other computational biology and bioinformatics journals also regularly publish bioimage informatics work. A European Union Cost action called NEUBIAS (network of european bioimage analysts) has been organizing annual conferences as well as bioimage analyst training schools and taggathons since 2017.
Software
There are several packages that make bioimage informatics methods available through a graphical user interface such asImageJ
ImageJ is a Java-based image processing program developed at the National Institutes of Health and the Laboratory for Optical and Computational Instrumentation (LOCI, University of Wisconsin). Its first version, ImageJ 1.x, is developed in the publ ...
, FIJI, CellProfiler
CellProfiler is free, open-source software designed to enable biologists without training in computer vision or programming to quantitatively measure phenotypes from thousands of images automatically. Advanced algorithms for image analysis are ava ...
chunkflow
o
Icy
Visualization and analysis platforms such a
Vaa3D
have appeared in recent years and have been used in both large scale projects especially for neuroscience and desktop applications. Other researchers develop their own methods, typically based on a programming language with good computer vision support such as Python, C++, or
MATLAB
MATLAB (an abbreviation of "MATrix LABoratory") is a proprietary multi-paradigm programming language and numeric computing environment developed by MathWorks. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementa ...
. ThMahotas
library for Python is one popular example. Although, examples of researcher developed methods in programming languages with less computer vision support as R exist (e.g. trackdem ).
See also
*Focus stacking
Focus stacking (also known as focal plane merging and z-stacking or focus blending) is a digital image processing technique which combines multiple images taken at different focus distances to give a resulting image with a greater depth of f ...
The technique of combining multiple images with difference focus distances into one.
* High-content screening High-content screening (HCS), also known as high-content analysis (HCA) or cellomics, is a method that is used in biological research and drug discovery to identify substances such as small molecules, peptides, or RNAi that alter the phenotype of ...
* digital pathology
Digital pathology is a sub-field of pathology that focuses on data management based on information generated from digitized specimen slides. Through the use of computer-based technology, digital pathology utilizes virtual microscopy. Glass slides ...
* Medical imaging
External links
Vaa3D: High-performance multi-dimensional image visualization and analysis
Bioformats
The Image file IO engine that supports dozens of formats
References
{{Informatics Bioinformatics