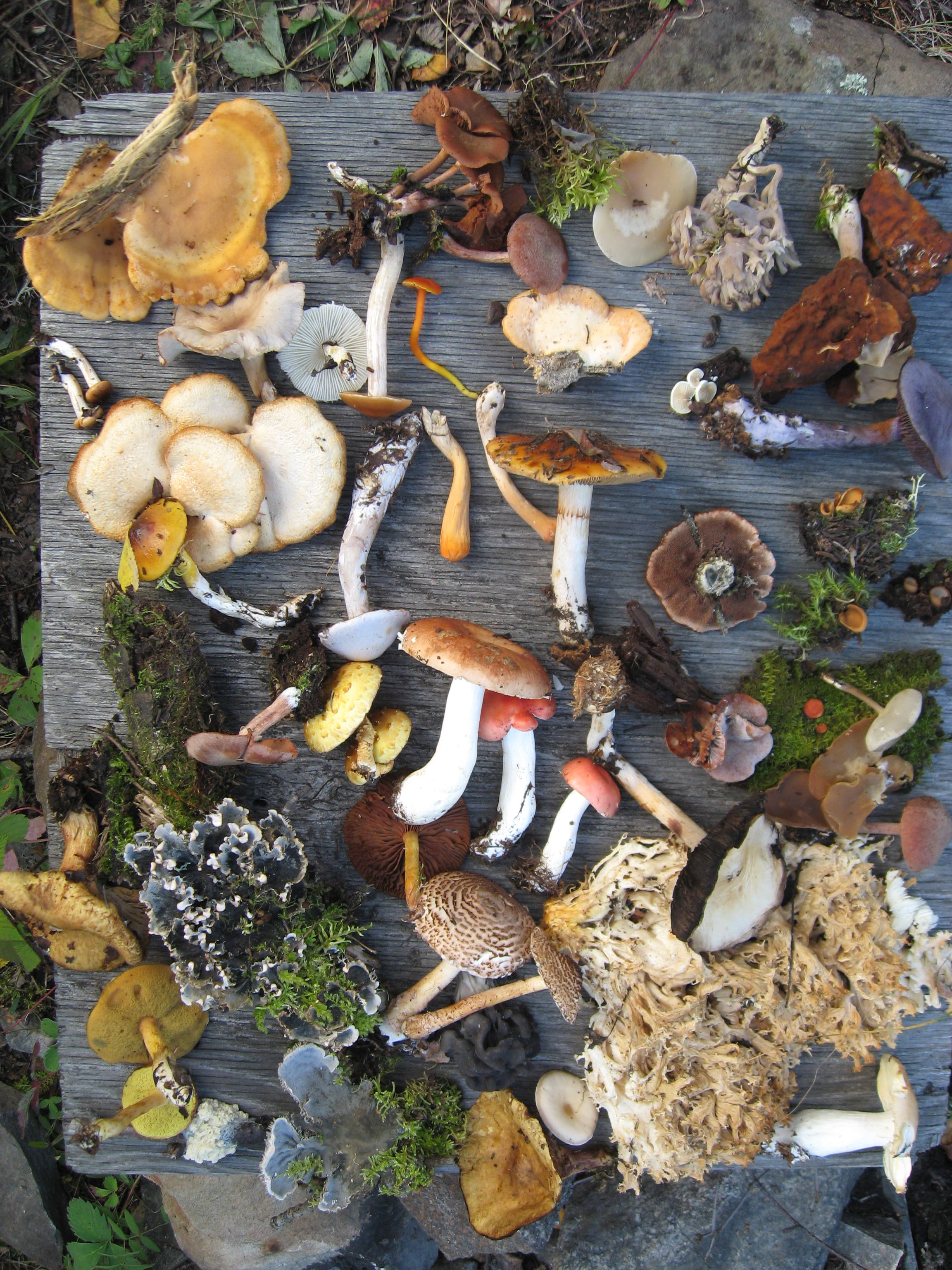

Biodiversity is the variability of
life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example
genetic variability
Genetic variability is either the presence of, or the generation of, genetic differences. It is defined as "the formation of individuals differing in genotype, or the presence of genotypically different individuals, in contrast to environmentally ...
,
species diversity,
ecosystem diversity and
phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ...
diversity.
Diversity is not distributed evenly on
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
. It is greater in the
tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
as a result of the warm
climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteoro ...
and high
primary productivity
Primary or primaries may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and labels
* Primary (band), from Australia
* Primary (musician), hip hop musician and record producer from South Korea
* Primary Music, Israeli record label
Works
* ...
in the region near the
equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumferen ...
. Tropical forest ecosystems cover less than one-fifth of Earth's terrestrial area and contain about 50% of the world's species. There are
latitudinal gradients in species diversity for both marine and terrestrial taxa.
Since
life began on Earth, six major
mass extinctions and several minor events have led to large and sudden drops in biodiversity. The
Phanerozoic
The Phanerozoic is the current and the latest of the four eon (geology), geologic eons in the Earth's geologic time scale, covering the time period from 538.8 million years ago to the present. It is the eon during which abundant animal and ...
aeon (the last 540 million years) marked a rapid growth in biodiversity via the
Cambrian explosion. In this period, the majority of
multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell (biology), cell, unlike unicellular organisms. All species of animals, Embryophyte, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organism ...
phyla
Phyla, the plural of ''phylum'', may refer to:
* Phylum, a biological taxon between Kingdom and Class
* by analogy, in linguistics, a large division of possibly related languages, or a major language family which is not subordinate to another
Phy ...
first appeared. The next 400 million years included repeated, massive biodiversity losses. Those events have been classified as
mass extinction events. In the
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
,
rainforest collapse may have led to a great loss of
plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
and
animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
life. The
Permian–Triassic extinction event
The Permian–Triassic extinction event (also known as the P–T extinction event, the Late Permian extinction event, the Latest Permian extinction event, the End-Permian extinction event, and colloquially as the Great Dying,) was an extinction ...
, 251 million years ago, was the worst; vertebrate recovery took 30 million years.
Human activities have led to an ongoing
biodiversity loss
Biodiversity loss happens when plant or animal species disappear completely from Earth (extinction) or when there is a decrease or disappearance of species in a specific area. Biodiversity loss means that there is a reduction in Biodiversity, b ...
and an accompanying loss of
genetic diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. It ranges widely, from the number of species to differences within species, and can be correlated to the span of survival for a species. It is d ...
. This process is often referred to as
Holocene extinction
The Holocene extinction, also referred to as the Anthropocene extinction or the sixth mass extinction, is an ongoing extinction event caused exclusively by human activities during the Holocene epoch. This extinction event spans numerous families ...
, or ''sixth mass extinction''. For example, it was estimated in 2007 that up to 30% of all species will be extinct by 2050.
for farming is a key reason why biodiversity is decreasing today.
Climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
also plays a role.
This can be seen for example in the
effects of climate change on biomes
Climate change is already now altering biomes, adversely affecting terrestrial and marine ecosystems. Climate change represents long-term changes in temperature and average weather patterns. This leads to a substantial increase in both the frequen ...
. This anthropogenic extinction may have started toward the end of the
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
, as some studies suggest that the
megafaunal extinction event that took place around the end of the last ice age partly resulted from overhunting.
Definitions

Biologists most often define ''biodiversity'' as the "totality of
gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
s,
species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
and
ecosystems
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
of a region".
An advantage of this definition is that it presents a unified view of the traditional types of biological variety previously identified:
*
taxonomic diversity (usually measured at the species diversity level)
*
ecological diversity (often viewed from the perspective of
ecosystem diversity)
* morphological diversity (which stems from
genetic diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. It ranges widely, from the number of species to differences within species, and can be correlated to the span of survival for a species. It is d ...
and
molecular diversity)
*
functional diversity (which is a measure of the number of functionally disparate species within a population (e.g. different feeding mechanism, different motility, predator vs prey, etc.))
''Biodiversity'' is most commonly used to replace the more clearly-defined and long-established terms,
species diversity and
species richness. However, there is no concrete definition for biodiversity, as its definition continues to be reimagined and redefined. To give a couple examples, the
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) defined biodiversity in 2019 as "the variability that exists among living organisms (both within and between species) and the ecosystems of which they are part." The
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
updated their website’s definition of biodiversity to be the "variability among living organisms from all sources." Both these definitions, although broad, give a current understanding of what is meant by the term biodiversity.
Number of species
According to estimates by Mora et al. (2011), there are approximately 8.7 million terrestrial species and 2.2 million oceanic species. The authors note that these estimates are strongest for eukaryotic organisms and likely represent the lower bound of prokaryote diversity.
Other estimates include:
* 220,000
vascular plants, estimated using the species-area relation method
* 0.7–1 million marine species
* 10–30 million
insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, ...
s; (of some 0.9 million we know today)
* 5–10 million
bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
;
* 1.5-3 million
fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
, estimates based on data from the tropics, long-term non-tropical sites and molecular studies that have revealed
cryptic speciation. Some 0.075 million species of fungi had been documented by 2001;
* 1 million
mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods) of two large orders, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari. However, most recent genetic analyses do not recover the two as eac ...
s
* The number of
microbial
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from antiquity, with an early attestation in ...
species is not reliably known, but the
Global Ocean Sampling Expedition dramatically increased the estimates of genetic diversity by identifying an enormous number of new genes from near-surface
plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms that drift in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) but are unable to actively propel themselves against ocean current, currents (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are ca ...
samples at various marine locations, initially over the 2004–2006 period. The findings may eventually cause a significant change in the way science defines
species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
and other taxonomic categories.
Since the rate of extinction has increased, many extant species may become extinct before they are described. Not surprisingly, in the
Animalia
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
the most studied groups are
birds
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
and
mammals
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three middle e ...
, whereas
fishes
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed ...
and
arthropods
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
are the least studied animal groups.
Current biodiversity loss
During the last century, decreases in biodiversity have been increasingly observed. It was estimated in 2007 that up to 30% of all species will be extinct by 2050.
Of these, about one eighth of known plant species are threatened with
extinction
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
.
Estimates reach as high as 140,000 species per year (based on
Species-area theory). This figure indicates
unsustainable ecological practices, because few species emerge each year. The rate of species loss is greater now than at any time in human history, with extinctions occurring at rates hundreds of times higher than
background extinction rates.
and expected to still grow in the upcoming years.
As of 2012, some studies suggest that 25% of all mammal species could be extinct in 20 years.
In absolute terms, the planet has lost 58% of its biodiversity since 1970 according to a 2016 study by the World Wildlife Fund. The Living Planet Report 2014 claims that "the number of mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish across the globe is, on average, about half the size it was 40 years ago". Of that number, 39% accounts for the terrestrial wildlife gone, 39% for the marine wildlife gone and 76% for the freshwater wildlife gone. Biodiversity took the biggest hit in
Latin America
Latin America is the cultural region of the Americas where Romance languages are predominantly spoken, primarily Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese. Latin America is defined according to cultural identity, not geogr ...
, plummeting 83 percent. High-income countries showed a 10% increase in biodiversity, which was canceled out by a loss in low-income countries. This is despite the fact that high-income countries use five times the ecological resources of low-income countries, which was explained as a result of a process whereby wealthy nations are outsourcing
resource depletion
Resource depletion occurs when a natural resource is consumed faster than it can be replenished. The value of a resource depends on its availability in nature and the cost of extracting it. By the law of supply and demand, the Scarcity, scarcer ...
to poorer nations, which are suffering the greatest ecosystem losses.
A 2017 study published in ''
PLOS One'' found that the biomass of insect life in Germany had declined by three-quarters in the last 25 years. Dave Goulson of
Sussex University stated that their study suggested that humans "appear to be making vast tracts of land inhospitable to most forms of life, and are currently on course for ecological Armageddon. If we lose the insects then everything is going to collapse."
In 2020 the
World Wildlife Foundation published a report saying that "biodiversity is being destroyed at a rate unprecedented in human history". The report claims that 68% of the population of the examined species were destroyed in the years 1970 – 2016.
Of 70,000 monitored species, around 48% are experiencing population declines from human activity (in 2023), whereas only 3% have increasing populations.
Rates of
decline in biodiversity in the current
sixth mass extinction match or exceed rates of loss in the five previous
mass extinction events in the
fossil record
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
. Biodiversity loss is in fact "one of the most critical manifestations of the
Anthropocene
''Anthropocene'' is a term that has been used to refer to the period of time during which human impact on the environment, humanity has become a planetary force of change. It appears in scientific and social discourse, especially with respect to ...
" (since around the 1950s); the continued decline of biodiversity constitutes "an unprecedented threat" to the continued existence of human civilization.
The reduction is caused primarily by
human impacts, particularly
habitat destruction
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease ...
.
Since the
Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistory, prehistoric period during which Rock (geology), stone was widely used to make stone tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years and ended b ...
, species loss has accelerated above the average basal rate, driven by human activity. Estimates of species losses are at a rate 100–10,000 times as fast as is typical in the fossil record.
Loss of biodiversity results in the loss of
natural capital that supplies
ecosystem goods and services. Species today are being wiped out at a rate 100 to 1,000 times higher than baseline, and the rate of extinctions is increasing. This process destroys the resilience and adaptability of life on Earth.
In 2006, many species were formally classified as
rare or
endangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
or
threatened; moreover, scientists have estimated that millions more species are at risk which have not been formally recognized. About 40 percent of the 40,177 species assessed using the
IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is an inventory of the global conservation status and extinction risk of biological ...
criteria are now listed as threatened with
extinction
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
—a total of 16,119. As of late 2022 9251 species were considered part of the IUCN's
critically endangered
An IUCN Red List critically endangered (CR or sometimes CE) species is one that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as facing an extremely high risk of extinction in the wild. As of December 2023, of t ...
.
Numerous scientists and the
IPBES ''
'' assert that
human population growth and
overconsumption
Overconsumption describes a situation where consumers overuse their available goods and services to where they can't, or don't want to, replenish or reuse them. In microeconomics, this is the point where the marginal cost of a consumer is greater ...
are the primary factors in this decline. However, other scientists have criticized this finding and say that loss of habitat caused by "the growth of commodities for export" is the main driver. A 2025 study found that human activities are responsible for biodiversity loss across all species and ecosystems.
Some studies have however pointed out that habitat destruction for the expansion of agriculture and the
overexploitation
Overexploitation, also called overharvesting or ecological overshoot, refers to harvesting a renewable resource to the point of diminishing returns. Continued overexploitation can lead to the destruction of the resource, as it will be unable to ...
of wildlife are the more significant drivers of contemporary biodiversity loss, not
climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
.
Distribution
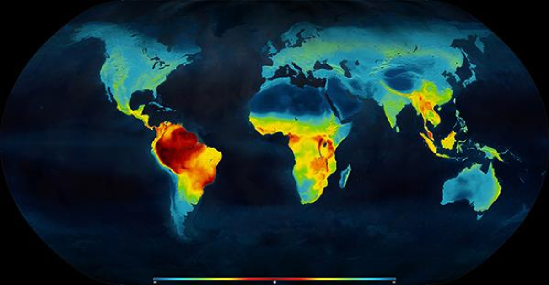
Biodiversity is not evenly distributed, rather it varies greatly across the globe as well as within regions and seasons. Among other factors, the diversity of all living things (
biota) depends on
temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
,
precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
,
altitude
Altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum (geodesy), datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context (e.g., aviation, geometr ...
,
soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by re ...
s,
geography
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding o ...
and the interactions between other species. The study of the spatial distribution of
organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
s, species and
ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
s, is the science of
biogeography
Biogeography is the study of the species distribution, distribution of species and ecosystems in geography, geographic space and through evolutionary history of life, geological time. Organisms and biological community (ecology), communities o ...
.
Diversity consistently measures higher in the
tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
and in other localized regions such as the
Cape Floristic Region
The Cape Floral Region is a floristic region located near the southern tip of South Africa. It is the only floristic region of the Cape Floristic Kingdom, and includes only one floristic province, known as the Cape Floristic Province.
The Cap ...
and lower in polar regions generally.
Rain forests that have had wet climates for a long time, such as
Yasuní National Park
Yasuní National Park () is a protected area comprising roughly between the Napo River, Napo and Curaray Rivers in Pastaza Province, Pastaza and Orellana Province, Orellana Provinces within Amazon basin, Amazonian Ecuador. The national park lie ...
in
Ecuador
Ecuador, officially the Republic of Ecuador, is a country in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west. It also includes the Galápagos Province which contain ...
, have particularly high biodiversity.
There is local biodiversity, which directly impacts daily life, affecting the availability of fresh water, food choices, and fuel sources for humans. Regional biodiversity includes habitats and ecosystems that synergizes and either overlaps or differs on a regional scale. National biodiversity within a country determines the ability for a country to thrive according to its habitats and ecosystems on a national scale. Also, within a country,
endangered species
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
are initially supported on a national level then internationally.
Ecotourism
Ecotourism is a form of nature-oriented tourism intended to contribute to the Ecological conservation, conservation of the natural environment, generally defined as being minimally impactful, and including providing both contributions to conserv ...
may be utilized to support the economy and encourages tourists to continue to visit and support species and ecosystems they visit, while they enjoy the available amenities provided. International biodiversity impacts global livelihood, food systems, and health. Problematic pollution, over consumption, and climate change can devastate international biodiversity. Nature-based solutions are a critical tool for a global resolution. Many species are in danger of becoming extinct and need world leaders to be proactive with the
Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework.
Terrestrial biodiversity is thought to be up to 25 times greater than ocean biodiversity. Forests harbour most of Earth's terrestrial biodiversity. The conservation of the world's biodiversity is thus utterly dependent on the way in which we interact with and use the world's forests.
[ Text was added from this source which has a Wikipedia-specific licence statement] A new method used in 2011, put the total number of species on Earth at 8.7 million, of which 2.1 million were estimated to live in the ocean.
However, this estimate seems to under-represent the diversity of microorganisms.
Forests provide habitats for 80 percent of amphibian
species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
, 75 percent of bird species and 68 percent of mammal species. About 60 percent of all vascular plants are found in tropical forests. Mangroves provide breeding grounds and nurseries for numerous species of fish and shellfish and help trap sediments that might otherwise adversely affect seagrass beds and coral reefs, which are habitats for many more marine species.
Forests span around 4 billion acres (nearly a third of the Earth's land mass) and are home to approximately 80% of the world's biodiversity. About 1 billion hectares are covered by primary forests. Over 700 million hectares of the world's woods are officially protected.
The biodiversity of forests varies considerably according to factors such as forest type, geography, climate and soils – in addition to human use.
Most forest habitats in temperate regions support relatively few animal and plant species and species that tend to have large geographical distributions, while the montane forests of Africa, South America and Southeast Asia and lowland forests of Australia, coastal Brazil, the Caribbean islands, Central America and insular Southeast Asia have many species with small geographical distributions.
Areas with dense human populations and intense agricultural land use, such as
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, parts of Bangladesh, China, India and North America, are less intact in terms of their biodiversity. Northern Africa, southern Australia, coastal Brazil, Madagascar and South Africa, are also identified as areas with striking losses in biodiversity intactness.
European forests in EU and non-EU nations comprise more than 30% of Europe's land mass (around 227 million hectares), representing an almost 10% growth since 1990.
Latitudinal gradients
Generally, there is an increase in biodiversity from the
poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
to the
tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
. Thus localities at lower
latitudes have more species than localities at higher
latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
s. This is often referred to as the latitudinal gradient in species diversity. Several ecological factors may contribute to the gradient, but the ultimate factor behind many of them is the greater mean temperature at the equator compared to that at the poles.
Even though terrestrial biodiversity declines from the equator to the poles,
some studies claim that this characteristic is unverified in
aquatic ecosystems, especially in
marine ecosystems. The latitudinal distribution of parasites does not appear to follow this rule.
Also, in terrestrial ecosystems the soil bacterial diversity has been shown to be highest in temperate climatic zones, and has been attributed to carbon inputs and habitat connectivity.
In 2016, an alternative hypothesis ("the
fractal
In mathematics, a fractal is a Shape, geometric shape containing detailed structure at arbitrarily small scales, usually having a fractal dimension strictly exceeding the topological dimension. Many fractals appear similar at various scale ...
biodiversity") was proposed to explain the biodiversity latitudinal gradient. In this study, the
species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
pool size and the fractal nature of ecosystems were combined to clarify some general patterns of this gradient. This hypothesis considers
temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
,
moisture
Moisture is the presence of a liquid, especially water, often in trace amounts. Moisture is defined as water in the adsorbed or absorbed phase. Small amounts of water may be found, for example, in the air (humidity), in foods, and in some comme ...
, and
net primary production (NPP) as the main variables of an ecosystem niche and as the axis of the ecological
hypervolume. In this way, it is possible to build fractal hyper volumes, whose
fractal dimension
In mathematics, a fractal dimension is a term invoked in the science of geometry to provide a rational statistical index of complexity detail in a pattern. A fractal pattern changes with the Scaling (geometry), scale at which it is measured.
It ...
rises to three moving towards the
equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumferen ...
.
Biodiversity Hotspots
A
biodiversity hotspot
A biodiversity hotspot is a ecoregion, biogeographic region with significant levels of biodiversity that is threatened by human habitation. Norman Myers wrote about the concept in two articles in ''The Environmentalist'' in 1988 and 1990, after ...
is a region with a high level of
endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
species that have experienced great
habitat loss
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease ...
. The term hotspot was introduced in 1988 by
Norman Myers.
While hotspots are spread all over the world, the majority are forest areas and most are located in the
tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
.
Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
's
Atlantic Forest is considered one such hotspot, containing roughly 20,000 plant species, 1,350 vertebrates and millions of insects, about half of which occur nowhere else.
The island of
Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
and
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
are also particularly notable.
Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuel ...
is characterized by high biodiversity, with the highest rate of species by area unit worldwide and it has the largest number of endemics (species that are not found naturally anywhere else) of any country. About 10% of the species of the Earth can be found in Colombia, including over 1,900 species of bird, more than in Europe and North America combined, Colombia has 10% of the world's mammals species, 14% of the amphibian species and 18% of the bird species of the world.
Madagascar dry deciduous forests and lowland rainforests possess a high ratio of
endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
.
Since the island separated from mainland
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
66 million years ago, many species and ecosystems have evolved independently.
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
's 17,000 islands cover and contain 10% of the world's
flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed with ...
s, 12% of mammals and 17% of
reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
s,
amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
s and
bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
s—along with nearly 240 million people. Many regions of high biodiversity and/or endemism arise from specialized
habitat
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ...
s which require unusual adaptations, for example,
alpine environments in high
mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher t ...
s, or
Northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54th parallel north, 54°N, or may be based on other ge ...
an peat
bog
A bog or bogland is a wetland that accumulates peat as a deposit of dead plant materials often mosses, typically sphagnum moss. It is one of the four main types of wetlands. Other names for bogs include mire, mosses, quagmire, and musk ...
s.
Accurately measuring differences in biodiversity can be difficult.
Selection bias
Selection bias is the bias introduced by the selection of individuals, groups, or data for analysis in such a way that proper randomization is not achieved, thereby failing to ensure that the sample obtained is representative of the population inte ...
amongst researchers may contribute to biased empirical research for modern estimates of biodiversity. In 1768, Rev.
Gilbert White succinctly observed of his
Selborne, Hampshire ''"all nature is so full, that that district produces the most variety which is the most examined."''
Evolution over geologic timeframes
Biodiversity is the result of 3.5 billion years of
evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, re ...
. The
origin of life
Abiogenesis is the natural process by which life arises from abiotic component, non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The prevailing scientific hypothesis is that the transition from non-living to organism, living entities on ...
has not been established by science, however, some evidence suggests that life may already have been well-established only a few hundred million years after the
formation of the Earth. Until approximately 2.5 billion years ago, all life consisted of
microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s –
archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
,
bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
, and
single-celled protozoan
Protozoa (: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a polyphyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic debris. Historically ...
s and
protist
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancest ...
s.
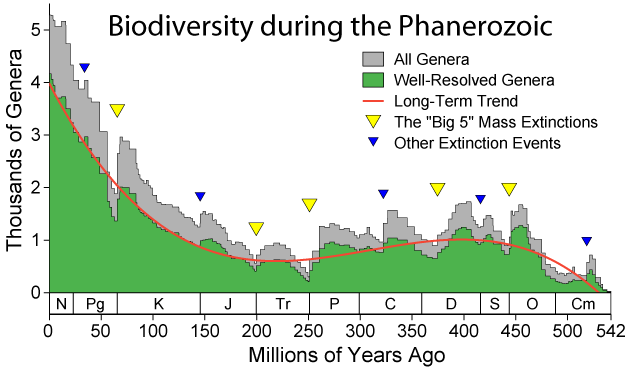
Biodiversity grew fast during the
Phanerozoic
The Phanerozoic is the current and the latest of the four eon (geology), geologic eons in the Earth's geologic time scale, covering the time period from 538.8 million years ago to the present. It is the eon during which abundant animal and ...
(the last 540 million years), especially during the so-called
Cambrian explosion—a period during which nearly every
phylum
In biology, a phylum (; : phyla) is a level of classification, or taxonomic rank, that is below Kingdom (biology), kingdom and above Class (biology), class. Traditionally, in botany the term division (taxonomy), division has been used instead ...
of
multicellular organism
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell (biology), cell, unlike unicellular organisms. All species of animals, Embryophyte, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organism ...
s first appeared.
However, recent studies suggest that this diversification had started earlier, at least in the
Ediacaran
The Ediacaran ( ) is a geological period of the Neoproterozoic geologic era, Era that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period at 635 Million years ago, Mya to the beginning of the Cambrian Period at 538.8 Mya. It is the last ...
, and that it continued in the
Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era, and the second of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon (geology), Eon. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years f ...
.
Over the next 400 million years or so,
invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
diversity showed little overall trend and
vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
diversity shows an overall exponential trend.
This dramatic rise in diversity was marked by periodic, massive losses of diversity classified as
mass extinction events.
A significant loss occurred in anamniotic limbed vertebrates when rainforests collapsed in the
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
,
but
amniotes
Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolved from amphibious stem tetrapod ancestors during the ...
seem to have been little affected by this event; their diversification slowed down later, around the
Asselian/
Sakmarian boundary, in the early
Cisuralian
The Cisuralian, also known as the Early Permian, is the first series/epoch of the Permian. The Cisuralian was preceded by the Pennsylvanian and followed by the Guadalupian. The Cisuralian Epoch is named after the western slopes of the Ural Mou ...
(Early
Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years, from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.902 Mya. It is the s ...
), about 293 Ma ago.
The worst was the
Permian-Triassic extinction event, 251 million years ago.
Vertebrates took 30 million years to recover from this event.
The most recent major
mass extinction event, the
Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event, also known as the K–T extinction, was the extinction event, mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth approximately 66 million years ago. The event cau ...
, occurred 66 million years ago. This period has attracted more attention than others because it resulted in the extinction of the
dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutio ...
s, which were represented by many lineages at the end of the
Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian ( ) is, in the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS) geologic timescale, the latest age (geology), age (uppermost stage (stratigraphy), stage) of the Late Cretaceous epoch (geology), Epoch or Upper Cretaceous series (s ...
, just before that extinction event. However, many other taxa were affected by this crisis, which affected even marine taxa, such as
ammonites
Ammonoids are extinct, (typically) coiled-shelled cephalopods comprising the subclass Ammonoidea. They are more closely related to living octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish (which comprise the clade Coleoidea) than they are to nautiluses (family N ...
, which also became extinct around that time.
The biodiversity of the past is called Paleobiodiversity. The
fossil record
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
suggests that the last few million years featured the greatest biodiversity in
history
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the Human history, human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some t ...
.
However, not all scientists support this view, since there is uncertainty as to how strongly the fossil record is biased by the greater availability and preservation of recent
geologic sections. Some scientists believe that corrected for sampling artifacts, modern biodiversity may not be much different from biodiversity 300 million years ago,
whereas others consider the fossil record reasonably reflective of the diversification of life.
Estimates of the present global macroscopic species diversity vary from 2 million to 100 million, with a best estimate of somewhere near 9 million,
the vast majority
arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s.
Diversity appears to increase continually in the absence of natural selection.
Diversification
The existence of a ''global
carrying capacity
The carrying capacity of an ecosystem is the maximum population size of a biological species that can be sustained by that specific environment, given the food, habitat, water, and other resources available. The carrying capacity is defined as the ...
'', limiting the amount of life that can live at once, is debated, as is the question of whether such a limit would also cap the number of species. While records of life in the sea show a
logistic pattern of growth, life on land (insects, plants and tetrapods) shows an
exponential rise in diversity.
As one author states, "Tetrapods have not yet invaded 64 percent of potentially habitable modes and it could be that without human influence the ecological and
taxonomic diversity of tetrapods would continue to increase exponentially until most or all of the available eco-space is filled."
It also appears that the diversity continues to increase over time, especially after mass extinctions.
On the other hand, changes through the
Phanerozoic
The Phanerozoic is the current and the latest of the four eon (geology), geologic eons in the Earth's geologic time scale, covering the time period from 538.8 million years ago to the present. It is the eon during which abundant animal and ...
correlate much better with the
hyperbolic
Hyperbolic may refer to:
* of or pertaining to a hyperbola, a type of smooth curve lying in a plane in mathematics
** Hyperbolic geometry, a non-Euclidean geometry
** Hyperbolic functions, analogues of ordinary trigonometric functions, defined u ...
model (widely used in
population biology
The term population biology has been used with different meanings.
In 1971, Edward O. Wilson ''et al''. used the term in the sense of applying mathematical models to population genetics, community ecology, and population dynamics. Alan Hasting ...
,
demography
Demography () is the statistical study of human populations: their size, composition (e.g., ethnic group, age), and how they change through the interplay of fertility (births), mortality (deaths), and migration.
Demographic analysis examine ...
and
macrosociology, as well as
fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserve ...
biodiversity) than with exponential and logistic models. The latter models imply that changes in diversity are guided by a first-order
positive feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop where the outcome of a process reinforces the inciting process to build momentum. As such, these forces can exacerbate the effects ...
(more ancestors, more descendants) and/or a
negative feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function (Mathematics), function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is feedback, fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused ...
arising from resource limitation. Hyperbolic model implies a second-order positive feedback.
Differences in the strength of the second-order feedback due to different intensities of interspecific competition might explain the faster rediversification of
ammonoids in comparison to
bivalves after the
end-Permian extinction.
The hyperbolic pattern of the
world population
In demographics of the world, world demographics, the world population is the total number of humans currently alive. It was estimated by the United Nations to have exceeded eight billion in mid-November 2022. It took around 300,000 years of h ...
growth arises from a second-order positive feedback between the population size and the rate of technological growth.
The hyperbolic character of biodiversity growth can be similarly accounted for by a feedback between diversity and community structure complexity.
The similarity between the curves of biodiversity and human population probably comes from the fact that both are derived from the interference of the hyperbolic trend with cyclical and
stochastic Stochastic (; ) is the property of being well-described by a random probability distribution. ''Stochasticity'' and ''randomness'' are technically distinct concepts: the former refers to a modeling approach, while the latter describes phenomena; i ...
dynamics.
[
]
Most biologists agree however that the period since human emergence is part of a new mass extinction, named the
Holocene extinction event, caused primarily by the impact humans are having on the environment. It has been argued that the present rate of extinction is sufficient to eliminate most species on the planet Earth within 100 years.
New species are regularly discovered (on average between 5–10,000 new species each year, most of them
insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, ...
s) and many, though discovered, are not yet classified (estimates are that nearly 90% of all
arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s are not yet classified).
Most of the terrestrial diversity is found in
tropical forest
Tropical forests are forested ecoregions with tropical climates – that is, land areas approximately bounded by the Tropic of Cancer, tropics of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn, Capricorn, but possibly affected by other factors such as prevailing ...
s and in general, the land has more species than the ocean; some 8.7 million species may exist on Earth, of which some 2.1 million live in the ocean.
Species diversity in geologic time frames
It is estimated that 5 to 50 billion species have existed on the planet. Assuming that there may be a maximum of about 50 million species currently alive, it stands to reason that greater than 99% of the planet's species went extinct prior to the evolution of humans. Estimates on the number of Earth's current
species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86% have not yet been described.
However, a May 2016 scientific report estimates that 1 trillion species are currently on Earth, with only one-thousandth of one percent described.
The total amount of related
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
base pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA ...
s on Earth is estimated at 5.0 x 10
37 and weighs 50 billion
tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton in the United States to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the s ...
s. In comparison, the total
mass
Mass is an Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsic property of a physical body, body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the physical quantity, quantity of matter in a body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physi ...
of the
biosphere
The biosphere (), also called the ecosphere (), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on the Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to mat ...
has been estimated to be as much as four trillion tons of
carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
.
In July 2016, scientists reported identifying a set of 355
gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
s from the
last universal common ancestor
The last universal common ancestor (LUCA) is the hypothesized common ancestral cell from which the three domains of life, the Bacteria, the Archaea, and the Eukarya originated. The cell had a lipid bilayer; it possessed the genetic code a ...
(LUCA) of all
organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
s living on Earth.
The
age of Earth
The age of Earth is estimated to be 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years. This age may represent the age of Earth's accretion, or core formation, or of the material from which Earth formed. This dating is based on evidence from radiometric age-dating of ...
is about 4.54 billion years.
The earliest undisputed evidence of
life
Life, also known as biota, refers to matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes. It is defined descriptively by the capacity for homeostasis, Structure#Biological, organisation, met ...
dates at least from 3.7 billion years ago, during the
Eoarchean
The Eoarchean ( ; also spelled Eoarchaean) is the first Era (geology), era of the Archean, Archean Eon of the geologic record. It spans 431 million years, from the end of the Hadean Eon 4031 annum, Mya to the start of the Paleoarchean Era 3600 M ...
era after a geological
crust started to solidify following the earlier molten
Hadean eon.
There are
microbial mat fossils
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
found in 3.48 billion-year-old
sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
discovered in
Western Australia
Western Australia (WA) is the westernmost state of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Aust ...
. Other early physical evidence of a
biogenic substance
A biogenic substance is a product made by or of life forms. While the term originally was specific to metabolite compounds that had toxic effects on other organisms, it has developed to encompass any constituents, secretions, and metabolites of p ...
is
graphite
Graphite () is a Crystallinity, crystalline allotrope (form) of the element carbon. It consists of many stacked Layered materials, layers of graphene, typically in excess of hundreds of layers. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable ...
in 3.7 billion-year-old
meta-sedimentary rocks discovered in
Western Greenland..
More recently, in 2015, "remains of
biotic life" were found in 4.1 billion-year-old rocks in Western
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
. According to one of the researchers, "If life arose relatively quickly on Earth...then it could be common in the
universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents. It comprises all of existence, any fundamental interaction, physical process and physical constant, and therefore all forms of matter and energy, and the structures they form, from s ...
."
Role and benefits of biodiversity

Ecosystem services
There have been many claims about biodiversity's effect on the
ecosystem services
Ecosystem services are the various benefits that humans derive from Ecosystem, ecosystems. The interconnected Biotic_material, living and Abiotic, non-living components of the natural environment offer benefits such as pollination of crops, clean ...
, especially ''provisioning'' and ''regulating services''.
Some of those claims have been validated, some are incorrect and some lack enough evidence to draw definitive conclusions.
Ecosystem services have been grouped in three types:
# Provisioning services which involve the production of renewable resources (e.g.: food, wood, fresh water)
# Regulating services which are those that lessen environmental change (e.g.: climate regulation, pest/disease control)
# Cultural services represent human value and enjoyment (e.g.: landscape aesthetics, cultural heritage, outdoor recreation and spiritual significance)
Experiments with controlled environments have shown that humans cannot easily build ecosystems to support human needs; for example
insect pollination cannot be mimicked, though there have been attempts to create artificial pollinators using
unmanned aerial vehicles
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) or unmanned aircraft system (UAS), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft with no human pilot, crew, or passengers onboard, but rather is controlled remotely or is autonomous.De Gruyter Handbook of Dron ...
. The economic activity of pollination alone represented between $2.1–14.6 billion in 2003. Other sources have reported somewhat conflicting results and in 1997
Robert Costanza
Robert Costanza (born September 14, 1950) is an American/Australian ecological economist and Professor at the UCL Institute for Global Prosperity, University College London. He is a Fellow of the Academy of the Social Sciences in Australia a ...
and his colleagues reported the estimated global value of ecosystem services (not captured in traditional markets) at an average of $33 trillion annually.
Provisioning services
With regards to provisioning services, greater species diversity has the following benefits:
* Greater species diversity of plants increases fodder yield (synthesis of 271 experimental studies).
* Greater species diversity of plants (i.e. diversity within a single species) increases overall
crop yield (synthesis of 575 experimental studies).
Although another review of 100 experimental studies reported mixed evidence.
* Greater species diversity of trees increases overall
wood production
Wood is a structural tissue/material found as xylem in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulosic fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin ...
(synthesis of 53 experimental studies).
However, there is not enough data to draw a conclusion about the effect of tree trait diversity on wood production.
Regulating services
With regards to regulating services, greater species diversity has the following benefits:
Greater species diversity
* of fish increases the stability of
fisheries yield (synthesis of 8 observational studies)
* of plants increases
carbon sequestration
Carbon sequestration is the process of storing carbon in a carbon pool. It plays a crucial role in Climate change mitigation, limiting climate change by reducing the amount of Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, carbon dioxide in the atmosphe ...
, but note that this finding only relates to actual uptake of carbon dioxide and not long-term storage; synthesis of 479 experimental studies)
* of plants increases
soil nutrient remineralization (synthesis of 103 experimental studies), increases soil organic matter (synthesis of 85 experimental studies) and decreases disease prevalence on plants (synthesis of 107 experimental studies)
* of natural pest enemies decreases herbivorous pest populations (data from two separate reviews; synthesis of 266 experimental and observational studies;
Synthesis of 18 observational studies.
Although another review of 38 experimental studies found mixed support for this claim, suggesting that in cases where mutual intraguild predation occurs, a single predatory species is often more effective
Agriculture
Agricultural diversity can be divided into two categories:
intraspecific diversity, which includes the genetic variation within a single species, like the potato (''
Solanum tuberosum'') that is composed of many different forms and types (e.g. in the U.S. they might compare russet potatoes with new potatoes or purple potatoes, all different, but all part of the same species, ''S. tuberosum''). The other category of agricultural diversity is called
interspecific diversity and refers to the number and types of different species.
Agricultural diversity can also be divided by whether it is 'planned' diversity or 'associated' diversity. This is a functional classification that we impose and not an intrinsic feature of life or diversity. Planned diversity includes the crops which a farmer has encouraged, planted or raised (e.g. crops, covers, symbionts, and livestock, among others), which can be contrasted with the associated diversity that arrives among the crops, uninvited (e.g. herbivores, weed species and pathogens, among others).
Associated biodiversity can be damaging or beneficial. The beneficial associated biodiversity include for instance wild pollinators such as wild bees and
syrphid
Hoverflies, also called flower flies or syrphids, make up the insect family Syrphidae. As their common name suggests, they are often seen hovering or nectaring at flowers; the adults of many species feed mainly on nectar and pollen, while the l ...
flies that pollinate crops
and natural enemies and antagonists to pests and pathogens. Beneficial associated biodiversity occurs abundantly in crop fields and provide multiple
ecosystem services
Ecosystem services are the various benefits that humans derive from Ecosystem, ecosystems. The interconnected Biotic_material, living and Abiotic, non-living components of the natural environment offer benefits such as pollination of crops, clean ...
such as pest control,
nutrient cycling
A nutrient cycle (or ecological recycling) is the movement and exchange of inorganic and organic matter back into the production of matter. Energy flow is a unidirectional and noncyclic pathway, whereas the movement of mineral nutrients is cyc ...
and pollination that support crop production.
Although about 80 percent of humans' food supply comes from just 20 kinds of plants, humans use at least 40,000 species. Earth's surviving biodiversity provides resources for increasing the range of food and other products suitable for human use, although the present extinction rate shrinks that potential.
Human health

Biodiversity's relevance to human health is becoming an international political issue, as scientific evidence builds on the global health implications of biodiversity loss.
This issue is closely linked with the issue of
climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
, as many of the anticipated
health risks of climate change are associated with changes in biodiversity (e.g. changes in populations and distribution of disease vectors, scarcity of fresh water, impacts on agricultural biodiversity and food resources etc.). This is because the species most likely to disappear are those that buffer against infectious disease transmission, while surviving species tend to be the ones that increase disease transmission, such as that of West Nile Virus,
Lyme disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a tick-borne disease caused by species of ''Borrelia'' bacteria, Disease vector, transmitted by blood-feeding ticks in the genus ''Ixodes''. It is the most common disease spread by ticks in th ...
and Hantavirus, according to a study done co-authored by Felicia Keesing, an ecologist at Bard College and Drew Harvell, associate director for Environment of the
Atkinson Center for a Sustainable Future (ACSF) at
Cornell University
Cornell University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university based in Ithaca, New York, United States. The university was co-founded by American philanthropist Ezra Cornell and historian and educator Andrew Dickson W ...
.
Some of the health issues influenced by biodiversity include dietary health and nutrition security, infectious disease, medical science and medicinal resources, social and psychological health. Biodiversity is also known to have an important role in reducing disaster risk, including rising sea levels. For example, wetland ecosystems along coastal communities serve as excellent water filtration systems, storage, and ultimately create a buffer region between the ocean and mainland neighborhoods in order to prevent water reaching these communities under climate change pressures or storm storages. Other examples of diverse species or organisms are present around the world, offering their resourceful utilities to provide protection of human survival.
Biodiversity provides critical support for drug discovery and the availability of medicinal resources. A significant proportion of drugs are derived, directly or indirectly, from biological sources: at least 50% of the pharmaceutical compounds on the US market are derived from plants, animals and
microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s, while about 80% of the world population depends on medicines from nature (used in either modern or traditional medical practice) for primary healthcare.
Only a tiny fraction of wild species has been investigated for medical potential.
Marine ecosystems are particularly important, especially their chemical and physical properties that have paved the way for numerous pharmaceutical achievements; the immense diversity of marine organisms have led to scientific discoveries including medical treatments to cancer, viral bacteria, AIDS, etc. This process of
bioprospecting can increase biodiversity loss, as well as violating the laws of the communities and states from which the resources are taken.
Business and industry
According to the
Boston Consulting Group
Boston Consulting Group, Inc. (BCG) is an American global management consulting firm founded in 1963 and headquartered in Boston, Massachusetts. It is one of the "Big Three (management consultancies), Big Three" (or MBB, the world's three large ...
, in 2021, the economic value that biodiversity has on society comes down to four definable terms: regulation, culture, habitat, and provisioning. To sum these up in a relatively short manner, biodiversity helps maintain habitat and animal functions that provide considerable amounts of resources that benefit the economy.
Biodiversity’s economic resources are worth at around $150 trillion annually which is roughly twice the world’s GDP. The loss of biodiversity is actually harming the GDP of the world by costing an estimated $5 trillion annually.
Business supply chains rely heavily on ecosystems remaining relatively maintained and nurtured. A disruption to these supply chains would negatively impact many businesses that would end up costing them more than what they are gaining.
Cultural and aesthetic value

Philosophically it could be argued that biodiversity has intrinsic aesthetic and spiritual value to
mankind ''in and of itself''. This idea can be used as a counterweight to the notion that
tropical forest
Tropical forests are forested ecoregions with tropical climates – that is, land areas approximately bounded by the Tropic of Cancer, tropics of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn, Capricorn, but possibly affected by other factors such as prevailing ...
s and other ecological realms are only worthy of conservation because of the services they provide.
Biodiversity also affords many non-material benefits including spiritual and aesthetic values, knowledge systems and education.
Measuring biodiversity
Analytical limits
Less than 1% of all species that have been described have been studied beyond noting their existence. The vast majority of Earth's species are microbial. Contemporary biodiversity physics is "firmly fixated on the visible
acroscopicworld". For example, microbial life is
metabolically and environmentally more diverse than multicellular life (see e.g.,
extremophile
An extremophile () is an organism that is able to live (or in some cases thrive) in extreme environments, i.e., environments with conditions approaching or stretching the limits of what known life can adapt to, such as extreme temperature, press ...
). "On the tree of life, based on analyses of small-subunit
ribosomal RNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal ...
, visible life consists of barely noticeable twigs. The inverse relationship of size and population recurs higher on the evolutionary ladder—to a first approximation, all multicellular species on Earth are insects".
Insect extinction rates are high—supporting the Holocene extinction hypothesis.
Biodiversity changes (other than losses)
Natural seasonal variations
Biodiversity naturally varies due to seasonal shifts. Spring's arrival enhances biodiversity as numerous species breed and feed, while winter's onset temporarily reduces it as some insects perish and migrating animals leave. Additionally, the seasonal fluctuation in plant and invertebrate populations influences biodiversity.
Introduced and invasive species

Barriers such as large
river
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of ...
s,
sea
A sea is a large body of salt water. There are particular seas and the sea. The sea commonly refers to the ocean, the interconnected body of seawaters that spans most of Earth. Particular seas are either marginal seas, second-order section ...
s,
oceans
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Antarctic/Southern, and ...
,
mountains
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher ...
and
deserts
A desert is a landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions create unique biomes and ecosystems. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the l ...
encourage diversity by enabling independent evolution on either side of the barrier, via the process of
allopatric speciation
Allopatric speciation () – also referred to as geographic speciation, vicariant speciation, or its earlier name the dumbbell model – is a mode of speciation that occurs when biological populations become geographically isolated from ...
. The term
invasive species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native spec ...
is applied to species that breach the natural barriers that would normally keep them constrained. Without barriers, such species occupy new territory, often supplanting native species by occupying their niches, or by using resources that would normally sustain native species.
Species are increasingly being moved by humans (on purpose and accidentally). Some studies say that diverse ecosystems are more resilient and resist invasive plants and animals. Many studies cite effects of invasive species on natives, but not extinctions.
Invasive species seem to increase local (
alpha diversity) diversity, which decreases turnover of diversity (
beta diversity
In ecology, beta diversity (β-diversity or true beta diversity) is the ratio between regional and local species diversity. The term was introduced by Robert Whittaker (ecologist), R. H. Whittaker together with the terms alpha diversity (α-diversi ...
). Overall
gamma diversity may be lowered because species are going extinct because of other causes, but even some of the most insidious invaders (e.g.: Dutch elm disease, emerald ash borer, chestnut blight in North America) have not caused their host species to become extinct.
Extirpation
Local extinction, also extirpation, is the termination of a species (or other taxon) in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with extinction, global extinctions.
Local extinctions ...
,
population decline
Population decline, also known as depopulation, is a reduction in a human population size. Throughout history, Earth's total world population, human population has estimates of historical world population, continued to grow but projections sugg ...
and
homogenization of regional biodiversity are much more common. Human activities have frequently been the cause of invasive species circumventing their barriers, by introducing them for food and other purposes. Human activities therefore allow species to migrate to new areas (and thus become invasive) occurred on time scales much shorter than historically have been required for a species to extend its range.
At present, several countries have already imported so many exotic species, particularly agricultural and ornamental plants, that their indigenous fauna/flora may be outnumbered. For example, the introduction of
kudzu from Southeast Asia to Canada and the United States has threatened biodiversity in certain areas. Another example are
pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae.
''World Flora Online'' accepts 134 species-rank taxa (119 species and 15 nothospecies) of pines as cu ...
s, which have invaded forests, shrublands and grasslands in the southern hemisphere.
Hybridization and genetic pollution

Endemic species can be threatened with
extinction
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
through the process of
genetic pollution
Genetic pollution is a term for uncontrolled gene flow into wild populations. It is defined as "the dispersal of contaminated altered genes from genetically engineered organisms to natural organisms, esp. by cross-pollination", but has come to be ...
, i.e. uncontrolled
hybridization,
introgression
Introgression, also known as introgressive hybridization, in genetics is the transfer of genetic material from one species into the gene pool of another by the repeated backcrossing of an interspecific hybrid with one of its parent species. Introg ...
and genetic swamping. Genetic pollution leads to homogenization or replacement of local
genomes as a result of either a numerical and/or
fitness advantage of an introduced species.
Hybridization and introgression are side-effects of introduction and invasion. These phenomena can be especially detrimental to
rare species
A rare species is a group of organisms that are very uncommon, scarce, or infrequently encountered. This designation may be applied to either a plant or animal taxon, and is distinct from the term ''endangered species, endangered'' or ''threatened ...
that come into contact with more abundant ones. The abundant species can interbreed with the rare species, swamping its
gene pool
The gene pool is the set of all genes, or genetic information, in any population, usually of a particular species.
Description
A large gene pool indicates extensive genetic diversity, which is associated with robust populations that can survi ...
. This problem is not always apparent from
morphological (outward appearance) observations alone. Some degree of
gene flow
In population genetics, gene flow (also known as migration and allele flow) is the transfer of genetic variation, genetic material from one population to another. If the rate of gene flow is high enough, then two populations will have equivalent ...
is normal adaptation and not all
gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
and
genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
constellations can be preserved. However, hybridization with or without introgression may, nevertheless, threaten a rare species' existence.
Conservation

Conservation biology
Conservation biology is the study of the conservation of nature and of Earth's biodiversity with the aim of protecting species, their habitats, and ecosystems from excessive rates of extinction and the erosion of biotic interactions. It is an i ...
matured in the mid-20th century as
ecologists
This is a list of notable ecologists.
A-D
* John Aber (United States)
* Aziz Ab'Saber (Brazil)
* Charles Christopher Adams (United States)
* Warder Clyde Allee (United States)
* Herbert G. Andrewartha (Australia)
* Sarah Martha Baker ( ...
,
naturalists and other
scientists
A scientist is a person who researches to advance knowledge in an area of the natural sciences.
In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, philosophers engaged in the philosophical study of nature ...
began to research and address issues pertaining to global biodiversity declines.
The conservation ethic advocates management of
natural resource
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest, and cultural value. ...
s for the purpose of sustaining biodiversity in
species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
,
ecosystems
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
, the
evolutionary process and human culture and society.
Conservation biology is reforming around strategic plans to protect biodiversity.
Preserving global biodiversity is a priority in strategic conservation plans that are designed to engage public policy and concerns affecting local, regional and global scales of communities, ecosystems and cultures. Action plans identify
ways of sustaining human well-being, employing
natural capital, macroeconomic policies including economic incentives, and
ecosystem services
Ecosystem services are the various benefits that humans derive from Ecosystem, ecosystems. The interconnected Biotic_material, living and Abiotic, non-living components of the natural environment offer benefits such as pollination of crops, clean ...
.
In the
EU Directive 1999/22/EC zoos are described as having a role in the preservation of the biodiversity of wildlife animals by conducting research or participation in
breeding programs.
Protection and restoration techniques
Removal of exotic species will allow the species that they have negatively impacted to recover their ecological niches. Exotic species that have become pests can be identified taxonomically (e.g., with
Digital Automated Identification SYstem (DAISY), using the
barcode of life). Removal is practical only given large groups of individuals due to the economic cost.
As sustainable populations of the remaining native species in an area become assured, "missing" species that are candidates for reintroduction can be identified using databases such as the ''
Encyclopedia of Life
The Encyclopedia of Life (EOL) is a free, online encyclopedia intended to document all of the 1.9 million living species known to science. It aggregates content to form "pages" for every known species. Content is compiled from existing trusted ...
'' and the
Global Biodiversity Information Facility
The Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) is an international organisation that focuses on making scientific data on biodiversity available via the Internet using web services. The data are provided by many institutions from around th ...
.
*
Biodiversity banking places a monetary value on biodiversity. One example is the Australian
Native Vegetation Management Framework.
*
Gene banks are collections of specimens and genetic material. Some banks intend to reintroduce banked species to the ecosystem (e.g., via tree nurseries).
* Reduction and better targeting of pesticides allows more species to survive in agricultural and urbanized areas.
* Location-specific approaches may be less useful for protecting migratory species. One approach is to create
wildlife corridor
A wildlife corridor, also known as a habitat corridor, or green corridor, is a designated area habitat (ecology), that connects wildlife populations that have been separated by human activities or structures, such as development, roads, or land ...
s that correspond to the animals' movements. National and other boundaries can complicate corridor creation.
Protected areas
Protected areas, including forest reserves and biosphere reserves, serve many functions including for affording protection to wild animals and their habitat. Protected areas have been set up all over the world with the specific aim of protecting and conserving plants and animals. Some scientists have called on the global community to designate as protected areas of 30 percent of the planet by 2030, and 50 percent by 2050, in order to mitigate biodiversity loss from anthropogenic causes. The target of protecting 30% of the area of the planet by the year 2030 (
30 by 30
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious and cultural significance in many societies ...
) was adopted by almost 200 countries in the
2022 United Nations Biodiversity Conference. At the moment of adoption (December 2022) 17% of land territory and 10% of ocean territory were protected.
In a study published 4 September 2020 in
Science Advances
''Science Advances'' is a peer-reviewed multidisciplinary open-access scientific journal established in early 2015 and published by the American Association for the Advancement of Science. The journal's scope includes all areas of science.
Hist ...
researchers mapped out regions that can help meet critical conservation and climate goals.
Protected areas safeguard nature and cultural resources and contribute to livelihoods, particularly at local level. There are over 238 563 designated protected areas worldwide, equivalent to 14.9 percent of the earth's land surface, varying in their extension, level of protection, and type of management (IUCN, 2018).
The benefits of protected areas extend beyond their immediate environment and time. In addition to conserving nature, protected areas are crucial for securing the long-term delivery of ecosystem services. They provide numerous benefits including the conservation of
genetic resources
Genetic resources are genetic material of actual or potential value, where genetic material means any material of plant, animal, microbial genetics, microbial or other origin containing functional units of heredity.
Genetic resources is one of the ...
for food and agriculture, the provision of medicine and health benefits, the provision of water, recreation and tourism, and for acting as a buffer against disaster. Increasingly, there is acknowledgement of the wider socioeconomic values of these natural ecosystems and of the ecosystem services they can provide.
National parks and wildlife sanctuaries
A
national park
A national park is a nature park designated for conservation (ethic), conservation purposes because of unparalleled national natural, historic, or cultural significance. It is an area of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that is protecte ...
is a large natural or near natural area set aside to protect large-scale ecological processes, which also provide a foundation for environmentally and culturally compatible, spiritual, scientific, educational, recreational and visitor opportunities. These areas are selected by governments or private organizations to protect natural biodiversity along with its underlying ecological structure and supporting environmental processes, and to promote education and recreation. The
International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the stat ...
(IUCN), and its World Commission on Protected Areas (WCPA), has defined "National Park" as its Category II type of protected areas.
Wildlife sanctuaries are areas of either shelter for animals who are unable to live in the wild on their own, or they are temporary rehabilitation centers for wildlife to improve in their overall health and wellbeing.
Both of these serve as places in which biodiversity can be preserved rather than harmed. According to an article published in the
National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an List of federal agencies in the United States, agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government, within the US Department of the Interior. The service manages all List ...
website, national parks aim their resources at maintaining animal and habitat integrity through conservation and preservation of their ecosystems. This along with educating the general public on wildlife functions, the aim for an increase in biodiversity is one of many goals trying to be focused on through national parks.
Forest protected areas
Forest protected areas are a subset of all protected areas in which a significant portion of the area is forest.
This may be the whole or only a part of the protected area.
Globally, 18 percent of the world's forest area, or more than 700 million hectares, fall within legally established protected areas such as national parks, conservation areas and game reserves.
There is an estimated 726 million ha of forest in protected areas worldwide. Of the six major world regions, South America has the highest share of forests in protected areas, 31 percent. The
forest
A forest is an ecosystem characterized by a dense ecological community, community of trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, ...
s play a vital role in harboring more than 45,000 floral and 81,000 faunal species of which 5150 floral and 1837 faunal species are
endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
. In addition, there are 60,065 different tree species in the world. Plant and animal species confined to a specific geographical area are called endemic species.
In
forest reserves, rights to activities like hunting and grazing are sometimes given to communities living on the fringes of the forest, who sustain their livelihood partially or wholly from forest resources or products.
Approximately 50 million hectares (or 24%) of European forest land is protected for biodiversity and landscape protection. Forests allocated for soil, water, and other ecosystem services encompass around 72 million hectares (32% of European forest area).
Role of society
Transformative change
In 2019, a summary for policymakers of the largest, most comprehensive study to date of biodiversity and ecosystem services, the ''
'', was published by the
(IPBES). It stated that "the state of nature has deteriorated at an unprecedented and accelerating rate". To fix the problem, humanity will need a transformative change, including
sustainable agriculture
Sustainable agriculture is agriculture, farming in sustainability, sustainable ways meeting society's present food and textile needs, without compromising the ability for current or future generations to meet their needs. It can be based on an ...
, reductions in
consumption and waste, fishing quotas and collaborative water management.
The concept of
nature-positive is playing a role in mainstreaming the goals of the
Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) for biodiversity.
The aim of mainstreaming is to embed biodiversity considerations into public and private practice to
conserve and
sustainably use biodiversity on global and local levels.
The concept of nature-positive refers to the societal goal to halt and reverse biodiversity loss, measured from a baseline of 2020 levels, and to achieve full so-called "nature recovery" by 2050.
Citizen science
Citizen science, also known as public participation in scientific research, has been widely used in environmental sciences and is particularly popular in a biodiversity-related context. It has been used to enable scientists to involve the general public in biodiversity research, thereby enabling the scientists to collect data that they would otherwise not have been able to obtain.
Volunteer observers have made significant contributions to on-the-ground knowledge about biodiversity, and recent improvements in technology have helped increase the flow and quality of occurrences from citizen sources. A 2016 study published in Biological Conservation registers the massive contributions that citizen scientists already make to data mediated by the
Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF). Despite some limitations of the dataset-level analysis, it is clear that nearly half of all occurrence records shared through the GBIF network come from datasets with significant volunteer contributions. Recording and sharing observations are enabled by several global-scale platforms, including
iNaturalist
iNaturalist is an American 501(c)(3) nonprofit social network of naturalists, citizen scientists, and biologists built on the concept of mapping and sharing observations of biodiversity across the globe. iNaturalist may be accessed via its web ...
and
eBird.
Legal status

International
* United Nations
Convention on Biological Diversity
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), known informally as the Biodiversity Convention, is a multilateral treaty. The Convention has three main goals: the conservation of biological diversity (or biodiversity); the sustainable use of its ...
(1992) and
Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety;
* UN BBNJ (
High Seas Treaty) 2023 Intergovernmental conference on an international legally binding instrument under the
UNCLOS on the conservation and sustainable use of marine biological diversity of areas beyond national jurisdiction (GA resolution 72/249)
* Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (
CITES
CITES (shorter acronym for the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, also known as the Washington Convention) is a multilateral treaty to protect endangered plants and animals from the threats of inte ...
);
*
Ramsar Convention
The Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance Especially as Waterfowl Habitat is an international treaty for the conservation and sustainable use of Ramsar site, Ramsar sites (wetlands). It is also known as the Convention on We ...
(Wetlands);
*
Bonn Convention on Migratory Species;
*
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
Convention concerning the Protection of the World's Cultural and Natural Heritage (indirectly by protecting biodiversity habitats)
*
UNESCO Global Geoparks
* Regional Conventions such as the Apia Convention
* Bilateral agreements such as the
Japan-Australia Migratory Bird Agreement.
Global agreements such as the
Convention on Biological Diversity
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), known informally as the Biodiversity Convention, is a multilateral treaty. The Convention has three main goals: the conservation of biological diversity (or biodiversity); the sustainable use of its ...
, give "sovereign national rights over biological resources" (not property). The agreements commit countries to "conserve biodiversity", "develop resources for sustainability" and "share the benefits" resulting from their use. Biodiverse countries that allow
bioprospecting or collection of natural products, expect a share of the benefits rather than allowing the individual or institution that discovers/exploits the resource to capture them privately. Bioprospecting can become a type of
biopiracy when such principles are not respected.
Sovereignty principles can rely upon what is better known as
Access and Benefit Sharing Agreements (ABAs). The Convention on Biodiversity implies
informed consent
Informed consent is an applied ethics principle that a person must have sufficient information and understanding before making decisions about accepting risk. Pertinent information may include risks and benefits of treatments, alternative treatme ...
between the source country and the collector, to establish which resource will be used and for what and to settle on a
fair agreement on benefit sharing.
On the 19 of December 2022, during the
2022 United Nations Biodiversity Conference every country on earth, with the exception of the
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
and the
Holy See
The Holy See (, ; ), also called the See of Rome, the Petrine See or the Apostolic See, is the central governing body of the Catholic Church and Vatican City. It encompasses the office of the pope as the Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishop ...
, signed onto the agreement which includes protecting 30% of land and oceans by 2030 (
30 by 30
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious and cultural significance in many societies ...
) and 22 other targets intended to reduce
biodiversity loss
Biodiversity loss happens when plant or animal species disappear completely from Earth (extinction) or when there is a decrease or disappearance of species in a specific area. Biodiversity loss means that there is a reduction in Biodiversity, b ...
.
The agreement includes also recovering 30% of earth degraded ecosystems and increasing funding for biodiversity issues.
European Union
In May 2020, the European Union published its Biodiversity Strategy for 2030. The biodiversity strategy is an essential part of the
climate change mitigation
Climate change mitigation (or decarbonisation) is action to limit the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that cause climate change. Climate change mitigation actions include energy conservation, conserving energy and Fossil fuel phase-out, repl ...
strategy of the European Union. From the 25% of the European budget that will go to fight climate change, large part will go to restore biodiversity
and
nature based solutions.
The
EU Biodiversity Strategy for 2030 include the next targets:
* Protect 30% of the sea territory and 30% of the land territory especially
Old-growth forest
An old-growth forest or primary forest is a forest that has developed over a long period of time without disturbance. Due to this, old-growth forests exhibit unique ecological features. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Natio ...
s.
* Plant 3 billion trees by 2030.
* Restore at least 25,000 kilometers of rivers, so they will become free flowing.
* Reduce the use of
Pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
s by 50% by 2030.
* Increase
Organic farming
Organic farming, also known as organic agriculture or ecological farming or biological farming,Labelling, article 30 o''Regulation (EU) 2018/848 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 May 2024 on organic production and labelling of ...
. In linked EU program
From Farm to Fork it is said, that the target is making 25% of EU agriculture organic, by 2030.
* Increase
biodiversity in agriculture.
* Give €20 billion per year to the issue and make it part of the business practice.
Approximately half of the global
GDP depend on nature. In Europe many parts of the economy that generate trillions of euros per year depend on nature. The benefits of
Natura 2000 alone in Europe are €200 – €300 billion per year.
National level laws
Biodiversity is taken into account in some political and judicial decisions:
* The relationship between law and ecosystems is very ancient and has consequences for biodiversity. It is related to private and public property rights. It can define protection for threatened ecosystems, but also some rights and duties (for example,
fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment (Freshwater ecosystem, freshwater or Marine ecosystem, marine), but may also be caught from Fish stocking, stocked Body of water, ...
and hunting rights).
* Law regarding species is more recent. It defines species that must be protected because they may be threatened by extinction. The U.S.
Endangered Species Act
The Endangered Species Act of 1973 (ESA; 16 U.S.C. § 1531 et seq.) is the primary law in the United States for protecting and conserving imperiled species. Designed to protect critically imperiled species from extinction as a "consequence of e ...
is an example of an attempt to address the "law and species" issue.
* Laws regarding gene pools are only about a century old. Domestication and plant breeding methods are not new, but advances in genetic engineering have led to tighter laws covering distribution of
genetically modified organisms
A genetically modified organism (GMO) is any organism whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering techniques. The exact definition of a genetically modified organism and what constitutes genetic engineering varies, with ...
, gene
patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling discl ...
s and process patents. Governments struggle to decide whether to focus on for example, genes, genomes, or organisms and species.
Uniform approval for use of biodiversity as a legal standard has not been achieved, however. Bosselman argues that biodiversity should not be used as a legal standard, claiming that the remaining areas of scientific uncertainty cause unacceptable administrative waste and increase litigation without promoting preservation goals.
India passed the
Biological Diversity Act in 2002 for the conservation of biological diversity in India. The Act also provides mechanisms for equitable sharing of benefits from the use of traditional biological resources and knowledge.
History of the term
* 1916 – The term ''biological diversity'' was used first by
J. Arthur Harris in "The Variable Desert", ''
Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it, with more than 150 Nobel Pri ...
'': "The bare statement that the region contains a flora rich in genera and species and of diverse geographic origin or affinity is entirely inadequate as a description of its real biological diversity."
* 1967 –
Raymond F. Dasmann used the term biological diversity in reference to the richness of living nature that conservationists should protect in his book ''A Different Kind of Country''.
* 1974 – The term ''natural diversity'' was introduced by
John Terborgh.
* 1980 –
Thomas Lovejoy
Thomas Eugene Lovejoy III (August 22, 1941December 25, 2021) was an American ecologist who was President of the Amazon Biodiversity Center, a Senior Fellow at the United Nations Foundation and a university professor in the Environmental Science a ...
introduced the term ''biological diversity'' to the scientific community in a book.
It rapidly became commonly used.
* 1985 – According to
Edward O. Wilson, the contracted form ''biodiversity'' was coined by W. G. Rosen: "The National Forum on BioDiversity ... was conceived by Walter G. Rosen ... Dr. Rosen represented the NRC/NAS throughout the planning stages of the project. Furthermore, he introduced the term ''biodiversity''".
* 1985 – The term "biodiversity" appears in the article, "A New Plan to Conserve the Earth's Biota" by
Laura Tangley.
* 1988 – The term biodiversity first appeared in publication.
* 1988 to Present – The
United Nations Environment Programme
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the Declaration of the United Nati ...
(UNEP) Ad Hoc Working Group of Experts on Biological Diversity in began working in November 1988, leading to the publication of the draft
Convention on Biological Diversity
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), known informally as the Biodiversity Convention, is a multilateral treaty. The Convention has three main goals: the conservation of biological diversity (or biodiversity); the sustainable use of its ...
in May 1992. Since this time, there have been 16 Conferences of the Parties (COPs) to discuss potential global political responses to biodiversity loss. Most recently
COP 16 in
Cali
Santiago de Cali (), or Cali, is the capital of the Valle del Cauca department, and the most populous city in southwest Colombia, with 2,280,522 residents estimate by National Administrative Department of Statistics, DANE in 2023. The city span ...
,
Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuel ...
in 2024.
See also
*
Biodiversity Informatics Biodiversity informatics is the application of informatics (academic field), informatics techniques to biodiversity information, such as Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy, biogeography or ecology. It is defined as the application of information technolog ...
*
Ecological indicator
*
Genetic diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. It ranges widely, from the number of species to differences within species, and can be correlated to the span of survival for a species. It is d ...
*
Global biodiversity
*
Index of biodiversity articles
*
International Day for Biological Diversity
*
Megadiverse countries
*
Soil biodiversity
*
Species diversity
*
30 by 30
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious and cultural significance in many societies ...
*
Artificialization
The artificialization of soil, an environment, or Biotope, natural or semi-natural habitat is the loss of its qualities: its Wilderness, naturalness, a quality that includes a self-sustaining capacity to harbor certain biodiversity, natural cycles ...
References
External links
Assessment Report on Diverse Values and Valuation of Natureby the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES), 2022.
NatureServe: This site serves as a portal for accessing several types of publicly available biodiversity dataBiodiversity Synthesis Report(PDF) by the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MA, 2005)
an interactive map from the
United Nations Environment Programme
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the Declaration of the United Nati ...
World Conservation Monitoring Centre
Biodiversity Heritage Library– Open access digital library of historical taxonomic literature
Biodiversity PMC– Open access digital library of biodiversity and ecological literature
Mapping of biodiversityEncyclopedia of Life– Documenting all species of life on Earth.
{{Authority control
Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
Biogeography
Population genetics
Species
 Biologists most often define ''biodiversity'' as the "totality of
Biologists most often define ''biodiversity'' as the "totality of  Biodiversity is not evenly distributed, rather it varies greatly across the globe as well as within regions and seasons. Among other factors, the diversity of all living things ( biota) depends on
Biodiversity is not evenly distributed, rather it varies greatly across the globe as well as within regions and seasons. Among other factors, the diversity of all living things ( biota) depends on  Biodiversity grew fast during the
Biodiversity grew fast during the 
 Biodiversity's relevance to human health is becoming an international political issue, as scientific evidence builds on the global health implications of biodiversity loss. This issue is closely linked with the issue of
Biodiversity's relevance to human health is becoming an international political issue, as scientific evidence builds on the global health implications of biodiversity loss. This issue is closely linked with the issue of  Philosophically it could be argued that biodiversity has intrinsic aesthetic and spiritual value to mankind ''in and of itself''. This idea can be used as a counterweight to the notion that
Philosophically it could be argued that biodiversity has intrinsic aesthetic and spiritual value to mankind ''in and of itself''. This idea can be used as a counterweight to the notion that  Barriers such as large
Barriers such as large  Endemic species can be threatened with
Endemic species can be threatened with 
