Bifolium From The on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A bifolium is a
A bifolium is a
 Given a
Given a
Bifolium at MathWorld
by Wolfram Plane curves Algebraic curves
quartic plane curve
In algebraic geometry, a quartic plane curve is a plane algebraic curve of the fourth degree. It can be defined by a bivariate quartic equation:
:Ax^4+By^4+Cx^3y+Dx^2y^2+Exy^3+Fx^3+Gy^3+Hx^2y+Ixy^2+Jx^2+Ky^2+Lxy+Mx+Ny+P=0,
with at least one of ...
with equation in Cartesian coordinate
In geometry, a Cartesian coordinate system (, ) in a plane is a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely by a pair of real numbers called ''coordinates'', which are the signed distances to the point from two fixed perpendicular o ...
s:
:
Construction and equations
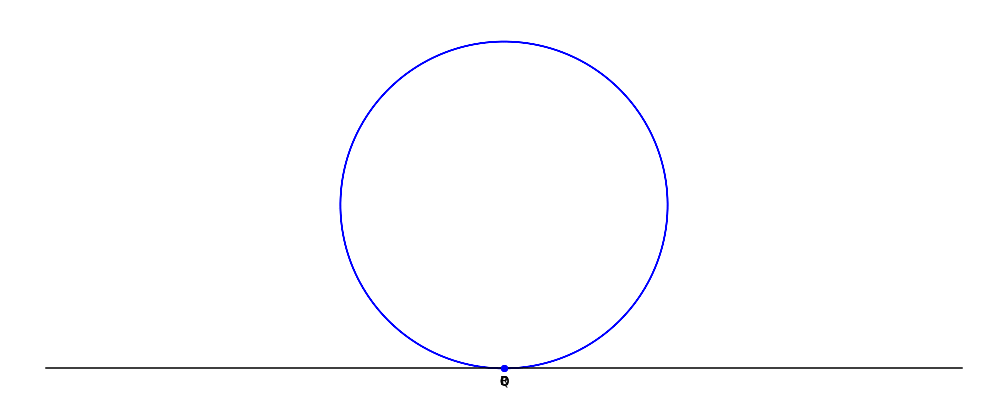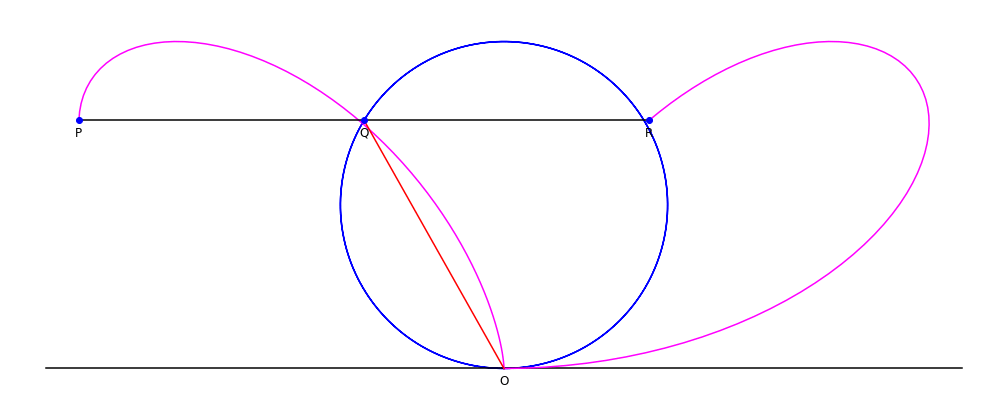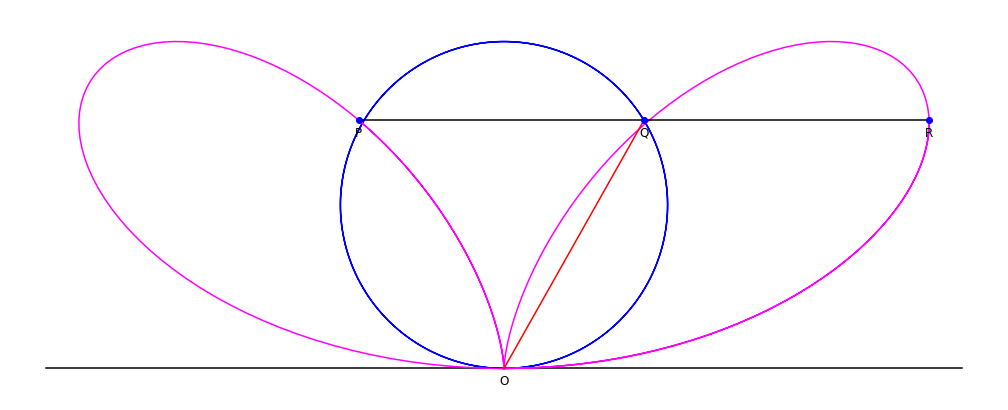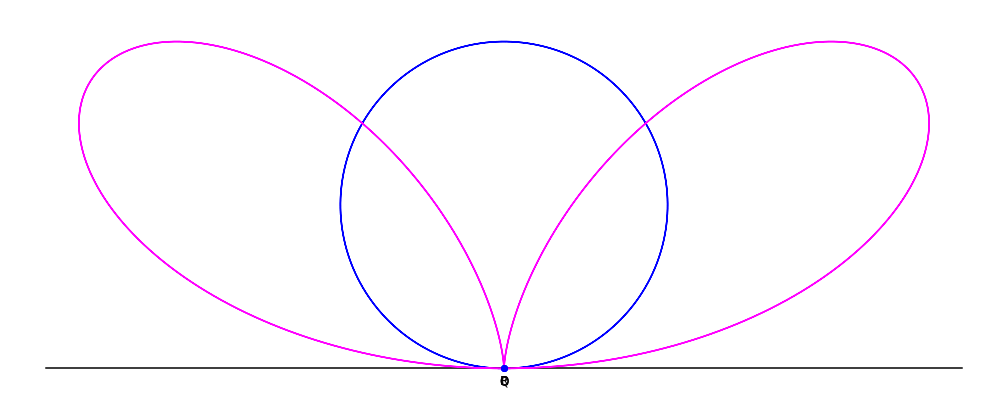
 Given a
Given a circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all point (geometry), points in a plane (mathematics), plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the Centre (geometry), centre. The distance between any point of the circle and the centre is cal ...
C through a point O, and line L tangent
In geometry, the tangent line (or simply tangent) to a plane curve at a given point is, intuitively, the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point. Leibniz defined it as the line through a pair of infinitely close points o ...
to the circle at point O: for each point Q on C, define the point P such that PQ is parallel
Parallel may refer to:
Mathematics
* Parallel (geometry), two lines in the Euclidean plane which never intersect
* Parallel (operator), mathematical operation named after the composition of electrical resistance in parallel circuits
Science a ...
to the tangent line L, and PQ = OQ. The collection of points P forms the bifolium.
In polar coordinates
In mathematics, the polar coordinate system specifies a given point (mathematics), point in a plane (mathematics), plane by using a distance and an angle as its two coordinate system, coordinates. These are
*the point's distance from a reference ...
, the bifolium's equation is
:
:while (first eqn.)
:
For ''a'' = 1, the total included area
Area is the measure of a region's size on a surface. The area of a plane region or ''plane area'' refers to the area of a shape or planar lamina, while '' surface area'' refers to the area of an open surface or the boundary of a three-di ...
is approximately 0.10.
See also
*Folium of Descartes
In geometry, the folium of Descartes (; named for René Descartes) is an algebraic curve defined by the implicit equation
x^3+y^3-3a\cdot xy=0.
dy/dx=(x^2-ay)/(ax-y^2), \,dx/dy=(ax-y^2)/(x^2-ay). History
The curve was first proposed and studi ...
* Trifolium curve
Clovers, also called trefoils, are plants of the genus ''Trifolium'' (), consisting of about 300 species of flowering plants in the legume family Fabaceae originating in Europe. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution with the highest diversity ...
Reference
{{ReflistExternal link
Bifolium at MathWorld
by Wolfram Plane curves Algebraic curves