Biaroza on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Byaroza (; ; also spelled ''Bereza''), formerly Byaroza-Kartuzskaya, is a town in Brest Region,
 During the
During the 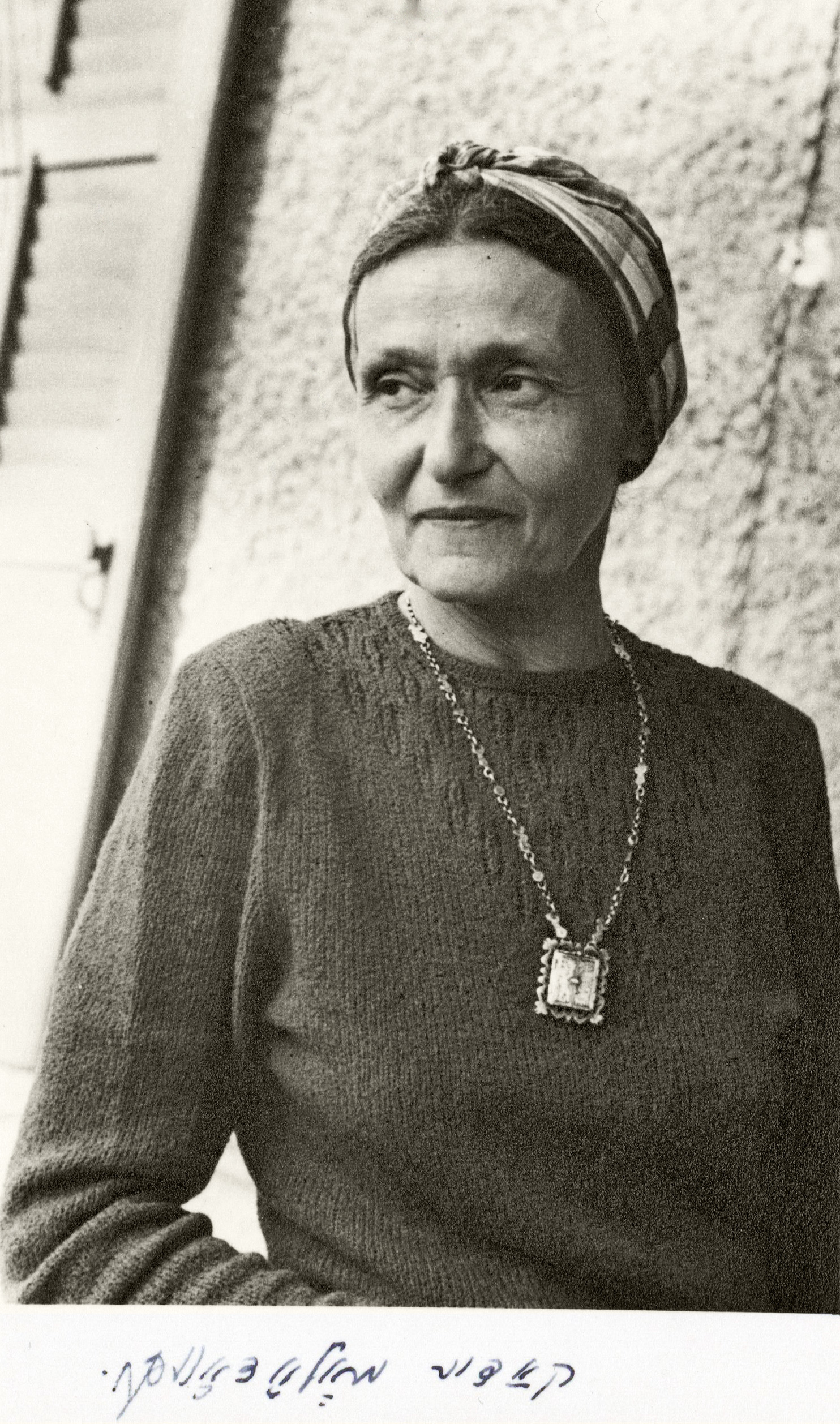
File:Бяроза. Новы касцёл.jpg, Catholic church in Byaroza
File:DSCN4095.JPG, Central street of Byaroza
File:BiarozaCyrvonyja.JPG, Memorial to Soviet pilots
Photos on Radzima.org
Biaroza on Googlemaps
on
Kartuz-Bereza cemetery
* {{Coord, 52, 33, N, 24, 58, E, type:city, display=title Holocaust locations in Belarus
Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an a ...
. It serves as the administrative center of Byaroza District. As of 2025, it has a population of 28,192.
History
The village of Biaroza (meaning ''birch'') was first mentioned in 1477 as part of theSlonim
Slonim is a town in Grodno Region, in western Belarus. It serves as the administrative center of Slonim District. It is located at the junction of the Shchara and Isa (river), Isa rivers, southeast of Grodno. As of 2025, it has a population of ...
paviet. In the 15th century, the village probably received the town charter
A city charter or town charter (generically, municipal charter) is a legal document (''charter'') establishing a municipality such as a city or town. The concept developed in Europe during the Middle Ages.
Traditionally, the granting of a charter ...
. Between 1538 and 1600 it was an important centre of Calvinism
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Christian, Presbyteri ...
. Later the town became the private property of the Radziwiłł family.
In the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
In the 17th century, the village belonged toSapieha
The House of Sapieha (; ; ; ) is a Polish-Lithuanian noble and magnate family of Ruthenian origin,Энцыклапедыя ВКЛ. Т.2, арт. "Сапегі" descending from the medieval boyars of Smolensk and Polotsk. Vernadsky, George. ...
family, who founded a fortified monastery and a palace here. In 1648, the monastery was presented to the Carthusian
The Carthusians, also known as the Order of Carthusians (), are a Latin enclosed religious order of the Catholic Church. The order was founded by Bruno of Cologne in 1084 and includes both monks and nuns. The order has its own rule, called th ...
monk
A monk (; from , ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a man who is a member of a religious order and lives in a monastery. A monk usually lives his life in prayer and contemplation. The concept is ancient and can be seen in many reli ...
s. They came from the Italian town of Treviso
Treviso ( ; ; ) is a city and (municipality) in the Veneto region of northern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Treviso and the municipality has 87.322 inhabitants (as of December 2024). Some 3,000 live within the Venetian wall ...
and settled here. In gratitude for this deed, Pope
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
Alexander VII
Pope Alexander VII (; 13 February 159922 May 1667), born Fabio Chigi, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 7 April 1655 to his death, in May 1667.
He began his career as a vice-papal legate, and he held various di ...
granted the title of a prince to Lew Sapieha
Lew Sapieha (; ; 4 April 1557 – 7 July 1633) was a nobleman and statesman of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. He became Great Secretary of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in 1580, Great Clerk of the Grand Duchy in 1581, Crown Chancellor in 1 ...
. The monastery was also expanded and became one of the biggest charterhouse
Charterhouse may refer to:
* Charterhouse (monastery), of the Carthusian religious order
Charterhouse may also refer to:
Places
* The Charterhouse, Coventry, a former monastery
* Charterhouse School, an English public school in Surrey
London ...
s (Carthusian
The Carthusians, also known as the Order of Carthusians (), are a Latin enclosed religious order of the Catholic Church. The order was founded by Bruno of Cologne in 1084 and includes both monks and nuns. The order has its own rule, called th ...
monasteries) in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
. The Carthusian order gave its name to the second part of the town's name in the form in which it has been used till late 1940s: ''Biaroza-Kartuzskaya'' (Polish: Bereza Kartuska).
 During the
During the Great Northern War
In the Great Northern War (1700–1721) a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern Europe, Northern, Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the ant ...
, the monastery housed a conference held by King Augustus II of Poland
Augustus II the Strong (12 May 1670 – 1 February 1733), was Elector of Saxony from 1694 as well as King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1697 to 1706 and from 1709 until his death in 1733. He belonged to the Albertine branch of the H ...
and Peter I of Russia
Peter I (, ;
– ), better known as Peter the Great, was the Tsar of all Russia from 1682 and the first Emperor of all Russia from 1721 until his death in 1725. He reigned jointly with his half-brother Ivan V until 1696. From this year, ...
. In 1706, the fortified monastery was put under siege and then taken by assault and looted by the forces of Charles XII of Sweden
Charles XII, sometimes Carl XII () or Carolus Rex (17 June 1682 – 30 November 1718 Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.), was King of Sweden from 1697 to 1718. He belonged to the House of Palatinate-Zweibrücken, a branch line of the House of ...
. Two years later, the Swedish forces looted the area again, which resulted in almost total depopulation of the town. It was also damaged by the armies of Alexander Suvorov
Count Alexander Vasilyevich Suvorov-Rymniksky, Prince of Italy () was a Russian general and military theorist in the service of the Russian Empire.
Born in Moscow, he studied military history as a young boy and joined the Imperial Russian ...
in 1772, during the Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partition (politics), partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place between 1772 and 1795, toward the end of the 18th century. They ended the existence of the state, resulting in the eli ...
.
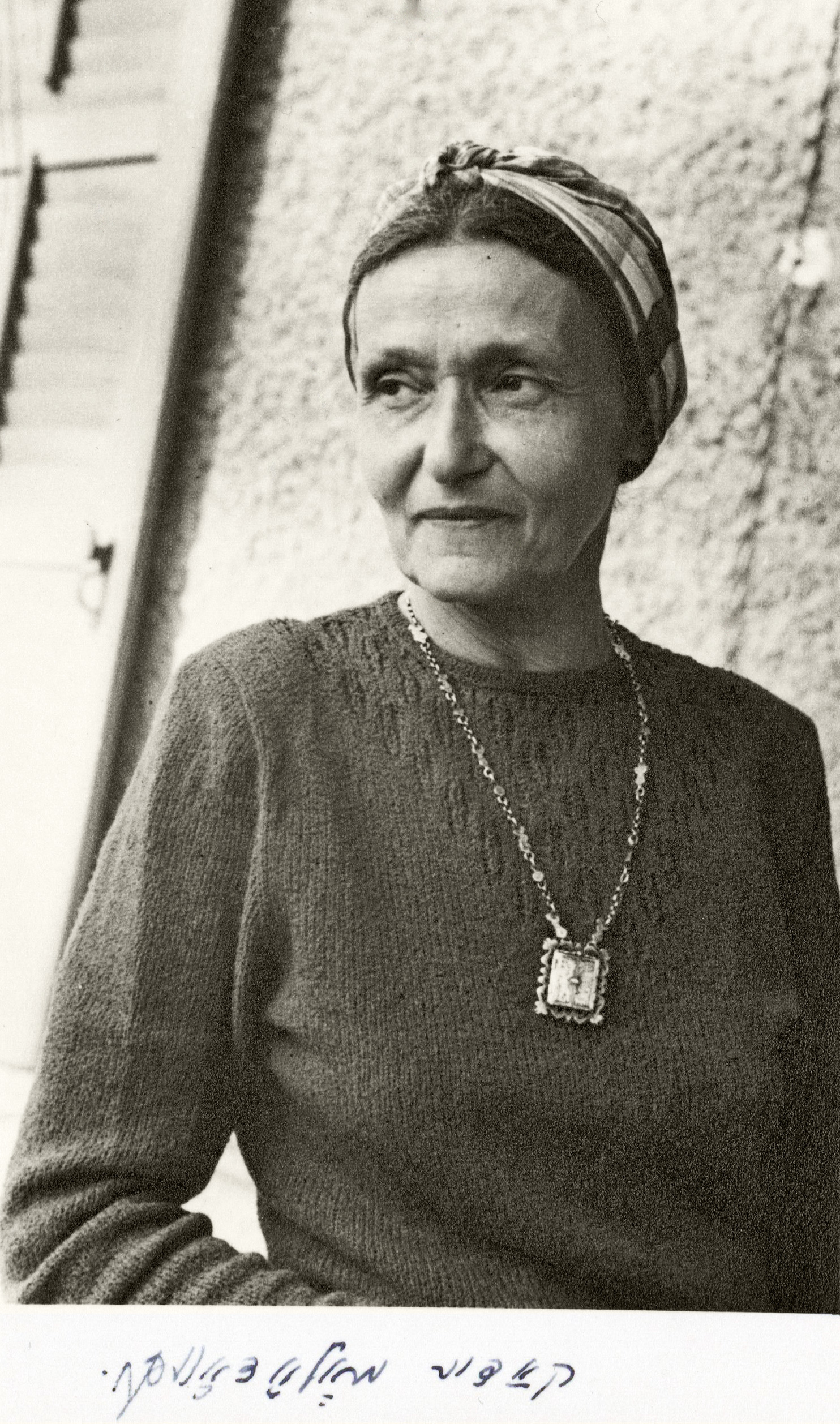
Under Russian rule
After the partitions, the town and the monastery were annexed byRussia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
in 1795. After the November Uprising
The November Uprising (1830–31) (), also known as the Polish–Russian War 1830–31 or the Cadet Revolution,
was an armed rebellion in Russian Partition, the heartland of Partitions of Poland, partitioned Poland against the Russian Empire. ...
of 1831 the town was captured by the Russian armies and then looted. The monastery was closed by tsarist authorities and in 1866, after the January Uprising
The January Uprising was an insurrection principally in Russia's Kingdom of Poland that was aimed at putting an end to Russian occupation of part of Poland and regaining independence. It began on 22 January 1863 and continued until the last i ...
, the whole complex was partially demolished, and the bricks were used for construction of a Russian prison and barracks nearby. The baroque church was destroyed in 1868. After the uprising, the town became a part of the so-called Pale of settlement
The Pale of Settlement was a western region of the Russian Empire with varying borders that existed from 1791 to 1917 (''de facto'' until 1915) in which permanent settlement by Jews was allowed and beyond which the creation of new Jewish settlem ...
and was repopulated with Jews expelled from other areas of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
. By the 20th century, they constituted more than 70% of the city's inhabitants. In 1842, a new road was opened between Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
and Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at ...
and passed through the town, which started a period of economic prosperity. In 1871, a Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at ...
-Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
railroad was laid only from the town, connecting the town with the nearby major cities of Brest and Minsk
Minsk (, ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach (Berezina), Svislach and the now subterranean Nyamiha, Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the administra ...
. In 1878, the town had a marketplace, 7 streets and approximately 200 houses. Both the town and the adjoining area had approximately 5,000 inhabitants. Apart from the Catholic and Uniate Churches, there was also a synagogue, Jewish baths and a market just outside the city limits.
In the 20th century
In 1915, during the First World War, the town was occupied by theImperial Germany
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
and in 1918 claimed by the short-lived Belarusian People's Republic
The Belarusian People's Republic (BNR; , ), also known as the Belarusian Democratic Republic, was a state proclaimed by the Council of the Belarusian Democratic Republic in its Second Constituent Charter on 9 March 1918 during World War I. The ...
. The town was captured by the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
on January 19, 1919, during the Soviet westward offensive of 1918–19
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the largest country by are ...
(Target-Vistula). Within one month, the Polish Army
The Land Forces () are the Army, land forces of the Polish Armed Forces. They currently contain some 110,000 active personnel and form many components of the European Union and NATO deployments around the world. Poland's recorded military histor ...
reclaimed the area, and recaptured the town on February 14, 1919. During the Polish-Bolshevik War the town became a notable location of two major battles including the war's very first and the second Battle of Bereza Kartuska (1920)
The Battle of Bereza Kartuska was fought between the Second Polish Republic and Soviet Russia around the village Bereza Kartuska (now Byaroza, Belarus) first on 14 February 1919, and again between 21 and 26 July 1920.
The first skirmish of Ber ...
. At the end of the Polish–Soviet War the town was ceded to Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
in the Peace of Riga
The Treaty of Riga was signed in Riga, Latvia, on between Poland on one side and Soviet Russia (acting also on behalf of Soviet Belarus) and Soviet Ukraine on the other, ending the Polish–Soviet War (1919–1921). The chief negotiators o ...
signed by Soviet Russia (acting also on behalf of Soviet Belarus). The peace treaty remained in force until the Soviet invasion of Poland
The Soviet invasion of Poland was a military conflict by the Soviet Union without a formal declaration of war. On 17 September 1939, the Soviet Union invaded Second Polish Republic, Poland from the east, 16 days after Nazi Germany invaded Polan ...
in 1939.
Polish prison
A Polish political prison camp was created in Bereza Kartuska in 1934. The former Russian barracks and prison were turned into aninternment
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without Criminal charge, charges or Indictment, intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects ...
camp for both Polish right-wing extremists from the ONR, Ukrainian separatists from the Organization of Ukrainian Nationalists
The Organisation of Ukrainian Nationalists (OUN; ) was a Ukrainian nationalist organization established on February 2, 1929 in Vienna, uniting the Ukrainian Military Organization with smaller, mainly youth, radical nationalist right-wing groups. ...
and members of the Communist Party of Poland
The interwar Communist Party of Poland (, KPP) was a communist party active in Poland during the Second Polish Republic. It resulted from a December 1918 merger of the Social Democracy of the Kingdom of Poland and Lithuania (SDKPiL) and the ...
and the Communist Party of Western Ukraine
The Communist Party of Western Ukraine (; ) was a clandestine political party in eastern interwar Poland. Until 1923 it was known as the Communist Party of Eastern Galicia (Komunistyczna Partia Wschodniej Galicji). The Young Communist League of ...
, and later also for members of opposition parties, journalists critical of the government and people suspected of common crimes. Inmates were sent there for up to three months without the involvement of the courts, based solely on the administrative decision of the police or the voivode
Voivode ( ), also spelled voivod, voievod or voevod and also known as vaivode ( ), voivoda, vojvoda, vaivada or wojewoda, is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe in use since the Early Mid ...
. In this way, many Belarusians who resisted Polonization
Polonization or Polonisation ()In Polish historiography, particularly pre-WWII (e.g., L. Wasilewski. As noted in Смалянчук А. Ф. (Smalyanchuk 2001) Паміж краёвасцю і нацыянальнай ідэяй. Польскі ...
found themselves in the Bereza Kartuska camp.Jan Zaprudnik
Jan Zaprudnik (9 August 1926 – 26 May 2022, born Siarhej Vilčycki) was a Belarusian Americans, Belarusian-American historian and publicist. He was also one of the leaders of the Belarusian Americans, Belarusian community in the United States ...
, "Belarus: At a Crossroads" (1993, ), p. 85
The legal basis for the camp opening was openly questioned and its existence was often criticized by opponents of the Sanacja
Sanation (, ) was a Polish political movement that emerged in the interwar period, prior to Józef Piłsudski's May Coup (Poland), May 1926 ''Coup d'État'', and gained influence following the coup. In 1928, its political activists went on to fo ...
movement, which from its inception called it a "concentration camp
A concentration camp is a prison or other facility used for the internment of political prisoners or politically targeted demographics, such as members of national or ethnic minority groups, on the grounds of national security, or for exploitati ...
". The camp was closed in September 1939, during the invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland, also known as the September Campaign, Polish Campaign, and Polish Defensive War of 1939 (1 September – 6 October 1939), was a joint attack on the Second Polish Republic, Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany, the Slovak R ...
.
After 1939
In 1939 the town was captured by the Red Army and incorporated into theByelorussian SSR
The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR, Byelorussian SSR or Byelorussia; ; ), also known as Soviet Belarus or simply Belarus, was a republic of the Soviet Union (USSR). It existed between 1920 and 1922 as an independent state, and ...
. After the outbreak of the German-Soviet War
The Eastern Front, also known as the Great Patriotic War (term), Great Patriotic War in the Soviet Union and its successor states, and the German–Soviet War in modern Germany and Ukraine, was a Theater (warfare), theatre of World War II ...
, the town was captured by the German Army
The German Army (, 'army') is the land component of the armed forces of Federal Republic of Germany, Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German together with the German Navy, ''Marine'' (G ...
on 23 June 1941. The German occupation lasted until 15 July 1944. During this time, Byaroza was administered as a part of Generalbezirk Wolhynien und Podolien of Reichskommissariat Ukraine
The ''Reichskommissariat Ukraine'' (RKU; ) was an administrative entity of the Reich Ministry for the Occupied Eastern Territories of Nazi Germany from 1941 to 1944. It served as the German civilian occupation regime in the Ukrainian SSR, and ...
.
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, a ghetto
A ghetto is a part of a city in which members of a minority group are concentrated, especially as a result of political, social, legal, religious, environmental or economic pressure. Ghettos are often known for being more impoverished than other ...
was created in the town for Jews who fled there from the surrounding areas. Under the Nazi German occupying administration — which had merged Byaroza, along with most of western Polesia
Polesia, also called Polissia, Polesie, or Polesye, is a natural (geographic) and historical region in Eastern Europe within the East European Plain, including the Belarus–Ukraine border region and part of eastern Poland. This region shou ...
, into the Reichskommissariat Ukraine
The ''Reichskommissariat Ukraine'' (RKU; ) was an administrative entity of the Reich Ministry for the Occupied Eastern Territories of Nazi Germany from 1941 to 1944. It served as the German civilian occupation regime in the Ukrainian SSR, and ...
— more than 8,000 people were killed in mass executions or were starved to death. Numerous pro-Soviet and pro-Ukrainian partisan units were active in the area around Byaroza before Red Army troops finally liberated the town on 15 July 1944. Repopulated with Belarusian and Russian peasants, the town was rebuilt after the destruction of World War II. After a minor building materials factory was opened in the town, another period of fast growth followed.
During the postwar period a Soviet Frontal Aviation
The Soviet Air Forces (, VVS SSSR; literally "Military Air Forces of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics"; initialism VVS, sometimes referred to as the "Red Air Force") were one of the air forces of the Soviet Union. The other was the Sovie ...
base, Osovcy was close to Biaroza.
In 1958-1967 a hydroelectric power station was built in the Biaroza Raion.
In 1991, after the dissolution of the USSR
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, the town became part of the independent Republic of Belarus
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a state in which political power rests with the public (people), typically through their representatives—in contrast to a monarchy. Although a ...
.
Mayors
* Berl (Dov) Ribak (1882 - 1915) * Naftali Levinson (1915 - 1919 acting, 1919 - 1939?)Heads of Biaroza District Executive Committee
* Yury Narkevich (2005 - 2016) * Leanid Martyniuk (since 2016)Landmarks
Although the 17th-century monastery was mostly destroyed in the 19th century, there are some ruins remaining. Among them are: * Historical gateway with a decorative façade * Parts of fortifications surrounding the monastery with several towers partially preserved * Ruins of the octagonal church tower * Ruins of the hospital * Several buildings later incorporated into the tsarist prison.Notable people
*Jakob Klatzkin
Jakob Klatzkin, Yakov/Jakub Klaczkin (; ; October 3, 1882, in Biaroza, Grodno Governorate, now Belarus – March 26, 1948, in Vevey, Switzerland) was a Jewish philosopher, publicist, author, and publisher.
Life
Klatzkin was born in Byaroza-Ka ...
, Jewish philosopher
* Kadia Molodowsky
Kadia Molodowsky (; also: Kadya Molodowsky; May 10, 1894, in Bereza Kartuska, now Byaroza, Belarus – March 23, 1975, in Philadelphia) was a Polish-American poet and writer in the Yiddish language, and a teacher of Yiddish and Hebrew. She pub ...
, Jewish poet and writer
* Kseniya Koçyiğit, Belarusian-born Azerbaijani professional volleyball player
See also
* Battle of Bereza KartuskaNotes
References
Bibliography
*External links
Photos on Radzima.org
Biaroza on Googlemaps
on
JewishGen
JewishGen is a non-profit organization founded in 1987 as an international electronic resource for Jewish genealogy. In 2003, JewishGen became an affiliate of the Museum of Jewish Heritage – A Living Memorial to the Holocaust in New York ...
Kartuz-Bereza cemetery
* {{Coord, 52, 33, N, 24, 58, E, type:city, display=title Holocaust locations in Belarus