Betti Reaction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Betti reaction is a
 Today, the name has grown to refer to any reaction of aldehydes, primary aromatic amines and phenols producing α-aminobenzylphenols.
Today, the name has grown to refer to any reaction of aldehydes, primary aromatic amines and phenols producing α-aminobenzylphenols.
 First, the lone-pair on the nitrogen of the imine deprotonates the phenol, pushing the
First, the lone-pair on the nitrogen of the imine deprotonates the phenol, pushing the
 The product of the Betti reaction is called the Betti base. The stereochemistry of the base was resolved into two isomers by using
The product of the Betti reaction is called the Betti base. The stereochemistry of the base was resolved into two isomers by using
Article
* Pirrone, F '' Gazz. Chim. Ital.'' 1936, ''66'', 518. * Pirrone, F '' Gazz. Chim. Ital.'' 1937, ''67'', 529. * Phillips, J. P. '' Chem. Rev.'' 1956, ''56'', 286. * Phillips, J. P.; Barrall, E. M. ''
chemical
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combin ...
addition
Addition (usually signified by the Plus and minus signs#Plus sign, plus symbol, +) is one of the four basic Operation (mathematics), operations of arithmetic, the other three being subtraction, multiplication, and Division (mathematics), divis ...
reaction of aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () (lat. ''al''cohol ''dehyd''rogenatum, dehydrogenated alcohol) is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred ...
s, primary aromatic
In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated system, conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected from conjugati ...
amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of elec ...
s and phenol
Phenol (also known as carbolic acid, phenolic acid, or benzenol) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile and can catch fire.
The molecule consists of a phenyl group () ...
s producing α-aminobenzylphenols.
The Betti reaction is a special case of the Mannich reaction
In organic chemistry, the Mannich reaction is a three-component organic reaction that involves the amino alkylation of an acidic proton next to a carbonyl () functional group by formaldehyde () and a primary or secondary amine () or ammonia () ...
.
History
The reaction is named after the Italian chemist Mario Betti (1857-1942). Betti worked at many universities in Italy, includingFlorence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025.
Florence ...
, Cagliari
Cagliari (, , ; ; ; Latin: ''Caralis'') is an Comune, Italian municipality and the capital and largest city of the island of Sardinia, an Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Italy. It has about 146,62 ...
, Siena
Siena ( , ; traditionally spelled Sienna in English; ) is a city in Tuscany, in central Italy, and the capital of the province of Siena. It is the twelfth most populated city in the region by number of inhabitants, with a population of 52,991 ...
, Genoa
Genoa ( ; ; ) is a city in and the capital of the Italian region of Liguria, and the sixth-largest city in Italy. As of 2025, 563,947 people live within the city's administrative limits. While its metropolitan city has 818,651 inhabitan ...
and Bologna
Bologna ( , , ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Emilia-Romagna region in northern Italy. It is the List of cities in Italy, seventh most populous city in Italy, with about 400,000 inhabitants and 150 different nationalities. Its M ...
, where he was the successor of Giacomo Ciamician. Betti's main research was focused on stereochemistry
Stereochemistry, a subdiscipline of chemistry, studies the spatial arrangement of atoms that form the structure of molecules and their manipulation. The study of stereochemistry focuses on the relationships between stereoisomers, which are defined ...
, and the resolution of racemic
In chemistry, a racemic mixture or racemate () is a mixture that has equal amounts (50:50) of left- and right-handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule or salt. Racemic mixtures are rare in nature, but many compounds are produced industrially as r ...
compounds, the relationship between molecular constitution and optical rotation
Optical rotation, also known as polarization rotation or circular birefringence, is the rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarization about the optical axis of linearly polarized light as it travels through certain materials. Circul ...
, as well asymmetric synthesis
Enantioselective synthesis, also called asymmetric synthesis, is a form of chemical synthesis. It is defined by IUPAC as "a chemical reaction (or reaction sequence) in which one or more new elements of chirality are formed in a substrate molecul ...
using chiral auxiliaries
In stereochemistry, a chiral auxiliary is a stereogenic group or unit that is temporarily incorporated into an organic compound in order to control the stereochemical outcome of the synthesis. The chirality present in the auxiliary can bias the st ...
or in the presence of polarized light
, or , is a property of transverse waves which specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. One example of a polarize ...
.
In 1939 Mario Betti was appointed the Senator of the Kingdom of Italy
The Senate of the Kingdom of Italy () was the upper house of the bicameral parliament of the Kingdom of Italy, officially created on 4 March 1848, acting as an evolution of the original Subalpine Senate. It was replaced on 1 January 1948 by the ...
.
In 1900 Betti hypothesized that 2-naphthol
2-Naphthol, or β-naphthol, is a fluorescent colorless (or occasionally yellow) crystalline solid with the formula C10H7OH. It is an isomer of 1-naphthol, differing by the location of the hydroxyl group on the naphthalene ring. The naphthols are ...
would be a good carbon nucleophile
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are ...
to the imine
In organic chemistry, an imine ( or ) is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond (). The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bon ...
produced from the reaction of benzaldehyde
Benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO) is an organic compound consisting of a benzene ring with a formyl substituent. It is among the simplest aromatic aldehydes and one of the most industrially useful.
It is a colorless liquid with a characteristic almond-li ...
and aniline
Aniline (From , meaning ' indigo shrub', and ''-ine'' indicating a derived substance) is an organic compound with the formula . Consisting of a phenyl group () attached to an amino group (), aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an in ...
. This led to the Betti reaction.Cardellicchio, C.; Capozzi, M.A.M.; Naso, F. '' Tetrahedron: Asymmetry''. 2010, ''21'', 507-517.()
 Today, the name has grown to refer to any reaction of aldehydes, primary aromatic amines and phenols producing α-aminobenzylphenols.
Today, the name has grown to refer to any reaction of aldehydes, primary aromatic amines and phenols producing α-aminobenzylphenols.
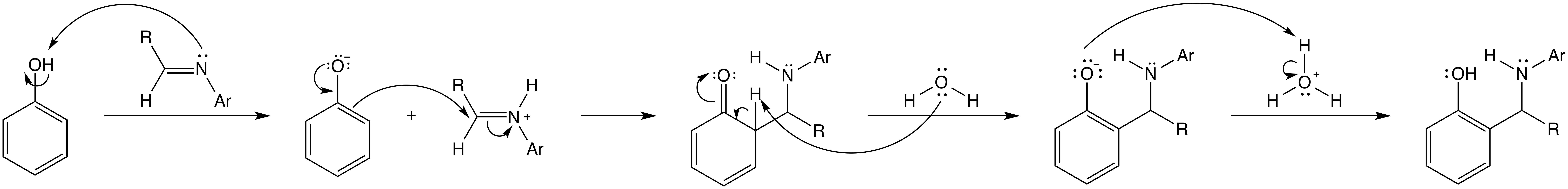
Mechanism
Thereaction mechanism
In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical reaction occurs.
A chemical mechanism is a theoretical conjecture that tries to describe in detail what takes place at each stage ...
begins with an imine condensation of a primary aromatic amine and formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is an organic compound with the chemical formula and structure , more precisely . The compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde. It is stored as ...
Once the imine is produced, it reacts with phenol
Phenol (also known as carbolic acid, phenolic acid, or benzenol) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile and can catch fire.
The molecule consists of a phenyl group () ...
in the presence of water to yield an α-aminobenzylphenol.
 First, the lone-pair on the nitrogen of the imine deprotonates the phenol, pushing the
First, the lone-pair on the nitrogen of the imine deprotonates the phenol, pushing the bond
Bond or bonds may refer to:
Common meanings
* Bond (finance), a type of debt security
* Bail bond, a commercial third-party guarantor of surety bonds in the United States
* Fidelity bond, a type of insurance policy for employers
* Chemical bond, t ...
ing electrons
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
onto the oxygen. The carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group with the formula , composed of a carbon atom double bond, double-bonded to an oxygen atom, and it is divalent at the C atom. It is common to several classes of organic compounds (such a ...
is then reformed and a double bond
In chemistry, a double bond is a covalent bond between two atoms involving four bonding electrons as opposed to two in a single bond. Double bonds occur most commonly between two carbon atoms, for example in alkenes. Many double bonds exist betw ...
in the benzene ring
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydr ...
attacks the carbon atom in the pronated imine cation. Water then acts as a base and deprotonates the α-carbon
In the nomenclature of organic chemistry, a locant is a term to indicate the position of a functional group or substituent within a molecule.
Numeric locants
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) recommends the use of n ...
, reforming the aromatic ring and pushing electrons onto oxygen. The oxygen, which now has a negative formal charge
In chemistry, a formal charge (F.C. or ), in the covalent view of chemical bonding, is the hypothetical charge assigned to an atom in a molecule, assuming that electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally between atoms, regardless of rela ...
, then attacks a hydrogen on the hydronium
In chemistry, hydronium (hydroxonium in traditional British English) is the cation , also written as , the type of oxonium ion produced by protonation of water. It is often viewed as the positive ion present when an Arrhenius acid is dissolved ...
, resulting in an α-aminobenzylphenol, with water as the only byproduct.
Betti Base
 The product of the Betti reaction is called the Betti base. The stereochemistry of the base was resolved into two isomers by using
The product of the Betti reaction is called the Betti base. The stereochemistry of the base was resolved into two isomers by using tartaric acid
Tartaric acid is a white, crystalline organic acid that occurs naturally in many fruits, most notably in grapes but also in tamarinds, bananas, avocados, and citrus. Its salt (chemistry), salt, potassium bitartrate, commonly known as cream of ta ...
.
Uses for the Betti base and its derivatives include:Cardellicchio, C.; Ciccarella, C.; Naso, F.; Schingaro,E.; Scordari, F. '' Tetrahedron: Asymmetry''. 1998, ''9'', 3667-3675. ()
*Enantioselective
In chemistry, stereoselectivity is the property of a chemical reaction in which a single reactant forms an unequal mixture of stereoisomers during a non- stereospecific creation of a new stereocenter or during a non-stereospecific transformation o ...
addition of diethylzinc
Diethylzinc, or DEZ, is an organozinc compound with the chemical formula . It is highly pyrophoric and reactive, consisting of a zinc center bound to two ethyl groups. This colourless liquid is an important reagent in organic chemistry. It is avail ...
to aryl
In organic chemistry, an aryl is any functional group or substituent derived from an aromatic ring, usually an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as phenyl and naphthyl. "Aryl" is used for the sake of abbreviation or generalization, and "Ar" is used ...
aldehydes.
*Enantioselective alkenylation of aldehydes.
*Preparation of stable boronate complexes, which can be alkylated Alkylation is a chemical reaction that entails transfer of an alkyl group. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene (or their equivalents). Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting al ...
to yield amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
precursors.
*Separation of enantiomers
In chemistry, an enantiomer (Help:IPA/English, /ɪˈnænti.əmər, ɛ-, -oʊ-/ Help:Pronunciation respelling key, ''ih-NAN-tee-ə-mər''), also known as an optical isomer, antipode, or optical antipode, is one of a pair of molecular entities whi ...
.
References
Further reading
* Betti, M. '' Gazz. Chim. Ital.'' 1900, ''30 II'', 301. * Betti, M. '' Gazz. Chim. Ital.'' 1903, ''33 II'', 2. *Organic Syntheses
''Organic Syntheses'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1921. It publishes detailed and checked procedures for the synthesis of organic compounds. A unique feature of the review process is that all of the data and expe ...
, Coll. Vol. 1, p.381 (1941); Vol. 9, p.60 (1929).Article
* Pirrone, F '' Gazz. Chim. Ital.'' 1936, ''66'', 518. * Pirrone, F '' Gazz. Chim. Ital.'' 1937, ''67'', 529. * Phillips, J. P. '' Chem. Rev.'' 1956, ''56'', 286. * Phillips, J. P.; Barrall, E. M. ''
J. Org. Chem.
''The Journal of Organic Chemistry'', colloquially known as ''JOC'', is a peer-reviewed scientific journal for original contributions of fundamental research in all branches of theory and practice in organic and bioorganic chemistry. It is publ ...
'' 1956, ''21'', 692.
* Kumar, A.; Kumar, M.; Gupta, M. K. '' Tetrahedron Lett.'' 2010, ''12'', 1582-1584.
{{Organic reactions
Addition reactions
Multiple component reactions
Name reactions