Bessel Points on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Airy points (after
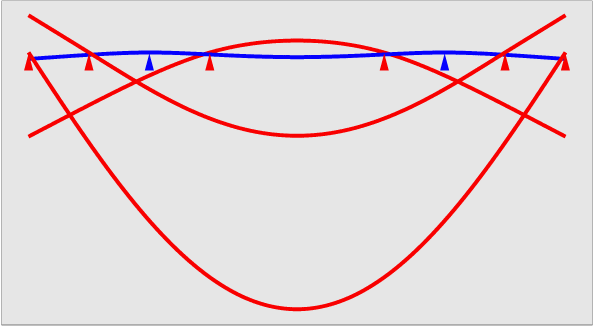 A kinematic support for a one-dimensional beam requires exactly two support points. Three or more support points will not share the load evenly (unless they are hinged in a non-rigid whiffle tree or similar). The position of those points can be chosen to minimize various forms of gravity deflection.
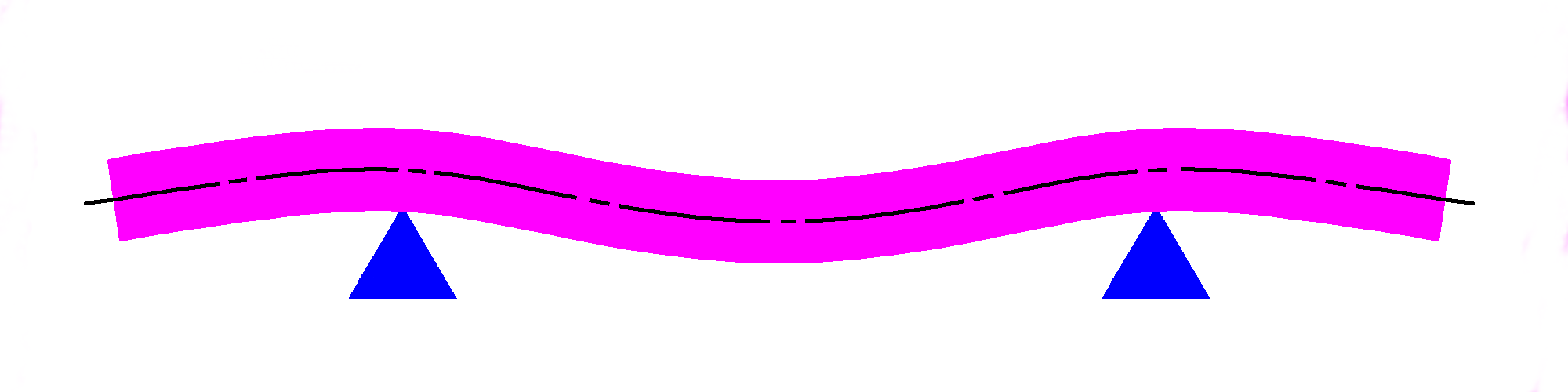
A beam supported at the ends will sag in the middle, resulting in the ends moving closer together and tilting upward. A beam supported only in the middle will sag at the ends, making a similar shape but upside down.
A kinematic support for a one-dimensional beam requires exactly two support points. Three or more support points will not share the load evenly (unless they are hinged in a non-rigid whiffle tree or similar). The position of those points can be chosen to minimize various forms of gravity deflection.
A beam supported at the ends will sag in the middle, resulting in the ends moving closer together and tilting upward. A beam supported only in the middle will sag at the ends, making a similar shape but upside down.
 Supporting a uniform beam at the Airy points produces zero angular deflection of the ends. The Airy points are symmetrically arranged around the centre of the length standard and are separated by a distance equal to
:
of the length of the rod.
"End standards", that is standards whose length is defined as the distance between their flat ends such as long
Supporting a uniform beam at the Airy points produces zero angular deflection of the ends. The Airy points are symmetrically arranged around the centre of the length standard and are separated by a distance equal to
:
of the length of the rod.
"End standards", that is standards whose length is defined as the distance between their flat ends such as long
 "Line standards" are measured between lines marked on their surfaces. They are much less convenient to use than end standards but, when the marks are placed on the
"Line standards" are measured between lines marked on their surfaces. They are much less convenient to use than end standards but, when the marks are placed on the
George Biddell Airy
Sir George Biddell Airy (; 27 July 18012 January 1892) was an English mathematician and astronomer, as well as the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics from 1826 to 1828 and the seventh Astronomer Royal from 1835 to 1881. His many achievements inc ...
) are used for precision measurement (metrology
Metrology is the scientific study of measurement. It establishes a common understanding of Unit of measurement, units, crucial in linking human activities. Modern metrology has its roots in the French Revolution's political motivation to stan ...
) to support a length standard in such a way as to minimise bending
In applied mechanics, bending (also known as flexure) characterizes the behavior of a slender structural element subjected to an external Structural load, load applied perpendicularly to a longitudinal axis of the element.
The structural eleme ...
or drop of a horizontally supported beam.
Choice of support points
 A kinematic support for a one-dimensional beam requires exactly two support points. Three or more support points will not share the load evenly (unless they are hinged in a non-rigid whiffle tree or similar). The position of those points can be chosen to minimize various forms of gravity deflection.
A beam supported at the ends will sag in the middle, resulting in the ends moving closer together and tilting upward. A beam supported only in the middle will sag at the ends, making a similar shape but upside down.
A kinematic support for a one-dimensional beam requires exactly two support points. Three or more support points will not share the load evenly (unless they are hinged in a non-rigid whiffle tree or similar). The position of those points can be chosen to minimize various forms of gravity deflection.
A beam supported at the ends will sag in the middle, resulting in the ends moving closer together and tilting upward. A beam supported only in the middle will sag at the ends, making a similar shape but upside down.
Airy points
 Supporting a uniform beam at the Airy points produces zero angular deflection of the ends. The Airy points are symmetrically arranged around the centre of the length standard and are separated by a distance equal to
:
of the length of the rod.
"End standards", that is standards whose length is defined as the distance between their flat ends such as long
Supporting a uniform beam at the Airy points produces zero angular deflection of the ends. The Airy points are symmetrically arranged around the centre of the length standard and are separated by a distance equal to
:
of the length of the rod.
"End standards", that is standards whose length is defined as the distance between their flat ends such as long gauge block
Gauge blocks (also known as gage blocks, Johansson gauges, slip gauges, or Jo blocks) are a system for producing precision lengths. The individual gauge block is a metal or ceramic block that has been precision grinding (abrasive cutting), grou ...
s or the , must be supported at the Airy points so that their length is well-defined; if the ends are not parallel, the measurement uncertainty
In metrology, measurement uncertainty is the expression of the statistical dispersion of the values attributed to a quantity measured on an interval or ratio scale.
All measurements are subject to uncertainty and a measurement result is complet ...
is increased because the length depends on which part of the end is measured. For this reason, the Airy points are commonly identified by inscribed marks or lines. For example, a 1000 mm length gauge would have an Airy point separation of 577.4 mm. A line or pair of lines would be marked onto the gauge 211.3 mm in from each end. Supporting the artifact at these points ensures that the calibrate
In measurement technology and metrology, calibration is the comparison of measurement values delivered by a device under test with those of a calibration standard of known accuracy. Such a standard could be another measurement device of known ...
d length is preserved.
Airy's 1845 paper derives the equation for equally spaced support points. In this case, the distance between each support is the fraction
:
the length of the rod. He also derives the formula for a rod which extends beyond the reference marks.
Bessel points

neutral plane
In mechanics, the neutral plane or neutral surface is a conceptual plane within a beam or cantilever. When loaded by a bending force, the beam bends so that the inner surface is in compression and the outer surface is in tension. The neutral pl ...
of the beam, allow greater accuracy.
To support a line standard, one wishes to minimise the ''linear'', rather than angular, motion of the ends. The Bessel points (after Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel
Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel (; 22 July 1784 – 17 March 1846) was a German astronomer, mathematician, physicist, and geodesist. He was the first astronomer who determined reliable values for the distance from the Sun to another star by the method ...
) are the points at which the length of the beam is maximized. Because this is a maximum
In mathematical analysis, the maximum and minimum of a function (mathematics), function are, respectively, the greatest and least value taken by the function. Known generically as extremum, they may be defined either within a given Interval (ma ...
, the effect of a small positioning error is proportional to the square of the error, an even smaller amount.
The Bessel points are located 0.5594 of the length of the rod apart, slightly closer than the Airy points.
Because line standards invariably extend beyond the lines marked on them, the optimal support points depend on both the overall length and the length to be measured. The latter is the quantity to be maximized, requiring a more complex calculation. For example, the 1927–1960 definition of the metre
The metre (or meter in US spelling; symbol: m) is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI). Since 2019, the metre has been defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of of ...
specified that the International Prototype Metre
During the French Revolution, the traditional units of measure were to be replaced by consistent measures based on natural phenomena. As a base unit of length, scientists had favoured the seconds pendulum (a pendulum with a half-period of o ...
bar was to be measured while "supported on two cylinders of at least one centimetre diameter, symmetrically placed in the same horizontal plane at a distance of 571 mm from each other." Those would be the Bessel points of a beam 1020 mm long.
Other support points of interest
Other sets of support points, even closer than the Bessel points, which may be wanted in some applications are: * The points for minimum sag, 0.5536 times the length. Minimum sag occurs when the centre of the rod sags the same amount as the end points, which is not quite the same thing as minimum ''horizontal'' motion of the ends. * Thenode
In general, a node is a localized swelling (a "knot") or a point of intersection (a vertex).
Node may refer to:
In mathematics
* Vertex (graph theory), a vertex in a mathematical graph
*Vertex (geometry), a point where two or more curves, lines ...
s of free vibration, 0.5516 times the length.
* The points for zero central sag (any closer and the beam rises between the support points): 0.5228 times the length.
See also
*History of measurement
The earliest recorded systems of weights and measures originate in the 3rd or 4th millennium BC. Even the very earliest civilizations needed measurement for purposes of agriculture, construction and trade. Early standard units might only have ap ...
* History of the metre
During the French Revolution, the traditional units of measure were to be replaced by consistent measures based on natural phenomena. As a base unit of length, scientists had favoured the seconds pendulum (a pendulum with a half-period of ...
* Neutral plane
In mechanics, the neutral plane or neutral surface is a conceptual plane within a beam or cantilever. When loaded by a bending force, the beam bends so that the inner surface is in compression and the outer surface is in tension. The neutral pl ...
* Test method
A test method is a method for a test in science or engineering, such as a physical test, chemical test, or statistical test. It is a specified procedure that produces a test result. To ensure accurate and relevant results, a test method should b ...
* Units of measurement
A unit of measurement, or unit of measure, is a definite magnitude (mathematics), magnitude of a quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same kind of quantity. Any other qua ...
* Weights and measures
A unit of measurement, or unit of measure, is a definite magnitude (mathematics), magnitude of a quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same kind of quantity. Any other qua ...
References