Berlinka on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Berlinka () is the informal Polish and Russian name given to sections of the unfinished Reichsautobahn Berlin-Königsberg, which was a pre-World War II German
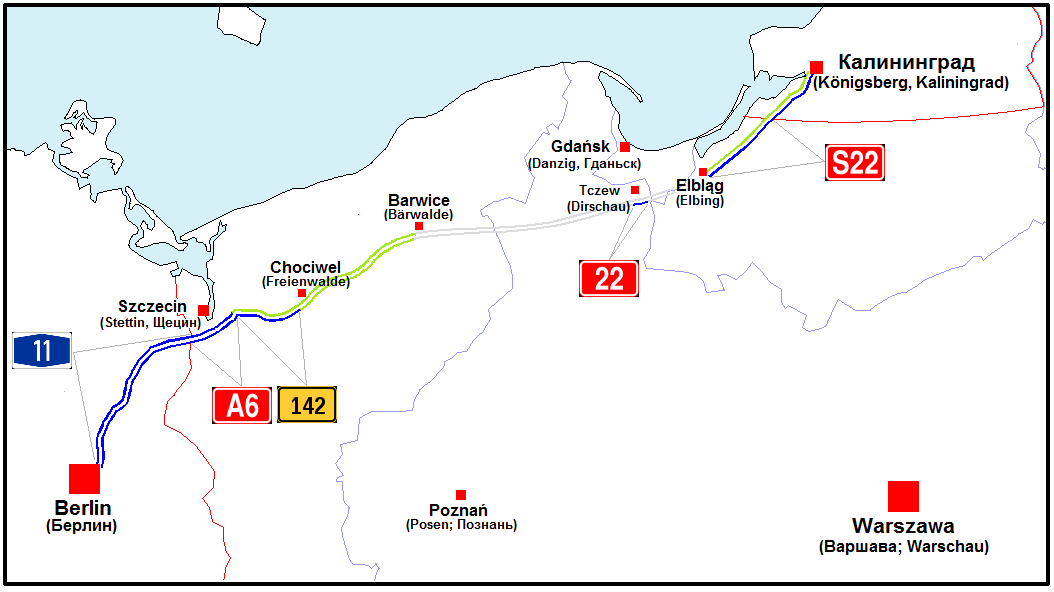 Eastern Prussia had been separated from Germany following the
Eastern Prussia had been separated from Germany following the
1937 map1938 map from Königsberg to Schalmey/Braunsberg
1938 map from Schalmey/Braunsberg to Elbing
1944 mapAutobahn-online
{{in lang, pl Buildings and structures completed in 1933 Roads in Germany Roads in Poland Roads in Russia
Reichsautobahn
The system was the beginning of the German autobahns under Nazi Germany. There had been previous plans for controlled-access highway
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traf ...
project to connect Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
with Königsberg
Königsberg (; ; ; ; ; ; , ) is the historic Germany, German and Prussian name of the city now called Kaliningrad, Russia. The city was founded in 1255 on the site of the small Old Prussians, Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teuton ...
in East Prussia
East Prussia was a Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1772 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 1871); following World War I it formed part of the Weimar Republic's ...
. In the late 1930s, the sections near these two cities were finished, but not the larger section in between. The German demand in 1939 to run this road across the Polish Corridor with extraterritorial status and Poland's refusal to allow this were used by Nazi Germany as a pretext to start a war. During the war, the Germans did not continue construction on a large scale and the route was never built. After the war, the German Democratic Republic
East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country in Central Europe from Foundation of East Germany, its formation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with West Germany (FRG) on ...
, the Polish People's Republic
The Polish People's Republic (1952–1989), formerly the Republic of Poland (1947–1952), and also often simply known as Poland, was a country in Central Europe that existed as the predecessor of the modern-day democratic Republic of Poland. ...
and the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
's Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast () is the westernmost federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of the Russian Federation. It is a Enclave and exclave, semi-exclave on the Baltic Sea within the Baltic region of Prussia (region), Prussia, surrounded by Pola ...
inherited the remnants.
Background
Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace ...
by the Polish Corridor of the Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 7 October 1918 and 6 October 1939. The state was established in the final stage of World War I ...
. By 1939, Poland had already refused demands made by Nazi Germany, including one for an extraterritorial
In international law, extraterritoriality or exterritoriality is the state of being exempted from the jurisdiction of local law, usually as the result of diplomatic negotiations.
Historically, this primarily applied to individuals, as jurisdict ...
corridor within the Polish territory. This fact was eventually used by Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
as one of the pretexts for the German invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland, also known as the September Campaign, Polish Campaign, and Polish Defensive War of 1939 (1 September – 6 October 1939), was a joint attack on the Second Polish Republic, Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany, the Slovak R ...
in 1939.
The road was planned under the Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic, officially known as the German Reich, was the German Reich, German state from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional republic for the first time in history; hence it is also referred to, and unofficially proclai ...
, but was partially constructed during the 1930s and early 1940s by the Third Reich
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a totalitarian dictat ...
.
Following territorial changes made after World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
it ran through three countries: the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
's Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast () is the westernmost federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of the Russian Federation. It is a Enclave and exclave, semi-exclave on the Baltic Sea within the Baltic region of Prussia (region), Prussia, surrounded by Pola ...
(today an exclave
An enclave is a territory that is entirely surrounded by the territory of only one other state or entity. An enclave can be an independent territory or part of a larger one. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is s ...
of the same name, in post-1991 Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
), Poland, and what had been East Germany
East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country in Central Europe from Foundation of East Germany, its formation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with West Germany (FRG) on ...
through to October 1990. Its original purpose gone, some segments of the road were incorporated into local road networks while most of it fell into disrepair. The border between the Kaliningrad Oblast and Poland was completely sealed to civilian traffic during the Cold War, given the high density of Soviet military installations in that area, which ensured the Berlinka section in that area saw almost no use. The border between Poland and East Germany was open to civilian traffic but the economies of the two countries were not well connected and auto traffic between them was not significant for many decades. Given these conditions, some segments of Berlinka became a minor tourist attraction in the years after the war, as an example of a Nazi-built autobahn preserved in an almost pristine state, carrying very little or no traffic. A number of movies made in Poland and the USSR that were set in Germany had their ''autobahn'' scenes shot on Berlinka sections. A popular Polish book and television series about Pan Samochodzik had a high speed car chase that was set on Berlinka (as at the time one of the few places in Poland where a high speed car chase was even plausible, given the execrable condition of other roads). In recent years that attraction has diminished as most of the stretches completed in the 1930s have been reconstructed to modern standards and largely lost their original appearance. Today the last remaining stretch in Poland that still has Nazi era construction features is signed as voivodeship road 142, north-east of Szczecin
Szczecin ( , , ; ; ; or ) is the capital city, capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the Poland-Germany border, German border, it is a major port, seaport, the la ...
. As that stretch is only a local road, it is unlikely to be rebuilt in the foreseeable future. On the Russian side, the remains of the old road are still visible () next to the E28 highway from the Polish-Russian border to the ring road of the city of Kaliningrad.
Along with constructing the motorway, after invading Poland, the Germans also quickly upgraded the main road going to East Prussia, in places paving it with concrete. Even though it is only a single carriageway road and not a motorway, it is also considered to be a part of the Berlinka's route. This section includes one interesting cloverleaf interchange
A cloverleaf interchange is a two-level interchange (road), interchange in which all turns are handled by slip roads. To go left (in right-hand traffic; reverse directions in left-driving regions), vehicles first continue as one road passe ...
() some south-southeast of Gdańsk
Gdańsk is a city on the Baltic Sea, Baltic coast of northern Poland, and the capital of the Pomeranian Voivodeship. With a population of 486,492, Data for territorial unit 2261000. it is Poland's sixth-largest city and principal seaport. Gdań ...
, and a large bridge over the Vistula
The Vistula (; ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest in Europe, at in length. Its drainage basin, extending into three other countries apart from Poland, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra i ...
south of Tczew
Tczew (, formerly ) is a city on the Vistula River in the Pomeranian Voivodeship, in northern Poland, with 59,111 inhabitants (December 2021). It is the capital of Tczew County and the largest city of the ethnocultural region of Kociewie within th ...
().
Construction
Construction began in late 1933, using unemployed German workers as part of the state's reforms to counteract theGreat Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
, the construction of the ''Reichsautobahn
The system was the beginning of the German autobahns under Nazi Germany. There had been previous plans for controlled-access highway
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traf ...
'' (RAB) network. The first 113 kilometre (70 mile) long segment near Stettin (now Szczecin), Stettiner Dreieck to Stettin-Süd, was opened on September 27, 1936. The segment from Königsberg
Königsberg (; ; ; ; ; ; , ) is the historic Germany, German and Prussian name of the city now called Kaliningrad, Russia. The city was founded in 1255 on the site of the small Old Prussians, Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teuton ...
to Elbing (now Elbląg
Elbląg (; ; ) is a city in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, in northern Poland, located in the eastern edge of the Żuławy region with 127,390 inhabitants, as of December 2021. It is the capital of Elbląg County.
Elbląg is one of the ol ...
) was opened in 1937. In 1937, beltway
A ring road (also known as circular road, beltline, beltway, circumferential (high)way, loop or orbital) is a road or a series of connected roads encircling a town, city or country. The most common purpose of a ring road is to assist in reducin ...
s near Stettin and Elbing were built.
In 1938, work slowed as Germany geared up for war
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or between such organi ...
, and workers were directed to other projects. The highway featured prominently in Nazi political rhetoric of 1939, as Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
's demands included an extraterritorial
In international law, extraterritoriality or exterritoriality is the state of being exempted from the jurisdiction of local law, usually as the result of diplomatic negotiations.
Historically, this primarily applied to individuals, as jurisdict ...
corridor—the Danzig Corridor through the Polish Corridor—which would connect Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
to Eastern Prussia. This, alongside other demands, was refused by the Polish government, and Hitler used this as one of the pretexts for the invasion of Poland in September 1939.
By October 1939, Poland was defeated, and work on the Berlinka resumed. The labour pool was increasingly composed of conscript workers from Poland. The Bäderstraße (near Rzęśnica and Wielgowo) to Stargard-Massow (near Łęczyca
Łęczyca (; in full the Royal Town of Łęczyca, ; ; ) is a town of inhabitants in central Poland. Situated in the Łódź Voivodeship, it is the county seat of the Łęczyca County. Łęczyca is a capital of the historical Łęczyca Land.
Or ...
) segment was built subsequently. Construction stopped in 1942, as military priorities once again took over available labour. In 1945, German forces, retreating along the Eastern Front, blew up most of the bridges to slow the Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
advance.
Aftermath
Because ofterritorial changes of Poland
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, belonging or connected to a particular country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually a geographic area which has not been granted the powers of self-government, ...
and Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
following the war, the road was divided and lost its importance as a route between German cities ( most of Prussia's German population was expelled to Germany). The part that remained within German borders became the Bundesautobahn 11 after reunification.
Certain segments of the route were nonetheless restored. In the Polish People's Republic
The Polish People's Republic (1952–1989), formerly the Republic of Poland (1947–1952), and also often simply known as Poland, was a country in Central Europe that existed as the predecessor of the modern-day democratic Republic of Poland. ...
, bridges over the Oder River
The Oder ( ; Czech and ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and its largest tributary the Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows through west ...
near Szczecin were restored soon after the war, as were the bridges on the Banówka River near the border with the Kaliningrad Oblast. In the 1970s, the planned part of the highway from Maszewo (near Łęczyca) to Chociwel was finished, and bridges on the Ina River restored.
With the end of the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
, and particularly with Poland joining the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
, increasing thought has been given to reconstructing the road as part of the European highway system. In the 1990s, a 14 kilometre (8.7 mile) long segment near the western Polish border was incorporated into the new A6 Autostrada (highway). A further , to the junction with National Road 10, was being restored and was scheduled to open for traffic in August 2007. An additional is to be upgraded at some future date and redesignated as part of the A6. The section between Elbląg and the border with Russia was completely reconstructed and opened as an express road, S22, in September 2008. In the course of the upgrade, the new modern carriageway was built in the space left for the second carriageway during original construction. At the same time, the original concrete carriageway was demolished almost along the entire length of the route, and only a few traces of it remain. All of the remaining original overpasses and bridges were demolished and replaced with modern works. Thus very few traces of the original German autobahn can be seen. Other part of the ''Berlinka'' are incorporated into ''voivodeship'' road 142, and ''expressroad'' 6/3. In the Russian Kaliningrad Oblast, it is incorporated into road P516.
As the original road was designed over 80 years ago, it would make little sense today to run a modern motorway along the same route as factors affecting road design changed greatly. Currently the road in Poland which will serve most of the route along which the Berlinka runs will be the S6 Expressway, set to the north of the Berlinka's route, closer to the Baltic coast and running from Szczecin to Gdańsk.
See also
* Borovsko Bridge * Danube-Oder Canal * M2 highway (Russia), the "Crimea" motorway from Moscow to the Ukraine border at Hoptivka, with an uncertain completion date to the Crimea.References
External links
1937 map
1938 map from Schalmey/Braunsberg to Elbing
1944 map
{{in lang, pl Buildings and structures completed in 1933 Roads in Germany Roads in Poland Roads in Russia