Berkhamsted ( ) is a historic market town in
Hertfordshire
Hertfordshire ( or ; often abbreviated Herts) is a ceremonial county in the East of England and one of the home counties. It borders Bedfordshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the north-east, Essex to the east, Greater London to the ...
, England, in the
Bulbourne valley, north-west of London. The town is a
civil parish
In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government. Civil parishes can trace their origin to the ancient system of parishes, w ...
with a
town council
A town council, city council or municipal council is a form of local government for small municipalities.
Usage of the term varies under different jurisdictions.
Republic of Ireland
In 2002, 49 urban district councils and 26 town commissi ...
within the
borough
A borough is an administrative division in various English language, English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
...
of
Dacorum
Dacorum is a Non-metropolitan district, local government district with borough status in the United Kingdom, borough status in Hertfordshire, England. The council is based in Hemel Hempstead. The borough also includes the towns of Berkhamsted ...
which is based in the neighbouring large
new town
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz (South Korean band), The Boyz
* New (album), ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
** New (Paul McCartney song), "New" (Paul McCartney song), 2013
* New (EP), ''New'' (EP), ...
of
Hemel Hempstead
Hemel Hempstead () is a town in the Dacorum district in Hertfordshire, England. It is located north-west of London; nearby towns and cities include Watford, St Albans and Berkhamsted. The population at the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 cens ...
. Berkhamsted, along with the adjoining village of
Northchurch, is encircled by countryside, much of it in the
Chiltern Hills
The Chiltern Hills or the Chilterns are a chalk escarpment in southern England, located to the north-west of London, covering across Oxfordshire, Buckinghamshire, Hertfordshire and Bedfordshire; they stretch from Goring-on-Thames in the south- ...
which is an
Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty
An Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB; , AHNE) is one of 46 areas of countryside in England, Wales, or Northern Ireland that has been designated for conservation due to its significant landscape value. Since 2023, the areas in England an ...
(AONB).
The
High Street
High Street is a common street name for the primary business street of a city, town, or village, especially in the United Kingdom and Commonwealth. It implies that it is the focal point for business, especially shopping. It is also a metonym fo ...
is on a pre-Roman route known by its Saxon name:
Akeman Street. The earliest written reference to Berkhamsted was in 970. The settlement was recorded as a ''burbium'' (
ancient borough
An ancient borough was a historic unit of lower-tier local government in England and Wales
England and Wales () is one of the Law of the United Kingdom#Legal jurisdictions, three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the co ...
) in the
Domesday Book
Domesday Book ( ; the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book") is a manuscript record of the Great Survey of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 at the behest of William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by ...
in 1086. The most notable event in the town's history occurred in December 1066. After
William the Conqueror
William the Conqueror (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), sometimes called William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England (as William I), reigning from 1066 until his death. A descendant of Rollo, he was D ...
defeated
King Harold's
Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced t ...
army at the
Battle of Hastings
The Battle of Hastings was fought on 14 October 1066 between the Norman-French army of William, Duke of Normandy, and an English army under the Anglo-Saxon King Harold Godwinson, beginning the Norman Conquest of England. It took place appr ...
, the Anglo-Saxon leadership surrendered to the
Norman encampment at Berkhamsted. The event was recorded in the
Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons.
The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the ninth century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of ...
. From 1066 to 1495,
Berkhamsted Castle
Berkhamsted Castle is a Norman motte-and-bailey castle in Berkhamsted, Hertfordshire. The castle was built to obtain control of a key route between London and the Midlands during the Norman conquest of England in the 11th century. Robert of ...
was a favoured residence of royalty and notable historical figures, including King
Henry II
Henry II may refer to:
Kings
* Saint Henry II, Holy Roman Emperor (972–1024), crowned King of Germany in 1002, of Italy in 1004 and Emperor in 1014
*Henry II of England (1133–89), reigned from 1154
*Henry II of Jerusalem and Cyprus (1271–1 ...
,
Edward, the Black Prince
Edward of Woodstock (15 June 1330 – 8 June 1376), known as the Black Prince, was the eldest son and heir apparent of King Edward III of England. He died before his father and so his son, Richard II of England, Richard II, succession to the Br ...
,
Thomas Becket
Thomas Becket (), also known as Saint Thomas of Canterbury, Thomas of London and later Thomas à Becket (21 December 1119 or 1120 – 29 December 1170), served as Lord Chancellor from 1155 to 1162, and then as Archbishop of Canterbury fr ...
and
Geoffrey Chaucer
Geoffrey Chaucer ( ; – 25 October 1400) was an English poet, author, and civil servant best known for ''The Canterbury Tales''. He has been called the "father of English literature", or, alternatively, the "father of English poetry". He w ...
. In the 13th and 14th centuries, the town was a
wool trading town, with a thriving local market. The oldest-known extant
jettied timber-framed building in Great Britain, built between 1277 and 1297, survives as a shop on the town's high street.
After the castle was abandoned in 1495, the town went into decline, losing its borough status in the second half of the 17th century. Colonel
Daniel Axtell, captain of the Parliamentary Guard at the trial and execution of King
Charles I in 1649, was among those
born in Berkhamsted. Modern Berkhamsted began to expand after the canal and the railway were built in the 19th century. In the 21st century, Berkhamsted has evolved into an affluent
commuter town
A commuter town is a populated area that is primarily residential rather than commercial or industrial. Routine travel from home to work and back is called commuting, which is where the term comes from. A commuter town may be called by many o ...
.
The town's literary connections include the 17th-century hymnist and poet
William Cowper
William Cowper ( ; – 25 April 1800) was an English poet and Anglican hymnwriter.
One of the most popular poets of his time, Cowper changed the direction of 18th-century nature poetry by writing of everyday life and scenes of the Engli ...
, the 18th-century writer
Maria Edgeworth
Maria Edgeworth (1 January 1768 – 22 May 1849) was a prolific Anglo-Irish novelist of adults' and children's literature. She was one of the first realist writers in children's literature and a significant figure in the evolution of the novel i ...
and the 20th-century novelist
Graham Greene
Henry Graham Greene (2 October 1904 – 3 April 1991) was an English writer and journalist regarded by many as one of the leading novelists of the 20th century.
Combining literary acclaim with widespread popularity, Greene acquired a re ...
. Arts institutions in the town include
The Rex (a well regarded independent cinema) and the
British Film Institute
The British Film Institute (BFI) is a film and television charitable organisation which promotes and preserves filmmaking and television in the United Kingdom. The BFI uses funds provided by the National Lottery to encourage film production, ...
's
BFI National Archive at King's Hill, which is one of the largest film and television archives in the world. Schools in the town include
Berkhamsted School, a co-educational boarding
independent school
A private school or independent school is a school not administered or funded by the government, unlike a State school, public school. Private schools are schools that are not dependent upon national or local government to finance their fina ...
(founded in 1541 by
John Incent,
Dean of St Paul's Cathedral);
Ashlyns School, a state school, whose history began as the
Foundling Hospital
The Foundling Hospital (formally the Hospital for the Maintenance and Education of Exposed and Deserted Young Children) was a children's home in London, England, founded in 1739 by the philanthropy, philanthropic Captain (nautical), sea captain ...
established in London by
Thomas Coram
Sea captain, Captain Thomas Coram ( – 29 March 1751) was an English sea captain and philanthropist who created the London Foundling Hospital in Lamb's Conduit Fields, Bloomsbury, to look after abandoned children on the streets of London. It is ...
in 1742; and
Ashridge Executive Education
Hult Ashridge Executive Education (also known as the Hult Ashridge) is the executive education arm of Hult International Business School, based in London, Dubai, and Hult's flagship executive education campus on the Ashridge Estate.
Formerly ...
, a business school offering degree level courses, which occupies the Grade I listed neo-Gothic
Ashridge House.
Toponymy

The earliest recorded spelling of the town's name is the 10th century
Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced t ...
''Beorhðanstædæ''. The first part may have originated from either the
Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
words ''beorg'', meaning "hill", or ''berc'' or ''beorc'', meaning "
birch
A birch is a thin-leaved deciduous hardwood tree of the genus ''Betula'' (), in the family Betulaceae, which also includes alders, hazels, and hornbeams. It is closely related to the beech- oak family Fagaceae. The genus ''Betula'' contains 3 ...
"; or from the older
Old Celtic word ''Bearroc'', meaning "hilly place". The latter part, "hamsted", derives from the Old English word for homestead. So the town's name could be either mean "homestead amongst the hills" or the "homestead among the birches".
Through history spellings of the town's name have changed. Local historian Rev John Wolstenholme Cobb identified over 50 different versions of the town's name since the writing of the
Domesday Book
Domesday Book ( ; the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book") is a manuscript record of the Great Survey of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 at the behest of William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by ...
(such as: "Berkstead", "Berkampsted", "Berkhampstead", "Muche Barkhamstede", "Berkhamsted Magna", "Great Berkhamsteed" and "Berkhamstead".)
The present spelling was officially adopted in 1937 when the local council formally changed its name from Great Berkhampstead to Berkhamsted.
The town's local nickname is "Berko".
History
Prehistory and Roman period
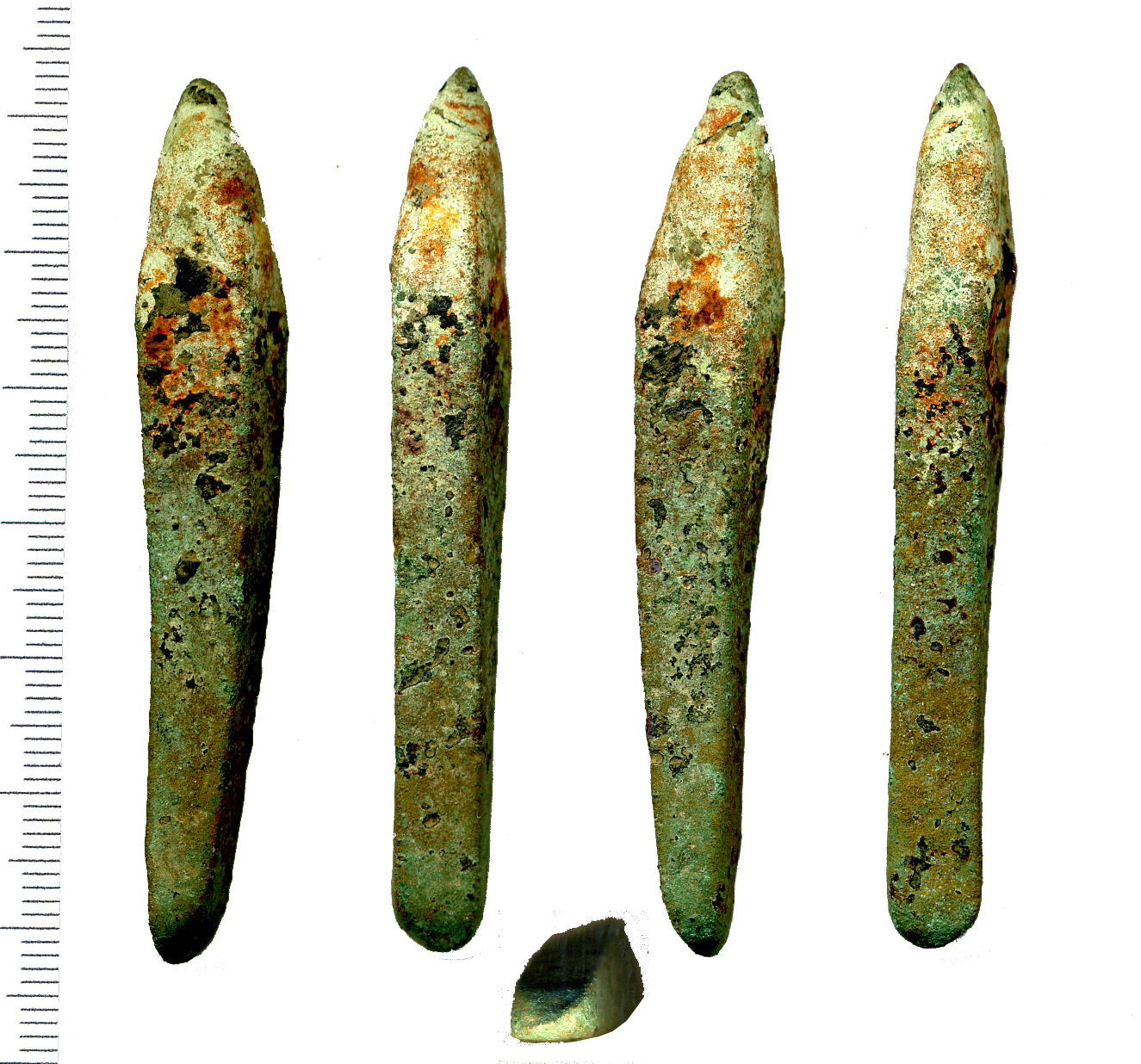

Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
,
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
,
Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
and Roman artefacts show that the Berkhamsted area of the
Bulbourne Valley has been settled for over 5,000 years. The discovery of a large number of worked flint chips provides Neolithic evidence of on-site flint knapping in the centre of Berkhamsted. Several settlements dating from the Neolithic to the Iron Age (about 4500–100 BC) have been discovered south of Berkhamsted. Three sections of a late
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
to
Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
(1200–100 BC) bank and ditch, wide by high and known as
Grim's Ditch
Grim's Ditch, Grim's Dyke (also Grimsdyke or Grimes Dike in derivative names) or Grim's Bank is a name shared by a number of prehistoric bank and ditch linear earthworks across England. They are of different dates and may have had different funct ...
, are found on the south side of the Bulbourne Valley.
Another Iron Age dyke with the same name is on Berkhamsted Common, on the north side of the valley.
In the late Iron Age, before the Roman occupation, the valley would have been within
Catuvellauni
The Catuvellauni (Common Brittonic: *''Catu-wellaunī'', "war-chiefs") were a Celtic tribe or state of southeastern Britain before the Roman conquest, attested by inscriptions into the 4th century.
The fortunes of the Catuvellauni and thei ...
territory.
The Bulbourne Valley was rich in timber and iron ore. In the late Iron Age, a area around
Northchurch became a major iron production centre, now considered to be one of the most important late Iron Age and Roman industrial areas in England.
Iron production led to the settlement of a Roman town at
Cow Roast, about northwest of Berkhamsted. Four Roman first century AD iron smelting
bloomeries at Dellfield ( northwest of the town centre) provide evidence of industrial activity in Berkhamsted. Production ceased at the end of the Roman period. Other evidence of
Roman-British occupation and activity in the Berkhamsted area, includes a pottery kiln on Bridgewater Road.
The town's high street still follows the line of the Roman-engineered
Akeman Street, which had been a pre-existing route from
St Albans
St Albans () is a cathedral city in Hertfordshire, England, east of Hemel Hempstead and west of Hatfield, Hertfordshire, Hatfield, north-west of London, south-west of Welwyn Garden City and south-east of Luton. St Albans was the first major ...
(''Verulamium'') to
Cirencester
Cirencester ( , ; see #Pronunciation, below for more variations) is a market town and civil parish in the Cotswold District of Gloucestershire, England. Cirencester lies on the River Churn, a tributary of the River Thames. It is the List of ...
(''Corinium'').
During Roman occupation the countryside close to
Verulamium
Verulamium was a town in Roman Britain. It was sited southwest of the modern city of St Albans in Hertfordshire, England. The major ancient Roman route Watling Street passed through the city, but was realigned in medieval times to bring trad ...
was subdivided into a series of farming estates. The Berkhamsted area appears to have been divided into two or three farming estates, each including one or more masonry
villa
A villa is a type of house that was originally an ancient Roman upper class country house that provided an escape from urban life. Since its origins in the Roman villa, the idea and function of a villa have evolved considerably. After the f ...
buildings, with tiled roofs and underfloor heating.
*The remains of a villa were found close to the river in 1973 in the adjacent village of Northchurch. The oldest building, made of timber, was built in AD 60, rebuilt using stone in the early 2nd century, and enlarged to a ten-room building around AD 150. The house may have been empty for a period, reoccupied in the 4th century, and abandoned in the late 4th or early 5th century.
*A Roman-British villa, dyke, and temple were found NNW of the castle, near Frithsden, at the edge of the Berkhamsted Golf Course. Excavations in 1954 revealed masonry foundations and
tessera
A tessera (plural: tesserae, diminutive ''tessella'') is an individual tile, usually formed in the shape of a square, used in creating a mosaic. It is also known as an abaciscus or abaculus.
Historical tesserae
In early antiquity, mo ...
e floors. Together, the villa, dyke and temple form a unique complex, suggesting occupation in the late Iron Age and Roman period.
*Two flint and tile walls from a Roman building were found north of Berkhamsted Castle in 1970. The construction of the castle's earthworks in the
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
may have damaged this building.
Anglo-Saxon settlement
The earliest written reference to Berkhamsted is in the will of
Ælfgifu Ælfgifu (also ''Ælfgyfu''; ''Elfgifa, Elfgiva, Elgiva'') is an Anglo-Saxon name, Anglo-Saxon feminine personal name, from ''ælf'' "elf" and ''gifu'' "gift".
When Emma of Normandy, the later mother of Edward the Confessor, became queen of Engla ...
(died AD 970), queen consort of King
Eadwig
Eadwig (also Edwy or Eadwig All-Fair, 1 October 959) was King of England from 23 November 955 until his death in 959. He was the elder son of Edmund I and his first wife Ælfgifu, who died in 944. Eadwig and his brother Edgar were you ...
of England (r. 955–959), who bequeathed large estates in five counties, including Berkhamsted.
The location and extent of early Saxon settlement of Berkhamsted is not clear. Rare Anglo-Saxon pottery dating from the 7th century onwards has been found between Chesham Road and St John's Well Lane, with water mills near Mill Street in use from the late 9th century, show that an Anglo-Saxon settlement existed in the centre of modern-day Berkhamsted. The nearest known structural evidence of the Anglo-Saxon period are in the south and west walls of St Mary's Northchurch, to the north-west of modern Berkhamsted. The church may have been an important
minster, attached to a high status Anglo-Saxon estate, which became part of the medieval manor of Berkhamsted after the
Norman conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Norman, French people, French, Flemish people, Flemish, and Bretons, Breton troops, all led by the Du ...
.
[.]
The parish of Berkhamsted St Mary's (in Northchurch) once stretched from the hamlet of
Dudswell, through Northchurch and Berkhamsted to the former hamlet of Bourne End. Within Berkhamsted, the Chapel of St James was a small church near St John's Well (a 'holy well' that was the town's principal source of drinking water in the
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
). The parish of this church (and later that of St Peter's) was an enclave of about surrounded by Berkhamsted St Mary's parish.
By the 14th century the adjoining village of "Berkhamsted St Mary" or "Berkhamsted Minor" name had become "North Church", later "Northchurch", to distinguish the village from the town of Berkhamsted.
1066 and the Domesday survey
The Anglo-Saxons surrendered the crown of England to
William the Conqueror
William the Conqueror (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), sometimes called William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England (as William I), reigning from 1066 until his death. A descendant of Rollo, he was D ...
at Berkhamsted in early December 1066.
After William defeated and killed
Harold II at the
Battle of Hastings
The Battle of Hastings was fought on 14 October 1066 between the Norman-French army of William, Duke of Normandy, and an English army under the Anglo-Saxon King Harold Godwinson, beginning the Norman Conquest of England. It took place appr ...
in October, he failed in an attempt to capture London from the south. William led his army around
London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
, crossing the
River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, s ...
at
Wallingford, "laying waste" while travelling through southeast England. At Berkhamsted, he received the surrender of
Edgar the Ætheling
Edgar is a commonly used masculine English given name, from an Anglo-Saxon name ''Edgar'' (composed of '' ead'' "rich, prosperous" and '' gar'' "spear").
Like most Anglo-Saxon names, it fell out of use by the Late Middle Ages; it was, howeve ...
(heir to the English throne),
Archbishop Ealdred,
Earl Edwin,
Earl Morcar and the leaders of London.
It is not known why the town was chosen as the meeting place, except that it was in a defensive location north-west of London. William was crowned in
Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an Anglican church in the City of Westminster, London, England. Since 1066, it has been the location of the coronations of 40 English and British m ...
on Christmas Day, 1066.
After his coronation, William granted the "Honour of Berkhamsted" to his half-brother,
Robert, Count of Mortain
Robert, Count of Mortain, first Earl of Cornwall of 2nd creation (–) was a Norman nobleman and the half-brother (on their mother's side) of King William the Conqueror. He was one of the very few proven companions of William the Conqueror at t ...
, who after William became the largest landholder in the country. Robert built a wooden fortification that later became a royal retreat for the monarchs of the
Norman and
Plantagenet
The House of Plantagenet ( /plænˈtædʒənət/ ''plan-TAJ-ə-nət'') was a royal house which originated from the French county of Anjou. The name Plantagenet is used by modern historians to identify four distinct royal houses: the Angev ...
dynasties.
According to the
Domesday Book
Domesday Book ( ; the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book") is a manuscript record of the Great Survey of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 at the behest of William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by ...
, the lord of Berkhamsted before the Norman conquest was Edmer Ator (also referred to as Eadmer Atule),
thegn
In later Anglo-Saxon England, a thegn or thane (Latin minister) was an aristocrat who ranked at the third level in lay society, below the king and ealdormen. He had to be a substantial landowner. Thanage refers to the tenure by which lands were ...
of
Edward the Confessor
Edward the Confessor ( 1003 – 5 January 1066) was King of England from 1042 until his death in 1066. He was the last reigning monarch of the House of Wessex.
Edward was the son of Æthelred the Unready and Emma of Normandy. He succeede ...
and King Harold. The Domesday survey records that there was enough land for 26 plough teams, but only 15 working teams. There were two flour mills (Upper and Lower Mill), woodland for 1,000 pigs, and a vineyard. The total population was calculated to be either 37 or 88 households; the families included 14 villagers, 15 smallholders, 6 slaves, a priest, a dyke builder (possibly working on the earthworks of the castle) and 52
burgesses.
[ Some historians have argued that the number of 52 burgesses in Berkhamsted was a clerical error, as it is a large number for a small town.]ancient borough
An ancient borough was a historic unit of lower-tier local government in England and Wales
England and Wales () is one of the Law of the United Kingdom#Legal jurisdictions, three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the co ...
) in the Tring
Tring is a market town and civil parish in the Borough of Dacorum, Hertfordshire, England. It is situated in a gap passing through the Chiltern Hills, classed as an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, from Central London.
Tring is linked ...
Hundred
100 or one hundred (Roman numerals, Roman numeral: C) is the natural number following 99 (number), 99 and preceding 101 (number), 101.
In mathematics
100 is the square of 10 (number), 10 (in scientific notation it is written as 102). The standar ...
.Marjorie Chibnall
Marjorie McCallum Chibnall (27 September 1915 – 23 June 2012) was an English historian, medievalist and Latin translator. She edited the ''Historia Ecclesiastica'' by Orderic Vitalis, with whom she shared the same birthplace of Atcham in S ...
argued that Robert, Count of Mortain intended Berkhamsted to be both a commercial and a defensive centre;
Royal medieval castle (11th to 15th centuries)
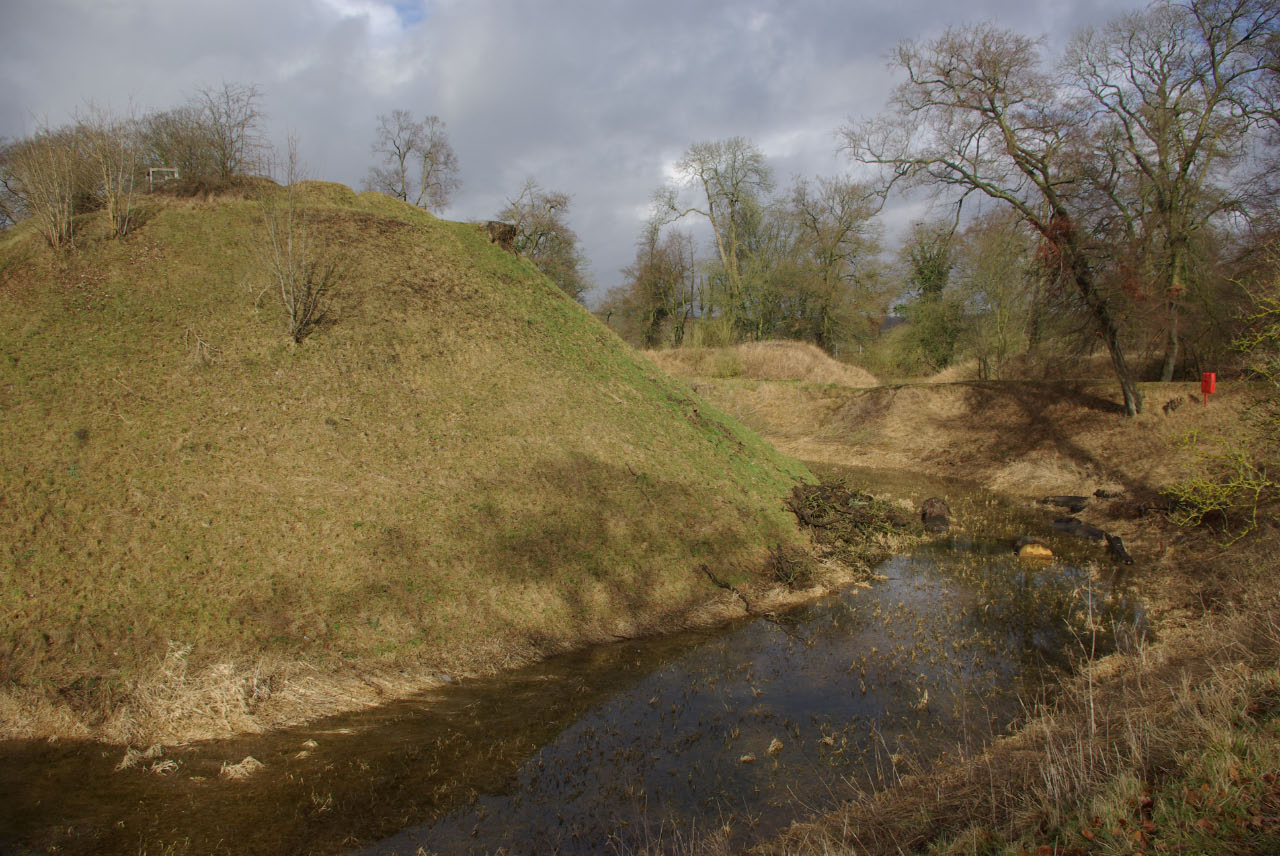
 Berkhamsted Castle is a (now ruined)
Berkhamsted Castle is a (now ruined) motte-and-bailey
A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade. Relatively eas ...
Norman castle.Radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for Chronological dating, determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of carbon-14, radiocarbon, a radioactive Isotop ...
of organic remains from within the motte indicates that it was probably built post-1066 (a dyke builder is recorded in the town at the time of the Domesday Book). The castle was a high-status residence and an administrative centre for large estates (including the Earldom of Cornwall).Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
the close proximity of the royal castle and court
A court is an institution, often a government entity, with the authority to adjudicate legal disputes between Party (law), parties and Administration of justice, administer justice in Civil law (common law), civil, Criminal law, criminal, an ...
helped fuel Berkhamsted's growth, prosperity and sense of importance. It created jobs for the local population, both within the castle itself and also, for example, in the large deer park[.] and in the vineyard
A vineyard ( , ) is a plantation of grape-bearing vines. Many vineyards exist for winemaking; others for the production of raisins, table grapes, and non-alcoholic grape juice. The science, practice and study of vineyard production is kno ...
, which were maintained alongside the castle.[.]
After Robert, Count of Mortain, the castle passed to his heir William, who rebelled against Henry I and lost the castle to the king. In 1155 Henry in turn gave it to his favourite Thomas Becket
Thomas Becket (), also known as Saint Thomas of Canterbury, Thomas of London and later Thomas à Becket (21 December 1119 or 1120 – 29 December 1170), served as Lord Chancellor from 1155 to 1162, and then as Archbishop of Canterbury fr ...
, who held it till 1165. Becket was later alleged to have spent over £300 on improvements to the castle, a claim that led Henry to accuse him of corruption and may have contributed to his downfall.King Richard I
Richard I (8 September 1157 – 6 April 1199), known as Richard the Lionheart or Richard Cœur de Lion () because of his reputation as a great military leader and warrior, was King of England from 1189 until his death in 1199. He also ru ...
and King John gave the castle to their queens, Berengaria of Navarre
Berengaria of Navarre (, , ; 1165–1170 – 23 December 1230) was Queen of England as the wife of Richard I of England. She was the eldest daughter of Sancho VI of Navarre and Sancha of Castile. As is the case with many of the medieval ...
and Isabella of Angoulême
Isabella (, ; c. 1186/ 1188 – 4 June 1246) was Queen of England from 1200 to 1216 as the second wife of King John, Countess of Angoulême in her own right from 1202 until her death in 1246, and Countess of La Marche from 1220 to 1246 as t ...
, respectively. In King John's reign, Geoffrey Fitz Peter (c. 1162–1213), Earl of Essex and the Chief Justiciar
Justiciar is the English form of the medieval Latin term or (meaning "judge" or "justice"). The Chief Justiciar was the king's chief minister, roughly equivalent to a modern Prime Minister of the United Kingdom.
The Justiciar of Ireland was ...
of England (effectively the king's principal minister) held the Honour and Manor of Berkhamsted from 1199 to 1212. During his time in the castle he was responsible for the foundation of the new parish church of St Peter (the size of which reflects the growing prosperity of the town); two hospitals, St John the Baptist and St John the Evangelist (one of which was a leper hospital), which survived until 1516; and for the layout of the town.Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter"), sometimes spelled Magna Charta, is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the Archbishop of Canterbury, Cardin ...
(1215), King John's reneging on the royal charter, the castle was besieged during the ensuing civil war, known as the First Barons' War
The First Barons' War (1215–1217) was a civil war in the Kingdom of England in which a group of rebellious major landowners (commonly referred to as English feudal barony, barons) led by Robert Fitzwalter waged war against John of England, K ...
, between John and barons supported by Prince Louis (the future Louis VIII of France
Louis VIII (5 September 1187 8 November 1226), nicknamed The Lion (), was King of France from 1223 to 1226. As a prince, he invaded Kingdom of England, England on 21 May 1216 and was Excommunication in the Catholic Church, excommunicated by a ...
), the French laid siege to Berkhamsted Castle (only a quarter of a mile from the town centre) in late December 1216. The queen's constable of the castle was the German Walerand Teutonicus.
After reducing the castle of Hertford, Louis marched on St Nicholas's day (6 December) to the castle of Berkhamsted and surrounded it with his engines of war. Whilst the English barons, after pitching their tents, were employed in setting them in order, the knights and soldiers of the garrison made a sally, seized the baggage and conveyances of the barons and gained possession of the standard of William de Mandeville with which they returned to the castle, regretting that they could do no further injury to them. On the same day, whilst the barons were sitting at table, the knights and soldiers of the garrison again made a sally, and, in order to put the barons in confusion, they carried before them the standard which they had taken a short time before, and thought to come on them unawares, but the latter were forewarned of this, and drove them back to the castle. When the following day dawned Louis ordered the petrarie (stone-throwing machines) and other engines of war to be erected around the city, which being done, they kept up a destructive shower of stones: but Waleran, a German, well tried in warfare, made a brave resistance against them and caused great slaughter amongst the excommunicated French.—The contemporary chronicler, Roger of Wendover, based at St Albans abbey, 12 miles from Berkhamsted, describing the siege
During the siege, Prince Louis introduced a new destructive siege engine to England at Berkhamsted, the counterweight ''trebuchet
A trebuchet () is a type of catapult that uses a hinged arm with a sling attached to the tip to launch a projectile. It was a common powerful siege engine until the advent of gunpowder. The design of a trebuchet allows it to launch projectiles ...
'' (or ''mangonel
The mangonel, also called the traction trebuchet, was a type of trebuchet used in Ancient China starting from the Warring States period, and later across Eurasia by the 6th century AD. Unlike the later counterweight trebuchet, the mangonel was ...
)''. After a siege of twenty days the young new King ( Henry III) ordered his constable to surrender the castle to Louis on 20 December. Following the siege at Berkhamsted Louis suffered several defeats. 11 September 1217 Louis signed the Treaty of Lambeth
The Treaty of Lambeth of 1217, also known as the Treaty of Kingston to distinguish it from the Treaty of Lambeth of 1212, was a peace treaty signed by Louis of France in September 1217 ending the campaign known as the First Barons' War to uphold ...
, relinquishing his claim to the English throne and surrendering French-held castles including Berkhamsted. Walerand went on to hold several other posts including the senior position of Lord Warden of the Cinque Ports
Lord Warden of the Cinque Ports is the name of a ceremonial post in the United Kingdom. The post dates from at least the 12th century, when the title was Keeper of the Coast, but it may be older. The Lord Warden was originally in charge of the ...
.
In 1227, Henry III's younger brother, Richard of Cornwall
Richard (5 January 1209 – 2 April 1272) was an English prince who was King of the Romans from 1257 until his death in 1272. He was the second son of John, King of England, and Isabella, Countess of Angoulême. Richard was nominal Count of ...
, was given the manor and castle, beginning the long association of the castle with the Earls and later the Dukes of Cornwall.[.]Earldom of Cornwall
The title of Earl of Cornwall was created several times in the Peerage of England before 1337, when it was superseded by the title Duke of Cornwall, which became attached to heirs-apparent to the throne.
Condor of Cornwall
*Condor of Cornwall, ...
. Richard's coat of arms as Earl of Cornwall, along with bezant
In the Middle Ages, the term bezant (, from Latin ) was used in Western Europe to describe several gold coins of the east, all derived ultimately from the Roman . The word itself comes from the Greek Byzantion, the ancient name of Constantinop ...
s, is included in Berkhamsted's coat of arms. Richard's wife, Sanchia of Provence
Sanchia of Provence (c. 1225 – 9 November 1261) was Queen of the Romans from 1257 until her death in 1261 as the wife of Richard of Cornwall, King Richard.
Sanchia was the third daughter of Ramon Berenguer IV, Count of Provence, and Bea ...
, died in the castle in 1260. Richard was succeeded by his son, Edmund, 2nd Earl of Cornwall
Edmund of Almain (26 December 1249 – 1300) was the second Earl of Cornwall of the fourth creation from 1272. He joined the Ninth Crusade in 1271, but never made it to the Holy Land. He was the regent of the Kingdom of England from 1286 to 1289 ...
, who founded Ashridge Priory
Ashridge Priory was a medieval college of Austin canons called variously the "Brothers of Penitence" or the " Boni Homines". It was founded by Edmund of Almain in 1283 who donated, among other things, a phial of Christ's blood to the abbey. It ...
, a college
A college (Latin: ''collegium'') may be a tertiary educational institution (sometimes awarding degrees), part of a collegiate university, an institution offering vocational education, a further education institution, or a secondary sc ...
of the monastic order of Bonhommes, in 1283. In 1300, after Edmund died, Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots (Latin: Malleus Scotorum), was King of England from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he was Lord of Ireland, and from 125 ...
took the castle; he subsequently granted it to his second queen, Margaret of France. In 1309, Edward I's and Margaret's son, Edward II
Edward II (25 April 1284 – 21 September 1327), also known as Edward of Caernarfon or Caernarvon, was King of England from 1307 until he was deposed in January 1327. The fourth son of Edward I, Edward became the heir to the throne follo ...
, granted Berkhamsted to his favourite, Piers Gaveston
Piers Gaveston, 1st Earl of Cornwall ( – 19 June 1312) was an English nobleman of Gascon origin, and the favourite of Edward II of England.
At a young age, Gaveston made a good impression on King Edward I, who assigned him to the househo ...
. In 1317, the castle was given to Edward II's queen, Isabella of France
Isabella of France ( – 22 August 1358), sometimes described as the She-Wolf of France (), was List of English royal consorts, Queen of England as the wife of Edward II of England, King Edward II, and ''de facto'' regent of England from 1327 ...
.
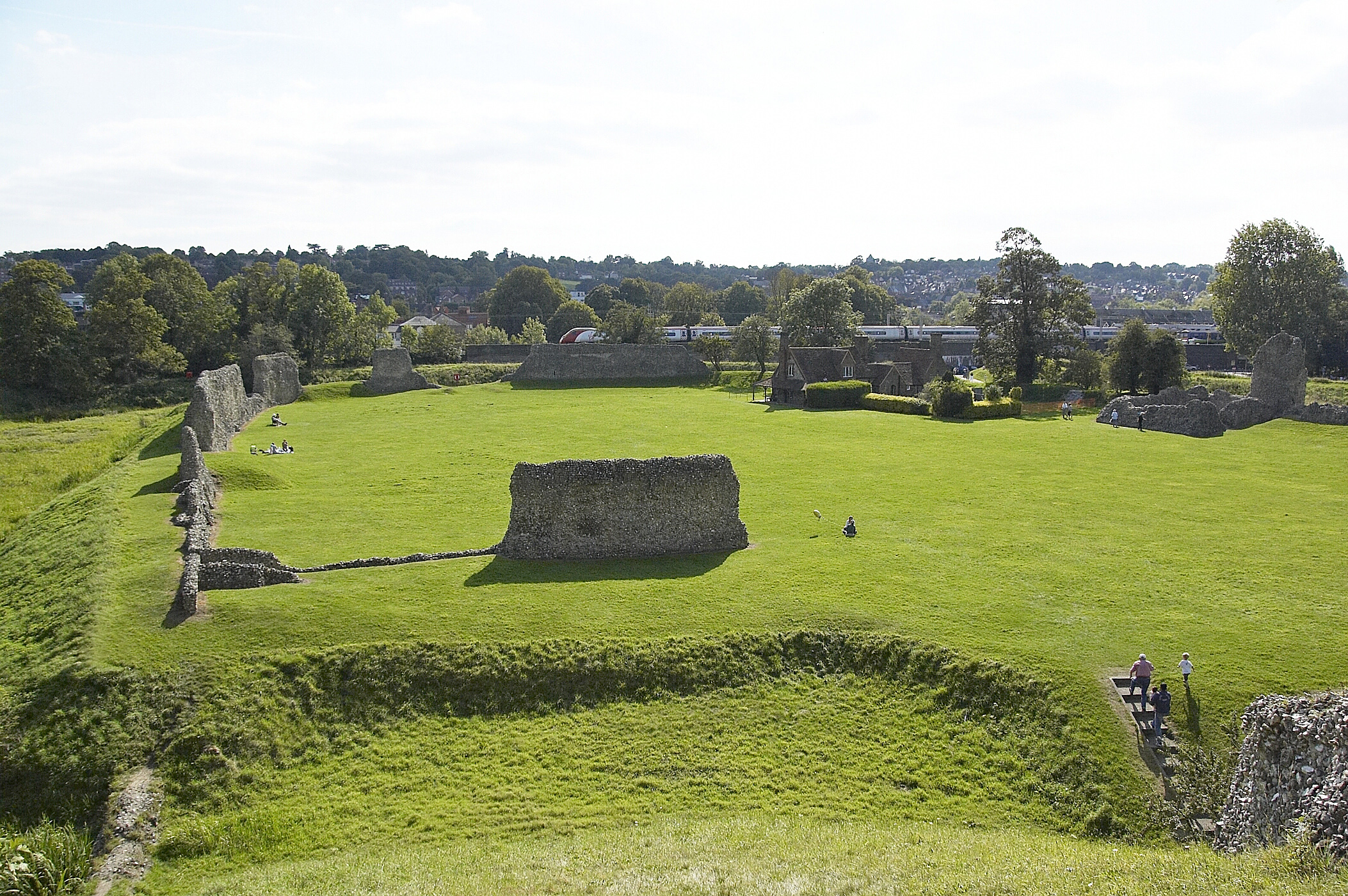

Edward III
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring royal authority after t ...
further developed the castle and gave it (as part of the Duchy of Cornwall) to his son, Edward, the Black Prince
Edward of Woodstock (15 June 1330 – 8 June 1376), known as the Black Prince, was the eldest son and heir apparent of King Edward III of England. He died before his father and so his son, Richard II of England, Richard II, succession to the Br ...
, who expanded the hunting grounds. The castle was used to hold royal prisoners, including John II of France
John II (; 26 April 1319 – 8 April 1364), called John the Good (French: ''Jean le Bon''), was King of France from 1350 until his death in 1364. When he came to power, France faced several disasters: the Black Death, which killed between a thir ...
. In 1361, Edward the Black Prince and Joan, the Maid of Kent, spent their honeymoon in Berkhamsted. Under Edward the Black Prince, Berkhamsted become a centre of English longbow
The English longbow was a powerful medieval type of bow, about long. While it is debated whether it originated in England or in Wales from the Welsh bow, by the 14th century the longbow was being used by both the English and the Welsh as ...
archery.Battle of Crécy
The Battle of Crécy took place on 26 August 1346 in northern France between a French army commanded by King PhilipVI and an English army led by King Edward III. The French attacked the English while they were traversing northern France ...
(1346) was the introduction of this new weapon onto the Western European battlefield. The longbow was a superior weapon to the cumbersome and slower crossbow. The Berkhamsted bowmen successfully took part in this significant battle in medieval Western European history.Battle of Poitiers
The Battle of Poitiers was fought on 19September 1356 between a Kingdom of France, French army commanded by King John II of France, King JohnII and an Kingdom of England, Anglo-Gascony, Gascon force under Edward the Black Prince, Edward, the ...
). Richard II
Richard II (6 January 1367 – ), also known as Richard of Bordeaux, was King of England from 1377 until he was deposed in 1399. He was the son of Edward, Prince of Wales (later known as the Black Prince), and Joan, Countess of Kent. R ...
inherited Berkhamsted Castle in 1377 and gave it to his favourites, Robert de Vere and John Holland.
In 1400, Henry IV lived in the castle after he deposed Richard, and he used the castle to imprison others attempting to obtain the throne. During this time, Geoffrey Chaucer
Geoffrey Chaucer ( ; – 25 October 1400) was an English poet, author, and civil servant best known for ''The Canterbury Tales''. He has been called the "father of English literature", or, alternatively, the "father of English poetry". He w ...
– later famous for writing ''The Canterbury Tales
''The Canterbury Tales'' () is a collection of 24 stories written in Middle English by Geoffrey Chaucer between 1387 and 1400. The book presents the tales, which are mostly written in verse, as part of a fictional storytelling contest held ...
'' – oversaw renovation work on the castle in his role as Clerk of the Works at Berkhamsted. It is unknown how much time he spent at Berkhamsted, but he knew John of Gaddesden, who lived in nearby Little Gaddesden
Little Gaddesden (pronounced ) is a village and civil parish in the borough of Dacorum, Hertfordshire north of Berkhamsted, close to the border with Bedfordshire. As well as Little Gaddesden village (population 694), the parish contains the se ...
and was the model for the Doctor of Phisick in ''The Canterbury Tales''. Henry V Henry V may refer to:
People
* Henry V, Duke of Bavaria (died 1026)
* Henry V, Holy Roman Emperor (1081/86–1125)
* Henry V, Duke of Carinthia (died 1161)
* Henry V, Count Palatine of the Rhine (–1227)
* Henry V, Count of Luxembourg (1216–1281 ...
and Henry VI owned the castle, the latter making use of it until he was overthrown in 1461. In 1469, Edward IV
Edward IV (28 April 1442 – 9 April 1483) was King of England from 4 March 1461 to 3 October 1470, then again from 11 April 1471 until his death in 1483. He was a central figure in the Wars of the Roses, a series of civil wars in England ...
gave the castle to his mother, Cecily Neville, Duchess of York. The arrival of Neville and her household at Berkhamsted had a significant social and financial impact on the town. Men and women from the town joined her service, such as Robert Incent who became her secretary and whose memorial brass can still be seen in St Peter's Church in Berkhamsted. Mother to both Edward IV and Richard III
Richard III (2 October 1452 – 22 August 1485) was King of England from 26 June 1483 until his death in 1485. He was the last king of the Plantagenet dynasty and its cadet branch the House of York. His defeat and death at the Battle of Boswor ...
, grandmother to Edward V
Edward V (2 November 1470 – ) was King of England from 9 April to 25 June 1483. He succeeded his father, Edward IV, upon the latter's death. Edward V was never crowned, and his brief reign was dominated by the influence of his uncle and Lord ...
, and mother in law to Henry VII, she was the last person to live in the castle.
Recent history of the castle
In 1833, the castle was the first building to receive statutory protection in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
. In 1834, construction of the railway embankment demolished the castle's gatehouse and adjacent earthworks. Today the castle ruins are managed by a charitable trust, the ''Berkhamsted Castle Trust'', in partnership with English Heritage
English Heritage (officially the English Heritage Trust) is a charity that manages over 400 historic monuments, buildings and places. These include prehistoric sites, a battlefield, medieval castles, Roman forts, historic industrial sites, Lis ...
, on behalf of the Duchy of Cornwall
A duchy, also called a dukedom, is a country, territory, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess, a ruler hierarchically second to the king or queen in Western European tradition.
There once existed an important difference between "sovereign ...
(which still officially owns the site), and are freely open to the public.
Medieval market town (12th to 15th centuries)
The town continued to develop separately on the old Akeman Street to the south of the castle and to the west of St Peter's Church; with a triangle formed by Mill Street, Castle Street and Back Lane pointing towards the castle. In 1156, Henry II
Henry II may refer to:
Kings
* Saint Henry II, Holy Roman Emperor (972–1024), crowned King of Germany in 1002, of Italy in 1004 and Emperor in 1014
*Henry II of England (1133–89), reigned from 1154
*Henry II of Jerusalem and Cyprus (1271–1 ...
officially recognised Berkhamsted as a town in a royal charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, but ...
, which confirmed the laws and customs enjoyed under Edward the Confessor
Edward the Confessor ( 1003 – 5 January 1066) was King of England from 1042 until his death in 1066. He was the last reigning monarch of the House of Wessex.
Edward was the son of Æthelred the Unready and Emma of Normandy. He succeede ...
, William I and Henry I, and freed the town's merchants from all tolls and dues. The charter also stated that no market could be set up within of the town.
The town became a trading centre on an important trade route in the 12th and 13th centuries, and received more royal charters. In 1216, Henry III relieved the men and merchants of the town from all tolls and taxes everywhere in England, and the English Plantagenet
The House of Plantagenet ( /plænˈtædʒənət/ ''plan-TAJ-ə-nət'') was a royal house which originated from the French county of Anjou. The name Plantagenet is used by modern historians to identify four distinct royal houses: the Angev ...
possessions in France, Normandy
Normandy (; or ) is a geographical and cultural region in northwestern Europe, roughly coextensive with the historical Duchy of Normandy.
Normandy comprises Normandy (administrative region), mainland Normandy (a part of France) and insular N ...
, Aquitaine
Aquitaine (, ; ; ; ; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Aguiéne''), archaic Guyenne or Guienne (), is a historical region of southwestern France and a former Regions of France, administrative region. Since 1 January 2016 it has been part of the administ ...
and Anjou. The growing wool trade
Wool is the textile fiber obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have some properties similar to animal wool.
...
brought prosperity to Berkhamsted from the 12th century until the early Tudor period
In England and Wales, the Tudor period occurred between 1485 and 1603, including the Elizabethan era during the reign of Elizabeth I (1558–1603). The Tudor period coincides with the dynasty of the House of Tudor in England, which began with ...
. Four wealthy Berkhamsted wool merchants were amongst a group in Bruges
Bruges ( , ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the province of West Flanders, in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is in the northwest of the country, and is the sixth most populous city in the country.
The area of the whole city amoun ...
to whom Edward III wrote in 1332,farrier
A farrier is a specialist in equine hoof care, including the trimming and balancing of horses' hooves and the placing of shoes on their hooves, if necessary. A farrier combines some blacksmith's skills (fabricating, adapting, and adju ...
s, two tailors, a brewer of mead
Mead (), also called honey wine, and hydromel (particularly when low in alcohol content), is an alcoholic beverage made by fermenting honey mixed with water, and sometimes with added ingredients such as fruits, spices, grains, or hops. The alco ...
, a blacksmith, carpenters, wood turners, tool makers, a manufacturer of roofing tiles and wine producers.turner
Turner may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Turner (surname), a common surname, including a list of people and fictional characters with the name
* Turner (given name), a list of people with the given name
*One who uses a lathe for tur ...
, a butcher, a fishmonger, a barber, an archer, a tailor, a cloth-napper, a miller
A miller is a person who operates a mill, a machine to grind a grain (for example corn or wheat) to make flour. Milling is among the oldest of human occupations. "Miller", "Milne" and other variants are common surnames, as are their equivalents ...
, a cook, a seller of salt and a huntsman. At this time, larger houses of merchants and castle officials appeared on the south side of the high street (including 173 High Street, the oldest known extant jettied building in England). In 1307 Berkhamsted was a large town by English medieval standards with an estimated population of 2,000 to 2,500. In 1355, there were five butchers, two bakers, nine brewers, two cobblers, a pelter, a tanner, five cloth dyers, six wheelwright
A wheelwright is a Artisan, craftsman who builds or repairs wooden wheels. The word is the combination of "wheel" and the word "wright" (which comes from the Old English word "''wryhta''", meaning a worker - as also in shipbuilding, shipwright ...
s, three smith
Smith may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Metalsmith, or simply smith, a craftsman fashioning tools or works of art out of various metals
* Smith (given name)
* Smith (surname), a family name originating in England
** List of people ...
s, six grain merchants, a skinner and a baker/butcher. In the 14th century, Berkhamsted (recorded as "Berchamstede") was considered to be one of the "best" market towns in the country. In a survey of 1357, Richard Clay was found to own a butcher's shop wide, William Herewood had two shops, and there were four other shops in length. In 1440, there is a reference to lime kilns.Edmund, 2nd Earl of Cornwall
Edmund of Almain (26 December 1249 – 1300) was the second Earl of Cornwall of the fourth creation from 1272. He joined the Ninth Crusade in 1271, but never made it to the Holy Land. He was the regent of the Kingdom of England from 1286 to 1289 ...
, founded Ashridge Priory
Ashridge Priory was a medieval college of Austin canons called variously the "Brothers of Penitence" or the " Boni Homines". It was founded by Edmund of Almain in 1283 who donated, among other things, a phial of Christ's blood to the abbey. It ...
in 1283, away and within the castle's park. At the foundation of the abbey, the Earl donated a phial claimed to contain Christ's blood. Pilgrim
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , , "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star.
Computer scientists and mathematicians often vocalize it as ...
s from all over Europe passed through the town to see the holy relic. The abbey grew quite wealthy as a result. Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots (Latin: Malleus Scotorum), was King of England from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he was Lord of Ireland, and from 125 ...
held parliament at the abbey in 1290 and spent Christmas there. Berkhamsted burgesses sent two members to parliament
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
in 1320, 1338 and 1341, but the town was not represented again.Black Prince
Edward of Woodstock (15 June 1330 – 8 June 1376), known as the Black Prince, was the eldest son and heir apparent of King Edward III of England. He died before his father and so his son, Richard II, succeeded to the throne instead. Edward n ...
took advantage of the Black Death
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic that occurred in Europe from 1346 to 1353. It was one of the list of epidemics, most fatal pandemics in human history; as many as people perished, perhaps 50% of Europe's 14th century population. ...
to extend the castle's park by , eventually producing a park covering .
Castle abandoned, the town in decline (16th to late 18th centuries)
 In the 16th century, the town fell into decline after abandonment of the castle following the death of Cicely Neville, Duchess of York, in 1495, and the rise of the nearby town of
In the 16th century, the town fell into decline after abandonment of the castle following the death of Cicely Neville, Duchess of York, in 1495, and the rise of the nearby town of Hemel Hempstead
Hemel Hempstead () is a town in the Dacorum district in Hertfordshire, England. It is located north-west of London; nearby towns and cities include Watford, St Albans and Berkhamsted. The population at the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 cens ...
(which was granted a Charter of Incorporation by Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
on 29 December 1539). The population of the town in 1563 has been estimated at only 545. In 1580, the castle ruins and the park were leased by Elizabeth I to Sir Edward Carey, for the nominal rent of one red rose
A rose is either a woody perennial plant, perennial flowering plant of the genus ''Rosa'' (), in the family Rosaceae (), or the flower it bears. There are over three hundred Rose species, species and Garden roses, tens of thousands of cultivar ...
each year. Stone from the castle was used to build Berkhamsted Place
Berkhamsted Place was an English country house which was erected sometime around 1580 in Berkhamsted, Hertfordshire, England. It was built by Sir Edward Carey, the keeper of the Jewels to Queen Elizabeth I from stones removed from Berkhamsted Cas ...
, a local school, and other buildings in the late 16th century. Brewing and maltings was noted as one of the town's principal industries in the reign of Elizabeth. Around 1583, a new market house was erected west of St Peter's Church at the end of Middle Row (alternatively named Le Shopperowe or Graball Row). The market house was destroyed in a fire in 1854.
In 1612, Berkhamsted Place was bought by Henry Frederick, Prince of Wales
Henry Frederick, Prince of Wales, (19 February 1594 – 6 November 1612), was the eldest son and heir apparent of King James VI and I and Anne of Denmark, Queen Anne. His name derives from his grandfathers: Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley; and Fr ...
for £4,000. Henry died later that year, and bequeathed the house to his brother Charles (later King Charles I), who leased the property to his tutor, Thomas Murray, and his wife, Mary Murray, who had been his nurse and Lady of the Privy Chamber
A privy chamber was the private apartment of a royal residence in England.
The Gentlemen of the Privy Chamber were noble-born servants to the Crown who would wait and attend on the King in private, as well as during various court activities, f ...
to the prince's mother. John Norden
John Norden (1625) was an English cartographer, chorographer and antiquary. He planned (but did not complete) a series of county maps and accompanying county histories of England, the '' Speculum Britanniae''. He was also a prolific write ...
wrote in 1616 that the making of malt was then the principal trade of the town.[ In 1618, ]James I James I may refer to:
People
*James I of Aragon (1208–1276)
* James I of Sicily or James II of Aragon (1267–1327)
* James I, Count of La Marche (1319–1362), Count of Ponthieu
* James I, Count of Urgell (1321–1347)
*James I of Cyprus (1334� ...
reaffirmed Berkhamsted's borough status with a charter. Following surveys in 1607 and 1612 the Duchy of Cornwall enclosed from the Common (now known as Coldharbour farm) despite local opposition led by Rev Thomas Newman. In 1639 the Duchy tried to enclose a further of the Berkhamsted and Northchurch Commons, but was prevented from doing so by William Edlyn of Norcott. The castle's park, which had reached by 1627, was broken up over the next two decades, shrinking to only , to the benefit of local farmers. In 1643, Berkhamsted was visited by a violent pestilential fever.[
Born in Berkhamsted, Colonel Daniel Axtell (1622 – 19 October 1660), a Baptist and a ]grocer
A grocery store (American English, AE), grocery shop or grocer's shop (British English, BE) or simply grocery is a retail store that primarily retails a general range of food Product (business), products, which may be Fresh food, fresh or Food p ...
's apprentice, played a zealous and prominent part in the English Civil War
The English Civil War or Great Rebellion was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Cavaliers, Royalists and Roundhead, Parliamentarians in the Kingdom of England from 1642 to 1651. Part of the wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of th ...
, both in England and in the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland
The Cromwellian conquest of Ireland (1649–1653) was the re-conquest of Ireland by the Commonwealth of England, initially led by Oliver Cromwell. It forms part of the 1641 to 1652 Irish Confederate Wars, and wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of the Three ...
. He participated as a lieutenant colonel in Pride's Purge
Pride's Purge is the name commonly given to an event that took place on 6 December 1648, when soldiers prevented members of Parliament considered hostile to the New Model Army from entering the House of Commons of England.
Despite defeat in the ...
of the Long Parliament
The Long Parliament was an Parliament of England, English Parliament which lasted from 1640 until 1660, making it the longest-lasting Parliament in English and British history. It followed the fiasco of the Short Parliament, which had convened f ...
(December 1648), arguably the only military ''coup d'état'' in English history, and commanded the Parliamentary Guard at the trial of King Charles I at Westminster Hall
Westminster Hall is a medieval great hall which is part of the Palace of Westminster in London, England. It was erected in 1097 for William II (William Rufus), at which point it was the largest hall in Europe. The building has had various functio ...
in 1649. During Cromwell's Protectorate, he appropriated Berkhamsted Place. Shortly after the Restoration of the monarchy under Charles II, the unrepentant Axtell was hanged, drawn and quartered
To be hanged, drawn and quartered was a method of torture, torturous capital punishment used principally to execute men convicted of High treason in the United Kingdom, high treason in medieval and early modern Britain and Ireland. The convi ...
as a regicide
Regicide is the purposeful killing of a monarch or sovereign of a polity and is often associated with the usurpation of power. A regicide can also be the person responsible for the killing. The word comes from the Latin roots of ''regis'' ...
.Dissenters
A dissenter (from the Latin , 'to disagree') is one who dissents (disagrees) in matters of opinion, belief, etc. Dissent may include political opposition to decrees, ideas or doctrines and it may include opposition to those things or the fiat of ...
in the second half of the century, and in 1700, there were 400 Baptists recorded as living in Berkhamsted. Three more shops are mentioned in the row next to the church, and the Parliamentary Survey of 1653 suggests that the area near the Market House was used for butchery.
Development of the modern town (19th and 20th centuries)
19th century urban growth
In the 17th and 18th centuries Hemel Hempstead, with its thriving market, eclipsed Berkhamsted as the major town in the area. Georgian Berkhamsted barely extended beyond the medieval triangle and the High Street. With the coming of the Industrial Age
The Industrial Age is a period of history that encompasses the changes in economic and social organization that began around 1760 in Great Britain and later in other countries, characterized chiefly by the replacement of hand tools with power-d ...
, Berkhamsted was well placed at a gateway through the Chilterns, between the markets of London and the industrial Midlands
The Midlands is the central region of England, to the south of Northern England, to the north of southern England, to the east of Wales, and to the west of the North Sea. The Midlands comprises the ceremonial counties of Derbyshire, Herefor ...
. The town became a link in the growing network of roads, canals and railways. These developments led Berkhamsted's population to expand once again. In 1801, the population of St Peter's parish had been 1,690 and by 1831, this had risen to 2,369 (484 houses). An 1835 description of the town found that "the houses are mostly of brick, and irregularly built, but are interspersed with a fair proportion of handsome residences". The town's population increased as "hundreds of men arrived to build the railway line and needed lodging"; by 1851, the population was 3,395, From 1850 large estates around Berkhamsted were sold, allowing for housing expansion. In 1851 the Pilkington Manor estate, east of Castle Street, was sold, and the land developed both as an industrial area and for artisans' dwellings. In 1868 streets of middle-class villas began to appear on the hill south of the High Street. Lower Kings Road was built by public subscription in 1885 to join Kings Road and the High Street to the station. In 1887, John Bartholomew's ''Gazetteer of the British Isles'' recorded the population at 4,485.
19th century industry and utilities
Industries in the 19th century included:
*''Timber:'' In the mid-18th century, Berkhamsted had been noted for turned wood products. Based on the extensive woodland resources of the area (principally alder
Alders are trees of the genus ''Alnus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The genus includes about 35 species of monoecious trees and shrubs, a few reaching a large size, distributed throughout the north temperate zone with a few species ex ...
and beech
Beech (genus ''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to subtropical (accessory forest element) and temperate (as dominant element of Mesophyte, mesophytic forests) Eurasia and North America. There are 14 accepted ...
), the milling and turning of wood was the town's most prominent industry in the 19th century. The Crimean War contracts for supplying the army with lance poles and tent pegs led to major expansion. The largest manufacturer was East & Sons.
*''Brush making:'' An offshoot of the timber industry. The largest employers were Goss Brushworks at the west end of the High Street (closed 1930s) and T.H. Nash in George Street (closed 1920s).
*''The Canal trade'' provided a considerable economic stimulus to the town, enabling the development of industries which involved bulk transport of materials. These included timber and malt.
*''Boat building:'' Berkhamsted also became a centre for the construction of the barges needed for the canal trades. A yard for building canal barges and other boats, between Castle Street and Raven's Lane wharves, was one of three important boatyards in Hertfordshire. It was owned by John Hatton until 1880 and then by William Costin until 1910, when it was taken over by Key's, the timber merchants which in 1969 was bought by another timber merchant J. Alsford before being redeveloped into flats in 1994. At this site, next to the canal, is the Berkhamsted Canadian totem pole.
*''Watercress:'' The construction of the canal had helped to drain the marshy areas along the valley of the River Bulbourne. In 1883, the ''Berkhamsted Times'' congratulated Mr Bedford on having converted the remaining "dirty ditches and offensive marshes" into watercress
Watercress or yellowcress (''Nasturtium officinale'') is a species of aquatic flowering plant in the cabbage family, Brassicaceae.
Watercress is a rapidly growing perennial plant native to Eurasia. It is one of the oldest known leaf vegetabl ...
beds.
*''Chemical:'' Cooper's sheep dip works. William Cooper was a vet who arrived in Berkhamsted in the early 1840s and experimented in treatments for scab in sheep. He formulated an innovative arsenic and sulphur sheep-dip. The Cooper family firm was later inherited by his nephew, Sir Richard Cooper, 1st Baronet
Sir Richard Powell Cooper, 1st Baronet (21 September 1847 – 30 July 1913) was a British industrial entrepreneur. He was a member of the Royal College of Veterinary Surgeons and inherited the family business, an agricultural chemical manufactu ...
.
*'' Nurserymen:'' Henry Lane's nurseryman business, founded in 1777, became one of the largest employers in the town in the 19th century. Extensive nurseries are shown on the 1878 Ordnance Survey 25 inch plan, at the western end of the town.
*''Iron working:'' Wood's Ironworks was set up in 1826 by James Wood.
Utilities in the 19th century included:
*''Gasworks:'' The Great Berkhamsted Gas, Light & Coke Co., at the junction of Water Lane and the Wilderness, was set up to provide street lighting in 1849. In 1906, the Berkhamsted Gas Works moved to Billet Lane; it closed in 1959.
*''Water and sewage:'' The Great Berkhamsted Waterworks Company was set up in 1864 on the High Street (on the present site of W.H. Smith and Boots). Mains drainage was first supplied in 1898–99, when effective sewerage was installed.
Provision for the destitute
In 1725 "An Account of Several Workhouses" records a parish workhouse
In Britain and Ireland, a workhouse (, lit. "poor-house") was a total institution where those unable to support themselves financially were offered accommodation and employment. In Scotland, they were usually known as Scottish poorhouse, poorh ...
in Berkhamsted, and a parliamentary report of 1777 refers to a parish workhouse for up to 34 inmates in Northchurch. A small "wretched, straw-thatched" house was used to house poor families in Berkhamsted, on the corner of what is now Park View Road, until it was demolished in the 1820s. In 1831 a bequest of £1,000 by the Revd George Nugent led to a new parish workhouse being set up on the site of a workhouse which had operated in a row of tenements on the High Street (at the Kitsbury Road junction) known as Ragged Row. The "Berkhampstead Poor Law
In English and British history, poor relief refers to government and ecclesiastical action to relieve poverty. Over the centuries, various authorities have needed to decide whose poverty deserves relief and also who should bear the cost of hel ...
Union" was formed in June 1835 covering ten parishes centred on the town. The Union took over the existing Berkhamsted parish workhouse, and by August 1835 it had become the sole workhouse for the union. The workhouse had no schoolroom, so in 1849 the Poor Law Board The Poor Law Board was established in the United Kingdom in 1847 as a successor body to the Poor Law Commission overseeing the administration of the Poor Law Amendment Act 1834. The board was abolished in 1871 and replaced by the Local Government ...
recommended that pauper children be sent to the local National School. However in 1858 the school complained about the state of the children attending from the workhouse. A fever ward was erected in 1855, and a full-time nurse was engaged in 1868. The workhouse system officially came to an end in 1930, and control over the workhouse was given to local council. Nugent House, the Berkhamsted workhouse, finally closed in 1935 and its function was relocated to Hemel Hemspstead. In 1841, the Countess of Bridgewater built a soup kitchen
A soup kitchen, food kitchen, or meal center is a place where food is offered to Hunger, hungry and homeless people, usually for no price, cost, or sometimes at a below-market price (such as coin Donation, donations). Frequently located in Low i ...
for the local poor within the ruins of Berkhamsted Castle. The soup kitchen was used by an estimated 15 per cent of the population of Berkhamsted (about 500 people) during the winter months, until at least 1897. The building still stands connected to the cottage in the castle grounds; why it was placed outside the town and inside the ruins of the historic castle is unknown. 
Land dispute: ''The Battle of Berkhamsted Common''
The ''Battle of Berkhamsted Common'' played an important part in the preservation of common land nationally. After 1604 the former Ashridge Priory became the home of the Edgerton family. In 1808–1814 Francis Egerton, 3rd Duke of Bridgewater
Francis Egerton, 3rd Duke of Bridgewater (21 May 1736 – 8 March 1803), known as Lord Francis Egerton until 1748, was a British nobleman from the Egerton family. He was the youngest son of the 1st Duke. He did not marry, and the dukedom expi ...
, demolished the old priory, and built a stately home, Ashridge House. In 1848 the estate passed to the Earls Brownlow, a branch of the Egerton family.
In 1866, Lord Brownlow of Ashridge House (encouraged by his mother, Lady Marian Alford) in an action similar to many other large estate holders tried to enclose Berkhamsted Common
Common may refer to:
As an Irish surname, it is anglicised from Irish Gaelic surname Ó Comáin.
Places
* Common, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland
* Boston Common, a central public park in Boston, Massachusetts
* Cambridge Com ...
with steel fences (built by Woods of Berkhamsted) in order to claim the land as part of his family's estate. In response to the enclosure action and in defence the historic right of the public to use the ancient common land, Augustus Smith MP and George Shaw-Lefevre organised local people and 120 hired men from London's East End to dismantle the fences on the night of 6 March, in what became known nationally as the Battle of Berkhamsted Common.National Trust
The National Trust () is a heritage and nature conservation charity and membership organisation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland.
The Trust was founded in 1895 by Octavia Hill, Sir Robert Hunter and Hardwicke Rawnsley to "promote the ...
in 1895) and the Commons Preservation Society. Lord Justice Romilly determined that pulling down a fence was no more violent an act than erecting one. The case, he said, rested on the legality of Brownlow's action in building the fence and the legal right of people to use the land. He ruled in favour of Smith. This decision, along with the Metropolitan Commons Act 1866, helped to ensure the protection of Berkhamsted Common and other open spaces nationally threatened with enclosure. In 1926 the common was acquired by the National Trust.
First World War
During the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, under the guidance of Lt Col Francis Errington, the Inns of Court Officers' Training Corps trained men from the legal profession as officers. Over the course of the war, 12,000 men travelled from Berkhamsted to fight on the Western Front. Their training included trench digging: of trenches were dug across the Common (of which remain). The Inns of Court War Memorial on the Common has the motto ''Salus Populi Suprema Lex''—the welfare of the people is the highest law—and states that the ashes of Colonel Errington were buried nearby.
20th century urban developments
In 1909 Sunnyside and later in 1935 Northchurch were added to Berkhamsted Urban District. Shortly after 1918 much of the extensive estate belonging to Berkhamsted Hall, at the east end of the High Street, was sold; many acres west of Swing Gate Lane were developed with council housing. More council housing was built at Gossoms End. Development on the north side of the valley was limited until the sale of the Ashridge estate in the 1930s, after which housing appeared at each end of Bridgewater Road. In the second half of the 20th century, many of the old industrial firms in Berkhamsted closed, while the numbers of commuters increased.
After the Second World War, in July 1946, the nearby town of Hemel Hempstead was designated a New Town
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz (South Korean band), The Boyz
* New (album), ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
** New (Paul McCartney song), "New" (Paul McCartney song), 2013
* New (EP), ''New'' (EP), ...
under the New Towns Act ("New Towns" were satellite urban developments around London to relieve London's population growth and housing shortages caused by the Blitz). In February 1947 the Government purchased of land and began construction. As a result Hemel Hempstead's population increased from 20,000 to over 90,000 today, making it the largest town in Hertfordshire. In 1974, the old hundred of Dacorum became the modern district of Dacorum formed under the Local Government Act 1972
The Local Government Act 1972 (c. 70) is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974. It was one of the most significant acts of Parliament to be passed by the Heath Gov ...
, based in Hemel Hempstead.
Geography
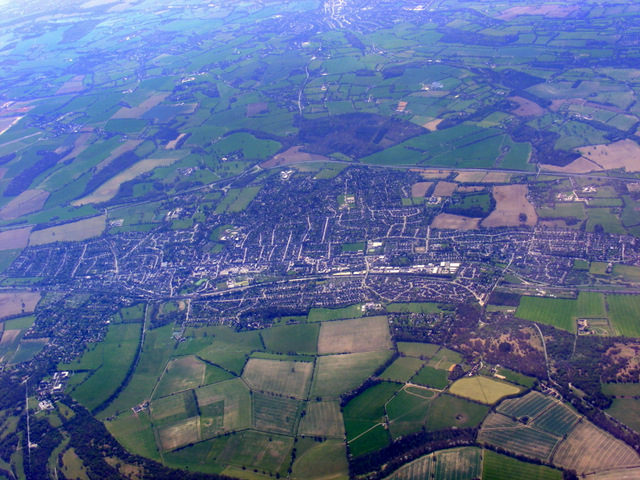 Berkhamsted is situated northwest of London within the
Berkhamsted is situated northwest of London within the Chiltern Hills
The Chiltern Hills or the Chilterns are a chalk escarpment in southern England, located to the north-west of London, covering across Oxfordshire, Buckinghamshire, Hertfordshire and Bedfordshire; they stretch from Goring-on-Thames in the south- ...
, part of a system of chalk downlands throughout eastern and southern England, believed to have formed between 84 and 100 million years ago in the Cretaceous Period
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ninth and longest geologi ...
when the area was a chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. Ch ...
-depositing marine environment. The town is located in a narrow northwest to southeast valley falling from above sea level to . The valley is at the southernmost limit of the Pleistocene glaciation ice erosion throughout the Chiltern scarp, giving it a smooth rounded appearance, with alluvial
Alluvium (, ) is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluvium is also sometimes called alluvial deposit. Alluvium is ...
soils in the valley bottom and chalk, clay and flint on the valley sides.Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic i ...
period (Middle Stone Age, mid to late 8th millennium BC), the local upland was mostly pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae.
''World Flora Online'' accepts 134 species-rank taxa (119 species and 15 nothospecies) of pines as cu ...
woodland and the low area of central Berkhamsted probably a grass-sedge
The Cyperaceae () are a family of graminoid (grass-like), monocotyledonous flowering plants known as wikt:sedge, sedges. The family (biology), family is large; botanists have species description, described some 5,500 known species in about 90 ...
fen. In the 6th Millennium BC the dense deciduous forest became well established. By the Mid to late 3rd millennium BC during the Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
period (the New Stone Age) human activity can be seen in wood clearances; the woodland being then dominated by lime tree
''Tilia'' is a genus of about 30 species of trees or bushes, native throughout most of the temperate Northern Hemisphere. The tree is known as linden for the European species, and basswood for North American species. In Great Britain and Irelan ...
s, with alder trees growing on the flood plain
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river. Floodplains stretch from the banks of a river channel to the base of the enclosing valley, and experience flooding during periods of high Discharge (hydrolog ...
. The River Bulbourne, a chalk stream
Chalk streams are rivers that rise from springs in landscapes with chalk bedrock. Since chalk is permeable, water easily percolates through the ground to the water table and chalk streams therefore receive little surface runoff. As a result, th ...
, runs through the valley for in a southeast direction, starting at Dudswell and the adjoining village of Northchurch and running through Berkhamsted, Bourne End and Boxmoor, where it merges with the River Gade at Two Waters in Apsley, near Hemel Hempstead. Rich in eels and other fish, it was fast-moving and full, and prone to frequent localised flooding. The river created a marsh environment (at times referred to as an 'unhealthy swamp') in the centre of the valley. The river powered the watermills (recorded in 1086) and fed the three moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch dug around a castle, fortification, building, or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. Moats can be dry or filled with water. In some places, moats evolved into more extensive water d ...
s of the large Norman Motte and Bailey
A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade. Relatively easy ...
castle, that stands close to the centre of the town where a small dry combe
A combe (; also spelled coombe or coomb and, in place names, comb) can refer either to a steep, narrow valley, or to a small valley or large hollow on the side of a hill; in any case, it is often understood simply to mean a small valley through w ...
joins the Bulbourne valley.  The countryside surrounding the town includes parts of the
The countryside surrounding the town includes parts of the Green Belt
A green belt or greenbelt is a policy, and land-use zone designation used in land-use planning to retain areas of largely undeveloped, wilderness, wild, or agricultural landscape, land surrounding or neighboring urban areas. Similar concepts ...
and the Chilterns Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty
An Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB; , AHNE) is one of 46 areas of countryside in England, Wales, or Northern Ireland that has been designated for conservation due to its significant landscape value. Since 2023, the areas in England an ...
. The Urban Nature Conservation Study (UNCS) recognises the town's hinterland as a biodiversity resource. The hills gently rise to an undulating and open plateau, which has a mix of arable farmland, common land and mixed oak
An oak is a hardwood tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' of the beech family. They have spirally arranged leaves, often with lobed edges, and a nut called an acorn, borne within a cup. The genus is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisp ...
, ash and beech
Beech (genus ''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to subtropical (accessory forest element) and temperate (as dominant element of Mesophyte, mesophytic forests) Eurasia and North America. There are 14 accepted ...
woodland. On the northeast side of town are the Berkhamsted and Northchurch commons
The commons is the cultural and natural resources accessible to all members of a society, including natural materials such as air, water, and a habitable Earth. These resources are held in common even when owned privately or publicly. Commons ...
, the largest in the Chilterns at , and forming a large arc running from Northchurch, through Frithsden and down to Potten End
Potten End is a village in west Hertfordshire, England. It is located in the Chiltern Hills, east-north-east of Berkhamsted, north west of Hemel Hempstead and two miles south east of the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural ...
. Ownership of Berkhamsted Common is divided between the National Trust
The National Trust () is a heritage and nature conservation charity and membership organisation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland.
The Trust was founded in 1895 by Octavia Hill, Sir Robert Hunter and Hardwicke Rawnsley to "promote the ...
and Berkhamsted Golf Club. Beyond the common is the historic wooded parkland of Ashridge
Ashridge is a Estate (land), country estate and stately home in Hertfordshire, England. It is situated in the Chiltern Hills, an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, about north of Berkhamsted and north west of London. The estate comprises ...
; once part of Berkhamsted Castle
Berkhamsted Castle is a Norman motte-and-bailey castle in Berkhamsted, Hertfordshire. The castle was built to obtain control of a key route between London and the Midlands during the Norman conquest of England in the 11th century. Robert of ...
's hunting park, it is now managed by the National Trust. Ashridge is part of the Chilterns Beech
Beech (genus ''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to subtropical (accessory forest element) and temperate (as dominant element of Mesophyte, mesophytic forests) Eurasia and North America. There are 14 accepted ...
wood Special Area of Conservation
A special area of conservation (SAC) is defined in the European Union's Habitats Directive (92/43/EEC), also known as the ''Directive on the Conservation of Natural Habitats and of Wild Fauna and Flora''. They are to protect the 220 habitats and ap ...
(SAC), a nationally important nature conservation area, and is also designated as a Site of Special Scientific Interest
A Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) in Great Britain, or an Area of Special Scientific Interest (ASSI) in the Isle of Man and Northern Ireland, is a conservation designation denoting a protected area in the United Kingdom and Isle ...
. Agriculture is more dominant to the south of the town; close to the Buckinghamshire border there are two former large country estates, Ashlyns and Rossway. The ancient woodland at Dickshills is also located here.burgage plots
Burgage is a medieval land terms, medieval land term used in Great Britain and Ireland, well established by the 13th century.
A burgage was a town ("borough" or "burgh") rental property (to use modern terms), owned by a king or lord. The propert ...
(to the north and south). The surviving burgage plot layout is the result of a comprehensive plan carried out at the beginning of the 13th century, most probably instigated by Geoffrey fitz Peter.Grand Junction Canal
The Grand Junction Canal is a canal in England from Braunston in Northamptonshire to the River Thames at Brentford, with a number of branches. The mainline was built between 1793 and 1805, to improve the route from the English Midlands, Midlan ...
in 1798. The canal intersects the river at numerous points, taking most of its water supply and helping to drain the valley. The locality became further urbanised when the London to Birmingham railway was built in 1836–37.Chiltern Hills
The Chiltern Hills or the Chilterns are a chalk escarpment in southern England, located to the north-west of London, covering across Oxfordshire, Buckinghamshire, Hertfordshire and Bedfordshire; they stretch from Goring-on-Thames in the south- ...
";
Neighbouring settlements
Traveling on the high street away from the town, along the Bulbourne valley south-eastwards towards London, the A4251 road passes through the village of Bourne End and the large new town
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz (South Korean band), The Boyz
* New (album), ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
** New (Paul McCartney song), "New" (Paul McCartney song), 2013
* New (EP), ''New'' (EP), ...
of Hemel Hempstead ( distant). To the south south-east is the large village of Bovingdon
Bovingdon is a village in Hertfordshire, England, south-west of Hemel Hempstead, and a civil parishes in England, civil parish within the local authority area of Dacorum. Situated close to the Buckinghamshire border, it forms the largest part ...
. Taking the A416 road south from Berkhamsted, along the Chiltern Hills
The Chiltern Hills or the Chilterns are a chalk escarpment in southern England, located to the north-west of London, covering across Oxfordshire, Buckinghamshire, Hertfordshire and Bedfordshire; they stretch from Goring-on-Thames in the south- ...
into Buckinghamshire
Buckinghamshire (, abbreviated ''Bucks'') is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England and one of the home counties. It is bordered by Northamptonshire to the north, Bedfordshire to the north-east, Hertfordshir ...
lies the nearby hamlet of Ashley Green and the fellow market towns
A market town is a Human settlement, settlement most common in Europe that obtained by custom or royal charter, in the Middle Ages, a market right, which allowed it to host a regular marketplace, market; this distinguished it from a village or ...
of Chesham
Chesham ( , ) is a market town and civil parish in Buckinghamshire, England, United Kingdom, south-east of the county town of Aylesbury, about north-west of Charing Cross, central London, and part of the London metropolitan area, London ...
( distant) and Amersham
Amersham ( ) is a market town and civil parish in Buckinghamshire, England, in the Chiltern Hills, northwest of central London, south-east of Aylesbury and north-east of High Wycombe. Amersham is part of the London commuter belt.
There ar ...
. Further southwest is the village of Great Missenden and to the west is the small market town of Wendover
Wendover is a town and civil parish at the foot of the Chiltern Hills in Buckinghamshire, England. It is situated at the point where the main road across the Chilterns between London and Aylesbury intersects with the once important road along t ...
.
Along the A4251 and valley northwestwards is the adjoining village of Northchurch, and the hamlets of Dudswell and Cow Roast, the village of Wigginton and the small market town of Tring
Tring is a market town and civil parish in the Borough of Dacorum, Hertfordshire, England. It is situated in a gap passing through the Chiltern Hills, classed as an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, from Central London.
Tring is linked ...
( distant) and the county town
In Great Britain and Ireland, a county town is usually the location of administrative or judicial functions within a county, and the place where public representatives are elected to parliament. Following the establishment of county councils in ...
of Buckinghamshire Aylesbury
Aylesbury ( ) is the county town of Buckinghamshire, England. It is home to the Roald Dahl Children's Gallery and the Aylesbury Waterside Theatre, Waterside Theatre. It is located in central Buckinghamshire, midway between High Wycombe and Milt ...
at ( distant). Following the Chiltern Hills northwards, to the north-northwest is the village of Aldbury; situated to the north of Berkhamsted are the villages of Ringshall and Little Gaddesden
Little Gaddesden (pronounced ) is a village and civil parish in the borough of Dacorum, Hertfordshire north of Berkhamsted, close to the border with Bedfordshire. As well as Little Gaddesden village (population 694), the parish contains the se ...
( distant); finally located to the north-east of the town are the villages and hamlets of Potten End
Potten End is a village in west Hertfordshire, England. It is located in the Chiltern Hills, east-north-east of Berkhamsted, north west of Hemel Hempstead and two miles south east of the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural ...
, Frithsden and Great Gaddesden. The nearest large settlements to the north of Berkhamsted are the Bedfordshire
Bedfordshire (; abbreviated ''Beds'') is a Ceremonial County, ceremonial county in the East of England. It is bordered by Northamptonshire to the north, Cambridgeshire to the north-east, Hertfordshire to the south and the south-east, and Buckin ...
towns of Dunstable
Dunstable ( ) is a market town and civil parish in Bedfordshire, England, east of the Chiltern Hills, north of London. There are several steep chalk escarpments, most noticeable when approaching Dunstable from the north. Dunstable is the fou ...
( distant) and Luton
Luton () is a town and borough in Bedfordshire, England. The borough had a population of 225,262 at the 2021 census.
Luton is on the River Lea, about north-west of London. The town's foundation dates to the sixth century as a Saxon settleme ...
(.
Climate
Like most of the United Kingdom, Berkhamsted has an oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate or maritime climate, is the temperate climate sub-type in Köppen climate classification, Köppen classification represented as ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of co ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (te ...
''Cfb'').
Near-real-time weather information can be retrieved from Berkhamsted Weather Station page on the Met Office
The Met Office, until November 2000 officially the Meteorological Office, is the United Kingdom's national weather and climate service. It is an executive agency and trading fund of the Department for Science, Innovation and Technology and ...
Weather Observation website.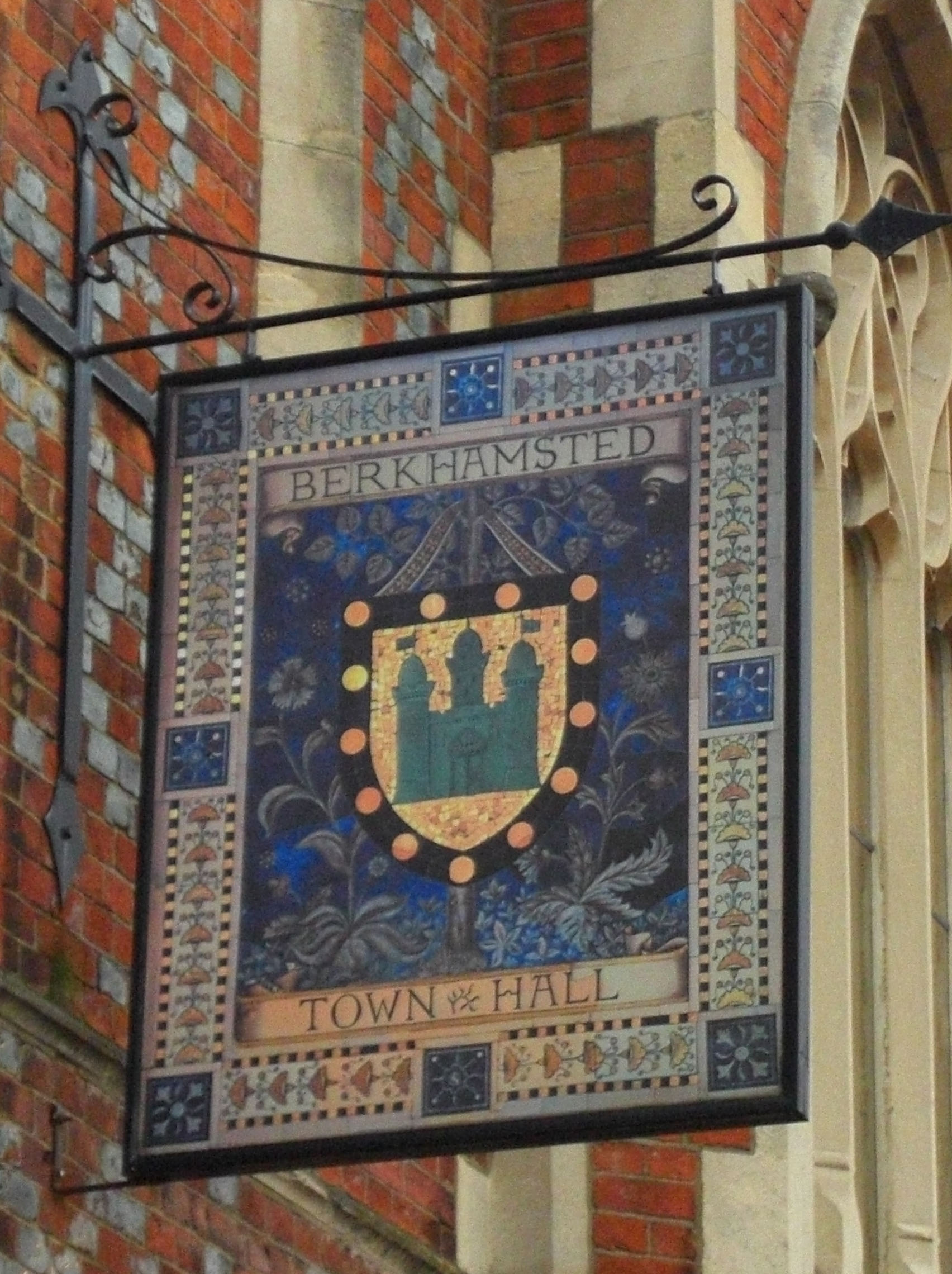 
Governance
Berkhamsted is within the UK parliamentary constituency of Harpenden and Berkhamsted. Following the 2024 United Kingdom general election
The 2024 United Kingdom general election was held on Thursday, 4 July 2024 to elect all 650 members of the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons. The opposition Labour Party (UK), Labour Party, led by Keir Starmer, won a lan ...
, Victoria Collins ( Liberal Democrats) is the constituency's current Member of Parliament (MP).
Berkhamsted has a town council, the first tier of local government that represents the local people to two higher tiers of local government, Dacorum Borough Council and Hertfordshire County Council
Hertfordshire County Council is the upper-tier local authority for the non-metropolitan county of Hertfordshire, in England. The council was created in 1889. It is responsible for a wide range of public services in the county, including social c ...
. The modern district of Dacorum based in Hemel Hempstead
Hemel Hempstead () is a town in the Dacorum district in Hertfordshire, England. It is located north-west of London; nearby towns and cities include Watford, St Albans and Berkhamsted. The population at the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 cens ...
was formed in 1974 under the Local Government Act 1972
The Local Government Act 1972 (c. 70) is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974. It was one of the most significant acts of Parliament to be passed by the Heath Gov ...
; the local government district
Local may refer to:
Geography and transportation
* Local (train), a train serving local traffic demand
* Local, Missouri, a community in the United States
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Local'' (comics), a limited series comic book by Bria ...
's main population centres include Hemel Hempstead, Tring
Tring is a market town and civil parish in the Borough of Dacorum, Hertfordshire, England. It is situated in a gap passing through the Chiltern Hills, classed as an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, from Central London.
Tring is linked ...
and the western part of Kings Langley
Kings Langley is a village, former manor and civil parish in Hertfordshire, England, north-west of London and to the south of the Chiltern Hills. It now forms part of the London commuter belt. The village is divided between two local governme ...
. Berkhamsted accounts for just over 12 per cent of the district's population of 153,300 in 2017.town council
A town council, city council or municipal council is a form of local government for small municipalities.
Usage of the term varies under different jurisdictions.
Republic of Ireland
In 2002, 49 urban district councils and 26 town commissi ...
elections the political composition of the council was Liberal Democrat 10; Conservative 3; Green 2 . Following the 2023 town council
A town council, city council or municipal council is a form of local government for small municipalities.
Usage of the term varies under different jurisdictions.
Republic of Ireland
In 2002, 49 urban district councils and 26 town commissi ...
elections the political composition of the council changed to Liberal Democrat 11; Green 2; Labour 2. In the 2021 local elections on 6 May, the Berkhamsted seat at Hertfordshire County Council was won with 51.8% of the vote by the Liberal Democrat Nigel Taylor, compared to the Conservative vote of 29.8%.
Administrative history
Berkhamsted was an ancient borough
An ancient borough was a historic unit of lower-tier local government in England and Wales
England and Wales () is one of the Law of the United Kingdom#Legal jurisdictions, three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the co ...
, but lost this status in the seventeenth century. The town was then governed by its parish vestry
A vestry was a committee for the local secular and ecclesiastical government of a parish in England, Wales and some English colony, English colonies. At their height, the vestries were the only form of local government in many places and spen ...
until the nineteenth century, in the same way as most rural areas. In 1835 Berkhamsted was made the centre of a poor law union
A poor law union was a geographical territory, and early local government unit, in Great Britain and Ireland.
Poor law unions existed in England and Wales from 1834 to 1930 for the administration of poor relief. Prior to the Poor Law Amendment ...
which covered the town and the surrounding parts of western Hertfordshire, as well as parts of Buckinghamshire. Under the Public Health Act 1872, sanitary districts were created, and the boards of guardians of poor law unions were made responsible for public health and local government for any part of their district not included in an urban authority. As Berkhamsted had no local board
A local board of health (or simply a ''local board'') was a local authority in urban areas of England and Wales from 1848 to 1894. They were formed in response to cholera epidemics and were given powers to control sewers, clean the streets, regulat ...
or other urban authority, it was therefore included in the rural sanitary district.Local Government Act 1894
The Local Government Act 1894 ( 56 & 57 Vict. c. 73) was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales outside the County of London. The act followed the reforms carried out at county leve ...
, rural sanitary districts became rural districts on 28 December 1894, and so the town became part of the Berkhampstead Rural District. Parish councils were also established under the act, to take over the civil functions of the old vestries. The new parish councils came into being on 31 December 1894 if an election had been needed to choose the first parish councillors, as was the case at Berkhamsted. The first meeting of the parish council was held on 31 December 1894 at the Town Hall
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or municipal hall (in the Philippines) is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses the city o ...
in Berkhamsted, with the first chairman of the parish council being Arthur Johnson, who was the rector of St Peter's Church in the town.
Berkhamsted Urban District (18981974)
Efforts to make the town independent of the rural district council continued. Eventually it was agreed that the parish would be split into a "Great Berkhampstead Urban" parish, which would become an urban district, and a "Great Berkhampstead Rural" parish, which would remain in the Berkhampstead Rural District. These changes came into force on 15 April 1898. The first meeting of the Great Berkhampstead Urban District Council was held on 15 April 1898, with David Osborn being elected the council's first chairman. The Great Berkhampstead Rural parish ceded land to the urban district in 1935 and was abolished two years later, being split between Nettleden with Potten End, Northchurch, and Great Gaddesden on 1 April 1937.
In 1908 the urban district council acquired a builder's yard and former Wesleyan chapel at 135 High Street (renumbered 161 High Street around 1950) to act as its offices and meeting place. By the 1930s the council needed more space. In 1936 the council bought the shop adjoining the old chapel. Both buildings were demolished and the new Berkhamsted Civic Centre was built on the site, which formally opened on 14 October 1938.
Until 1937 the official name of the council's area was the "Great Berkhampstead Urban District". At a meeting on 15 April 1937 the council discussed whether to change the name. It was commented that the inclusion of the "Great" in particular caused problems for people looking for the council's telephone number in the directory. The spelling "Berkhamsted" was also the more commonly used by this time. The change of name to "Berkhamsted Urban District" was agreed, and came into effect on 19 July 1937. The neighbouring Berkhampstead Rural District followed suit a few months later, becoming Berkhamsted Rural District on 1 November 1937.[
Berkhamsted Urban District was abolished under the ]Local Government Act 1972
The Local Government Act 1972 (c. 70) is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974. It was one of the most significant acts of Parliament to be passed by the Heath Gov ...
, becoming part of the district
A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or county, counties, several municipality, municip ...
of Dacorum on 1 April 1974. Berkhamsted Town Council was created as a successor parish
Successor parishes are Civil parishes in England, civil parishes with a parish councils in England, parish council, created in England in 1974. They replaced, with the same boundaries, a selected group of Urban district (England and Wales), urban d ...
to the old urban district council. The town council continues to be based at the Civic Centre at 161 High Street.
Demography
Homes
The Hertfordshire Local Information System (HertsLIS) website (based on data from the Office for National Statistics
The Office for National Statistics (ONS; ) is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department which reports directly to the Parliament of the United Kingdom, UK Parliament.
Overview
The ONS is responsible fo ...
and other UK government departments) has the following data regarding the 7,363 households in Berkhamsted in 2011. 72 per cent of homes were owner occupied (34 per cent owned outright and 38 per cent owned with a mortgage) compared to 63 per cent for England. 26.5 per cent of homes were rented (13 per cent each for social rented and private rented) compared to a national figure of 34.5 per cent. In 2011, 77 per cent of household spaces in Berkhamsted were houses or bungalows and 23 per cent were flats or maisonettes. 30 per cent of houses and bungalows were detached compared to 22 per cent nationally: 47 per cent of dwellings are semi-detached or terraced, compared to 55 per cent nationally. According to HertsLIS in the third quarter of 2017 the average price of houses and flats in Berkhamsted was £724,900, compared to £474,400 for Hertfordshire, and £304,500 for England. Detached houses were £1,070,600 compared to £424,400 nationally.Sunday Times
''The Sunday Times'' is a British Sunday newspaper whose circulation makes it the largest in Britain's quality press market category. It was founded in 1821 as ''The New Observer''. It is published by Times Newspapers Ltd, a subsidiary of N ...
'Best Places to Live 2018' list, with the average prices of different types of homes in Berkhamsted ranging from £273,760 for starter homes to £999,920 for family homes, with rents from £850 to £2,490 per calendar month.Rightmove
Rightmove plc is a British company which runs rightmove.co.uk, the UK's largest online real estate property portal. Rightmove is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index.
History
Rightmove was incorporat ...
the average cost of a home in Berkhamsted was £696,949. The majority of sales in the town were detached properties, with an average selling value of £1,076,244. The average terraced dwelling price was £563,291 and the average semi-detached properties went for £657,436. Overall, in 2021 property house prices in Berkhamsted were four per cent up on the previous year and five per cent up on the 2018 peak of £661,336.
Employment and economic wellbeing
In mid-2016, the Office for National Statistics
The Office for National Statistics (ONS; ) is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department which reports directly to the Parliament of the United Kingdom, UK Parliament.
Overview
The ONS is responsible fo ...
estimated the working age population of Berkhamsted (males and females aged 16 to 64) as 11,400, i.e. 62 per cent of the town's population. People from Berkhamsted were employed as follows: 17.5 per cent worked as managers, directors and senior officials; 27.5 per cent professional occupations and 8.5 per cent in associate professional and technical occupations; 10 per cent were employed in administrative and secretarial occupations; 7 per cent in skilled trades; 6 per cent Caring, leisure and other service occupations; 5 per cent were in sales and customer service occupations; 3 per cent were in process, plant and machine operatives; and 5.5 per cent worked in elementary occupations.Office for National Statistics
The Office for National Statistics (ONS; ) is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department which reports directly to the Parliament of the United Kingdom, UK Parliament.
Overview
The ONS is responsible fo ...
on benefit claimants by constituency, the number of claimants on Jobseeker's Allowance (unemployment benefit) in Berkhamsted's South West Hertfordshire parliamentary constituency was 1.7 per cent, compared to 7.8 per cent for the UK.
Diversity
Looking at broad ethnic heritage in 2011, HertsLIS data found that 90 per cent of residents were described as white British. Of the remainder, 1 per cent were Irish, 4 per cent were of other white origin, 1.7 per cent were described as mixed or multiple ethnic, 2.1 per cent were Asian or Asian British, 0.3 per cent were black African/Caribbean or black British and 0.3 per cent were Arab or any other ethnic group. Regarding religious beliefs in 2011, of the 92 per cent of residents who stated a religious preference, 30 per cent were non-religious and 59 per cent were Christian; other faiths included 0.4 per cent Buddhist, 0.5 per cent Jewish, 0.5 per cent Muslim and 0.1 per cent Sikh.
Relationships and education
In 2011 the marital and civil partnership statuses of residents aged 16 and over were as follows: 28 per cent single, 56 per cent married, 0.1 per cent in a registered same-sex civil partnership, 2 per cent separated, 8 per cent divorced or legally dissolved same-sex civil partnership, and 6 per cent widowed or surviving partner from a same-sex civil partnership. Looking at the qualifications table, 12 per cent of residents had no qualifications, 10 per cent reached level 1, 13 per cent achieved level 2, 2 per cent had apprenticeship qualifications, 10 per cent were level 3 and 49 per cent achieved level 4 or above.
Transport
Road
In 1762, this section of Akeman Street became part of the Sparrows Herne Turnpike Road, a main thoroughfare between London and Aylesbury; it was notorious for its rutted and pitted state, even after becoming a toll road
A toll road, also known as a turnpike or tollway, is a public or private road for which a fee (or ''Toll (fee), toll'') is assessed for passage. It is a form of road pricing typically implemented to help recoup the costs of road construction and ...
. Many coaching inn
The coaching inn (also coaching house or staging inn) was a vital part of Europe's inland transport infrastructure until the development of the railway, providing a resting point ( layover) for people and horses. The inn served the needs of t ...
s thrived along its route, including, in Berkhamsted, the King's Arms (where the exiled King Louis XVIII of France carried on a romance with Polly Page, the innkeeper's daughter).A41 road
The A41 is a trunk road between London and Birkenhead, England. Now in parts replaced by motorways, it passes through or near Watford, Kings Langley, Hemel Hempstead, Aylesbury, Bicester, Solihull, Birmingham, West Bromwich, Wolverhampton, New ...
now passes south-west of Berkhamsted. A study of car ownership in Berkhamsted, Northchurch and Tring found that 43–45 per cent of households had two or more cars, compared to the county average of 40 per cent and the national average of 29 per cent. Conversely, the proportion of households who did not own a car was 14–20 per cent (about 7 per cent lower than the national average).Whipsnade Zoo
Whipsnade Zoo, formerly known as ZSL Whipsnade Zoo and Whipsnade Wild Animal Park, is a zoo located in Whipsnade, near Dunstable, Bedfordshire, England. It is one of two zoos (the other being London Zoo in Regent's Park, London) that is owned b ...
. Services include the 30, 31, 62, 207, 500 (Aylesbury and Watford), 501, 502 and 532. Buses are managed by Hertfordshire County Council
Hertfordshire County Council is the upper-tier local authority for the non-metropolitan county of Hertfordshire, in England. The council was created in 1889. It is responsible for a wide range of public services in the county, including social c ...
's '' Intalink'' transport service.
Canal
 In 1798, the
In 1798, the Grand Junction Canal
The Grand Junction Canal is a canal in England from Braunston in Northamptonshire to the River Thames at Brentford, with a number of branches. The mainline was built between 1793 and 1805, to improve the route from the English Midlands, Midlan ...
(built by William Jessop
William Jessop (23 January 1745 – 18 November 1814) was an English civil engineer, best known for his work on canals, harbours and early railways in the late 18th and early 19th centuries.
Early life
Jessop was born in Devonport, Devon, the ...
) from the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, s ...
at Brentford
Brentford is a suburban town in West (London sub region), West London, England and part of the London Borough of Hounslow. It lies at the confluence of the River Brent and the River Thames, Thames, west of Charing Cross.
Its economy has dive ...
reached Berkhamsted; it reached Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands, within the wider West Midlands (region), West Midlands region, in England. It is the Lis ...
in 1805. Castle Wharf, the port of Berkhamsted, on the south side of the canal between Ravens Lane and Castle Street, was the centre of the town's canal trade, navigation and boat building activities. It was a hub of the country's inland water transport system, linking the ports and industrial centres of the country. Goods transported included coal, grain, building materials and manure. Timber yards, boating wharves, breweries, boat building and chemical works flourished as a result of the canal, with over 700 workers employed locally. It is still known as the ''Port of Berkhamsted''. Separately, Francis Egerton, 3rd Duke of Bridgewater
Francis Egerton, 3rd Duke of Bridgewater (21 May 1736 – 8 March 1803), known as Lord Francis Egerton until 1748, was a British nobleman from the Egerton family. He was the youngest son of the 1st Duke. He did not marry, and the dukedom expi ...
(the "Canal Duke" and "father of the inland waterway system"), lived in Ashridge, near Berkhamsted. The canal became part of the Grand Union Canal
The Grand Union Canal in England is part of the Canals of the United Kingdom, British canal system. It is the principal navigable waterway between London and the Midlands. Starting in London, one arm runs to Leicester and another to Birmi ...
in 1929.
Railway
 In 1834, after opposition from
In 1834, after opposition from turnpike trusts
Turnpike trusts were bodies set up by individual Acts of Parliament, with powers to collect road tolls for maintaining the principal roads in Britain from the 17th but especially during the 18th and 19th centuries. At the peak, in the 1830s, ...
and local landowners was resolved, the first Berkhamsted railway station was built by chief engineer Robert Stephenson
Robert Stephenson , (honoris causa, Hon. causa) (16 October 1803 – 12 October 1859) was an English civil engineer and designer of locomotives. The only son of George Stephenson, the "Father of Railways", he built on the achievements of hi ...
. Though the castle was the first building to receive statutory protection from Parliament, the railway embankment obliterated the old castle barbican
A barbican (from ) is a fortified outpost or fortified gateway, such as at an outer defense perimeter of a city or castle, or any tower situated over a gate or bridge which was used for defensive purposes.
Europe
Medieval Europeans typically b ...
and adjacent earthworks. Most of the raw materials used to build the railway were transported by the canal. The present station was built in 1875 when the railway was widened. It is unusual, on its line, in that most of the original buildings have been retained. The 'large trunk station' is located immediately next to Berkhamsted Castle on one side and overlooks the Grand Junction Canal on the other. The station is situated north-west of London Euston on the West Coast Main Line
The West Coast Main Line (WCML) is one of the most important railway corridors in the United Kingdom, connecting the major cities of London and Glasgow with branches to Birmingham, Manchester, Liverpool and Edinburgh. It is one of the busiest ...
.'
One and a half million journeys are made annually to and from Berkhamsted, the vast majority by commuters to and from London. Principal services, operated by West Midlands Trains
West Midlands Trains (WMT) is a British train operating company. It operates passenger trains on the West Midlands franchise between London and the English Midlands under two trading names: within the West Midlands region as West Midlands Rai ...
, run between London Euston and , with additional trains running to and . Southern also runs an hourly service direct to East Croydon, via .
Economy and commerce
In 1986, farming, service and light industry were characteristic local employers. In 2015, schools and retail (predominantly Waitrose
Waitrose Limited, trading as Waitrose & Partners, is a British supermarket chain, founded in 1904 as Waite, Rose & Taylor, later shortened to Waitrose. In 1937, it was acquired by the John Lewis Partnership, the UK's largest employee-owned b ...
) were the town's largest employers; these are both situated in Berkhamsted Castle ward.Transition Town
The terms transition town, transition initiative and transition model refer to grassroots, grassroot community projects that aim to increase self-sufficiency to reduce the potential effects of peak oil, Global warming, climate destruction, and eco ...
community.
Education
Independent schools
Berkhamsted School is a private
Private or privates may refer to:
Music
* "In Private", by Dusty Springfield from the 1990 album ''Reputation''
* Private (band), a Denmark-based band
* "Private" (Ryōko Hirosue song), from the 1999 album ''Private'', written and also recorded ...
public school. It was founded in 1541 by Dean John Incent, ( 1480–1545) Born in Berkhamsted ''circa'' 1480, John Incent was the Dean of St Paul's Cathedral
St Paul's Cathedral, formally the Cathedral Church of St Paul the Apostle, is an Anglican cathedral in London, England, the seat of the Bishop of London. The cathedral serves as the mother church of the Diocese of London in the Church of Engl ...
in London from 1540 to 1545 (during the early years of the English Reformation
The English Reformation began in 16th-century England when the Church of England broke away first from the authority of the pope and bishops Oath_of_Supremacy, over the King and then from some doctrines and practices of the Catholic Church ...
).
Incent was noted as one of the agents of the Lord Chancellor Thomas Cromwell
Thomas Cromwell (; – 28 July 1540) was an English statesman and lawyer who served as List of English chief ministers, chief minister to King Henry VIII from 1534 to 1540, when he was beheaded on orders of the king, who later blamed false cha ...
responsible for the sequestration of religious properties during the Dissolution of the Monasteries Incent financed the foundation of Berkhamsted school from the combined revenues of the town's two medieval hospitals, St John the Baptist and St John the Evangelist, which he had closed down in 1516. In 1523 he took the lands of the two former hospitals and joined them to his own land, donating the enlarged estate towards the creation of a school. In 1541 he obtained a royal charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, but ...
for ''"one chauntry perpetual and schools for boys not exceeding 144 to be called Dean Incent's Free School in Berkhamstedde"''. John Incent died intestate
Intestacy is the condition of the estate of a person who dies without a legally valid will, resulting in the distribution of their estate under statutory intestacy laws rather than by their expressed wishes. Alternatively this may also apply ...
18 months after his school opened. To protect the school from legal challenges, it was incorporated by an Act of Parliament as ''The Free Schole of King Edwarde the Sixte in Berkhampstedde''. Amongst the school's former students was the author Graham Greene
Henry Graham Greene (2 October 1904 – 3 April 1991) was an English writer and journalist regarded by many as one of the leading novelists of the 20th century.
Combining literary acclaim with widespread popularity, Greene acquired a re ...
. The school's oldest building, the Old Hall, was built in 1544 and is Grade I listed. Contemporary records state that Incent ''"builded with all speed a fair schoole lartge and great all of brick very sumptuously"'', and ''"when ye said school was thus finished, ye Deane sent for ye cheafe men of ye towne into ye school where he kneeling gave thanks to Almighty God"''. In 1988, the school merged with Berkhamsted School for Girls (another large independent school in the town), which had been founded in 1888.
State schools
 In the 1970s, the town adopted a three-tier
In the 1970s, the town adopted a three-tier state school
A state school, public school, or government school is a primary school, primary or secondary school that educates all students without charge. They are funded in whole or in part by taxation and operated by the government of the state. State-f ...
education system, but reverted to the two-tier system of primary and secondary schools in 2013.
Primary schools are: Victoria (founded in 1838), Bridgewater, Greenway, St Thomas More, Swing Gate, Thomas Coram and Westfield. The secondary school is Ashlyns School, a Foundation school
In England and Wales, a foundation school is a state-funded school in which the school governor, governing body has greater freedom in the running of the school than in Community school (England and Wales), community schools.
Foundation schools ...
with 1,200 pupils aged 11 to 19 years; it is a specialist language college. The school started in the 18th century, when Thomas Coram
Sea captain, Captain Thomas Coram ( – 29 March 1751) was an English sea captain and philanthropist who created the London Foundling Hospital in Lamb's Conduit Fields, Bloomsbury, to look after abandoned children on the streets of London. It is ...
, a philanthropic ship's captain, was appalled by the abandoned babies and children starving and dying in London. He campaigned for a hospital to accommodate them and was successfully granted a royal charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, but ...
"for the Maintenance and Education of Exposed and Deserted Children" in 1739. Three years later, in 1742, he established the Foundling Hospital
The Foundling Hospital (formally the Hospital for the Maintenance and Education of Exposed and Deserted Young Children) was a children's home in London, England, founded in 1739 by the philanthropy, philanthropic Captain (nautical), sea captain ...
at Lamb's Conduit Fields in Bloomsbury
Bloomsbury is a district in the West End of London, part of the London Borough of Camden in England. It is considered a fashionable residential area, and is the location of numerous cultural institution, cultural, intellectual, and educational ...
, London. It was the first children's charity in the country and a precedent for incorporated associational charities everywhere. The school moved to its purpose-built location in Berkhamsted in 1935. The residential home side at Berkhamsted closed following the Children Act 1948, when family-centred care replaced institutional care. In 1951 Hertfordshire County Council took over running the school. The large school contains stained glass windows, especially around the chapel
A chapel (from , a diminutive of ''cappa'', meaning "little cape") is a Christianity, Christian place of prayer and worship that is usually relatively small. The term has several meanings. First, smaller spaces inside a church that have their o ...
, a staircase and many monuments from the original London hospital. The school's chapel formerly housed an organ donated by George Frideric Handel
George Frideric (or Frederick) Handel ( ; baptised , ; 23 February 1685 – 14 April 1759) was a German-British Baroque composer well-known for his operas, oratorios, anthems, concerti grossi, and organ concerti.
Born in Halle, Germany, H ...
. The school was used a backdrop to the 2007 comedy film, '' Son of Rambow''. 
Business school
Hult Ashridge
Hult Ashridge Executive Education (also known as the Hult Ashridge) is the executive education arm of Hult International Business School, based in London, Dubai, and Hult's flagship executive education campus on the Ashridge Estate.
Formerly ...
(formerly Ashridge Business School/Ashridge Executive Education) is located in the Grade I listed Ashridge House, the former stately home of the Duke of Bridgewater, set in of rolling parkland, two miles outside Berkhamsted. The house occupies the site of the earlier Ashridge Priory
Ashridge Priory was a medieval college of Austin canons called variously the "Brothers of Penitence" or the " Boni Homines". It was founded by Edmund of Almain in 1283 who donated, among other things, a phial of Christ's blood to the abbey. It ...
, a college
A college (Latin: ''collegium'') may be a tertiary educational institution (sometimes awarding degrees), part of a collegiate university, an institution offering vocational education, a further education institution, or a secondary sc ...
of the monastic order of Bonhommes founded in 1283 by Edmund, 2nd Earl of Cornwall
Edmund of Almain (26 December 1249 – 1300) was the second Earl of Cornwall of the fourth creation from 1272. He joined the Ninth Crusade in 1271, but never made it to the Holy Land. He was the regent of the Kingdom of England from 1286 to 1289 ...
, who resided in the castle. After the Dissolution of the Monasteries, Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
bequeathed the property to his daughter, Elizabeth. In 1800, it was the home of Francis Egerton, 3rd Duke of Bridgewater
Francis Egerton, 3rd Duke of Bridgewater (21 May 1736 – 8 March 1803), known as Lord Francis Egerton until 1748, was a British nobleman from the Egerton family. He was the youngest son of the 1st Duke. He did not marry, and the dukedom expi ...
, affectionately known as the Father of Inland Navigation.James Wyatt
James Wyatt (3 August 1746 – 4 September 1813) was an English architect, a rival of Robert Adam in the Neoclassicism, neoclassical and neo-Gothic styles. He was elected to the Royal Academy of Arts in 1785 and was its president from 1805 to ...
with later work by his nephew Jeffrey Wyattville. Architecture critic Nikolaus Pevsner
Sir Nikolaus Bernhard Leon Pevsner (30 January 1902 – 18 August 1983) was a German-British art historian and architectural historian best known for his monumental 46-volume series of county-by-county guides, ''The Buildings of England'' (195 ...
described it as the "largest of the romantic palaces near London ... a spectacular composition". In 1928, Urban Hanlon Broughton
Urban Hanlon Broughton (12 April 1857 – 30 January 1929) was an English civil engineer who went to work in the United States, married an American heiress, returned to England and was for three-and-a-half years a Conservative Member of Parlia ...
purchased the house as a gift for the Conservative Party intended to commemorate former prime minister Andrew Bonar Law. For its first 15 years it was a "College of Citizenship", established to help the party develop its intellectual forces in struggles with socialist organisations such as the Fabian Society
The Fabian Society () is a History of the socialist movement in the United Kingdom, British socialist organisation whose purpose is to advance the principles of social democracy and democratic socialism via gradualist and reformist effort in ...
. It became a cross between a think-tank
A think tank, or public policy institute, is a research institute that performs research and advocacy concerning topics such as social policy, political strategy, economics, military, technology, and culture. Most think tanks are non-governme ...
and a training centre, with Arthur Bryant as its educational adviser.
In 2015, Ashridge merged with Hult International Business School
Hult International Business School (also known as Hult Business School or Hult) is a private business school with campuses in London, San Francisco, Dubai, New York City, and Cambridge, Massachusetts. Hult is named for the school's benefactor B ...
, an American business school with campuses in seven cities around the world. Its activities include open and tailored executive education
Executive education (ExEd or Exec. Ed) refers to academic programs at graduate-level business schools for executives, business leaders and managers, globally. These programs are generally non-credit and non-degree-granting, but sometimes lead to ...
programmes, MBA
A Master of Business Administration (MBA) is a professional degree focused on business administration. The core courses in an MBA program cover various areas of business administration; elective courses may allow further study in a particular a ...
, MSc and Diploma qualifications, organisation consulting
A consultant (from "to deliberate") is a professional (also known as ''expert'', ''specialist'', see variations of meaning below) who provides advice or services in an area of specialization (generally to medium or large-size corporations). Cons ...
, applied research
Applied science is the application of the scientific method and scientific knowledge to attain practical goals. It includes a broad range of disciplines, such as engineering and medicine. Applied science is often contrasted with basic science, ...
and online learning. Ashridge is the only UK specialist business school with degree-awarding powers, giving it the equivalent status to a university in awarding its degrees.
Religious sites
The oldest extant church locally is St Mary's in the adjacent village of Northchurch. Between 1087 and 1104, there is reference to a chaplain called Godfrey and to a chapel of St James with parochial status within St Mary's Berkhamsted's parish. The chapel situated close to St Johns, located close to St John's Lane, was the base for a small community of monks, the Brotherhood of St John the Baptist, in the 11th and 12th centuries.[.]
During King John's reign, Geoffrey Fitz Peter, was instrumental in the foundation the parish church of St Peter, and in 1222, Robert de Tuardo, was registered as the first known rector. Because of the church's proximity to the castle, the reigning monarch was patron
Patronage is the support, encouragement, privilege, or financial aid that an organization or individual bestows on another. In the history of art, art patronage refers to the support that princes, popes, and other wealthy and influential people ...
of Berkhamsted rectors for several centuries. In 1648, St Peter's Church was requisitioned during the English Civil War
The English Civil War or Great Rebellion was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Cavaliers, Royalists and Roundhead, Parliamentarians in the Kingdom of England from 1642 to 1651. Part of the wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of th ...
by General Fairfax as a military prison
A military prison is a prison operated by a military. Military prisons are used variously to house prisoners of war, unlawful combatants, those whose freedom is deemed a national security risk by the military or national authorities, and members o ...
to hold soldiers captured from the siege of Colchester
The siege of Colchester occurred in the summer of 1648 when the Second English Civil War reignited in several areas of Britain. Colchester found itself in the thick of the unrest when a Cavalier, Royalist army on its way through East Angli ...
. The poet William Cowper
William Cowper ( ; – 25 April 1800) was an English poet and Anglican hymnwriter.
One of the most popular poets of his time, Cowper changed the direction of 18th-century nature poetry by writing of everyday life and scenes of the Engli ...
was christened in St Peter's, where his father John Cowper was rector.
The parish church of St Peter, which stands on the high street, is one of the largest churches in Hertfordshire.transept
A transept (with two semitransepts) is a transverse part of any building, which lies across the main body of the building. In cruciform ("cross-shaped") cruciform plan, churches, in particular within the Romanesque architecture, Romanesque a ...
s is . The oldest part of the church is the chancel
In church architecture, the chancel is the space around the altar, including the Choir (architecture), choir and the sanctuary (sometimes called the presbytery), at the liturgical east end of a traditional Christian church building. It may termi ...
, which is dated at c. 1200; it is in the Early English style common in that period. Further additions were made up until the 15th century; in 1871, it underwent a restoration by William Butterfield
William Butterfield (7 September 1814 – 23 February 1900) was a British Gothic Revival architect and associated with the Oxford Movement (or Tractarian Movement). He is noted for his use of polychromy.
Biography
William Butterfield was bo ...
. There are two altar tombs with alabaster effigies dating from the 14th century: the tombs are of a knight (thought to be Henry of Berkhamsted, one of the Black Prince's lieutenants at the Battle of Crecy
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
) and his lady. There are two other Anglican
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the ...
churches in the town – 'St Michael and All Angels' (Sunnyside)(original building 1886) and 'All Saints' Church & St Martha's' (built in 1906, to cater for the growing population in the west end of the town). In 1842 a detached churchyard to St Peter's Church was established, using land to the rear of Egerton House (where the Rex cinema now stands) on Rectory Lane. It expanded to 3.275 acres and was phased out of use in 1976.
The town has a strong Non-conformist tradition, in 1672 a survey found that there were 400 Anglian conformists and 150 Non-conformists in Berkhamsted, when such beliefs could bring you foul of the law. The Baptist
Baptists are a Christian denomination, denomination within Protestant Christianity distinguished by baptizing only professing Christian believers (believer's baptism) and doing so by complete Immersion baptism, immersion. Baptist churches ge ...
community in Berkhamsted, dates from 1640 making it one of the oldest nationally; first gathering in secret, they built a large chapel in 1722, and moved to their current place of worship at the junction of Ravens Lane on the High Street in 1864. A Quaker
Quakers are people who belong to the Religious Society of Friends, a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations. Members refer to each other as Friends after in the Bible, and originally, others referred to them as Quakers ...
community is present in the town from the second half of the 17th century, they opened their Meeting House
A meeting house (also spelled meetinghouse or meeting-house) is a building where religious and sometimes private meetings take place.
Terminology
Nonconformist (Protestantism), Nonconformist Protestant denominations distinguish between a:
* chu ...
in 1818 on the High Street opposite St John's Well Lane. The Congregationlists can be traced back to 1780, they now worship combined with the Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a historically Reformed Protestant tradition named for its form of church government by representative assemblies of elders, known as "presbyters". Though other Reformed churches are structurally similar, the word ''Pr ...
church at St Andrew's United Reformed Church on the corner of Castle Street and Chapel Street. The Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a Protestant Christianity, Christian Christian tradition, tradition whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's brother ...
s arrived with the hundreds of men who came to build the railway, via various places of worship, today they share All Saints' Church with the Anglians. The Evangelist (Latter Day Saints) began life has part of the Plymouth Brethren
The Plymouth Brethren or Assemblies of Brethren are a low church and Nonconformist (Protestantism), Nonconformist Christian movement whose history can be traced back to Dublin, Ireland, in the mid to late 1820s, where it originated from Anglica ...
, their Hope Hall opened in 1875, which was rechristened the Kings Road Evangelical Church in 1969. The Roman Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
tradition from the 17th to 20th century appears to be limited, General de Gaulle worshiped at their original Church of the Sacred Heart in Park View Road, they moved to a larger modern church in 1980 on Park Street.
Culture and leisure
Literary connections
Geoffrey Chaucer
Geoffrey Chaucer ( ; – 25 October 1400) was an English poet, author, and civil servant best known for ''The Canterbury Tales''. He has been called the "father of English literature", or, alternatively, the "father of English poetry". He w ...
was clerk of works at Berkhamsted Castle from 1389 and based his Doctor of Phisick in ''The Canterbury Tales
''The Canterbury Tales'' () is a collection of 24 stories written in Middle English by Geoffrey Chaucer between 1387 and 1400. The book presents the tales, which are mostly written in verse, as part of a fictional storytelling contest held ...
'' on John of Gaddesden, who lived in nearby Little Gaddesden. William Cowper
William Cowper ( ; – 25 April 1800) was an English poet and Anglican hymnwriter.
One of the most popular poets of his time, Cowper changed the direction of 18th-century nature poetry by writing of everyday life and scenes of the Engli ...
was born in Berkhamsted Rectory in 1731. Although he moved away when still a boy, there are frequent references to the town in his poems and letters. In the Victorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the reign of Queen Victoria, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. Slightly different definitions are sometimes used. The era followed the ...
, Cowper became a cult figure and Berkhamsted was a place of pilgrimage for his devotees. Maria Edgeworth
Maria Edgeworth (1 January 1768 – 22 May 1849) was a prolific Anglo-Irish novelist of adults' and children's literature. She was one of the first realist writers in children's literature and a significant figure in the evolution of the novel i ...
, a prolific Anglo-Irish writer of adults' and children's literature who was a significant figure in the evolution of the novel in Europe, lived in Berkhamsted as a child in the 18th century.J. M. Barrie
Sir James Matthew Barrie, 1st Baronet, (; 9 May 1860 19 June 1937) was a Scottish novelist and playwright, best remembered as the creator of Peter Pan. He was born and educated in Scotland and then moved to London, where he wrote several succe ...
's Peter Pan
Peter Pan is a fictional character created by Scottish novelist and playwright J. M. Barrie. A free-spirited and mischievous young boy who can fly and never grows up, Peter Pan spends his never-ending childhood having adventures on the mythical ...
. A little later, novelist Graham Greene
Henry Graham Greene (2 October 1904 – 3 April 1991) was an English writer and journalist regarded by many as one of the leading novelists of the 20th century.
Combining literary acclaim with widespread popularity, Greene acquired a re ...
was born in Berkhamsted and educated at Berkhamsted School, alongside literary contemporaries Claud Cockburn, Peter Quennell
Sir Peter Courtney Quennell (9 March 1905 – 27 October 1993) was an English biographer, literary historian, editor, essayist, journalist, poet and critic. He wrote extensively on social history. In his ''Times'' obituary he was described as "th ...
, Humphrey Trevelyan and Cecil Parrott.Ed Reardon's Week
''Ed Reardon's Week'' is a sitcom on BBC Radio 4 recorded semi-naturalistically in the style of a radio drama. It concerns the story of a curmudgeonly middle-aged writer described in the show's publicity material as an "author, pipesmoker, cons ...
resides in Berkhamsted.
Cinema
 The Rex cinema is regarded by some, including ''
The Rex cinema is regarded by some, including ''The Daily Telegraph
''The Daily Telegraph'', known online and elsewhere as ''The Telegraph'', is a British daily broadsheet conservative newspaper published in London by Telegraph Media Group and distributed in the United Kingdom and internationally. It was found ...
'', as Britain's most beautiful cinema. Described by Dame Judi Dench
Dame Judith Olivia Dench (born 9 December 1934) is an English actress. Widely considered one of Britain's greatest actors, she is noted for her versatility, having appeared in films and television, as well as for her numerous roles on the stage ...
as "absolutely awe-inspiring", the Rex was declared Britain's Best Cinema in the inaugural ''Guardian
Guardian usually refers to:
* Legal guardian, a person with the authority and duty to care for the interests of another
* ''The Guardian'', a British daily newspaper
(The) Guardian(s) may also refer to:
Places
* Guardian, West Virginia, Unit ...
'' film awards in 2014. Built in 1937, the Rex is recognised by English Heritage
English Heritage (officially the English Heritage Trust) is a charity that manages over 400 historic monuments, buildings and places. These include prehistoric sites, a battlefield, medieval castles, Roman forts, historic industrial sites, Lis ...
as a fine example of a 1930s art deco
Art Deco, short for the French (), is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design that first Art Deco in Paris, appeared in Paris in the 1910s just before World War I and flourished in the United States and Europe during the 1920 ...
cinema. The cinema was designed by architect David Evelyn Nye for the Shipman and King circuit. Closed in 1988, the cinema was extensively restored in 2004 and has become a thriving independent local cinema. The Rex frequently has sold-out houses for evening showings, the cinema is a "movie palace with all the original art deco trimmings" (its interior features decorations of sea waves and shells). Inside is a step "back into the golden age of film" when going to the movies was an experience; the cinema features luxurious seating and two licensed bars. It is managed by its owner James Hannaway, who introduces films. Sometimes there is a question-and-answer session with directors and actors involved in the films; these sessions have included Dame Judi Dench, Charles Dance, Mike Leigh
Mike Leigh (born 20 February 1943) is an English screenwriter, producer, director and former actor with a film, theatre, and television career spanning more than 60 years. His accolades include prizes at the Cannes Film Festival, the Berlin In ...
and Terry Jones
Terence Graham Parry Jones (1 February 1942 – 21 January 2020) was a Welsh actor, comedian, director, historian, writer and member of the Monty Python comedy troupe.
After graduating from Oxford University with a degree in English, Jones a ...
.
Prior to the cinema's construction, an Elizabethan
The Elizabethan era is the epoch in the Tudor period of the history of England during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I (1558–1603). Historians often depict it as the golden age in English history. The Roman symbol of Britannia (a female per ...
mansion, Egerton House, had occupied the site at the east end of the high street for 350 years. The house was occupied briefly (1904–07) by Arthur
Arthur is a masculine given name of uncertain etymology. Its popularity derives from it being the name of the legendary hero King Arthur.
A common spelling variant used in many Slavic, Romance, and Germanic languages is Artur. In Spanish and Ital ...
and Sylvia Llewelyn Davies, whose children were J. M. Barrie
Sir James Matthew Barrie, 1st Baronet, (; 9 May 1860 19 June 1937) was a Scottish novelist and playwright, best remembered as the creator of Peter Pan. He was born and educated in Scotland and then moved to London, where he wrote several succe ...
's inspiration for Peter Pan
Peter Pan is a fictional character created by Scottish novelist and playwright J. M. Barrie. A free-spirited and mischievous young boy who can fly and never grows up, Peter Pan spends his never-ending childhood having adventures on the mythical ...
.
British Film Institute National Archive at King's Hill
Rarely open to the public, the BFI National Archive's "The J. Paul Getty, Jr. Conservation Centre" in Berkhamsted is the archive of the British Film Institute
The British Film Institute (BFI) is a film and television charitable organisation which promotes and preserves filmmaking and television in the United Kingdom. The BFI uses funds provided by the National Lottery to encourage film production, ...
. With over 275,000 feature, non-fiction and short films (dating from 1894) and 210,000 television programmes, it is one of the largest film archives in the world. Two of the archive's collections were added to the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
) UK Memory of the World Register, in 2011. The archive collects, preserves, restores and shares the films and television programmes which have shaped and recorded British life and times since the development of motion picture film in the late 19th century. The majority of the collection is British-originated material, but the archive also features internationally significant holdings from around the world and films that feature key British actors and the work of British directors.
Sport and outdoor pursuits
The town benefits from having a large National Trust Common and woodland on its long north-east edge. Running east–west through the centre of the town, along the town's length the Grand Union Canal (once an important trade artery) today it provides an open space with recreational opportunities, and acts with the small River Bulbourne as a wildlife corridor
A wildlife corridor, also known as a habitat corridor, or green corridor, is a designated area habitat (ecology), that connects wildlife populations that have been separated by human activities or structures, such as development, roads, or land ...
through the town.Heritage Lottery Fund
The National Lottery Heritage Fund, formerly the Heritage Lottery Fund (HLF), distributes a share of National Lottery funding, supporting a wide range of heritage projects across the United Kingdom.
History
The fund's predecessor bodies were ...
and the Big Lottery Fund
The National Lottery Community Fund, legally named the Big Lottery Fund, is a non-departmental public body responsible for distributing funds raised by the National Lottery for " good causes".
It is the largest community funder in the UK and ...
from the National Lottery (United Kingdom)
The National Lottery is the state-franchising, franchised national lottery established in 1994 in the United Kingdom. It is regulated by the Gambling Commission, and is operated by Allwyn Entertainment, who took over from Camelot Group (who ha ...
to repurpose the Rectory Lane Cemetery - as one of 12 sites across the country sharing £32m. The grant is to restored heritage features and create a new green community space in the town.
The Berkhamsted Bowmen are the oldest archery
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a Bow and arrow, bow to shooting, shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting ...
club in England.Cricket
Cricket is a Bat-and-ball games, bat-and-ball game played between two Sports team, teams of eleven players on a cricket field, field, at the centre of which is a cricket pitch, pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two Bail (cr ...
Club competes in the Herts League and in 2015 it ran twenty-five separate teams. The club is based at the Berkhamsted Community Cricket and Sports Club, Kitcheners Field, Castle Hill, Berkhamsted. The nine Berkhamsted and Hemel Hempstead Hockey Club teams are based just outside the town at Cow Roast, playing their matches on their astroturf pitch at the club grounds in Cow Roast. There are two Bowls
Bowls, also known as lawn bowls or lawn bowling, is a sport in which players try to roll their ball (called a bowl) closest to a smaller ball (known as a "jack" or sometimes a "kitty"). The bowls are shaped (biased), so that they follow a curve ...
clubs, Berkhamsted and Kitcheners.
The town's football club, Berkhamsted FC, play in the Southern Football League
The Southern League is a football competition featuring semi-professional clubs from East Anglia, the South and Midlands of England, and South Wales. Together with the Isthmian League and the Northern Premier League it forms levels seven a ...
Division One Central, part of the 8th Level in the English League (the town's football ground is at Broadwater). The team was formed in 2009 after the demise of Berkhamsted Town FC, which had been established in 1895. Founded in 1996, Berkhamsted Raiders CFC football club was recognised as the FA Charter Standard Community Club of the Year at the English Football Association Community Awards in 2014 and awarded the UEFA
The Union of European Football Associations (UEFA ; ; ) is one of six continental bodies of governance in association football. It governs football, futsal and beach soccer, beach football in Europe and the List of transcontinental countries#A ...
Grassroots Silver Award in 2015 for their work across the local community. The club, in 2023, had more than 1,300 affiliated players, including 250 girls in 94 youth teams plus Senior, Veterans, Ladies, Walking Football and Inclusive Football sections. In 2022, the Club was awarded the Herts FA Grassroots Club of the Year.
There is a sports centre off Douglas Gardens, managed by EveryoneActive. The facilities comprise a large indoor multi-purpose sports hall, squash courts, swimming pool and outdoor all-weather pitch. This facility is complemented by dual use of the leisure facilities of Ashlyns School and Berkhamsted Collegiate School. A deficit in leisure space is compounded by a high level of sports participation locally and consequent heavy use of outdoor sports pitches. Berkhamsted and the surrounding area has a variety of road cycling
Cycling, also known as bicycling or biking, is the activity of riding a bicycle or other types of pedal-driven human-powered vehicles such as balance bikes, unicycles, tricycles, and quadricycles. Cycling is practised around the world fo ...
and mountain biking
Mountain biking (MTB) is a sport of riding bicycles off-road, often over rough terrain, usually using specially designed mountain bikes. Mountain bikes share similarities with other bikes but incorporate features designed to enhance durability ...
routes, including traffic-free off-road routes in Ashridge Estate. The town was visited by the Tour of Britain
The Tour of Britain is a multi-stage cycling race, conducted on British roads, in which participants race across Great Britain to complete the race in the fastest time.
The event dates back to the first British stage races held just after th ...
in 2014.
Media
Berkhamsted is within the BBC London
BBC London is the BBC English Region producing local radio, television, teletext and online services in London, Surrey and parts of the surrounding areas of the Home Counties. Its output includes the daily '' BBC London'' news bulletin and w ...
and ITV London
ITV London is the on-air brand name used by ''ITV Broadcasting Limited'' for two broadcast franchises of ITV, Carlton Television (weekdays) and London Weekend Television (weekends) in the London ITV region. Its terrestrial digital signal is ...
region. Television signals are received from the Crystal Palace TV transmitter and the local relay transmitter situated in Hemel Hempstead
Hemel Hempstead () is a town in the Dacorum district in Hertfordshire, England. It is located north-west of London; nearby towns and cities include Watford, St Albans and Berkhamsted. The population at the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 cens ...
.
Local radio stations are BBC Three Counties Radio on 103.8 FM, Heart Hertfordshire on 96.6 FM, Greatest Hits Radio Bucks, Beds and Herts (formerly Mix 96.2) on 92.2 FM and community based stations, Radio Dacorum and Tring Radio, which both broadcast online.
The town is served by the local newspaper, Hemel Hempstead Gazette & Express.
Sites of interest
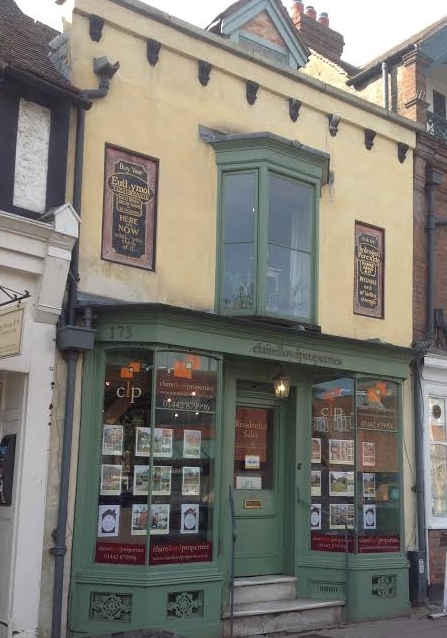 The majority of Berkhamsted's eighty-five listed or scheduled historical sites are on in the high street and the medieval core of the town (a significant number of them contain timber frames). Four are scheduled, one is Grade I, seven are Grade II*, the remaining 75 are Grade II. In addition to the sites noted in the article above (such as the castle and schools) the following structures and locations are of interest:
* 173 High Street is a Victorian façade hiding what is considered to be the oldest extant jettied timber-framed building in Great Britain, dated by
The majority of Berkhamsted's eighty-five listed or scheduled historical sites are on in the high street and the medieval core of the town (a significant number of them contain timber frames). Four are scheduled, one is Grade I, seven are Grade II*, the remaining 75 are Grade II. In addition to the sites noted in the article above (such as the castle and schools) the following structures and locations are of interest:
* 173 High Street is a Victorian façade hiding what is considered to be the oldest extant jettied timber-framed building in Great Britain, dated by dendrochronology
Dendrochronology (or tree-ring dating) is the scientific method of chronological dating, dating tree rings (also called growth rings) to the exact year they were formed in a tree. As well as dating them, this can give data for dendroclimatology, ...
of structural timbers to between 1277 and 1297.goldsmith
A goldsmith is a Metalworking, metalworker who specializes in working with gold and other precious metals. Modern goldsmiths mainly specialize in jewelry-making but historically, they have also made cutlery, silverware, platter (dishware), plat ...
's shop with a workshop behind. It is now believed to have been a jettied service wing to a larger aisled hall house, which has since disappeared.almshouses
An almshouse (also known as a bede-house, poorhouse, or hospital) is charitable organization, charitable public housing, housing provided to people in a particular community, especially during the Middle Ages. They were often built for the povert ...
built in 1684.
* The Bourne School, at 222 High Street, was the legacy by Thomas Bourne (1656–1729) (Master of the Company of Framework Knitters) to build a charity school
Charity schools, sometimes called blue coat schools, or simply the Blue School, were significant in the history of education in England. They were built and maintained in various parishes by the voluntary contributions of the inhabitants to ...
in Berkhamsted for 20 boys and 10 girls. The front was rebuilt in 1854 in Jacobean-style red brick; it is not clear if any part of the building predates 1854. In 1875, the pupils were transferred to the National School and the funds used for scholarships.
* The site now occupied by the Pennyfarthing Hotel dates from the 16th century, having been a monastic building used as accommodation for religious guests passing through Berkhamsted or going to the monastery at Ashridge.
* Berkhamsted Town Hall
Berkhamsted Town Hall is a Grade II Listed building, listed municipal building in the High Street, Berkhamsted, Hertfordshire, England.
History
The current building was commissioned to replace a 16th century town hall in Church Lane which stil ...
, a Victorian gothic market house and town hall, designed by architect Edward Buckton Lamb (built in 1859, extended in 1890 and restored in 1983–1999), was built by public subscription from Berkhamstedians. It comprised a market hall (now the Copper House restaurant), a large assembly hall and rooms for the Mechanics' Institute
Mechanics' institutes, also known as mechanics' institutions, sometimes simply known as institutes, and also called schools of arts (especially in the Australian colonies), were educational establishments originally formed to provide adult edu ...
. When Berkhamsted became part of the new Dacorum Borough Council (based in Hemel Hempstead) there were plans to demolish the building; these plans were stopped in the 1970s and 1980s by a ten-year citizens' campaign, which eventually ended at the High Court.
 * The Berkhamsted
* The Berkhamsted Canadian
Canadians () are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being ''C ...
totem pole
Totem poles () are monumental carvings found in western Canada and the northwestern United States. They are a type of Northwest Coast art, consisting of poles, posts or pillars, carved with symbols or figures. They are usually made from large t ...
sits adjacent to the canal, close to Castle Street Bridge. In the early 1960s, Roger Alsford, a great-grandson of the founder of the timber company, James Alsford (1841–1912), went to work at the Tahsis lumber mill on Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are of land. The island is the largest ...
. During a strike, he was rescued from starvation by a local Kwakiutl community. Alsford's brother, William John Alsford, visited the island, and in gratitude for the local people's hospitality, commissioned a totem pole from the Canadian First Nations
First nations are indigenous settlers or bands.
First Nations, first nations, or first peoples may also refer to:
Indigenous groups
*List of Indigenous peoples
*First Nations in Canada, Indigenous peoples of Canada who are neither Inuit nor Mé ...
artist Henry Hunt.[.] The western red cedar
''Thuja plicata'' is a large evergreen coniferous tree in the family Cupressaceae, native to the Pacific Northwest of North America. Its common name is western redcedar in the U.S. or western red cedar in the UK, and it is also called pacific re ...
pole, high and in diameter, was carved by Hunt at Thunderbird Park, a centre for First Nation monuments. The completed pole was shipped to Britain and erected at Alsford's Wharf in 1968. Alsford's warehouses were replaced in 1994 by a private housing development which limit access to the pole, so that it can be viewed only at a distance from the public road. It is one of only a handful of totem poles in the United Kingdom, others being on display at the British Museum
The British Museum is a Museum, public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is the largest in the world. It documents the story of human cu ...
and Horniman Museum
The Horniman Museum and Gardens is a museum in Forest Hill, London, England. Commissioned in 1898, it opened in 1901 and was designed by Charles Harrison Townsend in the Modern Style. It has displays of anthropology, natural history and music ...
in London, Windsor Great Park
Windsor Great Park is a Royal Park of to the south of the town of Windsor, Berkshire, Windsor on the border of Berkshire and Surrey in England. It is adjacent to the private Home Park, Windsor, Home Park, which is nearer the castle. The park ...
, Bushy Park
Bushy Park in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames is the second largest of London's Royal Parks, at in area, after Richmond Park. The park, most of which is open to the public, is immediately north of Hampton Court Palace and Hampton ...
and the Yorkshire Sculpture Park
The Yorkshire Sculpture Park (YSP) is an art gallery, with both open-air and indoor exhibition spaces, in West Bretton, Wakefield, in West Yorkshire, England. It shows work by British and international artists, including Henry Moore and Barb ...
. The carvings on the totem pole represent four figures from First Nations legend: at the top sits Raven
A raven is any of several large-bodied passerine bird species in the genus '' Corvus''. These species do not form a single taxonomic group within the genus. There is no consistent distinction between crows and ravens; the two names are assigne ...
, the trickster and creator deity; he sits on the head of Sunman, who has outstretched arms representing the rays of the sun and wears a ''copper'' (a type of ceremonial shield); Sunman stands on the fearsome witch-spirit Dzunukwa
Dzunuḵ̓wa (pronounced "zoo-noo-kwah"), also Tsonoqua, Tsonokwa, Basket Ogress, is a figure in Kwakwakaʼwakw mythology and Nuu-chah-nulth mythology.
Description
She is an ancestor of the Namgis clan through her son, Tsilwalagame. She is ven ...
; at the base is the two-headed warrior sea serpent, Sisiutl, who has up-stretched wings.
* Ashridge
Ashridge is a Estate (land), country estate and stately home in Hertfordshire, England. It is situated in the Chiltern Hills, an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, about north of Berkhamsted and north west of London. The estate comprises ...
is a country estate and stately home
300px, Oxfordshire.html" ;"title="Blenheim Palace - Oxfordshire">Blenheim Palace - Oxfordshire
An English country house is a large house or mansion in the English countryside. Such houses were often owned by individuals who also owned a To ...
. Ashridge House is a large Gothic Revival
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic or neo-Gothic) is an Architectural style, architectural movement that after a gradual build-up beginning in the second half of the 17th century became a widespread movement in the first half ...
country house
image:Blenheim - Blenheim Palace - 20210417125239.jpg, 300px, Blenheim Palace - Oxfordshire
An English country house is a large house or mansion in the English countryside. Such houses were often owned by individuals who also owned a Townhou ...
built between 1808 and 1814. Since 2015 it has been the home of Hult International Business School
Hult International Business School (also known as Hult Business School or Hult) is a private business school with campuses in London, San Francisco, Dubai, New York City, and Cambridge, Massachusetts. Hult is named for the school's benefactor B ...
's Ashridge Executive Education
Hult Ashridge Executive Education (also known as the Hult Ashridge) is the executive education arm of Hult International Business School, based in London, Dubai, and Hult's flagship executive education campus on the Ashridge Estate.
Formerly ...
programme ( see above for more information about the building). The surrounding country estate is a park managed by the National Trust
The National Trust () is a heritage and nature conservation charity and membership organisation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland.
The Trust was founded in 1895 by Octavia Hill, Sir Robert Hunter and Hardwicke Rawnsley to "promote the ...
, consisting of of native broadleaf woodlands, commons and chalk downland on a Chiltern ridge just to the north of Berkhamsted. Ashridge has been featured many times in film and television series due to its distinction as an area of natural beauty. Scenes were filmed for '' Sleepy Hollow'' at Golden Valley and ''Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire
''Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire'' is a fantasy novel written by British author J. K. Rowling. It is the fourth novel in the ''Harry Potter'' series. It follows Harry Potter (character), Harry Potter, a wizard in his fourth year at Hogwar ...
'' at Ashridge's ancient Frithsden Beeches Wood. The climbable monument to Francis Egerton, 3rd Duke of Bridgewater
Francis Egerton, 3rd Duke of Bridgewater (21 May 1736 – 8 March 1803), known as Lord Francis Egerton until 1748, was a British nobleman from the Egerton family. He was the youngest son of the 1st Duke. He did not marry, and the dukedom expi ...
, a tall Doric column with urn (a Grade II* listed building), stands in a grove within Ashridge.
Associations with the town
Twin towns
Berkhamsted is twinned with:
* Beaune
Beaune (; in Burgundian: ''Beane'') is widely considered to be the wine capital of Burgundy in the Côte d'Or department in eastern France. It is located between Lyon and Dijon. Beaune is one of the key wine centers in France, and a major ...
, Burgundy, FranceConnecticut
Connecticut ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. ...
, in the United States. The latter presented a gavel and block on 4 July 1976, the U.S. bicentennial, which Berkhamsted Town Council now uses in meetings.
Arms
Footnotes
References
Sources
*
*
::(see also Birtchnell, Percy (1975) ''Bygone Berkhamsted''. Luton: White Crescent Press )
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Berkhamsted Town Council
Berkhamsted Local History & Museum Society
The above society's Collection of Old Photographs of Berkhamsted and its citizens
Dacorum Heritage Trust
{{good article
Dacorum
Towns in Hertfordshire
Civil parishes in Hertfordshire
Market towns
 The earliest recorded spelling of the town's name is the 10th century
The earliest recorded spelling of the town's name is the 10th century 

 Berkhamsted Castle is a (now ruined)
Berkhamsted Castle is a (now ruined) 
 In the 16th century, the town fell into decline after abandonment of the castle following the death of Cicely Neville, Duchess of York, in 1495, and the rise of the nearby town of
In the 16th century, the town fell into decline after abandonment of the castle following the death of Cicely Neville, Duchess of York, in 1495, and the rise of the nearby town of 
 Berkhamsted is situated northwest of London within the
Berkhamsted is situated northwest of London within the  The countryside surrounding the town includes parts of the
The countryside surrounding the town includes parts of the 

 In 1798, the
In 1798, the  In 1834, after opposition from
In 1834, after opposition from  In the 1970s, the town adopted a three-tier
In the 1970s, the town adopted a three-tier  The Rex cinema is regarded by some, including ''
The Rex cinema is regarded by some, including '' The majority of Berkhamsted's eighty-five listed or scheduled historical sites are on in the high street and the medieval core of the town (a significant number of them contain timber frames). Four are scheduled, one is Grade I, seven are Grade II*, the remaining 75 are Grade II. In addition to the sites noted in the article above (such as the castle and schools) the following structures and locations are of interest:
* 173 High Street is a Victorian façade hiding what is considered to be the oldest extant jettied timber-framed building in Great Britain, dated by
The majority of Berkhamsted's eighty-five listed or scheduled historical sites are on in the high street and the medieval core of the town (a significant number of them contain timber frames). Four are scheduled, one is Grade I, seven are Grade II*, the remaining 75 are Grade II. In addition to the sites noted in the article above (such as the castle and schools) the following structures and locations are of interest:
* 173 High Street is a Victorian façade hiding what is considered to be the oldest extant jettied timber-framed building in Great Britain, dated by  * The Berkhamsted
* The Berkhamsted