Bavarian State on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a
 With the revolt of
With the revolt of
 When the
When the
 World War I led to the abolition of monarchy all over Germany in 1918. The Bavarian monarchy was the first to fall when on 8 November 1918 Socialist politician Kurt Eisner proclaimed the People's State of Bavaria. Eisner headed a new, republican government as minister-president. On 12 November, King Ludwig III of Bavaria, Ludwig III signed the Anif declaration, releasing both civil and military officers from their oaths, which the Eisner government interpreted as an abdication.
After losing the Bavarian Landtag elections in the Weimar Republic, January 1919 elections, Eisner was assassinated in February 1919, ultimately leading to a Communist revolt and the short-lived Bavarian Soviet Republic being proclaimed 6 April 1919. After violent suppression by elements of the German Army and notably the Freikorps, the Bavarian Soviet Republic fell in May 1919. The Constitution of Bavaria, Bamberg Constitution (') was enacted on 12 or 14 August 1919 and came into force on 15 September 1919, placing the Free State of Bavaria (Weimar Republic), Free State of Bavaria inside the Weimar Republic.
Extremist activity further increased, notably the 1923 Beer Hall Putsch led by the NSDAP, Nazis, and Munich and Nuremberg became seen as strongholds of Nazism during the Weimar Republic and Nazi Germany, Nazi dictatorship. However, in the crucial German federal election, March 1933, the Nazis received less than 50% of the votes cast in Bavaria.
As a manufacturing centre, Munich was heavily bombed during World War II and was occupied by United States Armed Forces, becoming a major part of the American Zone of Allied-occupied Germany, which lasted from 1945 to 1947, and then of Bizone.
The Rhenish Palatinate was detached from Bavaria in 1946 and made part of the new state Rhineland-Palatinate. In 1949, Bavaria became part of the
World War I led to the abolition of monarchy all over Germany in 1918. The Bavarian monarchy was the first to fall when on 8 November 1918 Socialist politician Kurt Eisner proclaimed the People's State of Bavaria. Eisner headed a new, republican government as minister-president. On 12 November, King Ludwig III of Bavaria, Ludwig III signed the Anif declaration, releasing both civil and military officers from their oaths, which the Eisner government interpreted as an abdication.
After losing the Bavarian Landtag elections in the Weimar Republic, January 1919 elections, Eisner was assassinated in February 1919, ultimately leading to a Communist revolt and the short-lived Bavarian Soviet Republic being proclaimed 6 April 1919. After violent suppression by elements of the German Army and notably the Freikorps, the Bavarian Soviet Republic fell in May 1919. The Constitution of Bavaria, Bamberg Constitution (') was enacted on 12 or 14 August 1919 and came into force on 15 September 1919, placing the Free State of Bavaria (Weimar Republic), Free State of Bavaria inside the Weimar Republic.
Extremist activity further increased, notably the 1923 Beer Hall Putsch led by the NSDAP, Nazis, and Munich and Nuremberg became seen as strongholds of Nazism during the Weimar Republic and Nazi Germany, Nazi dictatorship. However, in the crucial German federal election, March 1933, the Nazis received less than 50% of the votes cast in Bavaria.
As a manufacturing centre, Munich was heavily bombed during World War II and was occupied by United States Armed Forces, becoming a major part of the American Zone of Allied-occupied Germany, which lasted from 1945 to 1947, and then of Bizone.
The Rhenish Palatinate was detached from Bavaria in 1946 and made part of the new state Rhineland-Palatinate. In 1949, Bavaria became part of the
 Bavaria is divided into seven administrative regions called ' (singular '). Each of these regions has a state agency called the ' (district government).
*
Bavaria is divided into seven administrative regions called ' (singular '). Each of these regions has a state agency called the ' (district government).
*
 The 71 rural districts are on the lowest level divided into 2,031 regular municipalities (called ', singular '). Together with the 25 independent cities (', which are in effect municipalities independent of ' administrations), there are a total of 2,056 municipalities in Bavaria.
In 44 of the 71 rural districts, there are a total of 215 unincorporated areas (as of 1 January 2005, called ', singular '), not belonging to any municipality, all uninhabited, mostly forested areas, but also four lakes (-without islands, -without island , , which are the three largest lakes of Bavaria, and ).
The 71 rural districts are on the lowest level divided into 2,031 regular municipalities (called ', singular '). Together with the 25 independent cities (', which are in effect municipalities independent of ' administrations), there are a total of 2,056 municipalities in Bavaria.
In 44 of the 71 rural districts, there are a total of 215 unincorporated areas (as of 1 January 2005, called ', singular '), not belonging to any municipality, all uninhabited, mostly forested areas, but also four lakes (-without islands, -without island , , which are the three largest lakes of Bavaria, and ).
 The 2023 Bavarian state election, last state elections were held on 8 October 2023. The CSU could almost maintain the results from the last elections with 37%. The Greens lost 3% compared to the last election with a result of 14.4%. The SPD lost again compared to the last election and was now at 8.4%. The liberals of the FDP were not able to reach the five-percent-threshold thus they are not part of the ''Landtag'' anymore, the second time after the 2013 elections. The right-wing populist Alternative for Germany (AfD) gained another 4% with 14.6% of the vote.
The center-right Free Voters party gained 15.8% of the votes and for the second time formed a government coalition with the CSU which led to the subsequent reelection of Markus Söder as Minister-President of Bavaria.
The 2023 Bavarian state election, last state elections were held on 8 October 2023. The CSU could almost maintain the results from the last elections with 37%. The Greens lost 3% compared to the last election with a result of 14.4%. The SPD lost again compared to the last election and was now at 8.4%. The liberals of the FDP were not able to reach the five-percent-threshold thus they are not part of the ''Landtag'' anymore, the second time after the 2013 elections. The right-wing populist Alternative for Germany (AfD) gained another 4% with 14.6% of the vote.
The center-right Free Voters party gained 15.8% of the votes and for the second time formed a government coalition with the CSU which led to the subsequent reelection of Markus Söder as Minister-President of Bavaria.

 Bavaria also is home to the headquarters of commercial vehicle manufacturer MAN Truck & Bus, MAN and aircraft engine manufacturer MTU Aero Engines. Many other global companies such as Adidas, Siemens, and Allianz also have headquarters in Bavarian cities and towns. Several American companies have set up research and development facilities in Bavaria such as Apple Inc., Apple, Google, IBM, Intel, Texas Instruments and Coherent, Inc., Coherent. Despite being hundreds of miles from the sea, companies such as Bavaria Yachtbau produce sailing yachts and motorboats.
Bavaria is the most visited state in Germany, as over 38.86 million Tourism, tourists visited Bavaria in 2023 alone, significantly higher than North Rhine-Westphalia, North Rhine-Westphalia's 23.58 million tourists. In 2019, tourism brought in a Gross value added, gross value of €28.1 billion ($28.918 billion), making up 4.9% of Bavaria's economy. Some significant tourist destinations include the Bavarian National Museum, Margravial Opera House, Deutsches Museum, Christmas markets in Nuremberg, Nuremberg and
Bavaria also is home to the headquarters of commercial vehicle manufacturer MAN Truck & Bus, MAN and aircraft engine manufacturer MTU Aero Engines. Many other global companies such as Adidas, Siemens, and Allianz also have headquarters in Bavarian cities and towns. Several American companies have set up research and development facilities in Bavaria such as Apple Inc., Apple, Google, IBM, Intel, Texas Instruments and Coherent, Inc., Coherent. Despite being hundreds of miles from the sea, companies such as Bavaria Yachtbau produce sailing yachts and motorboats.
Bavaria is the most visited state in Germany, as over 38.86 million Tourism, tourists visited Bavaria in 2023 alone, significantly higher than North Rhine-Westphalia, North Rhine-Westphalia's 23.58 million tourists. In 2019, tourism brought in a Gross value added, gross value of €28.1 billion ($28.918 billion), making up 4.9% of Bavaria's economy. Some significant tourist destinations include the Bavarian National Museum, Margravial Opera House, Deutsches Museum, Christmas markets in Nuremberg, Nuremberg and
 Bavaria has a population of approximately 13.1 million inhabitants (2020). Eight of the List of cities in Germany with more than 100,000 inhabitants, 80 largest cities in Germany are located within Bavaria with Munich being the largest (1,484,226 inhabitants, approximately 6.1 million when including the broader metropolitan area), followed by
Bavaria has a population of approximately 13.1 million inhabitants (2020). Eight of the List of cities in Germany with more than 100,000 inhabitants, 80 largest cities in Germany are located within Bavaria with Munich being the largest (1,484,226 inhabitants, approximately 6.1 million when including the broader metropolitan area), followed by
 Bavarian culture (''
Bavarian culture (''
GenussBayern
since the 1990s. Recipes and museums can also be found there. With a total of 54 Geographical indications and traditional specialities in the European Union, specialities protected under European law, Bavaria is the No. 1 speciality region in Germany. Bavarian products such as ‘Bavarian beer’, ‘Nuremberg bratwurst’, ‘Allgäu mountain cheese’ and ‘Schrobenhausen asparagus’ are just as much a part of the official EU list 'eAmbrosia' of prestigious regional culinary specialities as the protected names “Champagne” and ‘Prosciutto di Parma’. Bavarian specialities, which are protected as geographical indications, are deeply rooted in their region of origin, important anchors of local identity and also tourist flagships - they are therefore at the heart of Bavarian cuisine. Restaurants that carry th
'Ausgezeichnete GenussKüche'
award (recognizable by a sign near the door) are known by locals for their certified, authentic Bavarian cuisine. At folk festivals and in many beer gardens, beer is traditionally served by the litre (in a ). Bavarians are particularly proud of the traditional , or beer purity law, initially established by the Duke of Bavaria for the City of Munich (i.e. the court) in 1487 and the duchy in 1516. According to this law, only three ingredients were allowed in beer: water, barley, and hops. In 1906 the made its way to all-German law, and remained a law in Germany until the EU partly struck it down in 1987 as incompatible with the European common market. German breweries, however, cling to the principle, and Bavarian breweries still comply with it in order to distinguish their beer brands. Bavarians are also known as some of the world's most prolific beer drinkers, with an average annual consumption of 130–135 liters per capita, as of 2018. Bavaria is also home to the Franconia (wine region), Franconia wine region, which is situated along the river Main (river), Main in Franconia. The region has produced wine (''Frankenwein'') for over 1,000 years and is famous for its use of the Bocksbeutel wine bottle. The production of wine forms an integral part of the regional culture, and many of its villages and cities hold their own wine festivals (Weinfeste) throughout the year.
Krustenbraten_mit_Dunkelbierso%C3%9Fe.jpg, Schweinsbraten
N%C3%BCrnberger_Rostbratw%C3%BCrste.JPG, Nürnberger Rostbratwürste
Official government website
* {{Authority control Bavaria, Boii States of Germany States of the Weimar Republic
state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
in the southeast of Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
. With an area of , it is the largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total land area of Germany, and with over 13.08 million inhabitants, it is the second most populous German state, behind only North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia or North-Rhine/Westphalia, commonly shortened to NRW, is a States of Germany, state () in Old states of Germany, Western Germany. With more than 18 million inhabitants, it is the List of German states by population, most ...
; however, due to its large land area, its population density is below the German average. Major cities include Munich
Munich is the capital and most populous city of Bavaria, Germany. As of 30 November 2024, its population was 1,604,384, making it the third-largest city in Germany after Berlin and Hamburg. Munich is the largest city in Germany that is no ...
(its capital and largest city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or their metrop ...
, which is also the third largest city in Germany), Nuremberg
Nuremberg (, ; ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the Franconia#Towns and cities, largest city in Franconia, the List of cities in Bavaria by population, second-largest city in the States of Germany, German state of Bav ...
, and Augsburg
Augsburg ( , ; ; ) is a city in the Bavaria, Bavarian part of Swabia, Germany, around west of the Bavarian capital Munich. It is a College town, university town and the regional seat of the Swabia (administrative region), Swabia with a well ...
.
The history of Bavaria
The history of Bavaria stretches from its earliest Human settlement, settlement and its formation as a stem duchy in the 6th century through its inclusion in the Holy Roman Empire to its status as an independent kingdom and finally as a large ''S ...
includes its earliest settlement by Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foot ...
tribes, followed by the conquests of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
in the 1st century BC, when the territory was incorporated into the provinces of Raetia
Raetia or Rhaetia ( , ) was a province of the Roman Empire named after the Rhaetian people. It bordered on the west with the country of the Helvetii, on the east with Noricum, on the north with Vindelicia, on the south-west with Transalpine ...
and Noricum
Noricum () is the Latin name for the kingdom or federation of tribes that included most of modern Austria and part of Slovenia. In the first century AD, it became a province of the Roman Empire. Its borders were the Danube to the north, R ...
. It became the Duchy of Bavaria
The Duchy of Bavaria () was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarians, Bavarian tribes and ruled by List of rulers of Bavaria, dukes (''duces'') ...
(a stem duchy
A stem duchy (, from '':wikt:Stamm, Stamm'', meaning "tribe", in reference to the Franks, Saxons, Baiuvarii, Bavarians and Alemanni, Swabians) was a constituent duchy of the Kingdom of Germany at the time of the extinction of the Carolingian dyna ...
) in the 6th century AD following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire
In modern historiography, the Western Roman Empire was the western provinces of the Roman Empire, collectively, during any period in which they were administered separately from the eastern provinces by a separate, independent imperial court. ...
. It was later incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
, became the independent Kingdom of Bavaria
The Kingdom of Bavaria ( ; ; spelled ''Baiern'' until 1825) was a German state that succeeded the former Electorate of Bavaria in 1806 and continued to exist until 1918. With the unification of Germany into the German Empire in 1871, the kingd ...
after 1806, joined the Prussian-led German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
in 1871 while retaining its title of kingdom, and finally became a state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
of the Federal Republic of Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen constituent states have a total population of over 84 ...
in 1949.
Bavaria has a distinct culture, largely because of its Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
heritage and conservative traditions, which includes a language
Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed language, signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing syste ...
, cuisine
A cuisine is a style of cooking characterized by distinctive ingredients, List of cooking techniques, techniques and Dish (food), dishes, and usually associated with a specific culture or geographic region. Regional food preparation techniques, ...
, architecture, festivals and elements of Alpine
Alpine may refer to any mountainous region. It may also refer to:
Places Europe
* Alps, a European mountain range
** Alpine states, which overlap with the European range
Australia
* Alpine, New South Wales, a Northern Village
* Alpine National P ...
symbolism. It also has the second-largest economy among the German states by GDP figures, giving it the status of a wealthy German region.
Contemporary Bavaria also includes parts of the historical regions of Franconia
Franconia ( ; ; ) is a geographical region of Germany, characterised by its culture and East Franconian dialect (). Franconia is made up of the three (governmental districts) of Lower Franconia, Lower, Middle Franconia, Middle and Upper Franco ...
and Swabia
Swabia ; , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of Swabia, one of ...
, in addition to Altbayern
Altbayern (; , also written Altbaiern, English: "Old Bavaria") is the territory and people of the three oldest parts of the present Free State of Bavaria, which were earlier known as Kurbayern (English: "Electoral Bavaria") after the former Elect ...
.
History
Antiquity
Though Bavaria has been occupied by humans since the Paleolithic era,Celtic tribes
This is a list of ancient Celts, Celtic peoples and tribes.
Continental Celts
Continental Celts were the Celtic peoples that inhabited mainland Europe and Anatolia (also known as Asia Minor). In the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC, Celts inhabited a la ...
of the Bronze Age, such as the Boii
The Boii (Latin language, Latin plural, singular ''Boius''; ) were a Celts, Celtic tribe of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul (present-day Northern Italy), Pannonia (present-day Austria and Hungary), present-day Ba ...
were the first documented inhabitants of the Bavarian Alps
The Bavarian Alps (, ) is a collective name for several mountain ranges of the Northern Limestone Alps within the German state of Bavaria.
Geography
The term in its wider sense refers to that part of the Eastern Alps that lies on Bavarian state ...
. In June 2023, Archeologists discovered a bronze sword, dated to the 14th century BC, in a former Celtic village; its workmanship so well-preserved "it almost shines." During the early modern era, these peoples were retrospectively romanticized as the most ancient culture of Bavaria, even though the Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
were relative newcomers to the region. Evidence of the ancient Straubing culture, Únětice culture
The Únětice culture, Aunjetitz culture or Unetician culture (, , , ) is an archaeological culture at the start of the Central European European Bronze Age, Bronze Age, dated roughly to about 2300–1600BC. The eponymous site for this culture, t ...
and La Tène culture
The La Tène culture (; ) was a Iron Age Europe, European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman Republic, Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age ...
may be found in what is Bavaria today.
Archeologists know of a large Celtic Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
settlement which was founded in Feldmoching-Hasenbergl
Feldmoching-Hasenbergl (Central Bavarian: ''Fejdmoching-Hosnbeagl'') is a borough in the northern part of the city of Munich in Bavaria, Germany. It contains the Munich S-Bahn, S-Bahn railway station of München-Feldmoching station, München-Fe ...
, in the North of suburban Munich. Evidence suggests up to 500 people lived in the village from 450 BC. Local life appears to have centred around what could be a town hall or temple, and continued in different forms up to 1000 AD. In Manching
Manching () is a municipality in the district of Pfaffenhofen, in Bavaria, Germany. It is situated on the river Paar, 7 km southeast of Ingolstadt. In the late Iron Age, there was a Celtic settlement, the Oppidum of Manching, on the locati ...
, Upper Bavaria, an unfortified and semi-urban society appears to have prospered between the 3rd century BC
The 3rd century BC started the first day of 300 BC and ended the last day of 201 BC. It is considered part of the Classical antiquity, Classical Era, Epoch (reference date), epoch, or historical period.
In the Mediterranean Basin, the first fe ...
until the early 1st century AD
File:1st century collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Jesus is crucified by Roman authorities in Judaea (17th century painting). Four different men (Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and Vespasian) claim the title of Emperor within the span of a year; T ...
. The settlement featured food ovens, pottery kilns and metallurgical furnaces. By 200 BC the community there was active in trade—finds of coins, along with an icon-like golden tree suggest it was trading with distant Italo-Greek communities.
In the 1st century BC, Bavaria was conquered by the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
. An imperial military camp was built 60 km north-west of where Munich sits today, under orders of Augustus Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
, between 8 and 5 BC. The camp later became the town of Augusta Vindelicorum
Augsburg ( , ; ; ) is a city in the Bavarian part of Swabia, Germany, around west of the Bavarian capital Munich. It is a university town and the regional seat of the Swabia with a well preserved Altstadt (historical city centre). Augsburg ...
, which would become the capital of the Roman province of Raetia. Another fort was founded in 60 AD, west of modern-day Manching, as evidenced by a legionnaire's sandal found near remains of an ancient fort. By the late 2nd century AD, Germanic tribes, including Marcomanni people, were pushing back on Roman forces of Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus ( ; ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 and a Stoicism, Stoic philosopher. He was a member of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty, the last of the rulers later known as the Five Good Emperors ...
and later, Commodus
Commodus (; ; 31 August 161 – 31 December 192) was Roman emperor from 177 to 192, first serving as nominal co-emperor under his father Marcus Aurelius and then ruling alone from 180. Commodus's sole reign is commonly thought to mark the end o ...
in the Marcomannic Wars
The Marcomannic Wars () were a series of wars lasting from about AD 166 until 180. These wars pitted the Roman Empire against principally the Germanic peoples, Germanic Marcomanni and Quadi and the Sarmatian Iazyges; there were related conflicts ...
. By 180 AD, Commodus had decided to abandon the annexed positions in Bavaria, leaving its control to Celtic and Germanic tribes.
Middle Ages
Around the year 500 AD, some elements of that victorious Marcomanni people helped form theBavarii
The Baiuvarii or Bavarii, sometimes simply called Bavarians (; ) were a Germanic people who lived in and near present-day southern Bavaria, which is named after them.
They began to appear in records by the 6th century AD, and their culture, lang ...
confederation, which incorporated Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
and Bavaria. In the 530s, the Merovingian dynasty
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from around the middle of the 5th century until Pepin the Short in 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the ...
incorporated the kingdom of Thuringia
Thuringia (; officially the Free State of Thuringia, ) is one of Germany, Germany's 16 States of Germany, states. With 2.1 million people, it is 12th-largest by population, and with 16,171 square kilometers, it is 11th-largest in area.
Er ...
after their defeat by the Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty
The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which wa ...
. The Baiuvarii
The Baiuvarii or Bavarii, sometimes simply called Bavarians (; ) were a Germanic people who lived in and near present-day southern Bavaria, which is named after them.
They began to appear in records by the 6th century AD, and their culture, lang ...
were Frankicised a century later. The Lex Thuringorum
The ''Lex Thuringorum'' ("Law of the Thuringians") is a law code that survives today in one 10th-century manuscript, the Codex Corbeiensis, alongside a copy of the ''Lex Saxonum'', the law of the Saxons. The code was compiled in the first decade of ...
documents an upper class nobility of ''adalingi''. From about 554 to 788, the house of Agilolfing
The Agilolfings were a noble family that ruled the Duchy of Bavaria on behalf of their Merovingian suzerains from about 550 until 788. A cadet branch of the Agilolfings also ruled the Kingdom of the Lombards intermittently from 616 to 712.
They ...
ruled the Duchy of Bavaria
The Duchy of Bavaria () was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarians, Bavarian tribes and ruled by List of rulers of Bavaria, dukes (''duces'') ...
, ending with Tassilo III who was deposed by Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
.
Tassilo I of Bavaria
Tassilo I (or ''Tassilon'') ( 560 – 610) was Duke of Bavaria from 591 to his death. According to Paul the Deacon, he was appointed as Bavarian ''rex'' by Childebert II, Frankish king of Austrasia, in 591, ending the war with the Franks. The war ...
tried unsuccessfully to hold the eastern frontier against the expansion of Slavic peoples
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeast Europe, Southeast ...
and the Pannonian Avars
The Pannonian Avars ( ) were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in the chronicles of the Rus' people, Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai (), or Pseudo-Avars in Byzantine Empi ...
around 600. Garibald II seems to have achieved a balance of power between 610 and 616.
At Hugbert's death in 735, the duchy
A duchy, also called a dukedom, is a country, territory, fiefdom, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess, a ruler hierarchically second to the king or Queen regnant, queen in Western European tradition.
There once existed an important differe ...
passed to Odilo of Bavaria
Odilo, also Oatilo or Uatilo (died 18 January 748) of the Agilolfing dynasty was Duke of Bavaria from 737 until his death in 748. He had the ''Lex Baiuvariorum'' compilation edited, the first ancient Germanic law collection of the Bavarians.
Lif ...
from the neighboring Alemannia. Odilo issued a Lex Baiuvariorum
The ''Lex Baiuvariorum'' was a collection of the tribal laws of the Bavarii of the sixth through eighth centuries. The first compilation was edited by Eberswind, first abbot of Niederaltaich, in 741 or 743. Duke Odilo, founder supplemented t ...
for Bavaria, completed the process of church organization in partnership with Saint Boniface
Boniface, OSB (born Wynfreth; 675 –5 June 754) was an English Benedictines, Benedictine monk and leading figure in the Anglo-Saxon mission to the Germanic parts of Francia during the eighth century. He organised significant foundations of ...
in 739, and tried to intervene in Frankish succession disputes by fighting for the claims of the Carolingian dynasty
The Carolingian dynasty ( ; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Franks, Frankish noble family named after Charles Martel and his grandson Charlemagne, descendants of the Pippinids, Arnulfi ...
. He was defeated near Augsburg
Augsburg ( , ; ; ) is a city in the Bavaria, Bavarian part of Swabia, Germany, around west of the Bavarian capital Munich. It is a College town, university town and the regional seat of the Swabia (administrative region), Swabia with a well ...
in 743 but continued to rule until his death in 748.
Saint Boniface
Boniface, OSB (born Wynfreth; 675 –5 June 754) was an English Benedictines, Benedictine monk and leading figure in the Anglo-Saxon mission to the Germanic parts of Francia during the eighth century. He organised significant foundations of ...
completed the people's conversion to Christianity in the early 8th century. Tassilo III of Bavaria Tassilo – also spelled Thassilo – is a male name of West Germanic
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic languages, Germanic family of languages (the others being the North Germanic langua ...
succeeded to rule Bavaria. He initially ruled under Frankish oversight but began to function independently from 763 onward. He was particularly noted for founding new monasteries and for expanding eastwards, oppressing Slavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and ...
in the eastern Alps
The Eastern Alps are usually defined as the area east of a line from Lake Constance and the Alpine Rhine valley, up to the Splügen Pass at the Main chain of the Alps, Alpine divide, and down the Liro (Como), Liro River to Lake Como in the south. ...
and along the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
and colonizing these lands. After 781, however, Charlemagne began to exert pressure and Tassilo III was deposed in 788. Dissenters attempted a coup against Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
at Regensburg
Regensburg (historically known in English as Ratisbon) is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the rivers Danube, Naab and Regen (river), Regen, Danube's northernmost point. It is the capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the ...
in 792, led by Pepin the Hunchback
Pepin (or Pippin) the Hunchback (, ; 768/769 – 811) was a Franks, Frankish prince. He was the eldest son of Charlemagne and noblewoman Himiltrude. He developed a kyphosis, humped back after birth, leading early medieval historians to give him ...
.
 With the revolt of
With the revolt of Henry II, Duke of Bavaria
Henry II (951 – 28 August 995), called the Wrangler or the Quarrelsome (), a member of the German royal Ottonian dynasty, was Duke of Bavaria from 955 to 976 and again from 985 to 995, as well as Duke of Carinthia from 989 to 995.
Life
He ...
in 976, Bavaria lost large territories in the south and southeast.
One of the most important dukes of Bavaria was Henry the Lion
Henry the Lion (; 1129/1131 – 6 August 1195), also known as Henry III, Duke of Saxony (ruled 1142-1180) and Henry XII, Duke of Bavaria (ruled 1156-1180), was a member of the Welf dynasty.
Henry was one of the most powerful German princes of ...
of the house of Welf
The House of Welf (also Guelf or Guelph) is a European dynasty that has included many German and British monarchs from the 11th to 20th century and Emperor Ivan VI of Russia in the 18th century. The originally Franconian family from the Meuse-Mo ...
, founder of Munich
Munich is the capital and most populous city of Bavaria, Germany. As of 30 November 2024, its population was 1,604,384, making it the third-largest city in Germany after Berlin and Hamburg. Munich is the largest city in Germany that is no ...
, and ''de facto'' the second most powerful man in the empire as the ruler of two duchies. When in 1180, Henry the Lion was deposed as Duke of Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ...
and Bavaria by his cousin, Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (; ), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death in 1190. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt am Main, Frankfurt on 4 March 1152 and crowned in Aa ...
(a.k.a. "Barbarossa" for his red beard), Bavaria was awarded as fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal alle ...
to the Wittelsbach
The House of Wittelsbach () is a former Bavarian dynasty, with branches that have ruled over territories including the Electorate of Bavaria, the Electoral Palatinate, the Electorate of Cologne, County of Holland, Holland, County of Zeeland, ...
family, counts palatinate of Schyren ("Scheyern" in modern German). They ruled for 738 years, from 1180 to 1918. In 1180, however, Styria
Styria ( ; ; ; ) is an Austrian Federal states of Austria, state in the southeast of the country. With an area of approximately , Styria is Austria's second largest state, after Lower Austria. It is bordered to the south by Slovenia, and cloc ...
was also separated from Bavaria. The Electorate of the Palatinate
The Electoral Palatinate was a Imperial State, constituent state of the Holy Roman Empire until it was annexed by the Electorate of Baden in 1803. From the end of the 13th century, its ruler was one of the Prince-electors who elected the Holy ...
by Rhine (''Kurpfalz'' in German) was also acquired by the House of Wittelsbach
The House of Wittelsbach () is a former Bavarian dynasty, with branches that have ruled over territories including the Electorate of Bavaria, the Electoral Palatinate, the Electorate of Cologne, County of Holland, Holland, County of Zeeland, ...
in 1214, which they would subsequently hold for six centuries.
The first of several divisions of the duchy of Bavaria occurred in 1255. With the extinction of the Hohenstaufen
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the Duchy of Swabia from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynast ...
in 1268, Swabia
Swabia ; , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of Swabia, one of ...
n territories were acquired by the Wittelsbach dukes. Emperor Louis the Bavarian acquired Brandenburg
Brandenburg, officially the State of Brandenburg, is a States of Germany, state in northeastern Germany. Brandenburg borders Poland and the states of Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It is the List of Ger ...
, Tyrol
Tyrol ( ; historically the Tyrole; ; ) is a historical region in the Alps of Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Empire and Austria-Hungary, f ...
, Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former provinces of the Netherlands, province on the western coast of the Netherland ...
and Hainaut for his House but released the Upper Palatinate
The Upper Palatinate (; , , ) is an administrative district in the east of Bavaria, Germany. It consists of seven districts and 226 municipalities, including three cities.
Geography
The Upper Palatinate is a landscape with low mountains and nume ...
for the Palatinate branch of the Wittelsbach in 1329. That time also Salzburg
Salzburg is the List of cities and towns in Austria, fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020 its population was 156,852. The city lies on the Salzach, Salzach River, near the border with Germany and at the foot of the Austrian Alps, Alps moun ...
finally became independent from the Duchy of Bavaria
The Duchy of Bavaria () was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarians, Bavarian tribes and ruled by List of rulers of Bavaria, dukes (''duces'') ...
.
In the 14th and 15th centuries, upper and lower Bavaria were repeatedly subdivided. Four Duchies existed after the division of 1392: Bavaria-Straubing
Bavaria-Straubing denotes the widely scattered territorial inheritance in the Wittelsbach house of Bavaria that were governed by independent dukes of Bavaria-Straubing between 1353 and 1432; a map (''illustration'') of these marches and outlier ...
, Bavaria-Landshut
Bavaria-Landshut () was a duchy in the Holy Roman Empire from 1353 to 1503.
History
The creation of the duchy was the result of the death of Emperor Louis IV the Bavarian. In the Treaty of Landsberg 1349, which divided up Louis's empire, his ...
, Bavaria-Ingolstadt
Bavaria-Ingolstadt ( or ') was a sub-duchy which was part of the Holy Roman Empire from 1392 to 1447.
History
After the death of Stephen II in 1375, his sons Stephen III, Frederick, and John II jointly ruled Bavaria-Landshut. After seventeen ...
and Bavaria-Munich
Bavaria-Munich () was a duchy that was a constituent state of the Holy Roman Empire from 1392 to 1505.
History
After the death of Stephen II, Duke of Bavaria, Stephen II in 1375, his sons Stephen III, Duke of Bavaria, Stephen III, Frederick, D ...
. In 1506 with the Landshut War of Succession
The War of the Succession of Landshut (''Landshuter Erbfolgekrieg'' in German) resulted from a dispute between the Duchies of Bavaria-Munich (''Bayern-München'' in German) and Bavaria-Landshut (''Bayern-Landshut'').
Background
George, Duk ...
, the other parts of Bavaria were reunited, and Munich became the sole capital. The country became a center of the Jesuit-inspired Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also sometimes called the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to, and as an alternative to or from similar insights as, the Protestant Reformations at the time. It w ...
.
Electorate of Bavaria
In 1623, the Bavarian duke replaced his relative of the Palatinate branch, theElectorate of the Palatinate
The Electoral Palatinate was a Imperial State, constituent state of the Holy Roman Empire until it was annexed by the Electorate of Baden in 1803. From the end of the 13th century, its ruler was one of the Prince-electors who elected the Holy ...
in the early days of the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
and acquired the powerful prince-elector
The prince-electors ( pl. , , ) were the members of the Electoral College of the Holy Roman Empire, which elected the Holy Roman Emperor. Usually, half of the electors were archbishops.
From the 13th century onwards, a small group of prince- ...
dignity in the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
, determining its Emperor thence forward, as well as special legal status under the empire's laws. During the early and mid-18th century the ambitions of the Bavarian prince electors led to several wars with Austria as well as occupations by Austria (War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict fought between 1701 and 1714. The immediate cause was the death of the childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700, which led to a struggle for control of the Spanish E ...
, War of the Austrian Succession with the election of a Wittelsbach emperor instead of a Habsburg).
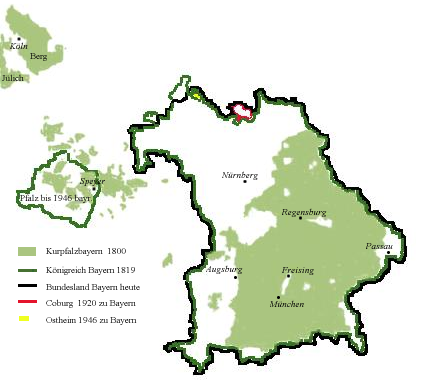
To mark the unification of Bavaria and the Electoral Palatinate, both being principal Wittelsbach territories, Elector Maximilian IV Joseph was crowned king of Bavaria. King Maximilian Joseph was quick to change the coat of arms. The various heraldic symbols were replaced and a classical Wittelsbach pattern introduced. The white and blue Lozenge (heraldry), lozenges symbolized the unity of the territories within the Bavarian kingdom.
The new state also comprised the Duchy of Jülich and Berg (state), Berg as these on their part were in personal union with the Palatinate.
Kingdom of Bavaria
 When the
When the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
dissolved under Napoleon's onslaught, Bavaria became a Kingdom of Bavaria, kingdom in 1806 and joined the Confederation of the Rhine.
The Duchy of Jülich was ceded to France and the Electoral Palatinate was divided between France and the Grand Duchy of Baden. The Duchy of Berg was given to Joachim Murat. The County of Tyrol and the federal state of Salzburg
Salzburg is the List of cities and towns in Austria, fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020 its population was 156,852. The city lies on the Salzach, Salzach River, near the border with Germany and at the foot of the Austrian Alps, Alps moun ...
were temporarily annexed with Bavaria but eventually ceded to Austria at the Congress of Vienna. In return, Bavaria was allowed to annex the modern-day region of Palatinate (region), Palatinate to the west of the Rhine and Franconia
Franconia ( ; ; ) is a geographical region of Germany, characterised by its culture and East Franconian dialect (). Franconia is made up of the three (governmental districts) of Lower Franconia, Lower, Middle Franconia, Middle and Upper Franco ...
in 1815.
Between 1799 and 1817, the leading minister, Count Maximilian Joseph von Montgelas, Montgelas, followed a strict policy of modernization copying Napoleonic France; he laid the foundations of centralized administrative structures that survived the monarchy and, in part, have retained core validity through to the 21st century. In May 1808, a first constitution was passed by Maximilian I Joseph of Bavaria, Maximilian I, being modernized in 1818. This second version established a bicameral Parliament with a House of Lords (''Kammer der Reichsräte'') and a House of Commons (''Kammer der Abgeordneten''). That constitution was followed until the collapse of the monarchy at the end of World War I.
After the rise of Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia in the early 18th century, Bavaria preserved its independence by playing off the rivalry of Prussia and Austrian Empire, Austria. Allied to Austria, it was defeated along with Austria in the 1866 Austro-Prussian War and was not incorporated into the North German Federation, North German Confederation of 1867, but the question of Unification of Germany, German unity was still alive. When Franco-Prussian War, France declared war on Prussia in 1870, all the south German states (Baden, Württemberg, Hessen-Darmstadt and Bavaria) aside from Austria, joined the Prussian forces and ultimately joined the Federation, which was renamed (German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
) in 1871.
Bavaria continued as a monarchy, and retained some special rights within the federation (such as railways and postal services and control of its army in peace times).
Part of the German Empire
When Bavaria became part of the newly formedGerman Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
, this action was considered controversial by Bavarian nationalism, Bavarian nationalists who had wanted to retain independence from the rest of Germany, as had Austria.
As Bavaria had a heavily Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
majority population, many people resented being ruled by the mostly Protestantism in Germany, Protestant northerners in Prussia. As a direct result of the Bavarian-Prussian feud, political parties formed to encourage Bavaria to break away and regain its independence.
In the early 20th century, Wassily Kandinsky, Paul Klee, Henrik Ibsen, and other artists were drawn to Bavaria, especially to the Schwabing district in Munich, a center of international artistic activity at the time.
Free State of Bavaria
 World War I led to the abolition of monarchy all over Germany in 1918. The Bavarian monarchy was the first to fall when on 8 November 1918 Socialist politician Kurt Eisner proclaimed the People's State of Bavaria. Eisner headed a new, republican government as minister-president. On 12 November, King Ludwig III of Bavaria, Ludwig III signed the Anif declaration, releasing both civil and military officers from their oaths, which the Eisner government interpreted as an abdication.
After losing the Bavarian Landtag elections in the Weimar Republic, January 1919 elections, Eisner was assassinated in February 1919, ultimately leading to a Communist revolt and the short-lived Bavarian Soviet Republic being proclaimed 6 April 1919. After violent suppression by elements of the German Army and notably the Freikorps, the Bavarian Soviet Republic fell in May 1919. The Constitution of Bavaria, Bamberg Constitution (') was enacted on 12 or 14 August 1919 and came into force on 15 September 1919, placing the Free State of Bavaria (Weimar Republic), Free State of Bavaria inside the Weimar Republic.
Extremist activity further increased, notably the 1923 Beer Hall Putsch led by the NSDAP, Nazis, and Munich and Nuremberg became seen as strongholds of Nazism during the Weimar Republic and Nazi Germany, Nazi dictatorship. However, in the crucial German federal election, March 1933, the Nazis received less than 50% of the votes cast in Bavaria.
As a manufacturing centre, Munich was heavily bombed during World War II and was occupied by United States Armed Forces, becoming a major part of the American Zone of Allied-occupied Germany, which lasted from 1945 to 1947, and then of Bizone.
The Rhenish Palatinate was detached from Bavaria in 1946 and made part of the new state Rhineland-Palatinate. In 1949, Bavaria became part of the
World War I led to the abolition of monarchy all over Germany in 1918. The Bavarian monarchy was the first to fall when on 8 November 1918 Socialist politician Kurt Eisner proclaimed the People's State of Bavaria. Eisner headed a new, republican government as minister-president. On 12 November, King Ludwig III of Bavaria, Ludwig III signed the Anif declaration, releasing both civil and military officers from their oaths, which the Eisner government interpreted as an abdication.
After losing the Bavarian Landtag elections in the Weimar Republic, January 1919 elections, Eisner was assassinated in February 1919, ultimately leading to a Communist revolt and the short-lived Bavarian Soviet Republic being proclaimed 6 April 1919. After violent suppression by elements of the German Army and notably the Freikorps, the Bavarian Soviet Republic fell in May 1919. The Constitution of Bavaria, Bamberg Constitution (') was enacted on 12 or 14 August 1919 and came into force on 15 September 1919, placing the Free State of Bavaria (Weimar Republic), Free State of Bavaria inside the Weimar Republic.
Extremist activity further increased, notably the 1923 Beer Hall Putsch led by the NSDAP, Nazis, and Munich and Nuremberg became seen as strongholds of Nazism during the Weimar Republic and Nazi Germany, Nazi dictatorship. However, in the crucial German federal election, March 1933, the Nazis received less than 50% of the votes cast in Bavaria.
As a manufacturing centre, Munich was heavily bombed during World War II and was occupied by United States Armed Forces, becoming a major part of the American Zone of Allied-occupied Germany, which lasted from 1945 to 1947, and then of Bizone.
The Rhenish Palatinate was detached from Bavaria in 1946 and made part of the new state Rhineland-Palatinate. In 1949, Bavaria became part of the Federal Republic of Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen constituent states have a total population of over 84 ...
, despite the Landtag of Bavaria, Bavarian Parliament voting against adopting the Basic Law of Germany, mainly because it was seen as not granting sufficient powers to the individual states (''Länder''), but at the same time declared that it would accept it if two-thirds of the other ''Länder'' ratified it. All of the other states ratified it, so it became law. Thus, during the Cold War, Bavaria was part of West Germany.
Bavarian identity
Bavarians have often emphasized a separate national identity and considered themselves as "Bavarians" first, "Germans" second. In the 19th-century sense, an independentKingdom of Bavaria
The Kingdom of Bavaria ( ; ; spelled ''Baiern'' until 1825) was a German state that succeeded the former Electorate of Bavaria in 1806 and continued to exist until 1918. With the unification of Germany into the German Empire in 1871, the kingd ...
existed from only 1806 to 1871. A separate Bavarian identity was emphasized more strongly when Bavaria joined the Prussia-dominated German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
in 1871, while the Bavarian nationalism, Bavarian nationalists wanted to keep Bavaria as Catholic and an independent state. Aside from the minority Bavaria Party, most Bavarians now accept Bavaria as part of Germany.
Another consideration is that Bavaria is not culturally uniform. While inhabitants Altbayern
Altbayern (; , also written Altbaiern, English: "Old Bavaria") is the territory and people of the three oldest parts of the present Free State of Bavaria, which were earlier known as Kurbayern (English: "Electoral Bavaria") after the former Elect ...
("Old Bavaria"), the regions forming the historic Bavaria before further acquisitions in 1806–1815, speak a Bavarian dialect of German, Franconia
Franconia ( ; ; ) is a geographical region of Germany, characterised by its culture and East Franconian dialect (). Franconia is made up of the three (governmental districts) of Lower Franconia, Lower, Middle Franconia, Middle and Upper Franco ...
in the north and Bavarian Swabia in the south west, have their unique culture, including different dialects of German, East Franconian German, East Franconian and Swabian German, Swabian, respectively.
Flags and coat of arms
Flags
Uniquely among German states, Bavaria has two official flags of equal status, one with a white and blue stripe, the other with white and blue diamond-shaped Lozenge (heraldry), lozenges. Either may be used by civilians and government offices, who are free to choose between them. Unofficial versions of the flag, especially a lozenge style with coat of arms, are sometimes used by civilians.Coat of arms
The modern coat of arms of Bavaria was designed by Eduard Ege in 1946, following heraldic traditions. * The Golden Lion: At the dexter chief, sable, a lion (heraldry), lion rampant Or, armed and langued gules. This represents the administrative region of Upper Palatinate. * The "Franconian Rake": At the sinister chief, per fess dancetty, gules, and argent. This represents the administrative regions of Upper, Middle and Lower Franconia. * The Blue "Pantier" (mythical creature from French heraldry, sporting a flame instead of a tongue): At the dexter base, argent, a Pantier rampant azure, armed Or and langued gules. This represents the regions of Lower and Upper Bavaria. * The Three Lions: At the sinister base, Or, three lions passant guardant sable, armed and langued gules. This represents Swabia. * The White-And-Blue inescutcheon: The escutcheon (heraldry), inescutcheon of white and blue fusils askance was originally the coat of arms of the Counts of Bogen, adopted in 1247 by the House of Wittelsbach. The white-and-blue fusils are indisputably the emblem of Bavaria and these arms today symbolize Bavaria as a whole. Along with the People's Crown, it is officially used as the Minor Coat of Arms. * The People's Crown (''Volkskrone''): The coat of arms is surmounted by a Crown (heraldry), crown with a golden band inset with precious stones and decorated with five ornamental leaves. This crown first appeared in the coat of arms to symbolize sovereignty of common people, the people after the royal crown was eschewed in 1923.Geography
Bavaria shares international borders with Austria (Salzburg
Salzburg is the List of cities and towns in Austria, fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020 its population was 156,852. The city lies on the Salzach, Salzach River, near the border with Germany and at the foot of the Austrian Alps, Alps moun ...
, Tyrol (state), Tyrol, Upper Austria and Vorarlberg) and the Czech Republic (Karlovy Vary Region, Karlovy Vary, Plzeň Region, Plzeň and South Bohemian Regions), as well as with Switzerland (across Lake Constance to the Canton of St. Gallen).
Neighboring states within Germany are Baden-Württemberg, Hesse, Thuringia
Thuringia (; officially the Free State of Thuringia, ) is one of Germany, Germany's 16 States of Germany, states. With 2.1 million people, it is 12th-largest by population, and with 16,171 square kilometers, it is 11th-largest in area.
Er ...
, and Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ...
. Two major rivers flow through the state: the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
(''Donau'') and the Main (river), Main. The Bavarian Forest and the Bohemian Forest form the vast majority of the frontier with the Czech Republic and Bohemia.
The Geographical midpoint of Europe#Geographic centre of the European Union, geographic center of the European Union is located in the northwestern corner of Bavaria.
Climate
At lower elevations the climate is classified according to Köppen climate classification, Köppen's guide as "Oceanic climate, Cfb" or "Humid continental climate, Dfb". At higher altitudes the climate becomes "Subarctic climate, Dfc" and "Tundra climate, ET". The summer months have been getting hotter in recent years. For example, June 2019 was the warmest June in Bavaria since weather observations have been recorded and the winter 2019/2020 was 3 degrees Celsius warmer than the average temperature for many years all over Bavaria. On 20 December 2019 a record temperature of was recorded in Piding. In general winter months are seeing more precipitation which is taking the form of rain more often than that of snow compared to the past. Extreme weather like the 2013 European floods or the 2019 European heavy snowfalls is occurring more and more often. One effect of the continuing warming is the melting of almost all Bavarian Alpine glaciers: Of the five glaciers of Bavaria only the Höllentalferner is predicted to exist over a longer time perspective. The Schneeferner#Südlicher Schneeferner, Südliche Schneeferner has almost vanished since the 1980s.Administrative divisions
Administrative regions
Altbayern
Altbayern (; , also written Altbaiern, English: "Old Bavaria") is the territory and people of the three oldest parts of the present Free State of Bavaria, which were earlier known as Kurbayern (English: "Electoral Bavaria") after the former Elect ...
:
*# Upper Palatinate
The Upper Palatinate (; , , ) is an administrative district in the east of Bavaria, Germany. It consists of seven districts and 226 municipalities, including three cities.
Geography
The Upper Palatinate is a landscape with low mountains and nume ...
(')
*# Upper Bavaria (')
*# Lower Bavaria (')
* Franconia
Franconia ( ; ; ) is a geographical region of Germany, characterised by its culture and East Franconian dialect (). Franconia is made up of the three (governmental districts) of Lower Franconia, Lower, Middle Franconia, Middle and Upper Franco ...
:
*# Upper Franconia (')
*# Middle Franconia (')
*# Lower Franconia (')
* Swabia
Swabia ; , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of Swabia, one of ...
:
*# Swabia (administrative region), Swabia (')
Bezirke
' (regional districts) are the third communal layer in Bavaria; the others are the ' and the ' or '. The ' in Bavaria are territorially identical with the ', but they are self-governing regional corporation, having their own parliaments. In the other larger states of Germany, there are only ' as administrative divisions and no self-governing entities at the level of the ' as the ' in Bavaria.Population and area
Districts
The second communal layer is made up of 71 rural districts (called ', singular ') that are comparable to counties, as well as the 25 independent cities (', singular '), both of which share the same administrative responsibilities. Rural districts: # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # Munich (district), München (') # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # # Independent cities: # Amberg # Ansbach # Aschaffenburg #Augsburg
Augsburg ( , ; ; ) is a city in the Bavaria, Bavarian part of Swabia, Germany, around west of the Bavarian capital Munich. It is a College town, university town and the regional seat of the Swabia (administrative region), Swabia with a well ...
# Bamberg
# Bayreuth
# Coburg, Germany, Coburg
# Erlangen
# Fürth
# Hof, Germany, Hof
# Ingolstadt
# Kaufbeuren
# Kempten im Allgäu, Kempten
# Landshut
# Memmingen
# Munich
Munich is the capital and most populous city of Bavaria, Germany. As of 30 November 2024, its population was 1,604,384, making it the third-largest city in Germany after Berlin and Hamburg. Munich is the largest city in Germany that is no ...
(''München'')
# Nuremberg
Nuremberg (, ; ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the Franconia#Towns and cities, largest city in Franconia, the List of cities in Bavaria by population, second-largest city in the States of Germany, German state of Bav ...
(''Nürnberg'')
# Passau
# Regensburg
Regensburg (historically known in English as Ratisbon) is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the rivers Danube, Naab and Regen (river), Regen, Danube's northernmost point. It is the capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the ...
# Rosenheim
# Schwabach
# Schweinfurt
# Straubing
# Weiden in der Oberpfalz, Weiden
# Würzburg
Municipalities
Major cities and towns
Politics
Bavaria has a multiparty system dominated by the conservative Christian Social Union of Bavaria, Christian Social Union (CSU), which has won every election since 1945 with the exception of the 1950 ballot. Other important parties are the Free Voters, which became the second largest party in the 2023 Bavarian state election, Alliance 90/The Greens, The Greens, which became the second biggest political party in the 2018 Bavarian state elections, and the center-left Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democrats (SPD), who had dominated the city ofMunich
Munich is the capital and most populous city of Bavaria, Germany. As of 30 November 2024, its population was 1,604,384, making it the third-largest city in Germany after Berlin and Hamburg. Munich is the largest city in Germany that is no ...
until 2020. Hitherto, Wilhelm Hoegner has been the only SPD candidate to ever become Minister-President; notable successors in office include multi-term Federal Minister Franz Josef Strauss, a key figure among West German conservatives during the Cold War years, and Edmund Stoiber, who both failed with their bids for Federal Chancellor of Germany, Chancellorship.
The German Alliance 90/The Greens, Greens and the center-right Free Voters of Bavaria, Free Voters have been represented in the state parliament since 1986 and 2008 respectively.
In the Bavaria state election, 2003, 2003 elections the CSU won a Supermajority, two-thirds supermajority – something no party had ever achieved in postwar Germany. However, in the subsequent Bavaria state election, 2008, 2008 elections the CSU lost the absolute majority for the first time in 46 years.
The losses were partly attributed by some to the CSU's stance for an anti-smoking bill. (A first anti-smoking law had been proposed by the CSU and passed but was watered down after the election, after which a referendum enforced a strict antismoking bill with a large majority).
Current Landtag
Government
The Constitution of Bavaria of the Free State of Bavaria was enacted on 8 December 1946. The new Bavarian Constitution became the basis for the Bavarian State after the Second World War. Bavaria has a unicameral ' (English: State Parliament), elected by universal suffrage. Until December 1999, there was also a ', or Bavarian Senate, Senate, whose members were chosen by social and economic groups in Bavaria, but following a referendum in 1998, this institution was abolished. The Bavarian State Government consists of the Minister-President of Bavaria, eleven Ministers and six Secretaries of State. The Minister-President is elected for a period of five years by the State Parliament and is head of state. With the approval of the State Parliament he appoints the members of the State Government. The State Government is composed of the: *Bayerische Staatskanzlei, State Chancellery (') *Ministry of the Bavarian Ministry of the Interior, Interior, for Sport and Integration (') *Ministry for Housing, Construction and Transport (') *Ministry of Justice (') *Ministry for Education and Culture (') *Ministry for Science and Art (') *Ministry of Finance and for Home Affairs (') *Ministry for Economic Affairs, Regional Development and Energy (') *Ministry for Environment and Consumer Protection (') *Ministry for Food, Agriculture and Forestry (') *Ministry for Family, Labour and Social Affairs (') *Ministry for Health and Care (') *Ministry for Digital Affairs (') Political processes also take place in the seven regions (' or ') in Bavaria, in the 71 rural districts (') and the 25 towns and cities forming their own districts ('), and in the 2,031 local authorities ('). In 1995 Bavaria introduced direct democracy on the local level in a referendum. This was initiated bottom-up by an association called ''Mehr Demokratie'' (English: More Democracy). This is a grass-roots organization which campaigns for the right to citizen-initiated referendums. In 1997 the Bavarian Supreme Court tightened the regulations considerably (including by introducing a turn-out quorum). Nevertheless, Bavaria has the most advanced regulations on local direct democracy in Germany. This has led to a spirited citizens' participation in communal and municipal affairs—835 referendums took place from 1995 through 2005.Minister-presidents of Bavaria since 1945

Designation as a "free state"
Unlike most German states (''Länder''), which simply designate themselves as "State of" (''Land [...]''), Bavaria uses the style of "Free State of Bavaria" (''Freistaat Bayern''). The difference from other states is purely terminological, as German constitutional law does not draw a distinction between "States" and "Free States". The situation is thus analogous to the United States, where Commonwealth (U.S. state), some states use the style "Commonwealth" rather than "State". The term "Free State", a creation of the 19th century and intended to be a German alternative to (or translation of) the Latin-derived ''republic,'' was common among the states of the Weimar Republic, after German monarchies had been abolished. Unlike most other states – many of which were new creations – Bavaria has resumed this terminology after World War II. Two other states,Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ...
and Thuringia
Thuringia (; officially the Free State of Thuringia, ) is one of Germany, Germany's 16 States of Germany, states. With 2.1 million people, it is 12th-largest by population, and with 16,171 square kilometers, it is 11th-largest in area.
Er ...
, also call themselves "Free States".
Arbitrary arrest and human rights
In July 2017, Bavaria's parliament enacted a new revision of the "Gefährdergesetz", allowing the authorities to imprison a person for a three months term, renewable indefinitely, when they have not committed a crime but it is assumed that they might commit a crime "in the near future". Critics like the prominent journalist Heribert Prantl have called the law "shameful" and compared it to Guantanamo Bay detention camp, assessed it to be in violation of the European Convention on Human Rights, and also compared it to the legal situation in Russia, where a similar law allows for imprisonment for a maximum term of two years (i.e., not indefinitely).Economy
Bavaria has one of the largest economies inGermany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
and Europe as a whole, having a Gross domestic product, GDP of €768.469 billion ($790.813 billion) in 2023, the second highest of the States of Germany, 16 German states, only behind North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia or North-Rhine/Westphalia, commonly shortened to NRW, is a States of Germany, state () in Old states of Germany, Western Germany. With more than 18 million inhabitants, it is the List of German states by population, most ...
which had a GDP of €839.074 billion ($863.6 billion) in 2023. Bavaria had a GDP per capita of €53,768 ($56,456) in 2022, giving it the third highest GDP per capita behind Bremen (state), Bremen in second and Hamburg in first. One of Bavaria's largest industries is the automotive industry, with Bavaria having four BMW and two Audi Factory, manufacturing plants and the headquarters of both companies. Bavaria has the second-most employees (207,829) in the automotive industry of all German states after Baden-Württemberg as of 2018. Other countries such as Czech Republic, Czechia, Austria, Switzerland and Italy have strong economic ties with Bavaria.
 Bavaria also is home to the headquarters of commercial vehicle manufacturer MAN Truck & Bus, MAN and aircraft engine manufacturer MTU Aero Engines. Many other global companies such as Adidas, Siemens, and Allianz also have headquarters in Bavarian cities and towns. Several American companies have set up research and development facilities in Bavaria such as Apple Inc., Apple, Google, IBM, Intel, Texas Instruments and Coherent, Inc., Coherent. Despite being hundreds of miles from the sea, companies such as Bavaria Yachtbau produce sailing yachts and motorboats.
Bavaria is the most visited state in Germany, as over 38.86 million Tourism, tourists visited Bavaria in 2023 alone, significantly higher than North Rhine-Westphalia, North Rhine-Westphalia's 23.58 million tourists. In 2019, tourism brought in a Gross value added, gross value of €28.1 billion ($28.918 billion), making up 4.9% of Bavaria's economy. Some significant tourist destinations include the Bavarian National Museum, Margravial Opera House, Deutsches Museum, Christmas markets in Nuremberg, Nuremberg and
Bavaria also is home to the headquarters of commercial vehicle manufacturer MAN Truck & Bus, MAN and aircraft engine manufacturer MTU Aero Engines. Many other global companies such as Adidas, Siemens, and Allianz also have headquarters in Bavarian cities and towns. Several American companies have set up research and development facilities in Bavaria such as Apple Inc., Apple, Google, IBM, Intel, Texas Instruments and Coherent, Inc., Coherent. Despite being hundreds of miles from the sea, companies such as Bavaria Yachtbau produce sailing yachts and motorboats.
Bavaria is the most visited state in Germany, as over 38.86 million Tourism, tourists visited Bavaria in 2023 alone, significantly higher than North Rhine-Westphalia, North Rhine-Westphalia's 23.58 million tourists. In 2019, tourism brought in a Gross value added, gross value of €28.1 billion ($28.918 billion), making up 4.9% of Bavaria's economy. Some significant tourist destinations include the Bavarian National Museum, Margravial Opera House, Deutsches Museum, Christmas markets in Nuremberg, Nuremberg and Munich
Munich is the capital and most populous city of Bavaria, Germany. As of 30 November 2024, its population was 1,604,384, making it the third-largest city in Germany after Berlin and Hamburg. Munich is the largest city in Germany that is no ...
and the annually held Oktoberfest event, which made €1.2 billion ($1.236 billion) in 2018 alone.
The Unemployment, unemployment rate stood at 2.9% in October 2018, the lowest in Germany and one of the lowest in the European Union.
Demographics
Nuremberg
Nuremberg (, ; ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the Franconia#Towns and cities, largest city in Franconia, the List of cities in Bavaria by population, second-largest city in the States of Germany, German state of Bav ...
(518,370 inhabitants, approximately 3.6 million when including the broader metropolitan area), Augsburg
Augsburg ( , ; ; ) is a city in the Bavaria, Bavarian part of Swabia, Germany, around west of the Bavarian capital Munich. It is a College town, university town and the regional seat of the Swabia (administrative region), Swabia with a well ...
(296,582 inhabitants) and Regensburg
Regensburg (historically known in English as Ratisbon) is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the rivers Danube, Naab and Regen (river), Regen, Danube's northernmost point. It is the capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the ...
(153,094 inhabitants). All other cities in Bavaria had less than 150,000 inhabitants each in 2020. Population density in Bavaria was , below the national average of . Foreign nationals resident in Bavaria (both immigrants and refugees/asylum seekers) were principally from other EU countries and Turkey.
Vital statistics
Culture
Some features of the Bavarian culture and mentality are remarkably distinct from the rest of Germany. Noteworthy differences (especially in rural areas, less significant in the major cities) can be found with respect to religion, traditions, and language.Religion
 Bavarian culture (''
Bavarian culture (''Altbayern
Altbayern (; , also written Altbaiern, English: "Old Bavaria") is the territory and people of the three oldest parts of the present Free State of Bavaria, which were earlier known as Kurbayern (English: "Electoral Bavaria") after the former Elect ...
'') has a long and predominant tradition of Catholic Church, Roman Catholic faith. Pope Pope Benedict XVI, Benedict XVI (Joseph Alois Ratzinger) was born in Marktl am Inn in Upper Bavaria and was Archbishop of Munich and Freising, Cardinal-Archbishop of Munich and Freising. Otherwise, the culturally Franconia
Franconia ( ; ; ) is a geographical region of Germany, characterised by its culture and East Franconian dialect (). Franconia is made up of the three (governmental districts) of Lower Franconia, Lower, Middle Franconia, Middle and Upper Franco ...
n and Swabia
Swabia ; , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of Swabia, one of ...
n regions of the modern State of Bavaria are historically more diverse in religiosity, with both Catholic and Protestant traditions. In 1925, 70.0% of the Bavarian population was Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, 28.8% was Protestant, 0.7% was Jewish, and 0.5% was placed in other religious categories.
46.9% of Bavarians adhered to Catholicism (a decline from 70.4% in 1970). 17.2 percent of the population adheres to the Evangelical Lutheran Church in Bavaria, which has also declined since 1970. Three percent was Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox and Muslims make up 4.0% of the population of Bavaria. 28.9 percent of Bavarians are irreligious or adhere to other religions.
Traditions
Bavarians commonly emphasize pride in their traditions. Traditional costumes collectively known as Tracht are worn on special occasions and include inAltbayern
Altbayern (; , also written Altbaiern, English: "Old Bavaria") is the territory and people of the three oldest parts of the present Free State of Bavaria, which were earlier known as Kurbayern (English: "Electoral Bavaria") after the former Elect ...
Lederhosen for males and Dirndl for females. Centuries-old folk music is performed. The Maypole tradition in Bavaria, Maibaum, or Maypole (which in the Middle Ages served as the community's business directory, as figures on the pole represented the trades of the village), and the bagpipes of the Upper Palatinate region bear witness to the Paganism in the Eastern Alps, ancient Celtic and Germanic remnants of cultural heritage of the region. There are many traditional Bavarian sports disciplines, e.g. the Aperschnalzen, competitive whipcracking.
Whether in Bavaria, overseas or with citizens from other nations Bavarians continue to cultivate their traditions. They hold festivals and dances to keep their heritage alive.
Food and drink
Bavarians tend to place a great value on food and drink. In addition to their renowned dishes, Bavarians also consume many items of food and drink which are unusual elsewhere in Germany; for example ("white sausage") or in some instances a variety of entrails. More than 285 typical Bavarian products have been recorded in the Bavarian specialities databaseGenussBayern
since the 1990s. Recipes and museums can also be found there. With a total of 54 Geographical indications and traditional specialities in the European Union, specialities protected under European law, Bavaria is the No. 1 speciality region in Germany. Bavarian products such as ‘Bavarian beer’, ‘Nuremberg bratwurst’, ‘Allgäu mountain cheese’ and ‘Schrobenhausen asparagus’ are just as much a part of the official EU list 'eAmbrosia' of prestigious regional culinary specialities as the protected names “Champagne” and ‘Prosciutto di Parma’. Bavarian specialities, which are protected as geographical indications, are deeply rooted in their region of origin, important anchors of local identity and also tourist flagships - they are therefore at the heart of Bavarian cuisine. Restaurants that carry th
'Ausgezeichnete GenussKüche'
award (recognizable by a sign near the door) are known by locals for their certified, authentic Bavarian cuisine. At folk festivals and in many beer gardens, beer is traditionally served by the litre (in a ). Bavarians are particularly proud of the traditional , or beer purity law, initially established by the Duke of Bavaria for the City of Munich (i.e. the court) in 1487 and the duchy in 1516. According to this law, only three ingredients were allowed in beer: water, barley, and hops. In 1906 the made its way to all-German law, and remained a law in Germany until the EU partly struck it down in 1987 as incompatible with the European common market. German breweries, however, cling to the principle, and Bavarian breweries still comply with it in order to distinguish their beer brands. Bavarians are also known as some of the world's most prolific beer drinkers, with an average annual consumption of 130–135 liters per capita, as of 2018. Bavaria is also home to the Franconia (wine region), Franconia wine region, which is situated along the river Main (river), Main in Franconia. The region has produced wine (''Frankenwein'') for over 1,000 years and is famous for its use of the Bocksbeutel wine bottle. The production of wine forms an integral part of the regional culture, and many of its villages and cities hold their own wine festivals (Weinfeste) throughout the year.
Language and dialects
Three German dialects are most commonly spoken in Bavaria: Austro-Bavarian in Old Bavaria (Upper Bavaria, Lower Bavaria, and the Upper Palatinate), Swabian German (an Alemannic German dialect) in the Bavarian part of Swabia (southwest) and East Franconian German in Franconia (north). In the small town Ludwigsstadt in the north, district Kronach in Upper Franconia, Thuringian dialect is spoken. During the 20th century an increasing part of the population began to speak Standard German (Hochdeutsch), mainly in the cities.Ethnography
Bavarians consider themselves to be Egalitarianism, egalitarian and informal. Their sociability can be experienced at the annual Oktoberfest, the world's largest beer festival, which welcomes around six million visitors every year, or in the famous beer gardens. In traditional Bavarian beer gardens, patrons may bring their own food but buy beer only from the brewery that runs the beer garden.Museums
There are around 1,300 museums in Bavaria, including museums of art and cultural history, castles and palaces, archaeological and natural history collections, museums of technological and industrial history, and farm and open-air museums. The history of Bavarian museums dates back to manorial Cabinet of curiosities, cabinets of curiosities and Treasury, treasuries. The art holdings of theHouse of Wittelsbach
The House of Wittelsbach () is a former Bavarian dynasty, with branches that have ruled over territories including the Electorate of Bavaria, the Electoral Palatinate, the Electorate of Cologne, County of Holland, Holland, County of Zeeland, ...
thus formed the first and essential foundation of later state museums. As early as the mid-16th century, Duke Albrecht V (r. 1550–1579) had collected paintings as well as Greek and Roman sculptures (or copies made of them). He had the Antiquarium in the Munich Residence built specifically for his collection of antique sculptures. The electors Maximilian I, Elector of Bavaria, Maximilian I (r. 1594–1651) and Maximilian II Emanuel, Elector of Bavaria, Max II. Emanuel (r. 1679–1726) expanded the art collections considerably. In the Age of Enlightenment at the end of the 18th century, there was a demand to open up art collections to the general public in the spirit of "popular education". But Museums were not founded by the state until the time of the art-loving Ludwig I of Bavaria, King Ludwig I (r. 1825–1848). In Munich, he built Glyptothek (opened 1830), Alte Pinakothek (opened 1836), and Neue Pinakothek (opened 1853). Also, the foundation of the Germanisches Nationalmuseum in Nuremberg (1852), the establishment of the Neue Pinakothek, which opened in 1853, and the Bavarian National Museum (1867) in Munich were of central importance for the development of museums in Bavaria in the 19th century. With the end of the monarchy in 1918, many castles and formerly Wittelsbach property passed to the young Free State. In particular, the castles of king Ludwig II of Bavaria, Ludwig II (r. 1864–1886) Neuschwanstein Castle, Neuschwanstein, Linderhof Palace, Linderhof and Herrenchiemsee, quickly became magnets for the public. Since then, the number of Bavarian Museums has grown considerably, from 125 in 1907 to around 1,300 today.
Sports
Football
Bavaria is home to several association football, football clubs including FC Bayern Munich, 1. FC Nürnberg, FC Augsburg, TSV 1860 Munich, SSV Jahn Regensburg, FC Ingolstadt 04 and SpVgg Greuther Fürth. Bayern Munich is the most successful football team in Germany having won a record 33 List of German football champions, German titles and 6 UEFA Champions League titles. They are followed by 1. FC Nürnberg who have won 9 titles. SpVgg Greuther Fürth have won 3 championships while TSV 1860 Munich have been champions once.Basketball
Bavaria is also home to four professional basketball teams, including FC Bayern Munich (Basketball), FC Bayern Munich, Brose Baskets Bamberg, s.Oliver Würzburg, Nürnberg Falcons BC, and TSV Oberhaching Tropics.Ice hockey
There are five Bavarian ice hockey teams playing in the German top-tier league Deutsche Eishockey Liga, DEL: EHC Red Bull München, Nürnberg Ice Tigers, Augsburger Panther, ERC Ingolstadt, and Straubing Tigers.Notable people
Notable people who have lived, or live currently, in Bavaria include: *Kings: Arnulf of Carinthia, Carloman of Bavaria, Charles the Fat, Lothair I, Louis the Child, Louis the German, Louis the Younger, Ludwig I of Bavaria, Ludwig II of Bavaria, Ludwig III of Bavaria, Maximilian I Joseph of Bavaria, Maximilian II of Bavaria, Otto, King of Bavaria *Religious leaders: Pope Benedict XVI (Joseph Aloisius Ratzinger); Pope Damasus II, Pope Victor II *Painters: Albrecht Dürer, Albrecht Altdorfer, Joseph Karl Stieler, Carl Spitzweg, Erwin Eisch, Franz von Lenbach, Franz Stuck, Franz von Stuck, Franz Marc, Gabriele Münter, Hans Holbein the Elder, Johann Christian Reinhart, Lucas Cranach the Elder, Lucas Cranach, Paul Klee *Classical musicians: Orlande de Lassus, Orlando di Lasso, Christoph Willibald Gluck, Leopold Mozart, Max Reger, Richard Wagner, Richard Strauss, Carl Orff, Johann Pachelbel, Theobald Boehm, Klaus Nomi *Other musicians: Hans-Jürgen Buchner, Barbara Dennerlein, Klaus Doldinger, Franzl Lang, Bands: Spider Murphy Gang, Sportfreunde Stiller, Obscura (band), Obscura, Michael Bredl *Opera singers: Jonas Kaufmann, Diana Damrau *Writers, poets and playwrights: Hans Sachs, Jean Paul, Friedrich Rückert, August von Platen-Hallermünde, Frank Wedekind, Christian Morgenstern, Oskar Maria Graf, Bertolt Brecht, Lion Feuchtwanger, Thomas Mann, Klaus Mann, Golo Mann, Ludwig Thoma, Michael Ende, Ludwig Aurbacher *Scientists: Max Planck, Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, Werner Heisenberg, Adam Ries, Joseph von Fraunhofer, Georg Ohm, Johannes Stark, Carl von Linde, Ludwig Prandtl, Rudolf Mössbauer, Lothar Rohde, Hermann Schwarz, Robert Huber, Martin Behaim, Levi Strauss, Rudolf Diesel, Feodor Lynen, Georges J. F. Köhler, Erwin Neher, Ernst Otto Fischer, Johann Deisenhofer *Physicians: Alois Alzheimer, Max Joseph von Pettenkofer, Sebastian Kneipp *Politicians: Ludwig Erhard, Horst Seehofer, Christian Ude, Kurt Eisner, Franz-Josef Strauß, Roman Herzog, Leonard John Rose, Henry Kissinger *Football players: Max Morlock, Karl Mai, Franz Beckenbauer, Sepp Maier, Gerd Müller, Paul Breitner, Bernd Schuster, Klaus Augenthaler, Lothar Matthäus, Philipp Lahm, Bastian Schweinsteiger, Holger Badstuber, Thomas Müller, Mario Götze, Dietmar Hamann, Stefan Reuter *Other sportspeople: Bernhard Langer, Dirk Nowitzki, Phoenix Sanders *Actors: Michael Herbig, Werner Stocker (actor), Werner Stocker, Helmut Fischer, Walter Sedlmayr, Gustl Bayrhammer, Ottfried Fischer, Ruth Drexel, Elmar Wepper, Fritz Wepper, Uschi Glas, Yank Azman *Entertainers: Siegfried Fischbacher, Thomas Gottschalk *Film directors: Helmut Dietl, Rainer Werner Fassbinder, Bernd Eichinger, Joseph Vilsmaier, Hans Steinhoff, Werner Herzog *Designers: Peter Schreyer, Damir Doma, Thomas Nast *Entrepreneurs: Charles Diebold, Adi Dassler, Rudolf Dassler, Levi Strauss, Ed Meier *Military: Claus von Stauffenberg *Nazis: Sepp Dietrich, Karl Fiehler, Karl Gebhardt, Hermann Göring, Heinrich Himmler, Alfred Jodl, Josef Kollmer, Josef Mengele, Ernst Röhm, Franz Ritter von Epp, Julius Streicher *Others: Kaspar Hauser, The Smith of Kochel, Mathias Kneißl, Matthias Klostermayr, Anneliese Michel, Herluka von BernriedSee also
* Outline of Germany * Former countries in Europe after 1815 * List of Bavaria-related topics * List of minister-presidents of Bavaria * List of rulers of BavariaNotes
References
Citations
General and cited sources
*External links
Official government website
* {{Authority control Bavaria, Boii States of Germany States of the Weimar Republic