Battle Of Spring Hill on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Battle of Spring Hill was fought November 29, 1864, at
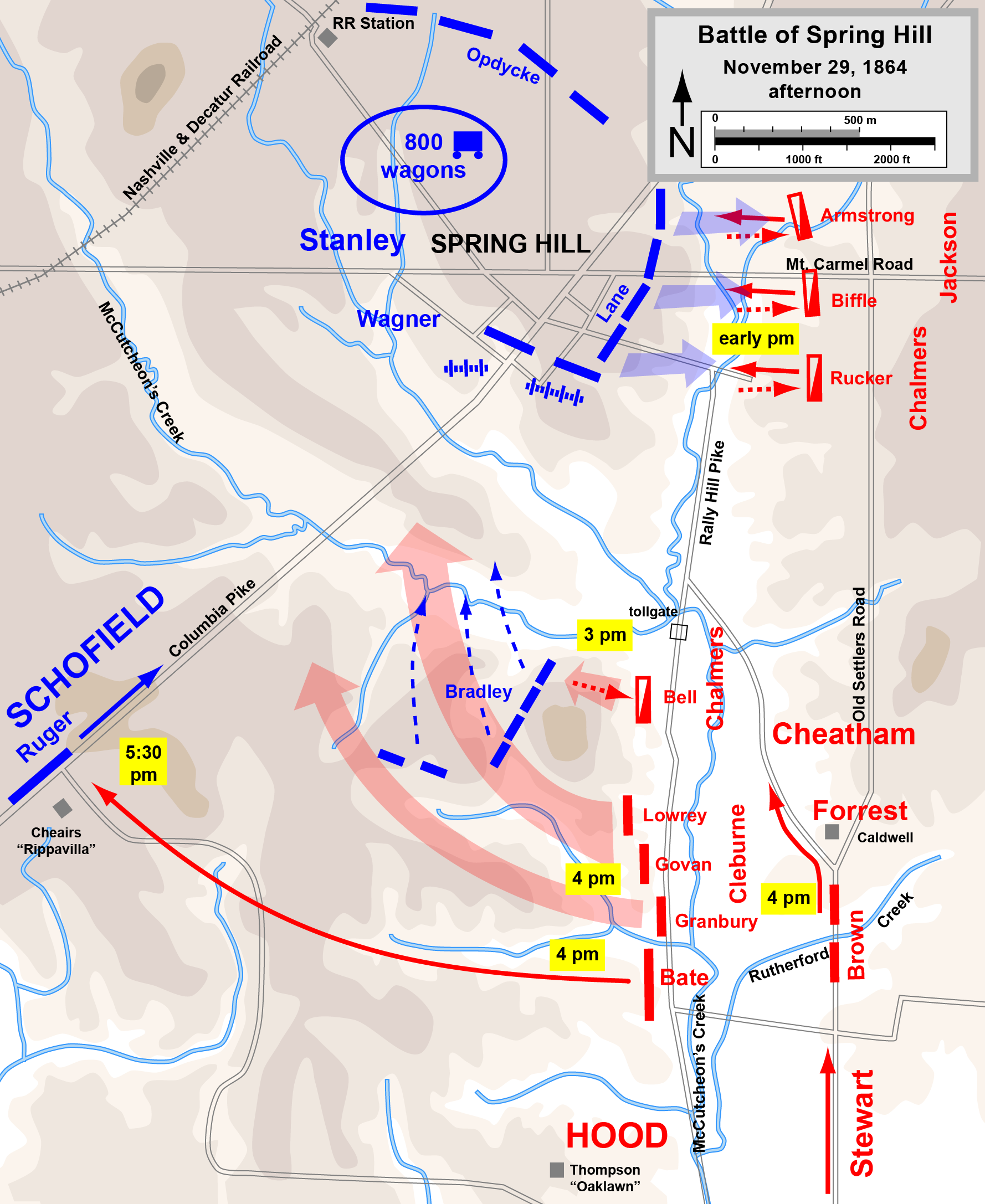 Forrest's cavalrymen approached Spring Hill on the Mount Carmel Road and at about 11:30 a.m. ran into pickets from the IV Corps. Stanley had moved north rapidly and formed up positions with Wagner's division that protected the village of Spring Hill on three sides. To the northwest of the village, the lines of Col. Emerson Opdycke's brigade protected the enormous supply trains, Brig. Gen.
Forrest's cavalrymen approached Spring Hill on the Mount Carmel Road and at about 11:30 a.m. ran into pickets from the IV Corps. Stanley had moved north rapidly and formed up positions with Wagner's division that protected the village of Spring Hill on three sides. To the northwest of the village, the lines of Col. Emerson Opdycke's brigade protected the enormous supply trains, Brig. Gen.  Cheatham was at that time attempting to find Bate and steer him into the combined attack. Brown sent two staff officers to find Cheatham and halted his troops while he awaited a decision. By the time Cheatham and Brown were able to speak, at around 6:15 p.m., the battlefield was in total darkness, and the two officers decided that an assault conducted then without knowing the condition of their right flank might be a disaster. Cheatham rode off to Hood's headquarters to consult with the army commander. Hood was furious that the attack had not proceeded as he intended and that the pike was still open. Cheatham said that he needed assistance from Stewart to protect his right flank, so Hood dispatched a staff officer to find Stewart. Having been up since 3 a.m., Hood was by this time very fatigued. He indulged in a large dinner at Oaklawn, which included considerable "toasting" of drinks, and went to bed at 9 p.m., confident that whatever setbacks his army had suffered during the day, they would be able to correct them in the morning and bag Schofield.
Earlier in the afternoon, Hood had brought up Stewart's corps across Rutherford Creek and directed him to move north of Spring Hill and cut off the Federal column. After taking a wrong turn, Stewart ended up at Forrest's headquarters at the Caldwell house. There he conferred with Forrest about the positions of the army, when suddenly one of Cheatham's staff officers arrived and directed in Hood's name that Stewart's corps move to support Brown's attack. After Stewart's column retraced its route, he arrived at Brown's command post, but was confused about the apparent disagreement in orders he was receiving, so he traveled back to Hood's headquarters for clarification. He informed Hood that because his men were tired and had been on the move since daylight—it was now 11 p.m.—he had ordered them to bivouac while they waited. Hood accepted the situation and told Stewart to head in the direction of Franklin in the morning after the men had rested.
Cheatham was at that time attempting to find Bate and steer him into the combined attack. Brown sent two staff officers to find Cheatham and halted his troops while he awaited a decision. By the time Cheatham and Brown were able to speak, at around 6:15 p.m., the battlefield was in total darkness, and the two officers decided that an assault conducted then without knowing the condition of their right flank might be a disaster. Cheatham rode off to Hood's headquarters to consult with the army commander. Hood was furious that the attack had not proceeded as he intended and that the pike was still open. Cheatham said that he needed assistance from Stewart to protect his right flank, so Hood dispatched a staff officer to find Stewart. Having been up since 3 a.m., Hood was by this time very fatigued. He indulged in a large dinner at Oaklawn, which included considerable "toasting" of drinks, and went to bed at 9 p.m., confident that whatever setbacks his army had suffered during the day, they would be able to correct them in the morning and bag Schofield.
Earlier in the afternoon, Hood had brought up Stewart's corps across Rutherford Creek and directed him to move north of Spring Hill and cut off the Federal column. After taking a wrong turn, Stewart ended up at Forrest's headquarters at the Caldwell house. There he conferred with Forrest about the positions of the army, when suddenly one of Cheatham's staff officers arrived and directed in Hood's name that Stewart's corps move to support Brown's attack. After Stewart's column retraced its route, he arrived at Brown's command post, but was confused about the apparent disagreement in orders he was receiving, so he traveled back to Hood's headquarters for clarification. He informed Hood that because his men were tired and had been on the move since daylight—it was now 11 p.m.—he had ordered them to bivouac while they waited. Hood accepted the situation and told Stewart to head in the direction of Franklin in the morning after the men had rested.
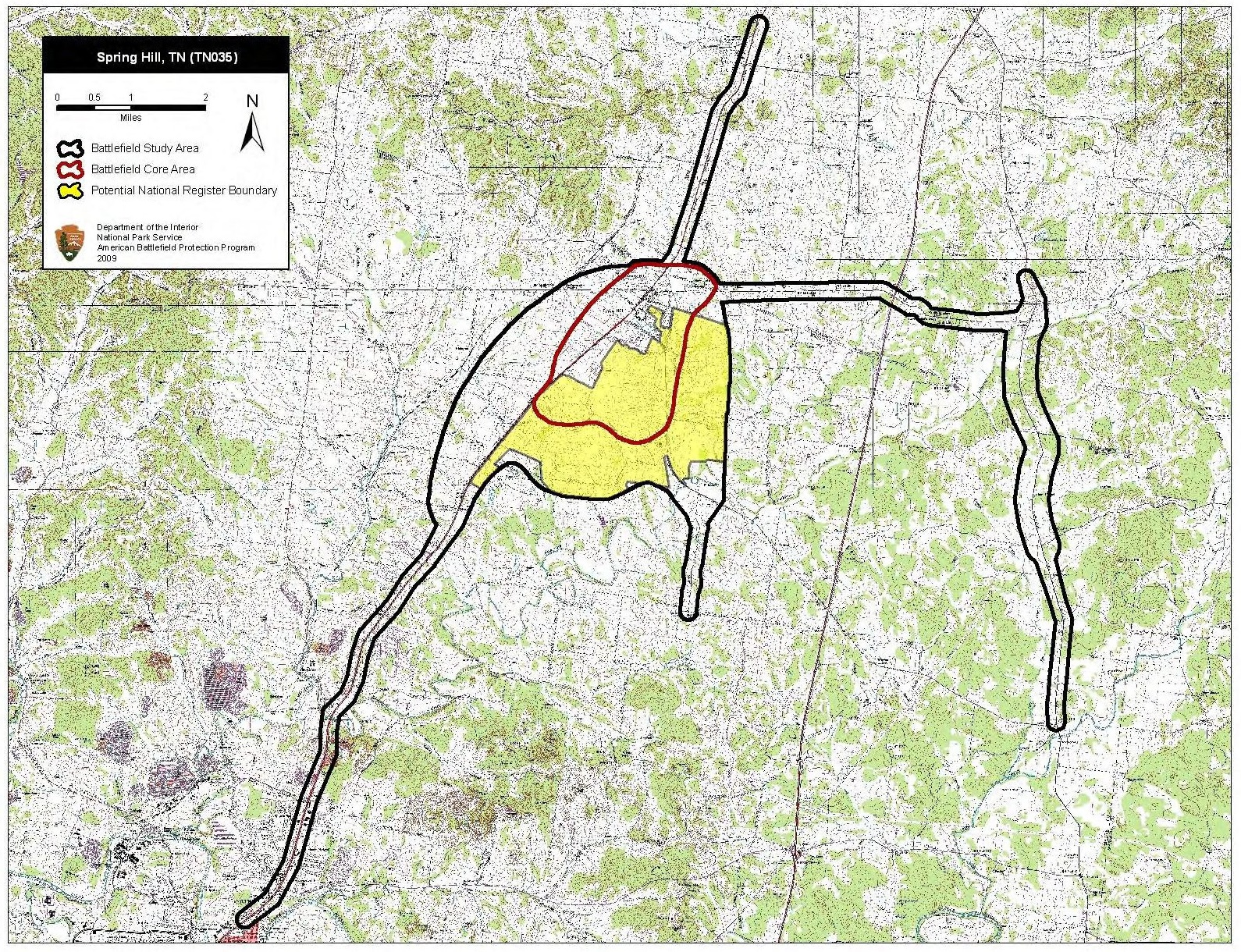 Portions of landscape have been altered, but most essential features remain. Industrial and residential development and
associated road and communication infrastructure are rapidly overtaking the historic battlefield. Protected lands include Rippavilla, Inc. (98.44 acres), Civil War Preservation Trust (70.00 acres), Tennessee Land Trust (82.70 acres), and Maury County Parks and Recreation Department (20.00 acres). The Civil War Preservation Trust was renamed
Portions of landscape have been altered, but most essential features remain. Industrial and residential development and
associated road and communication infrastructure are rapidly overtaking the historic battlefield. Protected lands include Rippavilla, Inc. (98.44 acres), Civil War Preservation Trust (70.00 acres), Tennessee Land Trust (82.70 acres), and Maury County Parks and Recreation Department (20.00 acres). The Civil War Preservation Trust was renamed
''The Civil War Battlefield Guide''
2nd ed. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Co., 1998. . * McPherson, James M., ed. ''Battle Chronicles of the Civil War: 1864''. Connecticut: Grey Castle Press, 1989. . First published in 1989 by McMillan. * Nevin, David, and the Editors of Time-Life Books. ''Sherman's March: Atlanta to the Sea''. Alexandria, VA: Time-Life Books, 1986. . * Sword, Wiley. ''The Confederacy's Last Hurrah: Spring Hill, Franklin, and Nashville''. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas, 1993. . First published with the title ''Embrace an Angry Wind'' in 1992 by HarperCollins. * Welcher, Frank J. ''The Union Army, 1861–1865 Organization and Operations''. Vol. 2, ''The Western Theater''. Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 1993. .
National Park Service battle description
CWSAC Report Update
''Advance and Retreat: Personal Experiences in the United States and Confederate States Armies''
Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 1996. . First published 1880 for the Hood Orphan Memorial Fund by G. T. Beauregard. * Shellenberger, Capt. John K
"The Battle of Spring Hill, Tennessee"
presentation to the Commandery of the State of Missouri,
Spring Hill Battlefield Page
Battle maps, photos, history articles, and battlefield news ( CWPT)
Animated history of the Franklin-Nashville Campaign
* {{authority control Spring Hill Spring Hill Spring Hill Spring Hill Maury County, Tennessee Spring Hill 1864 in Tennessee November 1864
Spring Hill, Tennessee
Spring Hill is a city in Maury and Williamson counties in the U.S. state of Tennessee, located approximately south of Nashville. Its population as of 2022 is 55,800. Spring Hill is recognized as the 4th fastest growing city in Tennessee by th ...
, as part of the Franklin-Nashville Campaign of the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
. The Confederate
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a political union of sovereign states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
Army of Tennessee
The Army of Tennessee was a Field army, field army of the Confederate States Army in the Western theater of the American Civil War, Western Theater of the American Civil War. Named for the Confederate States of America, Confederate state of Tenn ...
, commanded by Lt. Gen. John Bell Hood
John Bell Hood (June 1 or June 29, 1831 – August 30, 1879) was a Confederate general during the American Civil War. Hood's impetuosity led to high losses among his troops as he moved up in rank. Bruce Catton wrote that "the decision to replace ...
, attacked a Union force under Maj. Gen. John M. Schofield
John McAllister Schofield (; September 29, 1831 – March 4, 1906) was an American soldier who held major commands during the American Civil War. He was appointed U.S. Secretary of War (1868–1869) under President Andrew Johnson and later serve ...
as it retreated from Columbia through Spring Hill. Because of a series of command failures, the Confederates were unable to inflict serious damage on the Federals and could not prevent their safe passage north to Franklin
Franklin may refer to:
People and characters
* Franklin (given name), including list of people and characters with the name
* Franklin (surname), including list of people and characters with the name
* Franklin (class), a member of a historic ...
during the night. The next day, Hood pursued Schofield and attacked his fortifications in the Battle of Franklin
The Battle of Franklin was fought on November 30, 1864, in Franklin, Tennessee, as part of the Franklin–Nashville Campaign of the American Civil War. It was one of the worst disasters of the war for the Confederate States Army. Confederate L ...
, resulting in severe Confederate casualties.
Background
Following his defeat in the Atlanta Campaign, Hood had hoped to lure Maj. Gen.William T. Sherman
William is a masculine given name of Germanic origin. It became popular in England after the Norman conquest in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is ...
into battle by disrupting his supply lines from Chattanooga
Chattanooga ( ) is a city in Hamilton County, Tennessee, United States, and its county seat. It is located along the Tennessee River and borders Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the south. With a population of 181,099 in 2020, it is Tennessee ...
to Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Georgia (U.S. state), most populous city in the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. It is the county seat, seat of Fulton County, Georg ...
. After a brief period in which he pursued Hood, Sherman elected instead to conduct his March to the Sea from Atlanta to Savannah, Georgia
Savannah ( ) is the oldest city in the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia and the county seat of Chatham County, Georgia, Chatham County. Established in 1733 on the Savannah River, the city of Savannah became the Kingdom of Great Brita ...
. He left forces under the command of Maj. Gen. George H. Thomas, the commander of the Army of the Cumberland
The Army of the Cumberland was one of the principal Union armies in the Western Theater during the American Civil War. It was originally known as the Army of the Ohio.
History
The origin of the Army of the Cumberland dates back to the creatio ...
, to defend Tennessee and defeat Hood: principally the IV Corps 4 Corps, 4th Corps, Fourth Corps, or IV Corps may refer to:
France
* 4th Army Corps (France)
* IV Cavalry Corps (Grande Armée), a cavalry unit of the Imperial French Army during the Napoleonic Wars
* IV Corps (Grande Armée), a unit of the Imperi ...
from the Army of the Cumberland, commanded by Maj. Gen. David S. Stanley, and the XXIII Corps from the Army of the Ohio
The Army of the Ohio was the name of two Union Army, Union armies in the American Civil War. The first army became the Army of the Cumberland and the second army was created in 1863.
History
1st Army of the Ohio
General Orders No. 97 appointed ...
, commanded by Maj. Gen. John Schofield
John McAllister Schofield (; September 29, 1831 – March 4, 1906) was an American soldier who held major commands during the American Civil War. He was appointed U.S. Secretary of War (1868–1869) under President Andrew Johnson and later serve ...
.
Hood moved through northern Alabama and concentrated his army at Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025.
Florence ...
from October 30 to November 21, waiting for supplies and to link up with his newly assigned cavalry commander, Maj. Gen. Nathan Bedford Forrest
Nathan Bedford Forrest (July 13, 1821October 29, 1877) was an List of slave traders of the United States, American slave trader, active in the lower Mississippi River valley, who served as a General officers in the Confederate States Army, Con ...
. Rather than attempting to pursue Sherman through Georgia, Hood decided to execute a new plan: move north into Tennessee, defeat Thomas's army before it could concentrate, seize the important manufacturing center of Nashville
Nashville, often known as Music City, is the capital and List of municipalities in Tennessee, most populous city in the U.S. state of Tennessee. It is the county seat, seat of Davidson County, Tennessee, Davidson County in Middle Tennessee, locat ...
, and continue north into Kentucky
Kentucky (, ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north, West Virginia to the ...
, possibly as far as the Ohio River
The Ohio River () is a river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing in a southwesterly direction from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, to its river mouth, mouth on the Mississippi Riv ...
. From this point, he could travel east to Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
to join up with Gen. Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee (January 19, 1807 – October 12, 1870) was a general officers in the Confederate States Army, Confederate general during the American Civil War, who was appointed the General in Chief of the Armies of the Confederate ...
at Petersburg. His theater commander, Gen. P.G.T. Beauregard
Pierre Gustave Toutant-Beauregard (May 28, 1818 – February 20, 1893) was an American military officer known as being the Confederate general who started the American Civil War at the battle of Fort Sumter on April 12, 1861. Today, he is comm ...
, urged Hood to take immediate action in an attempt to distract Sherman's advance, emphasizing the importance of moving before Thomas could consolidate his forces.
The Army of Tennessee marched north from Florence on November 21 in three columns: Maj. Gen. Benjamin F. Cheatham's corps on the left, Lt. Gen. Stephen D. Lee's in the center, and Lt. Gen. Alexander P. Stewart's on the right, all screened aggressively by Forrest's cavalry. Schofield, who commanded Stanley's corps as well as his own, retreated in the face of this advance, marching rapidly north from Pulaski to Columbia. The Federals were able to reach Columbia and erect fortifications just hours before the Confederates arrived.
On November 24–29, the "Battle of Columbia
The Battle of Columbia was a series of military actions that took place November 24–29, 1864, in Maury County, Tennessee, as part of the Franklin-Nashville Campaign of the American Civil War. It concluded the movement of Lt. Gen. John Be ...
" was a series of skirmishes and artillery bombardments against Columbia. On November 28, Thomas directed Schofield to begin preparations for a withdrawal north to Franklin
Franklin may refer to:
People and characters
* Franklin (given name), including list of people and characters with the name
* Franklin (surname), including list of people and characters with the name
* Franklin (class), a member of a historic ...
. He was expecting (incorrectly) that Maj. Gen. Andrew J. Smith's XVI Corps arrival from Missouri was imminent and he wanted the combined force to defend against Hood on the line of the Harpeth River
The Harpeth River, long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed June 8, 2011 is one of the major streams of north-central Middle Tennessee, United States, and one of the major ...
at Franklin instead of the Duck River at Columbia. Schofield sent his 800-wagon supply train out in front, guarded by part of the IV Corps division of Brig. Gen. George D. Wagner. On the same day, Hood sent the three cavalry divisions under Nathan Bedford Forrest miles east of Columbia, where they crossed the river and headed north.
On November 29 Hood sent Cheatham's and Stewart's corps on a flanking march north, crossing the Duck River at Davis's Ford east of Columbia while two divisions of Lee's corps and most of the army's artillery remained on the southern bank to deceive Schofield into thinking a general assault was planned against Columbia. Hood, riding near the head of the column with Cheatham's corps, planned to interpose his army between Schofield and Thomas, hoping to defeat Schofield as the Federals retreated north from Columbia. Stewart's corps followed Cheatham, and they were followed by the division of Maj. Gen. Edward "Allegheny" Johnson (Lee's corps). The rest of Lee's corps remained south of Columbia, demonstrating with artillery fire against Schofield's men north of the Duck.
Cavalry skirmishing between Brig. Gen. James H. Wilson's Union cavalry and Forrest's Confederate troopers continued throughout the day as the Confederates advanced. Forrest's wide turning movement with 4,000 troopers had forced Wilson north to Hurt's Corner, preventing the Union horsemen from interfering with Hood's infantry advance. By 10 a.m. on November 29, Forrest ordered his men to turn west toward Spring Hill. Wilson sent multiple messages to Schofield warning of Hood's advance, but it was not until dawn on November 29 that Schofield believed the reports, understood the deception represented by Lee's artillery bombardment, and realized the predicament he was in. He sent Stanley north with the IV Corps division of Brig. Gen. Nathan Kimball
Nathan Kimball (November 22, 1822 – January 21, 1898) was a physician, politician, postmaster, and military officer, serving as a general in the Union army during the American Civil War. He was the first statewide commander of the Grand Arm ...
, the remainder of Wagner's division, and the bulk of the Federal reserve artillery. Their mission initially was to protect the trains, but also to hold the crossroads at Spring Hill to allow the entire army to withdraw safely to Franklin.
Opposing forces
Union
Confederate
Battle
 Forrest's cavalrymen approached Spring Hill on the Mount Carmel Road and at about 11:30 a.m. ran into pickets from the IV Corps. Stanley had moved north rapidly and formed up positions with Wagner's division that protected the village of Spring Hill on three sides. To the northwest of the village, the lines of Col. Emerson Opdycke's brigade protected the enormous supply trains, Brig. Gen.
Forrest's cavalrymen approached Spring Hill on the Mount Carmel Road and at about 11:30 a.m. ran into pickets from the IV Corps. Stanley had moved north rapidly and formed up positions with Wagner's division that protected the village of Spring Hill on three sides. To the northwest of the village, the lines of Col. Emerson Opdycke's brigade protected the enormous supply trains, Brig. Gen. Luther P. Bradley
Luther Prentice Bradley (December 8, 1822 – March 13, 1910) was an American soldier who served as a Union Army, Union general officer during the American Civil War.
Early life
Bradley was born in New Haven, Connecticut on December 8, 1822. ...
's brigade. Lane's brigade rushed forward and pushed back the dismounted cavalrymen, primarily Brig. Gen. Frank C. Armstrong's Mississippi brigade. Forrest received a message from Hood to hold the position at all hazards until the infantry could arrive. Maj. Gen. Patrick R. Cleburne
Major general, Major-General Patrick Ronayne Cleburne ( ; March 16, 1828November 30, 1864) was a senior Officer (armed forces), officer in the Confederate States Army who commanded infantry in the Western Theater of the American Civil War, West ...
's division of Cheatham's corps arrived midafternoon on Forrest's left. The cavalrymen, low on ammunition, pulled out of the line and moved north to be ready to cover a further advance of Hood's army, or to block Schofield's withdrawal.
Forrest's men moved south and he directed the brigade of Brig. Gen. Tyree H. Bell
Tyree Harris Bell (September 5, 1815 – August 30, 1902) was a Confederate States Army General officers in the Confederate States Army#Brigadier general, brigadier general, during the American Civil War.
As Lieutenant colonel (United States) ...
of Chalmer's division to drive off what he thought was a small force of cavalry from a knoll south of McCutcheon's Creek. They were actually engaging with Bradley's brigade, which drove them back immediately with heavy artillery support. The chastened Forrest remarked, "They was in there sure enough, wasn't they, Chalmers?"
The first command miscommunication of the battle took place upon Hood's arrival as he established his headquarters at the Absalom Thompson house, "Oaklawn". Cheatham had ordered his division under Maj. Gen. William B. Bate
William Brimage Bate (October 7, 1826March 9, 1905) was a planter and slaveholder, Confederate officer, and politician in Tennessee. After the Reconstruction era, he served as the 23rd governor of Tennessee from 1883 to 1887. He was elected to th ...
to move against Spring Hill in concert with Cleburne, forming up on the Irishman's left. Hood then personally ordered Bate to move towards the Columbia Pike and "sweep toward Columbia." Neither Bate nor Hood bothered to inform Cheatham of this change in orders. Bate's men advanced about 3,000 yards in battle formation before they reached the pike, a journey taking over two hours. At about 5:30 p.m., his lead element, sharpshooters under Maj. Thomas D. Caswell, fired on a Federal column approaching from their left—Maj. Gen. Thomas H. Ruger's division of the XXIII Corps, the vanguard of Schofield's main body. But before the two divisions could engage in battle, an officer from Cheatham's staff arrived to insist that Bate follow Cheatham's original orders and join Cleburne's attack. Late that night, Bate reported the contact with the Federal column, but Cheatham discounted the importance of the encounter.
Back in Columbia, Schofield became convinced at about 3 p.m. that the Confederates would not attack him there and at 3:30 he joined two brigades from Ruger's division on the march to Spring Hill. He ordered his remaining force to remain until dark and then join him on the march north. As soon as Schofield departed, Stephen D. Lee coincidentally began an attack against the Union position, although he had considerable difficulty deploying pontoon bridges for the river crossing. By the time the bulk of his two divisions were able to cross, the senior Union commander left behind at Columbia, Brig. Gen. Jacob D. Cox, began his withdrawal and the final troops departed up the Franklin Pike by 10 p.m.
Cleburne's 3,000 men began an ''en echelon'' attack against Bradley's brigade at about 4 p.m. From right to left, his brigades were led by Brig. Gens. Mark P. Lowrey, Daniel C. Govan
Daniel Chevilette Govan (July 4, 1829 – March 12, 1911) was an American miner, planter, and soldier. He served as a Confederate general during the American Civil War, prominent in campaigns and battles in the Western Theater.
Early life an ...
, and Hiram B. Granbury
Hiram Bronson Granbury (March 1, 1831 – November 30, 1864) was a lawyer and county judge in Texas before the American Civil War. He organized a volunteer company for the Confederate States Army after the outbreak of the Civil War and became ...
. Bell's cavalry brigade supported on the right, although they remained low on ammunition and had little effect in the fight. Whereas Cheatham was expecting Cleburne to drive north into Spring Hill, Hood's intention was to use this formation to sweep toward the turnpike and wheel left to intercept Schofield's arriving units, but he apparently had not observed the location of the Union positions south of the town. The stairstep echelon formation was therefore less effective against Bradley's fortified position on their right and front, allowing only Lowrey's brigade to engage them initially. After Lowrey requested assistance, Cleburne personally led Govan's Arkansas brigade forward, wheeling them into a northern alignment against Bradley's right flank. The attack by Govan and Lowrey outflanked Bradley and his men fled in disorder. Cleburne's two brigades chased them vigorously, and they were stopped short of the turnpike only by heavy fire from the IV Corps artillery, placed earlier by Stanley on a knoll north of the creek.
By this time, Cheatham's division under Maj. Gen. John C. Brown
John Calvin Brown (January 6, 1827August 17, 1889) was a Confederate Army officer and an American politician and businessman. Although he originally opposed secession, Brown fought for the Confederacy during the American Civil War, eventually ...
(Cheatham's own division before he assumed corps command) had crossed Rutherford Creek and was moved into position by Cheatham for another attack on Spring Hill, on Cleburne's right. In the gathering darkness, the sounds of Brown's guns would be the signal for Cleburne's men to resume their attack. Brown did not attack, however. His brigade commander on the right, Brig. Gen. Otho F. Strahl, reported that there were Union troops in position on his right flank and front and that Forrest's cavalrymen, promised to protect his right flank, did not seem to be present. Since his brigade under Brig. Gen. States Rights Gist
States Rights Gist (September 3, 1831 – November 30, 1864) was a lawyer and militia general in South Carolina, and later a Confederate Army brigadier general during the American Civil War. He gained prominence during the war but was killed at t ...
had not yet arrived to join the attack, Brown decided to consult with his corps commander before proceeding.
 Cheatham was at that time attempting to find Bate and steer him into the combined attack. Brown sent two staff officers to find Cheatham and halted his troops while he awaited a decision. By the time Cheatham and Brown were able to speak, at around 6:15 p.m., the battlefield was in total darkness, and the two officers decided that an assault conducted then without knowing the condition of their right flank might be a disaster. Cheatham rode off to Hood's headquarters to consult with the army commander. Hood was furious that the attack had not proceeded as he intended and that the pike was still open. Cheatham said that he needed assistance from Stewart to protect his right flank, so Hood dispatched a staff officer to find Stewart. Having been up since 3 a.m., Hood was by this time very fatigued. He indulged in a large dinner at Oaklawn, which included considerable "toasting" of drinks, and went to bed at 9 p.m., confident that whatever setbacks his army had suffered during the day, they would be able to correct them in the morning and bag Schofield.
Earlier in the afternoon, Hood had brought up Stewart's corps across Rutherford Creek and directed him to move north of Spring Hill and cut off the Federal column. After taking a wrong turn, Stewart ended up at Forrest's headquarters at the Caldwell house. There he conferred with Forrest about the positions of the army, when suddenly one of Cheatham's staff officers arrived and directed in Hood's name that Stewart's corps move to support Brown's attack. After Stewart's column retraced its route, he arrived at Brown's command post, but was confused about the apparent disagreement in orders he was receiving, so he traveled back to Hood's headquarters for clarification. He informed Hood that because his men were tired and had been on the move since daylight—it was now 11 p.m.—he had ordered them to bivouac while they waited. Hood accepted the situation and told Stewart to head in the direction of Franklin in the morning after the men had rested.
Cheatham was at that time attempting to find Bate and steer him into the combined attack. Brown sent two staff officers to find Cheatham and halted his troops while he awaited a decision. By the time Cheatham and Brown were able to speak, at around 6:15 p.m., the battlefield was in total darkness, and the two officers decided that an assault conducted then without knowing the condition of their right flank might be a disaster. Cheatham rode off to Hood's headquarters to consult with the army commander. Hood was furious that the attack had not proceeded as he intended and that the pike was still open. Cheatham said that he needed assistance from Stewart to protect his right flank, so Hood dispatched a staff officer to find Stewart. Having been up since 3 a.m., Hood was by this time very fatigued. He indulged in a large dinner at Oaklawn, which included considerable "toasting" of drinks, and went to bed at 9 p.m., confident that whatever setbacks his army had suffered during the day, they would be able to correct them in the morning and bag Schofield.
Earlier in the afternoon, Hood had brought up Stewart's corps across Rutherford Creek and directed him to move north of Spring Hill and cut off the Federal column. After taking a wrong turn, Stewart ended up at Forrest's headquarters at the Caldwell house. There he conferred with Forrest about the positions of the army, when suddenly one of Cheatham's staff officers arrived and directed in Hood's name that Stewart's corps move to support Brown's attack. After Stewart's column retraced its route, he arrived at Brown's command post, but was confused about the apparent disagreement in orders he was receiving, so he traveled back to Hood's headquarters for clarification. He informed Hood that because his men were tired and had been on the move since daylight—it was now 11 p.m.—he had ordered them to bivouac while they waited. Hood accepted the situation and told Stewart to head in the direction of Franklin in the morning after the men had rested.
Aftermath
The Battle of Spring Hill was a minor affair in terms of casualties—about 350 Union and 500 Confederate—but the result of miscommunication and simply bad military management was that during the night all of Schofield's command, including Cox, passed from Columbia through Spring Hill while the Confederate commanders slept. The passage of the army did not go unnoticed by some of the soldiers, but no concerted effort was made to block the pike. Brig. Gen. Lawrence S. Ross's cavalry brigade attempted to block the passage of the supply trains north of Spring Hill, at Thompson's Station, but accompanying Federal infantry drove them off. A private soldier woke up the commanding general at 2 a.m. and reported he saw the Union column moving north, but Hood did nothing beyond sending a dispatch to Cheatham to fire on passing traffic. By 6:00 a.m. on November 30, all of Schofield's army was well north of Spring Hill and its vanguard had reached Franklin, where it began to build breastworks south of town. In the morning Hood discovered Schofield's escape, and after an angry conference with his subordinate commanders in which he blamed all but himself for the failure, ordered his army to resume its pursuit, setting up the disastrousBattle of Franklin
The Battle of Franklin was fought on November 30, 1864, in Franklin, Tennessee, as part of the Franklin–Nashville Campaign of the American Civil War. It was one of the worst disasters of the war for the Confederate States Army. Confederate L ...
that afternoon.
Spring Hill had been, arguably, Hood's best chance to isolate and defeat the Union army (Thomas L. Connelly
Thomas Lawrence Connelly (February 14, 1938 – January 18, 1991) was an American historian and author who specialized in the Civil War era. He is perhaps best known for his book, ''The Marble Man: Robert E. Lee and His Image in American Society' ...
, historian of the Army of Tennessee, argues that the importance of Spring Hill has been overblown and that Schofield had three alternative routes to either Franklin or Nashville.) Recriminations for the lost opportunity soon began flying. Rumors circulated about Brown being drunk, but they were never substantiated and he was later elected governor of Tennessee. Hood believed that Cheatham was most responsible, although he also had criticism for two of Cheatham's division commanders, Cleburne and Brown. His official report said, "Major-General Cheatham was ordered to attack the enemy at once vigorously and get possession of the pike, and, although these orders were frequently and earnestly repeated, he made but a feeble and partial attack, failing to reach the point indicated." Historians Thomas L. Connelly, Eric Jacobson, and Wiley Sword have each assigned blame to both Hood and Cheatham.
A variety of theories about Hood's personal failures have occupied historians for years. One of the more persistent is that the general was debilitated from ingesting laudanum
Laudanum is a tincture of opium containing approximately 10% powdered opium by weight (the equivalent of 1% morphine). Laudanum is prepared by dissolving extracts from the opium poppy (''Papaver somniferum'') in alcohol (ethanol).
Reddish-br ...
in the evening, attempting to relieve the pain and irritation to his amputated leg by the long, damp ride over rough roads that day. Eric Jacobson's book, ''For Cause & for Country'', lists many authors who have supported this story, but he states that "there is no evidence that Hood took any sort of drugs, or even alcohol, at Spring Hill."
Battlefield Preservation
 Portions of landscape have been altered, but most essential features remain. Industrial and residential development and
associated road and communication infrastructure are rapidly overtaking the historic battlefield. Protected lands include Rippavilla, Inc. (98.44 acres), Civil War Preservation Trust (70.00 acres), Tennessee Land Trust (82.70 acres), and Maury County Parks and Recreation Department (20.00 acres). The Civil War Preservation Trust was renamed
Portions of landscape have been altered, but most essential features remain. Industrial and residential development and
associated road and communication infrastructure are rapidly overtaking the historic battlefield. Protected lands include Rippavilla, Inc. (98.44 acres), Civil War Preservation Trust (70.00 acres), Tennessee Land Trust (82.70 acres), and Maury County Parks and Recreation Department (20.00 acres). The Civil War Preservation Trust was renamed Civil War Trust
The American Battlefield Trust is a charitable organization (501(c)(3)) whose primary focus is in the preservation of battlefields of the Revolutionary War, the War of 1812, and the American Civil War, through the acquisition of battlefield lan ...
in 2011 and in May 2018 became a division of American Battlefield Trust
The American Battlefield Trust is a charitable organization (501(c)(3)) whose primary focus is in the preservation of battlefields of the Revolutionary War, the War of 1812, and the American Civil War, through the acquisition of battlefield lan ...
. The Trust and its partners have acquired and preserved a total of of the battlefield in three transactions since 1996.American Battlefield Trust
The American Battlefield Trust is a charitable organization (501(c)(3)) whose primary focus is in the preservation of battlefields of the Revolutionary War, the War of 1812, and the American Civil War, through the acquisition of battlefield lan ...
"Saved Land" webpage. Accessed May 25, 2018.
Notes
References
* Connelly, Thomas L. ''Autumn of Glory: The Army of Tennessee 1862–1865''. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press, 1971. . * David J. Eicher, Eicher, David J. ''The Longest Night: A Military History of the Civil War''. New York: Simon & Schuster, 2001. . * Jacobson, Eric A., and Richard A. Rupp. ''For Cause & for Country: A Study of the Affair at Spring Hill and the Battle of Franklin''. Franklin, TN: O'More Publishing, 2007. . * Kennedy, Frances H., ed''The Civil War Battlefield Guide''
2nd ed. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Co., 1998. . * McPherson, James M., ed. ''Battle Chronicles of the Civil War: 1864''. Connecticut: Grey Castle Press, 1989. . First published in 1989 by McMillan. * Nevin, David, and the Editors of Time-Life Books. ''Sherman's March: Atlanta to the Sea''. Alexandria, VA: Time-Life Books, 1986. . * Sword, Wiley. ''The Confederacy's Last Hurrah: Spring Hill, Franklin, and Nashville''. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas, 1993. . First published with the title ''Embrace an Angry Wind'' in 1992 by HarperCollins. * Welcher, Frank J. ''The Union Army, 1861–1865 Organization and Operations''. Vol. 2, ''The Western Theater''. Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 1993. .
National Park Service battle description
CWSAC Report Update
Further reading
* Hood, John Bell''Advance and Retreat: Personal Experiences in the United States and Confederate States Armies''
Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 1996. . First published 1880 for the Hood Orphan Memorial Fund by G. T. Beauregard. * Shellenberger, Capt. John K
"The Battle of Spring Hill, Tennessee"
presentation to the Commandery of the State of Missouri,
MOLLUS
The Military Order of the Loyal Legion of the United States (MOLLUS), or, simply, the Loyal Legion, is a United States military order organized on April 15, 1865, by three veteran officers of the Union Army. The original membership was consisted ...
, February 2, 1907.
*Gillum, Jamie. ''Twenty-five Hours to Tragedy: The Battle of Spring Hill and Operations on November 29, 1864: Precursor to the Battle of Franklin''. Jamie Gillum, 2014. .
External links
Spring Hill Battlefield Page
Battle maps, photos, history articles, and battlefield news ( CWPT)
Animated history of the Franklin-Nashville Campaign
* {{authority control Spring Hill Spring Hill Spring Hill Spring Hill Maury County, Tennessee Spring Hill 1864 in Tennessee November 1864