Battle Of Big Hole on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Battle of the Big Hole was fought in
 After the
After the
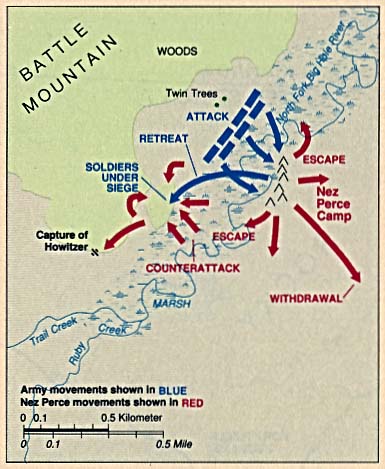 Between Gibbon's position and the Nez Perce encampment, which consisted of 89 tipis in a ''V''-shaped pattern, was the waist-deep and
Between Gibbon's position and the Nez Perce encampment, which consisted of 89 tipis in a ''V''-shaped pattern, was the waist-deep and 
 The battle was costly for both sides. Gibbon's force was unfit to pursue the Nez Perce. Gibbon suffered 29 dead (23 soldiers and six civilian volunteers) and 40 wounded (36 soldiers and four civilians) of whom two later died. His casualties amounted to more than 30 percent of his force. No precise estimate of Nez Perce casualties exists although their total dead probably amounted to between 70 and 90, of whom less than 33 were warriors and most were women and children. Yellow Wolf claimed that only 12 "real fighters, but our best" died in the battle. Chief Joseph and his brother Ollokot's wives were wounded.
The battle was costly for both sides. Gibbon's force was unfit to pursue the Nez Perce. Gibbon suffered 29 dead (23 soldiers and six civilian volunteers) and 40 wounded (36 soldiers and four civilians) of whom two later died. His casualties amounted to more than 30 percent of his force. No precise estimate of Nez Perce casualties exists although their total dead probably amounted to between 70 and 90, of whom less than 33 were warriors and most were women and children. Yellow Wolf claimed that only 12 "real fighters, but our best" died in the battle. Chief Joseph and his brother Ollokot's wives were wounded.
7th U.S. Infantry *Left Battalion **Company A: Captain William Logan, ''in reserve'' **Company K: Captain James M. J. Sanno **Company D: Captain Richard Comba, ''senior battalion officer'' **Scouts and Volunteers: Lieutenant James H. Bradley **Bitterroot Civilian Volunteers: "Captain" John B. Catlin, ''attached to Bradley's command'' *Right Battalion **Company F: Captain Constant Williams **Company G: Captain George Browning **Company I: Captain Charles C. Rawn, ''senior battalion officer'' 2nd U.S. Cavalry *Company L, detachment: (attached to Bradley's command) Artillery *12lb Mountain Howitzer: Sgt Daley, Sgt Fredericksp.257
/ref>
Nez Perce National Historic Trail
Nez Perce Trail Foundation
{{DEFAULTSORT:Big Hole, Battle Of The Battles in 1877 1877 in Montana Territory 1877 in the United States Battles of the Nez Perce War August 1877 Battles in Montana
Montana Territory
The Territory of Montana was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 26, 1864, until November 8, 1889, when it was admitted as the 41st state in the Union as the state of Montana.
Original boundaries
...
, August 9–10, 1877, between the United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary Land warfare, land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of th ...
and the Nez Perce
The Nez Perce (; autonym in Nez Perce language: , meaning 'we, the people') are an Indigenous people of the Plateau who still live on a fraction of the lands on the southeastern Columbia River Plateau in the Pacific Northwest. This region h ...
tribe of Native Americans during the Nez Perce War
The Nez Perce War was an armed conflict in 1877 in the Western United States that pitted several bands of the Nez Perce tribe of Native Americans and their allies, a small band of the ''Palouse'' tribe led by Red Echo (''Hahtalekin'') and ...
. Both sides suffered heavy casualties. The Nez Perce withdrew in good order from the battlefield and continued their long fighting retreat that would result in their attempt to reach Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
and asylum.
Located in Beaverhead County, the battle site is between the continental divide
A continental divide is a drainage divide on a continent such that the drainage basin on one side of the divide feeds into one ocean or sea, and the basin on the other side either feeds into a different ocean or sea, or else is endorheic, not ...
at Chief Joseph Pass
Chief Joseph Pass ( elev. ) is a mountain pass on the continental divide of the Rocky Mountains in the northwestern United States joining Lemhi County, Idaho, and Beaverhead County, Montana. The pass is in the Bitterroot Mountains and is trav ...
and the town of Wisdom
Wisdom, also known as sapience, is the ability to apply knowledge, experience, and good judgment to navigate life’s complexities. It is often associated with insight, discernment, and ethics in decision-making. Throughout history, wisdom ha ...
.
Background
 After the
After the Battle of the Clearwater
The Battle of the Clearwater (July 11–12, 1877) was a battle in the Idaho Territory between the Nez Perce under Chief Joseph and the United States Army. Under General O. O. Howard, the army surprised a Nez Perce village; the Nez Perce counte ...
in Idaho Territory
The Territory of Idaho was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 3, 1863, until July 3, 1890, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as Idaho.
History
1860s
The territory ...
on July 11–12, the Nez Perce leaders led their people on an extensive trek to escape the soldiers of Brigadier General Oliver Otis Howard
Oliver Otis Howard (November 8, 1830 – October 26, 1909) was a career United States Army officer and a Union general in the Civil War. As a brigade commander in the Army of the Potomac, Howard lost his right arm while leading his men again ...
. The Nez Perce crossed into Montana Territory via rugged Lolo Pass, and after a brief confrontation at Fort Fizzle on July 28, they entered the Bitterroot Valley
The Bitterroot Valley is located in southwestern Montana, along the Bitterroot River between the Bitterroot Range and Sapphire Mountains, in the Northwestern United States.
Geography
The valley extends approximately from Lost Trail Pass in I ...
and proceeded southward. Looking Glass
A mirror, also known as a looking glass, is an object that Reflection (physics), reflects an image. Light that bounces off a mirror forms an image of whatever is in front of it, which is then focused through the lens of the eye or a camera ...
seems to have taken over leadership from Chief Joseph
''Hin-mah-too-yah-lat-kekt'' (or ''hinmatóowyalahtq̓it'' in Americanist orthography; March 3, 1840 – September 21, 1904), popularly known as Chief Joseph, Young Joseph, or Joseph the Younger, was a leader of the wal-lam-wat-kain (Wallowa) ...
; he pledged to the white settlers in the Bitterroot Valley that the Nez Perce would pass through their valley without violence and they did so, even trading and purchasing supplies from white merchants.
Looking Glass persuaded the Nez Perce that Howard was far behind and that the citizens of Montana did not want war with them. Thus, their progress was leisurely and they took few precautions for defense, not sending out scouts or setting pickets to guard their encampments. They left the Bitterroot Valley, crossed a mountain range, and camped in the Big Hole Basin, pausing to replenish their tipi
A tipi or tepee ( ) is a conical lodge tent that is distinguished from other conical tents by the smoke flaps at the top of the structure, and historically made of animal hides or pelts or, in more recent generations, of canvas stretched on ...
poles from the surrounding forest. The Nez Perce numbered about 750 people in all with about 200 warriors.
Unknown to the Nez Perce, Colonel John Gibbon
John Gibbon (April 20, 1827 – February 6, 1896) was a career United States Army officer who fought in the American Civil War and the Indian Wars.
Early life
Gibbon was born in the Holmesburg, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, Holmesburg section ...
had left Fort Shaw with 161 officers and men and one howitzer. Following the trail of the Nez Perce he collected 45 civilian volunteers in the Bitterroot Valley. On August 8, a detachment led by Lieutenant James Bradley discovered the Nez Perce camp along the North Fork of the Big Hole River. That night Gibbon marched overland to the Nez Perce camp, reaching it at dawn, leaving his howitzer
The howitzer () is an artillery weapon that falls between a cannon (or field gun) and a mortar. It is capable of both low angle fire like a field gun and high angle fire like a mortar, given the distinction between low and high angle fire break ...
and a pack train to follow behind with a guard of twenty men. He had come to fight: his orders were no prisoners and no negotiations.
Battle
 Between Gibbon's position and the Nez Perce encampment, which consisted of 89 tipis in a ''V''-shaped pattern, was the waist-deep and
Between Gibbon's position and the Nez Perce encampment, which consisted of 89 tipis in a ''V''-shaped pattern, was the waist-deep and willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, of the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 350 species (plus numerous hybrids) of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions.
Most species are known ...
-lined North Fork of the Big Hole River
The Big Hole River is a tributary of the Jefferson River, approximately 153 miles (246 km) long, in Beaverhead County, Montana, Beaverhead County, in southwestern Montana, United States. It is the last habitat in the contiguou ...
. Approaching the Nez Perce encampment on foot at dawn, Gibbon's men encountered an old Nez Perce man and killed him. The soldiers crossed the river and rushed into the village and began firing into the tipis where most of the Nez Perce were still sleeping. The Indians were taken by surprise and fled in all directions. Gibbon's men fired indiscriminately at men, women, and children – although some of the women were said to have been armed and shooting back at the soldiers. Lieutenant James H. Bradley, leading Gibbon's left wing, was killed early in the battle. Leaderless, his men did not continue their advance and left the northern part of the village unoccupied, giving a refuge and a rallying point to the Nez Perce.
Gibbon halted his men in their pursuit, not wishing his force to be scattered, and ordered them to burn the tipis. This proved difficult to do and the pause gave the Nez Perce time to regroup. The voices of White Bird and Looking Glass rallying their men from the opposite end of the village were heard by the soldiers. From sheltered positions the Nez Perce began to return fire. Gibbon's horse was hit and he was wounded in the leg and several other soldiers were killed. As usual, the Nez Perce's marksmanship was excellent – although, according to the warrior Yellow Wolf, most of the Nez Perce warriors had fled without their weapons and only a few were armed.
Twenty minutes after his entry into the village, Gibbon, realizing that he was in an "untenable position", ordered a retreat across the river to a timbered area 300 or 400 yards distant and out of view of the village. The soldiers dug rifle pits and constructed rock and log barriers. At this point Gibbon's howitzer appeared on the battlefield and fired two or three ineffectual rounds. The Nez Perce killed or wounded most of the howitzer crew, who abandoned the gun, but not before dismantling it.
Gibbon feared that the Nez Perce, who he believed outnumbered him, although they probably did not, would overrun his position, but instead the battle settled down into a sniping duel between about 60 Nez Perce under Ollokot
Ollokot (Ollikut álok'at) (born 1840s – died 30 September 1877), was a war leader of the Wallowa band of Nez Perce Indians and a leader of the young warriors in the Nez Perce War in 1877.
Early life
Ollokot was the son of Tuekakas or Old ...
and the soldiers. The Nez Perce had collected arms and ammunition left behind by the soldiers in their retreat. At one point the Nez Perce set fires and attempted to burn the soldiers out of their position, but the wind shifted and the fire burned itself out. That afternoon the Nez Perce continued sniping at the soldiers while their women packed up, gathered the horse herd, and moved out south, going about 18 miles to Lake Creek where they made camp – this time with defensive works.
Gibbon had serious problems that night. His men had no food, save a dead horse, no water, and many seriously wounded men to tend to. A little water was obtained from the river by volunteers who crept through the Indian lines. Several of the civilian volunteers had had enough of the battle and slipped away. Gibbon sent out messengers to search for the much larger force of Howard, who was following him, and request immediate relief.
The next day, August 10, twenty to thirty Nez Perce sharpshooters kept the soldiers holed up in their fortifications all day. The Nez Perce warriors left that night, leaving Gibbon and his soldiers alone but immobile on the battlefield. Howard, and an advance party of 29 cavalrymen and 17 Bannock
Bannock may mean:
* Bannock (British and Irish food), a kind of bread, cooked on a stone or griddle served mainly in Scotland but consumed throughout the British Isles
* Bannock (Indigenous American food), various types of bread, usually prepare ...
scouts, found Gibbon the next morning after a ride in a day and a night.
Casualties
 The battle was costly for both sides. Gibbon's force was unfit to pursue the Nez Perce. Gibbon suffered 29 dead (23 soldiers and six civilian volunteers) and 40 wounded (36 soldiers and four civilians) of whom two later died. His casualties amounted to more than 30 percent of his force. No precise estimate of Nez Perce casualties exists although their total dead probably amounted to between 70 and 90, of whom less than 33 were warriors and most were women and children. Yellow Wolf claimed that only 12 "real fighters, but our best" died in the battle. Chief Joseph and his brother Ollokot's wives were wounded.
The battle was costly for both sides. Gibbon's force was unfit to pursue the Nez Perce. Gibbon suffered 29 dead (23 soldiers and six civilian volunteers) and 40 wounded (36 soldiers and four civilians) of whom two later died. His casualties amounted to more than 30 percent of his force. No precise estimate of Nez Perce casualties exists although their total dead probably amounted to between 70 and 90, of whom less than 33 were warriors and most were women and children. Yellow Wolf claimed that only 12 "real fighters, but our best" died in the battle. Chief Joseph and his brother Ollokot's wives were wounded.
Aftermath
Gibbon's success in surprising the Nez Perce caused Looking Glass's prestige as a leader to plummet. He had promised them they would be safe in Montana and instead nearly every Nez Perce family had suffered a loss in the battle. Chief Joseph seems to have resumed his role as the principal leader of the Nez Perce although Looking Glass would continue to be a battlefield leader. For the Nez Perce the losses in the battle were grievous. They had anticipated that, by leavingIdaho
Idaho ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest and Mountain states, Mountain West subregions of the Western United States. It borders Montana and Wyoming to the east, Nevada and Utah to the south, and Washington (state), ...
, they might leave the war behind them and live peacefully. Now, they knew that they could expect no quarter in future battles. Howard's forces, newly arrived on the battlefield, took up the pursuit and followed Joseph toward Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park is a List of national parks of the United States, national park of the United States located in the northwest corner of Wyoming, with small portions extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U ...
. The Nez Perce again clashed with the army ten days later on August 20 at the Battle of Camas Meadows.
The battlefield is preserved in the Big Hole National Battlefield
Big Hole National Battlefield preserves a battlefield in the western United States, located in Beaverhead County, Montana. In 1877, the Nez Perce fought a delaying action against the U.S. Army's 7th Infantry Regiment here on August 9 and 10, du ...
unit of the Nez Perce National Historical Park
The Nez Perce National Historical Park is a United States National Historical Park comprising 38 sites located across the states of Idaho, Montana, Oregon, and Washington (state), Washington, which include traditional aboriginal lands of the Nez ...
, located along State Highway 43.
Order of Battle
District of Western Montana: ColonelJohn Gibbon
John Gibbon (April 20, 1827 – February 6, 1896) was a career United States Army officer who fought in the American Civil War and the Indian Wars.
Early life
Gibbon was born in the Holmesburg, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, Holmesburg section ...
7th U.S. Infantry *Left Battalion **Company A: Captain William Logan, ''in reserve'' **Company K: Captain James M. J. Sanno **Company D: Captain Richard Comba, ''senior battalion officer'' **Scouts and Volunteers: Lieutenant James H. Bradley **Bitterroot Civilian Volunteers: "Captain" John B. Catlin, ''attached to Bradley's command'' *Right Battalion **Company F: Captain Constant Williams **Company G: Captain George Browning **Company I: Captain Charles C. Rawn, ''senior battalion officer'' 2nd U.S. Cavalry *Company L, detachment: (attached to Bradley's command) Artillery *12lb Mountain Howitzer: Sgt Daley, Sgt Fredericks
/ref>
References
Sources
* *External links
Nez Perce National Historic Trail
Nez Perce Trail Foundation
{{DEFAULTSORT:Big Hole, Battle Of The Battles in 1877 1877 in Montana Territory 1877 in the United States Battles of the Nez Perce War August 1877 Battles in Montana