Battle At Pharsalus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Battle of Pharsalus was the decisive battle of
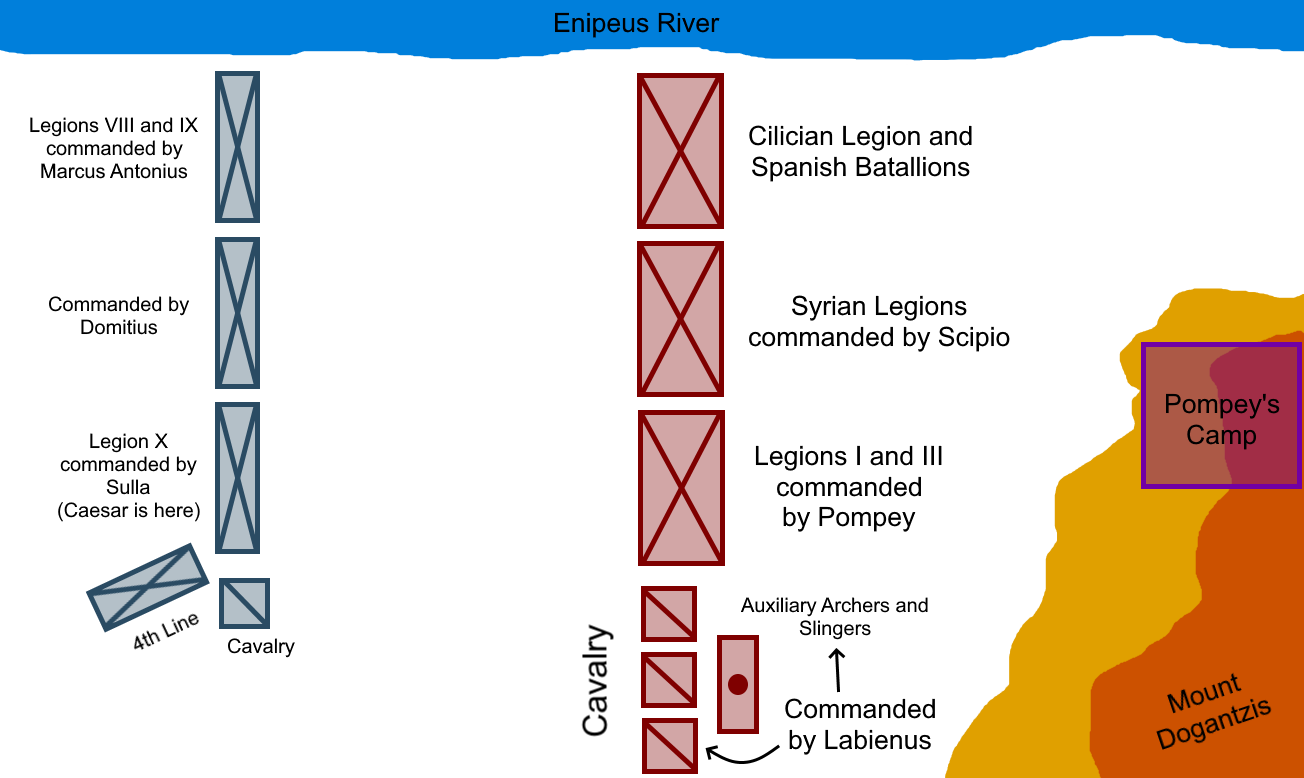 The two generals deployed their legions in the traditional three lines (''
The two generals deployed their legions in the traditional three lines (''
"Palaepharsalus, Pharsalus, Pharsalia"
''Classical Philology'', Vol. 46, No. 2 (Apr., 1951), pp. 111–115. * Gwatkin, William E. (1956)
"Some Reflections on the Battle of Pharsalus"
''Transactions and Proceedings of the American Philological Association'', Vol. 87. * James, Steven (2016)
"48 BC: The Battle of Pharsalus"
* Lucas, Frank Laurence (1921)
"The Battlefield of Pharsalos"
''Annual of the British School at Athens'', No. XXIV, 1919–21
* Nordling, John G. (2006)
"Caesar's Pre-Battle Speech at Pharsalus (B.C. 3.85.4): ''Ridiculum Acri Fortius ... Secat Res''"
''The Classical Journal'', Vol. 101, No. 2 (Dec. – Jan., 2005/2006), pp. 183–189. * Pelling, C.B.R. (1973)
"Pharsalus"
''Historia: Zeitschrift für Alte Geschichte''. Bd. 22, H. 2 (2nd Qtr., 1973), pp. 249–259. * Perrin, B. (1885)
"Pharsalia, Pharsalus, Palaepharsalus"
''The American Journal of Philology'', Vol. 6, No. 2 (1885), pp. 170–189. * Postgate, J.P. (1905)
"Pharsalia Nostra"
''The Classical Review'', Vol. 19, No. 5 (Jun., 1905), pp. 257–260. * Rambaud, Michel (1955)
"Le Soleil de Pharsale"
''Historia: Zeitschrift für Alte Geschichte '', Vol. 3, No. 4. * Searle, Arthur (1907)
"Note on the Battle of Pharsalus"
''Harvard Studies in Classical Philology'', Vol. 18 (1907), pp. 213–218.
Caesar's account of the battle
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pharsalus, Battle of 48 BC 40s BC conflicts 1st-century BC battles 1st century BC in Greece Battles in ancient Thessaly Battles involving the Roman Republic Battles of Caesar's civil war Macedonia (Roman province) Caesar's invasion of Macedonia Pompey Farsala
Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was a civil war during the late Roman Republic between two factions led by Julius Caesar and Pompey. The main cause of the war was political tensions relating to Caesar's place in the Republic on his expected ret ...
fought on 9 August 48 BC near Pharsalus Pharsalus may refer to:
* ''Pharsalus'' (planthopper), a genus of insects in the family Ricaniidae
* Farsala
Farsala (), known in Antiquity as Pharsalos (, ), is a town in southern Thessaly, in Greece. Farsala is located in the southern part ...
in Central Greece. Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil wa ...
and his allies formed up opposite the army of the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
under the command of Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey ( ) or Pompey the Great, was a Roman general and statesman who was prominent in the last decades of the Roman Republic. ...
. Pompey had the backing of a majority of Roman senators and his army significantly outnumbered the veteran Caesarian legions.
Pressured by his officers, Pompey reluctantly engaged in battle and suffered an overwhelming defeat, ultimately fleeing the camp and his men, disguised as an ordinary citizen. Eventually making his way to Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, he was assassinated upon his arrival at the order of Ptolemy XIII
Ptolemy XIII Theos Philopator (, ''Ptolemaĩos''; c. 62 BC – 13 January 47 BC) was Pharaoh of Egypt from 51 to 47 BC, and one of the last members of the Ptolemaic dynasty (305–30 BC). He was the son of Ptolemy XII and the brother of and co ...
.
Prelude
Following the start of theCivil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
, Caesar had captured Rome, forced Pompey and his allies to withdraw from Italy, and defeated Pompey's legates in Spain. In the campaign season for 48 BC, Caesar crossed the Adriatic and advanced on Dyrrachium. There, he besieged it, but was defeated.
Caesar then withdrew east into Thessaly, partly to relieve one of his legates from attack by Metellus Scipio
Quintus Caecilius Metellus Pius Scipio (c. 95 – 46 BC), often referred to as Metellus Scipio, was a Roman senator and military commander. During the civil war between Julius Caesar and the senatorial faction led by Pompey, he was a staunch sup ...
's forces arriving from Syria. He besieged Gomphi after it resisted him. Pompey pursued, seeking to spare Italy from invasion by concluding the war on Greek soil, to prevent Caesar from defeating Metellus Scipio's forces arriving from Syria, and under pressure from his overconfident allies who accused him of prolonging the war to extend his command.
Date
The decisive battle took place on 9 August 48 BC according to the Republican calendar.Location
The location of the battlefield was for a long time the subject of controversy among scholars. Caesar himself, in his ''Commentarii de Bello Civili
'' Commentarii de Bello Civili'' (''Commentaries on the Civil War''), or ''Bellum Civile'', is an account written by Julius Caesar of his war against Gnaeus Pompeius and the Roman Senate. It consists of three books covering the events of 49– ...
'', mentions few place-names; and although the battle is called after Pharsalos by modern authors, four ancient writers – the author of the ''Bellum Alexandrinum'' (48.1), Frontinus
Sextus Julius Frontinus (c. 40 – 103 AD) was a Roman civil engineer, author, soldier and senator of the late 1st century AD. He was a successful general under Domitian, commanding forces in Roman Britain, and on the Rhine and Danube frontier ...
(''Strategemata'' 2.3.22), Eutropius (20), and Orosius
Paulus Orosius (; born 375/385 – 420 AD), less often Paul Orosius in English, was a Roman priest, historian and theologian, and a student of Augustine of Hippo. It is possible that he was born in '' Bracara Augusta'' (now Braga, Portugal), ...
(6.15.27) – place it specifically at ''Palae''pharsalus ("Old" Pharsalus). Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
in his ''Geographica'' (''Γεωγραφικά'') mentions both old and new Pharsaloi, and notes that the Thetideion, the temple to Thetis
Thetis ( , or ; ) is a figure from Greek mythology with varying mythological roles. She mainly appears as a sea nymph, a goddess of water, and one of the 50 Nereids, daughters of the ancient sea god Nereus.
When described as a Nereid in Cl ...
south of Scotoussa, was near both. In 198 BC, in the Second Macedonian War
The Second Macedonian War (200–197 BC) was fought between Macedon, led by Philip V of Macedon, and Rome, allied with Pergamon and Rhodes. Philip was defeated and was forced to abandon all possessions in southern Greece, Thrace and Asia Minor. ...
, Philip V of Macedon
Philip V (; 238–179 BC) was king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon from 221 to 179 BC. Philip's reign was principally marked by the Social War (220–217 BC), Social War in Greece (220-217 BC) ...
sacked Palaepharsalos (Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding i ...
, ''Ab Urbe Condita
''Ab urbe condita'' (; 'from the founding of Rome, founding of the City'), or (; 'in the year since the city's founding'), abbreviated as AUC or AVC, expresses a date in years since 753 BC, 753 BC, the traditional founding of Rome. It is ...
'' 32.13.9), but left new Pharsalos untouched. These two details perhaps imply that the two cities were not close neighbours. Many scholars, therefore, unsure of the site of Palaepharsalos, followed Appian
Appian of Alexandria (; ; ; ) was a Greek historian with Roman citizenship who prospered during the reigns of the Roman Emperors Trajan, Hadrian, and Antoninus Pius.
He was born c. 95 in Alexandria. After holding the senior offices in the pr ...
(2.75) and located the battle of 48 BC south of the Enipeus or close to Pharsalos (today's Pharsala
Farsala (), known in Antiquity as Pharsalos (, ), is a town in southern Thessaly, in Greece. Farsala is located in the southern part of Larissa regional unit, and is one of its largest settlements. Farsala is an economic and agricultural centre ...
). Among the scholars arguing for the south side are Béquignon (1928), Bruère (1951), and Gwatkin (1957).
An increasing number of scholars, however, have argued for a location on the north side of the river. These include Perrin (1885), Holmes (1908), Lucas
Lucas or LUCAS may refer to:
People
* Lucas (surname)
* Lucas (given name)
Arts and entertainment
* Luca Family Singers, or the Lucas, a 19th-century African-American singing group
* Lucas, a 1960s Swedish pop group formed by Janne Lucas Perss ...
(1921), Rambaud (1955), Pelling (1973), Morgan (1983), and Sheppard (2006). John D. Morgan in his definitive "Palae-pharsalus – the Battle and the Town", shows that Palaepharsalus cannot have been at Palaiokastro, as Béquignon thought (a site abandoned c. 500 BC), nor the hill of Fatih-Dzami within the walls of Pharsalus itself, as Kromayer (1903, 1931) and Gwatkin thought; and Morgan argues that it is probably also not the hill of Khtouri (Koutouri), some 7 miles north-west of Pharsalus on the south bank of the Enipeus, as Lucas and Holmes thought, although that remains a possibility. However, Morgan believes it is most likely to have been the hill just east of the village of (Krini Larisas, formerly Driskoli) very close to the ancient highway from Larisa to Pharsalus. This site is some north of Pharsalus, and three miles north of the river Enipeus, and not only has remains dating back to Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
times but also signs of habitation in the 1st century BC and later. The identification seems to be confirmed by the location of a place misspelled "Palfari" or "Falaphari" shown on a medieval route map of the road just north of Pharsalus. Morgan places Pompey's camp a mile to the west of Krini, just north of the village of Avra (formerly Sarikayia), and Caesar's camp some four miles to the east-south-east of Pompey's. According to this reconstruction, therefore, the battle took place not between Pharsalus and the river, as Appian wrote, but between Old Pharsalus and the river.
An interesting side-note on Palaepharsalus is that it was sometimes identified in ancient sources with Phthia
Phthia (; or Φθίη ''Phthía, Phthíē'') was a city or district in ancient Thessaly according to Greek mythology.
In Literature
It is frequently mentioned in Homer's ''Iliad'' as the home of the Myrmidons, the contingent led by Achilles i ...
, the home of Achilles
In Greek mythology, Achilles ( ) or Achilleus () was a hero of the Trojan War who was known as being the greatest of all the Greek warriors. The central character in Homer's ''Iliad'', he was the son of the Nereids, Nereid Thetis and Peleus, ...
. Near Old and New Pharsalus was a "Thetideion", or temple dedicated to Thetis
Thetis ( , or ; ) is a figure from Greek mythology with varying mythological roles. She mainly appears as a sea nymph, a goddess of water, and one of the 50 Nereids, daughters of the ancient sea god Nereus.
When described as a Nereid in Cl ...
, the mother of Achilles
In Greek mythology, Achilles ( ) or Achilleus () was a hero of the Trojan War who was known as being the greatest of all the Greek warriors. The central character in Homer's ''Iliad'', he was the son of the Nereids, Nereid Thetis and Peleus, ...
. However, Phthia
Phthia (; or Φθίη ''Phthía, Phthíē'') was a city or district in ancient Thessaly according to Greek mythology.
In Literature
It is frequently mentioned in Homer's ''Iliad'' as the home of the Myrmidons, the contingent led by Achilles i ...
, the kingdom of Achilles and his father Peleus
In Greek mythology, Peleus (; Ancient Greek: Πηλεύς ''Pēleus'') was a hero, king of Phthia, husband of Thetis and the father of their son Achilles. This myth was already known to the hearers of Homer in the late 8th century BC.
Biogra ...
, is more usually identified with the lower valley of the Spercheios
The Spercheios (, ''Sperkheiós''), also known as the Spercheus from its Latinization of names, Latin name, is a river in Phthiotis in Central Greece (geographic region), central Greece. It is long, and its drainage area is . It was worshipped a ...
river, much further south.
Name of the battle
Although it is often called the Battle of Pharsalus by modern historians, this name was rarely used in the ancient sources. Caesar merely calls it the ''proelium in Thessaliā'' ("battle in Thessalia");Marcus Tullius Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, orator, writer and Academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises tha ...
and Hirtius
Aulus Hirtius (; – 43 BC) was consul of the Roman Republic in 43 BC and a writer on military subjects. He was killed during his consulship in battle against Mark Antony at the Battle of Mutina.
Biography
He was a legate of Julius Caesar's st ...
call it the ''Pharsālicum proelium'' ("Pharsalic battle") or ''pugna Pharsālia'' ("Pharsalian battle"), and similar expressions are also used in other authors. But Hirtius (if he is the author of the de Bello Alexandrino
''De Bello Alexandrino'' (also ''Bellum Alexandrinum''; ''On the Alexandrine War'') is a Latin work continuing Julius Caesar's commentaries, '' De Bello Gallico'' and '' De Bello Civili''. It details Caesar's campaigns in Alexandria and Asia.
A ...
) also refers to the battle as having taken place at ''Palaepharsalus'', and this name also occurs in Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
, Frontinus
Sextus Julius Frontinus (c. 40 – 103 AD) was a Roman civil engineer, author, soldier and senator of the late 1st century AD. He was a successful general under Domitian, commanding forces in Roman Britain, and on the Rhine and Danube frontier ...
, Eutropius, and Orosius
Paulus Orosius (; born 375/385 – 420 AD), less often Paul Orosius in English, was a Roman priest, historian and theologian, and a student of Augustine of Hippo. It is possible that he was born in '' Bracara Augusta'' (now Braga, Portugal), ...
. Lucan
Marcus Annaeus Lucanus (3 November AD 39 – 30 April AD 65), better known in English as Lucan (), was a Roman poet, born in Corduba, Hispania Baetica (present-day Córdoba, Spain). He is regarded as one of the outstanding figures of the Imper ...
in his poem about the Civil War regularly uses the name ''Pharsālia'', and this term is also used by the epitomiser of Livy and by Tacitus.Morgan (1983), p. 27. The only ancient sources to refer to the battle as being at Pharsalus are a certain calendar known as the Fasti Amiternini and the Greek authors Plutarch
Plutarch (; , ''Ploútarchos'', ; – 120s) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo (Delphi), Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', ...
, Appian
Appian of Alexandria (; ; ; ) was a Greek historian with Roman citizenship who prospered during the reigns of the Roman Emperors Trajan, Hadrian, and Antoninus Pius.
He was born c. 95 in Alexandria. After holding the senior offices in the pr ...
, and Polyaenus
Polyaenus or Polyenus ( ; see ae (æ) vs. e; , "much-praised") was a 2nd-century Roman Macedonian author and rhetorician, known best for his ''Stratagems in War'' (), which has been preserved. He was born in Bithynia, Asia Minor. The ''Suda'' c ...
. It has therefore been argued by some scholars that "Pharsalia" would be a more accurate name for the battle than Pharsalus.
Opposing armies
The total number of soldiers on each side is unknown because ancient accounts of the battle focused primarily on giving the numbers of Italian legionaries only, regarding allied non-citizen contingents as inferior and inconsequential. According to Caesar, his own army included 22,000 Romanlegionaries
The ancient Rome, Roman legionary (in Latin ''legionarius''; : ''legionarii'') was a citizen soldier of the Roman army. These soldiers would conquer and defend the territories of ancient Rome during the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Republic and ...
distributed throughout 80 cohorts (8 legions), alongside 1,000 Gallic and Germanic cavalry. All of Caesar's legions were understrength; some only had about a thousand men at the time of Pharsalus, due partly to losses at Dyrrhachium and partly to Caesar's wish to rapidly advance with a picked body as opposed to a ponderous movement with a large army. Another source adds that he had recruited Greek light infantry from Dolopia
Dolopia () is a mountainous region of Greece, located north of Aetolia.
Geography
Dolopia was located between Epirus and Thessaly, eventually absorbed into the latter. It was a mountainous district in the southwestern corner of Thessaly, lying bet ...
, Acarnania
Acarnania () is a region of west-central Greece that lies along the Ionian Sea, west of Aetolia, with the Achelous River for a boundary, and north of the gulf of Calydon, which is the entrance to the Gulf of Corinth. Today it forms the western part ...
and Aetolia
Aetolia () is a mountainous region of Greece on the north coast of the Gulf of Corinth, forming the eastern part of the modern regional unit of Aetolia-Acarnania.
Geography
The Achelous River separates Aetolia from Acarnania to the west; on ...
; these numbered no more than a few thousand. Caesar, Appian and Plutarch give Pompey an army of 45,000 Roman infantry. Osorius describes Pompey as having 88 cohorts of Roman infantry, which at full strength would come to 44,000 men, while Brunt and Wylie estimated Pompey's Roman infantry as being as 38,000 men, and Greenhalgh said they contained a maximum of 36,000.
It was in his auxiliary troops and in particular his cavalry, all of which vastly outnumbered Caesar's own, that Pompey had his greatest advantage. He seems to have had at his disposal anywhere between 5,000 and 7,000 cavalry, and thousands of archers, sling
Sling may refer to:
Places
*Sling, Anglesey, Wales
* Sling, Gloucestershire, England, a small village in the Forest of Dean
People with the name
* Otto Šling (1912–1952), repressed Czech communist functionary
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ...
ers and light infantrymen in general. These all formed a remarkably diverse group, including Gallic and Germanic horsemen alongside all polyglot peoples of the east – namely Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
, Thracians
The Thracians (; ; ) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area that today is shared betwee ...
, and Anatolians
The Anatolians were a group of Indo-European peoples who inhabited Anatolia as early as the 3rd millennium BC. Identified by their use of the now-extinct Anatolian languages, they were one of the oldest collective Indo-European ethno-linguistic ...
from the Balkans and Syrians
Syrians () are the majority inhabitants of Syria, indigenous to the Levant, most of whom have Arabic, especially its Levantine Arabic, Levantine and Mesopotamian Arabic, Mesopotamian dialects, as a mother tongue. The culture of Syria, cultural ...
, Phoenicians
Phoenicians were an ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syrian coast. They developed a maritime civi ...
and Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
from the Levant. To this heterogeneous force Pompey added horsemen conscripted from his own slaves. Many of the foreigners were serving under their own rulers, for more than a dozen despots and petty kings under Roman influence in the east were Pompey's personal clients and some elected to attend in person, or send proxies.
Caesarian legions
Caesar had the following legions with him: * the VI legion (later called Ferrata) veterans of his Gallic Wars * the VII legion (later called Claudia Pia Fidelis) veterans of his Gallic Wars * the VIII legion (later called Augusta) veterans of his Gallic Wars * the IX legion (later called Hispana) veterans of his Gallic Wars * the X legion (Equestris, later called Gemina) veterans of his Gallic Wars * the XI legion (later called Paterna and Claudia Pia Fidelis, the same title as the seventh) veterans of his Gallic Wars * the XII legion (later called Fulminata) veterans of his Gallic Wars * the XIII legion (later also called Gemina, the 'twin' to the tenth) veterans of his Gallic Wars The bulk of Caesar's army at Pharsalus was made up of his veterans from the Gallic Wars; very experienced, battle-hardened troops who were absolutely devoted to their commander.Deployment
 The two generals deployed their legions in the traditional three lines (''
The two generals deployed their legions in the traditional three lines (''triplex acies
Roman infantry tactics are the theoretical and historical deployment, formation, and manoeuvres of the Roman infantry from the start of the Roman Republic to the fall of the Western Roman Empire. The original Roman army was made up of ''hoplite, ...
''), with Pompey's right and Caesar's left flanks resting on river Enipeus. As the stream provided enough protection to that side, Pompey moved almost all of his cavalry, archers, and slingers to the left, to make the most of their numerical strength. Only a small force of 500–600 Pontic
Pontic, from the Greek ''pontos'' (, ), or "sea", may refer to:
The Black Sea Places
* The Pontic colonies, on its northern shores
* Pontus (region), a region on its southern shores
* The Pontic–Caspian steppe, steppelands stretching from nor ...
cavalry and some Cappadocia
Cappadocia (; , from ) is a historical region in Central Anatolia region, Turkey. It is largely in the provinces of Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde. Today, the touristic Cappadocia Region is located in Nevşehir ...
n light infantry was placed on his right flank. Pompey stationed his strongest legions in the center and wings of his infantry line, and dispersed some 2,000 re-enlisted veterans throughout the entire line in order to inspire the less experienced. The Pompeian cohorts were arrayed in an unusually thick formation, 10 men deep: their task was just to tie down the enemy foot while Pompey's cavalry, his key to victory, swept through Caesar's flank and rear. The column of legions was divided under command of three subordinates, with Lentulus
Lentulus may refer to:
* Gnaeus Cornelius Lentulus Clodianus, Roman senator and commander against Spartacus
* Publius Cornelius Lentulus Sura, Roman senator and Catilinarian conspirator
* Publius Cornelius Lentulus Spinther, Roman senator
* Lu ...
in charge of the left, Scipio of the center and Ahenobarbus the right. Labienus
Titus Labienus (17 March 45 BC) was a high-ranking military officer in the late Roman Republic. He served as tribune of the Plebs in 63 BC. Although mostly remembered as one of Julius Caesar's best lieutenants in Gaul and mentioned frequently ...
was entrusted with command of the cavalry charge, while Pompey himself took up a position behind the left wing in order to oversee the course of the battle.
Caesar also deployed his men in three lines, but, being outnumbered, had to thin his ranks to a depth of only six men, in order to match the frontage presented by Pompey. His left flank, resting on the Enipeus River, consisted of his battle-worn IX legion supplemented by the VIII legion, these were commanded by Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman people, Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the Crisis of the Roman Republic, transformation of the Roman Republic ...
. The VI, XII, XI and XIII formed the centre and were commanded by Domitius, then came the VII and upon his right he placed his favored X legion, giving Sulla
Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix (, ; 138–78 BC), commonly known as Sulla, was a Roman people, Roman general and statesman of the late Roman Republic. A great commander and ruthless politician, Sulla used violence to advance his career and his co ...
command of this flank – Caesar himself took his stand on the right, across from Pompey. Upon seeing the disposition of Pompey's army Caesar grew discomforted, and further thinned his third line in order to form a fourth line on his right: this to counter the onslaught of the enemy cavalry, which he knew his numerically inferior cavalry could not withstand. He gave this new line detailed instructions for the role they would play, hinting that upon them would rest the fortunes of the day, and gave strict orders to his third line not to charge until specifically ordered.
Battle
There was significant distance between the two armies, according to Caesar. Pompey ordered his men not to charge, but to wait until Caesar's legions came into close quarters; Pompey's adviser Gaius Triarius believed that Caesar's infantry would be fatigued and fall into disorder if they were forced to cover twice the expected distance of a battle march. Also, stationary troops were expected to be able to defend better againstpila
Pila may refer to:
Architecture
* Pila (architecture), a type of veranda in Sri Lankan farm houses
Places
*Pila, Buenos Aires, a town in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina
*Pila Partido, a country subdivision in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina
*P ...
throws. Seeing that Pompey's army was not advancing, Caesar's infantry under Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman people, Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the Crisis of the Roman Republic, transformation of the Roman Republic ...
and Gnaeus Domitius Calvinus
Gnaeus Domitius Calvinus was a Roman general, senator and consul (both in 53 BC and 40 BC) who was a loyal partisan of Caesar and Octavianus.
Biography
Domitius Calvinus came from a noble family and was elected consul for 53 BC, despite a n ...
started the advance. As Caesar's men neared throwing distance, without orders, they stopped to rest and regroup before continuing the charge; Pompey's right and centre line held as the two armies collided.
As Pompey's infantry fought, Labienus
Titus Labienus (17 March 45 BC) was a high-ranking military officer in the late Roman Republic. He served as tribune of the Plebs in 63 BC. Although mostly remembered as one of Julius Caesar's best lieutenants in Gaul and mentioned frequently ...
ordered the Pompeian cavalry on his left flank to attack Caesar's cavalry; as expected they successfully pushed back Caesar's cavalry. Caesar then revealed his hidden fourth line of infantry and surprised Pompey's cavalry charge; Caesar's men were ordered to leap up and use their pila
Pila may refer to:
Architecture
* Pila (architecture), a type of veranda in Sri Lankan farm houses
Places
*Pila, Buenos Aires, a town in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina
*Pila Partido, a country subdivision in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina
*P ...
to thrust at Pompey's cavalry instead of throwing them. Pompey's cavalry panicked and suffered hundreds of casualties, as Caesar's cavalry came about and charged after them. After failing to reform, the rest of Pompey's cavalry retreated to the hills, leaving the left wing of his legions exposed to the hidden troops as Caesar's cavalry wheeled around their flank. Caesar then ordered in his third line, containing his most battle-hardened veterans, to attack. This broke Pompey's left wing troops, who fled the battlefield.
After routing Pompey's cavalry, Caesar threw in his last line of reservesa move which at this point meant that the battle was more or less decided. Pompey lost the will to fight as he watched both cavalry and legions under his command break formation and flee from battle, and he retreated to his camp, leaving the rest of his troops at the centre and right flank to their own devices. He ordered the garrisoned auxiliaries to defend the camp as he gathered his family, loaded up gold, and threw off his general's cloak to make a quick escape. As the rest of Pompey's army were left confused, Caesar urged his men to end the day by routing the rest of Pompey's troops and capturing the Pompeian camp. They complied with his wishes; after finishing off the remains of Pompey's men, they furiously attacked the camp walls. The Thracians and the other auxiliaries who were left in the Pompeian camp, in total seven cohorts, defended bravely, but were not able to fend off the assault.
Caesar had won his greatest victory, claiming to have only lost about 200 soldiers and 30 centurions and assigning the Optimate losses to be 60,000 men.Caesar, BC III 99,1. These numbers seem suspiciously exaggerated with Appian
Appian of Alexandria (; ; ; ) was a Greek historian with Roman citizenship who prospered during the reigns of the Roman Emperors Trajan, Hadrian, and Antoninus Pius.
He was born c. 95 in Alexandria. After holding the senior offices in the pr ...
suggesting the Caesarean losses to be as many as 1,200 men and the Pompeian losses to be 6,000. In his history of the war, Caesar would praise his own men's discipline and experience, and remembered each of his centurion
In the Roman army during classical antiquity, a centurion (; , . ; , or ), was a commander, nominally of a century (), a military unit originally consisting of 100 legionaries. The size of the century changed over time; from the 1st century BC ...
s by name. He also questioned Pompey's decision not to charge.
Aftermath
Pompey, despairing of the defeat, fled with his advisors overseas to Mytilene and thence to Cilicia where he held a council of war; at the same time, Cato and supporters at Dyrrachium attempted first to hand over command toMarcus Tullius Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, orator, writer and Academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises tha ...
, who refused, deciding instead to return to Italy. They then regrouped at Corcyra and went thence to Libya. Others, including Marcus Junius Brutus
Marcus Junius Brutus (; ; 85 BC – 23 October 42 BC) was a Roman politician, orator, and the most famous of the assassins of Julius Caesar. After being adopted by a relative, he used the name Quintus Servilius Caepio Brutus, which was reta ...
sought Caesar's pardon, travelling over marshlands to Larissa where he was then welcomed graciously by Caesar in his camp. Pompey's council of war decided to flee to Egypt, which had in the previous year supplied him with military aid.
In the aftermath of the battle, Caesar captured Pompey's camp and burned Pompey's correspondence. He then announced that he would forgive all who asked for mercy. Pompeian naval forces in the Adriatic and Italy mostly withdrew or surrendered.
Hearing of Pompey's flight to Egypt, Caesar remained in hot pursuit, first landing in Asia and reaching Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
on 2 October 48 BC, where he learnt of Pompey's murder and then was embroiled in a dynastic dispute between Ptolemy XIII
Ptolemy XIII Theos Philopator (, ''Ptolemaĩos''; c. 62 BC – 13 January 47 BC) was Pharaoh of Egypt from 51 to 47 BC, and one of the last members of the Ptolemaic dynasty (305–30 BC). He was the son of Ptolemy XII and the brother of and co ...
and Cleopatra
Cleopatra VII Thea Philopator (; The name Cleopatra is pronounced , or sometimes in both British and American English, see and respectively. Her name was pronounced in the Greek dialect of Egypt (see Koine Greek phonology). She was ...
.
Importance
Paul K. Davis wrote that "Caesar's victory took him to the pinnacle of power, effectively ending the Republic." The battle itself did not end the civil war but it was decisive and gave Caesar a much needed boost in legitimacy. Until then much of the Roman world outside Italy supported Pompey and his allies due to the extensive list of clients he held in all corners of the Republic. After Pompey's defeat former allies began to align themselves with Caesar as some came to believe the gods favored him, while for others it was simple self-preservation. The ancients took great stock in success as a sign of favoritism by the gods. This is especially true of success in the face of almost certain defeat – as Caesar experienced at Pharsalus. This allowed Caesar to parlay this single victory into a huge network of willing clients to better secure his hold over power and force the Optimates into near exile in search for allies to continue the fight against Caesar.In popular culture
The battle gives its name to the following artistic, geographical, and business concerns: * ''Pharsalia
''De Bello Civili'' (; ''On the Civil War''), more commonly referred to as the ''Pharsalia'' (, neuter plural), is a Latin literature, Roman Epic poetry, epic poem written by the poet Lucan, detailing the Caesar's civil war, civil war between Ju ...
'', a poem by Lucan
Marcus Annaeus Lucanus (3 November AD 39 – 30 April AD 65), better known in English as Lucan (), was a Roman poet, born in Corduba, Hispania Baetica (present-day Córdoba, Spain). He is regarded as one of the outstanding figures of the Imper ...
* Pharsalia, New York
Pharsalia is a town in Chenango County, New York, United States. The population was 593 at the 2010 census. The town was named after Pharsalia, which is a commonly accepted name of the decisive battle in the Great Roman Civil War, where Julius ...
, U.S.
* Pharsalia Technologies, Inc.
In Alexandre Dumas
Alexandre Dumas (born Alexandre Dumas Davy de la Pailleterie, 24 July 1802 – 5 December 1870), also known as Alexandre Dumas , was a French novelist and playwright.
His works have been translated into many languages and he is one of the mos ...
' ''The Three Musketeers
''The Three Musketeers'' () is a French historical adventure novel written and published in 1844 by French author Alexandre Dumas. It is the first of the author's three d'Artagnan Romances. As with some of his other works, he wrote it in col ...
'', the author makes reference to Caesar's purported order that his men try to cut the faces of their opponents – their vanity supposedly being of more value to them than their lives.
In Mankiewicz's 1963 film ''Cleopatra
Cleopatra VII Thea Philopator (; The name Cleopatra is pronounced , or sometimes in both British and American English, see and respectively. Her name was pronounced in the Greek dialect of Egypt (see Koine Greek phonology). She was ...
'', the immediate aftermath of Pharsalus is used as an opening scene to set the action in motion.
Notes
Citations
References
* * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Bruère, Richard Treat, (1951)"Palaepharsalus, Pharsalus, Pharsalia"
''Classical Philology'', Vol. 46, No. 2 (Apr., 1951), pp. 111–115. * Gwatkin, William E. (1956)
"Some Reflections on the Battle of Pharsalus"
''Transactions and Proceedings of the American Philological Association'', Vol. 87. * James, Steven (2016)
"48 BC: The Battle of Pharsalus"
* Lucas, Frank Laurence (1921)
"The Battlefield of Pharsalos"
''Annual of the British School at Athens'', No. XXIV, 1919–21
* Nordling, John G. (2006)
"Caesar's Pre-Battle Speech at Pharsalus (B.C. 3.85.4): ''Ridiculum Acri Fortius ... Secat Res''"
''The Classical Journal'', Vol. 101, No. 2 (Dec. – Jan., 2005/2006), pp. 183–189. * Pelling, C.B.R. (1973)
"Pharsalus"
''Historia: Zeitschrift für Alte Geschichte''. Bd. 22, H. 2 (2nd Qtr., 1973), pp. 249–259. * Perrin, B. (1885)
"Pharsalia, Pharsalus, Palaepharsalus"
''The American Journal of Philology'', Vol. 6, No. 2 (1885), pp. 170–189. * Postgate, J.P. (1905)
"Pharsalia Nostra"
''The Classical Review'', Vol. 19, No. 5 (Jun., 1905), pp. 257–260. * Rambaud, Michel (1955)
"Le Soleil de Pharsale"
''Historia: Zeitschrift für Alte Geschichte '', Vol. 3, No. 4. * Searle, Arthur (1907)
"Note on the Battle of Pharsalus"
''Harvard Studies in Classical Philology'', Vol. 18 (1907), pp. 213–218.
External links
Caesar's account of the battle
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pharsalus, Battle of 48 BC 40s BC conflicts 1st-century BC battles 1st century BC in Greece Battles in ancient Thessaly Battles involving the Roman Republic Battles of Caesar's civil war Macedonia (Roman province) Caesar's invasion of Macedonia Pompey Farsala