Battery Energy Storage System on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A battery energy storage system (BESS), battery storage power station, battery energy grid storage (BEGS) or battery grid storage is a type of
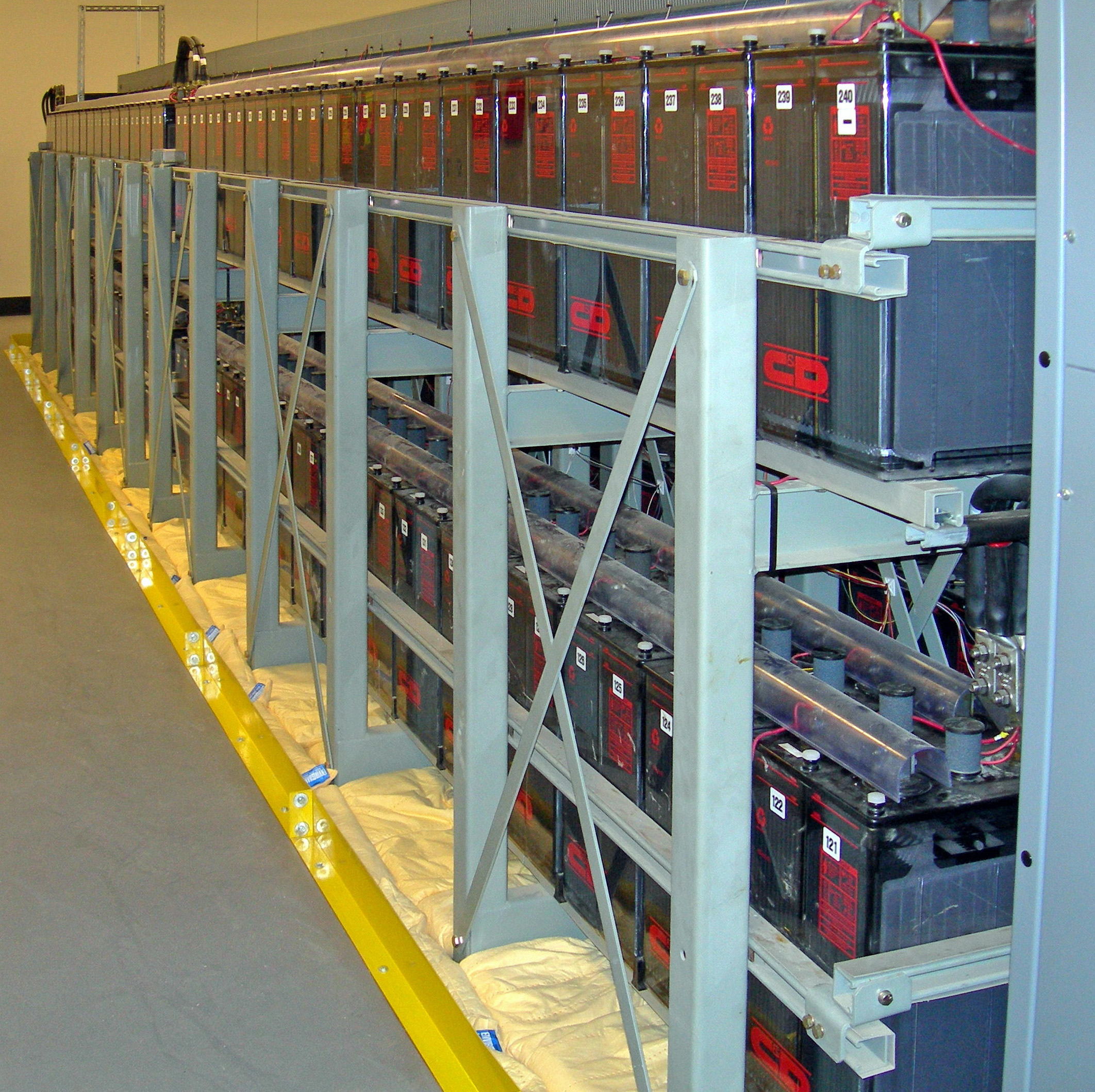

 Battery storage power plants and
Battery storage power plants and
(PDF; 826 kB), The Electrochemical Society Interface, 2010, (engl.) Since 2010, more and more utility-scale battery storage plants rely on lithium-ion batteries, as a result of the fast decrease in the cost of this technology, caused by the electric automotive industry.
 Since they do not have any mechanical parts, battery storage power plants offer extremely short control times and start times, as little as 10 ms. They can therefore help dampen the fast oscillations that occur when electrical power networks are operated close to their maximum capacity or when grids suffer anomalies. These instabilities – fluctuations with periods of as much as 30 seconds – can produce peak swings of such amplitude that they can cause regional blackouts. Some of the parameters are voltage, frequency and phase. A properly sized battery storage power plant can efficiently counteract these oscillations; therefore, applications are found primarily in those regions where electrical power systems are operated at full capacity, leading to a risk of instability. However, some batteries have insufficient control systems, failing during moderate disruptions they should have tolerated. Batteries are also commonly used for
Since they do not have any mechanical parts, battery storage power plants offer extremely short control times and start times, as little as 10 ms. They can therefore help dampen the fast oscillations that occur when electrical power networks are operated close to their maximum capacity or when grids suffer anomalies. These instabilities – fluctuations with periods of as much as 30 seconds – can produce peak swings of such amplitude that they can cause regional blackouts. Some of the parameters are voltage, frequency and phase. A properly sized battery storage power plant can efficiently counteract these oscillations; therefore, applications are found primarily in those regions where electrical power systems are operated at full capacity, leading to a risk of instability. However, some batteries have insufficient control systems, failing during moderate disruptions they should have tolerated. Batteries are also commonly used for
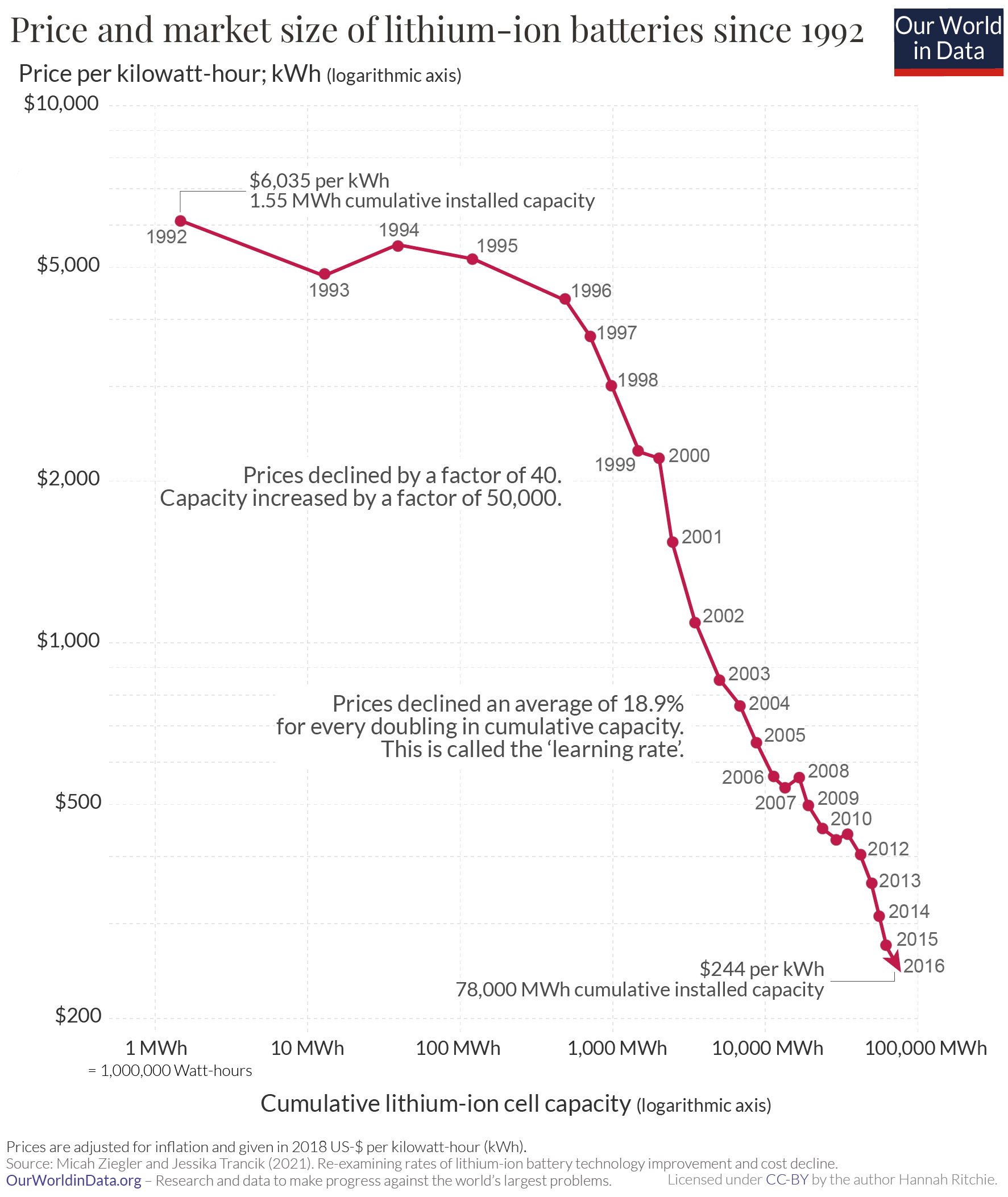
 While the capacity of grid batteries is small compared to the other major form of grid storage, pumped hydroelectricity, the battery market is growing very fast as price drops. Relative to 2010, batteries and photovoltaics have followed roughly the same downward price curve due to the
While the capacity of grid batteries is small compared to the other major form of grid storage, pumped hydroelectricity, the battery market is growing very fast as price drops. Relative to 2010, batteries and photovoltaics have followed roughly the same downward price curve due to the
energy storage
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production. A device that stores energy is generally called an Accumulator (energy), accumulator or Batte ...
technology that uses a group of batteries in the grid to store electrical energy
Electrical energy is the energy transferred as electric charges move between points with different electric potential, that is, as they move across a voltage, potential difference. As electric potential is lost or gained, work is done changing the ...
. Battery storage is the fastest responding dispatchable source of power on electric grid
An electrical grid (or electricity network) is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids consist of power stations, electrical substations to step voltage up or down, electric power tran ...
s, and it is used to stabilise those grids, as battery storage can transition from standby to full power in under a second to deal with grid contingencies.
Battery energy storage systems are generally designed to deliver their full rated power for durations ranging from 1 to 4 hours, with emerging technologies extending this to longer durations to meet evolving grid demands. Battery storage can be used for short-term peak power
''Peak power'' refers to the maximum of the instantaneous power waveform, which, for a sine wave, is always twice the average power. For other waveforms, the relationship between peak power and average power is the peak-to-average power ratio (PAP ...
and ancillary services
Ancillary services are the services necessary to support the transmission of electric power from power plant, generators to consumers given the obligations of control areas and transmission utilities within those control areas to maintain reliable ...
, such as providing operating reserve
In electricity networks, the operating reserve is the generating capacity available to the system operator within a short interval of time to meet demand in case a generator goes down or there is another disruption to the supply. Most power sy ...
and frequency control to minimize the chance of power outage
A power outage, also called a blackout, a power failure, a power blackout, a power loss, a power cut, or a power out is the complete loss of the electrical power network supply to an end user.
There are many causes of power failures in an el ...
s. They are often installed at, or close to, other active or disused power stations and may share the same grid connection to reduce costs. Since battery storage plants require no deliveries of fuel, are compact compared to generating stations and have no chimneys or large cooling systems, they can be rapidly installed and placed if necessary within urban areas, close to customer load, or even inside customer premises.
As of 2021, the power and capacity of the largest individual battery storage system is an order of magnitude
In a ratio scale based on powers of ten, the order of magnitude is a measure of the nearness of two figures. Two numbers are "within an order of magnitude" of each other if their ratio is between 1/10 and 10. In other words, the two numbers are ...
less than that of the largest pumped-storage power plants, the most common form of grid energy storage
Grid energy storage, also known as large-scale energy storage, are technologies connected to the electrical power grid that store energy for later use. These systems help balance supply and demand by storing excess electricity from variabl ...
. For example, the Bath County Pumped Storage Station, the second largest in the world, can store 24GWh of electricity and dispatch 3GW while the first phase of Vistra Energy's Moss Landing Energy Storage Facility can store 1.2GWh and dispatch 300MW. However, grid batteries do not have to be large — a high number of smaller ones (often as hybrid power) can be widely deployed across a grid for greater redundancy and large overall capacity.
As of 2019, battery power storage is typically cheaper than open cycle gas turbine power for use up to two hours, and there was around 365 GWh of battery storage deployed worldwide, growing rapidly.
Levelized cost of storage
Different methods of electricity generation can incur a variety of different costs, which can be divided into three general categories: 1) wholesale costs, or all costs paid by utilities associated with acquiring and distributing electricity to ...
(LCOS) has fallen rapidly. From 2014 to 2024, cost halving time was 4.1 years. The price was US$150 per MWh in 2020, and further reduced to US$117 by 2023.
Construction

 Battery storage power plants and
Battery storage power plants and uninterruptible power supplies
An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) or uninterruptible power source is a type of continual power system that provides automated backup electric power to a load when the input power source or mains power fails. A UPS differs from a tradition ...
(UPS) are comparable in technology and function. However, battery storage power plants are larger.
For safety and security, the actual batteries are housed in their own structures, like warehouses or containers. As with a UPS, one concern is that electrochemical energy is stored or emitted in the form of direct current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional electric current, flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor (material), conductor such as a wire, but can also flow throug ...
(DC), while electric power networks are usually operated with alternating current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in w ...
(AC). For this reason, additional inverter
A power inverter, inverter, or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on the particular device employed. Inverters do the op ...
s are needed to connect the battery storage power plants to the high voltage network. This kind of power electronics include gate turn-off thyristor
A gate turn-off thyristor (GTO) is a type of high-power (e.g. 1200 V AC) thyristor that unlike a normal thyristor is fully controllable and can be turned On and Off by their gate lead.
It was invented by General Electric.
Device descrip ...
, commonly used in high-voltage direct current
A high-voltage direct current (HVDC) electric power transmission system uses direct current (DC) for electric power transmission, in contrast with the more common alternating current (AC) transmission systems. Most HVDC links use voltages betwe ...
(HVDC) transmission.
Various accumulator systems may be used depending on the power-to-energy ratio, the expected lifetime and the costs. In the 1980s, lead-acid batteries were used for the first battery-storage power plants. During the next few decades, nickel–cadmium and sodium–sulfur batteries were increasingly used.Batteries for Large-Scale Stationary Electrical Energy Storage(PDF; 826 kB), The Electrochemical Society Interface, 2010, (engl.) Since 2010, more and more utility-scale battery storage plants rely on lithium-ion batteries, as a result of the fast decrease in the cost of this technology, caused by the electric automotive industry.
Lithium-ion batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically conducting solids to store energy. Li-ion batteries are characterized by higher specific energy, energy ...
are mainly used. A 4-hour flow vanadium redox battery at 175 MW / 700 MWh opened in 2024. Lead-acid batteries are still used in small budget applications.
Safety
Most of the BESS systems are composed of securely sealedbattery pack
A battery pack is a set of any number of (preferably) identical Battery (electricity), batteries or individual battery cells. They may be configured in a series, parallel or a mixture of both to deliver the desired voltage and current. The term ' ...
s, which are electronically monitored and replaced once their performance falls below a given threshold. Batteries suffer from cycle ageing, or deterioration caused by charge–discharge cycles. This deterioration is generally higher at high charging rates and higher depth of discharge. This aging cause a loss of performance (capacity or voltage decrease), overheating, and may eventually lead to critical failure (electrolyte leaks, fire, explosion). Sometimes battery storage power stations are built with flywheel storage power systems in order to conserve battery power. Flywheels may handle rapid fluctuations better than older battery plants.
BESS warranties
In law, a warranty is an expressed or implied promise or assurance of some kind. The term's meaning varies across legal subjects. In property law, it refers to a covenant by the grantor of a deed. In insurance law, it refers to a promise by the ...
typically include lifetime limits on energy throughput, expressed as number of charge–discharge cycles.
Lead-acid based batteries
Lead-acid batteries, as a first-generation technology, are generally used in older BESS systems. Some examples are 1.6 MW peak, 1.0 MW continuous battery was commissioned in 1997. Compared to modern rechargeable batteries, lead-acid batteries have relatively lowenergy density
In physics, energy density is the quotient between the amount of energy stored in a given system or contained in a given region of space and the volume of the system or region considered. Often only the ''useful'' or extractable energy is measure ...
. Despite this, they are able to supply high surge currents. However, non-sealed lead-acid batteries produce hydrogen and oxygen from the aqueous electrolyte when overcharged. The water has to be refilled regularly to avoid damage to the battery; and, the inflammable gases have to be vented out to avoid explosion risks. However, this maintenance has a cost, and recent batteries such as Li-ion batteries do not have such an issue.
Lithium based batteries
Lithium-ion batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically conducting solids to store energy. Li-ion batteries are characterized by higher specific energy, energy ...
are designed to have a long lifespan without maintenance. They generally have high energy density and low self-discharge. Due to these properties, most modern BESS are lithium-ion-based batteries.
A drawback of some types of lithium-ion batteries is fire safety, mostly ones containing cobalt. The number of BESS incidents has remained around 10–20 per year (mostly within the first 2–3 years of age), despite the large increase in number and size of BESS. Thus failure rate
Failure is the social concept of not meeting a desirable or intended objective, and is usually viewed as the opposite of success. The criteria for failure depends on context, and may be relative to a particular observer or belief system. On ...
has decreased. Failures occurred mostly in controls and balance of system, while 11% occurred in cells.
Examples of BESS fire accidents include individual modules in 23 battery farms in South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
in 2017 to 2019, a Tesla Megapack in Geelong
Geelong ( ) (Wathawurrung language, Wathawurrung: ''Djilang''/''Djalang'') is a port city in Victoria, Australia, located at the eastern end of Corio Bay (the smaller western portion of Port Phillip Bay) and the left bank of Barwon River (Victo ...
, the fire and subsequent explosion of a battery module in Arizona
Arizona is a U.S. state, state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States, sharing the Four Corners region of the western United States with Colorado, New Mexico, and Utah. It also borders Nevada to the nort ...
, and the cooling liquid short circuit
A short circuit (sometimes abbreviated to short or s/c) is an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path with no or very low electrical impedance. This results in an excessive current flowing through the circuit ...
ing incidents and fire at the Moss Landing LG battery.
This resulted in more research in recent years for mitigation measures for fire safety.
By 2024, the lithium iron phosphate (LFP) battery has become another significant type for large storages due to the high availability of its components, longer lifetime and higher safety compared to nickel-based Li-ion chemistries. An LFP-based energy storage system that was installed in Paiyun Lodge on Mt. Jade (Yushan) (the highest alpine lodge in Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
) and operated since 2016, has, as of 2024, operated without a safety incident.
Sodium-based batteries
Alternatively, sodium-based batteries are increasingly being considered for BESS applications. Compared to lithium-ion batteries, sodium-ion batteries have somewhat lower cost, better safety characteristics, and similar power delivery characteristics. However it has a lower energy density compared to lithium-ion batteries. Its working principle and cell construction are similar to those oflithium-ion battery
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically conducting solids to store energy. Li-ion batteries are characterized by higher specific energy, energ ...
(LIB) types, but it replaces lithium
Lithium (from , , ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the ...
with sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
as the intercalating ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
. Some sodium-based batteries can also operate safely at high temperatures (sodium–sulfur battery
A sodium–sulfur (NaS) battery is a type of molten-salt battery, molten-salt battery (electricity), battery that uses liquid sodium and liquid sulfur electrodes. This type of battery has a similar energy density to lithium-ion battery, lithium-i ...
). Some notable sodium battery producers with high safety claims include (non-exclusive) Altris AB, SgNaPlus and Tiamat. Sodium-based batteries are not fully commercialised yet. The largest BESS utilizing sodium-ion technology started operating in 2024 in Hubei province, boasts a capacity of 50 MW / 100 MWh.
Operating characteristics
 Since they do not have any mechanical parts, battery storage power plants offer extremely short control times and start times, as little as 10 ms. They can therefore help dampen the fast oscillations that occur when electrical power networks are operated close to their maximum capacity or when grids suffer anomalies. These instabilities – fluctuations with periods of as much as 30 seconds – can produce peak swings of such amplitude that they can cause regional blackouts. Some of the parameters are voltage, frequency and phase. A properly sized battery storage power plant can efficiently counteract these oscillations; therefore, applications are found primarily in those regions where electrical power systems are operated at full capacity, leading to a risk of instability. However, some batteries have insufficient control systems, failing during moderate disruptions they should have tolerated. Batteries are also commonly used for
Since they do not have any mechanical parts, battery storage power plants offer extremely short control times and start times, as little as 10 ms. They can therefore help dampen the fast oscillations that occur when electrical power networks are operated close to their maximum capacity or when grids suffer anomalies. These instabilities – fluctuations with periods of as much as 30 seconds – can produce peak swings of such amplitude that they can cause regional blackouts. Some of the parameters are voltage, frequency and phase. A properly sized battery storage power plant can efficiently counteract these oscillations; therefore, applications are found primarily in those regions where electrical power systems are operated at full capacity, leading to a risk of instability. However, some batteries have insufficient control systems, failing during moderate disruptions they should have tolerated. Batteries are also commonly used for peak shaving
Load management, also known as demand-side management (DSM), is the process of balancing the supply of electricity on the network with the electrical load by adjusting or controlling the load rather than the power station output. This can be ach ...
for periods of up to a few hours. A more recent use is strengthening transmission, as long power lines can be operated closer to their capacity when batteries handle the local difference between supply and demand.
Storage plants can also be used in combination with an intermittent renewable energy source in stand-alone power systems.
Largest grid batteries
Under construction
Planned
Market development and deployment

learning rate
In machine learning and statistics, the learning rate is a tuning parameter in an optimization algorithm that determines the step size at each iteration while moving toward a minimum of a loss function. Since it influences to what extent newly ...
. Cells are the major cost component, costing 30-40% of a full system.
At the end of 2024, China had 62 GW / 141 GWh of battery power stations. In 2020, China added 1,557 MW to its battery storage capacity, while storage facilities for photovoltaics
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commerciall ...
projects accounting for 27% of the capacity, to the total 3,269 MW of electrochemical energy storage capacity.
USA installed 12.3 GW and 37.1 GWh of batteries in 2024. In 2022, US capacity doubled to 9 GW / 25 GWh. At the end of 2021, the capacity grew to 4,588 MW. The 2021 price of a 60 MW / 240 MWh (4-hour) battery installation in the United States was US$379/usable kWh, or US$292/nameplate kWh, a 13% drop from 2020. In 2010, the United States had 59 MW of battery storage capacity from 7 battery power plants. This increased to 49 plants comprising 351 MW of capacity in 2015. In 2018, the capacity was 869 MW from 125 plants, capable of storing a maximum of 1,236 MWh of generated electricity. By the end of 2020, the battery storage capacity reached 1,756 MW. The US market for storage power plants in 2015 increased by 243% compared to 2014.
In June 2024 the capacity was 4.6 GW of power and 5.9 GWh of energy in the United Kingdom. In 2022, UK capacity grew by 800 MWh, ending at 2.4 GW / 2.6 GWh. As of May 2021, 1.3 GW of battery storage was operating, with 16 GW of projects in the pipeline potentially deployable over the next few years.
As of the end of 2024, Europe had reached 61 GWh of installed battery energy storage capacity, after adding 21 GWh that year. Germany and Italy each contributed approximately 6 GWh to this growth. The average installation cost during 2024 ranged between €300 and €400 per kilowatt-hour. By comparison, Europe deployed 1.9 GW of new battery capacity in 2022.
Japan’s energy sector has also undergone significant growth in renewable energy capacity. expanding by over 30% within five years, which has contributed to a sharp increase in demand for battery energy storage systems (BESS). More than half of the 2.4 GW of BESS capacity awarded in recent long-term low-carbon power auctions was allocated to foreign-owned companies or consortia. Projects approved in 2024 alone comprise more than 1.37 GW of power capacity and over 6.7 GWh of energy capacity. The country’s Long-Term Decarbonization Power Source Auction supports BESS deployment by guaranteeing fixed cost recovery over a 20-year period. However, constraints such as limited price volatility and a price floor in Japan’s power market may limit investment returns for storage operators, signaling the need for further regulatory reform.
Some developers are also utilizing retired electric vehicle batteries to build second-life storage systems, with costs potentially 50% lower than those of new battery installations. Nonetheless, due to the declining cost of new batteries, buyers of second-life systems may only be willing to pay around 10% of the original cost. In 2024, a 53 MWh battery storage facility built from approximately 900 used electric vehicle batteries was commissioned in Texas.
Following a major blackout on 28 April 2025, which severed the Iberian grid from the rest of Europe in just five seconds and caused economic losses estimated at up to €4.5 billion, the importance of system resilience has become increasingly prominent in Spain. Battery Energy Storage Systems are now regarded as a key pillar of the Spanish energy transition. Major utilities such as Iberdrola and Solaria are now actively developing hybrid solar-plus-storage projects to mitigate the impact of solar overproduction and declining market prices. Solaria alone has launched eight new BESS installations in Castilla y León and Castilla-La Mancha.
See also
*List of energy storage power plants
This is a list of energy storage power plants worldwide, other than pumped hydro storage. Many individual energy storage plants augment electrical grids by capturing excess electrical energy during periods of low demand and storing it in other ...
References
{{electricity generation, state=collapsed Storage power station Power stations Grid energy storage