Barque Of St. Peter on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
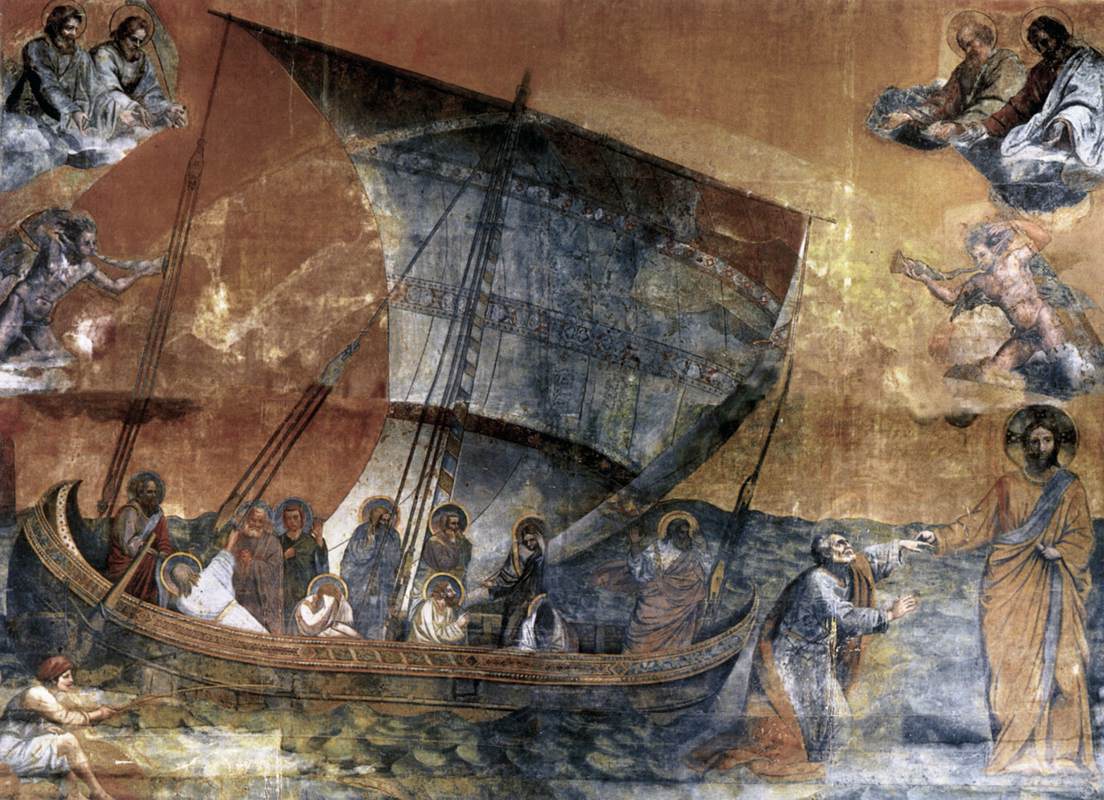 The Barque of Saint Peter symbolises the
The Barque of Saint Peter symbolises the
 1627 AD
1627 AD
 The Barque of Saint Peter symbolises the
The Barque of Saint Peter symbolises the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
as a barque
A barque, barc, or bark is a type of sailing ship, sailing vessel with three or more mast (sailing), masts of which the fore mast, mainmast, and any additional masts are Square rig, rigged square, and only the aftmost mast (mizzen in three-maste ...
. Saint Peter
Saint Peter (born Shimon Bar Yonah; 1 BC – AD 64/68), also known as Peter the Apostle, Simon Peter, Simeon, Simon, or Cephas, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus and one of the first leaders of the Jewish Christian#Jerusalem ekklēsia, e ...
, the first pope
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
, was a fisherman who became one of the twelve Apostles
An apostle (), in its literal sense, is an emissary. The word is derived from Ancient Greek ἀπόστολος (''apóstolos''), literally "one who is sent off", itself derived from the verb ἀποστέλλειν (''apostéllein''), "to se ...
of Jesus. The Catholic Church believes that all succeeding popes, as his successors, steer the Barque. This may explain the etymology of the central part of churches, the nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type ...
, which stems from the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
word for ship, ''navis''.
History
The image of the Barque of St. Peter is tied to Noah's Ark in the First Epistle of Peter 3:20-21 and Jesuscalming the storm
Calming the storm is one of the miracles of Jesus in the Gospels, reported in Matthewbr>8:23–27 Markbr>4:35–41 and Lukebr>8:22–25(the Synoptic Gospels). This episode is distinct from Jesus' walk on water, which also involves a boat on ...
at the sea of Galilee
The Sea of Galilee (, Judeo-Aramaic languages, Judeo-Aramaic: יַמּא דטבריא, גִּנֵּיסַר, ), also called Lake Tiberias, Genezareth Lake or Kinneret, is a freshwater lake in Israel. It is the lowest freshwater lake on Earth ...
in Mark 4:35-41.
Catholicism
Between 150 and 240 ADTertullian
Tertullian (; ; 155 – 220 AD) was a prolific Early Christianity, early Christian author from Roman Carthage, Carthage in the Africa (Roman province), Roman province of Africa. He was the first Christian author to produce an extensive co ...
, "the founder of Western theology", referred to the Church as a ship in ''De Baptismo (''On Baptism):''"...the apostles then served the turn of baptism when in their little ship, were sprinkled and covered with the waves: that Peter himself also was immersed enough when he walked on the sea." It is, however, as I think, one thing to be sprinkled or intercepted by the violence of the sea; another thing to be baptized in obedience to the discipline of religion. But that little ship did present a figure of the Church, in that she is disquieted "in the sea", that is, in the world, "by the waves", that is, by persecutions and temptations; the Lord, through patience, sleeping as it were, until, roused in their last extremities by the prayers of the saints, He checks the world, 0and restores tranquility to His own."''Circa 195 AD
Clement of Alexandria
Titus Flavius Clemens, also known as Clement of Alexandria (; – ), was a Christian theology, Christian theologian and philosopher who taught at the Catechetical School of Alexandria. Among his pupils were Origen and Alexander of Jerusalem. A ...
approved the use of a ship as a symbol for signet rings in the third book of his ''Paedagogus
''Paedagogus'' (, "Pedagogue") is the second in the great trilogy of Clement of Alexandria.
Having laid a foundation in the knowledge of divine truth in the first book, he goes on in the ''Paedagogus'' to develop a Christian ethic. His design ...
'': ''"...let our seals be either a dove, or a fish, or a ship scudding before the wind, or a musical lyre, which Polycrates used, or a ship's anchor, which Seleucus got engraved as a device; and if there be one fishing, he will remember the apostle, and the children drawn out of the water."''Between 375 and 380 AD In the book II of the
Apostolic Constitutions
The ''Apostolic Constitutions'' or ''Constitutions of the Holy Apostles'' (Latin: ''Constitutiones Apostolorum'') is a Christian collection divided into eight books which is classified among the Church Orders, a genre of early Christian litera ...
:''"When you call an assembly of the Church as one that is the commander of a great ship, appoint the assemblies to be made with all possible skill, charging the deacons as mariners to prepare places for the brethren as for passengers, with all due care and decency. And first, let the building be long, with its head to the east, with its vestries on both sides at the east end, and so it will be like a ship. In the middle let the bishop's throne be placed, and on each side of him let the presbytery sit down; and let the deacons stand near at hand, in close and small girt garments, for they are like the mariners and managers of the ship"''In 1298 AD the ''Bark of St. Peter'', commonly known as the ''Navicella,'' by
Giotto
Giotto di Bondone (; – January 8, 1337), known mononymously as Giotto, was an List of Italian painters, Italian painter and architect from Florence during the Late Middle Ages. He worked during the International Gothic, Gothic and Italian Ren ...
was commissioned for the Old Saint Peter's Basilica
Old St. Peter's Basilica was the church buildings that stood, from the 4th to 16th centuries, where St. Peter's Basilica stands today in Vatican City. Construction of the basilica, built over the historical site of the Circus of Nero, began dur ...
in Rome.
In 1241 AD Pope Gregory IX
Pope Gregory IX (; born Ugolino di Conti; 1145 – 22 August 1241) was head of the Catholic Church and the ruler of the Papal States from 19 March 1227 until his death in 1241. He is known for issuing the '' Decretales'' and instituting the Pa ...
or Pope Innocent IV
Pope Innocent IV (; – 7 December 1254), born Sinibaldo Fieschi, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 25 June 1243 to his death in 1254.
Fieschi was born in Genoa and studied at the universities of Parma and Bolo ...
, in response to the destruction of the Genoese fleet in the Battle of Giglio, said:
: ''Niteris incassum navem submergere Petri / Fluctuat at numquam mergitur illa ratis.''
: "In vain you strive to submerge the ship of Peter — this vessel rocks but is never submerged."
This distich
In poetry, a couplet ( ) or distich ( ) is a pair of successive Line (poetry), lines that rhyme and have the same Metre (poetry), metre. A couplet may be formal (closed) or run-on (open). In a formal (closed) couplet, each of the two lines is en ...
would inspire the motto
A motto (derived from the Latin language, Latin , 'mutter', by way of Italian language, Italian , 'word' or 'sentence') is a Sentence (linguistics), sentence or phrase expressing a belief or purpose, or the general motivation or intention of a ...
of Paris and be featured on Paris' coat of arms.
In the twelfth volume (1596) of the ''Annales Ecclesiastici
(full title ; "Ecclesiastical annals from Christ's nativity to 1198"), consisting of twelve folio volumes, is a history of the first 12 centuries of the Christian Church, written by Caesar Baronius and Odorico Raynaldi and published betwee ...
'' historian Cardinal Baronius
Cesare Baronio, C.O. (as an author also known as Caesar Baronius; 30 August 1538 – 30 June 1607) was an Italian Oratorian, cardinal and historian of the Catholic Church. His best-known works are his ''Annales Ecclesiastici'' ("Ecclesiast ...
writes on the condition of the Irish Church in 566 AD:''"...having made shipwreck in consequence of not following the Barque of St. Peter"''
Eastern Orthodox
TheEastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, officially the Orthodox Catholic Church, and also called the Greek Orthodox Church or simply the Orthodox Church, is List of Christian denominations by number of members, one of the three major doctrinal and ...
utilises the similar Ark of Salvation in its iconography as a representation of the Church.
Islam
In Islam, theHadith
Hadith is the Arabic word for a 'report' or an 'account f an event and refers to the Islamic oral tradition of anecdotes containing the purported words, actions, and the silent approvals of the Islamic prophet Muhammad or his immediate circle ...
known as the Hadith of the Ark
The hadith of the ark () is a saying (hadith) attributed to the Islamic prophet Muhammad that likens his household (Ahl al-Bayt) to Noah's ark; whoever turns to them is saved and whoever turns away from them perishes. Reported by both Shia and Su ...
a ship is similarly used to symbolise the only way to salvation. In it Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
compares his Ahl al-Bayt
() refers to the family of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. In Sunni Islam, the term has also been extended to all descendants of the Banu Hashim (Muhammad's clan) and even to all Muslims. In Shia Islam, the term is limited to Muhammad, his daugh ...
, his household, to Noah's ark as the only way to salvation. The Hadith says:Behold! The similitude of my Ahlul Bayt, is like that of the Ark of Noah: The one who embarks it, will have saved himself, and the one who turns away from it, is doomed.
Modern usage
Coat of Arms
*Archdiocese of Vancouver
The Roman Catholic Metropolitan Archdiocese of Vancouver () is a Roman Catholic Latin archdiocese that includes part of the Canadian province of British Columbia.
Its cathedral archiepiscopal see is the Holy Rosary Cathedral (Vancouver), Holy R ...
* City of Paris
Flags
*Flag of Paris
The flag of Paris is vertically divided between the traditional colours of Paris, blue and red, both of which also feature in the city's coat of arms of Paris, coat of arms. Red is identified with Saint Denis of Paris, Saint Denis (a martyr who ...
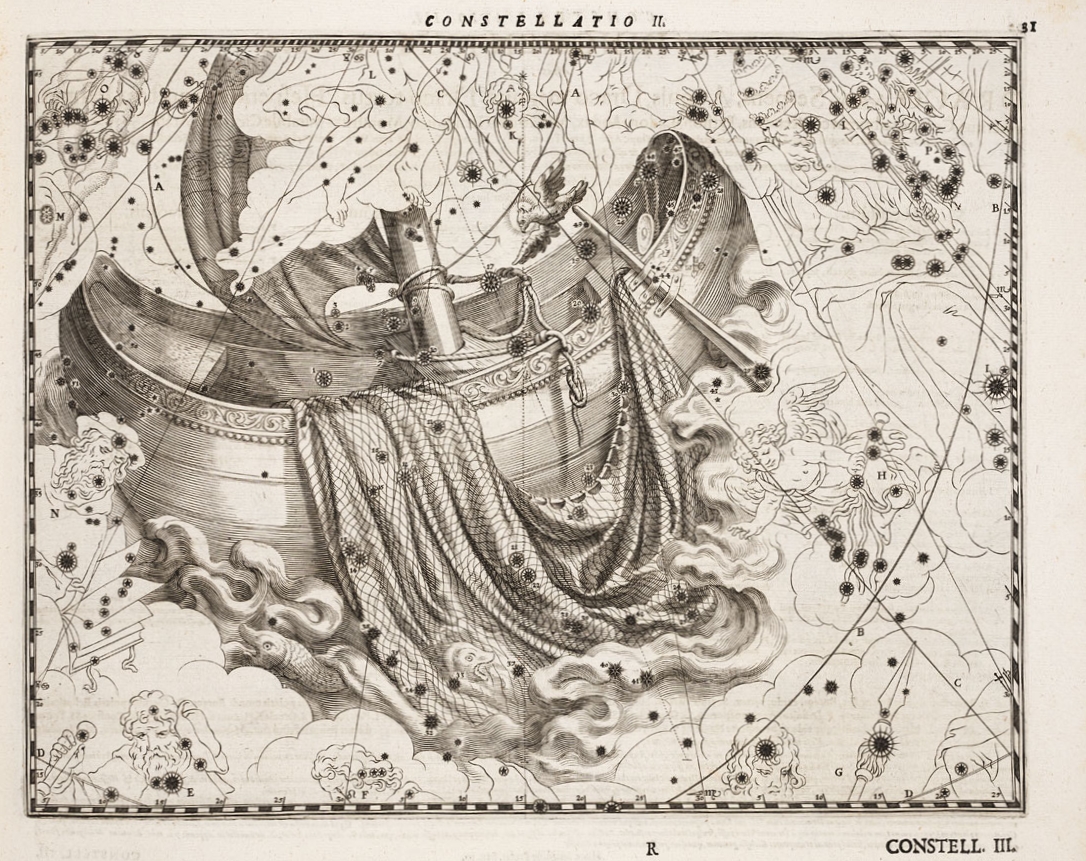
''Coelum Stellatum Christianum''
 1627 AD
1627 AD Julius Schiller
Julius Schiller (c. 1580 – 1627) was a lawyer from Augsburg who, like his fellow citizen and colleague Johann Bayer, published a star atlas in celestial cartography.
In the year of his death, Schiller, with Bayer's assistance, published ...
in his book ''Coelum Stellatum Christianum
The ''Coelum Stellatum Christianum'' is a star atlas published in 1627 by Julius Schiller ( 1580–1627), with the collaboration of Johann Bayer (1572–1625). In the treatise, which was published by Andreas Aperger at Augsburg during the same yea ...
'' attempted to Christianise the constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
s. Schiller depicted Ursa Major
Ursa Major, also known as the Great Bear, is a constellation in the Northern Sky, whose associated mythology likely dates back into prehistory. Its Latin name means "greater (or larger) bear", referring to and contrasting it with nearby Ursa M ...
as the Barque of St. Peter.
References
{{Reflist History of the Catholic Church Barques Saint Peter