Barlow lens on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Barlow lens, named after Peter Barlow, is a type of diverging
 In its
In its 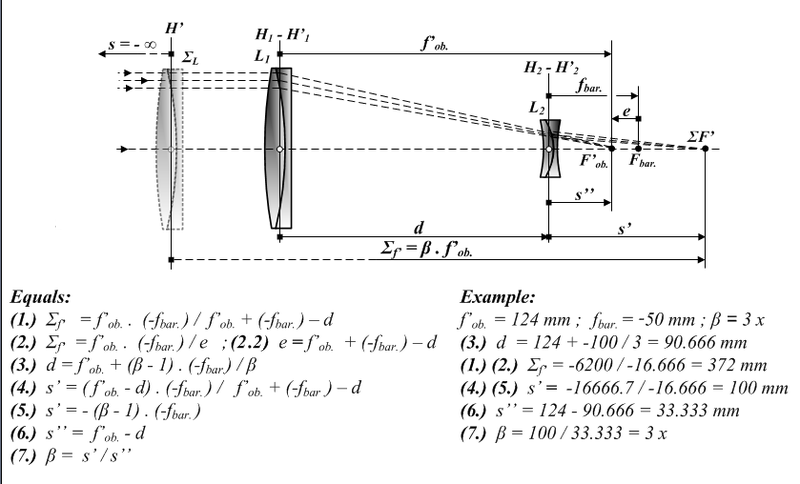 Astronomical Barlow lenses are rated for the amount of magnification they induce. Most commonly, Barlow lenses are 2x or 3x, but adjustable Barlows are also available. The power of an adjustable Barlow lens is changed by adding an extension tube between the Barlow and the eyepiece to increase the magnification.
The amount of magnification is one more than the distance between the Barlow lens and the eyepiece lens, when the distance is measured in units of the focal length of the Barlow lens. A standard Barlow lens is housed in a tube that is one Barlow focal-length long, so that a focusing lens inserted into the end of the tube will be separated from the Barlow lens at the other end by one Barlow focal-length, and hence produce a 2x magnification over and above what the eyepiece would have produced alone. If the length of a standard 2x Barlow lens' tube is doubled, then the lenses are separated by two Barlow focal lengths and it becomes a 3x Barlow. Similarly, if the tube length is tripled, then the lenses are separated by three Barlow focal lengths and it becomes a 4x Barlow, and so on.
A common misconception is that higher magnification always equates to a higher-quality image. However, the quality of the image is in practice generally limited by the quality of the optics (lenses) or by the atmospheric viewing conditions, not by magnification.
Astronomical Barlow lenses are rated for the amount of magnification they induce. Most commonly, Barlow lenses are 2x or 3x, but adjustable Barlows are also available. The power of an adjustable Barlow lens is changed by adding an extension tube between the Barlow and the eyepiece to increase the magnification.
The amount of magnification is one more than the distance between the Barlow lens and the eyepiece lens, when the distance is measured in units of the focal length of the Barlow lens. A standard Barlow lens is housed in a tube that is one Barlow focal-length long, so that a focusing lens inserted into the end of the tube will be separated from the Barlow lens at the other end by one Barlow focal-length, and hence produce a 2x magnification over and above what the eyepiece would have produced alone. If the length of a standard 2x Barlow lens' tube is doubled, then the lenses are separated by two Barlow focal lengths and it becomes a 3x Barlow. Similarly, if the tube length is tripled, then the lenses are separated by three Barlow focal lengths and it becomes a 4x Barlow, and so on.
A common misconception is that higher magnification always equates to a higher-quality image. However, the quality of the image is in practice generally limited by the quality of the optics (lenses) or by the atmospheric viewing conditions, not by magnification.
Sidney F. Ray, Scientific photography and applied imaging, p. 492
A teleconverter increases the effective focal length of the photographic lens it is attached to, making it a telephoto lens. A true telephoto lens uses a configuration similar to a Barlow lens to obtain a shorter tube length for a given focal length.
lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements'') ...
which, used in series with other optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of optical instruments, instruments that use or Photodetector, detect it. Optics usually describes t ...
in an optical system, increases the effective focal length
The focal length of an Optics, optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the Multiplicative inverse, inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system Converge ...
of an optical system as perceived by all components that are after it in the system. The practical result is that inserting a Barlow lens magnifies the image. A real Barlow lens is not a single glass element, because that would generate chromatic aberration
In optics, chromatic aberration (CA), also called chromatic distortion, color aberration, color fringing, or purple fringing, is a failure of a lens to focus all colors to the same point. It is caused by dispersion: the refractive index of the ...
, and spherical aberration if the lens is not aspheric. More common configurations use three or more elements for achromatic correction or apochromatic
An apochromat, or apochromatic lens (apo), is a photographic or other lens that has better correction of chromatic and spherical aberration than the much more common achromat lenses.
The prefix ''apo-'' comes from the Greek preposition ''ἀ ...
correction and higher image quality.
Telescope use
 In its
In its astronomical
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest include ...
use, a Barlow lens may be placed immediately before an eyepiece
An eyepiece, or ocular lens, is a type of lens that is attached to a variety of optical devices such as Optical telescope, telescopes and microscopes. It is named because it is usually the lens that is closest to the eye when someone looks thro ...
to effectively decrease the eyepiece's focal length
The focal length of an Optics, optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the Multiplicative inverse, inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system Converge ...
by the amount of the Barlow's divergence. Since the magnification
Magnification is the process of enlarging the apparent size, not physical size, of something. This enlargement is quantified by a size ratio called optical magnification. When this number is less than one, it refers to a reduction in size, so ...
provided by a telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using len ...
and eyepiece is equal to the telescope's focal length divided by the eyepiece's focal length, this has the effect of increasing the magnification of the image.
 Astronomical Barlow lenses are rated for the amount of magnification they induce. Most commonly, Barlow lenses are 2x or 3x, but adjustable Barlows are also available. The power of an adjustable Barlow lens is changed by adding an extension tube between the Barlow and the eyepiece to increase the magnification.
The amount of magnification is one more than the distance between the Barlow lens and the eyepiece lens, when the distance is measured in units of the focal length of the Barlow lens. A standard Barlow lens is housed in a tube that is one Barlow focal-length long, so that a focusing lens inserted into the end of the tube will be separated from the Barlow lens at the other end by one Barlow focal-length, and hence produce a 2x magnification over and above what the eyepiece would have produced alone. If the length of a standard 2x Barlow lens' tube is doubled, then the lenses are separated by two Barlow focal lengths and it becomes a 3x Barlow. Similarly, if the tube length is tripled, then the lenses are separated by three Barlow focal lengths and it becomes a 4x Barlow, and so on.
A common misconception is that higher magnification always equates to a higher-quality image. However, the quality of the image is in practice generally limited by the quality of the optics (lenses) or by the atmospheric viewing conditions, not by magnification.
Astronomical Barlow lenses are rated for the amount of magnification they induce. Most commonly, Barlow lenses are 2x or 3x, but adjustable Barlows are also available. The power of an adjustable Barlow lens is changed by adding an extension tube between the Barlow and the eyepiece to increase the magnification.
The amount of magnification is one more than the distance between the Barlow lens and the eyepiece lens, when the distance is measured in units of the focal length of the Barlow lens. A standard Barlow lens is housed in a tube that is one Barlow focal-length long, so that a focusing lens inserted into the end of the tube will be separated from the Barlow lens at the other end by one Barlow focal-length, and hence produce a 2x magnification over and above what the eyepiece would have produced alone. If the length of a standard 2x Barlow lens' tube is doubled, then the lenses are separated by two Barlow focal lengths and it becomes a 3x Barlow. Similarly, if the tube length is tripled, then the lenses are separated by three Barlow focal lengths and it becomes a 4x Barlow, and so on.
A common misconception is that higher magnification always equates to a higher-quality image. However, the quality of the image is in practice generally limited by the quality of the optics (lenses) or by the atmospheric viewing conditions, not by magnification.
Photography use
Teleconverters are variations on Barlow lenses that have been adapted for photographic use.A teleconverter increases the effective focal length of the photographic lens it is attached to, making it a telephoto lens. A true telephoto lens uses a configuration similar to a Barlow lens to obtain a shorter tube length for a given focal length.
Microscope use
Inmicroscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view subjects too small to be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical mic ...
the Barlow lens is used to increase working distance and ''decrease'' magnification. The lenses are " objective lenses" that are mounted in front of the microscope's last objective element. Barlow lenses for microscopes can be found with magnifications ranging from 0.3× to 2×. Some standard lenses are 2×, which decreases the working distance by half and doubles the magnification, 0.75× (3/4×), which increases the working distance by 4/3× (1.33×) and decreases the magnification by 0.75×, and a 0.5× Barlow doubles the working distance and halves the magnification.
See also
*Secondary lens
In photography, a secondary lens or accessory lens is a photographic lens, lens designed to be used in conjunction with another lens, called the ''primary lens''.
A secondary lens may be designed to be used either in front of the primary lens, b ...
* Teleconverter
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Barlow Lens Lenses