Barber surgeon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The barber surgeon was one of the most common European medical practitioners of the
The barber surgeon was one of the most common European medical practitioners of the
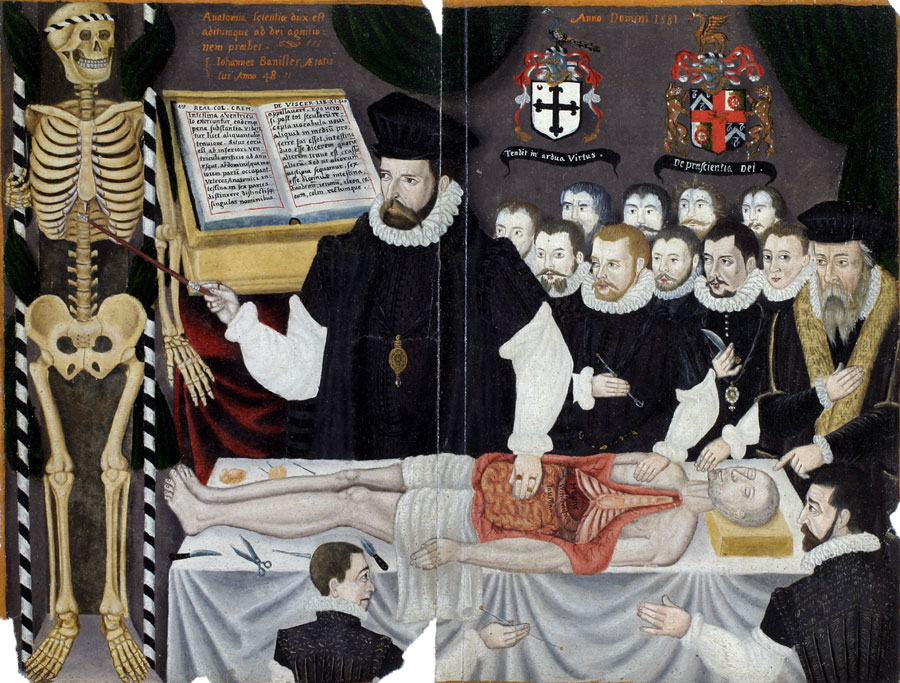 Formal recognition of surgeons' skills (in England at least) goes back to 1540, when the Fellowship of Surgeons (who existed as a distinct profession but were not "Doctors/Physicians" for reasons including that, as a trade, they were trained by apprenticeship rather than academically) merged with the Company of Barbers, a London livery company, to form the Company of Barber-Surgeons. However, the trade was gradually put under pressure by the medical profession and in 1745, the surgeons split from the Barbers' Company (which still exists) to form the Company of Surgeons. In 1800 a
Formal recognition of surgeons' skills (in England at least) goes back to 1540, when the Fellowship of Surgeons (who existed as a distinct profession but were not "Doctors/Physicians" for reasons including that, as a trade, they were trained by apprenticeship rather than academically) merged with the Company of Barbers, a London livery company, to form the Company of Barber-Surgeons. However, the trade was gradually put under pressure by the medical profession and in 1745, the surgeons split from the Barbers' Company (which still exists) to form the Company of Surgeons. In 1800 a
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, generally charged with caring for soldiers during and after battle. In this era, surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery s ...
was seldom conducted by physicians. Instead, barbers, who possessed razors and dexterity, were responsible for tasks ranging from cutting hair to pulling teeth to amputating limbs.
In this period, surgical mortality was very high due to blood loss, shock and infection. Yet, since doctors thought that bloodletting
Bloodletting (or blood-letting) was the deliberate withdrawal of blood from a patient to prevent or cure illness and disease. Bloodletting, whether by a physician or by leeches, was based on an ancient system of medicine in which blood and othe ...
to balance "humours" would improve health, barbers also used bloodletting razors and applied leech
Leeches are segmented parasitism, parasitic or Predation, predatory worms that comprise the Class (biology), subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the Oligochaeta, oligochaetes, which include the earthwor ...
es. Meanwhile, physicians considered themselves to be above surgery. Physicians mostly observed during surgery and offered consulting, but otherwise often chose academia or working in universities.
Middle Ages in Europe
Due to religious and sanitary monastic regulations, monks had to maintain theirtonsure
Tonsure () is the practice of cutting or shaving some or all of the hair on the scalp as a sign of religious devotion or humility. The term originates from the Latin word ' (meaning "clipping" or "shearing") and referred to a specific practice in ...
(the traditional baldness on the top of the head of Catholic monks). This created a market for barbers, because each monastery had to train or hire a barber. They would perform bloodletting and minor surgeries, pull teeth and prepare ointments. The first barber surgeons to be recognized as such worked in monasteries around AD 1000.
Because physicians performed surgery so rarely, the Middle Ages saw a proliferation of barbers, among other medical "paraprofessionals", including cataract couchers, herniotomists, lithotomists, midwives, and pig gelders. In 1254, Bruno da Longobucco, an Italian physician who wrote about surgery, expressed concern about barbers performing phlebotomies and scarifications.
Barbers in France and Italy
In 16th centuryParis
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
, barber-surgery was divided into two categories: "Surgeons of the Short Robe" and "Surgeons of the Long Robe." "Surgeons of the Long Robe", a qualification offered in institutions such as the College of St. Cosme, required students to take a formal exam. This was opposed to "Surgeons of the Short Robe", who did not need to take an exam to qualify and, alongside barbering, would perform minor surgical procedures. However, despite the different education requirements, both types of surgeons were called "barber-surgeons". This distinction between "short coat" and "long coat" continued in surgery until relatively recently Eventually, in 1660, the barber surgeons recognized the physicians' dominance.France
From the 1540s in France, the translation into French of the works of ancient authors allowed progress in the transmission of knowledge: barber-surgeons could add to their manual skills, and ancient surgical knowledge could be conformed to actual practice. New problems arose in war surgery, without equivalents in the past: wounds caused by firearms and mutilations caused byartillery
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and l ...
. The barber-surgeon was required to treat all the effects on the surface of the body, the doctor treating those on the inside.
There was already social mobility between surgeons and barber-surgeons. A surgeon's apprenticeship began with the practice of shaving. The young surgeon could thus have a source of income before mastering the surgery of his time. In the context of Renaissance humanism, this practical experience took place outside of academic scholasticism. The action is clearly sanctioned by the results, visible to all. For Michel de Montaigne
Michel Eyquem, Seigneur de Montaigne ( ; ; ; 28 February 1533 – 13 September 1592), commonly known as Michel de Montaigne, was one of the most significant philosophers of the French Renaissance. He is known for popularising the the essay ...
, compared to medicine:
Italy
In Italy, barbers were not as common. The Salerno medical school trained physicians to be competent surgeons, as did the schools in Bologna and Padua. In Florence, physicians and surgeons were separate, but the Florentine Statute concerning the Art of Physicians and Pharmacists in 1349 gave barbers an inferior legal status compared to surgeons.Barbers in Spain
Surgical practices in the Iberian Peninsula date back to the Megalithic era (2000 BC), with evidence oftrepanation
Trepanning, also known as trepanation, trephination, trephining or making a burr hole (the verb ''trepan'' derives from Old French from Medieval Latin from Ancient Greek, Greek , literally "borer, auger"), is a surgical intervention in which a ...
. Until the Renaissance, Spanish surgery followed Greek, Arab, and medieval traditions, with significant progress in the 16th century through anatomical studies. Despite this, military, naval, and barber-surgeons performed operations, as physicians distanced themselves from surgery. A royal decree regulated barber-surgeons in Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
. There were active barber surgeons operating in Valencia
Valencia ( , ), formally València (), is the capital of the Province of Valencia, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Valencian Community, the same name in Spain. It is located on the banks of the Turia (r ...
in the 15th century. One notable practitioner was Antonio Fernando de Medrano, a professional barber surgeon active in Madrid
Madrid ( ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in Spain, most populous municipality of Spain. It has almost 3.5 million inhabitants and a Madrid metropolitan area, metropolitan area population of approximately 7 million. It i ...
during the 17th century.
The establishment of surgical chairs in Spanish universities in the late 16th century gave surgery social and academic recognition, but a standardized system emerged only in the 18th century with the Reales Colegios de Cirugía (Royal Colleges of Surgeons), founded by military surgeons. The first institutions in Cádiz (1748) and Barcelona (1764), led by Virgili, were followed by Madrid (1780), founded by Antoni de Gimbernat. These colleges formally integrated surgery into medical education, solidifying its scientific status.
Barbers in the British Isles in the early modern period
 Formal recognition of surgeons' skills (in England at least) goes back to 1540, when the Fellowship of Surgeons (who existed as a distinct profession but were not "Doctors/Physicians" for reasons including that, as a trade, they were trained by apprenticeship rather than academically) merged with the Company of Barbers, a London livery company, to form the Company of Barber-Surgeons. However, the trade was gradually put under pressure by the medical profession and in 1745, the surgeons split from the Barbers' Company (which still exists) to form the Company of Surgeons. In 1800 a
Formal recognition of surgeons' skills (in England at least) goes back to 1540, when the Fellowship of Surgeons (who existed as a distinct profession but were not "Doctors/Physicians" for reasons including that, as a trade, they were trained by apprenticeship rather than academically) merged with the Company of Barbers, a London livery company, to form the Company of Barber-Surgeons. However, the trade was gradually put under pressure by the medical profession and in 1745, the surgeons split from the Barbers' Company (which still exists) to form the Company of Surgeons. In 1800 a royal charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, but ...
was granted to this company and the Royal College of Surgeons
The Royal College of Surgeons is an ancient college (a form of corporation) established in England to regulate the activity of surgeons. Derivative organisations survive in many present and former members of the Commonwealth. These organisations ...
in London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
came into being. Later it was renamed to cover all of England—equivalent colleges exist for Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
and Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
as well as many of the old UK colonies (e.g., Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
).
Barbers in medieval Finland
There are few studies on barber surgeons inFinland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
. The first known account is that of Hinzikinus from 1324 to 1326, originating from Turku
Turku ( ; ; , ) is a city in Finland and the regional capital of Southwest Finland. It is located on the southwestern coast of the country at the mouth of the Aura River (Finland), River Aura. The population of Turku is approximately , while t ...
, a city in the southern region of the country, who provided medical preparation and wound care for Viceroy Matts Kettilmundson. The second barber surgeon documented was Henrik Bardskärare, who worked in the castle of Vyborg in Finland (currently a part of Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
). Each company of 400–500 men in the Swedish Army was assigned a barber during the rule of King Gustav I Vasa in the 16th century. A barber surgeon was available to tend to the injured in almost every division. In 1571, the barbers organized into a professional guild that governed their training, jobs, pay, and the number of barbers. Barbers from other countries could join the guild as well. The guild mandated that barber surgeons receive their training from established masters as apprentices, and in order to receive their degrees, the apprentices had to pass an exam. The guild provided guidelines for the barber surgeons' fees or pay, which varied and occasionally depended on how many patients were treated and surgeries were carried out.
Traditions in the 21st century
Few traces of barbers' links with the surgical side of the medical profession remain. One is the traditional red and white barber's pole, or a modified instrument from a blacksmith, which is said to represent the blood and bandages associated with their historical role. In the United Kingdom, Ireland, Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa, another vestige is the use of the titles ''Mr'', ''Ms'', ''Mrs'', or ''Miss'' rather than ''Dr'' by physicians when they complete their surgery qualifications by, for example, the award of an MRCS or FRCS diploma. This practice dates back to the days when surgeons were not required to obtain a university education in medicine, and is retained despite the fact that all surgeons in these countries must earn a medical degree and spend additional years in surgical training and certification.See also
*City physician
City physician (German language, German: ; , , from Latin ) was a historical title in the Late Middle Ages for a physician appointed by the city council. The city physician was responsible for the health of the population, particularly the poor, ...
* Feldsher
* Elinor Sneshell
* List of barbers
* Magdalena Bendzisławska
References
External links
{{Authority control Medieval occupations History of surgery Historical health care occupations