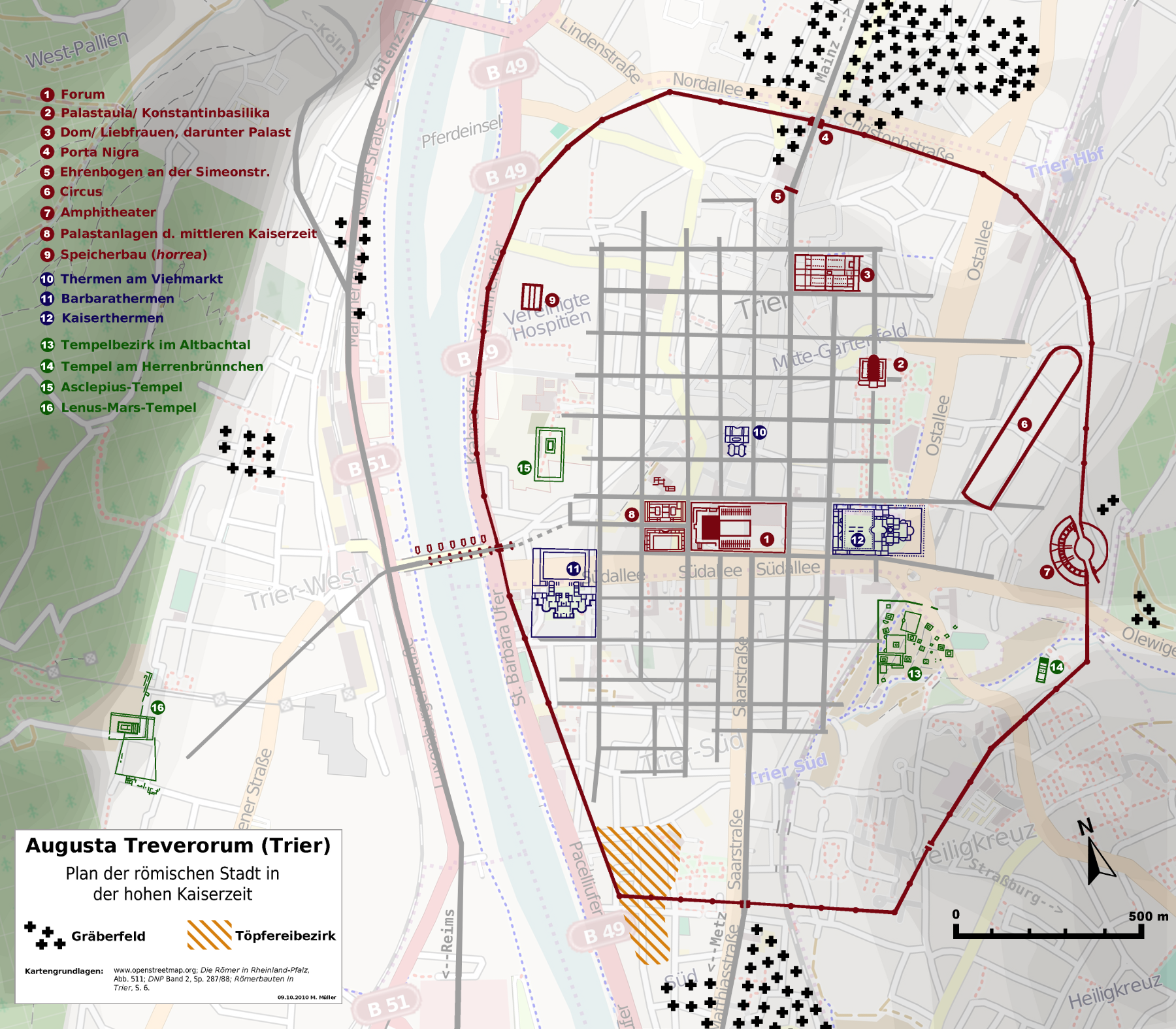
Barbara Baths on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Barbara Baths (German: Barbarathermen) are a large Roman bath complex in ''

Barbarathermen Trier ca. 360-370 n.Chr.jpg, Model of Augusta Treverorum showing location of Barbarathermen Trier ca. 360–370 AD
File:Barbarathermen Trier Merian 1646(1548).jpg, ca 1548 from an engraving by
Augusta Treverorum
Augusta Treverorum (Latin for "City of Augustus in the Land of the Treveri") was a Ancient Rome, Roman city on the Moselle River, from which modern Trier emerged.
The date of the city's founding is placed between the construction of the first Rom ...
'', modern-day Trier
Trier ( , ; ), formerly and traditionally known in English as Trèves ( , ) and Triers (see also Names of Trier in different languages, names in other languages), is a city on the banks of the Moselle (river), Moselle in Germany. It lies in a v ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
. Stretching over 42,000 square meters, it is the largest Roman bath north of the Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
. Along with other sites in Trier, the bath complex was designated a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
in 1986 as part of the Roman Monuments, Cathedral of St. Peter and Church of Our Lady in Trier site, because of its historical importance and sprawling architecture.
History


Roman Period
The Barbara Baths were built in the second half of the 2nd century C.E. along with a burst of building activity including a new bridge, anamphitheater
An amphitheatre ( U.S. English: amphitheater) is an open-air venue used for entertainment, performances, and sports. The term derives from the ancient Greek ('), from ('), meaning "on both sides" or "around" and ('), meaning "place for vie ...
and large forum. The Barbara Baths were built to meet the growing need for bathing in Trier when the Forum Baths became too small, the Barbara Baths, when completed, would measure 172 m x 240 m and encompass two city blocks. Their size would also increase demand for water, which would be supplied from the Ruwer aqueduct. This burst of activity appears to be a part of displays of wealth fitting the seat of the Roman Procurator of Gallia Belgica
Gallia Belgica ("Belgic Gaul") was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire located in the north-eastern part of Roman Gaul, in what is today primarily northern France, Belgium, and Luxembourg, along with parts of the Netherlands and German ...
Germania Inferior
''Germania Inferior'' ("Lower Germania") was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed ''Germania Secunda'' in the 4th century AD, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Cl ...
and Germania Superior
Germania Superior ("Upper Germania") was an imperial province of the Roman Empire. It comprised an area of today's western Switzerland, the French Jura and Alsace regions, and southwestern Germany. Important cities were Besançon ('' Vesont ...
. The bathing rooms and swimming pool
A swimming pool, swimming bath, wading pool, paddling pool, or simply pool, is a structure designed to hold water to enable Human swimming, swimming and associated activities. Pools can be built into the ground (in-ground pools) or built abo ...
was modeled after baths from North Africa. The heated rooms of the bathhouse are notable for using a two-story hypocaust. A marble torso of an Amazon warrior, now in the Landesmuseum Mainz, indicates that the bath complex would have been elaborately decorated with imported statues from Italy. It remained in use through the end of the fourth century. But the complex fell out of use during the early fifth century as Trier was repeatedly sacked during the Migration Period
The Migration Period ( 300 to 600 AD), also known as the Barbarian Invasions, was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories ...
.
Later usage
The extensive ruins were used as for many things following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. As early as the 5th century C.E. there are recognizable remains of residential buildings, the beginnings of the suburb of St. Barbara. Early Christian grave inscriptions demonstrate a possibleMerovingian
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from around the middle of the 5th century until Pepin the Short in 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the ...
period church. Later in the Middle ages fortifications were installed in the ruins as seen in Matthäus Merian Matthäus is a given name or surname. Notable people with the name include:
;Surname
* Lothar Matthäus, (born 1961), German former football player and manager
;Given name
* Matthäus Aurogallus, Professor of Hebrew at the University of Wittenberg ...
and Alexandre Wiltheim's drawings. Stating in 1611 C.E. the remains were recycled as building material for constructing a Jesuit College, which was later destroyed.
Current Remains
Only the foundations and the subterranean service tunnels have survived, but the technical details of the sewer systems, the furnaces, the pools, and the heating system can be studied better than in the other two baths of Trier. The site is open to visitors and the remains can be viewed from a footbridge, with waysides along the bridge to help visitors.Gallery
Matthäus Merian Matthäus is a given name or surname. Notable people with the name include:
;Surname
* Lothar Matthäus, (born 1961), German former football player and manager
;Given name
* Matthäus Aurogallus, Professor of Hebrew at the University of Wittenberg ...
published 1646
File:Barbarathermen Trier Wiltheim 1620 4.jpg, Ruins of Barbara Baths by Alexandre Wiltheim, c. 1620
File:Barbarathermen Trier Wiltheim 1620 3.jpg, Ruins of Barbara Baths by Alexandre Wiltheim, c. 1620
File:Barbarathermen Trier Wiltheim 1620 1.jpg, Ruins of Barbara Baths by Alexandre Wiltheim, c. 1620
File:Barbarathermen Trier Wiltheim 1620 2.jpg, Ruins of Barbara Baths by Alexandre Wiltheim, c. 1620
File:Barbarathermen Trier, Bauhütte Trier 1990 2.jpg, Conservation and restoration of the Roman ruins (1990)
File:Barbarathermen, Bauhütte Trier.jpg, Conservation and restoration of the Roman ruins (1990)
File:Trier Barbarathermen.jpg, Barbara Baths Today
File:Trier1123.jpg, Sleeping Cupid in Rheinisches Landesmuseum Trier
See also
*Ancient Roman bathing
Bathing played a major part in ancient Roman culture and society. It was one of the most common daily activities and was practiced across a wide variety of social classes.
Though many contemporary cultures see bathing as a private activity cond ...
* Thermae
In ancient Rome, (from Greek , "hot") and (from Greek ) were facilities for bathing. usually refers to the large Roman Empire, imperial public bath, bath complexes, while were smaller-scale facilities, public or private, that existed i ...
* Forum Baths
* Trier Imperial Baths
* List of Roman public baths
This is a list of ancient Roman public baths (''thermae'').
Urban baths
Algeria
* Timgad
* Guelma (Calama)
* Héliopolis, Algeria, Héliopolis
* Hammam Meskoutine (Aquae Tibilitanae)
* Hammam Righa (Aquae Calidae)
* Hammam Essalih ...
References
External links
* * {{Authority control World Heritage Sites in Germany Buildings and structures in Trier Ancient Roman baths History of Trier Ancient Roman buildings and structures in Germany