Banat Of Temeswar on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


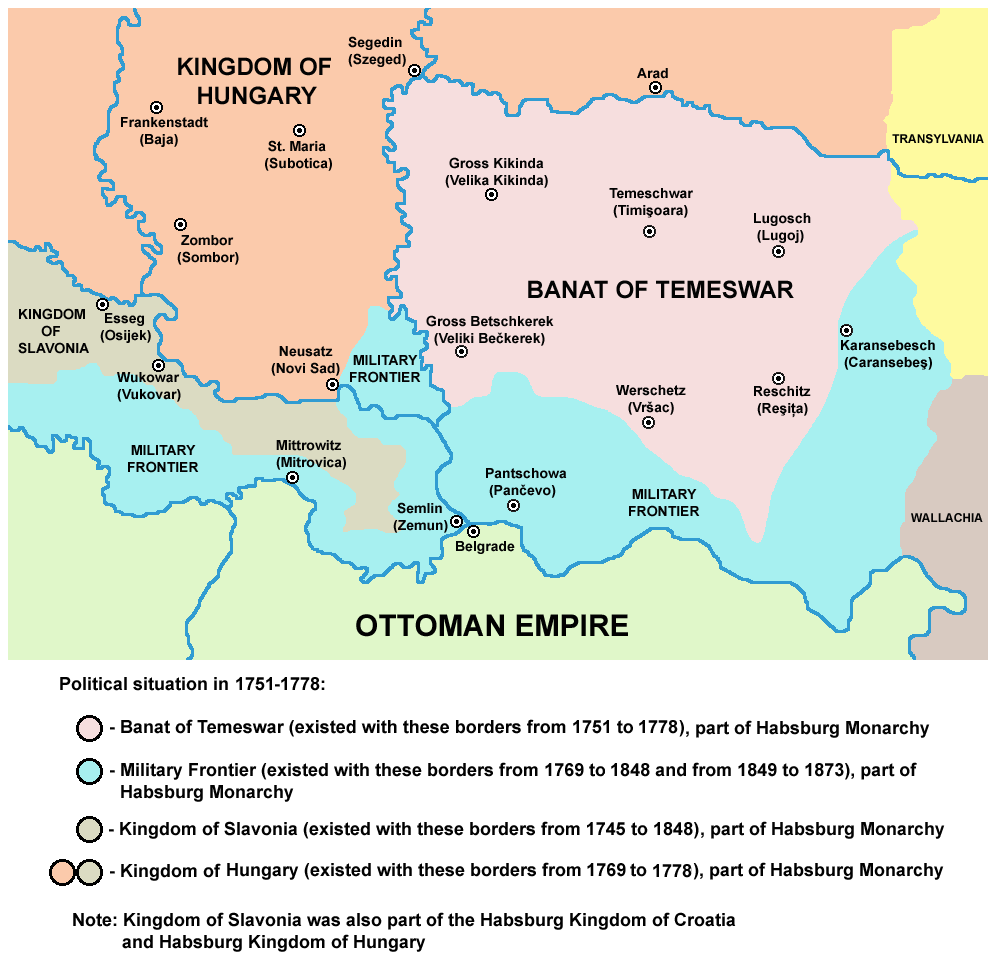 The Banat of Temeswar or Banat of Temes was a Habsburg province that existed between 1718 and 1778. It was located in the present day region of
The Banat of Temeswar or Banat of Temes was a Habsburg province that existed between 1718 and 1778. It was located in the present day region of
Ethnic Geography of the Hungarian Minority on the Carpathian Basin
Simon Publications LLC, 1998, pp 140 -141 until the 1740s, because the Habsburgs regarded them as "politically unreliable". Thus, Hungarians were almost totally absent from Banat in the first half of the 18th century. After the permission was given, Hungarian settlers arrived from different parts of the kingdom (mainly from
Map
Map
{{DEFAULTSORT:Banat Of Temeswar 1718 establishments in the Habsburg monarchy 1778 disestablishments in the Habsburg monarchy


 The Banat of Temeswar or Banat of Temes was a Habsburg province that existed between 1718 and 1778. It was located in the present day region of
The Banat of Temeswar or Banat of Temes was a Habsburg province that existed between 1718 and 1778. It was located in the present day region of Banat
Banat ( , ; ; ; ) is a geographical and Historical regions of Central Europe, historical region located in the Pannonian Basin that straddles Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. It is divided among three countries: the eastern part lie ...
, which was named after this province. The province was abolished in 1778 and the following year it was incorporated into the Habsburg Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
.
Duality of name
In the official documents of the time and also in all of native languages of the region, the name of the province appears in two basic forms, first derived from the name of Temeswar (Timișoara
Timișoara (, , ; , also or ; ; ; see #Etymology, other names) is the capital city of Timiș County, Banat, and the main economic, social and cultural center in Western Romania. Located on the Bega (Tisza), Bega River, Timișoara is consider ...
), second derived from the name of Temes region: in German - , Romanian - , Serbian - , , Hungarian - and Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
- .
History
Before the Habsburg province was established, several other entities had existed in the Banat region, including: the Voivodeship of Glad (9th century), the Voivodeship of Ahtum (11th century), the medievalKingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
(11th - 16th century) and one of its frontier provinces
the Banate of Severin (from 1233 to the 16th century), the Ottoman province named Eyalet of Temeşvar (1552–1716), and the Banate of Lugos and Karansebes province within the Principality of Transylvania (16th–17th century), which was under the suzerainty of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
as a whole.
Although after the Austro-Ottoman war (1683–1697) and before the treaty of Karlowitz (1699) most parts of Banat were temporarily controlled by the forces of Prince Eugene of Savoy; in consequence of the treaty, the Ottoman sovereignty was recognized over the region with the fort of Temeşvar. However, as a result of the Spanish Succession War and the Rákóczi's War for Independence, the Habsburgs were inclined to direct their attention elsewhere within their country, and there was no attempt on their part to gain any territories from the Ottomans until 1710.
In the Austro-Turkish War of 1716-18, Prince Eugene of Savoy conquered the Banat region from the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
, which was recognized by the Treaty of Passarowitz (1718). The Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
then established a new military administrative region there under the name of Banat of Temeswar. The capital of the province became Temeswar. The province remained under military administration until 1751 when civil administration was introduced in northern parts of the region by Empress Maria Theresa of Austria.
From 1718 to 1739, Banat of Temeswar included not only the Banat region, but also parts of present-day eastern Serbia along the southern bank of the Danube river. Following the Treaty of Belgrade (1739), areas along the southern bank of Danube returned under Ottoman control. In 1751, the southern parts of Banat were excluded from the province and the Banatian Military Frontier was established in that area.
The Banat of Temeswar was abolished on 6 June 1778, and on 23 April 1779, it was incorporated into the Habsburg Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
, while its former territory was divided into three counties: Torontál, Temes and Krassó. The southern part of the Banat region, which was part of the Banat of Temeswar until 1751, remained part of the Military Frontier (Banat Krajina
The Banat Military Frontier or simply Banat Frontier (; ; ) was a district of the Habsburg monarchy's Military Frontier during the 18th and 19th centuries. It was located in southern parts of the Banat region. It was formed in 1764, out of territo ...
) until 1873.
In 1849 following the Revolutions of 1848/1849 the Banat of Temeswar was resurrected as part of the new Voivodeship of Serbia and Banat of Temeswar crown land, which combined the former lands of the Banat of Temeswar with most of those from the self-proclaimed Serbian Vojvodina (excluding those parts of both within the military frontier). The former Banat counties of Torontál, Temes and Krassó were transformed into the of Groß Bečkerek, Temesvár and Lugos respectively. It was once again abolished in 1860; the counties were restored and re-merged into Hungary.
Population
The province was bound to repopulate after the Habsburg conquest because it had a low population density on the grounds that the territory sustained a lot of adversity from the previous wars. The population density was among the lowest in Europe; some researchers suggest that it was around 1 person / square kilometres. According to the first census conducted by the Habsburg military authorities, the population of Banat numbered about 20,000 inhabitants, mostly Serbs. The former Muslim population of Banat had left the area immediately before and during the Habsburg conquest. The low population density resulted in the territory being repopulated by German families coming from Austrian and southern German lands, Romanians coming from Wallachia and Transylvania, by Slovaks from the north, and by Serb refugees coming from the Ottoman Empire, while some Serbs arrived in the area from other parts of theHabsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
. Colonization of various ethnic groups in the area lasted until the early 19th century. The government organized regimental districts which mostly had Serb population with special privileges in exchange for defending the borders. The area also lost its Hungarian population in the 16th century, but Hungarians were not allowed to returnKároly Kocsis, Eszter Kocsisné Hodosi,Ethnic Geography of the Hungarian Minority on the Carpathian Basin
Simon Publications LLC, 1998, pp 140 -141 until the 1740s, because the Habsburgs regarded them as "politically unreliable". Thus, Hungarians were almost totally absent from Banat in the first half of the 18th century. After the permission was given, Hungarian settlers arrived from different parts of the kingdom (mainly from
Transdanubia
Transdanubia ( ; , or ', ) is a traditional region of Hungary. It is also referred to as Hungarian Pannonia, or Pannonian Hungary.
Administrative divisions Traditional interpretation
The borders of Transdanubia are the Danube River (north and ...
, Csongrád county and the Jász and Kun districts).
According to data from 1774, the population of the Banat of Temeswar was composed of:Miodrag Milin, Vekovima zajedno (Iz istorije srpsko-rumunskih odnosa), Temišvar, 1995.
* Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, ...
= 220,000
* Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Southeastern Europe who share a common Serbian Cultural heritage, ancestry, Culture of Serbia, culture, History of Serbia, history, and Serbian lan ...
and Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
= 100,000
* Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
= 53,000
* Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former pa ...
and Bulgarians
Bulgarians (, ) are a nation and South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and its neighbouring region, who share a common Bulgarian ancestry, culture, history and language. They form the majority of the population in Bulgaria, ...
= 2,400
* Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
= 340
The first official census took part during the rule of Joseph II, from the late 18th century. This shows Romanian majority in the east, Serbian in the west, and numerous German population in the whole area.
Governors
Governors of Banat of Temeswar did not have the title of "ban". They were military governors and chefs of provincial administration (in German: Militärpräsidenten der Landesadministration des Temescher Banats).Johann Heinrich Schwicker: Geschichte des Temeser Banats, LaVergne TN USA 2010 * Claudius Florimund Mercy (1716–1734) * Johann Andreas von Hamilton (1734–1738) * Wilhelm Reinhard von Neipperg (1738–1739) * August Jakob Heinrich von Suckow (1739–1740) * Franz Anton Leopold Ponz von Engelshofen (1740–1757) * Ferdinand Philipp von Harsch (1757–1758) * Anton von Puebla (1758–1759) * Siegmund Friedrich Samuel von Lietzen (1759–1769) * Maximilian Joseph von Mitrowsky (1769–1775) * Johann Franz Anton von Zedtwitz (1775–1779)See also
*Banat
Banat ( , ; ; ; ) is a geographical and Historical regions of Central Europe, historical region located in the Pannonian Basin that straddles Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. It is divided among three countries: the eastern part lie ...
* Banat Krajina
The Banat Military Frontier or simply Banat Frontier (; ; ) was a district of the Habsburg monarchy's Military Frontier during the 18th and 19th centuries. It was located in southern parts of the Banat region. It was formed in 1764, out of territo ...
* Ottoman Province of Temeşvar
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * Marin, Irina. ''Contested Frontiers in the Balkans: Ottoman, Habsburg, and Communist Rivalries in Eastern Europe'' (I.B. Tauris, distributed by Palgrave Macmillan; 2013) 228 pages; focuses on the Banat of Temesvar * Miodrag Milin, ''Vekovima zajedno (Iz istorije srpsko-rumunskih odnosa)'', Temišvar, 1995. * Forţiu, Sorin. ''Denumirea Banatului în epoca modernă (sec. XVIII - XX): Banatus Timisvariensis vel Banatus Temesiensis?'', in: Descoperiţi Banatul - Timişoara, Biblioteca Banaterra - Cartea 1, Editura Waldpress, Timişoara, 2009, 192 pg., ISBN 978-973 -7878-44-1; p. 104-144.External links
Map
Map
{{DEFAULTSORT:Banat Of Temeswar 1718 establishments in the Habsburg monarchy 1778 disestablishments in the Habsburg monarchy