BMP-2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The BMP-2 (''Boyevaya Mashina Pekhoty'', , literally "combat machine/vehicle f theinfantry") is an amphibious
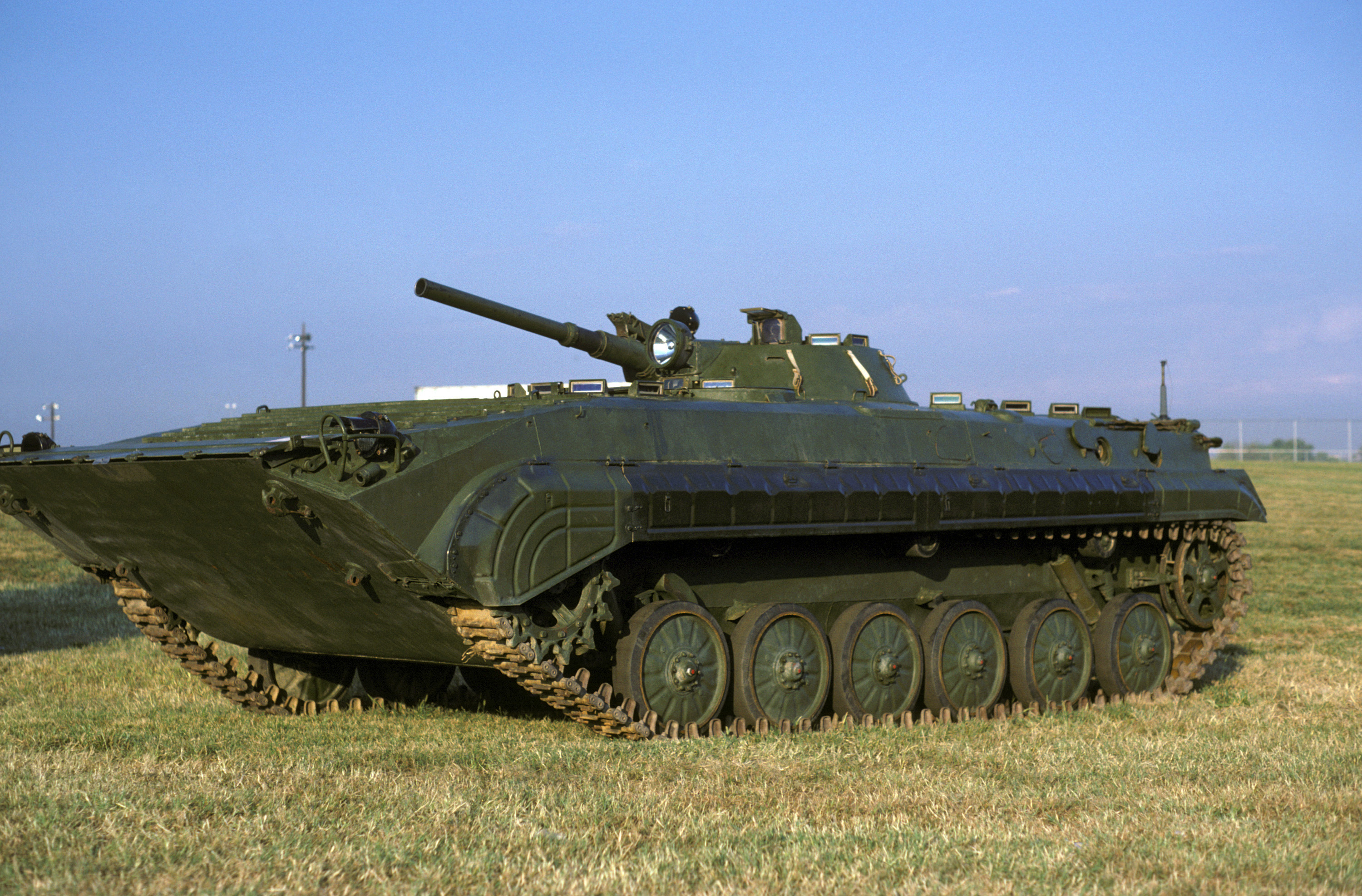 Although the
Although the
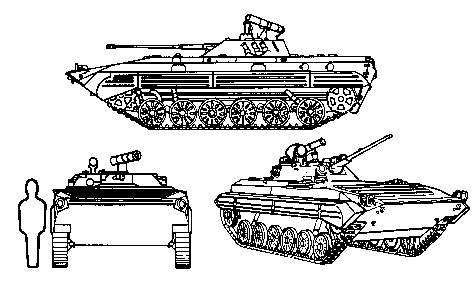 The BMP-2 is broadly similar to the BMP-1. The most significant changes are:
* The commander now sits with the gunner in an enlarged, two-man turret.
* Armament changed to the 2A42 30 mm autocannon and the 9P135M ATGM launcher capable of firing SACLOS guided 9M111 "Fagot" (AT-4 Spigot), 9M113 "Konkurs" (AT-5 Spandrel) and 9M113M "Konkurs-M" (AT-5B Spandrel B) anti-tank missiles.
* Only seven troops can be carried instead of eight.
* Two rear infantry roof hatches instead of four.
* Slightly improved armour.
The BMP-2 is broadly similar to the BMP-1. The most significant changes are:
* The commander now sits with the gunner in an enlarged, two-man turret.
* Armament changed to the 2A42 30 mm autocannon and the 9P135M ATGM launcher capable of firing SACLOS guided 9M111 "Fagot" (AT-4 Spigot), 9M113 "Konkurs" (AT-5 Spandrel) and 9M113M "Konkurs-M" (AT-5B Spandrel B) anti-tank missiles.
* Only seven troops can be carried instead of eight.
* Two rear infantry roof hatches instead of four.
* Slightly improved armour.
 In the Soviet Army, BMPs were typically issued to the motor rifle battalions of tank regiments. In a typical motor-rifle division, one motor-rifle regiment had BMPs, the other two had wheeled BTRs.
Proliferation varied greatly among the rest of the Warsaw Pact nations. For example, at least some East German motor-rifle divisions were recorded to have all three motor-rifle regiments with BMPs, ranging down to the Romanian and Bulgarian Armies, some of whose divisions had no BMPs at all.
Poland planned to replace its BWP-1 with BWP-2 (BMP-2 and BMP-2D); but, because of financial problems, only ordered 62 vehicles in 1988, which were delivered in 1989. Since obtaining a sufficient number of BWP-2 vehicles after the political changes of 1989 became impossible, Poland was forced to abandon this plan. The 62 BWP-2 that Poland bought were sold to Angola in 1995. However, after shipping 42 of the IFVs and receiving a partial payment of 6.3 million USD, Angola withdrew from the deal, refusing to take the remaining 20 vehicles. These 20 additional vehicles were later sold to Togo and left Poland in 1997.BMP-2 Pancerni.net 1
In the Soviet Army, BMPs were typically issued to the motor rifle battalions of tank regiments. In a typical motor-rifle division, one motor-rifle regiment had BMPs, the other two had wheeled BTRs.
Proliferation varied greatly among the rest of the Warsaw Pact nations. For example, at least some East German motor-rifle divisions were recorded to have all three motor-rifle regiments with BMPs, ranging down to the Romanian and Bulgarian Armies, some of whose divisions had no BMPs at all.
Poland planned to replace its BWP-1 with BWP-2 (BMP-2 and BMP-2D); but, because of financial problems, only ordered 62 vehicles in 1988, which were delivered in 1989. Since obtaining a sufficient number of BWP-2 vehicles after the political changes of 1989 became impossible, Poland was forced to abandon this plan. The 62 BWP-2 that Poland bought were sold to Angola in 1995. However, after shipping 42 of the IFVs and receiving a partial payment of 6.3 million USD, Angola withdrew from the deal, refusing to take the remaining 20 vehicles. These 20 additional vehicles were later sold to Togo and left Poland in 1997.BMP-2 Pancerni.net 1
. Pancerni.abajt.pl. Retrieved 20 September 2011.


 * 1975–2002:
* 1975–2002:
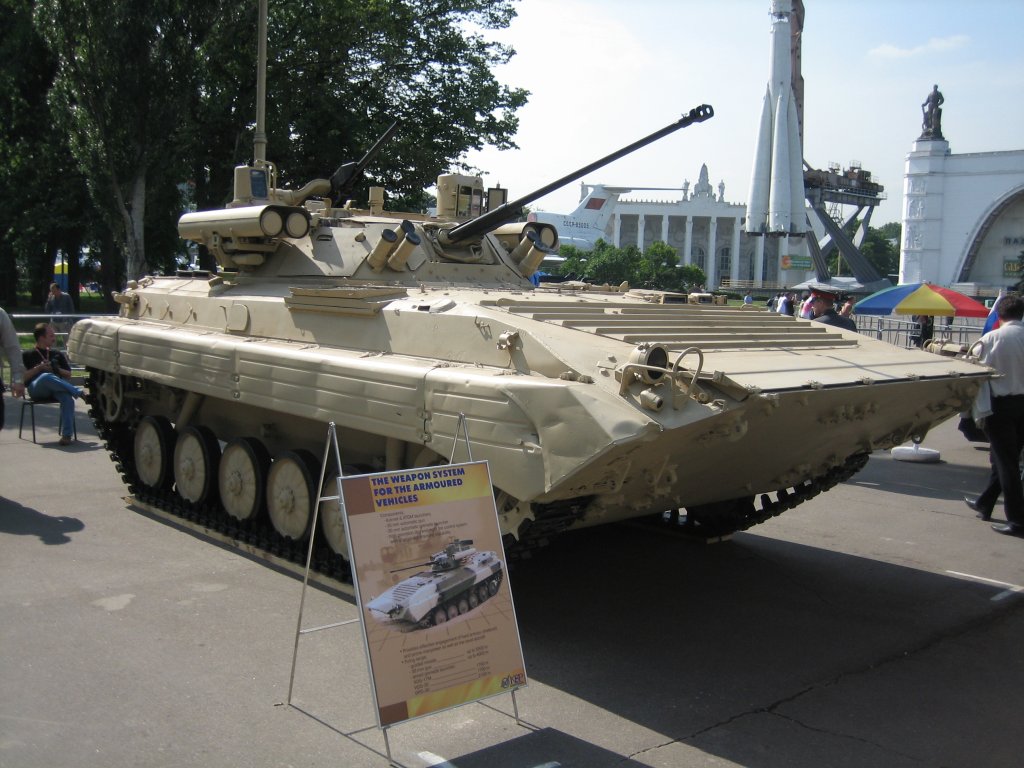
 * BMP-2 obr. 1980 – Initial production model.
** BMP-2 obr. 1984 – Improved version with "kovriki" armour on turret front.
*** BMP-2 obr. 1986 – Late-production model with new BPK-2-42 sight instead of the BPK-1-42.
** BMP-2D (D stands for ''dorabotanaya'' – modified) – Fitted with additional spaced type steel appliqué armour on the hull sides, under the driver's and commander's stations, and 6 mm thick appliqué armour on the turret. Owing to the added weight, the vehicle is no longer amphibious. It also has provision for mounting a mine clearing system under the nose of the vehicle. In service since 1982, it saw service during
* BMP-2 obr. 1980 – Initial production model.
** BMP-2 obr. 1984 – Improved version with "kovriki" armour on turret front.
*** BMP-2 obr. 1986 – Late-production model with new BPK-2-42 sight instead of the BPK-1-42.
** BMP-2D (D stands for ''dorabotanaya'' – modified) – Fitted with additional spaced type steel appliqué armour on the hull sides, under the driver's and commander's stations, and 6 mm thick appliqué armour on the turret. Owing to the added weight, the vehicle is no longer amphibious. It also has provision for mounting a mine clearing system under the nose of the vehicle. In service since 1982, it saw service during
Photos
* VPV (VPV stands for ''vyprošťovací pásové vozidlo'') – BVP-2 conversion into an ARV developed at the ZTS Martin Research and Development Institute and production commenced at the ZTS Martin plant (which is now in Slovakia) in 1984. It is equipped with a powered crane with 5 tonnes capacity, heavy winch, wider troop compartment etc. Hatches on top of the turret and the troop compartment were removed. The vehicle is divided into four compartments: engine, commander's, driver's and repair/cargo. The crew consists of a commander/crane operator, driver/welder/slinger and a logistician/mechanic. The vehicle is armed with a pintle-mounted 7.62 mm PKT light machine gun. A small number of those vehicles was also based on BVP-1.
 * BMP-2 "Sarath" ("
* BMP-2 "Sarath" ("
. Ofbindia.gov.in. Retrieved 20 September 2011. built by
. Armstrade.sipri.org. Retrieved 20 September 2011. 550 BMP-1s and BMP-2s in service in 1992. Between 60 and 80 BMP-1s and BMP-2s were delivered from Russia after 2002. * – 225 along with 2,250 9M111 Fagot ATGMs were ordered in 1989 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1990 and 1991. 54 BVP-2s and BVP-2Ks were ordered in 1994 from Slovakia and delivered between 1995 and 1996. 64 were ordered in 1998 from Ukraine and delivered between 1998 and 1999 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Ukrainian service). Estimated to have 220 BMP-2 and 760 BMP-2M in service as of 2023 * – 65, along with 650 9M111 Fagot ATGMs, were ordered in 1987 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1987. 7 were ordered in 1993 from Hungary and delivered in 1993 (the vehicles were previously in Hungarian service and were sold via Czech Republic). 42 BMP-2s were ordered in 1994 from Poland and delivered between 1994 and 1995 (the vehicles were previously in Polish service). 65 were ordered in 1997 from Russia and delivered in 1998 (the vehicles were possibly previously in Soviet and later Russian service). 62 were ordered in 1999 from Belarus and delivered in 1999 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Belarusian service). 31 were ordered in 1999 from Ukraine and delivered in 1999 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Ukrainian service). 250 BMP-1 and BMP-2 in service as of 2023 * – 15 as of 2023
 * – 101 in service with the army and 168 BMP-1 and BMP-2 in service with the State Border Service as of 2023
* – 906 as of 2023
* – 120 in service as of 2025. 200 inherited from former Czechoslovakia.
* – 110 BMP-2MD in service as of 2025.
* – 101 in service with the army and 168 BMP-1 and BMP-2 in service with the State Border Service as of 2023
* – 906 as of 2023
* – 120 in service as of 2025. 200 inherited from former Czechoslovakia.
* – 110 BMP-2MD in service as of 2025.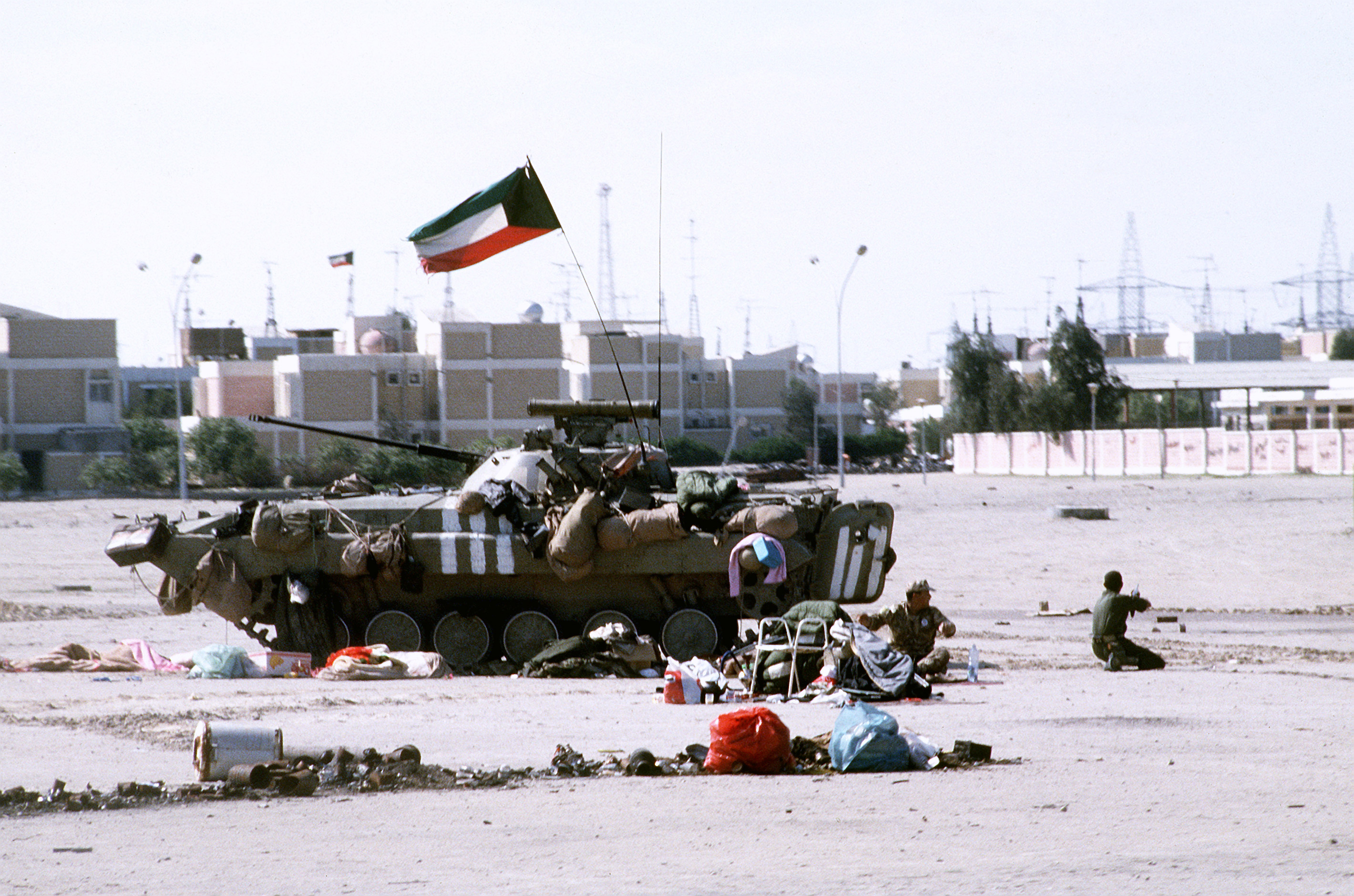 * – 245 along with 2,450 9M111 Fagot ATGMs were ordered in 1988 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1989 and 1990. Some captured or destroyed by the Iraqi forces. 46 along with 460 9M111 Fagot ATGMs were ordered in 1994 from Russia and delivered between 1994 and 1995. 76 in service as of 2023
* – 90 as of 2023
* – Unknown number in service with the Government of National Unity
* – 2 in service as of 2023
* – 11 were ordered in 2001 from Ukraine and delivered in 2001 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Ukrainian service). 10 BMP-2 and 1 BMP-2K in service as of 2023
* Popular Mobilization Forces − Unknown number in service
* – 2,350 BMP-2 and BMP-2M in service with the army, 300 in service with the Naval Infantry, and an unknown number in service with the 1st Army Corps, 2nd Army Corps, and National Guard as of 2023 As of February 6, 2025, Russia has been visually confirmed to have lost at least 1,851 BMP-2s of various variants (1,396 destroyed, 41 damaged, 158 abandoned, and 256 captured)
* – 90 in service as of 2025.
* – 4 were ordered in 1994 from Ukraine and delivered in 1994 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Ukrainian service). 36 were ordered in 2001 from Russia and delivered in 2001. 49 in service as of 2023
* – 6 were ordered in 1995 from Ukraine and delivered in 1996 (the vehicles were probably previously in Soviet and later Ukrainian service). 9 were ordered in 2003 from Belarus and delivered in 2003 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Belarusian service). Unknown number in service as of 2023
* – 400 were ordered in 1987 from the Soviet Union and were delivered between 1987 and 1988. Unknown number in service as of 2023
* – 15 as of 2023
* – 20 ordered in 1996 from Poland and delivered in 1997. 20 in service as of 2023
*
* – 245 along with 2,450 9M111 Fagot ATGMs were ordered in 1988 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1989 and 1990. Some captured or destroyed by the Iraqi forces. 46 along with 460 9M111 Fagot ATGMs were ordered in 1994 from Russia and delivered between 1994 and 1995. 76 in service as of 2023
* – 90 as of 2023
* – Unknown number in service with the Government of National Unity
* – 2 in service as of 2023
* – 11 were ordered in 2001 from Ukraine and delivered in 2001 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Ukrainian service). 10 BMP-2 and 1 BMP-2K in service as of 2023
* Popular Mobilization Forces − Unknown number in service
* – 2,350 BMP-2 and BMP-2M in service with the army, 300 in service with the Naval Infantry, and an unknown number in service with the 1st Army Corps, 2nd Army Corps, and National Guard as of 2023 As of February 6, 2025, Russia has been visually confirmed to have lost at least 1,851 BMP-2s of various variants (1,396 destroyed, 41 damaged, 158 abandoned, and 256 captured)
* – 90 in service as of 2025.
* – 4 were ordered in 1994 from Ukraine and delivered in 1994 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Ukrainian service). 36 were ordered in 2001 from Russia and delivered in 2001. 49 in service as of 2023
* – 6 were ordered in 1995 from Ukraine and delivered in 1996 (the vehicles were probably previously in Soviet and later Ukrainian service). 9 were ordered in 2003 from Belarus and delivered in 2003 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Belarusian service). Unknown number in service as of 2023
* – 400 were ordered in 1987 from the Soviet Union and were delivered between 1987 and 1988. Unknown number in service as of 2023
* – 15 as of 2023
* – 20 ordered in 1996 from Poland and delivered in 1997. 20 in service as of 2023
*  * – 890 in service with the army and 1 in service with the National Guard prior to the
* – 890 in service with the army and 1 in service with the National Guard prior to the
 * − In February 2023, it was estimated to have 100 BMP-2s. Seized by Azerbaijan after the 2023 Nagorno-Karabakh clashes
* – 279 ordered in 1978 and produced between 1983 and 1989. Passed on to the successor states.
* – 24 were ordered in 1985 from the Soviet Union and were delivered between 1986 and 1987 (the vehicles were possibly produced in Czechoslovakia). Passed on to the unified German state.
* – 24, taken from East Germany's army, all sold to other countries or given to the museums.
* – 200 were ordered in 1986 from the Soviet Union and were delivered between 1987 and 1989(some of the vehicles were possibly produced in Czechoslovakia). 1,000 BMP-1 and BMP-2 in service in 1989, and 900 BMP-1 and BMP-2 in 2001. Possibly captured some from Kuwait in the First Persian Gulf War. All destroyed in the 2003 invasion of Iraq and later scrapped.
* – 37 BMP-2 ordered from the Soviet Union in 1986 and delivered in 1987. None remain in service in 2023
* – Unknown number of BMP-2 received from Ukraine and Russia.
* – 62 BMP-2s and BMP-2Ds (all of which were designed as BWP-2) ordered in 1988 and delivered in 1989. All 62 vehicles were sold to Angola in 1994. Only 42 were shipped. The remaining 20 were sold to Togo.
* – 4 were ordered and delivered from Russia in 1992 (the vehicles were second-hand). None remain in service in 2023
* – 26,000 BMP-1s and BMP-2s in service in 1989. Passed on to successor states.
* − In February 2023, it was estimated to have 100 BMP-2s. Seized by Azerbaijan after the 2023 Nagorno-Karabakh clashes
* – 279 ordered in 1978 and produced between 1983 and 1989. Passed on to the successor states.
* – 24 were ordered in 1985 from the Soviet Union and were delivered between 1986 and 1987 (the vehicles were possibly produced in Czechoslovakia). Passed on to the unified German state.
* – 24, taken from East Germany's army, all sold to other countries or given to the museums.
* – 200 were ordered in 1986 from the Soviet Union and were delivered between 1987 and 1989(some of the vehicles were possibly produced in Czechoslovakia). 1,000 BMP-1 and BMP-2 in service in 1989, and 900 BMP-1 and BMP-2 in 2001. Possibly captured some from Kuwait in the First Persian Gulf War. All destroyed in the 2003 invasion of Iraq and later scrapped.
* – 37 BMP-2 ordered from the Soviet Union in 1986 and delivered in 1987. None remain in service in 2023
* – Unknown number of BMP-2 received from Ukraine and Russia.
* – 62 BMP-2s and BMP-2Ds (all of which were designed as BWP-2) ordered in 1988 and delivered in 1989. All 62 vehicles were sold to Angola in 1994. Only 42 were shipped. The remaining 20 were sold to Togo.
* – 4 were ordered and delivered from Russia in 1992 (the vehicles were second-hand). None remain in service in 2023
* – 26,000 BMP-1s and BMP-2s in service in 1989. Passed on to successor states.
Russian-Manufactured Armored Vehicle Vulnerability in Urban Combat: The Chechnya Experience
Red Thrust Star, January 1997
SOVIET BMP-2 Infantry Fighting Vehicle – Walk around photos
BMP-2M Berezhok and other upgrades on V. Kuzmin's photo blog
BMP-2M Berezhok walk-around on Prime Portal
{{Portal bar, Soviet Union Tracked infantry fighting vehicles Cold War armoured fighting vehicles of the Soviet Union Tracked reconnaissance vehicles Amphibious infantry fighting vehicles Infantry fighting vehicles of the Soviet Union Infantry fighting vehicles of the Cold War Infantry fighting vehicles of India Kurganmashzavod products Military vehicles introduced in the 1980s
infantry fighting vehicle
An infantry fighting vehicle (IFV), also known as a mechanized infantry combat vehicle (MICV), is a type of armoured fighting vehicle and armoured personnel carrier used to carry infantry into battle and provide direct fire, direct-fire suppo ...
introduced in the 1980s in the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, following on from the BMP-1
The BMP-1 is a Soviet Union, Soviet Amphibious vehicle, amphibious tracked infantry fighting vehicle that has been in service from 1966 to the present. BMP stands for ''Boyevaya Mashina Pyekhoty 1'' (), meaning "infantry fighting vehicle, 1st ...
of the 1960s.
Development history
BMP-1
The BMP-1 is a Soviet Union, Soviet Amphibious vehicle, amphibious tracked infantry fighting vehicle that has been in service from 1966 to the present. BMP stands for ''Boyevaya Mashina Pyekhoty 1'' (), meaning "infantry fighting vehicle, 1st ...
was a revolutionary design, its main armament, the 2A28 Grom and the 9S428 ATGM launcher capable of firing 9M14 Malyutka
The 9M14 Malyutka (; "Little one", NATO reporting name: AT-3 Sagger) is a manual command to line of sight (MCLOS) wire-guided anti-tank guided missile (ATGM) system developed in the Soviet Union. It was the first man-portable anti-tank guided mi ...
(NATO: AT-3A Sagger A) and 9M14M Malyutka-M (NATO: AT-3B Sagger B) ATGMs, quickly became obsolete. Therefore, the Soviet Union decided to produce an updated and improved version of the BMP-1. The main emphasis was put on improving the main armament. In 1972, work got under-way to develop an improved version of the BMP-1.
During its combat debut in the 1973 Arab-Israeli War, Egyptian and Syrian BMPs proved vulnerable to .50 calibre machine-gun fire in the sides and rear, and to 105 mm M40 recoilless rifles. The 2A28 Grom proved inaccurate beyond 500 metres, and the 9M14 Malyutka missile could not be guided effectively from the confines of the turret.
Several Soviet technical teams were sent to Syria in the wake of the war to gather information. These lessons, combined with observations of western AFV developments, resulted in a replacement project for the original BMP in 1974. The result was the BMP-1P upgrade, which was intended as a stopgap to address the most serious problems with the existing design.
Smoke grenade launchers were added to the rear of the turret and the manually guided 9M14 Malyutka missile system was replaced with the semi-automatically guided 9K111 Fagot / 9M113 Konkurs
The 9M113 ''Konkurs'' (; ; NATO reporting name AT-5 ''Spandrel'') is a Soviet SACLOS wire-guided anti-tank missile.
A development of the 9K111 Fagot with greater firepower, the 9M113 Konkurs can use the same launchers and is very similar vis ...
system. The BMP-1P was in production by the late 1970s. Existing BMP-1s were gradually upgraded to the BMP-1P standard during the 1980s.
Design
 The BMP-2 is broadly similar to the BMP-1. The most significant changes are:
* The commander now sits with the gunner in an enlarged, two-man turret.
* Armament changed to the 2A42 30 mm autocannon and the 9P135M ATGM launcher capable of firing SACLOS guided 9M111 "Fagot" (AT-4 Spigot), 9M113 "Konkurs" (AT-5 Spandrel) and 9M113M "Konkurs-M" (AT-5B Spandrel B) anti-tank missiles.
* Only seven troops can be carried instead of eight.
* Two rear infantry roof hatches instead of four.
* Slightly improved armour.
The BMP-2 is broadly similar to the BMP-1. The most significant changes are:
* The commander now sits with the gunner in an enlarged, two-man turret.
* Armament changed to the 2A42 30 mm autocannon and the 9P135M ATGM launcher capable of firing SACLOS guided 9M111 "Fagot" (AT-4 Spigot), 9M113 "Konkurs" (AT-5 Spandrel) and 9M113M "Konkurs-M" (AT-5B Spandrel B) anti-tank missiles.
* Only seven troops can be carried instead of eight.
* Two rear infantry roof hatches instead of four.
* Slightly improved armour.
Layout
In the centre of the vehicle is the welded steel turret, which seats the commander and gunner, both of whom have hatches. The commander sits to the right and has three day-vision periscopes, a 1PZ-3 day-sight designed for anti-aircraft use with 1.2× and 4× magnification, an OU-3GA2 infra-red searchlight, a TNP-165A designator and a TKN-3B binocular sight with 4.75× day magnification and 4× night-sight magnification. The gunner sits to the commander's left and has a smaller rectangular hatch with a rearward-facing day periscope. There are three other day periscopes facing forward and left. The gunner has a BPK-1-42 binocular sight with a moon/starlight vision range of 650 metres, or 350 metres using the infra-red searchlight, and a TNPT-1 designator. An FG-126 infra-red searchlight is mounted coaxially to the 30 mm cannon. The driver sits in the front left of the vehicle, with the engine in a separate compartment to his right. The driver has his own entry hatch above him, with three day-vision periscopes. The centre TNPO-170A periscope can be replaced with either a TNPO-350B extended periscope for amphibious operation or a TVNE-1PAnight vision
Night vision is the ability to see in low-light conditions, either naturally with scotopic vision or through a night-vision device. Night vision requires both sufficient spectral range and sufficient intensity range. Humans have poor night v ...
scope. An infantryman sits immediately behind the driver, and has a firing port
A firing port, sometimes called a pistol port, is a small opening in armored vehicles, Fortification, fortified structures like bunkers, or other armored equipment that allows small arms to be safely fired out of the vehicle at enemy infantry, oft ...
and vision block. TNPO-170A periscopes are used throughout the vehicle and are electrically heated.
In the BMP-1 and BMP-2, ammunition is stored near or even inside the compartment, which can lead to a catastrophic failure in case of a hull breach.
Mobility
The BMP-1 and BMP-2 share the same chassis and have almost identical road performance. The BMP-2 is heavier, but also has a more powerful engine to compensate. The BMP-2 is amphibious with little preparation, using hydrodynamic fairings to convert track momentum into water jets. Peacetime regulations require that any BMPs entering water must have a working radio set, since its bearings are not airtight and it can be carried away by currents in case of loss of engine power (the vehicle lacks an anchor).Weapons
The main armament is a turret with a stabilized 30 mm 2A42 autocannon with dual ammunition feeds, which provide a choice of 3UBR6 AP-T and 3UOR6 HE-T / 3UOF8 HE-I ammunition and 9M113 Konkurs ATGM. The gun has a selectable rate of fire, either slow at 200 to 300 rounds per minute or fast at 550 rounds per minute. This gives a continuous fire time of 100–150 seconds (or only 55 seconds, depending on the rate of fire chosen) before running out of ammunition. The original stabilization provides reasonable accuracy up to a speed of about 35 kilometres per hour. The AP-T ammunition can penetrate 15 millimetres of armour at sixty degrees at 1,500 metres. A new APDS-T tungsten round can penetrate 25 millimetres at the same distance. A typical ammunition load is 160 rounds of AP ammunition and 340 rounds of HE ammunition. The ammunition sits in two trays located on the turret rear floor. The gun can be fired from either the commander's or the gunner's station. The commander's 1PZ-3 sight is specifically designed for anti-aircraft operation. Combined with the high maximum elevation of 74 degrees, it allows the 30 mm cannon to be used effectively against helicopters and slow flying aircraft. The turret traverse and elevation are powered and it can traverse 360 degrees in 10.28 seconds and elevate through 74 degrees in 12.33 seconds. Reloading the BMP-2's 30 mm cannon can be somewhat problematic and can take up to two hours, even if the ammunition is prepared. The cannon is normally only used on the slow rate of fire, otherwise, fumes from the weapon would build up in the turret faster than the extractor fan can remove them. The effective range of the 30 mm cannon is up to 1,500 metres against armour, 4,000 metres against ground targets, and 2,500 metres against air targets. A coaxial 7.62 mm PKT machine gun is mounted to the left of the 30 mm cannon. 2,000 rounds of ammunition are carried for it. On the roof of the turret is an ATGM launcher. On Russian vehicles this fires 9M113 Konkurs missiles. On export models it normally fires 9K111 Fagot missiles. A ground-mount for the missile is carried, allowing it to be used away from the vehicle. The missiles are a substantial improvement on the 9M14 Malyutka missiles used on the BMP-1, in both range and accuracy. Behind the turret is the troop compartment that holds six troops. A seventh sits just behind the driver. The troops sit back to back, along the center of the vehicle. Down each side of the compartment are three firing ports with periscopes. Access to the compartment is by the two rear doors, which hold fuel tanks. Both doors have integral periscopes. The left door has a firing port. In addition to the main weapons, it can carry a man-portable surface-to-air missile launcher and two missiles, and an RPG launcher and five rounds. The vehicle is fitted with a PAZ overpressure NBC system and fire suppression system, and carries a GPK-59gyrocompass
A gyrocompass is a type of non-magnetic compass which is based on a fast-spinning disc and the rotation of the Earth (or another planetary body if used elsewhere in the universe) to find geographical Direction (geometry), direction automaticall ...
.
Countermeasures
The original BMP-1 had a vulnerability in its mine protection scheme, which only became obvious during the war in Afghanistan. The one-man-turret fighting vehicle seated its driver and commander in tandem layout, in the front-left side of the hull alongside the diesel engine. When a BMP-1 hit a tilt-rod anti-tankland mine
A land mine, or landmine, is an explosive weapon often concealed under or camouflaged on the ground, and designed to destroy or disable enemy targets as they pass over or near it. Land mines are divided into two types: anti-tank mines, wh ...
its steeply sloped lower front glacis armour plate allowed the mine's arming rod to tilt with little resistance until the maximum deflection was reached, at which time the mine was already well under the chassis.
When it subsequently detonated, the blast usually killed both the driver and the vehicle commander. This shortcoming was addressed in the BMP-2 design, where the tank commander shares the well-armoured two-man turret with the gunner. The driver's station has been enlarged and he is provided with an armored driver's seat, in addition to extra belly armor in the lower front.
The IFV lacks the ability to install add-on protection packages like slat armor
Slat armor (or slat armour in British English), also known as bar armor, cage armor, and standoff armor, is a type of vehicle armor designed to protect against high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) attacks, as used by anti-tank guided missiles (ATG ...
cages or explosive reactive armor
Reactive armour is a type of vehicle armour used in protecting vehicles, especially modern tanks, against shaped charges and hardened kinetic energy penetrators. The most common type is ''explosive reactive armour'' (ERA), but variants includ ...
(ERA). The BMP-2's armor is very similar to the original BMP-1, resistant to 23 mm armor-piercing rounds on its frontal arc from 500 meters (and immune to 12.7 mm armor-piercing from the same angle) and to 7.62x39 mm armor-piercing rounds to its sides. Its armor is slightly thinner than the BMP-1's but the higher-quality steel used in its construction grants it the same effective protection.
The basic hull armor on the BMP-2 can be easily penetrated by any shaped-charge missile, from the 66 mm LAW
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior, with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been variously described as a science and as the ar ...
on up. One important modification carried out as the result of operational experience in Afghanistan was the fitting of a second layer of stand-off armor, usually a high resistant ballistic rubber-like material, to act as spaced armour
Armour with two or more plates spaced a distance apart falls under the category of spaced armour. Spaced armour can be sloped or unsloped. When sloped, it reduces the penetrating power of bullets and solid shot, as after penetrating each plate ...
around the top of the hull sides and around the turret.
According to Russian sources, the vehicles repaired as of November 2023 are equipped with attachments to install additional protection kits.
Service history
. Pancerni.abajt.pl. Retrieved 20 September 2011.
Combat history


 * 1975–2002:
* 1975–2002: Angolan Civil War
The Angolan Civil War () was a civil war in Angola, beginning in 1975 and continuing, with interludes, until 2002. The war began immediately after Angola became independent from Portugal in November 1975. It was a power struggle between two for ...
(Angola, UNITA
The National Union for the Total Independence of Angola (, abbr. UNITA) is the second-largest political party in Angola. Founded in 1966, UNITA fought alongside the People's Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA) and the National Liberat ...
)
* 1979–1989: Soviet–Afghan War
The Soviet–Afghan War took place in the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan from December 1979 to February 1989. Marking the beginning of the 46-year-long Afghan conflict, it saw the Soviet Union and the Armed Forces of the Democratic Republic o ...
(Soviet Union, Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
)
* 1980–1988: Iran–Iraq War
The Iran–Iraq War, also known as the First Gulf War, was an armed conflict between Iran and Iraq that lasted from September 1980 to August 1988. Active hostilities began with the Iraqi invasion of Iran and lasted for nearly eight years, unti ...
(Iraq)
* 1988–1993: Georgian Civil War (Georgia)
** 1991–1992: War in South Ossetia
** 1992–1993: War in Abkhazia
* 1988–1994: First Nagorno-Karabakh War
The First Nagorno-Karabakh War was an ethnic conflict, ethnic and territorial conflict that took place from February 1988 to May 1994, in the enclave of Nagorno-Karabakh in southwestern Azerbaijan, between the majority ethnic Armenians of Nag ...
(Armenia, Azerbaijan)
* 1989: Georgian-Ossetian conflict
** 2008 – War in South Ossetia
* 1990–1991: Gulf War
, combatant2 =
, commander1 =
, commander2 =
, strength1 = Over 950,000 soldiers3,113 tanks1,800 aircraft2,200 artillery systems
, page = https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/GAOREPORTS-PEMD-96- ...
(Iraq, Kuwait)
* 1991–present Somali Civil War
The Somali Civil War (; ) is an List of ongoing armed conflicts, ongoing civil war that is taking place in Somalia. It grew out of resistance to the military junta which was led by Siad Barre during the 1980s. From 1988 to 1990, the Somali Armed ...
* 1992–1997: Tajikistani Civil War
The Tajikistani Civil War,, group=pron also known as the Tajik Civil War, began in May 1992 and ended in June 1997. Regional groups from the Garm and Gorno-Badakhshan regions of Tajikistan rose up against the newly formed government of Preside ...
(Russia, Tajikistan)
* 1994: Yemeni Civil War (1994)
The Yemeni civil war (), also known as the Summer War of 1994 (), was a civil war fought between the two Yemeni forces of the pro-union northern and the socialist separatist southern Yemeni states and their supporters. The war resulted in the ...
(North Yemen)
* 1994–1996: First Chechen War
The First Chechen War, also referred to as the First Russo-Chechen War, was a struggle for independence waged by the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria against the invading Russia, Russian Federation from 1994 to 1996. After a mutually agreed on treaty ...
(Russia)
* 1998: Six-Day War of Abkhazia
* 1998: Second Congo War
The Second Congo War, also known as Africa's World War or the Great War of Africa, was a major conflict that began on 2 August 1998, in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, just over a year after the First Congo War. The war initially erupted ...
(Angola)
* 1999: Second Chechen War
Names
The Second Chechen War is also known as the Second Chechen Campaign () or the Second Russian Invasion of Chechnya from the Chechens, Chechen insurgents' point of view.Федеральный закон № 5-ФЗ от 12 января 19 ...
(Russia)
* 2001: War in Afghanistan (2001–2021)
The war in Afghanistan was a prolonged armed conflict lasting from 2001 to 2021. It began with United States invasion of Afghanistan, the invasion by a Participants in Operation Enduring Freedom, United States-led coalition under the name Oper ...
(Afghanistan, Czech Republic)
* 2003: Iraq War
The Iraq War (), also referred to as the Second Gulf War, was a prolonged conflict in Iraq lasting from 2003 to 2011. It began with 2003 invasion of Iraq, the invasion by a Multi-National Force – Iraq, United States-led coalition, which ...
** 2003 invasion of Iraq (Iraq)
* 2003–2004 Indonesian offensive in Aceh (Indonesia)
* 2004: Iran–PJAK conflict (Iran)
* 2008: Russo-Georgian War
The August 2008 Russo-Georgian War, also known as the Russian invasion of Georgia,Occasionally, the war is also referred to by other names, such as the Five-Day War and August War. was a war waged against Georgia by the Russian Federation and the ...
(Russia, Georgia)
* 2011–present: Syrian civil war (Syria, rebel forces)
* 2014–present: Russo-Ukrainian War
The Russo-Ukrainian War began in February 2014 and is ongoing. Following Ukraine's Revolution of Dignity, Russia Russian occupation of Crimea, occupied and Annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation, annexed Crimea from Ukraine. It then ...
(Ukraine, Russia)
** 2014–2022: War in Donbas
The war in Donbas, or the Donbas war, was a phase of the Russo-Ukrainian War in the eastern Donbas region of Ukraine. The war Timeline of the war in Donbas (2014), began in April 2014, when Russian separatist forces in Ukraine, Russian para ...
** 2022–present: Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thou ...
* 2015: Yemeni Civil War (2014–present) Yemeni civil war may refer to several conflicts which have taken place in Yemen:
* North Yemen civil war, 1962–1970
* South Yemen civil war
The South Yemeni crisis, colloquially referred to in Yemen as the events of '86, was a failed coup d ...
(Houthis, Pro-Hadi forces)
* 2016: 2016 Nagorno-Karabakh clashes (Armenia, Azerbaijan)
* 2020: 2020–2021 China–India skirmishes (India)
* 2020: Second Nagorno-Karabakh War
The Second Nagorno-Karabakh War was an armed conflict in 2020 that took place in the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh and the Armenian-occupied territories surrounding Nagorno-Karabakh, surrounding occupied territories. It was a major esca ...
(Armenia, Azerbaijan)
* 2021: 2021 Kyrgyzstan–Tajikistan clashes (Kyrgyzstan)
* 2022: 2022 Kyrgyzstan–Tajikistan clashes (Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan)
* 2025: 2025 India-Pakistan Conflict (India)
Variants

Soviet Union and Russian Federation
 * BMP-2 obr. 1980 – Initial production model.
** BMP-2 obr. 1984 – Improved version with "kovriki" armour on turret front.
*** BMP-2 obr. 1986 – Late-production model with new BPK-2-42 sight instead of the BPK-1-42.
** BMP-2D (D stands for ''dorabotanaya'' – modified) – Fitted with additional spaced type steel appliqué armour on the hull sides, under the driver's and commander's stations, and 6 mm thick appliqué armour on the turret. Owing to the added weight, the vehicle is no longer amphibious. It also has provision for mounting a mine clearing system under the nose of the vehicle. In service since 1982, it saw service during
* BMP-2 obr. 1980 – Initial production model.
** BMP-2 obr. 1984 – Improved version with "kovriki" armour on turret front.
*** BMP-2 obr. 1986 – Late-production model with new BPK-2-42 sight instead of the BPK-1-42.
** BMP-2D (D stands for ''dorabotanaya'' – modified) – Fitted with additional spaced type steel appliqué armour on the hull sides, under the driver's and commander's stations, and 6 mm thick appliqué armour on the turret. Owing to the added weight, the vehicle is no longer amphibious. It also has provision for mounting a mine clearing system under the nose of the vehicle. In service since 1982, it saw service during Soviet–Afghan War
The Soviet–Afghan War took place in the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan from December 1979 to February 1989. Marking the beginning of the 46-year-long Afghan conflict, it saw the Soviet Union and the Armed Forces of the Democratic Republic o ...
. During that conflict, western observers saw the vehicle for the first time and gave it a designation BMP-2E.
** BMP-2K (K stands for ''komandirskaya'' – command) – Command variant fitted with two whip antennas mounted on the rear of the hull, one behind the turret and one on the right-hand side of the rear of the vehicle, one IFF antenna (pin stick) on the left-hand side of the rear of the vehicle and a support for a telescopic mast in the front of the IFF antenna. The firing port equipped with the periscope was removed from either side of the vehicle. The antennae on the turret was removed. The radio equipment consists ether of the R-123M and R-130M radio sets, or the more modern R-173, R-126 and R-10. The crew consists of six men.
** BMP-2M – This is the general designator for upgraded (''modernizirovannyj'') versions.
*** The upgrade package from 2008 consists of the UTD-23 400 hp (294 kW) turbocharged engine, BPK-3-42 gunner`s sight and TKN-AI commander`s sight, additional passive armour, an AG-17 "Plamya" grenade launcher and a KBM-2 air conditioning unit. Furthermore, the upgraded vehicle will have an improved suspension with road wheels of higher load carrying capacity, enhanced-hardness torsion bars, power-consuming shock absorbers and tracks with rubber pad shoes.
*** BMP-2M "Berezhok" – Modernized version from KBP. This version has B05Ya01 Berezhok turret equipped with 2A42 30mm autocannon, PKMT 7.62mm coaxial machine gun, AGS-30 grenade launcher, 2+2 launchers for ATGM 9M133M "Kornet-M" and new day/night sights SOZh-TM (as found on BMP-3). Hull is fitted with armored side skirts and slat (cage) armor. There is an improved UTD-23 diesel engine (400 hp) coupled with automatic transmission. Suspension is also improved. This upgrade was selected by Algeria, and Russia will upgrade several hundred of its vehicles.
** BMO-1 (''boyevaya mashina ognemyotchikov'') – Transport vehicle for a flamethrower squad armed with 30 RPO-A "Shmel" 93 mm thermobaric rocket launchers. It is equipped with storage racks and a dummy turret. The crew consists of seven soldiers. It entered service in 2001.
Former Czechoslovakia
* BVP-2 (''bojové vozidlo pěchoty'') – Czechoslovak-produced version of BMP-2. * BVP-2V or VR 1p (''vozidlo velitele roty'') – Company commander's vehicle with tent, telescopic mast and radiosets RF 1325 (x 2), IPRS 32, RF 1301 and NS 2480DPhotos
* VPV (VPV stands for ''vyprošťovací pásové vozidlo'') – BVP-2 conversion into an ARV developed at the ZTS Martin Research and Development Institute and production commenced at the ZTS Martin plant (which is now in Slovakia) in 1984. It is equipped with a powered crane with 5 tonnes capacity, heavy winch, wider troop compartment etc. Hatches on top of the turret and the troop compartment were removed. The vehicle is divided into four compartments: engine, commander's, driver's and repair/cargo. The crew consists of a commander/crane operator, driver/welder/slinger and a logistician/mechanic. The vehicle is armed with a pintle-mounted 7.62 mm PKT light machine gun. A small number of those vehicles was also based on BVP-1.
India
 * BMP-2 "Sarath" ("
* BMP-2 "Sarath" ("Chariot
A chariot is a type of vehicle similar to a cart, driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid Propulsion, motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk O ...
of Victory"), also known as BMP-II – Indian licence-produced variant of the BMP-2,Ordnance Factory Board. Ofbindia.gov.in. Retrieved 20 September 2011. built by
Ordnance Factory Medak
Ordnance Factory Medak (OFMK) (Hindi: आयुध निर्माणी मेदक), previously called Ordnance Factory Project Medak (OFPM) while in its development stage, is a factory owned by Armoured Vehicles Nigam Limited, a company t ...
since 1987. The turret is equipped with an ATGM
An anti-tank guided missile (ATGM), anti-tank missile, anti-tank guided weapon (ATGW) or anti-armor guided weapon is a guided missile primarily designed to hit and destroy heavily armored military vehicles. ATGMs range in size from shoulder ...
launcher while each vehicle can carry 4 missiles.
** The first vehicle, assembled from components supplied by KBP, was ready in 1987. By 1999, about 90% of the complete vehicle and its associated systems were being produced in India. It was estimated that, by 2007, 1,250 vehicles had been built. As of February 2020, around 2,500 Saraths were made.
**On June 2, 2020, India's Ministry of Defence announced placement of an order of 156 BMP-2 Sarath vehicles (Infantry Combat Vehicles) for the Indian Army
The Indian Army (IA) (ISO 15919, ISO: ) is the Land warfare, land-based branch and largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Commander-in-Chief, Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head ...
's infantry units. The order will be executed by state owned Ordnance Factory Board, and BMP-2/2K Sarath will be produced by Ordnance Factory Medak
Ordnance Factory Medak (OFMK) (Hindi: आयुध निर्माणी मेदक), previously called Ordnance Factory Project Medak (OFPM) while in its development stage, is a factory owned by Armoured Vehicles Nigam Limited, a company t ...
. The delivery is expected to be complete by 2023.
India has also developed the following versions of the "Sarath":
*BMP-2 Light Tank
A light tank is a Tank classification, tank variant initially designed for rapid movements in and out of combat, to outmaneuver heavier tanks. It is smaller with thinner vehicle armour, armor and a less powerful tank gun, main gun, tailored for ...
– DRDO developed light tank on BMP-2 Chassis DRDO light tank.
*BMP-2K "Sarath" Carrier Command Post Tracked – Command vehicle, similar to the Soviet/Russian version.
*BMP-2M – Upgraded BMP-2 shown in DEFEXPO 2022 with a loitering munition
A loitering munition, also known as a suicide drone, kamikaze drone, or exploding drone, is a weapon with a warhead that is typically designed to Loiter (aeronautics), loiter until a target is designated, then crash into it.fire-control system
A fire-control system (FCS) is a number of components working together, usually a gun data computer, a director and radar, which is designed to assist a ranged weapon system to target, track, and hit a target. It performs the same task as a hum ...
. The upgrades include with TISAS (Thermal Imaging Stand Alone Sights), better fire control, two thermobaric
A thermobaric weapon, also called an aerosol bomb, or a vacuum bomb, is a type of explosive weapon, explosive munition that works by Dust explosion, dispersing an aerosol cloud of gas, liquid or powdered explosive. The fuel is usually a single ...
missiles and two tandem warhead Konkurs missiles. It also has an integrated TI sight, a Laser Range Finder
A laser rangefinder, also known as a laser telemeter or laser distance meter, is a rangefinder that uses a laser beam to determine the distance to an object. The most common form of laser rangefinder operates on the time of flight principle by ...
(LRF), and has an Automatic Grenade Launcher
An automatic grenade launcher (AGL) or grenade machine gun is a grenade launcher that is capable of fully automatic fire, and is typically loaded with either an Belt (firearm), ammunition belt or Magazine (firearm), magazine.
These weapons are oft ...
(AGL) mounted on the turret which is also stabilised in the horizontal plane. Indian Army will upgrade the older variants to BMP-2M variant at an initial rate of 100 units per year. Later the rate will be increased to 125 per year. On 14 March 2024, Ministry of Defence
A ministry of defence or defense (see American and British English spelling differences#-ce.2C -se, spelling differences), also known as a department of defence or defense, is the part of a government responsible for matters of defence and Mi ...
signed an initial contract with Armoured Vehicle Nigam Limited to upgrade 693 units to BMP-2M configuration.
* Armoured Ambulance – This version retains the turret but without the gun or smoke grenade launchers. The troop compartment has been modified to carry four stretchers.
*Armoured Vehicle Tracked Light Repair – Armoured recovery vehicle, fitted with a light hydraulic crane.
*Armoured Amphibious Dozer (AAD) – Turret-less combat engineer vehicle, fitted with a folding dozer blade at the rear, mine ploughs, a main winch with a capacity of 8,000 kg and a rocket-propelled earth anchor for self-recovery.
* Armoured Engineer Reconnaissance Vehicle (AERV) – This version has no gun and is fitted with specialised equipment, including an echo-sounder, a water current metre, a laser range finder and GPS. On the left rear of the hull, a marking system with 40 rods is fitted.
* NBC
The National Broadcasting Company (NBC) is an American commercial broadcast television and radio network serving as the flagship property of the NBC Entertainment division of NBCUniversal, a subsidiary of Comcast. It is one of NBCUniversal's ...
Reconnaissance Vehicle
A reconnaissance vehicle, also known as a scout vehicle, is a military vehicle used for forward reconnaissance. Both tracked and wheeled reconnaissance vehicles are in service. In some nations, light tanks such as the M551 Sheridan and AMX-13 h ...
(NBCRV) – For detection of nuclear, biological and chemical contamination. The NBCRV was developed by DRDO and VRDE and has been ordered by the Indian army.
* Carrier Mortar Tracked Vehicle – This turret-less version has an 81 mm mortar mounted in the modified troop compartment. The mortar is fired through an opening in the hull roof that has two hinged doors. It has a max. range of 5,000 m and a normal rate of fire of 6–8 rds/min. There is also a longe-range version of the mortar. The vehicle carries 108 mortar rounds and is also fitted with a 7.62 mm machine gun with 2,350 rounds. Crew: 2+4. The first prototype was completed in 1997.
* NAMICA (''Nag Missile Carrier'') – part of the Nag ATGM. The Nag missile is launched from a retractable armoured launcher that contains six launch tubes and the guidance package. "Nag" is a fire-and-forget top-attack ATGM
An anti-tank guided missile (ATGM), anti-tank missile, anti-tank guided weapon (ATGW) or anti-armor guided weapon is a guided missile primarily designed to hit and destroy heavily armored military vehicles. ATGMs range in size from shoulder ...
with a tandem-HEAT warhead and a range of at least 4 km.
* Akash – Air-defence missile system that is based on a modified "Sarath" chassis with 7 road wheels. On top of the hull there's a launcher for three SAMs with a range of 27 km and semi-active homing guidance.
*Trishul Combat Vehicle – A variant with four Trishul SAM launchers and a Flycatcher radar system. The vehicle entered trials in 2001, but never entered service.
* Rajendra – This is a multifunctional 3-D phased radar (MUFAR), associated with the "Akash" system. It is also based on the stretched chassis.
* BMP-2 UGV "Muntra
Muntra is a family of unmanned vehicle, unmanned armored vehicle developed by India's Defence Research and Development Organisation. The name stands for "Mission Unmanned Tracked"
Design
Muntra is a family modified Soviet BMP-2 armored personn ...
" – is a family of unmanned reconnaissance vehicles developed by DRDO, The Muntra family has several versions such as "S" version is fitted with equipment used to detect nuclear, biological and chemical contamination while the "M" version is designed to detect mines and "N" for operations in Nuclear and chemical contaminated areas.
* 105 mm Self-Propelled Gun – This is OFB's mechanized version of the Indian Indian Light Field Gun (EQPT 105/37 LFG E2) with 42 rounds stowed. The gun is mounted in a lightly armoured turret. The 105 mm SPG was shown for the first time in public in February 2010 during DEFEXPO-2010 in New Delhi and was planned to replace the FV433 Abbot SPG
FV433, 105mm, Field Artillery, Self-Propelled "Abbot" is the self-propelled artillery, or more specifically self-propelled gun (SPG), variant of the British Army FV430 series of armoured fighting vehicles (AFVs), using much of the chassis of th ...
in the Indian army, but it wasn't accepted into service.
Israel
* BMP-2 upgrade designed by Nimda fitting it with new power unit and automatic transmission which improves both mobility and reliability.Poland
* BWP-2 – The Polish designation for the BMP-2 and BMP-2D, which stands for "Bojowy Wóz Piechoty".Finland
* BMP-2MD – Finnish modernisation of the BMP-2, which includes thermal camouflage, thermal sights, anti-aircraft sight and new day/night optics for the gunner and commander, heated cabin and seats, new external storage boxes functioning also as spaced armour and new radio and communications systems.Operators
Current operators
* – 150 along with 1,500 9M111 Fagot ATGMs were ordered in 1987 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1987 and 1991 (some of the vehicles were possibly previously in Soviet service).SIPRI Arms Transfers Database. Armstrade.sipri.org. Retrieved 20 September 2011. 550 BMP-1s and BMP-2s in service in 1992. Between 60 and 80 BMP-1s and BMP-2s were delivered from Russia after 2002. * – 225 along with 2,250 9M111 Fagot ATGMs were ordered in 1989 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1990 and 1991. 54 BVP-2s and BVP-2Ks were ordered in 1994 from Slovakia and delivered between 1995 and 1996. 64 were ordered in 1998 from Ukraine and delivered between 1998 and 1999 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Ukrainian service). Estimated to have 220 BMP-2 and 760 BMP-2M in service as of 2023 * – 65, along with 650 9M111 Fagot ATGMs, were ordered in 1987 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1987. 7 were ordered in 1993 from Hungary and delivered in 1993 (the vehicles were previously in Hungarian service and were sold via Czech Republic). 42 BMP-2s were ordered in 1994 from Poland and delivered between 1994 and 1995 (the vehicles were previously in Polish service). 65 were ordered in 1997 from Russia and delivered in 1998 (the vehicles were possibly previously in Soviet and later Russian service). 62 were ordered in 1999 from Belarus and delivered in 1999 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Belarusian service). 31 were ordered in 1999 from Ukraine and delivered in 1999 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Ukrainian service). 250 BMP-1 and BMP-2 in service as of 2023 * – 15 as of 2023

International Institute for Strategic Studies
The International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS) is an international research institute or think tank focusing on defence and security issues. Since 1997, its headquarters have been at Arundel House in London. It has offices on four co ...
: The Military Balance 2025 20 were ordered in 1988 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1988 and 1989. Further 84 were ordered in 1991 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1992 by Russia.
* – 40 were ordered in 2004 from Ukraine and were delivered between 2004 and 2005 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Ukrainian service). 89 in service as of 2023
* – 700 BMP-2 "Sarath" ordered in 1984 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1987 and 1991 (most produced in India). 400 BMP-2 "Sarath" ordered in 1985 and produced in India between 1992 and 1995 at Ordnance Factory Medak
Ordnance Factory Medak (OFMK) (Hindi: आयुध निर्माणी मेदक), previously called Ordnance Factory Project Medak (OFPM) while in its development stage, is a factory owned by Armoured Vehicles Nigam Limited, a company t ...
of Ordnance Factories Board
The Directorate of Ordnance (Coordination & Services) (abbreviated: DOO(C&S)) is an authority under the Department of Defence Production (DDP) of Ministry of Defence (MoD), Government of India. Its primary work is to management, give instructi ...
under Russian licence. 123 BMP-2K ordered in 2006 from Russia and delivered between 2007 and 2008. 2,400 BMP-2 Sarath, plus an unknown number of BMP-2K and armored engineering vehicles in service as of 2023
* – 1,500 ordered in 1991 from Russia and 413 were delivered between 1993 and 2001 of which 82 were delivered directly by Russia and 331 were assembled in Iran. 400 in service as of 2023
* – 9 ordered in 1998 from Ukraine and delivered in 1998 (the vehicles were possibly previously in Soviet and later Ukrainian service and were sold via Slovakia). 2 ordered in 1998 from Ukraine and delivered in 1998 (the vehicles were possibly previously in Soviet and later Ukrainian service and were sold via Slovakia). 11 BVP-2s ordered in 1999 from Slovakia and delivered in 2000 (the vehicles were probably previously in Czechoslovak and later Slovakian service). 22 ex-Czech BVP-2s are currently in service in the Marine Corps as of 2023
* – 2 ordered in 2002 from Angola and delivered in 2002 (the vehicles were previously in Angolan service). 1 ordered in 2003 from Ukraine and delivered in 2003 (the vehicle probably was previously in Ukrainian service). 10 BMP-1 and BMP-2 in 2023, possibly non-operational
* – 280 in service as of 2023
Transnistria
Transnistria, officially known as the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic and locally as Pridnestrovie, is a Landlocked country, landlocked Transnistria conflict#International recognition of Transnistria, breakaway state internationally recogn ...
* – 430 BMP-2 and 4 BMP-2D as of 2023
* – 31 were ordered in 2003 from Ukraine and were delivered between 2004 and 2005 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Ukrainian service). 37 as of 2023
* – Unknown amount used for opposing force
An opposing force (alternatively enemy force, abbreviated OPFOR or OpFor) is a military unit tasked with representing an enemy, usually for training purposes in war game scenarios. The related concept of aggressor squadron is used by some ai ...
units.
 * – 890 in service with the army and 1 in service with the National Guard prior to the
* – 890 in service with the army and 1 in service with the National Guard prior to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thou ...
* – 270 in service as of 2023
* – Around 20 along with 500 9M111 Fagot ATGMs were ordered in 1982 from the Soviet Union and were delivered between 1982 and 1984. 300 BMP-1 and BMP-2 in service as of 2023
* – 100 were ordered in 2002 from Ukraine and were delivered between 2003 and 2004 (the vehicles were probably previously in Soviet and later Ukrainian service). Between 180 and 188 BMP-2Ds were ordered in 2004 from Russia and were delivered between 2004 and 2005. Unknown number in service as of 2023
** − Unknown number in service as of 2023
Former operators
See also
* BMD-1 – related family of Soviet airborne fighting vehicles *Combat Vehicle 90
The Combat Vehicle 90 (CV90) (, strf 90 or Stridsfordon 90) is a family of Swedish tracked armoured combat vehicles designed by the Swedish Defence Materiel Administration (FMV), Hägglund & Söner and Bofors during the mid-1980s to early ...
* BMP-1
The BMP-1 is a Soviet Union, Soviet Amphibious vehicle, amphibious tracked infantry fighting vehicle that has been in service from 1966 to the present. BMP stands for ''Boyevaya Mashina Pyekhoty 1'' (), meaning "infantry fighting vehicle, 1st ...
– predecessor vehicle
* BMP-3 – successor vehicle
* M113/BMP-2 – US armored personnel carrier visually modified as a BMP-2 for training exercises
Notes
References
* * * Tsouras, P.G. ''Changing Orders: The evolution of the World's Armies, 1945 to the Present'' Facts On File, Inc, 1994. * FM 100-60 * Ustyantsev, Sergej Viktorovich; Kolmakov Dmitrij Gennadevich ''Boyeviye mashiny Uralvagonzavoda. Tank T-72'' * A.V. Karpenko (1996) ''Obozreniye Bronetankovoj Tekhniki (1905–1995 gg.)'' Nevskij Bastion * * * * *Further reading
* Grau, Lester WRussian-Manufactured Armored Vehicle Vulnerability in Urban Combat: The Chechnya Experience
Red Thrust Star, January 1997
External links
SOVIET BMP-2 Infantry Fighting Vehicle – Walk around photos
BMP-2M Berezhok and other upgrades on V. Kuzmin's photo blog
BMP-2M Berezhok walk-around on Prime Portal
{{Portal bar, Soviet Union Tracked infantry fighting vehicles Cold War armoured fighting vehicles of the Soviet Union Tracked reconnaissance vehicles Amphibious infantry fighting vehicles Infantry fighting vehicles of the Soviet Union Infantry fighting vehicles of the Cold War Infantry fighting vehicles of India Kurganmashzavod products Military vehicles introduced in the 1980s