Auto Insurance on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
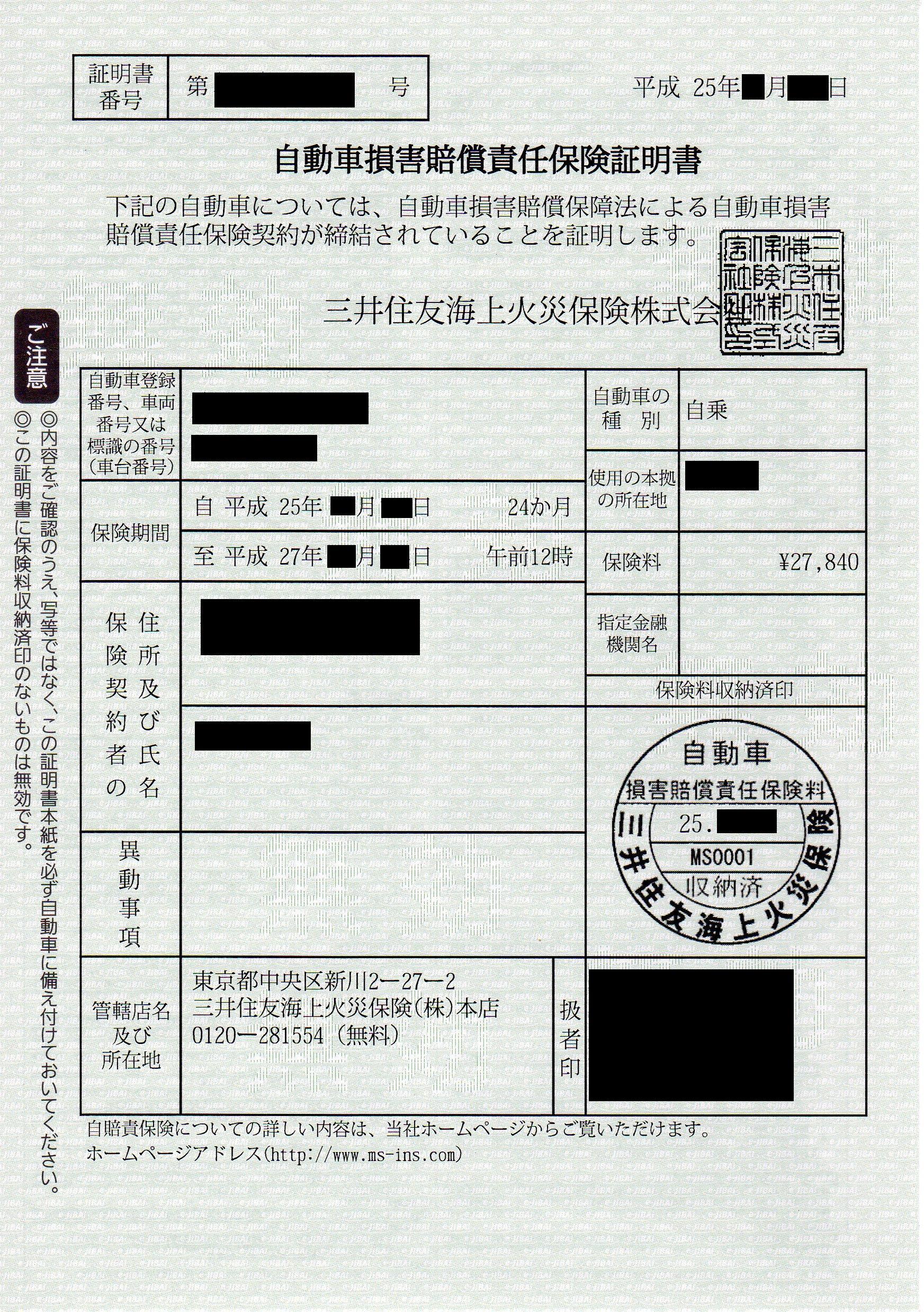 Vehicle insurance (also known as car insurance, motor insurance, or auto insurance) is
Vehicle insurance (also known as car insurance, motor insurance, or auto insurance) is
. Ibc.ca (1 January 2003). Facility insurance policies are offered by the "facility association residual market" (or "FARM"), as a last resort since auto insurance is mandatory in Canada, for private and commercial high-risk drivers who cannot buy a policy in the voluntary market (regular auto insurance).
 Since 1939, it has been compulsory to have third-party personal insurance before keeping a motor vehicle in all federal states of
Since 1939, it has been compulsory to have third-party personal insurance before keeping a motor vehicle in all federal states of
193.178.1.79. The Road Traffic Act, 1961 (which is currently in force) repealed the 1933 act but replaced these sections with functionally identical sections. From 1968, those making deposits require the consent of the Minister for Transport to do so, with the sum specified by the Minister. Those not exempted from obtaining insurance must obtain a certificate of insurance from their insurance provider, and display a portion of this (an insurance disc) on their vehicles' windscreen (if fitted). The certificate in full must be presented to a police station within ten days if requested by an officer. Proof of having insurance or an exemption must also be provided to pay for the motor tax. Those injured or suffering property damage/loss due to uninsured drivers can claim against the Motor Insurance Bureau of Ireland's uninsured drivers fund, as can those injured (but not those suffering damage or loss) from hit and run offences.
 The Road Traffic Act 1930, of the
The Road Traffic Act 1930, of the
Auto Insurance Rates Are 70% Higher If You Live In A Black Neighborhood
Time.com.
E.U. Court to Insurers: Stop Making Men Pay More
Time.com. The Court ruled that car-insurance companies were discriminating against men. However, in some places, such as the UK, companies have used the standard practice of discrimination based on profession to still use gender as a factor, albeit indirectly. Professions which are more typically practised by men are deemed as being more risky even if they had not been prior to the Court's ruling while the converse is applied to professions predominant among women.{{cite news, url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/finance/personalfinance/insurance/motorinsurance/11521781/Men-are-still-charged-more-than-women-for-car-insurance-despite-EU-rule-change.html , archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220112/https://www.telegraph.co.uk/finance/personalfinance/insurance/motorinsurance/11521781/Men-are-still-charged-more-than-women-for-car-insurance-despite-EU-rule-change.html , archive-date=12 January 2022 , url-access=subscription , url-status=live, title=Men Are Still Charged More than Women for Car Insurance Despite EU Rule Change, date=10 April 2015, last1=Palmer, first1=Kate{{cbignore Another effect of the ruling has been that, while the premiums for men have been lowered, they have been raised for women. This equalisation effect has also been seen in other types of insurance for individuals, such as
Progressive.com. Snapshot is currently available in 46 states plus the District of Columbia. Because insurance is regulated at the state level, Snapshot is currently not available in Alaska, California, Hawaii, and North Carolina. Driving data is transmitted to the company using an on-board telematic device. The device connects to a car's OnBoard Diagnostic ( OBD-II) port (all petrol automobiles in the USA built after 1996 have an OBD-II.) and transmits speed, time of day and number of miles the car is driven. Cars that are driven less often, in less-risky ways, and at less-risky times of day, can receive large discounts. Progressive has received patents on its methods and systems of implementing usage-based insurance and has licensed these methods and systems to other companies. Metromile also uses an OBDII-based system for their mileage-based insurance. They offer a true pay-per-mile insurance where behavior or driving style is not taken into account, and the user only pays a base rate along with a fixed rate per mile. The OBD-II device measures mileage and then transmits mileage data to servers. This is supposed to be an affordable car insurance policy for low-mileage drivers. Metromile is currently only offering personal car insurance policies and is available in California, Oregon, Washington, and Illinois.
US patent application 20090063201 "SoberTeen driving insurance"
{{webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100618063009/http://www.peertopatent.org/patent/20090063201/activity , date=18 June 2010 . Peertopatent.org (20 May 2009). ''See Behavior-based safety''. Behaviour based Insurance focusing upon driving is often called
insurance
Insurance is a means of protection from financial loss in which, in exchange for a fee, a party agrees to compensate another party in the event of a certain loss, damage, or injury. It is a form of risk management, primarily used to protect ...
for cars
A car, or an automobile, is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of cars state that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people rather than cargo. There are around one billio ...
, truck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport freight, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame construct ...
s, motorcycle
A motorcycle (motorbike, bike; uni (if one-wheeled); trike (if three-wheeled); quad (if four-wheeled)) is a lightweight private 1-to-2 passenger personal motor vehicle Steering, steered by a Motorcycle handlebar, handlebar from a saddle-style ...
s, and other road vehicles. Its primary use is to provide financial protection against physical damage or bodily injury resulting from traffic collision
A traffic collision, also known as a motor vehicle collision, or car crash, occurs when a vehicle collides with another vehicle, pedestrian, animal, road debris, or other moving or stationary obstruction, such as a tree, pole or building. Tr ...
s and against liability that could also arise from incidents in a vehicle. Vehicle insurance may additionally offer financial protection against theft
Theft (, cognate to ) is the act of taking another person's property or services without that person's permission or consent with the intent to deprive the rightful owner of it. The word ''theft'' is also used as a synonym or informal shor ...
of the vehicle, and against damage to the vehicle sustained from events other than traffic collisions, such as vandalism
Vandalism is the action involving deliberate destruction of or damage to public or private property.
The term includes property damage, such as graffiti and defacement directed towards any property without permission of the owner. The t ...
, weather or natural disaster
A natural disaster is the very harmful impact on a society or community brought by natural phenomenon or Hazard#Natural hazard, hazard. Some examples of natural hazards include avalanches, droughts, earthquakes, floods, heat waves, landslides ...
s, and damage sustained by colliding with stationary objects. The specific terms of vehicle insurance vary with legal regulation
Regulation is the management of complex systems according to a set of rules and trends. In systems theory, these types of rules exist in various fields of biology and society, but the term has slightly different meanings according to context. Fo ...
s in each region.
History
Widespread use of the motor car began after theFirst World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
in urban areas. Cars were relatively fast and dangerous by that stage, yet there was still no compulsory form of car insurance anywhere in the world. This meant that injured victims would rarely get any compensation in a crash, and drivers often faced considerable costs for damage to their car and property.
A compulsory car insurance scheme was introduced in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
with the Road Traffic Act 1930. This ensured that all vehicle owners and drivers had to be insured for their liability for injury or death to third parties while their vehicle was being used on a public road. Ireland replicated the obligation via the Road Traffic Act, 1933. Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
enacted similar legislation in 1939 called the "Act on the Implementation of Compulsory Insurance for Motor Vehicle Owners". The EU (then EEC) required mandatory insurance cover be mandated by all member states, from 1973.
Public policies
In most jurisdictions, it is compulsory to have vehicle insurance before using or keeping a motor vehicle on public roads. Most jurisdictions relate insurance to both the car and the driver; however, the degree of each varies greatly. Several jurisdictions have experimented with a "pay-as-you-drive" insurance plan which utilizes either a tracking device in the vehicle or vehicle diagnostics. This could address issues of uninsured motorists by providing additional options and also charge based on the distance driven, which could theoretically increase the efficiency of the insurance, through streamlined collection.Australia
InAustralia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
, every state has its own ''Compulsory Third-Party'' (CTP) insurance scheme. CTP covers only personal injury liability in a vehicle crash. ''Comprehensive'' and ''Third-Party Property Damage, with or without Fire and Theft'' insurance, are sold separately.
* ''Comprehensive'' insurance covers damages to third-party vehicles, other third-party property and the insured vehicle.
* ''Third-Party Property Damage'' insurance covers damage to third-party property and vehicles, but not the insured vehicle.
* ''Third-Party Property Damage with Fire and Theft'' insurance covers the insured vehicle against fire and theft as well as damage to third-party property and vehicles.
Compulsory Third-Party Insurance
CTP insurance is compulsory in every state in Australia and is paid as part of vehicle registration. It covers the vehicle owner and any person who drives the vehicle against claims for liability for death or injury to people caused by the fault of the vehicle owner or driver. CTP may include any kind of physical harm, bodily injuries and may cover the cost of all reasonable medical treatment for injuries received in the crash, loss of wages, cost of care services and, in some cases, compensation for pain and suffering. Each state in Australia has a different scheme. Third-Party Property insurance or Comprehensive insurance covers the third party with the repairing cost of the vehicle, any property damage or medication expenses as a result of a crash by the insured. They are not to be confused with Compulsory Third-Party insurance, which is for injuries or death of someone in a motor crash. InNew South Wales
New South Wales (commonly abbreviated as NSW) is a States and territories of Australia, state on the Eastern states of Australia, east coast of :Australia. It borders Queensland to the north, Victoria (state), Victoria to the south, and South ...
, each vehicle must be insured before it can be registered. It is often called a 'greenslip', because of its colour. There are five licensed CTP insurers in New South Wales. Suncorp holds licences for GIO and AAMI and Allianz holds one licence. The remaining two licences are held by QBE and NRMA Insurance (NRMA). APIA and Shannons and InsureMyRide insurance also supply CTP insurance licensed by GIO.
A privately provided scheme also applies in the Australian Capital Territory
The Australian Capital Territory (ACT), known as the Federal Capital Territory until 1938, is an internal States and territories of Australia, territory of Australia. Canberra, the capital city of Australia, is situated within the territory, an ...
through AAMI, APIA, GIO and NRMA. Vehicle owners pay for CTP as part of their vehicle registration.
In Queensland
Queensland ( , commonly abbreviated as Qld) is a States and territories of Australia, state in northeastern Australia, and is the second-largest and third-most populous state in Australia. It is bordered by the Northern Territory, South Austr ...
, CTP is included in the registration fee for a vehicle. There is a choice of private insurer – Allianz, QBE and Suncorp and price is government controlled.
In South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories by area, which in ...
, since July 2016, CTP is no longer provided by the Motor Accident Commission. The government has now licensed four private insurers – AAMI, Allianz, QBE and SGIC – to offer CTP insurance SA. Since July 2019, vehicle owners can choose their own CTP insurer and new insurers may also enter the market.
There are three states and one territory that do not have a private CTP scheme. In Victoria, the Transport Accident Commission provides CTP through a levy in the vehicle registration fee, known as the TAC charge. A similar scheme exists in Tasmania
Tasmania (; palawa kani: ''Lutruwita'') is an island States and territories of Australia, state of Australia. It is located to the south of the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland, and is separated from it by the Bass Strait. The sta ...
through the Motor Accidents Insurance Board. A similar scheme applies in Western Australia
Western Australia (WA) is the westernmost state of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Aust ...
, through the Insurance Commission of Western Australia (ICWA). The Northern Territory scheme is managed through Territory Insurance Office (TIO).
Bangladesh
For all types of motor insurance policies inBangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
, the limit of liability has been fixed by the law. Currently, the limits are too low to compensate the victims. In respect of Act Only Liability Motor Vehicle Insurance, the compensation for personal injuries and property damage to third parties is BDT 20,000 for death, for severe injury, for injury, and for property damage. The limits are under review by the governmental bodies.
Canada
Several Canadian provinces (British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
, Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada. It is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and to the south by the ...
, Manitoba
Manitoba is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population ...
and Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
) provide a public auto insurance system while in the rest of the country insurance is provided privately. The third-party insurance is privatized in Quebec and is mandatory. The province covers everything but the vehicle(s). Basic auto insurance is mandatory throughout Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
(with some exceptions, such as government vehicles) with each province's government determining which benefits are included as minimum required auto insurance coverage and which benefits are options available for those seeking additional coverage. Accident benefits coverage is mandatory everywhere except for Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the populatio ...
. All provinces in Canada have some form of no-fault insurance available to crash victims. The difference from province to province is the extent to which tort or no-fault is emphasized. International drivers entering Canada are permitted to drive any vehicle their licence allows for the three-month period for which they are allowed to use their international licence. International laws provide visitors to the country with an International Insurance Bond (IIB) until this three-month period is over in which the international driver must provide themselves with Canadian Insurance. The IIB is reinstated every time the international driver enters the country. Damage to the driver's own vehicle is optional – one notable exception to this is in Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada. It is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and to the south by the ...
, where SGI provides collision coverage (less than a $1000 deductible
In an insurance policy, the deductible (in British English, the excess) is the amount paid
Out-of-pocket expenses, out of pocket by the policy holder before an insurance provider will pay any expenses. In general usage, the term ''deductible'' m ...
, such as a collision damage waiver) as part of its basic insurance policy. In Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada. It is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and to the south by the ...
, residents have the option to have their auto insurance through a tort system but less than 0.5% of the population have taken this option.Insurance Bureau of Canada. Ibc.ca (1 January 2003). Facility insurance policies are offered by the "facility association residual market" (or "FARM"), as a last resort since auto insurance is mandatory in Canada, for private and commercial high-risk drivers who cannot buy a policy in the voluntary market (regular auto insurance).
China
Traffic Compulsory Insurance provides protection in the event of third party injuries, third party property losses, etc. The minimum liability cover is RMB180,000 (US$) for death and injury/per crash, RMB18,000 (US$) for medical expense, and RMB2,000 (US$) for physical loss. Additional 3rd Party Liability Insurance also known as Commercial Motor Insurance provides extra cover up to RMB10,000,000 (US$) excluding the driver and passengers. Driver and Passenger insurance covers the driver and passengers, whilst Vehicle Damage and Theft Insurance covers vehicle damage and the objects contained inside. Excess Waiver Insurance is an additional option that waives any deductibles. Some differences apply in different regions:Hong Kong
According to section 4(1) of the Motor Vehicles Insurance (Third-Party Risks) Ordinance (Cap. 272 of the Laws of Hong Kong), all users of a car, include its permitted users, must have insurance or some other security with respect to third-party risks. Third party insurance protects the policyholder against liability of death or bodily injury to third party up to and/or damage to third party property up to as a result of crash arising out of the use of the insured vehicle. Comprehensive Motor Insurance is also available.Macau
The mandatory minimum legal requirement Third Party Liability ("TPL") Cover is MOP1,500,000 per crash and MOP30,000,000 per year, protecting against the legal liability arising from a traffic crash causing loss and damages to any third party.. Comprehensive Motor Insurance is also available.European Union
In theEuropean Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
, from the introduction of Directive 1972/166/EEC, insurance cover is mandatory, with the statutory minimum cover being revised every five years, the most recent revision, via Directive (EU) 2021/2118 (the ‘‘Motor Insurance Directive’’ or ‘‘MID’’) requires:
* in the case of personal injury, a minimum amount of cover of €1,300,000 (US$) per injured party or €6,450,000 (US$) per claim, irrespective of the number of parties;
* in the case of damage to property, €1,300,000 (US$) per accident.
In some European languages, comprehensive non-mandatory insurance is known as ''casco'' (Casualty and Collision).
Germany
 Since 1939, it has been compulsory to have third-party personal insurance before keeping a motor vehicle in all federal states of
Since 1939, it has been compulsory to have third-party personal insurance before keeping a motor vehicle in all federal states of Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
. In addition, every vehicle owner is free to take out a comprehensive insurance policy. All types of car insurance are provided by several private insurers. The amount of insurance contribution is determined by several criteria, like the region, the type of car or the personal way of driving.
The minimum coverage defined by German law for car liability insurance / third-party personal insurance is €7,500,000 for bodily injury (damage to people), €500,000 for property damage and €50,000 for financial/fortune loss which is in no direct or indirect coherence with bodily injury or property damage. Insurance companies usually offer all-in/combined single limit insurance policies of €50,000,000 or €100,000,000 (about €141,000,000) for bodily injury, property damage and other financial/fortune loss (usually with a bodily injury coverage limitation of €8–15,000,000 for each bodily injured person).
Hungary
Third party vehicle insurance is mandatory for all vehicles inHungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
. No exemption is possible by money deposit. The premium covers all damage up to HUF 500m (about €1.8m) per crash without deductible. The coverage is extended to HUF 1,250m (about €4.5m) in case of personal injuries. Vehicle insurance policies from all EU countries and some non-EU countries are valid in Hungary based on bilateral or multilateral agreements. Visitors with vehicle insurance not covered by such agreements are required to buy a monthly, renewable policy at the border.
Ireland
The Road Traffic Act, 1933 requires all drivers of mechanically propelled vehicles in public places to have at least third-party insurance, or to have obtained exemption – generally by depositing a (large) sum of money to the High Court as a guarantee against claims. In 1933, this figure was set at £15,000.Road Traffic Act, 1933, Section 61193.178.1.79. The Road Traffic Act, 1961 (which is currently in force) repealed the 1933 act but replaced these sections with functionally identical sections. From 1968, those making deposits require the consent of the Minister for Transport to do so, with the sum specified by the Minister. Those not exempted from obtaining insurance must obtain a certificate of insurance from their insurance provider, and display a portion of this (an insurance disc) on their vehicles' windscreen (if fitted). The certificate in full must be presented to a police station within ten days if requested by an officer. Proof of having insurance or an exemption must also be provided to pay for the motor tax. Those injured or suffering property damage/loss due to uninsured drivers can claim against the Motor Insurance Bureau of Ireland's uninsured drivers fund, as can those injured (but not those suffering damage or loss) from hit and run offences.
Italy
The law 990/1969 requires that each motor vehicle or trailer standing or moving on a public road have third-party insurance (called RCA, ). Historically, a part of the certificate of insurance must be displayed on the windscreen of the vehicle. This latter requirement was revoked in 2015, when a national database of insured vehicles was built by the Insurance Company Association (ANIA, ') and the National Transportation Authority (') to verify (by private citizens and public authorities) if a vehicle is insured. There is no exemption policy to this law disposition. Driving without the necessary insurance for that vehicle is an offence that can be prosecuted by the police and fines range from 841 to 3,287 euros. Police forces also have the power to seize a vehicle that does not have the necessary insurance in place, until the owner of the vehicle pays a fine and signs a new insurance policy. The same provision is applied when the vehicle is standing on a public road. Minimal insurance policies cover only third parties (including the insured person and third parties carried with the vehicle, but not the driver, if the two do not coincide). ''Third parties, fire and theft'' is a common insurance policy, while the all-inclusive policies (''kasko'' policy) which include also damages of the vehicle causing the crash or the injuries. It is also common to include a renounce clause of the insurance company to compensate the damages against the insured person in some cases (usually in case of DUI or other infringement of the law by the driver). The victims of crashes caused by non-insured vehicles could be compensated by the Road's Victim Warranty Fund ('), which is covered by a fixed amount (2.5%, as 2015) of each RCA insurance premium.Netherlands
Third-party vehicle insurance is a mandatory requirement for every vehicle in theNetherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
. This obligation is mandatory based on article 2 of the . When a vehicle is not insured the owner will receive a fine from the RDW (). The third-party vehicle insurance is called a where WA stands for which means legal liability. In general there are three types of auto insurance in the Netherlands: (liability insurance), (limited frame coverage), and (full frame coverage). Limited frame and full frame coverage will provide more coverage against certain additional risks which are not covered by the mandatory legal third-party coverage. For example limited frame coverage will provide coverage against damage caused by the weather such as storm and flooding. Also fire damage and theft of the car is covered. Full frame coverage will provide coverage against all risks mentioned plus damage to the car caused by the driver himself.
Spain
Each motor vehicle on a public road is required to have third party insurance (called ). Police forces have the power to seize vehicles that do not have the necessary insurance in place, until the owner of the vehicle pays the fine and signs a new insurance policy. Driving without the necessary insurance for that vehicle is an offence that will be prosecuted by the police and will receive a penalty. The same provision is applied when the vehicle is standing on a public road. The minimum insurance policy covers only third parties (including the insured person and third parties carried with the vehicle, but not the driver, if the two do not coincide). ''Third parties, fire and theft'' is a common insurance policy. Victims of accidents caused by non-insured vehicles may be compensated by a Warranty Fund, which is covered by a fixed amount for each insurance premium.PPcn{{ Since 2013 it is possible to contract an insurance by days as is possible in countries such as Germany and the UK.Bulgaria
Liability insurance (called {{lang, bg, Гражданска отговорност) is compulsory for each motor vehicle driven on public roads and covers third parties for injuries up to 10 420 000 BGN and property damage up to 2 100 000 BGN per insured incident.{{cn, date=February 2025Romania
Romanian law mandates Răspundere Auto Civilă, a motor-vehicle liability insurance for all vehicle owners to cover damages to third parties.Indonesia
Third-party vehicle insurance is a mandatory requirement inIndonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
and each individual car and motorcycle must be insured or the vehicle will not be considered legal; this compulsory auto insurance is legally called the Road Traffic Accidents Compulsory Coverage Fund ({{langx, id, Dana Pertanggungan Wajib Kecelakaan Lalu Lintas Jalan, DPWKLLJ). Therefore, a motorist cannot drive the vehicle until it is insured. DPWKLLJ was introduced in 1964 and merely covers body injuries, and is operated by a SOE called {{ill, PT Jasa Raharja (Persero), id, Jasa Raharja. DPWKLLJ is included, through an annual premium called the ''Compulsory Donation to the Road Traffic Accident Fund'' ({{langx, id, Sumbangan Wajib Dana Kecelakaan Lalu Lintas Jalan, ''SWDKLLJ''),{{Cite journal , last1=Sitorus , first1=Budi , last2=Sitorus , first2=Antoni S. , last3=Harsono , first3=Tulus Irpan , last4=Sitorus , first4=Christina Natalia , date=8 June 2022 , title=Persepsi Masyarakat Terhadap Sumbangan Wajib Dana Kecelakaan Lalu Lintas Jalan Dan Kebijakan Perlindungan Kecelakaan Jalan , url=https://ktj.pktj.ac.id/ktj/article/view/426 , journal=Jurnal Keselamatan Transportasi Jalan (Indonesian Journal of Road Safety) , language=en , volume=9 , issue=1 , pages=60–70 , doi=10.46447/ktj.v9i1.426 , issn=2721-7248, doi-access=free in the annual vehicle tax which is paid to the local ''Samsat'' (''Sistem Administrasi Manunggal di bawah Satu Atap''), which is responsible for cars and roads.
India
{{Main, Motor Vehicle Insurance (India) Auto insurance in India covers the loss of or damage caused to the automobile or its parts due to natural and man-made calamities. It provides ''accident cover for individual owners'' of the vehicle while driving and also for ''passengers and third party legal liability''. There are certain general insurance companies who also offer online insurance service for the vehicle.{{cn, date=February 2025 Auto insurance is a compulsory requirement for all new vehicles used whether for commercial or personal use. Insurance companies have tie-ups with leading automobile manufacturers. They offer their customers instant auto quotes. Premiums are determined by a number of factors and the amount of premium increases with the rise in the price of the vehicle. The claims of the auto insurance in India can be accidental, theft claims or third party claims. Certain documents are required for claiming auto insurance, like duly signed claim form, Registration Certificate copy of the vehicle, driving license copy, First information report copy, original estimate and policy copy.{{cn, date=February 2025 There are different types of auto insurance in India: *Private car insurance – the fastest growing sector in India as it is compulsory for all new cars. The amount of premium depends on the make and value of the car, state where the car is registered and the year of manufacture. This amount can be reduced by asking the insurer for a no claim bonus (NCB) if no claim is made for insurance in previous year. *Two wheeler insurance – covers accidental insurance for the driver of the vehicle. The amount of premium depends on the current showroom price multiplied by the depreciation rate fixed by the Tariff Advisory Committee at the beginning of a policy period.{{cn, date=February 2025 *Commercial vehicle insurance – provides cover for all the vehicles which are not used for personal purposes like trucks and HMVs. The amount of premium depends on the showroom price of the vehicle at the commencement of the insurance period, make of the vehicle and the place of registration of the vehicle.{{cn, date=February 2025Malaysia
{{unref-section, date=February 2025 In Malaysia, renewing car insurances is a very common thing. In general, there are four types of car insurance available for Malaysians: * Act cover This is the minimum cover corresponding to the terms of the Road Transport Act 1987. The insurance concerns the legal liability for death or physical injury to the third party (not include the passengers), so it is hardly ever written by insurers. * Third-party coverage This type is compulsory to buy for every vehicle so it is the most basic and common car insurance, which insures you against claims for the injury or damage to the third party or its property in a crash. * Third-party, fire, and theft coverage In addition to third-party coverage, this policy also provides insurance for your own vehicle due to fire, crash or theft. * Comprehensive coverage This policy provides the widest coverage, i.e. the third party's physical injury and death, third party's vehicle damage and your own vehicle's damage caused by fire, theft or a crash. This type of insurance is usually designed for luxury vehicles.New Zealand
WithinNew Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
, the Accident Compensation Corporation
The Accident Compensation Corporation (ACC) () is the New Zealand Crown entity responsible for administering the country's No-fault insurance, no-fault accidental injury compensation scheme, commonly referred to as the ACC scheme. The scheme pro ...
(ACC) provides nationwide no-fault personal injury insurance. Injuries involving motor vehicles operating on public roads are covered by the Motor Vehicle Account, for which premiums are collected through levies on petrol and through vehicle licensing fees.
Norway
{{unref-section, date=February 2025 InNorway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
, the vehicle owner must provide the minimum liability insurance for his/her vehicle(s) – of any kind. Otherwise, the vehicle is illegal to use. If a person drives a vehicle belonging to someone else and has a crash, the insurance will cover for damage done. Note that the policy carrier can choose to limit the coverage to only apply for family members or persons over a certain age.
Russian Federation
{{unref-section, date=February 2025 In Russia motor vehicle liability insurance is mandatory for all owners and known as OSAGO. Insurance of the vehicle itself ("Casco") is technically voluntary, but may be mandated in some circumstances, e.g. if the car is leased.South Africa
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
allocates a percentage of the money from fuel into the Road Accident Fund, which goes towards compensating third parties in crashes.
United Arab Emirates
When buying car insurance in theUnited Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE), or simply the Emirates, is a country in West Asia, in the Middle East, at the eastern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is a Federal monarchy, federal elective monarchy made up of Emirates of the United Arab E ...
, the traffic department requires a 13-month insurance certificate each time a person registers or renews a vehicle registration. In Dubai, vehicle insurance is compulsory as per the UAE RTA law. There are two types of motor insurance policies in Dubai, Third-Party Liability Insurance and Comprehensive Motor Insurance.{{citation needed, date=July 2019
It is mandatory to have third-party liability insurance for every individual vehicle owner in Dubai
Dubai (Help:IPA/English, /duːˈbaɪ/ Help:Pronunciation respelling key, ''doo-BYE''; Modern Standard Arabic, Modern Standard Arabic: ; Emirati Arabic, Emirati Arabic: , Romanization of Arabic, romanized: Help:IPA/English, /diˈbej/) is the Lis ...
. This insurance policy is the most basic form of vehicle insurance Dubai as it covers the third-party property damage or bodily injuries caused by the insured vehicle.{{citation needed, date=July 2019
Policyholder's own vehicle damage such as fire, theft, and accidental collision is not covered under the third-party liability insurance policy.{{citation needed, date=July 2019
United Kingdom
{{main, Vehicle insurance in the United KingdomUK Government
His Majesty's Government, abbreviated to HM Government or otherwise UK Government, is the central government, central executive authority of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
, introduced a law that required every person who used a vehicle on the road to have at least third-party personal injury insurance. Today, this law is contained in the Road Traffic Act 1988. Section 143 of that Act requires that motorists be insured against liability for injuries to others (including passengers) and for damage to other persons' property, resulting from use of a vehicle on a public road or in other public places. The regulations were last revised via The Motor Vehicles (Compulsory Insurance) Regulations 2016 No. 1193, the amendment increased the minimum guaranteed property cover to £1,200,000 (US${{Formatnum:{{To USD round, 1200000, GBR, sf=3 ) per accident, personal injury cover remains unlimited. Failure to insure a vehicle can result in the vehicle being seized, the driver fined a minimum of £300 (US${{Formatnum:{{To USD round, 300, GBR, sf=2 ) and issued with six to eight penalty driving points (IN10).
United States
{{main, Vehicle insurance in the United States The regulations for vehicle insurance differ with each of the 50 US states and other territories, with each U.S. state having its own mandatory minimum coverage requirements (''see separate main article''). Forty-nine U.S. states and the District of Columbia require drivers to have insurance coverage for both bodily injury and property damage, with New Hampshire being the exception, but the minimum amount of coverage required by law varies by state. For example, minimum bodily injury liability coverage requirements range from $30,000 inArizona
Arizona is a U.S. state, state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States, sharing the Four Corners region of the western United States with Colorado, New Mexico, and Utah. It also borders Nevada to the nort ...
to $100,000 in Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
and Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
, while minimum property damage liability requirements range from $5,000 to $25,000 in most states.
Coverage levels
{{unref-section, date=February 2025 Vehicle insurance can cover some or all of the following items: * The insured party (medical payments) * Property damage caused by the insured * The insured vehicle (physical damage) * Third parties (car and people, property damage and bodily injury) * Third party, fire and theft * In some jurisdictions coverage for injuries to persons riding in the insured vehicle is available without regard to fault in the auto crash (No Fault Auto Insurance) * The cost to rent a vehicle if yours is damaged. * The cost to tow your vehicle to a repair facility. * Crashes involving uninsured motorists. Different policies specify the circumstances under which each item is covered. For example, a vehicle can be insured against theft, fire damage, or crash damage independently. If a vehicle is declared a total loss and the vehicle's market value is less than the amount that is still owed to the bank that is financing the vehicle, GAP insurance may cover the difference. Not all auto insurance policies include GAP insurance. GAP insurance is often offered by the finance company at time the vehicle is purchased.Excess
An excess payment, also known as adeductible
In an insurance policy, the deductible (in British English, the excess) is the amount paid
Out-of-pocket expenses, out of pocket by the policy holder before an insurance provider will pay any expenses. In general usage, the term ''deductible'' m ...
, is a fixed contribution that must be paid each time a car is repaired with the charges billed to an automotive insurance policy. Normally this payment is made directly to the crash repair "garage" (the term "garage" refers to an establishment where vehicles are serviced and repaired) when the owner collects the car. If one's car is declared to be a " write-off" (or " totaled"), then the insurance company will deduct the excess agreed on the policy from the settlement payment it makes to the owner.
If the crash was the other driver's fault, and this fault is accepted by the third party's insurer, then the vehicle owner may be able to reclaim the excess payment from the other person's insurance company.
The excess itself can also be protected by a motor excess insurance policy.{{citation needed, date=July 2016
Compulsory excess
A compulsory excess is the minimum excess payment the insurer will accept on the insurance policy. Minimum excesses vary according to the personal details, driving record and the insurance company. For example, young or inexperienced drivers and types of incident can incur additional compulsory excess charges.Voluntary excess
To reduce the insurance premium, the insured party may offer to pay a higher excess (deductible) than the compulsory excess demanded by the insurance company. The voluntary excess is the extra amount, over and above the compulsory excess, that is agreed to be paid in the event of a claim on the policy. As a bigger excess reduces thefinancial risk
Financial risk is any of various types of risk associated with financing, including financial transactions that include company loans in risk of default. Often it is understood to include only downside risk, meaning the potential for financi ...
carried by the insurer, the insurer is able to offer a significantly lower premium.
Basis of premium charges
{{Main, Auto insurance risk selection Depending on the jurisdiction, the insurance premium can be either mandated by the government or determined by the insurance company, in accordance with a framework of regulations set by the government. Often, the insurer will have more freedom to set the price on physical damage coverages than on mandatory liability coverages. When the premium is not mandated by the government, it is usually derived from the calculations of anactuary
An actuary is a professional with advanced mathematical skills who deals with the measurement and management of risk and uncertainty. These risks can affect both sides of the balance sheet and require investment management, asset management, ...
, based on statistical data. The premium can vary depending on many factors that are believed to affect the expected cost of future claims. Those factors can include the car characteristics, the coverage selected (deductible
In an insurance policy, the deductible (in British English, the excess) is the amount paid
Out-of-pocket expenses, out of pocket by the policy holder before an insurance provider will pay any expenses. In general usage, the term ''deductible'' m ...
, limit, covered perils), the profile of the driver (age
Age or AGE may refer to:
Time and its effects
* Age, the amount of time someone has been alive or something has existed
** East Asian age reckoning, an Asian system of marking age starting at 1
* Ageing or aging, the process of becoming older
...
, gender
Gender is the range of social, psychological, cultural, and behavioral aspects of being a man (or boy), woman (or girl), or third gender. Although gender often corresponds to sex, a transgender person may identify with a gender other tha ...
, driving history) and the usage of the car (commute to work or not, predicted annual distance driven).
Neighbourhood
The address of the owner can affect the premiums. Areas with high crime rates generally lead to higher costs of insurance.{{Cite web , url=http://www.ibc.ca/nt/insurance-101/critters/insurance-101-cost-of-insurance-affected-by-neighbourhood , title=Neighbourhoods and Auto Insurance Rates , website=Insurance Bureau of Canada , language=en , access-date=22 September 2017Mondalek, Alexandra (20 November 2015Auto Insurance Rates Are 70% Higher If You Live In A Black Neighborhood
Time.com.
Gender
Because male drivers, especially younger ones, are on average often regarded as tending to drive more aggressively, the premiums charged for policies on vehicles whose primary driver is male are often higher. This discrimination may be dropped if the driver is past a certain age. Apparently, this method is based on statistics showing that young male drivers have a higher accident rate. On 1 March 2011, theEuropean Court of Justice
The European Court of Justice (ECJ), officially the Court of Justice (), is the supreme court of the European Union in matters of European Union law. As a part of the Court of Justice of the European Union, it is tasked with interpreting ...
decided insurance companies who used gender as a risk factor when calculating insurance premiums were breaching EU equality laws.Cendrowicz, Leo (2 March 2011E.U. Court to Insurers: Stop Making Men Pay More
Time.com. The Court ruled that car-insurance companies were discriminating against men. However, in some places, such as the UK, companies have used the standard practice of discrimination based on profession to still use gender as a factor, albeit indirectly. Professions which are more typically practised by men are deemed as being more risky even if they had not been prior to the Court's ruling while the converse is applied to professions predominant among women.{{cite news, url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/finance/personalfinance/insurance/motorinsurance/11521781/Men-are-still-charged-more-than-women-for-car-insurance-despite-EU-rule-change.html , archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220112/https://www.telegraph.co.uk/finance/personalfinance/insurance/motorinsurance/11521781/Men-are-still-charged-more-than-women-for-car-insurance-despite-EU-rule-change.html , archive-date=12 January 2022 , url-access=subscription , url-status=live, title=Men Are Still Charged More than Women for Car Insurance Despite EU Rule Change, date=10 April 2015, last1=Palmer, first1=Kate{{cbignore Another effect of the ruling has been that, while the premiums for men have been lowered, they have been raised for women. This equalisation effect has also been seen in other types of insurance for individuals, such as
life insurance
Life insurance (or life assurance, especially in the Commonwealth of Nations) is a contract
A contract is an agreement that specifies certain legally enforceable rights and obligations pertaining to two or more parties. A contract typical ...
.
Age
Teenage drivers who have no driving record will have higher car insurance premiums. However, young drivers are often offered discounts if they undertake further driver training on recognized courses, such as the Pass Plus scheme in the UK, or if they install atelematics
Telematics is an interdisciplinary field encompassing telecommunications, vehicular technologies (road transport, road safety, etc.), electrical engineering (sensors, instrumentation, wireless communications, etc.), and computer science (multimedia ...
device to monitor their driving style. In the US many insurers offer a good-grade discount to students with a good academic record and resident-student discounts to those who live away from home. Generally insurance premiums tend to become lower at the age of 25. Some insurance companies offer "stand alone" car insurance policies specifically for teenagers with lower premiums. By placing restrictions on teenagers' driving (forbidding driving after dark, or giving rides to other teens, for example), these companies effectively reduce their risk.{{citation needed, date=August 2019
U.S. driving history
In most U.S. states, moving violations, including running red lights and speeding, assess points on a driver's driving record. Since more points indicate an increased risk of future violations, insurance companies periodically review drivers' records, and may raise premiums accordingly. Rating practices, such as debit for a poor driving history, are not dictated by law. Many insurers allow one moving violation every three to five years before increasing premiums. Crashes affect insurance premiums similarly. Depending on the severity of the crash and the number of points assessed, rates can increase by as much as twenty to thirty percent.{{citation needed, date=August 2019 Any motoring convictions should be disclosed to insurers, as the driver is assessed by risk from prior experiences while driving on the road.Marital status
Statistics show that married drivers average fewer crashes than the rest of the population so policy owners who are married often receive lower premiums than single persons.{{cite book, author1=Miller, Roger LeRoy , author2=Stafford, Alan D. , name-list-style=amp , title=Economic Education for Consumers, url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KmsptGIoV2oC&pg=PA475, access-date=6 September 2011, date=16 January 2009, publisher=Cengage Learning, isbn=978-0-538-44888-8, page=475Profession
The profession of the driver may be used as a factor to determine premiums. Certain professions may be deemed more likely to result in damages if they regularly involve more travel or the carrying of expensive equipment or stock or if they are predominant either among women or among men.Vehicle classification
Two of the most important factors that go into determining the underwriting risk on motorized vehicles are: performance capability and retail cost. The most commonly available providers of auto insurance have underwriting restrictions against vehicles that are either designed to be capable of higher speeds and performance levels, or vehicles that retail above a certain dollar amount. Vehicles that are commonly considered luxury automobiles usually carry more expensive physical damage premiums because they are more expensive to replace. Vehicles that can be classified as high performance autos will carry higher premiums generally because there is greater opportunity for risky driving behavior. Motorcycle insurance may carry lower property-damage premiums because the risk of damage to other vehicles is minimal, yet have higher liability or personal-injury premiums, because motorcycle riders face different physical risks while on the road. Risk classification on automobiles also takes into account the statistical analysis of reported theft, accidents, and mechanical malfunction on every given year, make, and model of auto.Distance
Some car insurance plans do not differentiate in regard to how much the car is used. There are however low-mileage discounts offered by some insurance providers. Other methods of differentiation would include over-road distance between the ordinary residence of a subject and their ordinary, daily destinations.Reasonable distance estimation
Another important factor in determining car insurance premiums involves the annual mileage put on the vehicle, and for what reason. Driving to and from work every day at a specified distance, especially in urban areas where common traffic routes are known, presents different risks than how a retiree who does not work any longer may use their vehicle. Common practice has been that this information was provided solely by the insured person, but some insurance providers have started to collect regularodometer
An odometer or odograph is an instrument used for measuring the distance traveled by a vehicle, such as a bicycle or car. The device may be electronic, mechanical, or a combination of the two (electromechanical). The noun derives from ancient Gr ...
readings to verify the risk.
Odometer-based systems
Cents Per Mile Now (1986) advocates classified odometer-mile rates, a type of usage-based insurance. After the company's risk factors have been applied, and the customer has accepted the per-mile rate offered, then customers buy prepaid miles of insurance protection as needed, like buying gallons of gasoline (litres of petrol). Insurance automatically ends when theodometer
An odometer or odograph is an instrument used for measuring the distance traveled by a vehicle, such as a bicycle or car. The device may be electronic, mechanical, or a combination of the two (electromechanical). The noun derives from ancient Gr ...
limit (recorded on the car's insurance ID card) is reached, unless more distance is bought. Customers keep track of miles on their own odometer to know when to buy more. The company does no after-the-fact billing of the customer, and the customer does not have to estimate a "future annual mileage" figure for the company to obtain a discount. In the event of a traffic stop, an officer could easily verify that the insurance is current, by comparing the figure on the insurance card to that on the odometer.
Critics point out the possibility of cheating the system by odometer tampering. Although the newer electronic odometers are difficult to roll back, they can still be defeated by disconnecting the odometer wires and reconnecting them later. However, as the Cents Per Mile Now website points out:
As a practical matter, resetting odometers requires equipment plus expertise that makes stealing insurance risky and uneconomical. For example, to steal {{convert, 20000, mi, km, -2, disp=sqbr of continuous protection while paying for only the 2000 in the 35000 to 37000 range on the odometer, the resetting would have to be done at least nine times, to keep the odometer reading within the narrow {{convert, 2000, mi, km, adj=on, disp=sqbr covered range. There are also powerful legal deterrents to this way of stealing insurance protection. Odometers have always served as the measuring device for resale value, rental and leasing charges, warranty limits, mechanical breakdown insurance, and cents-per-mile tax deductions or reimbursements for business or government travel. Odometer tampering, detected during claim processing, voids the insurance and, under decades-old state and federal law, is punishable by heavy fines and jail.Under the cents-per-mile system, rewards for driving less are delivered automatically, without the need for administratively cumbersome and costly GPS technology. Uniform per-mile exposure measurement for the first time provides the basis for statistically valid rate classes. Insurer premium income automatically keeps pace with increases or decreases in driving activity, cutting back on resulting insurer demand for rate increases and preventing today's windfalls to insurers, when decreased driving activity lowers costs but not premiums.
GPS-based system
In 1998, the Progressive Insurance company started a pilot program in Texas, in which drivers received a discount for installing a GPS-based device that tracked their driving behavior and reported the results via cellular phone to the company. The program was discontinued in 2000. In following years many policies (including Progressive) have been trialed and successfully introduced worldwide into what are referred to as Telematic Insurance. Such 'telematic' policies typically are based on black-box insurance technology, such devices derive from a stolen vehicle and fleet tracking but are used for insurance purposes. Since 2010 GPS-based and Telematic Insurance systems have become more mainstream in the auto insurance market not just aimed at specialised auto-fleet markets or high value vehicles (with an emphasis on stolen vehicle recovery). Modern GPS-based systems are branded as 'PAYD' Pay As You Drive insurance policies, 'PHYD' Pay How You Drive or since 2012 Smartphone auto insurance policies which utilise smartphones as a GPS sensor. A detailed survey of the smartphone as measurement probe for insurance telematics is provided inOBDII-based system
The Progressive Corporation
The Progressive Corporation is an American insurance company. Progressive is currently the #2 auto insurer in the United States behind State Farm. The company was co-founded in 1937 by Jack Green and Joseph M. Lewis, and is headquartered in Ma ...
launched Snapshot to give drivers a customized insurance rate based on recording how, how much, and when their car is driven."Snapshot, Snapshot Discount: Pay As You Drive (PAYD)"Progressive.com. Snapshot is currently available in 46 states plus the District of Columbia. Because insurance is regulated at the state level, Snapshot is currently not available in Alaska, California, Hawaii, and North Carolina. Driving data is transmitted to the company using an on-board telematic device. The device connects to a car's OnBoard Diagnostic ( OBD-II) port (all petrol automobiles in the USA built after 1996 have an OBD-II.) and transmits speed, time of day and number of miles the car is driven. Cars that are driven less often, in less-risky ways, and at less-risky times of day, can receive large discounts. Progressive has received patents on its methods and systems of implementing usage-based insurance and has licensed these methods and systems to other companies. Metromile also uses an OBDII-based system for their mileage-based insurance. They offer a true pay-per-mile insurance where behavior or driving style is not taken into account, and the user only pays a base rate along with a fixed rate per mile. The OBD-II device measures mileage and then transmits mileage data to servers. This is supposed to be an affordable car insurance policy for low-mileage drivers. Metromile is currently only offering personal car insurance policies and is available in California, Oregon, Washington, and Illinois.
Credit ratings
Insurance companies have started using credit ratings of their policyholders to determine risk. Drivers with good credit scores get lower insurance premiums, as it is believed that they are more financially stable, more responsible and have the financial means to better maintain their vehicles. Those with lower credit scores can have their premiums raised or insurance canceled outright. It has been shown that good drivers with spotty credit records could be charged higher premiums than bad drivers with good credit records.Behavior-based insurance
The use of non-intrusive load monitoring to detect drunk driving and other risky behaviors has been proposed. A US patent application combining this technology with a usage-based insurance product to create a new type of behavior based auto insurance product is currently open for public comment on peer to patent.{{webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100618063009/http://www.peertopatent.org/patent/20090063201/activity , date=18 June 2010 . Peertopatent.org (20 May 2009).
Telematics
Telematics is an interdisciplinary field encompassing telecommunications, vehicular technologies (road transport, road safety, etc.), electrical engineering (sensors, instrumentation, wireless communications, etc.), and computer science (multimedia ...
or Telematics2.0 in some cases monitoring focus upon behavioural analysis such as smooth driving.
Repair insurance
{{Globalize, section, USA, 2name=the United States, date=September 2012 Auto repair insurance is an extension ofcar insurance
Vehicle insurance (also known as car insurance, motor insurance, or auto insurance) is insurance for automobile, cars, trucks, motorcycles, and other road vehicles. Its primary use is to provide financial protection against physical damage or bo ...
available in all 50 of the United States that covers the natural wear and tear on a vehicle, independent of damages related to a car crash.
Some drivers opt to buy the insurance as a means of protection against costly breakdowns unrelated to a crash. In contrast to more standard and basic coverages such as comprehensive and collision insurance, auto repair insurance does not cover a vehicle when it is damaged in a collision, during a natural disaster or at the hands of vandals.
For many it is an attractive option for protection after the warranties on their cars expire.
Providers can also offer sub-divisions of auto repair insurance. There is standard repair insurance which covers the wear and tear of vehicles, and naturally occurring breakdowns. Some companies will only offer mechanical breakdown insurance, which only covers repairs necessary when breakable parts need to be fixed or replaced. These parts include transmissions, oil pumps, piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder (engine), cylinder a ...
s, timing gears, flywheels, valves, axles and joints.{{cite news
, url=https://www.foxbusiness.com/features/auto-repair-insurance-pledges-to-pay-your-breakdown-bills
, title=Auto repair insurance pledges to pay your breakdown bills
, first=Michele
, last=Lerner
, date=14 April 2016
, access-date=2 June 2018
, publisher=Fox Business
In several countries insurance companies offer direct repair programs (DRP) so that their customers have easy access to a recommended car body repair shop. Some also offer one-stop shopping where a damaged car can get dropped off and an adjuster handles the claim, the car is fixed and often a replacement rental car is provided. When repairing the vehicle the car body repair shop is obliged to follow the instructions regarding the choice of original equipment manufacturer (OEM), original equipment supplier parts (OES), Matching Quality spare parts (MQ) and generic replacement parts. Both DRPs and non OEM parts help to keep costs down and keep insurance prices competitive. AIRC (International Car body repair Association) General Secretary Karel Bukholczer made clear that DRP's have had big impact on car body repair shops.{{Cite web , url=https://www.autohaus.de/nachrichten/7-autohaus-schadenforum-kaputt-gemachte-e-maerkte-1084913.html , title=Kaputt(gemachte)e Märkte - autohaus.de , website=www.autohaus.de , access-date=2 June 2018
See also
* Alcohol exclusion laws * Assigned risk * Automobile costs * Damage waiver for rental cars * Extended coverage * Family purpose doctrine * Guaranteed asset protection insurance *Health insurance
Health insurance or medical insurance (also known as medical aid in South Africa) is a type of insurance that covers the whole or a part of the risk of a person incurring medical expenses. As with other types of insurance, risk is shared among ma ...
* International Motor Insurance Card System
An International Motor Insurance Card System is an arrangement between authorities and insurance organizations of multiple states to ensure that victims of road accident, road traffic accidents do not suffer from the fact that injuries or damage s ...
* Insurance Information and Enforcement System
* Omnibus clause
References
{{ReflistExternal links
*{{Commons category-inline, Car insurance {{Insurance {{Authority control Types of insurance Car costs