Aurora Borealis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An aurora ( aurorae or auroras),
also commonly known as the northern lights (aurora borealis) or southern lights (aurora australis), is a natural light display in
 Auroras are most commonly observed in the "auroral zone", a band approximately 6° (~660 km) wide in latitude centered on 67° north and south. The region that currently displays an aurora is called the "auroral oval". The oval is displaced by the solar wind, pushing it about 15° away from the geomagnetic pole (not the geographic pole) in the noon direction and 23° away in the midnight direction. The peak equatorward extent of the oval is displaced slightly from geographic midnight. It is centered about 3–5° nightward of the magnetic pole so that auroral arcs reach furthest toward the equator when the magnetic pole in question is in between the observer and the Sun, which is called magnetic midnight.
Early evidence for a geomagnetic connection comes from the statistics of auroral observations.
Auroras are occasionally seen in latitudes below the auroral zone when a geomagnetic storm temporarily enlarges the auroral oval. Large geomagnetic storms are most common during the peak of the 11-year
Auroras are most commonly observed in the "auroral zone", a band approximately 6° (~660 km) wide in latitude centered on 67° north and south. The region that currently displays an aurora is called the "auroral oval". The oval is displaced by the solar wind, pushing it about 15° away from the geomagnetic pole (not the geographic pole) in the noon direction and 23° away in the midnight direction. The peak equatorward extent of the oval is displaced slightly from geographic midnight. It is centered about 3–5° nightward of the magnetic pole so that auroral arcs reach furthest toward the equator when the magnetic pole in question is in between the observer and the Sun, which is called magnetic midnight.
Early evidence for a geomagnetic connection comes from the statistics of auroral observations.
Auroras are occasionally seen in latitudes below the auroral zone when a geomagnetic storm temporarily enlarges the auroral oval. Large geomagnetic storms are most common during the peak of the 11-year
 * A mild ''glow'', near the horizon. These can be close to the limit of visibility, but can be distinguished from moonlit clouds because stars can be seen undiminished through the glow.
* ''Patches'' or ''surfaces'' that look like clouds.
* ''Arcs'' curve across the sky.
* ''Rays'' are light and dark stripes across arcs, reaching upwards by various amounts.
* ''Coronas'' cover much of the sky and diverge from one point on it.
Brekke (1994) also described some auroras as "curtains". The similarity to curtains is often enhanced by folds within the arcs. Arcs can fragment or break up into separate, at times rapidly changing, often rayed features that may fill the whole sky. These are also known as ''discrete auroras'', which are at times bright enough to read a newspaper at night.
These forms are consistent with auroras being shaped by Earth's magnetic field. The appearances of arcs, rays, curtains, and coronas are determined by the shapes of the luminous parts of the atmosphere and a viewer's position.
* A mild ''glow'', near the horizon. These can be close to the limit of visibility, but can be distinguished from moonlit clouds because stars can be seen undiminished through the glow.
* ''Patches'' or ''surfaces'' that look like clouds.
* ''Arcs'' curve across the sky.
* ''Rays'' are light and dark stripes across arcs, reaching upwards by various amounts.
* ''Coronas'' cover much of the sky and diverge from one point on it.
Brekke (1994) also described some auroras as "curtains". The similarity to curtains is often enhanced by folds within the arcs. Arcs can fragment or break up into separate, at times rapidly changing, often rayed features that may fill the whole sky. These are also known as ''discrete auroras'', which are at times bright enough to read a newspaper at night.
These forms are consistent with auroras being shaped by Earth's magnetic field. The appearances of arcs, rays, curtains, and coronas are determined by the shapes of the luminous parts of the atmosphere and a viewer's position.
 * Blue: At yet lower altitudes, atomic oxygen is uncommon, and molecular nitrogen and ionized molecular nitrogen take over in producing visible light emission, radiating at a large number of wavelengths in both red and blue parts of the spectrum, with 428 nm (blue) being dominant. Blue and purple emissions, typically at the lower edges of the "curtains", show up at the highest levels of solar activity. The molecular nitrogen transitions are much faster than the atomic oxygen ones.
* Ultraviolet: Ultraviolet radiation from auroras (within the optical window but not visible to the human eye) has been observed with the requisite equipment. Ultraviolet auroras have also been seen on Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn.
* Infrared: Infrared radiation, in wavelengths that are within the optical window, is also part of many auroras.
* Yellow and pink are a mix of red and green or blue. Yellow and pink auroras are relatively rare and are associated with high solar activity. Other shades of red, as well as orange and gold, also may be seen on rare occasions. As red, green, and blue are linearly independent colours, additive synthesis could, in theory, produce most human-perceived colours, but the ones mentioned in this article comprise a virtually exhaustive list.
* Blue: At yet lower altitudes, atomic oxygen is uncommon, and molecular nitrogen and ionized molecular nitrogen take over in producing visible light emission, radiating at a large number of wavelengths in both red and blue parts of the spectrum, with 428 nm (blue) being dominant. Blue and purple emissions, typically at the lower edges of the "curtains", show up at the highest levels of solar activity. The molecular nitrogen transitions are much faster than the atomic oxygen ones.
* Ultraviolet: Ultraviolet radiation from auroras (within the optical window but not visible to the human eye) has been observed with the requisite equipment. Ultraviolet auroras have also been seen on Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn.
* Infrared: Infrared radiation, in wavelengths that are within the optical window, is also part of many auroras.
* Yellow and pink are a mix of red and green or blue. Yellow and pink auroras are relatively rare and are associated with high solar activity. Other shades of red, as well as orange and gold, also may be seen on rare occasions. As red, green, and blue are linearly independent colours, additive synthesis could, in theory, produce most human-perceived colours, but the ones mentioned in this article comprise a virtually exhaustive list.
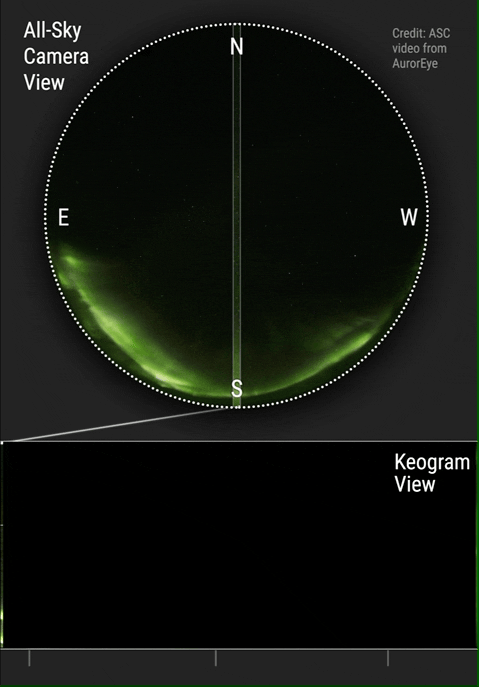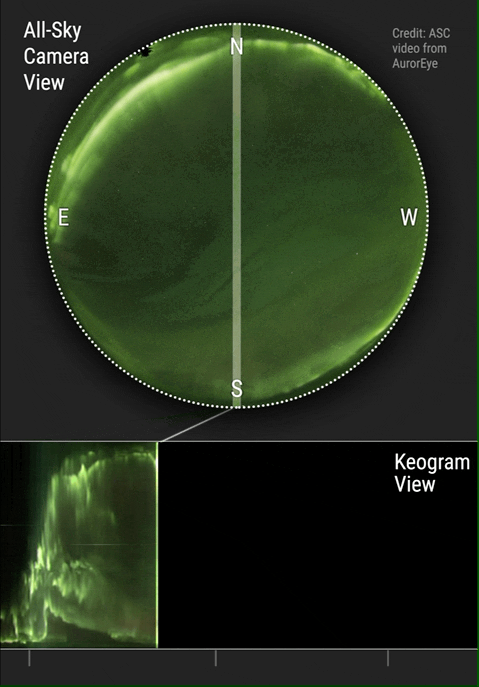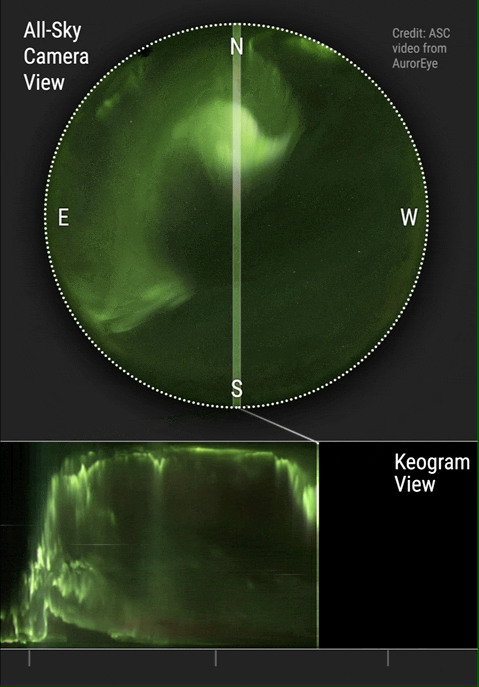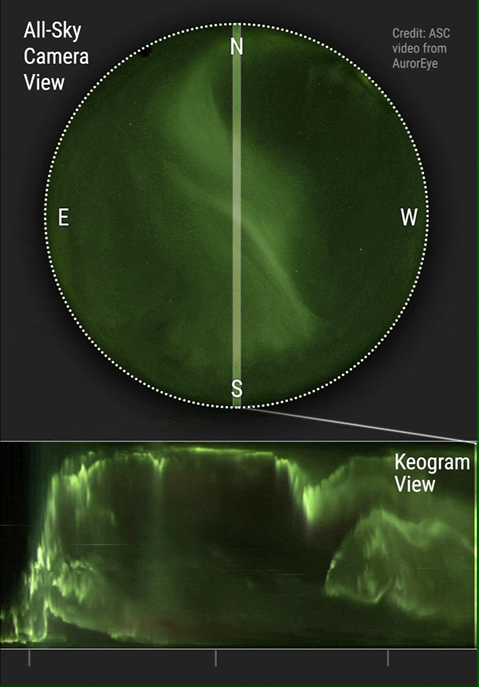 Auroras change with time. Over the night they begin with glows and progress toward coronas, although they may not reach them. They tend to fade in the opposite order. Until about 1963, it was thought that these changes were due to the rotation of the Earth under a pattern fixed with respect to the Sun. Later, it was found by comparing all-sky films of auroras from different places (collected during the
Auroras change with time. Over the night they begin with glows and progress toward coronas, although they may not reach them. They tend to fade in the opposite order. Until about 1963, it was thought that these changes were due to the rotation of the Earth under a pattern fixed with respect to the Sun. Later, it was found by comparing all-sky films of auroras from different places (collected during the
 # Acceleration of auroral charged particles invariably accompanies a magnetospheric disturbance that causes an aurora. This mechanism, which is believed to predominantly arise from strong electric fields along the magnetic field or wave-particle interactions, raises the velocity of a particle in the direction of the guiding magnetic field. The pitch angle is thereby decreased and increases the chance of it being precipitated into the atmosphere. Both electromagnetic and electrostatic waves, produced at the time of greater geomagnetic disturbances, make a significant contribution to the energizing processes that sustain an aurora. Particle acceleration provides a complex intermediate process for transferring energy from the solar wind indirectly into the atmosphere.
# Acceleration of auroral charged particles invariably accompanies a magnetospheric disturbance that causes an aurora. This mechanism, which is believed to predominantly arise from strong electric fields along the magnetic field or wave-particle interactions, raises the velocity of a particle in the direction of the guiding magnetic field. The pitch angle is thereby decreased and increases the chance of it being precipitated into the atmosphere. Both electromagnetic and electrostatic waves, produced at the time of greater geomagnetic disturbances, make a significant contribution to the energizing processes that sustain an aurora. Particle acceleration provides a complex intermediate process for transferring energy from the solar wind indirectly into the atmosphere.
 The details of these phenomena are not fully understood. However, it is clear that the prime source of auroral particles is the solar wind feeding the magnetosphere, the reservoir containing the radiation zones and temporarily magnetically trapped particles confined by the geomagnetic field, coupled with particle acceleration processes.
The details of these phenomena are not fully understood. However, it is clear that the prime source of auroral particles is the solar wind feeding the magnetosphere, the reservoir containing the radiation zones and temporarily magnetically trapped particles confined by the geomagnetic field, coupled with particle acceleration processes.
 Earth's
Earth's
 In the traditions of
In the traditions of  In Scandinavia, the first mention of (the northern lights) is found in the Norwegian chronicle from AD 1230. The chronicler has heard about this phenomenon from compatriots returning from
In Scandinavia, the first mention of (the northern lights) is found in the Norwegian chronicle from AD 1230. The chronicler has heard about this phenomenon from compatriots returning from  A variety of Native American myths surround the spectacle. The European explorer Samuel Hearne travelled with Chipewyan Dene in 1771 and recorded their views on the ('caribou'). According to Hearne, the Dene people saw the resemblance between an aurora and the sparks produced when caribou fur is stroked. They believed that the lights were the spirits of their departed friends dancing in the sky, and when they shone brightly it meant that their deceased friends were very happy.
During the night after the
A variety of Native American myths surround the spectacle. The European explorer Samuel Hearne travelled with Chipewyan Dene in 1771 and recorded their views on the ('caribou'). According to Hearne, the Dene people saw the resemblance between an aurora and the sparks produced when caribou fur is stroked. They believed that the lights were the spirits of their departed friends dancing in the sky, and when they shone brightly it meant that their deceased friends were very happy.
During the night after the
 Both
Both
Alt URL
* * * * *
Current global map showing the probability of visible aurora
Aurora – Forecasting
(archived 24 November 2016)
Official MET aurora forecasting in Iceland
Aurora Borealis – Predicting
– Online Converter – ''Northern Lights'' Latitude
Aurora Service Europe
– Aurora forecasts for Europe (archived 11 March 2019)
Live Northern Lights webstream
World's Best Aurora
– The Northwest Territories is the world's Northern Lights mecca.
Amazing time-lapse video of Aurora Borealis
– Shot in Iceland over the winter of 2013/2014
Popular video of Aurora Borealis
– Taken in Norway in 2011
Aurora Photo Gallery
– Views taken 2009–2011 (archived 4 October 2011)
– "Full-Sky Aurora" over Eastern
Videos and Photos – Auroras at Night
(archived 2 September 2010)
Video (47:40)
– ''Northern Lights'' – Documentary
Video (5:00)
– Northern lights video in real time
Video (01:42)
– ''Northern Light – Story of
Video (1:55)
(time-lapse) − Auroras – Ground-Level View from
Video (2:43)
(time-lapse) − Auroras – Ground-Level View from
Video (0:45)
ISS Timelapse: Aurora Australis {{Authority control Terrestrial plasmas Space plasmas Polar regions of the Earth Atmospheric optical phenomena Earth phenomena Electrical phenomena Light sources Planetary science Sources of electromagnetic interference Articles containing video clips Space weather Geomagnetism
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
's sky, predominantly observed in high-latitude regions (around the Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway ( ...
and Antarctic
The Antarctic (, ; commonly ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the South Pole, lying within the Antarctic Circle. It is antipodes, diametrically opposite of the Arctic region around the North Pole.
The Antar ...
). Auroras display dynamic patterns of radiant lights that appear as curtains, rays, spirals or dynamic flickers covering the entire sky.
Auroras are the result of disturbances in the Earth's magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior Dynamo ...
caused by enhanced speeds of solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the Stellar corona, corona. This Plasma (physics), plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy betwee ...
from coronal holes and coronal mass ejections. These disturbances alter the trajectories of charged particle
In physics, a charged particle is a particle with an electric charge. For example, some elementary particles, like the electron or quarks are charged. Some composite particles like protons are charged particles. An ion, such as a molecule or atom ...
s in the magnetospheric plasma. These particles, mainly electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
s and proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an e ...
s, precipitate into the upper atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
( thermosphere/exosphere
The exosphere is a thin, atmosphere-like volume surrounding a planet or natural satellite where molecules are gravitationally bound to that body, but where the density is so low that the molecules are essentially collision-less. In the case of ...
). The resulting ionization
Ionization or ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive Electric charge, charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged at ...
and excitation of atmospheric constituents emit light of varying color and complexity. The form of the aurora, occurring within bands around both polar regions, is also dependent on the amount of acceleration
In mechanics, acceleration is the Rate (mathematics), rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Acceleration is one of several components of kinematics, the study of motion. Accelerations are Euclidean vector, vector ...
imparted to the precipitating particles.
Other planet
A planet is a large, Hydrostatic equilibrium, rounded Astronomical object, astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets b ...
s in the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
, brown dwarf
Brown dwarfs are substellar objects that have more mass than the biggest gas giant planets, but less than the least massive main sequence, main-sequence stars. Their mass is approximately 13 to 80 Jupiter mass, times that of Jupiter ()not big en ...
s, comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that warms and begins to release gases when passing close to the Sun, a process called outgassing. This produces an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere or Coma (cometary), coma surrounding ...
s, and some natural satellite
A natural satellite is, in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet, or small Solar System body (or sometimes another natural satellite). Natural satellites are colloquially referred to as moons, a deriv ...
s also host auroras.
Etymology
The term ''aurora borealis'' has been attributed to two sources:Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642), commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei ( , , ) or mononymously as Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a poly ...
in 1619, and Pierre Gassendi
Pierre Gassendi (; also Pierre Gassend, Petrus Gassendi, Petrus Gassendus; 22 January 1592 – 24 October 1655) was a French philosopher, Catholic priest, astronomer, and mathematician. While he held a church position in south-east France, he a ...
in 1621. The term entered the English language in 1828.
The word ''aurora'' is derived from the name of the Roman goddess of the dawn, Aurora
An aurora ( aurorae or auroras),
also commonly known as the northern lights (aurora borealis) or southern lights (aurora australis), is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly observed in high-latitude regions (around the Arc ...
, who travelled from east to west announcing the coming of the Sun. ''Aurora'' was first used in English in the 14th century. The words ''borealis'' and ''australis'' are derived from the names of the ancient gods of the north wind ( Boreas) and the south wind ( Auster or ''australis'') in Greco-Roman mythology
Classical mythology, also known as Greco-Roman mythology or Greek and Roman mythology, is the collective body and study of myths from the ancient Greeks and ancient Romans. Mythology, along with philosophy and political thought, is one of the ...
.
Occurrence
 Auroras are most commonly observed in the "auroral zone", a band approximately 6° (~660 km) wide in latitude centered on 67° north and south. The region that currently displays an aurora is called the "auroral oval". The oval is displaced by the solar wind, pushing it about 15° away from the geomagnetic pole (not the geographic pole) in the noon direction and 23° away in the midnight direction. The peak equatorward extent of the oval is displaced slightly from geographic midnight. It is centered about 3–5° nightward of the magnetic pole so that auroral arcs reach furthest toward the equator when the magnetic pole in question is in between the observer and the Sun, which is called magnetic midnight.
Early evidence for a geomagnetic connection comes from the statistics of auroral observations.
Auroras are most commonly observed in the "auroral zone", a band approximately 6° (~660 km) wide in latitude centered on 67° north and south. The region that currently displays an aurora is called the "auroral oval". The oval is displaced by the solar wind, pushing it about 15° away from the geomagnetic pole (not the geographic pole) in the noon direction and 23° away in the midnight direction. The peak equatorward extent of the oval is displaced slightly from geographic midnight. It is centered about 3–5° nightward of the magnetic pole so that auroral arcs reach furthest toward the equator when the magnetic pole in question is in between the observer and the Sun, which is called magnetic midnight.
Early evidence for a geomagnetic connection comes from the statistics of auroral observations. Elias Loomis
Elias Loomis (August 7, 1811 – August 15, 1889) was an American mathematician. He served as a professor of mathematics and natural philosophy at Case Western Reserve University, Western Reserve College (now Case Western Reserve University), the ...
(1860), and later Hermann Fritz (1881) and Sophus Tromholt (1881) in more detail, established that the aurora appeared mainly in the auroral zone.
In northern latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
s, the effect is known as the aurora borealis or the northern lights. The southern counterpart, the aurora australis or the southern lights, has features almost identical to the aurora borealis and changes simultaneously with changes in the northern auroral zone. The aurora australis is visible from high southern latitudes in Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
, the Southern Cone, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
, Australasia
Australasia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising Australia, New Zealand (overlapping with Polynesia), and sometimes including New Guinea and surrounding islands (overlapping with Melanesia). The term is used in a number of different context ...
, the Falkland Islands
The Falkland Islands (; ), commonly referred to as The Falklands, is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and from Cape Dub ...
, and under exceptional circumstances as far north as Uruguay
Uruguay, officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay, is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast, while bordering the Río de la Plata to the south and the A ...
. The aurora borealis is visible from areas around the Arctic such as Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the regi ...
, Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenlan ...
, the Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ) (alt. the Faroes) are an archipelago in the North Atlantic Ocean and an autonomous territory of the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. Located between Iceland, Norway, and the United Kingdom, the islands have a populat ...
, Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also ...
, Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
, Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
, and Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
. A geomagnetic storm
A geomagnetic storm, also known as a magnetic storm, is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere that is driven by interactions between the magnetosphere and large-scale transient Plasma (physics), plasma and magnetic field structur ...
causes the auroral ovals (north and south) to expand, bringing the aurora to lower latitudes or higher in the south. On rare occasions, the aurora borealis can be seen as far south as the Mediterranean and the southern states of the US while the aurora australis can be seen as far north as New Caledonia
New Caledonia ( ; ) is a group of islands in the southwest Pacific Ocean, southwest of Vanuatu and east of Australia. Located from Metropolitan France, it forms a Overseas France#Sui generis collectivity, ''sui generis'' collectivity of t ...
and the Pilbara region in Western Australia
Western Australia (WA) is the westernmost state of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Aust ...
. During the Carrington Event, the greatest geomagnetic storm ever observed, auroras were seen even in the tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
.
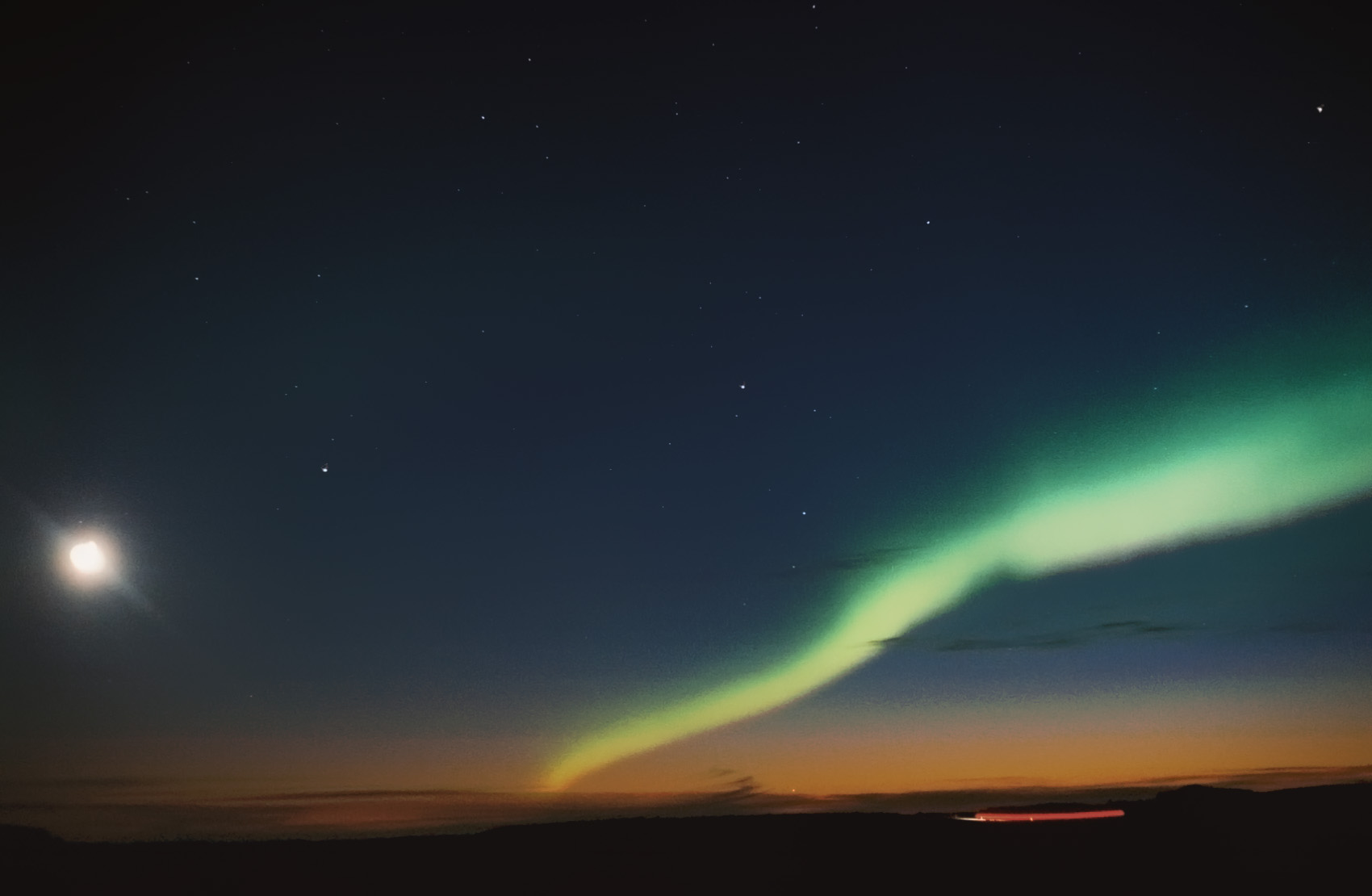
Auroras seen within the auroral oval may be directly overhead. From farther away, they illuminate the poleward horizon as a greenish glow, or sometimes a faint red, as if the Sun were rising from an unusual direction. Auroras also occur poleward of the auroral zone as either diffuse patches or arcs, which can be subvisual.sunspot
Sunspots are temporary spots on the Sun's surface that are darker than the surrounding area. They are one of the most recognizable Solar phenomena and despite the fact that they are mostly visible in the solar photosphere they usually aff ...
cycle or during the three years after the peak. An electron spirals (gyrates) about a field line at an angle that is determined by its velocity vectors, parallel and perpendicular, respectively, to the local geomagnetic field vector B. This angle is known as the "pitch angle" of the particle. The distance, or radius, of the electron from the field line at any time is known as its Larmor radius. The pitch angle increases as the electron travels to a region of greater field strength nearer to the atmosphere. Thus, it is possible for some particles to return, or mirror, if the angle becomes 90° before entering the atmosphere to collide with the denser molecules there. Other particles that do not mirror enter the atmosphere and contribute to the auroral display over a range of altitudes. Other types of auroras have been observed from space; for example, "poleward arcs" stretching sunward across the polar cap, the related "theta aurora", and "dayside arcs" near noon. These are relatively infrequent and poorly understood. Other interesting effects occur such as pulsating aurora, "black aurora" and their rarer companion "anti-black aurora" and subvisual red arcs. In addition to all these, a weak glow (often deep red) is observed around the two polar cusps, the field lines separating the ones that close through Earth from those that are swept into the tail and close remotely.
Images
Early work on the imaging of the auroras was done in 1949 by the University of Saskatchewan using the SCR-270 radar. The altitudes where auroral emissions occur were revealed by Carl Størmer and his colleagues, who used cameras to triangulate more than 12,000 auroras. They discovered that most of the light is produced between above the ground while extending at times to more than .Forms
According to Clark (2007), there are five main forms that can be seen from the ground, from least to most visible: * A mild ''glow'', near the horizon. These can be close to the limit of visibility, but can be distinguished from moonlit clouds because stars can be seen undiminished through the glow.
* ''Patches'' or ''surfaces'' that look like clouds.
* ''Arcs'' curve across the sky.
* ''Rays'' are light and dark stripes across arcs, reaching upwards by various amounts.
* ''Coronas'' cover much of the sky and diverge from one point on it.
Brekke (1994) also described some auroras as "curtains". The similarity to curtains is often enhanced by folds within the arcs. Arcs can fragment or break up into separate, at times rapidly changing, often rayed features that may fill the whole sky. These are also known as ''discrete auroras'', which are at times bright enough to read a newspaper at night.
These forms are consistent with auroras being shaped by Earth's magnetic field. The appearances of arcs, rays, curtains, and coronas are determined by the shapes of the luminous parts of the atmosphere and a viewer's position.
* A mild ''glow'', near the horizon. These can be close to the limit of visibility, but can be distinguished from moonlit clouds because stars can be seen undiminished through the glow.
* ''Patches'' or ''surfaces'' that look like clouds.
* ''Arcs'' curve across the sky.
* ''Rays'' are light and dark stripes across arcs, reaching upwards by various amounts.
* ''Coronas'' cover much of the sky and diverge from one point on it.
Brekke (1994) also described some auroras as "curtains". The similarity to curtains is often enhanced by folds within the arcs. Arcs can fragment or break up into separate, at times rapidly changing, often rayed features that may fill the whole sky. These are also known as ''discrete auroras'', which are at times bright enough to read a newspaper at night.
These forms are consistent with auroras being shaped by Earth's magnetic field. The appearances of arcs, rays, curtains, and coronas are determined by the shapes of the luminous parts of the atmosphere and a viewer's position.
Colours and wavelengths of auroral light
* Red: At its highest altitudes, excited atomic oxygen emits at 630 nm (red); low concentration of atoms and lower sensitivity of eyes at this wavelength make this colour visible only under more intense solar activity. The low number of oxygen atoms and their gradually diminishing concentration is responsible for the faint appearance of the top parts of the "curtains". Scarlet, crimson, and carmine are the most often seen hues of red for the auroras. * Green: At lower altitudes, the more frequent collisions suppress the 630 nm (red) mode: rather the 557.7 nm emission (green) dominates. A fairly high concentration of atomic oxygen and higher eye sensitivity in green make green auroras the most common. The excited molecular nitrogen (atomic nitrogen being rare due to the high stability of the N2 molecule) plays a role here, as it can transfer energy by collision with an oxygen atom, which then radiates it away at the green wavelength. (Red and green can also mix together to produce pink or yellow hues.) The rapid decrease in concentration of atomic oxygen below about 100 km is responsible for the abrupt-looking end of the lower edges of the curtains. Both the 557.7 and 630.0 nm wavelengths correspond to forbidden transitions of atomic oxygen, a slow mechanism responsible for the graduality (0.7 s and 107 s respectively) of flaring and fading. * Blue: At yet lower altitudes, atomic oxygen is uncommon, and molecular nitrogen and ionized molecular nitrogen take over in producing visible light emission, radiating at a large number of wavelengths in both red and blue parts of the spectrum, with 428 nm (blue) being dominant. Blue and purple emissions, typically at the lower edges of the "curtains", show up at the highest levels of solar activity. The molecular nitrogen transitions are much faster than the atomic oxygen ones.
* Ultraviolet: Ultraviolet radiation from auroras (within the optical window but not visible to the human eye) has been observed with the requisite equipment. Ultraviolet auroras have also been seen on Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn.
* Infrared: Infrared radiation, in wavelengths that are within the optical window, is also part of many auroras.
* Yellow and pink are a mix of red and green or blue. Yellow and pink auroras are relatively rare and are associated with high solar activity. Other shades of red, as well as orange and gold, also may be seen on rare occasions. As red, green, and blue are linearly independent colours, additive synthesis could, in theory, produce most human-perceived colours, but the ones mentioned in this article comprise a virtually exhaustive list.
* Blue: At yet lower altitudes, atomic oxygen is uncommon, and molecular nitrogen and ionized molecular nitrogen take over in producing visible light emission, radiating at a large number of wavelengths in both red and blue parts of the spectrum, with 428 nm (blue) being dominant. Blue and purple emissions, typically at the lower edges of the "curtains", show up at the highest levels of solar activity. The molecular nitrogen transitions are much faster than the atomic oxygen ones.
* Ultraviolet: Ultraviolet radiation from auroras (within the optical window but not visible to the human eye) has been observed with the requisite equipment. Ultraviolet auroras have also been seen on Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn.
* Infrared: Infrared radiation, in wavelengths that are within the optical window, is also part of many auroras.
* Yellow and pink are a mix of red and green or blue. Yellow and pink auroras are relatively rare and are associated with high solar activity. Other shades of red, as well as orange and gold, also may be seen on rare occasions. As red, green, and blue are linearly independent colours, additive synthesis could, in theory, produce most human-perceived colours, but the ones mentioned in this article comprise a virtually exhaustive list.
Changes with time
 Auroras change with time. Over the night they begin with glows and progress toward coronas, although they may not reach them. They tend to fade in the opposite order. Until about 1963, it was thought that these changes were due to the rotation of the Earth under a pattern fixed with respect to the Sun. Later, it was found by comparing all-sky films of auroras from different places (collected during the
Auroras change with time. Over the night they begin with glows and progress toward coronas, although they may not reach them. They tend to fade in the opposite order. Until about 1963, it was thought that these changes were due to the rotation of the Earth under a pattern fixed with respect to the Sun. Later, it was found by comparing all-sky films of auroras from different places (collected during the International Geophysical Year
The International Geophysical Year (IGY; ), also referred to as the third International Polar Year, was an international scientific project that lasted from 1 July 1957 to 31 December 1958. It marked the end of a long period during the Cold War w ...
) that they often undergo global changes in a process called auroral substorm. They change in a few minutes from quiet arcs all along the auroral oval to active displays along the dark side and after 1–3 hours they gradually change back. Changes in auroras over time are commonly visualized using keograms.
At shorter time scales, auroras can change their appearances and intensity, sometimes so slowly as to be difficult to notice, and at other times rapidly down to the sub-second scale. The phenomenon of pulsating auroras is an example of intensity variations over short timescales, typically with periods of 2–20 seconds. This type of aurora is generally accompanied by decreasing peak emission heights of about 8 km for blue and green emissions and above-average solar wind speeds ().
Other auroral radiation
In addition, the aurora and associated currents produce a strong radio emission around 150 kHz known as auroral kilometric radiation (AKR), discovered in 1972. Ionospheric absorption makes AKR only observable from space. X-ray emissions, originating from the particles associated with auroras, have also been detected.Noise
Auroranoise
Noise is sound, chiefly unwanted, unintentional, or harmful sound considered unpleasant, loud, or disruptive to mental or hearing faculties. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrat ...
, similar to a crackling noise, begins about above Earth's surface and is caused by charged particles in an inversion layer of the atmosphere formed during a cold night. The charged particles discharge when particles from the Sun hit the inversion layer, creating the noise.
Abnormal types
STEVE
In 2016, more than fifty citizen science observations described what was to them an unknown type of aurora which they named " STEVE", for "Strong Thermal Emission Velocity Enhancement". STEVE is not an aurora but is caused by a wide ribbon of hot plasma at an altitude of , with a temperature of and flowing at a speed of (compared to outside the ribbon).Picket-fence aurora
The processes that cause STEVE are also associated with a picket-fence aurora, although the latter can be seen without STEVE. It is an aurora because it is caused by the precipitation of electrons in the atmosphere but it appears outside the auroral oval, closer to theequator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumferen ...
than typical auroras. When the picket-fence aurora appears with STEVE, it is below.
Dune aurora
First reported in 2020, and confirmed in 2021, the dune aurora phenomenon was discovered by Finnish citizen scientists. It consists of regularly spaced, parallel stripes of brighter emission in the green diffuse aurora which gives the impression of sand dunes. The phenomenon is believed to be caused by the modulation of atomic oxygen density by a large-scale atmospheric wave travelling horizontally in a waveguide through an inversion layer in the mesosphere in presence ofelectron precipitation Electron precipitation (also called energetic electron precipitation or EEP) is an atmospheric phenomenon that occurs when previously trapped electrons enter the Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere, thus creating communications interferences and ...
.
Horse-collar aurora
Horse-collar auroras (HCA) are auroral features in which the auroral ellipse shifts poleward during the dawn and dusk portions and the polar cap becomes teardrop-shaped. They form during periods when the interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) is permanently northward, when the IMF clock angle is small. Their formation is associated with the closure of the magnetic flux at the top of the dayside magnetosphere by the double lobe reconnection (DLR). There are approximately 8 HCA events per month, with no seasonal dependence, and that the IMF must be within 30 degrees of northwards.Conjugate auroras
Conjugate auroras are nearly exact mirror-image auroras found at conjugate points in the northern and southern hemispheres on the same geomagnetic field lines. These generally happen at the time of theequinox
A solar equinox is a moment in time when the Sun appears directly above the equator, rather than to its north or south. On the day of the equinox, the Sun appears to rise directly east and set directly west. This occurs twice each year, arou ...
es, when there is little difference in the orientation of the north and south geomagnetic poles to the Sun. Attempts were made to image conjugate auroras by aircraft from Alaska and New Zealand in 1967, 1968, 1970, and 1971, with some success.
Causes
A full understanding of the physical processes that lead to different types of auroras is still incomplete, but the basic cause involves the interaction of thesolar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the Stellar corona, corona. This Plasma (physics), plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy betwee ...
with Earth's magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior Dynamo ...
. The varying intensity of the solar wind produces effects of different magnitudes but includes one or more of the following physical scenarios.
# A quiescent solar wind flowing past Earth's magnetosphere steadily interacts with it and can inject solar wind particles directly onto the geomagnetic field lines that are 'open', as opposed to being 'closed' in the opposite hemisphere and provide diffusion through the bow shock. It can also cause particles already trapped in the radiation belts to precipitate into the atmosphere. Once particles are lost to the atmosphere from the radiation belts, under quiet conditions, new ones replace them only slowly, and the loss cone becomes depleted. In the magnetotail, however, particle trajectories seem constantly to reshuffle, probably when the particles cross the very weak magnetic field near the equator. As a result, the flow of electrons in that region is nearly the same in all directions ("isotropic") and assures a steady supply of leaking electrons. The leakage of electrons does not leave the tail positively charged, because each leaked electron lost to the atmosphere is replaced by a low-energy electron drawn upward from the ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays ...
. Such replacement of "hot" electrons by "cold" ones is in complete accord with the second law of thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law based on Universal (metaphysics), universal empirical observation concerning heat and Energy transformation, energy interconversions. A simple statement of the law is that heat always flows spont ...
. The complete process, which also generates an electric ring current around Earth, is uncertain.
# Geomagnetic disturbance from an enhanced solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the Stellar corona, corona. This Plasma (physics), plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy betwee ...
causes distortions of the magnetotail ("magnetic substorms"). These 'substorms' tend to occur after prolonged spells (on the order of hours) during which the interplanetary magnetic field has had an appreciable southward component. This leads to a higher rate of interconnection between its field lines and those of Earth. As a result, the solar wind moves magnetic flux (tubes of magnetic field lines, 'locked' together with their resident plasma) from the day side of Earth to the magnetotail, widening the obstacle it presents to the solar wind flow and constricting the tail on the night-side. Ultimately some tail plasma can separate (" magnetic reconnection"); some blobs (" plasmoids") are squeezed downstream and are carried away with the solar wind; others are squeezed toward Earth where their motion feeds strong outbursts of auroras, mainly around midnight ("unloading process"). A geomagnetic storm resulting from greater interaction adds many more particles to the plasma trapped around Earth, also producing enhancement of the "ring current". Occasionally the resulting modification of Earth's magnetic field can be so strong that it produces auroras visible at middle latitudes, on field lines much closer to the equator than those of the auroral zone.
#:  # Acceleration of auroral charged particles invariably accompanies a magnetospheric disturbance that causes an aurora. This mechanism, which is believed to predominantly arise from strong electric fields along the magnetic field or wave-particle interactions, raises the velocity of a particle in the direction of the guiding magnetic field. The pitch angle is thereby decreased and increases the chance of it being precipitated into the atmosphere. Both electromagnetic and electrostatic waves, produced at the time of greater geomagnetic disturbances, make a significant contribution to the energizing processes that sustain an aurora. Particle acceleration provides a complex intermediate process for transferring energy from the solar wind indirectly into the atmosphere.
# Acceleration of auroral charged particles invariably accompanies a magnetospheric disturbance that causes an aurora. This mechanism, which is believed to predominantly arise from strong electric fields along the magnetic field or wave-particle interactions, raises the velocity of a particle in the direction of the guiding magnetic field. The pitch angle is thereby decreased and increases the chance of it being precipitated into the atmosphere. Both electromagnetic and electrostatic waves, produced at the time of greater geomagnetic disturbances, make a significant contribution to the energizing processes that sustain an aurora. Particle acceleration provides a complex intermediate process for transferring energy from the solar wind indirectly into the atmosphere.
 The details of these phenomena are not fully understood. However, it is clear that the prime source of auroral particles is the solar wind feeding the magnetosphere, the reservoir containing the radiation zones and temporarily magnetically trapped particles confined by the geomagnetic field, coupled with particle acceleration processes.
The details of these phenomena are not fully understood. However, it is clear that the prime source of auroral particles is the solar wind feeding the magnetosphere, the reservoir containing the radiation zones and temporarily magnetically trapped particles confined by the geomagnetic field, coupled with particle acceleration processes.
Auroral particles
The immediate cause of the ionization and excitation of atmospheric constituents leading to auroral emissions was discovered in 1960, when a pioneering rocket flight from Fort Churchill in Canada revealed a flux of electrons entering the atmosphere from above. Since then an extensive collection of measurements has been acquired painstakingly and with steadily improving resolution since the 1960s by many research teams using rockets and satellites to traverse the auroral zone. The main findings have been that auroral arcs and other bright forms are due to electrons that have been accelerated during the final few 10,000 km or so of their plunge into the atmosphere. These electrons often, but not always, exhibit a peak in their energy distribution, and are preferentially aligned along the local direction of the magnetic field. Electrons are mainly responsible for diffuse and pulsating auroras have, in contrast, a smoothly falling energy distribution, and an angular (pitch-angle) distribution favouring directions perpendicular to the local magnetic field. Pulsations were discovered to originate at or close to the equatorial crossing point of auroral zone magnetic field lines. Protons are also associated with auroras, both discrete and diffuse.Atmosphere
Auroras result from emissions ofphoton
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can ...
s in Earth's upper atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
, above , from ionized nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
atoms regaining an electron, and oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
atoms and nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
-based molecules returning from an excited state
In quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Add ...
to the ground state. They are ionized or excited by the collision of particles precipitated into the atmosphere. Both incoming electrons and protons may be involved. Excitation energy is lost within the atmosphere by the emission of a photon, or by collision with another atom or molecule:
;Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
emissions: green or orange-red, depending on the amount of energy absorbed.
;Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
emissions:blue, purple, or red; blue and purple if the molecule regains an electron after it has been ionized, red if returning to ground state from an excited state.
Oxygen is unusual in terms of its return to ground state: it can take 0.7 seconds to emit the 557.7 nm green light and up to two minutes for the red 630.0 nm emission. Collisions with other atoms or molecules absorb the excitation energy and prevent emission; this process is called collisional quenching. Because the highest parts of the atmosphere contain a higher percentage of oxygen and lower particle densities, such collisions are rare enough to allow time for oxygen to emit red light. Collisions become more frequent progressing down into the atmosphere due to increasing density, so red emissions do not have time to happen, and eventually, even green light emissions are prevented.
The change in auroral colour with altitude is therefore explained—oxygen red is predominant at high altitudes, followed by oxygen green and nitrogen blue/purple/red, then finally other hues of nitrogen blue/purple/red where particle collisions prevent oxygen from emissions. Green is the most common colour. Then comes pink, a mixture of light green and red, followed by pure red, then yellow (a mixture of red and green), and finally, pure blue.
Precipitating protons generally produce optical emissions as incident hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
atoms after gaining electrons from the atmosphere. Proton auroras are usually observed at lower latitudes.
Ionosphere
Bright auroras are generally associated with Birkeland currents (Schield et al., 1969; Zmuda and Armstrong, 1973), which flow down into the ionosphere on one side of the pole and out on the other. In between, some of the current connects directly through the ionospheric E layer (125 km); the rest ("region 2") detours, leaving again through field lines closer to the equator and closing through the "partial ring current" carried by magnetically trapped plasma. The ionosphere is an ohmic conductor, so some consider that such currents require a driving voltage, which an, as yet unspecified, dynamo mechanism can supply. Electric field probes in orbit above the polar cap suggest voltages of the order of 40,000 volts, rising up to more than 200,000 volts during intense magnetic storms. In another interpretation, the currents are the direct result of electron acceleration into the atmosphere by wave/particle interactions. Ionospheric resistance has a complex nature and leads to a secondaryHall current
The Hall effect is the production of a voltage, potential difference (the Hall voltage) across an electrical conductor that is wikt:transverse, transverse to an electric current in the conductor and to an applied magnetic field wikt:perpendicul ...
flow. Due to physics, the magnetic disturbance on the ground due to the main current almost cancels out, so most of the observed effect of auroras is due to a secondary current, the auroral electrojet. An auroral electrojet index (measured in nanotesla) is regularly derived from ground data and serves as a general measure of auroral activity. Kristian Birkeland
Kristian Olaf Bernhard Birkeland (born 13 December 1867 – 15 June 1917) was a Norway, Norwegian space physics, space physicist, inventor, and professor of physics at the University of Oslo, Royal Fredriks University in Oslo. He is best remembe ...
deduced that the currents flowed in the east–west directions along the auroral arc, and such currents, flowing from the dayside toward (approximately) midnight were later named "auroral electrojets" (see also Birkeland currents). The ionosphere can contribute to the formation of auroral arcs via the feedback
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause and effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handle ...
instability under high ionospheric resistance conditions, observed at night time and in the dark Winter hemisphere.
Interaction of the solar wind with Earth
Earth is constantly immersed in thesolar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the Stellar corona, corona. This Plasma (physics), plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy betwee ...
, a flow of magnetized hot plasma (a gas of free electrons and positive ions) emitted by the Sun in all directions, a result of the two-million-degree temperature of the Sun's outermost layer, the corona. The solar wind reaches Earth with a velocity typically around 400 km/s, a density of around 5 ions/cm3, and a magnetic field intensity of around 2–5 nT (for comparison, Earth's surface field is typically 30,000–50,000 nT). During magnetic storms, in particular, flows can be several times faster; the interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) may also be much stronger. Joan Feynman
Joan Feynman (March 31, 1927 – July 21, 2020) was an American astrophysicist and space physicist. She made contributions to the study of solar wind particles and fields, sun-Earth relations, and magnetospheric physics. She was known for cre ...
deduced in the 1970s that the long-term averages of solar wind speed correlated with geomagnetic activity. Her work resulted from data collected by the Explorer 33
Explorer 33, also known as IMP-D and AIMP-1, is a spacecraft in the Explorer program launched by NASA on 1 July 1966 on a mission of scientific exploration. It was the fourth satellite launched as part of the Interplanetary Monitoring Platform ...
spacecraft.
The solar wind and magnetosphere consist of plasma (ionized gas), which conducts electricity. It is well known (since Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday (; 22 September 1791 – 25 August 1867) was an English chemist and physicist who contributed to the study of electrochemistry and electromagnetism. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic inducti ...
's work around 1830) that when an electrical conductor is placed within a magnetic field while relative motion occurs in a direction that the conductor cuts ''across'' (or is cut ''by''), rather than ''along'', the lines of the magnetic field, an electric current is induced within the conductor. The strength of the current depends on a) the rate of relative motion, b) the strength of the magnetic field, c) the number of conductors ganged together, and d) the distance between the conductor and the magnetic field, while the ''direction'' of flow is dependent upon the direction of relative motion. Dynamos make use of this basic process ("the dynamo effect"), any and all conductors, solid or otherwise are so affected, including plasmas and other fluids.
The IMF originates on the Sun, linked to the sunspot
Sunspots are temporary spots on the Sun's surface that are darker than the surrounding area. They are one of the most recognizable Solar phenomena and despite the fact that they are mostly visible in the solar photosphere they usually aff ...
s, and its field lines (lines of force) are dragged out by the solar wind. That alone would tend to line them up in the Sun-Earth direction, but the rotation of the Sun angles them at Earth by about 45 degrees forming a spiral in the ecliptic plane, known as the Parker spiral. The field lines passing Earth are therefore usually linked to those near the western edge ("limb") of the visible Sun at any time.
The solar wind and the magnetosphere, being two electrically conducting fluids in relative motion, should be able in principle to generate electric currents by dynamo action and impart energy from the flow of the solar wind. However, this process is hampered by the fact that plasmas conduct readily along magnetic field lines, but less readily perpendicular to them. Energy is more effectively transferred by the temporary magnetic connection between the field lines of the solar wind and those of the magnetosphere. Unsurprisingly this process is known as magnetic reconnection. As already mentioned, it happens most readily when the interplanetary field is directed southward, in a similar direction to the geomagnetic field in the inner regions of both the north magnetic pole
The north magnetic pole, also known as the magnetic north pole, is a point on the surface of Earth's Northern Hemisphere at which the Earth's magnetic field, planet's magnetic field points vertically downward (in other words, if a magnetic comp ...
and south magnetic pole.
Auroras are more frequent and brighter during the intense phase of the solar cycle when coronal mass ejections increase the intensity of the solar wind.
Magnetosphere
magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior Dynamo ...
is shaped by the impact of the solar wind on Earth's magnetic field. This forms an obstacle to the flow, diverting it, at an average distance of about 70,000 km (11 Earth radii or Re), producing a bow shock 12,000 km to 15,000 km (1.9 to 2.4 Re) further upstream. The width of the magnetosphere abreast of Earth is typically 190,000 km (30 Re), and on the night side, a long "magnetotail" of stretched field lines extends to great distances (> 200 Re).
The high-latitude magnetosphere is filled with plasma as the solar wind passes Earth. The flow of plasma into the magnetosphere increases with additional turbulence, density, and speed in the solar wind. This flow is favoured by a southward component of the IMF, which can then directly connect to the high latitude geomagnetic field lines. The flow pattern of magnetospheric plasma is mainly from the magnetotail toward Earth, around Earth and back into the solar wind through the magnetopause
The magnetopause is the abrupt boundary between a magnetosphere and the surrounding Plasma (physics), plasma. For planetary science, the magnetopause is the boundary between the planet's magnetic field and the solar wind. The location of the ma ...
on the day-side. In addition to moving perpendicular to Earth's magnetic field, some magnetospheric plasma travels down along Earth's magnetic field lines, gains additional energy and loses it to the atmosphere in the auroral zones. The cusps of the magnetosphere, separating geomagnetic field lines that close through Earth from those that close remotely allow a small amount of solar wind to directly reach the top of the atmosphere, producing an auroral glow.
On 26 February 2008, THEMIS probes were able to determine, for the first time, the triggering event for the onset of magnetospheric substorms. Two of the five probes, positioned approximately one-third the distance to the Moon, measured events suggesting a magnetic reconnection event 96 seconds prior to auroral intensification.
Geomagnetic storm
A geomagnetic storm, also known as a magnetic storm, is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere that is driven by interactions between the magnetosphere and large-scale transient Plasma (physics), plasma and magnetic field structur ...
s that ignite auroras may occur more often during the months around the equinox
A solar equinox is a moment in time when the Sun appears directly above the equator, rather than to its north or south. On the day of the equinox, the Sun appears to rise directly east and set directly west. This occurs twice each year, arou ...
es. It is not well understood, but geomagnetic storms may vary with Earth's seasons. Two factors to consider are the tilt of both the solar and Earth's axis to the ecliptic plane. As Earth orbits throughout the year, it experiences an interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) from different latitudes of the Sun, which is tilted at 8 degrees. Similarly, the 23-degree tilt of Earth's axis about which the geomagnetic pole rotates with a diurnal variation changes the daily average angle that the geomagnetic field presents to the incident IMF throughout the year. These factors combined can lead to minor cyclical changes in the detailed way that the IMF links to the magnetosphere. In turn, this affects which energy from the solar wind can reach Earth's inner magnetosphere and thereby enhance auroras. Recent evidence in 2021 has shown that individual separate substorms may in fact be correlated networked communities.
Auroral particle acceleration
Just as there are many types of aurora, there are many different mechanisms that accelerate auroral particles into the atmosphere. Electron aurora in Earth's auroral zone (i.e. commonly visible aurora) can be split into two main categories with different immediate causes: diffuse and discrete aurora. Diffuse aurora appear relatively structureless to an observer on the ground, with indistinct edges and amorphous forms. Discrete aurora are structured into distinct features with well-defined edges such as arcs, rays, and coronas; they also tend to be much brighter than diffuse aurora. In both cases, the electrons that eventually cause the aurora start out as electrons trapped by the magnetic field in Earth'smagnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior Dynamo ...
. These trapped particles bounce back and forth along magnetic field lines and are prevented from hitting the atmosphere by the magnetic mirror formed by the increasing magnetic field strength closer to Earth. The magnetic mirror's ability to trap a particle depends on the particle's pitch angle: the angle between its direction of motion and the local magnetic field. An aurora is created by processes that decrease the pitch angle of many individual electrons, freeing them from the magnetic trap and causing them to hit the atmosphere.
In the case of diffuse auroras, the electron pitch angles are altered by their interaction with various plasma waves. Each interaction is essentially wave-particle scattering
In physics, scattering is a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities (including particles and radiat ...
; the electron energy after interacting with the wave is similar to its energy before interaction, but the direction of motion is altered. If the final direction of motion after scattering is close to the field line (specifically, if it falls within the loss cone) then the electron will hit the atmosphere. Diffuse auroras are caused by the collective effect of many such scattered electrons hitting the atmosphere. The process is mediated by the plasma waves, which become stronger during periods of high geomagnetic activity, leading to increased diffuse aurora at those times.
In the case of discrete auroras, the trapped electrons are accelerated toward Earth by electric fields that form at an altitude of about 4000–12000 km in the "auroral acceleration region". The electric fields point away from Earth (i.e. upward) along the magnetic field line. Electrons moving downward through these fields gain a substantial amount of energy (on the order of a few keV) in the direction along the magnetic field line toward Earth. This field-aligned acceleration decreases the pitch angle for all of the electrons passing through the region, causing many of them to hit the upper atmosphere. In contrast to the scattering process leading to diffuse auroras, the electric field increases the kinetic energy of all of the electrons transiting downward through the acceleration region by the same amount. This accelerates electrons starting from the magnetosphere with initially low energies (tens of eV or less) to energies required to create an aurora (100s of eV or greater), allowing that large source of particles to contribute to creating auroral light.
The accelerated electrons carry an electric current along the magnetic field lines (a Birkeland current). Since the electric field points in the same direction as the current, there is a net conversion of electromagnetic energy into particle energy in the auroral acceleration region (an electric load). The energy to power this load is eventually supplied by the magnetized solar wind flowing around the obstacle of Earth's magnetic field, although exactly how that power flows through the magnetosphere is still an active area of research. While the energy to power the aurora is ultimately derived from the solar wind, the electrons themselves do not travel directly from the solar wind into Earth's auroral zone; magnetic field lines from these regions do not connect to the solar wind, so there is no direct access for solar wind electrons.
Some auroral features are also created by electrons accelerated by dispersive Alfvén waves. At small wavelengths, transverse to the background magnetic field (comparable to the electron inertial length or ion gyroradius), Alfvén waves develop a significant electric field parallel to the background magnetic field. This electric field can accelerate electrons to keV energies, sufficient to produce auroral arcs. If the electrons have a speed close to that of the wave's phase velocity, they are accelerated in a manner analogous to a surfer catching an ocean wave. This constantly changing wave electric field can accelerate electrons along the field line, causing some of them to hit the atmosphere. Electrons accelerated by this mechanism tend to have a broad energy spectrum, in contrast to the sharply peaked energy spectrum typical of electrons accelerated by quasi-static electric fields.
In addition to the discrete and diffuse electron aurora, proton aurora is caused when magnetospheric protons collide with the upper atmosphere. The proton gains an electron in the interaction, and the resulting neutral hydrogen atom emits photons. The resulting light is too dim to be seen with the naked eye. Other aurora not covered by the above discussion include transpolar arcs (formed poleward of the auroral zone), cusp aurora (formed in two small high-latitude areas on the dayside), and some non-terrestrial auroras.
Historically significant events
The discovery of a 1770 Japanesediary
A diary is a written or audiovisual memorable record, with discrete entries arranged by date reporting on what has happened over the course of a day or other period. Diaries have traditionally been handwritten but are now also often digita ...
in 2017 depicting auroras above the ancient Japanese capital of Kyoto
Kyoto ( or ; Japanese language, Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in the Kansai region of Japan's largest and most populous island of Honshu. , the city had a population of 1.46 million, making it t ...
suggested that the storm may have been 7% larger than the Carrington event, which affected telegraph networks.
The auroras that resulted from the Carrington event on both 28 August and 2 September 1859, are thought to be the most spectacular in recent history. In a paper to the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
on 21 November 1861, Balfour Stewart described both auroral events as documented by a self-recording magnetograph at the Kew Observatory
The King's Observatory (called for many years the Kew Observatory) is a Grade I listed building in Richmond, London. Now a private dwelling, it formerly housed an astronomical observatory, astronomical and Terrestrial magnetism, terrestrial mag ...
and established the connection between the 2 September 1859 auroral storm and the Carrington–Hodgson flare event when he observed that "It is not impossible to suppose that in this case our luminary was taken ''in the act''." The second auroral event, which occurred on 2 September 1859, was a result of the (unseen) coronal mass ejection associated with the exceptionally intense Carrington–Hodgson white light solar flare on 1 September 1859. This event produced auroras so widespread and extraordinarily bright that they were seen and reported in published scientific measurements, ship logs, and newspapers throughout the United States, Europe, Japan, and Australia. It was reported by ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
'' that in Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
on Friday 2 September 1859, the aurora was "so brilliant that at about one o'clock ordinary print could be read by the light". One o'clock EST time on Friday 2 September would have been 6:00 GMT; the self-recording magnetograph at the Kew Observatory
The King's Observatory (called for many years the Kew Observatory) is a Grade I listed building in Richmond, London. Now a private dwelling, it formerly housed an astronomical observatory, astronomical and Terrestrial magnetism, terrestrial mag ...
was recording the geomagnetic storm
A geomagnetic storm, also known as a magnetic storm, is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere that is driven by interactions between the magnetosphere and large-scale transient Plasma (physics), plasma and magnetic field structur ...
, which was then one hour old, at its full intensity. Between 1859 and 1862, Elias Loomis
Elias Loomis (August 7, 1811 – August 15, 1889) was an American mathematician. He served as a professor of mathematics and natural philosophy at Case Western Reserve University, Western Reserve College (now Case Western Reserve University), the ...
published a series of nine papers on the Great Auroral Exhibition of 1859 in the '' American Journal of Science'' where he collected worldwide reports of the auroral event.See:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
That aurora is thought to have been produced by one of the most intense coronal mass ejection
A coronal mass ejection (CME) is a significant ejection of plasma mass from the Sun's corona into the heliosphere. CMEs are often associated with solar flares and other forms of solar activity, but a broadly accepted theoretical understandin ...
s in history. It is also notable for the fact that it is the first time that the phenomena of auroral activity and electricity were unambiguously linked. This insight was made possible not only due to scientific magnetometer measurements of the era but also as a result of a significant portion of the of telegraph
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas ...
lines then in service being significantly disrupted for many hours throughout the storm. Some telegraph lines, however, seem to have been of the appropriate length and orientation to produce a sufficient geomagnetically induced current from the electromagnetic field
An electromagnetic field (also EM field) is a physical field, varying in space and time, that represents the electric and magnetic influences generated by and acting upon electric charges. The field at any point in space and time can be regarde ...
to allow for continued communication with the telegraph operator power supplies switched off. The following conversation occurred between two operators of the American Telegraph Line between Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
and Portland, Maine
Portland is the List of municipalities in Maine, most populous city in the U.S. state of Maine and the county seat, seat of Cumberland County, Maine, Cumberland County. Portland's population was 68,408 at the 2020 census. The Portland metropolit ...
, on the night of 2 September 1859 and reported in the ''Boston Traveller'':
The conversation was carried on for around two hours using no battery power at all and working solely with the current induced by the aurora, and it was said that this was the first time on record that more than a word or two was transmitted in such manner. Such events led to the general conclusion that
In May 2024, a series of solar storms caused the aurora borealis to be observed from as far south as Ferdows, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
.
Historical views and folklore
The earliest datable record of an aurora was recorded in the ''Bamboo Annals
The ''Bamboo Annals'' ( zh, t=竹書紀年, p=Zhúshū Jìnián), also known as the ''Ji Tomb Annals'' ( zh, t=汲冢紀年, p=Jí Zhǒng Jìnián), is a chronicle of ancient China.
It begins in the earliest legendary time (the age of the Yellow E ...
'', a historical chronicle of the history of ancient China, in 977 or 957 BC.
An aurora was described by the Greek explorer
Exploration is the process of exploring, an activity which has some Expectation (epistemic), expectation of Discovery (observation), discovery. Organised exploration is largely a human activity, but exploratory activity is common to most organis ...
Pytheas in the 4th century BC. Seneca wrote about auroras in the first book of his '' Naturales Quaestiones'', classifying them, for instance, as ('barrel-like'); ('chasm'); ('bearded'); ('like cypress trees'); and describing their manifold colours. He wrote about whether they were above or below the clouds and recalled that under Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus ( ; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was Roman emperor from AD 14 until 37. He succeeded his stepfather Augustus, the first Roman emperor. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC to Roman politician Tiberius Cl ...
, an aurora formed above the port city of Ostia that was so intense and red that a cohort of the army, stationed nearby for fire duty, galloped to the rescue. It has been suggested that Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
depicted the aurora borealis in his ''Natural History
Natural history is a domain of inquiry involving organisms, including animals, fungi, and plants, in their natural environment, leaning more towards observational than experimental methods of study. A person who studies natural history is cal ...
'' when he refers to , , "falling red flames", and "daylight in the night".
The earliest depiction of the aurora may have been in Cro-Magnon cave paintings of northern Spain dating to 30,000 BC.
The oldest known written record of the aurora was in a Chinese legend written around 2600 BC. On autumn around 2000 BC.
In Japanese folklore
Japanese folklore encompasses the informally learned folk traditions of Japan and the Japanese people as expressed in its oral traditions, Tradition, customs, and material culture.
In Japanese, the term is used to describe folklore. The Folklor ...
, pheasants were considered messengers from heaven. However, researchers from Japan's Graduate University for Advanced Studies and National Institute of Polar Research claimed in March 2020 that red pheasant tails witnessed across the night sky over Japan in 620 A.D., might be a red aurora produced during a magnetic storm.
 In the traditions of
In the traditions of Aboriginal Australians
Aboriginal Australians are the various indigenous peoples of the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland and many of its islands, excluding the ethnically distinct people of the Torres Strait Islands.
Humans first migrated to Australia (co ...
, the Aurora Australis is commonly associated with fire. For example, the Gunditjmara people
The Gunditjmara or Gunditjamara, also known as Dhauwurd Wurrung, are an Aboriginal Australian, Aboriginal people of southwestern Victoria (Australia), Victoria in Australia. They are the traditional owners, Traditional Owners of the areas now enc ...
of western Victoria called auroras ('ashes'), while the Gunai people
The Kurnai () people Aboriginal Australian nation of south-east Australia. They are the Traditional owners, Traditional Custodians of most of present-day Gippsland and much of the southern slopes of the Victorian Alps. The Kurnai nation is comp ...
of eastern Victoria perceived auroras as bushfires
A wildfire, forest fire, or a bushfire is an unplanned and uncontrolled fire in an area of Combustibility and flammability, combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identified as a ...
in the spirit world. The Dieri people of South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories by area, which in ...
say that an auroral display is , an evil spirit creating a large fire. Similarly, the Ngarrindjeri people of South Australia refer to auroras seen over Kangaroo Island
Kangaroo Island (, ) is Australia's third-largest island, after Tasmania and Melville Island, Northern Territory, Melville Island. It lies in the state of South Australia, southwest of Adelaide. Its closest point to the mainland is Snapper Poi ...
as the campfires of spirits in the 'Land of the Dead'. The Dieri and Ngarrindjeri communities in southwest Queensland
Queensland ( , commonly abbreviated as Qld) is a States and territories of Australia, state in northeastern Australia, and is the second-largest and third-most populous state in Australia. It is bordered by the Northern Territory, South Austr ...
believe the auroras to be the fires of the ''Oola Pikka'', ghostly spirits who spoke to the people through auroras. Sacred law forbade anyone except male elders from watching or interpreting the messages of ancestors they believed were transmitted through an aurora.
Among the Māori people
Māori () are the Indigenous peoples of Oceania, indigenous Polynesians, Polynesian people of mainland New Zealand. Māori originated with settlers from East Polynesia, who arrived in New Zealand in several waves of Māori migration canoes, c ...
of New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
, aurora australis or ("great torches in the sky") were lit by ancestors who sailed south to a "land of ice" (or their descendants); these people were said to be Ui-te-Rangiora's expedition party who had reached the Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the world ocean, generally taken to be south of 60th parallel south, 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. With a size of , it is the seco ...
. around the 7th century.
Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenlan ...
, and he gives three possible explanations: that the ocean was surrounded by vast fires; that the sun flares could reach around the world to its night side; or that glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
s could store energy so that they eventually became fluorescent.
Walter William Bryant wrote in his book ''Kepler'' (1920) that Tycho Brahe
Tycho Brahe ( ; ; born Tyge Ottesen Brahe, ; 14 December 154624 October 1601), generally called Tycho for short, was a Danish astronomer of the Renaissance, known for his comprehensive and unprecedentedly accurate astronomical observations. He ...
"seems to have been something of a homeopathist, for he recommends sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms ...
to cure infectious diseases 'brought on by the sulfurous vapours of the Aurora Borealis.
In 1778, Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin (April 17, 1790) was an American polymath: a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher and Political philosophy, political philosopher.#britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the m ...
theorized in his paper ''Aurora Borealis, Suppositions and Conjectures towards forming a Hypothesis for its Explanation'' that an aurora was caused by a concentration of electrical charge in the polar regions intensified by the snow and moisture in the air:
Observations of the rhythmic movement of compass needles due to the influence of an aurora were confirmed in the Swedish city of Uppsala
Uppsala ( ; ; archaically spelled ''Upsala'') is the capital of Uppsala County and the List of urban areas in Sweden by population, fourth-largest city in Sweden, after Stockholm, Gothenburg, and Malmö. It had 177,074 inhabitants in 2019.
Loc ...
by Anders Celsius
Anders Celsius (; 27 November 170125 April 1744) was a Swedes, Swedish astronomer, physicist and mathematician. He was professor of astronomy at Uppsala University from 1730 to 1744, but traveled from 1732 to 1735 visiting notable observatories ...
and Olof Hiorter. In 1741, Hiorter was able to link large magnetic fluctuation to the observation of an aurora overhead. This evidence helped to support their theory that 'magnetic storms' are responsible for such compass fluctuations.
 A variety of Native American myths surround the spectacle. The European explorer Samuel Hearne travelled with Chipewyan Dene in 1771 and recorded their views on the ('caribou'). According to Hearne, the Dene people saw the resemblance between an aurora and the sparks produced when caribou fur is stroked. They believed that the lights were the spirits of their departed friends dancing in the sky, and when they shone brightly it meant that their deceased friends were very happy.
During the night after the
A variety of Native American myths surround the spectacle. The European explorer Samuel Hearne travelled with Chipewyan Dene in 1771 and recorded their views on the ('caribou'). According to Hearne, the Dene people saw the resemblance between an aurora and the sparks produced when caribou fur is stroked. They believed that the lights were the spirits of their departed friends dancing in the sky, and when they shone brightly it meant that their deceased friends were very happy.
During the night after the Battle of Fredericksburg
The Battle of Fredericksburg was fought December 11–15, 1862, in and around Fredericksburg, Virginia, in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. The combat between the Union Army, Union Army of the Potomac commanded by Major general ( ...
, an aurora was seen from the battlefield. The Confederate Army
The Confederate States Army (CSA), also called the Confederate army or the Southern army, was the military land force of the Confederate States of America (commonly referred to as the Confederacy) during the American Civil War (1861–1865), fi ...
took this as a sign that God was on their side, as the lights were rarely seen so far south. The painting '' Aurora Borealis'' by Frederic Edwin Church
Frederic Edwin Church (May 4, 1826 – April 7, 1900) was an American landscape painting, landscape painter born in Hartford, Connecticut. He was a central figure in the Hudson River School of American landscape painters, best known for paintin ...
is widely interpreted to represent the conflict of the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
.
A mid-19th-century British source says auroras were a rare occurrence before the 18th century. It quotes Halley as saying that before the aurora of 1716, no such phenomenon had been recorded for more than 80 years, and none of any consequence since 1574. It says no appearance is recorded in the ''Transactions of the French Academy of Sciences'' between 1666 and 1716; and that one aurora recorded in ''Berlin Miscellany'' for 1797 was called a very rare event. One observed in 1723 at Bologna
Bologna ( , , ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Emilia-Romagna region in northern Italy. It is the List of cities in Italy, seventh most populous city in Italy, with about 400,000 inhabitants and 150 different nationalities. Its M ...
was stated to be the first ever seen there. Celsius
The degree Celsius is the unit of temperature on the Celsius temperature scale "Celsius temperature scale, also called centigrade temperature scale, scale based on 0 ° for the melting point of water and 100 ° for the boiling point ...
(1733) states the oldest residents of Uppsala
Uppsala ( ; ; archaically spelled ''Upsala'') is the capital of Uppsala County and the List of urban areas in Sweden by population, fourth-largest city in Sweden, after Stockholm, Gothenburg, and Malmö. It had 177,074 inhabitants in 2019.
Loc ...
thought the phenomenon a great rarity before 1716. The period between approximately 1645 and 1715 corresponds to the Maunder minimum in sunspot activity.
In Robert W. Service's satirical poem " The Ballad of the Northern Lights" (1908), a Yukon prospector discovers that the aurora is the glow from a radium mine. He stakes his claim, then goes to town looking for investors.
In the early 1900s, the Norwegian scientist Kristian Birkeland
Kristian Olaf Bernhard Birkeland (born 13 December 1867 – 15 June 1917) was a Norway, Norwegian space physics, space physicist, inventor, and professor of physics at the University of Oslo, Royal Fredriks University in Oslo. He is best remembe ...
developed a theory foundational to the current understanding of geomagnetism and polar auroras.
In Sami
Acronyms
* SAMI, ''Synchronized Accessible Media Interchange'', a closed-captioning format developed by Microsoft
* Saudi Arabian Military Industries, a government-owned defence company
* South African Malaria Initiative, a virtual expertise ne ...
mythology, the northern lights are caused by the deceased who bled to death cutting themselves, their blood spilling on the sky. Many aboriginal peoples of northern Eurasia and North America share similar beliefs of northern lights being the blood of the deceased, some believing they are caused by dead warriors' blood spraying on the sky as they engage in playing games, riding horses, or having fun in some other way.
Extraterrestrial auroras
 Both
Both Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
and Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant, with an average radius of about 9 times that of Earth. It has an eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 tim ...
have magnetic fields that are stronger than Earth's (Jupiter's equatorial field strength is 4.3 gauss
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (; ; ; 30 April 177723 February 1855) was a German mathematician, astronomer, Geodesy, geodesist, and physicist, who contributed to many fields in mathematics and science. He was director of the Göttingen Observat ...
, compared to 0.3 gauss for Earth), and both have extensive radiation belts. Auroras have been observed on both gas planets, most clearly using the Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the Orbiting Solar Observatory, first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most ...
, and the ''Cassini'' and ''Galileo'' spacecraft, as well as on Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It is a gaseous cyan-coloured ice giant. Most of the planet is made of water, ammonia, and methane in a Supercritical fluid, supercritical phase of matter, which astronomy calls "ice" or Volatile ( ...
and Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun. It is the List of Solar System objects by size, fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 t ...
.
The auroras on Saturn seem, like Earth's, to be powered by the solar wind. However, Jupiter's auroras are more complex. Jupiter's main auroral oval is associated with the plasma produced by the volcanic moon Io, and the transport of this plasma within the planet's magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior Dynamo ...
. An uncertain fraction of Jupiter's auroras are powered by the solar wind. In addition, the moons, especially Io, are also powerful sources of aurora. These arise from electric currents along field lines ("field aligned currents"), generated by a dynamo mechanism due to the relative motion between the rotating planet and the moving moon. Io, which has active volcanism and an ionosphere, is a particularly strong source, and its currents also generate radio emissions, which have been studied since 1955. Using the Hubble Space Telescope, auroras over Io, Europa, and Ganymede have all been observed.
Auroras have also been observed on Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
and Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
. Venus has no magnetic field so Venusian auroras appear as bright and diffuse patches of varying shape and intensity, sometimes distributed over the full disc of the planet. A Venusian aurora originates when electrons from the solar wind collide with the night-side atmosphere.
An aurora was detected on Mars, on 14 August 2004, by the SPICAM instrument aboard ''Mars Express
''Mars Express'' is a space exploration mission by the European Space Agency, European Space Agency (ESA) exploring the planet Mars and its moons since 2003, and the first planetary mission attempted by ESA.
''Mars Express'' consisted of two ...
''. The aurora was located at Terra Cimmeria, in the region of 177° east, 52° south. The total size of the emission region was about 30 km across, and possibly about 8 km high. By analysing a map of crustal magnetic anomalies compiled with data from the Mars Global Surveyor, scientists observed that the region of the emissions corresponded to an area where the strongest magnetic field is localized. This correlation indicated that the origin of the light emission was a flux of electrons moving along the crust magnetic lines and exciting the upper atmosphere of Mars.
Between 2014 and 2016, cometary auroras were observed on comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko by multiple instruments on the Rosetta spacecraft. The auroras were observed at far-ultraviolet wavelengths. Coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to Nociception, respond normally to Pain, painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal Circadian rhythm, sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate ...
observations revealed atomic emissions of hydrogen and oxygen caused by the photodissociation (not photoionization, like in terrestrial auroras) of water molecules in the comet's coma. The interaction of accelerated electrons from the solar wind with gas particles in the coma is responsible for the aurora. Since comet 67P has no magnetic field, the aurora is diffusely spread around the comet.
Exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first confirmed detection of an exoplanet was in 1992 around a pulsar, and the first detection around a main-sequence star was in 1995. A different planet, first det ...
s, such as hot Jupiter
Hot Jupiters (sometimes called hot Saturns) are a class of gas giant exoplanets that are inferred to be physically similar to Jupiter (i.e. Jupiter analogue, Jupiter analogues) but that have very short orbital periods (). The close proximity to t ...
s, have been suggested to experience ionization in their upper atmospheres and generate an aurora modified by weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloud cover, cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmo ...
in their turbulent troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth. It contains 80% of the total mass of the Atmosphere, planetary atmosphere and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the ...
s. However, there is no current detection of an exoplanet aurora.
The first ever extra-solar auroras were discovered in July 2015 over the brown dwarf
Brown dwarfs are substellar objects that have more mass than the biggest gas giant planets, but less than the least massive main sequence, main-sequence stars. Their mass is approximately 13 to 80 Jupiter mass, times that of Jupiter ()not big en ...
star LSR J1835+3259. The mainly red aurora was found to be a million times brighter than the northern lights, a result of the charged particles interacting with hydrogen in the atmosphere. It has been speculated that stellar winds may be stripping off material from the surface of the brown dwarf to produce their own electrons. Another possible explanation for the auroras is that an as-yet-undetected body around the dwarf star is throwing off material, as is the case with Jupiter and its moon Io.
See also
*Airglow
Airglow is a faint emission of light by a planetary atmosphere. In the case of Earth's atmosphere, this optical phenomenon causes the night sky never to be completely dark, even after the effects of starlight and diffuse sky radiation, diffuse ...
* Aurora (heraldry)
* Heliophysics
Heliophysics (from the prefix "wikt:helio-, helio", from Attic Greek ''hḗlios'', meaning Sun, and the noun "physics": the science of matter and energy and their interactions) is the physics of the Sun and its connection with the Solar System. ...
* List of solar storms
Solar storms of different types are caused by disturbances on the Sun, most often from coronal mass ejections (CMEs) and solar flares from active regions, or, less often, from coronal holes. Minor to active solar storms (i.e. storming restrict ...
* Paschen's law
* Space tornado
* Space weather
Explanatory notes
References
Further reading
* * These two both include detailed descriptions of historical observations and descriptions. * * * * *Alt URL
* * * * *
External links
*Current global map showing the probability of visible aurora
Aurora – Forecasting
(archived 24 November 2016)
Official MET aurora forecasting in Iceland
Aurora Borealis – Predicting
– Online Converter – ''Northern Lights'' Latitude
Aurora Service Europe
– Aurora forecasts for Europe (archived 11 March 2019)
Live Northern Lights webstream
World's Best Aurora
– The Northwest Territories is the world's Northern Lights mecca.
Multimedia
Amazing time-lapse video of Aurora Borealis
– Shot in Iceland over the winter of 2013/2014
Popular video of Aurora Borealis
– Taken in Norway in 2011
Aurora Photo Gallery
– Views taken 2009–2011 (archived 4 October 2011)
– "Full-Sky Aurora" over Eastern
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
. December 2011
Videos and Photos – Auroras at Night
(archived 2 September 2010)
Video (47:40)
– ''Northern Lights'' – Documentary
Video (5:00)
– Northern lights video in real time
Video (01:42)
– ''Northern Light – Story of
Geomagnetic Storm
A geomagnetic storm, also known as a magnetic storm, is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere that is driven by interactions between the magnetosphere and large-scale transient Plasma (physics), plasma and magnetic field structur ...
'' (Terschelling
Terschelling (; ; Terschelling dialect: ''Schylge'') is a Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality and an island in the northern Netherlands, one of the West Frisian Islands. It is situated between the islands of Vlieland and Ameland.
...
Island – 6/7 April 2000) (archived 17 August 2011)
Video (1:55)
(time-lapse) − Auroras – Ground-Level View from
Finnish Lapland
Lapland is the largest and northernmost Regions of Finland, region of Finland. The 21 municipalities in the region cooperate in a Regional Council. Lapland borders the Finnish region of North Ostrobothnia in the south. It also borders the Gul ...
2011
Video (2:43)
(time-lapse) − Auroras – Ground-Level View from
Tromsø
Tromsø is a List of towns and cities in Norway, city in Tromsø Municipality in Troms county, Norway. The city is the administrative centre of the municipality as well as the administrative centre of Troms county. The city is located on the is ...
, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
, 24 November 2010
Video (0:45)
ISS Timelapse: Aurora Australis {{Authority control Terrestrial plasmas Space plasmas Polar regions of the Earth Atmospheric optical phenomena Earth phenomena Electrical phenomena Light sources Planetary science Sources of electromagnetic interference Articles containing video clips Space weather Geomagnetism