Attic Base on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

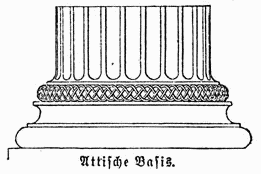 Attic base is the term given in
Attic base is the term given in
 Attic base is the term given in
Attic base is the term given in architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and construction, constructi ...
to the base of Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
Ionic order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic classical order, orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric order, Doric and the Corinthian order, Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan order, Tuscan (a plainer Doric) ...
columns, consisting of an upper and lower torus
In geometry, a torus (: tori or toruses) is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a circle in three-dimensional space one full revolution about an axis that is coplanarity, coplanar with the circle. The main types of toruses inclu ...
, separated by a ''scotia'' (hollow concave molding) and fillet
Fillet may refer to:
*Annulet (architecture), part of a column capital, also called a fillet
*Fillet (aircraft), a fairing smoothing the airflow at a joint between two components
*Fillet (clothing), a headband
*Fillet (heraldry), diminutive of the ...
s.
It was the favorite of the Romans, and was also employed by them for columns of the Corinthian and Composite order
The Composite order is a mixed order, combining the volutes of the Ionic order capital with the acanthus leaves of the Corinthian order.Henig, Martin (ed.), ''A Handbook of Roman Art'', p. 50, Phaidon, 1983, In many versions the composite o ...
s. The style can be seen in Byzantine architecture
Byzantine architecture is the architecture of the Byzantine Empire, or Eastern Roman Empire, usually dated from 330 AD, when Constantine the Great established a new Roman capital in Byzantium, which became Constantinople, until the Fall of Cons ...
as well; in the Romanesque period a great number of antique Roman columns were salvaged and reused in the interiors and on the porticos of churches, often incorporating the Attic base.
References
Columns and entablature {{architecturalelement-stub