Astures on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Astures or Asturs, also named Astyrs, were the
The Astures or Asturs, also named Astyrs, were the
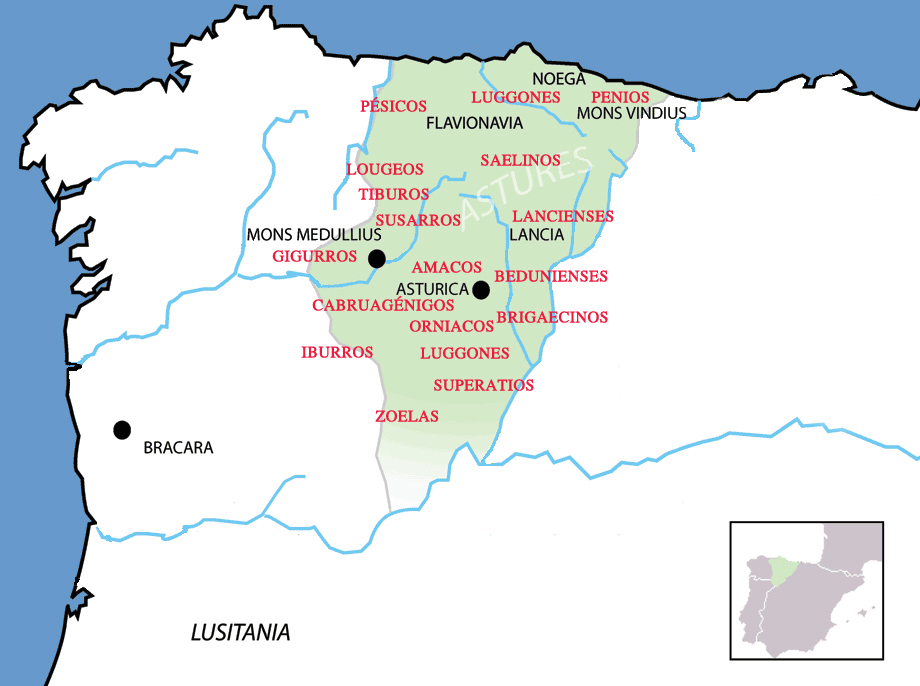 The Asturian homeland encompassed the modern autonomous community of
The Asturian homeland encompassed the modern autonomous community of
 At a later date, in the beginning of the
At a later date, in the beginning of the
Detailed map of the Pre-Roman Peoples of Iberia (around 200 BCE)
*http://www.celtiberia.net {{Pre-Roman peoples in Iberia History of Asturias Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula Celtic tribes of the Iberian Peninsula Ancient peoples of Spain Tribes conquered by Rome
Hispano-Celtic
Hispano-Celtic is a term for all forms of Celtic spoken in the Iberian Peninsula before the arrival of the Romans (c. 218 BC, during the Second Punic War). In particular, it includes:
* A northeastern inland language attested at a relati ...
inhabitants of the northwest area of Hispania
Hispania was the Ancient Rome, Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two Roman province, provinces: Hispania Citerior and Hispania Ulterior. During the Principate, Hispania Ulterior was divide ...
that now comprises almost the entire modern autonomous community
The autonomous communities () are the first-level administrative divisions of Spain, created in accordance with the Spanish Constitution of 1978, with the aim of guaranteeing limited autonomy to the nationalities and regions that make up Sp ...
of the Principality of Asturias
Asturias (; ; ) officially the Principality of Asturias, is an autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensive with the provinces of Spain, province of Asturias and contains some of the territory t ...
, the modern province of León, and the northern part of the modern province of Zamora (all in Spain), and eastern Trás os Montes in Portugal. They were a horse-riding highland cattle-raising people who lived in circular huts of stone drywall construction. The Albiones were a major tribe from western Asturias
Asturias (; ; ) officially the Principality of Asturias, is an autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensive with the provinces of Spain, province of Asturias and contains some of the territory t ...
. Isidore of Seville
Isidore of Seville (; 4 April 636) was a Spania, Hispano-Roman scholar, theologian and Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Seville, archbishop of Seville. He is widely regarded, in the words of the 19th-century historian Charles Forbes René de Montal ...
gave an etymology as coming from a ''river Astura'', identified by David Magie as the Órbigo River in the plain of León, and by others as the modern Esla River.
Location
 The Asturian homeland encompassed the modern autonomous community of
The Asturian homeland encompassed the modern autonomous community of Asturias
Asturias (; ; ) officially the Principality of Asturias, is an autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensive with the provinces of Spain, province of Asturias and contains some of the territory t ...
and the León, eastern Lugo
Lugo (, ) is a city in northwestern Spain in the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Galicia (Spain), Galicia. It is the capital of the Lugo (province), province of Lugo. The municipality had a population of 100,060 in 2024, ...
, Orense, and northern Zamora provinces, along with the northeastern tip of the Portuguese region of Trás-os-Montes. Here they held the towns of ''Lancia'' ( Villasabariego – León), ''Asturica'' ( Astorga – León), ''Mons Medullius'' ( Las Medulas? – León), ''Bergidum'' ( Cacabelos, near Villafranca del Bierzo – León), ''Bedunia'' ( Castro de Cebrones – León), ''Aliga'' ( Alixa? – León), ''Curunda'' ( Castro de Avelãs, Trás-os-Montes), ''Lucus Asturum'' ( Lugo de Llanera – Asturias), ''Brigaetium'' ( Benavente – Zamora), and ''Nemetobriga'' ( A Pobra de Trives – Ourense), which was the religious center.
Origins
The Astures may have been part of the early Hallstatt expansion that left the Bavarian-Bohemian homeland and migrated into Gaul, some continuing over the mountains into Spain and Portugal. By the 6th century BC, they occupied castros (hillforts), such as Coanna and Mohias near Navia on the coast of the Bay of Biscay. From the Roman point-of-view, expressed in the brief remarks of the historiansFlorus
Three main sets of works are attributed to Florus (a Roman cognomen): ''Virgilius orator an poeta'', the ''Epitome of Roman History'' and a collection of 14 short poems (66 lines in all). As to whether these were composed by the same person, or ...
, epitomising Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding i ...
, and Orosius
Paulus Orosius (; born 375/385 – 420 AD), less often Paul Orosius in English, was a Roman priest, historian and theologian, and a student of Augustine of Hippo. It is possible that he was born in '' Bracara Augusta'' (now Braga, Portugal), ...
, the Astures were divided into two factions, following the natural division made by the alpine karst
Karst () is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble carbonate rocks such as limestone and Dolomite (rock), dolomite. It is characterized by features like poljes above and drainage systems with sinkholes and caves underground. Ther ...
mountains of the Picos de Europa
Picos is a municipality in the state of Piauí in the Northeast region of Brazil. Picos is the state's third-largest city, located in the south-central region of Piauí and is the most economically developed city in the region. The city's fin ...
range: the ''Transmontani'' (located in the modern Asturias
Asturias (; ; ) officially the Principality of Asturias, is an autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensive with the provinces of Spain, province of Asturias and contains some of the territory t ...
, "beyond"— that is, north of— the Picos de Europa
Picos is a municipality in the state of Piauí in the Northeast region of Brazil. Picos is the state's third-largest city, located in the south-central region of Piauí and is the most economically developed city in the region. The city's fin ...
) and ''Cismontani'' (located on the "near" side, in the modern area of León). The Transmontani, placed between the Navia River and the central massif
A massif () is a principal mountain mass, such as a compact portion of a mountain range, containing one or more summits (e.g. France's Massif Central). In mountaineering literature, ''massif'' is frequently used to denote the main mass of an ...
of the Picos de Europa, comprised the Iburri, Luggones, Paesici, Paenii, Saelini, Vinciani, Viromenici and Baedunienses; the Cismontani included the , Cabruagenigi, Lancienses, Lougei, Tiburi, Brigaecini, Orniaci, Superatii, Gigurri, Zoelae and Susarri (which dwelled around Asturica Augusta
Asturica Augusta was a Ancient Rome, Roman city corresponding to the Spanish city of Astorga, Spain, Astorga, in the province of León, Spain, León. Founded around 14 B.C. as a camp of the Legio X Gemina, at the beginning of the first century it ...
, in the ''Astura'' river valley, and was the main Astur town in Roman times). Prior to the Roman conquest in the late 1st century BC, they were united into a tribal federation with the mountain-top citadel of ''Asturica'' ( Astorga) as their capital.
Culture
Recentepigraphic
Epigraphy () is the study of inscriptions, or epigraphs, as writing; it is the science of identifying graphemes, clarifying their meanings, classifying their uses according to dates and cultural contexts, and drawing conclusions about the wr ...
studies suggest that they spoke a ‘Q-Celtic
The Celtic languages ( ) are a branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, descended from the hypothetical Proto-Celtic language. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edward Lhuyd in 170 ...
’ language akin to the neighbouring Gallaeci
The Gallaeci (also Callaeci or Callaici; ) were a Celtic tribal complex who inhabited Gallaecia, the north-western corner of Iberia, a region roughly corresponding to what is now the Norte Region in northern Portugal, and the Spanish regions ...
Lucenses and Braccarenses (see Gallaecia
Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia, northern Portugal, Asturias and Leon and the later Kingdom of Gallaecia. The Roman cities inclu ...
). Although the Celtic language was lost during the Roman era
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Em ...
, it still endures in many names of villages and geographical features, mostly associated to Celtic deities: the parish of Taranes and the villages of Tereñes, Táranu, Tarañu and Torañu related to the god Taranis
Taranis (sometimes Taranus or Tanarus) is a Celtic thunder god attested in literary and epigraphic sources.
The Roman poet Lucan's epic ''Pharsalia'' mentions Taranis, Esus, and Teutates as gods to whom the Gauls sacrificed humans. This rare ...
, the parish of Lugones related to the god Lugus
Lugus (sometimes Lugos or Lug) is a Celtic god whose worship is attested in the epigraphic record. No depictions of the god are known. Lugus perhaps also appears in Ancient Rome, Roman sources and medieval Insular Celts, Insular mythology.
Va ...
or the parish of Beleño related to the god Belenus
Belenus (Gaulish: ''Belenos'', ''Belinos'') is an ancient Celtic healing god. The cult of Belenus stretched from the Italian Peninsula to the British Isles, with a main sanctuary located at Aquileia, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic coast. Through ...
, just to name a few.
According to classic authors, their family structure was matrilineal
Matrilineality, at times called matriliny, is the tracing of kinship through the female line. It may also correlate with a social system in which people identify with their matriline, their mother's lineage, and which can involve the inheritan ...
, whereby the woman inherits the ownership of property. The Astures lived in hill fort
A hillfort is a type of fortification, fortified refuge or defended settlement located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typical of the late Bronze Age Europe, European Bronze Age and Iron Age Europe, Iron Age. So ...
s, established in strategic areas and built with round walls in today's Asturias
Asturias (; ; ) officially the Principality of Asturias, is an autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensive with the provinces of Spain, province of Asturias and contains some of the territory t ...
and the mountainous areas of León, and with rectangular walls in flatter areas, similarly to their fellow Galicians
Galicians ( or ''pobo galego''; ) are an ethnic group primarily residing in Galicia, northwest Iberian Peninsula. Historical emigration resulted in populations in other parts of Spain, Europe, and the Americas. Galicians possess distinct cu ...
. Their warrior class consisted of men and women and both sexes were considered fierce fighters.
Religion
Most of their tribes, like the Lugones, worshipped the Celtic godLugh
Lugh or Lug (; ) is a figure in Irish mythology. A member of the Tuatha Dé Danann, a group of supernatural beings, Lugh is portrayed as a warrior, a king, a master craftsman and a saviour.Olmsted, Garrett. ''The Gods of the Celts and the I ...
, and references to other Celtic deities like Taranis
Taranis (sometimes Taranus or Tanarus) is a Celtic thunder god attested in literary and epigraphic sources.
The Roman poet Lucan's epic ''Pharsalia'' mentions Taranis, Esus, and Teutates as gods to whom the Gauls sacrificed humans. This rare ...
or Belenos still remain in the toponomy of the places inhabited by the Astures. They may have venerated the deity Busgosu.
Way of life
The Astures were vigoroushunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived Lifestyle, lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, esp ...
highlanders who raided Roman outposts in the lowlands; a reputation enhanced by ancient authors, such as Florus
Three main sets of works are attributed to Florus (a Roman cognomen): ''Virgilius orator an poeta'', the ''Epitome of Roman History'' and a collection of 14 short poems (66 lines in all). As to whether these were composed by the same person, or ...
("''Duae validissmae gentes, Cantabriae et Astures, immunes imperii agitabant''")Florus
Three main sets of works are attributed to Florus (a Roman cognomen): ''Virgilius orator an poeta'', the ''Epitome of Roman History'' and a collection of 14 short poems (66 lines in all). As to whether these were composed by the same person, or ...
, ''Epitomae Historiae Romanae'', II, 33. and Paulus Orosius ("''duas fortissimas Hispaniae gentes''"), but archeological evidence confirms that they also engaged in stock-raising in mountain pastures, complemented by subsistence farming on the slopes and in the lower valleys. They mostly reared sheep, goats, a few oxen and a local breed of mountain horse famed in Antiquity, the Asturcon, which still exists today. According to Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
, these were small-stature saddle horses, slightly larger than ponies, of graceful walk and very fast, being trained for both hunting and mountain warfare.
During a large part of the year they used acorn
The acorn is the nut (fruit), nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera ''Quercus'', ''Notholithocarpus'' and ''Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains a seedling surrounded by two cotyledons (seedling leaves), en ...
s as a staple food source, drying and powdering them and using the flour for a type of easily preserved bread; from their few sown fields that they had during the pre-Roman period, they harvested barley
Barley (), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikele ...
from which they produced beer (''Zythos''), as well as wheat and flax
Flax, also known as common flax or linseed, is a flowering plant, ''Linum usitatissimum'', in the family Linaceae. It is cultivated as a food and fiber crop in regions of the world with temperate climates. In 2022, France produced 75% of t ...
. Due to the scarcity of their agricultural production, as well as their strong war-like character, they made frequent incursions into the lands of the Vaccaei
The Vaccaei or Vaccei were a pre- Roman Celtic people of Spain, who inhabited the sedimentary plains of the central Duero valley, in the Meseta Central of northern Hispania (specifically in Castile and León).
Origins
Also designated Vaccaena ...
, who had a much more developed agriculture. Lucan calls them "Pale seekers after gold" ("''Asturii scrutator pallidus auri''").
History
The Astures entered the historical record in the late 3rd century BC, being listed amongst the Iberian Peninsula mercenaries ofHasdrubal Barca
Hasdrubal Barca (245– 22June 207BC), a latinization of names, latinization of ʿAzrubaʿal () son of Hamilcar Barca, was a Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian general in the Second Punic War. He was the brother of Hannibal and Mago Barca.
Youth and ...
's army at the battle of Metaurus River in 207 BC. Silius Italicus
Tiberius Catius Asconius Silius Italicus (, c. 26 – c. 101 AD) was a Roman senator, orator and epic poet of the Silver Age of Latin literature. His only surviving work is the 17-book '' Punica'', an epic poem about the Second Punic War and the ...
also mentions an Astur mercenary contingent in Hannibal
Hannibal (; ; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Punic people, Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Ancient Carthage, Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Punic War.
Hannibal's fat ...
's army, led by a chieftain named Cydnus.Silius Italicus
Tiberius Catius Asconius Silius Italicus (, c. 26 – c. 101 AD) was a Roman senator, orator and epic poet of the Silver Age of Latin literature. His only surviving work is the 17-book '' Punica'', an epic poem about the Second Punic War and the ...
, '' Punica'', III, 325-343. After the 2nd Punic War, their history is less clear. Rarely mentioned in the sources regarding the Lusitanian, Celtiberian or Sertorian War
The Sertorian War was a civil war in the Roman Republic fought from 80 to 72 BC between two Roman factions, one led by Quintus Sertorius and another led by the senate as constituted in the aftermath of Sulla's civil war. The war was fough ...
s, the Astures re-emerged only at the later 1st Century BC, when they provided auxiliary troops to the Pompeian army led by the generals' Lucius Afranius and Marcus Petreius that faced Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil wa ...
at the battle of Ilerda (Lérida
Lleida (, ; ; ''#Name, see below'') is a city in the west of Catalonia, Spain. It is the capital and largest town in Segrià, Segrià county, the Ponent, Ponent region and the province of Lleida. Geographically, it is located in the Catalan Cent ...
) in 49 BC, during the 2nd Roman Civil War.
Led by Gausón, a former mercenary commander, the Astures joined forces with the Cantabri to resist Emperor Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
's conquest of the whole of the Iberian northwest, even backing an unsuccessful Vaccaei
The Vaccaei or Vaccei were a pre- Roman Celtic people of Spain, who inhabited the sedimentary plains of the central Duero valley, in the Meseta Central of northern Hispania (specifically in Castile and León).
Origins
Also designated Vaccaena ...
revolt in 29 BC. The campaign against the Astures and Cantabri tribes proved so difficult that it required the presence of the emperor himself to bolster the seven legions and one naval squadron involved. The first Roman campaign against the Astures (the '' Bellum Asturicum''), which commenced in the spring of 26 BC, was successfully concluded in 25 BC with the ceremonial surrender of Mons Medullus to Augustus in person, allowing the latter to return to Rome and ostentatiously close the gates of the temple of Janus
In ancient Roman religion and myth, Janus ( ; ) is the god of beginnings, gates, transitions, time, duality, doorways, passages, frames, and endings. He is usually depicted as having two faces. The month of January is named for Janus (''Ianu ...
that same year. The reduction of the remaining Asture holdouts was entrusted to Publius Carisius, the legate of Lusitania
Lusitania (; ) was an ancient Iberian Roman province encompassing most of modern-day Portugal (south of the Douro River) and a large portion of western Spain (the present Extremadura and Province of Salamanca). Romans named the region after th ...
, who, after managing to trap Gauson and the remnants of his troops at the hillfort
A hillfort is a type of fortification, fortified refuge or defended settlement located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typical of the late Bronze Age Europe, European Bronze Age and Iron Age Europe, Iron Age. So ...
of Lancia, subsequently forced them to surrender when he threatened to set fire to the town. The Astures were subdued by the Romans but were never fully conquered, and their tribal way of life changed very little.
As far as the official Roman history was concerned, the fall of this last redoubt marked the conclusion of the conquest of the Asturian lands, which henceforth were included alongside Gallaecia
Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia, northern Portugal, Asturias and Leon and the later Kingdom of Gallaecia. The Roman cities inclu ...
and Cantabria
Cantabria (, ; ) is an autonomous community and Provinces of Spain, province in northern Spain with Santander, Cantabria, Santander as its capital city. It is called a , a Nationalities and regions of Spain, historic community, in its current ...
into the new Transduriana Province under the suffect consul
The consuls were the highest elected public officials of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC). Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the ''cursus honorum''an ascending sequence of public offices to which politicians aspire ...
Lucius Sestius Albanianus Quirinalis. This was followed by the establishment of military garrisons at ''Castrum
''Castra'' () is a Latin language, Latin term used during the Roman Republic and Roman Empire for a military 'camp', and ''castrum'' () for a 'Fortification, fort'. Either could refer to a building or plot of land, used as a fortified milita ...
'' '' Legio VII Gemina'' ( León) and ''Petavonium'' ( Rosinos de Vidriales – Zamora), along with colonies at ''Asturica Augusta'' ( Astorga) and '' Lucus Asturum'' ( Lugo de Llanera – Asturias
Asturias (; ; ) officially the Principality of Asturias, is an autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensive with the provinces of Spain, province of Asturias and contains some of the territory t ...
).
In spite of the harsh pacification policies implemented by Augustus, the Asturian country remained an unstable region subjected to sporadic revolts – often carried out in collusion with the Cantabri – and persistent guerrilla activity that kept the Roman occupation forces busy until the mid-1st century AD. New risings occurred in 24–22 BC (the 2nd Astur-Cantabrian War), in 20–18 BC (3rd Astur-Cantabrian 'War') – sparked off by runaway Cantabrian slaves returning from Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . Ac ...
– both of which were brutally quashed by General Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa
Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa (; BC – 12 BC) was a Roman general, statesman and architect who was a close friend, son-in-law and lieutenant to the Roman emperor Augustus. Agrippa is well known for his important military victories, notably the B ...
and again in 16–13 BC when Augustus crushed the last joint Astur-Cantabrian rebellion.
Romanization
Incorporated into theRoman province
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as Roman g ...
of Hispania Tarraconensis
Hispania Tarraconensis was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania. It encompassed much of the northern, eastern and central territories of modern Spain along with modern North Region, Portugal, northern Portugal. Southern Spain, the region now ...
, the assimilation of the Asturian region into the Roman world was a slow and hazardous process, with its partially romanized people retaining the Celtic language
The Celtic languages ( ) are a branch of the Indo-European language family, descended from the hypothetical Proto-Celtic language. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edward Lhuyd in 1707, following Paul-Yves ...
, religion and much of their ancient culture throughout the Roman Imperial period. This included their martial traditions, which enabled them to provide the Roman Army with several auxiliary cavalry and infantry units (''Ala I Asturum'', ''Ala II Asturum'', ''Cohors I Asturum'', ''Cohors II Asturum'', ''Cohors V Asturum'', ''Cohors VI Asturum'', ''Cohors I Asturum et Callaecorum'') that participated in Emperor Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; ; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54), or Claudius, was a Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusus and Ant ...
's invasion of Britain in AD 43–60, and which continued to serve into the late Empire. However, epigraphic evidence in the form of an inscribed votive stele
A stele ( ) or stela ( )The plural in English is sometimes stelai ( ) based on direct transliteration of the Greek, sometimes stelae or stelæ ( ) based on the inflection of Greek nouns in Latin, and sometimes anglicized to steles ( ) or stela ...
dedicated by a '' Primipilus Centurion
In the Roman army during classical antiquity, a centurion (; , . ; , or ), was a commander, nominally of a century (), a military unit originally consisting of 100 legionaries. The size of the century changed over time; from the 1st century BC ...
'' of '' Legio VI Victrix'' decorated for bravery in actionCIL XI 395, from Ariminum; cf: B. Dobson, ''Die Primipilares'' (''Beihefte der Bonner Jahrbücher XXXVII''), Köln 1978, pp. 198–200. confirms that the Astures staged a revolt in AD 54, prompting another vicious guerrilla war – unrecorded by surviving ancient sources – that lasted for fourteen years but the situation was finally calm around AD 68.
The early Middle Ages
During the Germanic invasions, the Astures resistedSuevi
file:1st century Germani.png, 300px, The approximate positions of some Germanic peoples reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 1st century. Suebian peoples in red, and other Irminones in purple.
The Suebi (also spelled Suavi, Suevi or Suebians ...
and Visigoth
The Visigoths (; ) were a Germanic people united under the rule of a king and living within the Roman Empire during late antiquity. The Visigoths first appeared in the Balkans, as a Roman-allied barbarian military group united under the comman ...
raids throughout the 5th century AD, only to be ultimately defeated and absorbed into the Visigothic Kingdom
The Visigothic Kingdom, Visigothic Spain or Kingdom of the Goths () was a Barbarian kingdoms, barbarian kingdom that occupied what is now southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to the 8th centuries. One of the Germanic people ...
by the Visigothic King Sisebut
Sisebut (; ; also ''Sisebuth'', ''Sisebur'', ''Sisebod'' or ''Sigebut''; 565 – February 621) was Visigothic Kingdom, King of the Visigoths and ruler of Hispania, Gallaecia, and Septimania from 612 until his death in 621. His rule was marked ...
in the early 6th century AD. However, the Astures continued to rebel, with King Wamba sending an expedition to the Asturian lands only twenty years before the Muslim invasion of the peninsula and the fall of the Visigothic kingdom. The Astures chose Pelagius of Asturias as their leader and in due course formed the Kingdom of Asturias.
Legacy
Reconquista
The ''Reconquista'' (Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese for ) or the fall of al-Andalus was a series of military and cultural campaigns that European Christian Reconquista#Northern Christian realms, kingdoms waged ag ...
period in the early Middle Ages, their name was preserved in the medieval Kingdom of Asturias
The Kingdom of Asturias was a kingdom in the Iberian Peninsula founded by the nobleman Pelagius who traditionally has been described as being of Visigothic stock. Modern research is leaning towards the view that Pelagius was of Hispano-Roman ...
and in the modern town of Astorga, León, whose designation still reflects its early Roman name of Asturica Augusta, the "Augustan settlement of the Astures".
See also
*Leonese people
The Leonese (Leonese language, Leonese: ''Llioneses;'' Spanish language, Spanish: ''Leoneses'') are a subgroup of Spaniards, native to historical region of León (historical region), León in Spain.
The Leonese Kingdom was an independent kingdo ...
*Asturian people
Asturians () are a Romance-speaking world, Romance ethnic group native to the autonomous community of Principality of Asturias, Asturias, in the North-West of the Iberian Peninsula.
Culture and society Heritage
The Asturians have Celts, Celti ...
* Astur-Cantabrian Wars
*Castro culture
Castro culture (, , , , meaning "culture of the hillforts") is the archaeological term for the material culture of the northwestern regions of the Iberian Peninsula (present-day northern and central Portugal together with the Spanish regions of ...
*Gallaecia
Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia, northern Portugal, Asturias and Leon and the later Kingdom of Gallaecia. The Roman cities inclu ...
* Eonavian
* Gausón
*Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula
This is a list of the pre- Roman people of the Iberian Peninsula (the Roman Hispania, i.e., modern Portugal, Spain and Andorra). Some closely fit the concept of a people, ethnic group or tribe. Others are confederations or even unions of tribe ...
*Leonese language
Leonese (''llionés, ḷḷionés, lionés'') is a set of vernacular Romance languages, Romance language varieties spoken in northern and western portions of the historical region of León (historical region), León in Spain (the modern provi ...
Notes
Sources
*Almagro-Gorbea, Martín, ''Les Celtes dans la péninsule Ibérique'', in ''Les Celtes'', Éditions Stock, Paris (1997) *Cunliffe, Barry, ''The Celts – A Very Short Introduction'', Oxford University Press (2003) *Duque, Ángel Montenegro ''et alli'', ''Historia de España 2 – colonizaciones y formacion de los pueblos prerromanos'', Editorial Gredos, Madrid (1989) *Lorrio Alvarado, Alberto José, ''Los Celtíberos'', Editorial Complutense, Alicante (1997) *Martino, Eutimio, ''Roma contra Cantabros y Astures – Nueva lectura de las fuentes'', Breviarios de la Calle del Pez n. º 33, Diputación provincial de León/Editorial Eal Terrae, Santander (1982) *Motoza, Francisco Burillo, ''Los Celtíberos – Etnias y Estados'', Crítica, Grijalbo Mondadori, S.A., Barcelona (1998, revised edition 2007) *Jiménez, Ana Bernardo (dirección), ''Astures – pueblos y culturas en la frontera del Imperio Romano'', Asociación Astures, Gran Enciclopedia Asturiana, Gijón (1995) , 84-7286-342-5 *Koch, John T.(ed.), ''Celtic Culture: A Historical Encyclopedia'', ABC-CLIO Inc., Santa Barbara, California (2006) , 1-85109-445-8Further reading
* F. Bartenstein, ''Bis ans Ende der bewohnten Welt. Die römische Grenz- und Expansionspolitik in der augusteischen Zeit'', Herbert Utz Verlag, München (2014) , pp. 71–127. *Berrocal-Rangel, Luis & Gardes, Philippe, ''Entre celtas e íberos'', Real Academia de la Historia/Fundación Casa de Velázquez, Madrid (2001) ISBNs 978-84-89512-82-5, 978-84-95555-10-6 *Heinrich Dyck, Ludwig, ''The Roman Barbarian Wars: The Era of Roman Conquest'', Author Solutions (2011) ISBNs 1426981821, 9781426981821 *Kruta, Venceslas, ''Les Celtes, Histoire et Dictionnaire: Des origines à la Romanization et au Christinisme'', Èditions Robert Laffont, Paris (2000) *Martín Almagro Gorbea, José María Blázquez Martínez, Michel Reddé, Joaquín González Echegaray, José Luis Ramírez Sádaba, and Eduardo José Peralta Labrador (coord.), ''Las Guerras Cántabras'', Fundación Marcelino Botín, Santander (1999) *Varga, Daniel, ''The Roman Wars in Spain: The Military Confrontation with Guerrilla Warfare'', Pen & Sword Military, Barnsley (2015) *Zapatero, Gonzalo Ruiz ''et alli'', ''Los Celtas: Hispania y Europa'', dirigido por Martín Almagro-Gorbea, Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Editorial ACTAS, S.l., Madrid (1993) ISBNs 8487863205, 9788487863202External links
Detailed map of the Pre-Roman Peoples of Iberia (around 200 BCE)
*http://www.celtiberia.net {{Pre-Roman peoples in Iberia History of Asturias Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula Celtic tribes of the Iberian Peninsula Ancient peoples of Spain Tribes conquered by Rome