asteroid moon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A minor-planet moon is an
 * Among '' trans-Neptunian objects'', it is common for the two orbiting components to be of comparable size, and for the semi-major axis of their orbits to be much larger − about 100 to 1000 primary radii. A significant proportion of these binaries are expected to be primordial.
**
* Among '' trans-Neptunian objects'', it is common for the two orbiting components to be of comparable size, and for the semi-major axis of their orbits to be much larger − about 100 to 1000 primary radii. A significant proportion of these binaries are expected to be primordial.
**
Orbits of Binary Asteroids with Adaptive Optics
(Franck Marchis)
(CBAT)
Johnston's Archive *
' a web page built and designed by F. Marchis and his collaborators (UC-Berkeley/SETI Institute) which contains the parameters of 169 multiple asteroid systems (last update May 9, 2009) {{Portal bar, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Science Moons Solar System
astronomical object
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists within the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are of ...
that orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an ...
s a minor planet
According to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a minor planet is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the Sun that is exclusively classified as neither a planet nor a comet. Before 2006, the IAU officially used the term ''minor ...
as its natural satellite
A natural satellite is, in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet, or small Solar System body (or sometimes another natural satellite). Natural satellites are colloquially referred to as moons, a deriv ...
. , there are 457 minor planets known or suspected to have moons. Discoveries of minor-planet moons (and binary objects, in general) are important because the determination of their orbits provides estimates on the mass
Mass is an Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsic property of a physical body, body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the physical quantity, quantity of matter in a body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physi ...
and density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the ratio of a substance's mass to its volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' (or ''d'') can also be u ...
of the primary, allowing insights into their physical properties that are generally not otherwise accessible.
Several of the moons are quite large compared to their primaries: 90 Antiope, Mors–Somnus and Sila–Nunam (95%), Patroclus–Menoetius, Altjira and Lempo–Hiisi (90%, with Lempo–Paha at 50%). The largest known minor-planet moon in ''absolute'' size is Pluto's largest moon Charon, which itself has about half the diameter of Pluto.
There are also several known ring systems around distant objects (see: '' Rings of Chariklo'' and ''Chiron
In Greek mythology, Chiron ( ; also Cheiron or Kheiron; ) was held to be the superlative centaur amongst his brethren since he was called the "wisest and justest of all the centaurs".
Biography
Chiron was notable throughout Greek mythology for ...
'').
Terminology
In addition to the terms ''satellite'' and ''moon'', the term "binary" (binary minor planet) is sometimes used for minor planets with one moon, and "triple" for minor planets with two moons. If one object is much bigger it is referred to as the ''primary'' and its companion as the ''secondary''. The term ''double asteroid'' is sometimes used for systems in which the asteroid and its moon are roughly the same size, while ''binary'' tends to be used independently from the relative sizes of the components. When binary minor planets are similar in size, theMinor Planet Center
The Minor Planet Center (MPC) is the official body for observing and reporting on minor planets under the auspices of the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Founded in 1947, it operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory.
Funct ...
(MPC) refers to them as " binary companions" instead of referring to the smaller body as a satellite. A good example of a true binary is the 90 Antiope system, identified in August 2000. Very small satellites are often referred to as moonlets.
Discovery milestones
Prior to the era of theHubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the Orbiting Solar Observatory, first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most ...
and space probes reaching the outer Solar System, attempts to detect satellites around asteroids were limited to optical observations from Earth. For example, in 1978, stellar occultation
Stellar means anything related to one or more stars (''stella''). The term may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Stellar (magazine), ''Stellar'' (magazine), an Irish lifestyle and fashion magazine
* Stellar Loussier, a character fro ...
observations were claimed as evidence of a satellite for the asteroid to 532 Herculina. However, later more-detailed imaging by the Hubble Telescope did not reveal a satellite, and the current consensus is that Herculina does not have a significant satellite. There were other similar reports of asteroids having companions (usually referred to as satellites) in the following years. A letter by astronomer Thomas Hamilton in the ''Sky & Telescope
''Sky & Telescope'' (''S&T'') is a monthly magazine covering all aspects of amateur and professional astronomy, including what to see in the sky tonight and new findings in astronomy. Other topics covered include:
*observing guides for planets, ...
'' magazine at this time pointed to apparently simultaneous impact craters on Earth (for example, the Clearwater Lakes in Quebec), suggesting that these craters were caused by pairs of gravitationally bound objects.
In 2014, 130 Elektra was discovered to have three moons, making it the only discovered quadruple asteroid.
Also in 1978, Pluto's largest moon Charon was discovered; however, at the time Pluto was still considered to be one of the major planets.
In 1993, the first asteroid moon was confirmed when the ''Galileo
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642), commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei ( , , ) or mononymously as Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a poly ...
'' probe discovered the small Dactyl orbiting 243 Ida
243 Ida is an asteroid in the Koronis family of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 29 September 1884 by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa at Vienna Observatory and named after Ida (nurse of Zeus), a nymph from Greek mythology. Later telesc ...
in the asteroid belt
The asteroid belt is a torus-shaped region in the Solar System, centered on the Sun and roughly spanning the space between the orbits of the planets Jupiter and Mars. It contains a great many solid, irregularly shaped bodies called asteroids ...
. The second was discovered around 45 Eugenia in 1998. In 2001, 617 Patroclus and its same-sized companion Menoetius became the first known binary asteroids in the Jupiter trojans. The first trans-Neptunian binary after Pluto–Charon, , was optically resolved in 2002.
Multiple systems
In 2005, the asteroid 87 Sylvia was discovered to have two satellites, making it the first known triple system (also called a triple minor planet or triple asteroid). This was followed by the discovery of a second moon orbiting 45 Eugenia. Also in 2005, the dwarf planet was discovered to have two moons, making it the second trans-Neptunian object afterPluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of Trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the Su ...
known to have more than one moon. Additionally, 216 Kleopatra and 93 Minerva were discovered to be triple asteroids in 2008 and 2009 respectively. There has been one discovered quadruple minor planet, that being 130 Elektra. Since the first few triple minor planets were discovered, more continue to be discovered. , the total number of known multiple systems among minor planets is 18 (including the Pluto and Haumea systems).
The following table lists all satellites of multiple systems, starting with Pluto, which was unnumbered when its first moon was discovered in 1978. The highest known multiplicities are for Pluto (a sextuple system) and 130 Elektra (a quadruple system).
Commonality
The data about the populations of binary objects are still patchy. In addition to the inevitable observational bias (dependence on the distance from Earth, size,albedo
Albedo ( ; ) is the fraction of sunlight that is Diffuse reflection, diffusely reflected by a body. It is measured on a scale from 0 (corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation) to 1 (corresponding to a body that reflects ...
and separation of the components) the frequency appears to be different among different categories of objects. Among asteroids, an estimated 2% would have satellites. Among trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs), an estimated 11% are thought to be binary or multiple objects, and the majority of the large TNOs have at least one satellite, including all four IAU-listed dwarf planets.
More than 50 binaries are known in each of the main groupings: near-Earth asteroids, belt asteroids, and trans-Neptunian objects
A trans-Neptunian object (TNO), also written transneptunian object, is any minor planet in the Solar System that orbits the Sun at a greater average distance than Neptune, which has an orbital semi-major axis of 30.1 astronomical units (AU).
T ...
, not including numerous claims based solely on light-curve variation.
Two binaries have been found so far among centaur
A centaur ( ; ; ), occasionally hippocentaur, also called Ixionidae (), is a creature from Greek mythology with the upper body of a human and the lower body and legs of a horse that was said to live in the mountains of Thessaly. In one version o ...
s with semi-major axes smaller than Neptune. Both are double ring systems around 2060 Chiron and 10199 Chariklo, discovered in 1993–2011 and 2013 respectively.
Origin
The origin of minor-planet moons is not currently known with certainty, and a variety of hypotheses exist. One such model is that minor-planet moons are formed from debris knocked off the primary by an impact. Other pairings may be formed when a small object is captured by the gravity of a larger one. Formation by collision is constrained by theangular momentum
Angular momentum (sometimes called moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of Momentum, linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a Conservation law, conserved quantity – the total ang ...
of the components, i.e. by the masses and their separation. Close binaries fit this model (e.g. Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of Trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the Su ...
– Charon). Distant binaries however, with components of comparable size, are unlikely to have followed this scenario, unless considerable mass has been lost in the event.
The distances of the components for the known binaries vary from a few hundreds of kilometres (243 Ida
243 Ida is an asteroid in the Koronis family of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 29 September 1884 by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa at Vienna Observatory and named after Ida (nurse of Zeus), a nymph from Greek mythology. Later telesc ...
, 3749 Balam) to more than 3000 km ( 379 Huenna) for the asteroids. Among TNOs, the known separations vary from 3,000 to 50,000 km.
Populations and classes
What is "typical" for a binary system tends to depend on its location in the Solar System (presumably because of different modes of origin and lifetimes of such systems in different populations of minor planets). * Among '' near-Earth asteroids'', satellites tend to orbit at distances of the order of 3–7 primary radii, and have diameters two to several times smaller than the primary. Since these binaries are all inner-planet crossers, it is thought that tidal stresses that occurred when the parent object passed close to a planet may be responsible for the formation of many of them, although collisions are thought to also be a factor in the creation of these satellites. * Among '' main-beltasteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet—an object larger than a meteoroid that is neither a planet nor an identified comet—that orbits within the Solar System#Inner Solar System, inner Solar System or is co-orbital with Jupiter (Trojan asteroids). As ...
s'', the satellites are usually much smaller than the primary (a notable exception being 90 Antiope), and orbit around 10 primary radii away. Many of the binary systems here are members of asteroid families, and a good proportion of satellites are expected to be fragments of a parent body whose disruption after an asteroid collision produced both the primary and satellite.
 * Among '' trans-Neptunian objects'', it is common for the two orbiting components to be of comparable size, and for the semi-major axis of their orbits to be much larger − about 100 to 1000 primary radii. A significant proportion of these binaries are expected to be primordial.
**
* Among '' trans-Neptunian objects'', it is common for the two orbiting components to be of comparable size, and for the semi-major axis of their orbits to be much larger − about 100 to 1000 primary radii. A significant proportion of these binaries are expected to be primordial.
** Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of Trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the Su ...
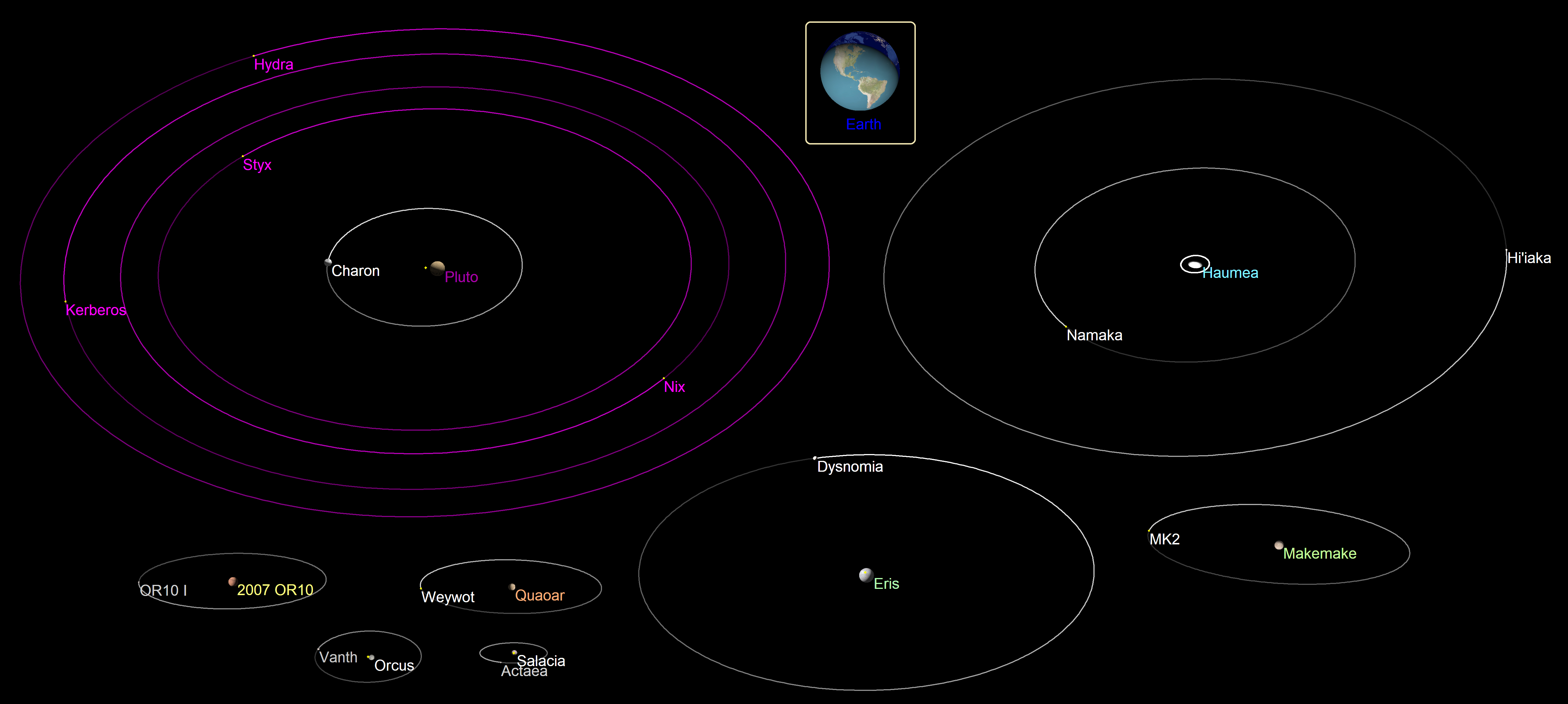
has five known moons. Its largest moon Charon has a radius of more than half that of Pluto, and is large enough to orbit a point outside Pluto's surface. In fact, each orbits the common barycenter between them, with Pluto's orbit entirely enclosed by Charon's; thus they form a binary system informally referred to as a double dwarf planet. Pluto's four other moons, Nix, Hydra, Kerberos, and Styx, are far smaller and orbit the Pluto–Charon system.
** Haumea has two moons with radii estimated around 155 km ( Hiʻiaka) and 85 km ( Namaka).
** has one known moon, S/2015 (136472) 1, estimated to be some in diameter.
** 47171 Lempo is a unique trans-Neptunian triple system: Lempo and its moon of roughly equal mass, Hiisi, form a close-proximity binary, separated by roughly 867 km. A second moon, Paha, orbits the Lempo–Hiisi binary at about 7411 km.
** has one known moon, Dysnomia. Its radius, based on its brightness, is estimated to be roughly between 150 and 350 km.
List
, there are 457 minor planets (systems) with 477 known companions. The following table is a listing of the total number of these systems by orbital class:Near-Earth objects
This is a list of near-Earth asteroids with companions. Candidate binaries with an unconfirmed status are displayed on a dark background. For an overview, see summary and introduction.Mars crossers
This is a list of Mars-crossing asteroids with companions. Candidate binaries with an unconfirmed status are displayed on a dark background. For an overview, see summary and introduction.Main-belt asteroids
This is a list of main-belt asteroids with companions. Candidate binaries with an unconfirmed status are displayed on a dark background. For an overview, see summary and introduction. The following binaries are double asteroids, with similarly sized components, and a barycenter outside of the larger object. # 90 Antiope – S/2000 (90) 1 # 854 Frostia – undesignated # 1313 Berna – undesignated # 2478 Tokai – undesignated # 3169 Ostro – undesignated # 3749 Balam – S/2002 (3749) 1 # 3905 Doppler – undesignated # 4674 Pauling – S/2004 (4674) 1 # 4951 Iwamoto – undesignated # 5674 Wolff – undesignated # 8474 Rettig – undesignated # 17246 Christophedumas – S/2004 (17246) 1 # – undesignated In addition, these bodies might be double asteroids, but due to errors in their size and orbit, it is uncertain. # 809 Lundia – undesignated # 1089 Tama – undesignated # 1509 Esclangona – S/2003 (1509) 1 # 4492 Debussy – undesignated # 11264 Claudiomaccone – undesignated # 22899 Alconrad – (22899) Alconrad I JuliekaibarretoJupiter trojans
This is a list of Jupiter trojans with companions. Candidate binaries with an unconfirmed status are displayed on a dark background. For an overview, see summary and introduction.Trans-Neptunian objects
This is a list of trans-Neptunian objects with companions. Candidate binaries with an unconfirmed status are displayed on a dark background. This list gives the companion's orbital period (Ps) in days rather than hours. For an overview, see summary and introduction.See also
*Lists of astronomical objects
This is a list of lists, grouped by type of astronomical object.
Solar System
* List of Solar System objects
* List of gravitationally rounded objects of the Solar System
* List of Solar System objects most distant from the Sun
* List of ...
*
*
* Satellite system (astronomy)
References
External links
* , Lecture at SETI talkOrbits of Binary Asteroids with Adaptive Optics
(Franck Marchis)
(CBAT)
Johnston's Archive *
' a web page built and designed by F. Marchis and his collaborators (UC-Berkeley/SETI Institute) which contains the parameters of 169 multiple asteroid systems (last update May 9, 2009) {{Portal bar, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Science Moons Solar System