Ascofuranone Biosynthesis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ascofuranone is an
antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
produced by various ascomycete fungi including '' Acremonium sclerotigenum'' that inhibits the ''Trypanosoma brucei
''Trypanosoma brucei'' is a species of parasitic Kinetoplastida, kinetoplastid belonging to the genus ''Trypanosoma'' that is present in sub-Saharan Africa. Unlike other protozoan parasites that normally infect blood and tissue cells, it is excl ...
'' alternative oxidase
The alternative oxidase (AOX) is an enzyme that forms part of the electron transport chain in mitochondria of different organisms. Proteins homologous to the mitochondrial oxidase and the related plastid terminal oxidase have also been identified ...
and is a lead compound in efforts to produce other drugs targeting this enzyme for the treatment of sleeping sickness
African trypanosomiasis is an insect-borne parasitic infection of humans and other animals.
Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT), also known as African sleeping sickness or simply sleeping sickness, is caused by the species '' Trypanosoma b ...
. The compound is effective both in vitro cell culture
Cell culture or tissue culture is the process by which cell (biology), cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. After cells of interest have been Cell isolation, isolated from living tissue, ...
and in infections in mice.
Ascofuranone has also been reported to have anti-tumor activity, and modulate the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
.
__TOC__Biosynthesis
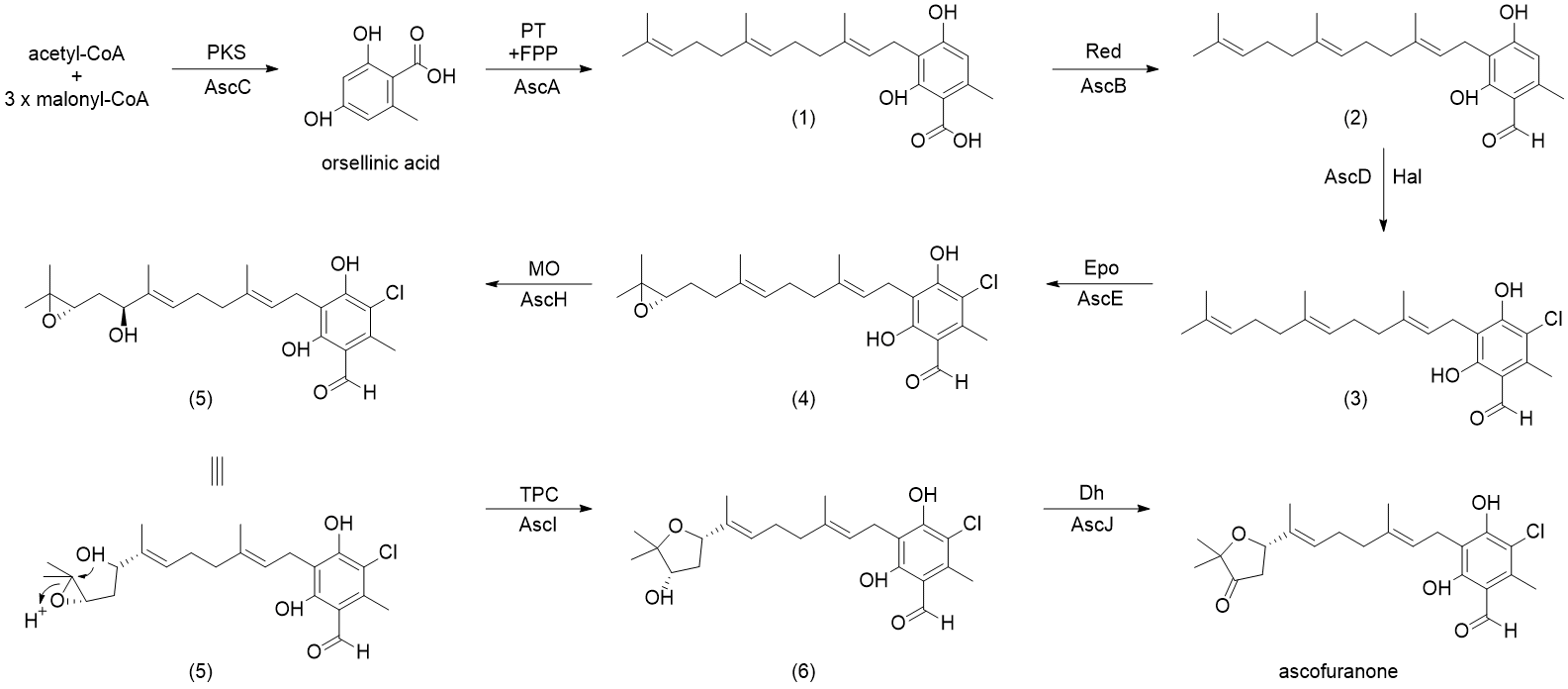
The proposed biosynthesis of ascofuranone was reported by Kita et al., as well as by Abe et al. The prenylation of orsellinic acid, followed by terminal cyclization through epoxidation is how ascofuranone can be synthesized. Compound (1), ilicicolinic acid B, was found to be produced from polyketide synthase (PKS) StBA and that AscCABD are responsible for the biosynthesis of ilicicolin A (3). Ilicicolin B (2) was found to be produced by expressing AscC (polyketide synthase) which is then followed by expression of AscA (prenyltransferase). AscD (flavin-dependent halogenase, flavin binding enzyme) is able to catalyze the chlorination of ilicicolinic acid B (2) to yield ilicicolin A (3). Expodiation of (3) by AscE (P450 monooxygenase) leads to the formation of ilicicolin A epoxide (4). Ilicicolin A epoxide can then be hydroxylated by AscH at C-16 (P450 monooygenase) to yield intermediate (5) which can then be cyclized by AscI (eight-transmembrane protein, TPC) into ascofuranol (6), specifically through 6-endo-tet cyclization. Finally, ascofuranol (6) can be oxidized by AscJ (NAD(P)-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase) leading to the formation of ascofuranone.
References
{{reflist Antibiotics Terpeno-phenolic compounds Aromatic aldehydes Ketones Chloroarenes Tetrahydrofurans Chlorine-containing natural products Resorcinols