Artillery wheel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The artillery wheel was a nineteenth-century and early-twentieth-century style of wagon, gun carriage, and automobile wheel. Rather than having its spokes mortised into a wooden nave (hub), it has them fitted together in a keystone fashion with miter joints, bolted into a two-piece metal nave. Its tyre is shrunk onto the rim in the usual way, but it may also be bolted on for security.
The design evolved over the nineteenth and early twentieth century, and was ultimately imitated in drawn steel for auto wheels, which sometimes show little immediate resemblance to most of their design ancestry.
 Wheels with wood spokes fitted together in a keystone fashion with miter joints, bolted into a two-piece metal
Wheels with wood spokes fitted together in a keystone fashion with miter joints, bolted into a two-piece metal 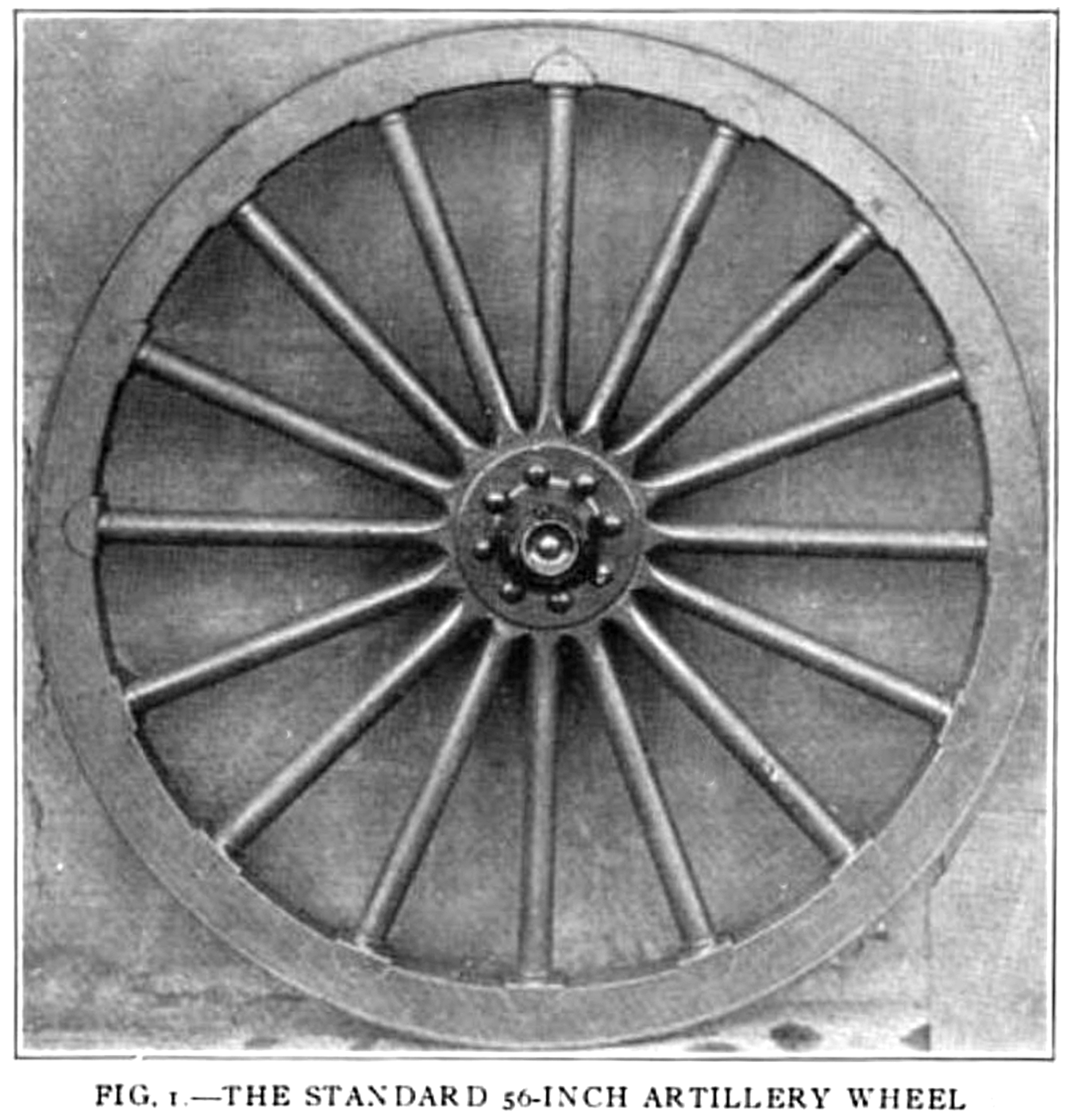 This wheel design that came to be called artillery wheels was extensively used with artillery. For example, this type of wheel was used on the pictured Armstrong gun, used in Japan in 1868. A similar design was used for a gun carriage for the
This wheel design that came to be called artillery wheels was extensively used with artillery. For example, this type of wheel was used on the pictured Armstrong gun, used in Japan in 1868. A similar design was used for a gun carriage for the
 Wood-spoke artillery wheels were used on early automobiles, as a stronger alternative to wire wheels. By the 1920s, many motor cars used wheels that looked at a glance like wooden artillery wheels, but which were of cast steel or welded from steel pressed sections. These too were usually called artillery wheels. Whether wood, pressed steel, or wire wheels were preferred varied greatly in different markets.
Wood-spoke artillery wheels were used on early automobiles, as a stronger alternative to wire wheels. By the 1920s, many motor cars used wheels that looked at a glance like wooden artillery wheels, but which were of cast steel or welded from steel pressed sections. These too were usually called artillery wheels. Whether wood, pressed steel, or wire wheels were preferred varied greatly in different markets.
File:Austin 40hp York landaulette 1907, Gaydon (cropped).jpg, 1908 aftermarket pressed and welded detachable
Wood artillery wheels
 Wheels with wood spokes fitted together in a keystone fashion with miter joints, bolted into a two-piece metal
Wheels with wood spokes fitted together in a keystone fashion with miter joints, bolted into a two-piece metal nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type ...
, were called "wedge wheels" by Walter Hancock who described them in 1834, as he used them on his steam-powered road vehicles. In response to Hancock's description, John Robison said he had wheels of the same description built in 1811 for artillery carriages, and that "A construction very analogous to this has long been in use in the Madras Artillery; in which service I have always understood that it gave every satisfaction."
 This wheel design that came to be called artillery wheels was extensively used with artillery. For example, this type of wheel was used on the pictured Armstrong gun, used in Japan in 1868. A similar design was used for a gun carriage for the
This wheel design that came to be called artillery wheels was extensively used with artillery. For example, this type of wheel was used on the pictured Armstrong gun, used in Japan in 1868. A similar design was used for a gun carriage for the US Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of the United Stat ...
's 3.2-inch gun in 1881, with a wheel diameter of , based on testing of an Archibald Wheel Company design. By 1917, the 14-spoke wheel evolved to have 16 spokes, high-carbon-steel tires, , felloes (8 sawed or 2 bent), improved spoke shoes, and dishing, to arrive at the "standard" wheel pictured.
For motor-drawn guns, the wheel further evolved, primarily to smaller diameters to accommodate solid rubber tires.
Motor vehicles
 Wood-spoke artillery wheels were used on early automobiles, as a stronger alternative to wire wheels. By the 1920s, many motor cars used wheels that looked at a glance like wooden artillery wheels, but which were of cast steel or welded from steel pressed sections. These too were usually called artillery wheels. Whether wood, pressed steel, or wire wheels were preferred varied greatly in different markets.
Wood-spoke artillery wheels were used on early automobiles, as a stronger alternative to wire wheels. By the 1920s, many motor cars used wheels that looked at a glance like wooden artillery wheels, but which were of cast steel or welded from steel pressed sections. These too were usually called artillery wheels. Whether wood, pressed steel, or wire wheels were preferred varied greatly in different markets.
British cars
Joseph Sankey and Sons developed and patented the first pressed-steel and welded detachable motor car wheel. Production started in 1908, with customers including Herbert Austin and, later,William Morris
William Morris (24 March 1834 – 3 October 1896) was an English textile designer, poet, artist, writer, and socialist activist associated with the British Arts and Crafts movement. He was a major contributor to the revival of traditiona ...
. By 1920, Sankey were supplying wheels to many UK manufacturers.
Though Sankey did not market their steel wheels as artillery wheels, the term ''Sankey wheels'' was used interchangeably with ''steel artillery wheels'' by 1930. Sankey belatedly, circa 1935, publicly recognized the connection of their steel wheels to artillery wheels.
US cars
In the 1930s, US manufacturers, whose markets often preferred wheels of substantial appearance, moved to stamped steel wheels which imitated large-hub artillery wheels.Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company (commonly known as Ford) is an American multinational corporation, multinational automobile manufacturer headquartered in Dearborn, Michigan, United States. It was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. T ...
adopted this in 1935, Chevrolet
Chevrolet ( ) is an American automobile division of the manufacturer General Motors (GM). In North America, Chevrolet produces and sells a wide range of vehicles, from subcompact automobiles to medium-duty commercial trucks. Due to the promi ...
brought out its now iconic wheel in 1936. These wheels were based on large-hub wheels, and do not superficially resemble most small-hub wood wheels.
Gallery
steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
wheel on a 1907 Austin
File:Steam 4WD car with artillery wheels.jpg, 4WD steam car with artillery wheels, c. 1918
File:Humber 9 20 1926.jpg, A 1927 Humber
The Humber is a large tidal estuary on the east coast of Northern England. It is formed at Trent Falls, Faxfleet, by the confluence of the tidal rivers River Ouse, Yorkshire, Ouse and River Trent, Trent. From there to the North Sea, it forms ...
with steel artillery wheels
File:'27 Ford Model T (Auto classique Ste-Rose '11).JPG, A 1927 Ford T with wood artillery wheels}
File:Wooden-spoked-wheel_on_a_1909_Rolls-Royce_Silver_Ghost.jpg, Later steel artillery wheels were often based on large-hub wood designs like this
File:Panzermuseum Munster 2010 0057.JPG, double solid tire wheel
See also
* Cart wheelReferences
External links
{{Commonscat-inline, Artillery wheels, position=left Carriages and mountings Wheels Auto parts Horse-drawn vehicle parts