Arthrosis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Osteoarthritis is a type of degenerative
 The main symptom is
The main symptom is
File:Osteo of the hand.jpg, Severe osteoarthritis and
 Lifestyle modification (such as weight loss and exercise) and
Lifestyle modification (such as weight loss and exercise) and
 Use of analgesia, intra-articular cortisone injection and consideration of hyaluronic acids and platelet-rich plasma are recommended for pain relief in people with knee osteoarthritis.
Local drug delivery by intra-articular injection may be more effective and safer in terms of increased bioavailability, less systemic exposure and reduced adverse events. Several intra-articular medications for symptomatic treatment are available on the market as follows.
Use of analgesia, intra-articular cortisone injection and consideration of hyaluronic acids and platelet-rich plasma are recommended for pain relief in people with knee osteoarthritis.
Local drug delivery by intra-articular injection may be more effective and safer in terms of increased bioavailability, less systemic exposure and reduced adverse events. Several intra-articular medications for symptomatic treatment are available on the market as follows.
 Globally, , approximately 250million people had osteoarthritis of the knee (3.6% of the population). Hip osteoarthritis affects about 0.85% of the population.
, osteoarthritis globally causes moderate to severe disability in 43.4 million people. Together, knee and hip osteoarthritis had a ranking for disability globally of 11th among 291 disease conditions assessed.
Globally, , approximately 250million people had osteoarthritis of the knee (3.6% of the population). Hip osteoarthritis affects about 0.85% of the population.
, osteoarthritis globally causes moderate to severe disability in 43.4 million people. Together, knee and hip osteoarthritis had a ranking for disability globally of 11th among 291 disease conditions assessed.
Knee osteoarthritis
'' was the 18th most common cause of years lived with disability (YLDs) in Europe, accounting for 1.28% of all YLDs. This has increased from 1.12% in 1990.
joint disease
An arthropathy is a disease of a joint. Types
Arthritis is a form of arthropathy that involves inflammation of one or more joints, while the term arthropathy may be used regardless of whether there is inflammation or not.
Joint diseases can be cla ...
that results from breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
. A form of arthritis
Arthritis is a general medical term used to describe a disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, Joint effusion, swelling, and decreased range of motion of ...
, it is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world, affecting 1 in 7 adults in the United States alone. The most common symptoms are joint pain
Arthralgia () literally means 'joint pain'. Specifically, arthralgia is a symptom of injury, infection, illness (in particular arthritis), or an allergic reaction to medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutic ...
and stiffness
Stiffness is the extent to which an object resists deformation in response to an applied force.
The complementary concept is flexibility or pliability: the more flexible an object is, the less stiff it is.
Calculations
The stiffness, k, of a ...
. Usually the symptoms progress slowly over years. Other symptoms may include joint swelling
A joint effusion is the presence of increased intra-articular fluid. It may affect any joint. Commonly it involves the knee (see knee effusion).
Diagnostic approach
The approach to diagnosis depends on the joint involved. While aspiration o ...
, decreased range of motion
Range of motion (or ROM) is the linear or angular distance that a moving object may normally travel while properly attached to another.
In biomechanics and strength training, ROM refers to the angular distance and direction a joint can move be ...
, and, when the back is affected, weakness or numbness of the arms and legs. The most commonly involved joints are the two near the ends of the fingers and the joint at the base of the thumbs, the knee and hip joints, and the joints of the neck and lower back. The symptoms can interfere with work and normal daily activities. Unlike some other types of arthritis, only the joints, not internal organs, are affected.
Possible causes include previous joint injury, abnormal joint or limb development, and inherited factors. Risk is greater in those who are overweight
Being overweight is having more body fat than is optimally healthy. Being overweight is especially common where food supplies are plentiful and lifestyles are sedentary.
, excess weight reached epidemic proportions globally, with more than ...
, have legs of different lengths, or have jobs that result in high levels of joint stress. Osteoarthritis is believed to be caused by mechanical stress on the joint and low grade inflammatory processes. It develops as cartilage is lost and the underlying bone becomes affected. As pain may make it difficult to exercise, muscle loss
Muscle atrophy is the loss of skeletal muscle mass. It can be caused by immobility, aging, malnutrition, medications, or a wide range of injuries or diseases that impact the musculoskeletal or nervous system. Muscle atrophy leads to muscle weakne ...
may occur. Diagnosis is typically based on signs and symptoms, with medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to revea ...
and other tests used to support or rule out other problems. In contrast to rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and h ...
, in osteoarthritis the joints do not become hot or red.
Treatment includes exercise, decreasing joint stress such as by rest or use of a cane
Cane or caning may refer to:
*Walking stick, or walking cane, a device used primarily to aid walking
* Assistive cane, a walking stick used as a mobility aid for better balance
* White cane, a mobility or safety device used by blind or visually i ...
, support group
In a support group, members provide each other with various types of help, usually nonprofessional and nonmaterial, for a particular shared, usually burdensome, characteristic. Members with the same issues can come together for sharing coping str ...
s, and pain medications
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic, antalgic, pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used for pain management. Analgesics are conceptually distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily reduce, and in so ...
. Weight loss may help in those who are overweight. Pain medications may include paracetamol
Paracetamol, or acetaminophen, is a non-opioid analgesic and antipyretic agent used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. It is a widely available over-the-counter drug sold under various brand names, including Tylenol and Panadol.
Parac ...
(acetaminophen) as well as NSAID
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
s such as naproxen
Naproxen, sold under the brand name Aleve among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain, menstrual cramps, and inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout and fever. It is taken orally. It ...
or ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes dysmenorrhea, painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It can be taken oral administration, ...
. Long-term opioid
Opioids are a class of Drug, drugs that derive from, or mimic, natural substances found in the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy plant. Opioids work on opioid receptors in the brain and other organs to produce a variety of morphine-like effects, ...
use is not recommended due to lack of information on benefits as well as risks of addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to use a drug or engage in a behavior that produces natural reward, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use can ...
and other side effects. Joint replacement
Joint replacement is a procedure of orthopedic surgery known also as arthroplasty, in which an arthritic or dysfunctional joint surface is replaced with an orthopedic prosthesis. Joint replacement is considered as a treatment when severe joint pai ...
surgery may be an option if there is ongoing disability despite other treatments. An artificial joint typically lasts 10 to 15 years.
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis, affecting about 237million people or 3.3% of the world's population as of 2015. It becomes more common as people age. Among those over 60 years old, about 10% of males and 18% of females are affected. Osteoarthritis is the cause of about 2% of years lived with disability.
Signs and symptoms
 The main symptom is
The main symptom is pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sense, sensory and emotional experience associated with, or res ...
, causing loss of ability and often stiffness. The pain is typically made worse by prolonged activity and relieved by rest. Stiffness is most common in the morning, and typically lasts less than thirty minutes after beginning daily activities, but may return after periods of inactivity. Osteoarthritis can cause a crackling noise (called "crepitus
Crepitus is "a grating sound or sensation produced by friction between bone and cartilage or the fractured parts of a bone".
Various types of crepitus that can be heard in joint pathologies are:
*Bone crepitus: This can be heard when two frag ...
") when the affected joint is moved, especially shoulder and knee joint. A person may also complain of joint locking and joint instability. These symptoms would affect their daily activities due to pain and stiffness. Some people report increased pain associated with cold temperature, high humidity, or a drop in barometric pressure, but studies have had mixed results.
Osteoarthritis commonly affects the hands, feet, spine
Spine or spinal may refer to:
Science Biology
* Spinal column, also known as the backbone
* Dendritic spine, a small membranous protrusion from a neuron's dendrite
* Thorns, spines, and prickles, needle-like structures in plants
* Spine (zoology), ...
, and the large weight-bearing
In orthopedics, weight-bearing is the amount of weight a patient puts on an injured body part. Generally, it refers to a leg, ankle or foot that has been Bone fracture, fractured or upon which surgery has been performed, but the term can also be us ...
joints, such as the hips
In vertebrate anatomy, the hip, or coxaLatin ''coxa'' was used by Celsus in the sense "hip", but by Pliny the Elder in the sense "hip bone" (Diab, p 77) (: ''coxae'') in medical terminology, refers to either an anatomical region or a joint ...
and knees, although in theory, any joint in the body can be affected. As osteoarthritis progresses, movement patterns (such as gait
Gait is the pattern of Motion (physics), movement of the limb (anatomy), limbs of animals, including Gait (human), humans, during Animal locomotion, locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on s ...
), are typically affected. Osteoarthritis is the most common cause of a knee effusion
Knee effusion, informally known as water on the knee, occurs when excess synovial fluid accumulates in or around the knee joint. It has many common causes, including arthritis, injury to the ligaments or meniscus, or fluid collecting in the burs ...
.
In smaller joints, such as at the fingers, hard bony enlargements, called Heberden's nodes (on the distal interphalangeal joints) or Bouchard's nodes
Bouchard's nodes are hard, bony outgrowths or gelatinous cysts on the proximal interphalangeal joints (the middle joints of fingers or toes). They are seen in osteoarthritis, where they are caused by the formation of calcific spurs of the articul ...
(on the proximal interphalangeal joints), may form, and though they are not necessarily painful, they do limit the movement of the fingers significantly. Osteoarthritis of the toes may be a factor causing formation of bunion
A bunion, also known as hallux valgus, is a deformity of the metatarsophalangeal joint, MTP joint connecting the big toe to the foot. The big toe often bends towards the other toes and the joint becomes red and painful. The onset of bunions is ...
s, rendering them red or swollen.
Causes
Damage from mechanical stress with insufficient self repair by joints is believed to be the primary cause of osteoarthritis. Sources of this stress may include misalignments of bones caused by congenital or pathogenic causes; mechanical injury; excess body weight; loss of strength in the muscles supporting a joint; and impairment of peripheral nerves, leading to sudden or uncoordinated movements. The risk of osteoarthritis increases with aging, history of joint injury, or family history of osteoarthritis. Howeverexercise
Exercise or workout is physical activity that enhances or maintains fitness and overall health. It is performed for various reasons, including weight loss or maintenance, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardio ...
, including running in the absence of injury, has not been found to increase the risk of knee osteoarthritis. Nor has cracking one's knuckles been found to play a role.
Primary
The development of osteoarthritis is correlated with a history of previous joint injury and with obesity, especially with respect to knees. Changes in sex hormone levels may play a role in the development of osteoarthritis, as it is more prevalent among post-menopausal women than among men of the same age. Conflicting evidence exists for the differences in hip and knee osteoarthritis in African Americans and Caucasians.Occupational
Increased risk of developing knee and hip osteoarthritis was found among those who work with manual handling (e.g. lifting), have physically demanding work, walk at work, and have climbing tasks at work (e.g. climb stairs or ladders). With hip osteoarthritis, in particular, increased risk of development over time was found among those who work in bent or twisted positions. For knee osteoarthritis, in particular, increased risk was found among those who work in a kneeling orsquatting position
Squatting is a versatile List of human positions, posture where the weight of the body is on the feet but the knees and hips are bent. In contrast, sitting involves supporting the weight of the body on the ischial tuberosities of the pelvis, with ...
, experience heavy lifting in combination with a kneeling or squatting posture, and work standing up. Women and men have similar occupational risks for the development of osteoarthritis.
Secondary
This type of osteoarthritis is caused by other factors but the resulting pathology is the same as for primary osteoarthritis: *Alkaptonuria
Alkaptonuria is a rare inherited genetic disease which is caused by a mutation in the ''HGD'' gene for the enzyme homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase (); if a person inherits an abnormal copy from both parents (it is a dominance relationship, recessive c ...
* Congenital
A birth defect is an abnormal condition that is present at childbirth, birth, regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disability, disabilities that may be physical disability, physical, intellectual disability, intellectual, or dev ...
disorders of joints
* Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
doubles the risk of having a joint replacement due to osteoarthritis and people with diabetes have joint replacements at a younger age than those without diabetes.
* Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
* Hemochromatosis
Iron overload is the abnormal and increased accumulation of total iron in the body, leading to organ damage. The primary mechanism of organ damage is oxidative stress, as elevated intracellular iron levels increase free radical formation via the ...
and Wilson's disease
Wilson's disease (also called hepatolenticular degeneration) is a genetic disorder characterized by the excess build-up of copper in the body. Symptoms are typically related to the brain and liver. Liver-related symptoms include vomiting, wea ...
* Inflammatory diseases (such as Perthes' disease), (Lyme disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a tick-borne disease caused by species of ''Borrelia'' bacteria, Disease vector, transmitted by blood-feeding ticks in the genus ''Ixodes''. It is the most common disease spread by ticks in th ...
), and all chronic forms of arthritis (e.g., costochondritis
Costochondritis, also known as chest wall pain syndrome or costosternal syndrome, is a benign inflammation of the upper Costochondral joint, costochondral (rib to cartilage) and costosternal joint, sternocostal (cartilage to sternum) joints. 90% ...
, gout
Gout ( ) is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by recurrent attacks of pain in a red, tender, hot, and Joint effusion, swollen joint, caused by the deposition of needle-like crystals of uric acid known as monosodium urate crysta ...
, and rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and h ...
). In gout, uric acid
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the Chemical formula, formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the meta ...
crystals cause the cartilage to degenerate at a faster pace.
* Injury
Injury is physiological damage to the living tissue of any organism, whether in humans, in other animals, or in plants.
Injuries can be caused in many ways, including mechanically with penetration by sharp objects such as teeth or with ...
to joints or ligaments (such as the ACL) as a result of an accident or orthopedic operations.
* Ligament
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have liga ...
ous deterioration or instability may be a factor.
* Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with dolichostenomelia, long arms, legs, Arachnodactyly, fingers, and toes. They also typically ha ...
* Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
* Joint infection
Pathophysiology
While osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that may cause gross cartilage loss and morphological damage to other joint tissues, more subtle biochemical changes occur in the earliest stages of osteoarthritis progression. The water content of healthy cartilage is finely balanced by compressive force driving water out andhydrostatic
Hydrostatics is the branch of fluid mechanics that studies fluids at hydrostatic equilibrium and "the pressure in a fluid or exerted by a fluid on an immersed body". The word "hydrostatics" is sometimes used to refer specifically to water and o ...
and osmotic pressure
Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure which needs to be applied to a Solution (chemistry), solution to prevent the inward flow of its pure solvent across a semipermeable membrane.
It is also defined as the measure of the tendency of a soluti ...
drawing water in. Collagen fibres exert the compressive force, whereas the Gibbs–Donnan effect
The Gibbs–Donnan effect (also known as the Donnan's effect, Donnan law, Donnan equilibrium, or Gibbs–Donnan equilibrium) is a name for the behaviour of charged particles near a semi-permeable membrane that sometimes fail to distribute evenly ...
and cartilage proteoglycans
Proteoglycans are proteins that are heavily glycosylation, glycosylated. The basic proteoglycan unit consists of a "core protein" with one or more covalent bond, covalently attached glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chain(s). The point of attachment is a ...
create osmotic pressure which tends to draw water in.
However, during onset of osteoarthritis, the collagen matrix becomes more disorganized and there is a decrease in proteoglycan content within cartilage. The breakdown of collagen fibers results in a net increase in water content. This increase occurs because whilst there is an overall loss of proteoglycans (and thus a decreased osmotic pull), it is outweighed by a loss of collagen.
Other structures within the joint can also be affected. The ligament
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have liga ...
s within the joint become thickened and fibrotic
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is the development of fibrous connective tissue in response to an injury. Fibrosis can be a normal connective tissue deposition or excessive tissue deposition caused by a disease.
Repeated injuries, chr ...
, and the menisci can become damaged and wear away. Menisci can be completely absent by the time a person undergoes a joint replacement
Joint replacement is a procedure of orthopedic surgery known also as arthroplasty, in which an arthritic or dysfunctional joint surface is replaced with an orthopedic prosthesis. Joint replacement is considered as a treatment when severe joint pai ...
. New bone outgrowths, called "spurs" or osteophyte
Osteophytes are Exostosis, exostoses (bony projections) that form along joint margins. They are distinct from enthesophytes, which are bone, bony projections that form at the attachment of a tendon or ligament. Osteophytes are not always distingui ...
s, can form on the margins of the joints, possibly in an attempt to improve the congruence of the articular cartilage
Hyaline cartilage is the glass-like (hyaline) and translucent cartilage found on many joint surfaces. It is also most commonly found in the ribs, nose, larynx, and trachea. Hyaline cartilage is pearl-gray in color, with a firm consistency and has ...
surfaces in the absence of the menisci. The subchondral bone volume increases and becomes less mineralized (hypo mineralization). All these changes can cause problems functioning. The pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sense, sensory and emotional experience associated with, or res ...
in an osteoarthritic joint has been related to thickened synovium and to subchondral bone lesions.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made with reasonable certainty based on history and clinical examination.X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
s may confirm the diagnosis. The typical changes seen on X-ray include: joint
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
space narrowing, subchondral sclerosis (increased bone formation around the joint), subchondral cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubb ...
formation, and osteophytes
Osteophytes are exostoses (bony projections) that form along joint margins. They are distinct from enthesophytes, which are bony projections that form at the attachment of a tendon or ligament. Osteophytes are not always distinguished from exost ...
. Plain films may not correlate with the findings on physical examination or with the degree of pain.
In 1990, the American College of Rheumatology
The American College of Rheumatology (ACR; until 1985 called American Rheumatism Association) is an organization of and for physicians, health professionals, and scientists that advances rheumatology through programs of education, research, advocac ...
, using data from a multi-center study, developed a set of criteria for the diagnosis of hand osteoarthritis based on hard tissue enlargement and swelling of certain joints. These criteria were found to be 92% sensitive and 98% specific
Specific may refer to:
* Specificity (disambiguation)
* Specific, a cure or therapy for a specific illness
Law
* Specific deterrence, focussed on an individual
* Specific finding, intermediate verdict used by a jury in determining the final ...
for hand osteoarthritis versus other entities such as rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthropathies.
osteopenia
Osteopenia, known as "low bone mass" or "low bone density", is a condition in which bone mineral density is low. Because their bones are weaker, people with osteopenia may have a higher risk of fractures, and some people may go on to develop o ...
of the carpal joint and 1st carpometacarpal joint
File:Gonarthrose-Knorpelaufbrauch.jpg, MRI of osteoarthritis in the knee, with characteristic narrowing of the joint space
File:Osteoarthritis left knee.jpg, Primary osteoarthritis of the left knee. Note the osteophytes
Osteophytes are exostoses (bony projections) that form along joint margins. They are distinct from enthesophytes, which are bony projections that form at the attachment of a tendon or ligament. Osteophytes are not always distinguished from exost ...
, narrowing of the joint space (arrow), and increased subchondral bone density (arrow).
File:Damaged cartilage Danish sow.png, Damaged cartilage from sows. (a) cartilage erosion (b) cartilage ulceration (c) cartilage repair (d) osteophyte (bone spur) formation.
File:Primary osteoarthrosis (2) at knee joint.jpg, Histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: 'tissue', 'suffering', and '' -logia'' 'study of') is the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopatholog ...
of osteoarthrosis of a knee joint in an elderly female
File:Primary osteoarthrosis (5) at knee joint.jpg, Histopathology of osteoarthrosis of a knee joint in an elderly female
File:Health joint.png, In a healthy joint, the ends of bones are encased in smooth cartilage. Together, they are protected by a joint capsule lined with a synovial membrane that produces synovial fluid
Synovial fluid, also called synovia, elp 1/sup> is a viscous, non-Newtonian fluid found in the cavities of synovial joints. With its egg white–like consistency, the principal role of synovial fluid is to reduce friction between the articul ...
. The capsule and fluid protect the cartilage, muscles, and connective tissues.
File:Joint with severe osteoathritis.png, With osteoarthritis, the cartilage becomes worn away. Spurs grow out from the edge of the bone, and synovial fluid increases. Altogether, the joint feels stiff and sore.
File:Osteoarthritis.png, Osteoarthritis
File:Osteoarthritis -- Smart-Servier (cropped).jpg, Bone (left) and clinical (right) changes of the hand in osteoarthritis
Classification
A number of classification systems are used for gradation of osteoarthritis: *WOMAC
The Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) is a widely used, proprietary set of standardized questionnaires used by health professionals to evaluate the condition of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee and hip ...
scale, taking into account pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sense, sensory and emotional experience associated with, or res ...
, stiffness and functional limitation.
* Kellgren-Lawrence grading scale
Radiographic systems to classify osteoarthritis vary by which joint is being investigated. In osteoarthritis, the choice of treatment is based on pain and decreased function, but radiography can be useful before surgery in order to prepare for the ...
for osteoarthritis of the knee. It uses only projectional radiography
Projectional radiography, also known as conventional radiography, is a form of radiography and medical imaging that produces two-dimensional images by X-ray radiation. The image acquisition is generally performed by radiographers, and the images a ...
features.
* Tönnis classification for osteoarthritis of the hip joint
In vertebrate anatomy, the hip, or coxaLatin ''coxa'' was used by Celsus in the sense "hip", but by Pliny the Elder in the sense "hip bone" (Diab, p 77) (: ''coxae'') in medical terminology, refers to either an anatomical region or a joint o ...
, also using only projectional radiography features.
Both primary generalized nodal osteoarthritis and erosive osteoarthritis (EOA, also called inflammatory osteoarthritis) are sub-sets of primary osteoarthritis. EOA is a much less common, and more aggressive inflammatory form of osteoarthritis which often affects the distal interphalangeal joints of the hand and has characteristic articular erosive changes on X-ray.
Management
 Lifestyle modification (such as weight loss and exercise) and
Lifestyle modification (such as weight loss and exercise) and pain medications
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic, antalgic, pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used for pain management. Analgesics are conceptually distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily reduce, and in so ...
are the mainstays of treatment. Acetaminophen
Paracetamol, or acetaminophen, is a non-opioid analgesic and antipyretic agent used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. It is a widely available over-the-counter drug sold under various brand names, including Tylenol and Panadol.
Parac ...
(also known as paracetamol) is recommended first line, with NSAIDs being used as add-on therapy only if pain relief is not sufficient. Medications that alter the course of the disease have not been found as of 2018. For overweight people, weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat (adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other conn ...
may help relieve pain due to hip arthritis. Recommendations include modification of risk factors through targeted interventions including 1) obesity and overweight, 2) physical activity, 3) dietary exposures, 4) comorbidities, 5) biomechanical factors, 6) occupational factors.
Successful management of the condition is often made more difficult by differing priorities and poor communication between clinicians and people with osteoarthritis. Realistic treatment goals can be achieved by developing a shared understanding of the condition, actively listening to patient concerns, avoiding medical jargon
Jargon, or technical language, is the specialized terminology associated with a particular field or area of activity. Jargon is normally employed in a particular Context (language use), communicative context and may not be well understood outside ...
and tailoring treatment plans to the patient's needs.
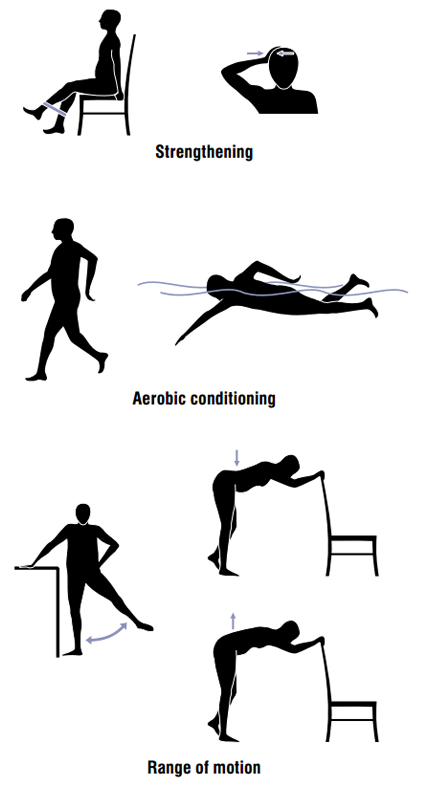
Exercise
Weight loss and exercise provide long-term treatment and are advocated in people with osteoarthritis. Weight loss and exercise are the most safe and effective long-term treatments, in contrast to short-term treatments which usually have risk of long-term harm. High impact exercise can increase the risk of joint injury, whereas low or moderate impact exercise, such as walking or swimming, is safer for people with osteoarthritis. A study has suggested that an increase in blood calcium levels had a positive impact on osteoarthritis. An adequate dietary calcium intake and regular weight-bearing exercise can increase calcium levels and is helpful in preventing osteoarthritis in the general population. There is also a weak protective effect factor of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol. However, this is not recommended since an increase in LDL has an increased chance of cardiovascular comorbidities. Moderate exercise may be beneficial with respect to pain and function in those with osteoarthritis of the knee and hip. These exercises should occur at least three times per week, under supervision, and focused on specific forms of exercise found to be most beneficial for this form of osteoarthritis. While some evidence supports certain physical therapies, evidence for a combined program is limited. Providing clear advice, making exercises enjoyable, and reassuring people about the importance of doing exercises may lead to greater benefit and more participation. Some evidence suggests that supervised exercise therapy may improve exercise adherence, although for knee osteoarthritis supervised exercise has shown the best results.Physical measures
There is not enough evidence to determine the effectiveness ofmassage therapy
Massage is the rubbing or kneading of the body's soft tissues. Massage techniques are commonly applied with hands, fingers, elbows, knees, forearms, feet, or a device. The purpose of massage is generally for the treatment of body stress or pa ...
. The evidence for manual therapy
Manual therapy, or manipulative therapy, is a treatment primarily used by physical therapists, occupational therapists, and massage therapists to treat musculoskeletal pain and disability. It mostly includes kneading and manipulation of muscle ...
is inconclusive. A 2015 review indicated that aquatic therapy is safe, effective, and can be an adjunct therapy for knee osteoarthritis.
Functional, gait, and balance training have been recommended to address impairments of position sense, balance, and strength in individuals with lower extremity arthritis, as these can contribute to a higher rate of falls in older individuals. For people with hand osteoarthritis, exercises may provide small benefits for improving hand function, reducing pain, and relieving finger joint stiffness.
A study showed that there is low quality evidence that weak knee extensor muscle increased the chances of knee osteoarthritis. Strengthening of the knee extensors could possibly prevent knee osteoarthritis.
Lateral wedge insoles and neutral insoles do not appear to be useful in osteoarthritis of the knee. Knee braces may help, but their usefulness has also been disputed. For pain management, heat can be used to relieve stiffness, and cold can relieve muscle spasms and pain. Among people with hip and knee osteoarthritis, exercise in water may reduce pain and disability, and increase quality of life in the short term. Therapeutic exercise programs, such as aerobics and walking, may reduce pain and improve physical functioning for up to 6 months after the end of the program for people with knee osteoarthritis. Hydrotherapy might also be an advantage on the management of pain, disability and quality of life reported by people with osteoarthritis.
Thermotherapy
A 2003Cochrane review
Cochrane is a British international charitable organisation formed to synthesize medical research findings to facilitate evidence-based choices about health interventions involving health professionals, patients and policy makers. It includes ...
of 7 studies between 1969 and 1999 found ice massage to be of significant benefit in improving range of motion and function, though not necessarily relief of pain. Cold packs could decrease swelling, but hot packs had no effect on swelling. Heat therapy could increase circulation, thereby reducing pain and stiffness, but with risk of inflammation and edema.
Medication
By mouth
Thepain medication
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic, antalgic, pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used for pain management. Analgesics are conceptually distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily reduce, and in so ...
paracetamol
Paracetamol, or acetaminophen, is a non-opioid analgesic and antipyretic agent used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. It is a widely available over-the-counter drug sold under various brand names, including Tylenol and Panadol.
Parac ...
(acetaminophen) is the first line treatment for osteoarthritis. Pain relief does not differ according to dosage. However, a 2015 review found acetaminophen to have only a small short-term benefit with some concerns on abnormal results for liver function test
Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel or liver panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial ...
. For mild to moderate symptoms effectiveness of acetaminophen is similar to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
s (NSAIDs) such as naproxen
Naproxen, sold under the brand name Aleve among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain, menstrual cramps, and inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout and fever. It is taken orally. It ...
, though for more severe symptoms NSAIDs may be more effective. NSAIDs are associated with greater side effects such as gastrointestinal bleeding
Gastrointestinal bleeding (GI bleed), also called gastrointestinal hemorrhage (GIB), is all forms of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the rectum. When there is significant blood loss over a short time, symptoms may includ ...
.
Another class of NSAIDs, COX-2 selective inhibitor
Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors (COX-2 inhibitors), also known as coxibs, are a type of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that directly target cyclooxygenase-2 ( COX-2), an enzyme responsible for inflammation and pain. Targeting selectivit ...
s (such as celecoxib
Celecoxib, sold under the brand name Celebrex among others, is a COX-2 inhibitor and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is used to treat the pain and inflammation in osteoarthritis, acute pain in adults, rheumatoid arthritis, psor ...
) are equally effective when compared to nonselective NSAIDs, and have lower rates of adverse gastrointestinal effects, but higher rates of cardiovascular disease such as myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
. They are also more expensive than non-specific NSAIDs. Benefits and risks vary in individuals and need consideration when making treatment decisions, and further unbiased research comparing NSAIDS and COX-2 selective inhibitors is needed. NSAIDS applied topically are effective for a small number of people. The COX-2 selective inhibitor rofecoxib
Rofecoxib is a COX-2-selective nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It was marketed by Merck & Co. to treat osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, acute pain conditions, migraine, and dysmenorrhea. Rofecoxib ...
was removed from the market in 2004, as cardiovascular events were associated with long term use.
Education is helpful in self-management of arthritis, and can provide coping methods leading to about 20% more pain relief when compared to NSAIDs alone.
Failure to achieve desired pain relief in osteoarthritis after two weeks should trigger reassessment of dosage and pain medication. Opioids
Opioids are a class of Drug, drugs that derive from, or mimic, natural substances found in the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy plant. Opioids work on opioid receptors in the brain and other organs to produce a variety of morphine-like effects, ...
by mouth, including both weak opioids such as tramadol
Tramadol, sold under the brand name Tramal among others, is an opioid analgesic, pain medication and a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) used to treat moderately severe pain. When taken by mouth in an immediate-release form ...
and stronger opioids, are also often prescribed. Their appropriateness is uncertain, and opioids are often recommended only when first line therapies have failed or are contraindicated. This is due to their small benefit and relatively large risk of side effects. The use of tramadol likely does not improve pain or physical function and likely increases the incidence of adverse side effects. Oral steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes t ...
s are not recommended in the treatment of osteoarthritis.
Use of the antibiotic doxycycline
Doxycycline is a Broad-spectrum antibiotic, broad-spectrum antibiotic of the Tetracycline antibiotics, tetracycline class used in the treatment of infections caused by bacteria and certain parasites. It is used to treat pneumonia, bacterial p ...
orally for treating osteoarthritis is not associated with clinical improvements in function or joint pain. Any small benefit related to the potential for doxycycline therapy to address the narrowing of the joint space is not clear, and any benefit is outweighed by the potential harm from side effects.
A 2018 meta-analysis found that oral collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a trip ...
supplementation for the treatment of osteoarthritis reduces stiffness but does not improve pain and functional limitation.
Topical
There are several NSAIDs available fortopical
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes ...
use, including diclofenac
Diclofenac, sold under the brand name Voltaren among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain and inflammatory diseases such as gout. It can be taken orally (swallowed by mouth), inserted rectally as a ...
. A Cochrane review from 2016 concluded that reasonably reliable evidence is available only for use of topical diclofenac and ketoprofen in people aged over 40 years with painful knee arthritis. Transdermal opioid pain medications are not typically recommended in the treatment of osteoarthritis. The use of topical
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes ...
capsaicin
Capsaicin (8-methyl-''N''-vanillyl-6-nonenamide) (, rarely ) is an active component of chili peppers, which are plants belonging to the genus ''Capsicum''. It is a potent Irritation, irritant for Mammal, mammals, including humans, and produces ...
to treat osteoarthritis is controversial, as some reviews found benefit while others did not.
Joint injections
 Use of analgesia, intra-articular cortisone injection and consideration of hyaluronic acids and platelet-rich plasma are recommended for pain relief in people with knee osteoarthritis.
Local drug delivery by intra-articular injection may be more effective and safer in terms of increased bioavailability, less systemic exposure and reduced adverse events. Several intra-articular medications for symptomatic treatment are available on the market as follows.
Use of analgesia, intra-articular cortisone injection and consideration of hyaluronic acids and platelet-rich plasma are recommended for pain relief in people with knee osteoarthritis.
Local drug delivery by intra-articular injection may be more effective and safer in terms of increased bioavailability, less systemic exposure and reduced adverse events. Several intra-articular medications for symptomatic treatment are available on the market as follows.
= Steroids
=Joint injection
In medicine, a joint injection (intra-articular injection) is a procedure used in the treatment of inflammatory joint conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, gout, tendinitis, bursitis, Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, and occasion ...
of glucocorticoids (such as hydrocortisone
Hydrocortisone is the name for the hormone cortisol when supplied as a medication. It is a corticosteroid and works as an anti-inflammatory and by immune suppression. Uses include conditions such as adrenocortical insufficiency, adrenogenit ...
) leads to short-term pain relief that may last between a few weeks and a few months.
A 2015 Cochrane review found that intra-articular corticosteroid injections of the knee did not benefit quality of life and had no effect on knee joint space; clinical effects one to six weeks after injection could not be determined clearly due to poor study quality. Another 2015 study reported negative effects of intra-articular corticosteroid injections at higher doses, and a 2017 trial showed reduction in cartilage thickness with intra-articular triamcinolone
Triamcinolone is a glucocorticoid used to treat certain skin diseases, allergies, and rheumatic disorders among others. It is also used to prevent worsening of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It can be taken in variou ...
every 12 weeks for 2 years compared to placebo. A 2018 study found that intra-articular triamcinolone is associated with an increase in intraocular pressure
Intraocular pressure (IOP) is the fluid pressure inside the eye. Tonometry is the method eye care professionals use to determine this. IOP is an important aspect in the evaluation of patients at risk of glaucoma. Most tonometers are calibrated t ...
.
= Hyaluronic acid
= Injections ofhyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid (; abbreviated HA; conjugate base hyaluronate), also called hyaluronan, is an anionic, nonsulfated glycosaminoglycan distributed widely throughout connective, epithelial, and neural tissues. It is unique among glycosaminog ...
have not produced improvement compared to placebo for knee arthritis, but did increase risk of further pain. In ankle osteoarthritis, evidence is unclear.
= Platelet-rich plasma
= The effectiveness of injections ofplatelet-rich plasma
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP), also known as autologous conditioned plasma, is a concentrate of plasma protein derived from whole blood, centrifuged to remove red blood cells but retaining platelets. Though promoted for treating various medical con ...
(PRP) is unclear; there are suggestions that such injections improve function but not pain, and are associated with increased risk. A 2014 Cochrane review of studies involving PRP found the evidence to be insufficient.
= Radiosynoviorthesis
= Injection ofbeta particle
A beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation (symbol β), is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus, known as beta decay. There are two forms of beta decay, β− decay and � ...
-emitting radioisotope
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess numbers of either neutrons or protons, giving it excess nuclear energy, and making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ...
s (called ''radiosynoviorthesis'') is used for the local treatment of inflammatory joint conditions.
Radiotherapy
Low-dose radiotherapy has been shown to improve pain and mobility of affected joints, primarily in extremities. It is approximately 70-90% effective, with minimal side effects.Ablation of knee sensory nerves
Radiofrequency ablation
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA), also called fulguration, is a medical procedure in which part of the electrical conduction system of the heart, tumor, sensory nerves or a dysfunctional tissue is ablated using the heat generated from medium fre ...
of sensory knee nerves, also called ''genicular neurotomy'' or ''genicular RFA'', is an outpatient
A patient is any recipient of health care services that are performed by healthcare professionals. The patient is most often ill or injured and in need of treatment by a physician, nurse, optometrist, dentist, veterinarian, or other healt ...
procedure used to reduce pain from knee osteoarthritis.
In the procedure for genicular RFA, a guide cannula is first directed under local anesthesia and imaging (ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
or fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy (), informally referred to as "fluoro", is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope () allows a surgeon to see t ...
) to each target genicular nerve, then the radiofrequency electrode is passed through the cannula, and the electrode tip is heated to about for one minute to cauterize a small segment of the nerve. The heat destroys that segment of the nerve, which is prevented from sending pain signals to the brain.
As of 2023, reviews of clinical outcomes indicated that efficacy for reducing knee pain was achieved by ablating three or more branches of the genicular nerve (one of the articular
The articular bone is part of the lower jaw of most vertebrates, including most jawed fish, amphibians, birds and various kinds of reptiles, as well as ancestral mammals.
Anatomy
In most vertebrates, the articular bone is connected to two o ...
branches of the tibial nerve
The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.
Structure Popliteal fossa
The tibial nerve is the larger terminal branch of the sciatic nerve with root val ...
). Other sources indicate 4-5 genicular nerve targets may be justified for ablation to optimize pain relief, while a 2022 analysis indicated that as many as 10 genicular nerve targets for RFA would produce better long-term relief of knee pain.
Knee pain relief of 50% or more following genicular RFA may last from several months to two years, and can be repeated by the same outpatient procedure when pain recurs.
Injection of phenol
Phenol (also known as carbolic acid, phenolic acid, or benzenol) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile and can catch fire.
The molecule consists of a phenyl group () ...
may be used as a neurolytic treatment of sensory knee nerves to relieve chronic pain from knee osteoarthritis.
Surgery
Bone fusion
Arthrodesis
Arthrodesis, also known as artificial ankylosis or syndesis, is the artificial induction of joint ossification between two bones by surgery. This is done to relieve intractable pain in a joint which cannot be managed by pain medication, splin ...
(fusion) of the bones may be an option in some types of osteoarthritis. An example is ankle osteoarthritis, in which ankle fusion
Ankle fusion, or ankle arthrodesis, is surgery of the ankle to fuse the bones to treat arthritis and for other purposes. There are different types of ankle fusion surgery. The surgery involves the use of screws, plates, medical nails, and other har ...
is considered to be the gold standard treatment in end-stage cases.
Joint replacement
If the impact of symptoms of osteoarthritis on quality of life is significant and more conservative management is ineffective, joint replacement surgery or resurfacing may be recommended. Evidence supports joint replacement for both knees and hips as it is both clinically effective and cost-effective. People who underwent total knee replacement had improved SF-12 quality of life scores, were feeling better compared to those who did not have surgery, and may have short- and long-term benefits for quality of life in terms of pain and function. The beneficial effects of these surgeries may be time-limited due to various environmental factors, comorbidities, and pain in other regions of the body. For people who have shoulder osteoarthritis and do not respond to medications, surgical options include a shoulder hemiarthroplasty (replacing a part of the joint), and total shoulder arthroplasty (replacing the joint). Biological joint replacement involves replacing the diseased tissues with new ones. This can either be from the person (autograft) or from a donor (allograft). People undergoing a joint transplant (osteochondral allograft) do not need to takeimmunosuppressants
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent the activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified ...
as bone and cartilage tissues have limited immune responses. Autologous articular cartilage transfer from a non-weight-bearing area to the damaged area, called osteochondral autograft transfer system, is one possible procedure that is being studied. When the missing cartilage is a focal defect, autologous chondrocyte implantation
Autologous chondrocyte implantation (ACI, ATC code ) is a biomedical treatment that repairs damages in articular cartilage. ACI provides pain relief while at the same time slowing down the progression or considerably delaying partial or total jo ...
is also an option.
Shoulder replacement
For those with osteoarthritis in the shoulder, a complete shoulder replacement is sometimes suggested to improve pain and function. Demand for this treatment is expected to increase by 750% by the year 2030. There are different options for shoulder replacement surgeries, however, there is a lack of evidence in the form of high-quality randomized controlled trials, to determine which type of shoulder replacement surgery is most effective in different situations, what are the risks involved with different approaches, or how the procedure compares to other treatment options. There is some low-quality evidence that indicates that when comparing total shoulder arthroplasty over hemiarthroplasty, no large clinical benefit was detected in the short term. It is not clear if the risk of harm differs between total shoulder arthroplasty or a hemiarthroplasty approach.Other surgical options
Osteotomy
An osteotomy is a surgical operation whereby a bone is cut to shorten or lengthen it or to change its alignment. It is sometimes performed to correct a hallux valgus, or to straighten a bone that has healed crookedly following a fracture. It i ...
may be useful in people with knee osteoarthritis, but has not been well studied and it is unclear whether it is more effective than non-surgical treatments or other types of surgery. Arthroscopic surgery
Arthroscopy (also called arthroscopic or keyhole surgery) is a minimally invasive surgery, surgical procedure on a joint in which an examination and sometimes treatment of damage is performed using an arthroscope, an endoscope that is inserted in ...
is largely not recommended, as it does not improve outcomes in knee osteoarthritis, and may result in harm. It is unclear whether surgery is beneficial in people with mild to moderate knee osteoarthritis.
Unverified treatments
Glucosamine and chondroitin
The effectiveness ofglucosamine
Glucosamine (C6H13NO5) is an amino sugar and a prominent precursor in the biochemical synthesis of glycosylated proteins and lipids. Glucosamine is part of the structure of two polysaccharides, chitosan and chitin. Glucosamine is one of the mo ...
is controversial. Reviews have found it to be equal to or slightly better than placebo
A placebo ( ) can be roughly defined as a sham medical treatment. Common placebos include inert tablets (like sugar pills), inert injections (like saline), sham surgery, and other procedures.
Placebos are used in randomized clinical trials ...
. A difference may exist between glucosamine sulfate and glucosamine hydrochloride, with glucosamine sulfate showing a benefit and glucosamine hydrochloride not. The evidence for glucosamine sulfate having an effect on osteoarthritis progression is somewhat unclear and if present likely modest. The Osteoarthritis Research Society International recommends that glucosamine be discontinued if no effect is observed after six months and the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care (United Kingdom), Department of Health and Social Care.
As the national health technolog ...
no longer recommends its use. Despite the difficulty in determining the efficacy of glucosamine, it remains a treatment option. The European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis (ESCEO) recommends glucosamine sulfate and chondroitin sulfate for knee osteoarthritis. Its use as a therapy for osteoarthritis is usually safe.
A 2015 Cochrane review of clinical trials of chondroitin
A chondroitin is a chondrin derivative.
Types include:
* Chondroitin sulfate
* Dermatan sulfate
Chondroitin as a supplement is now commonly used (often in combination with glucosamine) in treating the joint disease of osteoarthritis. In contra ...
found that most were of low quality, but that there was some evidence of short-term improvement in pain and few side effects; it does not appear to improve or maintain the health of affected joints.
Supplements
Avocado–soybean unsaponifiables (ASU) is an extract made fromavocado oil
Avocado oil is an edible oil extracted from the pulp of avocados, the fruit of ''Persea americana''. It is used as an edible oil both raw and for cooking, where it is noted for its high smoke point. It is also used for lubrication and in cosmetic ...
and soybean oil
Soybean oil (British English: soyabean oil) is a vegetable oil extracted from soybean (''Glycine max'') legumes. It is one of the most widely consumed cooking oils and the second most consumed vegetable oil. As a drying oil, processed soybean oil ...
sold under many brand name
A brand is a name, term, design, symbol or any other feature that distinguishes one seller's goods or service from those of other sellers. Brands are used in business, marketing, and advertising for recognition and, importantly, to create and ...
s worldwide as a dietary supplement
A dietary supplement is a manufactured product intended to supplement a person's diet by taking a pill (pharmacy), pill, capsule (pharmacy), capsule, tablet (pharmacy), tablet, powder, or liquid. A supplement can provide nutrients eithe ...
and as a prescription drug
A prescription drug (also prescription medication, prescription medicine or prescription-only medication) is a pharmaceutical drug that is permitted to be dispensed only to those with a medical prescription. In contrast, over-the-counter drugs c ...
in France. A 2014 Cochrane review found that while ASU might help relieve pain in the short term for some people with osteoarthritis, it does not appear to improve or maintain the health of affected joints. The review noted a high-quality, two-year clinical trial comparing ASU to chondroitin
A chondroitin is a chondrin derivative.
Types include:
* Chondroitin sulfate
* Dermatan sulfate
Chondroitin as a supplement is now commonly used (often in combination with glucosamine) in treating the joint disease of osteoarthritis. In contra ...
which has uncertain efficacy in osteoarthritis with no difference between the two agents. The review also found there is insufficient evidence of ASU safety.
A few high-quality studies of ''Boswellia serrata
''Boswellia serrata'' is a plant that produces Indian frankincense. The plant is native to much of India and the Punjab region that extends into Pakistan.
Sustainability
''Boswellia serrata'' is currently at risk of being eradicated because of n ...
'' show consistent, but small, improvements in pain and function. Curcumin
Curcumin is a bright yellow chemical produced by plants of the ''Curcuma longa'' species. It is the principal curcuminoid of turmeric (''Curcuma longa''), a member of the ginger family, Zingiberaceae. It is sold as a herbal supplement, cosmetic ...
, phytodolor, and s-adenosyl methionine
''S''-Adenosyl methionine (SAM), also known under the commercial names of SAMe, SAM-e, or AdoMet, is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation. Although these anabolic reactions occur thro ...
(SAMe) may be effective in improving pain. A 2009 Cochrane review recommended against the routine use of SAMe, as there has not been sufficient high-quality clinical research
Clinical research is a branch of medical research that involves people and aims to determine the effectiveness (efficacy) and safety of medications, devices, diagnostic products, and treatment regimens intended for improving human health. The ...
to prove its effect. A 2021 review found that hydroxychloroquine
Hydroxychloroquine, sold under the brand name Plaquenil among others, is a medication used to prevent and treat malaria in areas where malaria remains sensitive to chloroquine. Other uses include treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, an ...
(HCQ) had no benefit in reducing pain and improving physical function in hand or knee osteoarthritis, and the off-label use of HCQ for people with osteoarthritis should be discouraged. There is no evidence for the use of colchicine
Colchicine is a medication used to prevent and treat gout, to treat familial Mediterranean fever and Behçet's disease, and to reduce the risk of myocardial infarction. The American College of Rheumatology recommends colchicine, nonstero ...
for treating the pain of hand or knee arthritis.
There is limited evidence to support the use of hyaluronan, methylsulfonylmethane, rose hip, capsaicin
Capsaicin (8-methyl-''N''-vanillyl-6-nonenamide) (, rarely ) is an active component of chili peppers, which are plants belonging to the genus ''Capsicum''. It is a potent Irritation, irritant for Mammal, mammals, including humans, and produces ...
, or vitamin D.
Acupuncture and other interventions
While acupuncture leads to improvements in pain relief, this improvement is small and may be of questionable importance. Waiting list–controlled trials for peripheral joint osteoarthritis do show clinically relevant benefits, but these may be due to placebo effects. Acupuncture does not seem to produce long-term benefits. Electrostimulation techniques such as TENS have been used for twenty years to treat osteoarthritis in the knee. However, there is no conclusive evidence to show that it reduces pain or disability. ACochrane review
Cochrane is a British international charitable organisation formed to synthesize medical research findings to facilitate evidence-based choices about health interventions involving health professionals, patients and policy makers. It includes ...
of low-level laser therapy found unclear evidence of benefit, whereas another review found short-term pain relief for osteoarthritic knees.
Further research is needed to determine if Balneotherapy, balnotherapy for osteoarthritis (mineral baths or spa treatments) improves a person's quality of life or ability to function. The use of ice or cold packs may be beneficial; however, further research is needed. There is no evidence of benefit from placing hot packs on joints.
There is low quality evidence that therapeutic ultrasound may be beneficial for people with osteoarthritis of the knee; however, further research is needed to confirm and determine the degree and significance of this potential benefit.
Therapeutic ultrasound is safe and helps reducing pain and improving physical function for knee osteoarthritis.
While phonophoresis does not improve functions, it may offer greater pain relief than standard non-drug ultrasound.
Continuous and pulsed ultrasound modes (especially 1 MHz, 2.5 W/cm2, 15min/ session, 3 session/ week, during 8 weeks protocol) may be effective in improving patients physical function and pain.
There is weak evidence suggesting that Electromagnetic field therapy, electromagnetic field treatment may result in moderate pain relief; however, further research is necessary and it is not known if electromagnetic field treatment can improve quality of life or function.
Hyaluronic acid, Viscosupplementation for osteoarthritis of the knee may have positive effects on pain and function at 5 to 13 weeks post-injection.
Epidemiology
Middle East and North Africa (MENA)
In the Middle East and North Africa from 1990 to 2019, the prevalence of people with hip osteoarthritis increased threefold over the three decades, a total of 1.28 million cases. It increased 2.88-fold, from 6.16 million cases to 17.75 million, between 1990 and 2019 for knee osteoarthritis. Hand osteoarthritis in MENA also increased 2.7-fold, from 1.6 million cases to 4.3 million from 1990 to 2019.United States
, osteoarthritis affected 52.5 million people in the United States, approximately 50% of whom were 65 years or older. It is estimated that 80% of the population have radiographic evidence of osteoarthritis by age 65, although only 60% of those will have symptoms. The rate of osteoarthritis in the United States is forecast to be 78 million (26%) adults by 2040. In the United States, there were approximately 964,000 hospitalizations for osteoarthritis in 2011, a rate of 31 stays per 10,000 population. With an aggregate cost of $14.8 billion ($15,400 per stay), it was the second-most expensive condition seen in US hospital stays in 2011. By payer, it was the second-most costly condition billed to Medicare and private insurance.Europe
In Europe, the number of individuals affected by osteoarthritis has increased from 27.9 million in 1990 to 50.8 million in 2019. Hand osteoarthritis was the second most prevalent type, affecting an estimated 12.5 million people. In 2019, 'Knee osteoarthritis
'' was the 18th most common cause of years lived with disability (YLDs) in Europe, accounting for 1.28% of all YLDs. This has increased from 1.12% in 1990.
India
In India, the number of individuals affected by osteoarthritis has increased from 23.46 million in 1990 to 62.35 million in 2019. Knee osteoarthritis was the most prevalent type of osteoarthritis, followed by hand osteoarthritis. In 2019, osteoarthritis was the 20th most common cause of years lived with disability (YLDs) in India, accounting for 1.48% of all YLDs, which increased from 1.25% and 23rd most common cause in 1990.History
Etymology
Osteoarthritis is derived from the prefix ''wikt:osteo-#English, osteo-'' (from ) combined with ''arthritis'' (from , , ), which is itself derived from ''wikt:arthr-, arthr-'' (from , , ) and ''wikt:-itis#English, -itis'' (from , , ), the latter suffix having come to be associated with inflammation. The ''-itis'' of osteoarthritis could be considered misleading as inflammation is not a conspicuous feature. Some clinicians refer to this condition as ''osteoarthrosis'' to signify the lack of inflammatory response, the suffix ''wikt:-osis#English, -osis'' (from , , ) simply referring to the pathosis itself.Other animals
Osteoarthritis has been reported in several species of animals all over the world, including marine animals and even some fossils; including but not limited to: cats, many rodents, cattle, deer, rabbits, sheep, camels, elephants, buffalo, hyena, lions, mules, pigs, tigers, kangaroos, dolphins, dugong, and horses. Osteoarthritis has been reported in fossils of the large carnivorous dinosaur ''Allosaurus fragilis''.Research
Therapies
Pharmaceutical agents that will alter the natural history of disease progression by arresting joint structural change and ameliorating symptoms are termed as Disease-modifying treatment, disease modifying therapy. Therapies under investigation include the following: * Strontium ranelate – may decrease degeneration in osteoarthritis and improve outcomes * Gene therapy – Gene therapy for osteoarthritis, Gene transfer strategies aim to target the disease process rather than the symptoms. Cell-mediated gene therapy is also being studied. One version was approved in South Korea for the treatment of moderate knee osteoarthritis, but later revoked for the mislabeling and the false reporting of an ingredient used. The drug was administered Joint injection, intra-articularly.Cause
As well as attempting to find disease-modifying agents for osteoarthritis, there is emerging evidence that a system-based approach is necessary to find the causes of osteoarthritis. A study conducted by scientists at the University of Twente found that osmolarity induced intracellular molecular crowding might drive the disease pathology.Diagnostic biomarkers
Guidelines outlining requirements for inclusion of soluble biomarkers in osteoarthritis clinical trials were published in 2015, but there are no validated biomarkers used clinically to detect osteoarthritis, as of 2021. A 2015 systematic review of biomarkers for osteoarthritis looking for molecules that could be used for risk assessments found 37 different biochemical markers ofbone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
and cartilage turnover in 25 publications. The strongest evidence was for urinary C-terminal telopeptide of type II collagen (uCTX-II) as a prognostic marker for knee osteoarthritis progression, and serum cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) levels as a prognostic marker for incidence of both knee and hip osteoarthritis. A review of biomarkers in hip osteoarthritis also found associations with uCTX-II. Procollagen type II C-terminal propeptide (PIICP) levels reflect type II collagen synthesis in body and within joint fluid PIICP levels can be used as a prognostic marker for early osteoarthritis.
References
External links
* {{Authority control Arthritis Skeletal disorders Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate