Art of the Upper Paleolithic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The art of the Upper Paleolithic represents the oldest form of
 Art of the European Upper Paleolithic includes rock and
Art of the European Upper Paleolithic includes rock and
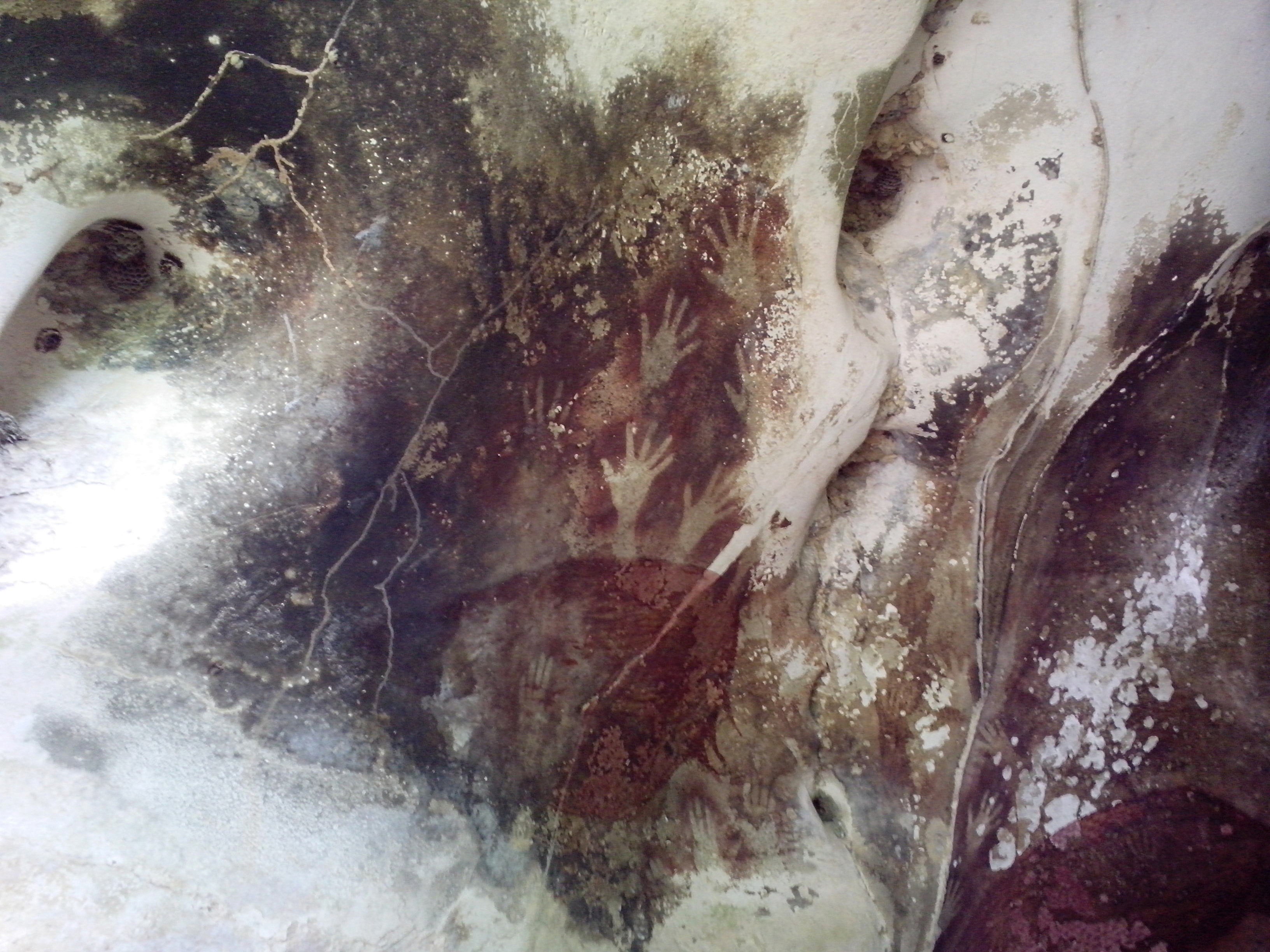 Cave paintings from the Indonesian island of
Cave paintings from the Indonesian island of

 The oldest known figurative art from
The oldest known figurative art from
EuroPreArt Database of European Prehistoric Art
Human Timeline (Interactive)
– Smithsonian,
Image Database Paleolithic art in Northern Spain
{{portal bar, Evolutionary biology
prehistoric art
In the history of art, prehistoric art is all art produced in preliterate, Prehistory, prehistorical cultures beginning somewhere in very late geological history, and generally continuing until that culture either develops writing or other met ...
. Figurative art
Figurative art, sometimes written as figurativism, describes artwork (particularly paintings and sculptures) that is clearly derived from real object sources and so is, by definition, representational. The term is often in contrast to abstract a ...
is present in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
, beginning around 50,000 years ago. Non-figurative cave painting
In archaeology, cave paintings are a type of parietal art (which category also includes petroglyphs, or engravings), found on the wall or ceilings of caves. The term usually implies prehistoric art, prehistoric origin. These paintings were often c ...
s, consisting of hand stencils and simple geometric shapes, are somewhat older, at least 40,000 years old, and possibly as old as 64,000 years. This latter estimate is due to a controversial 2018 study based on uranium-thorium dating, which would imply Neanderthal
Neanderthals ( ; ''Homo neanderthalensis'' or sometimes ''H. sapiens neanderthalensis'') are an extinction, extinct group of archaic humans who inhabited Europe and Western and Central Asia during the Middle Pleistocene, Middle to Late Plei ...
authorship and qualify as art of the Middle Paleolithic.
"we present dating results for three sites in Spain that show that cave art emerged in Iberia substantially earlier than previously thought. Uranium-thorium (U-Th) dates on carbonate crusts overlying paintings provide minimum ages for a red linear motif in La Pasiega (Cantabria), a hand stencil in Maltravieso (Extremadura), and red-painted speleothems in Ardales (Andalucía). Collectively, these results show that cave art in Iberia is older than 64.8 thousand years (ka). This cave art is the earliest dated so far and predates, by at least 20 ka, the arrival of modern humans in Europe, which implies Neandertal authorship."
The emergence of figurative art has been interpreted as reflecting the emergence of full behavioral modernity
Behavioral modernity is a suite of behavioral and cognitive traits believed to distinguish current ''Homo sapiens'' from other anatomically modern humans, hominins, and primates. Most scholars agree that modern human behavior can be characteri ...
, and is part of the defining characteristics separating the Upper Paleolithic from the Middle Paleolithic
The Middle Paleolithic (or Middle Palaeolithic) is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle P ...
. The discovery of cave art of comparable age to the oldest European samples in Indonesia has established that similar artistic traditions existed both in eastern and in western Eurasia 40,000 years ago. This has been taken to suggest an artistic tradition dating to more than 50,000 years ago, spread along the southern coast of Eurasia in the original coastal migration movement.M. Aubert et al. (2014): "two figurative animal depictions from seven cave sites in the Maros karsts of Sulawesi, we show that rock art traditions on this Indonesian island are at least compatible in age with the oldest European art. ..Among the implications, it can now be demonstrated that humans were producing rock art by ~40 kyr ago at opposite ends of the Pleistocene Eurasian world." In 2018, the discovery of a figurative painting of an unknown animal was announced; it was over 40,000 years old, and was found in a cave on the Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
n island of Borneo
Borneo () is the List of islands by area, third-largest island in the world, with an area of , and population of 23,053,723 (2020 national censuses). Situated at the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, it is one of the Greater Sunda ...
. In July 2021, scientists reported the discovery of a bone carving
file:Alaska Grasendes Karibu c1910 Linden-Museum.jpg, Grazing caribou made in Alaska 1910 - Linden Museum
Bone carving is creating art, tools, and other goods by carving bone, animal bones, antlers, and horn (anatomy), horns. It can result in ...
, one of the world's oldest works of art, made by Neanderthal
Neanderthals ( ; ''Homo neanderthalensis'' or sometimes ''H. sapiens neanderthalensis'') are an extinction, extinct group of archaic humans who inhabited Europe and Western and Central Asia during the Middle Pleistocene, Middle to Late Plei ...
s about 51,000 years ago. On July 3, 2024, the journal ''Nature
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the Ecosphere (planetary), ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the Scientific law, laws, elements and phenomenon, phenomena of the physic ...
'' published research findings indicating that the cave paintings, which depict anthropomorphic
Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human traits, emotions, or intentions to non-human entities. It is considered to be an innate tendency of human psychology. Personification is the related attribution of human form and characteristics to ...
figures interacting with a pig and measure 36 by 15 inches, in Leang Karampuang are approximately 51,200 years old.
European Upper Paleolithic art is known informally as "Ice Age art", in reference to the last glacial period.
Europe
 Art of the European Upper Paleolithic includes rock and
Art of the European Upper Paleolithic includes rock and cave painting
In archaeology, cave paintings are a type of parietal art (which category also includes petroglyphs, or engravings), found on the wall or ceilings of caves. The term usually implies prehistoric art, prehistoric origin. These paintings were often c ...
, jewelry
Jewellery (or jewelry in American English) consists of decorative items worn for personal adornment such as brooches, ring (jewellery), rings, necklaces, earrings, pendants, bracelets, and cufflinks. Jewellery may be attached to the body or the ...
, drawing, carving, engraving and sculpture in clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impuriti ...
, bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
, antler, stone and ivory, such as the Venus figurines
A Venus figurine is any Upper Palaeolithic statue portraying a woman, usually carved in the round.Fagan, Brian M., Beck, Charlotte, "Venus Figurines", beliefs '' The Oxford Companion to Archaeology'', 1996, Oxford University Press, pp. 740– ...
, and musical instruments
A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person who pl ...
such as flutes
The flute is a member of a family of musical instruments in the woodwind group. Like all woodwinds, flutes are aerophones, producing sound with a vibrating column of air. Flutes produce sound when the player's air flows across an opening. In th ...
.
Decoration was also made on functional tools, such as spear throwers, perforated batons and lamps.
Engraving
Engraving is the practice of incising a design on a hard, usually flat surface by cutting grooves into it with a Burin (engraving), burin. The result may be a decorated object in itself, as when silver, gold, steel, or Glass engraving, glass ar ...
s on flat pieces of stones are found in considerable numbers (up to 5,000 at one Spanish site) at sites with the appropriate geology, with the marks sometimes so shallow and faint that the technique involved is closer to drawing
Drawing is a Visual arts, visual art that uses an instrument to mark paper or another two-dimensional surface, or a digital representation of such. Traditionally, the instruments used to make a drawing include pencils, crayons, and ink pens, some ...
– many of these were not spotted by the earliest excavators, and found by later teams in spoil heaps. Painted plaques are less common. It is possible that they were used in rituals, or alternatively heated on a fire and wrapped as personal warmers. Either type of use may account for the many broken examples, often with the fragments dispersed over some distance (up to 30 metres apart at Gönnersdorf). Many sites have large quantities of flat stones apparently used as flooring, with only a minority decorated.
Some of the oldest works of art were found in the Swabian Jura
The Swabian Jura ( , more rarely ), sometimes also named Swabian Alps in English, is a mountain range in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, extending from southwest to northeast and in width. It is named after the region of Swabia. It is part of th ...
, in Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg ( ; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a states of Germany, German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million i ...
, Germany. The Venus figurine
A Venus figurine is any Upper Palaeolithic statue portraying a woman, usually carved in the round.Fagan, Brian M., Beck, Charlotte, "Venus Figurines", beliefs '' The Oxford Companion to Archaeology'', 1996, Oxford University Press, pp. 740–7 ...
known as the Venus of Hohle Fels
The Venus of Hohle Fels (also known as the Venus of Schelklingen; in German variously ') is an Upper Paleolithic Venus figurine made of mammoth ivory that was unearthed in 2008 in Hohle Fels, a cave near Schelklingen, Germany, part of the Ca ...
and the Löwenmensch (Lion-Human) statuette of Hohlenstein-Stadel both date to approximately 40,000 years ago. The so-called Adorant from the Geißenklösterle cave dates to about the same time.
Other fine examples of art from the Upper Palaeolithic (broadly 40,000 to 10,000 years ago) include cave painting
In archaeology, cave paintings are a type of parietal art (which category also includes petroglyphs, or engravings), found on the wall or ceilings of caves. The term usually implies prehistoric art, prehistoric origin. These paintings were often c ...
(such as at Chauvet, Lascaux
Lascaux ( , ; , "Lascaux Cave") is a network of caves near the village of Montignac, Dordogne, Montignac, in the Departments of France, department of Dordogne in southwestern France. Over 600 Parietal art, parietal cave painting, wall paintin ...
, Altamira, Cosquer, and Pech Merle
Pech Merle is a French hillside cave at Cabrerets, in the Lot département of the Occitania
Occitania is the historical region in Southern Europe where the Occitan language was historically spoken and where it is sometimes used as a se ...
), incised / engraved cave art such as at Creswell Crags
Creswell Crags is an enclosed limestone gorge on the border between Derbyshire and Nottinghamshire, England, near the villages of Creswell and Whitwell. The cliffs in the ravine contain several caves that were occupied during the last ice age ...
, portable art (such as animal carvings and sculptures like the Venus of Willendorf
The Venus of Willendorf is an Venus figurine estimated to have been made years ago. It was recovered on 7 August 1908 from an archaeological dig conducted by Josef Szombathy, Hugo Obermaier, and Josef Bayer at a Paleolithic site near Willendorf ...
), and open-air art (such as the rock art of the Côa Valley and in Portugal; Domingo García and Siega Verde in Spain; and in France). There are numerous carved or engraved pieces of bone and ivory, such as the Swimming Reindeer found in France from the Magdalenian
Magdalenian cultures (also Madelenian; ) are later cultures of the Upper Paleolithic and Mesolithic in western Europe. They date from around 17,000 to 12,000 years before present. It is named after the type site of Abri de la Madeleine, a ro ...
period. These include spear throwers, including one shaped like a mammoth, and many of the type of objects called a bâton de commandement.
The animals depicted are prey sought by the Paleolithic hunters,
such as reindeer
The reindeer or caribou (''Rangifer tarandus'') is a species of deer with circumpolar distribution, native to Arctic, subarctic, tundra, taiga, boreal, and mountainous regions of Northern Europe, Siberia, and North America. It is the only re ...
,
horses
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 milli ...
,
bison
A bison (: bison) is a large bovine in the genus ''Bison'' (from Greek, meaning 'wild ox') within the tribe Bovini. Two extant taxon, extant and numerous extinction, extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American ...
s,
mammoth
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus.'' They lived from the late Miocene epoch (from around 6.2 million years ago) into the Holocene until about 4,000 years ago, with mammoth species at various times inhabi ...
,
the woolly rhinoceros
The woolly rhinoceros (''Coelodonta antiquitatis'') is an extinct species of rhinoceros that inhabited northern Eurasia during the Pleistocene epoch. The woolly rhinoceros was a member of the Pleistocene megafauna. The woolly rhinoceros was larg ...
,
and birds,
as well as apex predator
An apex predator, also known as a top predator or superpredator, is a predator at the top of a food chain, without natural predators of its own.
Apex predators are usually defined in terms of trophic dynamics, meaning that they occupy the hig ...
s such as
lions panthers or leopards,
hyenas
Hyenas or hyaenas ( ; from Ancient Greek , ) are feliformia, feliform carnivoran mammals belonging to the Family (biology), family Hyaenidae (). With just four extant species (each in its own genus), it is the fifth-smallest family in the orde ...
and bear
Bears are carnivoran mammals of the family (biology), family Ursidae (). They are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats ...
s.
The human form was represented comparatively rarely (relative to the depiction of animals);
most notable are the Venus figurines
A Venus figurine is any Upper Palaeolithic statue portraying a woman, usually carved in the round.Fagan, Brian M., Beck, Charlotte, "Venus Figurines", beliefs '' The Oxford Companion to Archaeology'', 1996, Oxford University Press, pp. 740– ...
(representation of the female form, emphasizing breasts and/or buttocks). The Lion-Human statuette of Hohlenstein-Stadel (Aurignacian
The Aurignacian () is an archaeological industry of the Upper Paleolithic associated with Cro-Magnon, Early European modern humans (EEMH) lasting from 43,000 to 26,000 years ago. The Upper Paleolithic developed in Europe some time after the L ...
) is a hybrid creature with a lion's head on a human body. Other possible hybrid figures are the Shaman of Trois-Frères and a "Bison-man" from the same cave system, another "Bison-man" from the Grotte de Gabillou in the Dordogne
Dordogne ( , or ; ; ) is a large rural departments of France, department in south west France, with its Prefectures in France, prefecture in Périgueux. Located in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region roughly half-way between the Loire Valley and ...
, and what might be a bird-headed man in the "Shaft of the Dead Man" in the Lascaux
Lascaux ( , ; , "Lascaux Cave") is a network of caves near the village of Montignac, Dordogne, Montignac, in the Departments of France, department of Dordogne in southwestern France. Over 600 Parietal art, parietal cave painting, wall paintin ...
caves.
Representation of males are rare prior to incipient Mesolithic.
Mesolithic examples include the " Pin Hole man" of Creswell Crags
Creswell Crags is an enclosed limestone gorge on the border between Derbyshire and Nottinghamshire, England, near the villages of Creswell and Whitwell. The cliffs in the ravine contain several caves that were occupied during the last ice age ...
, Derbyshire.
There is evidence for some craft specialization, and the transport over considerable distances of materials such as stone and, above all marine shells, much used for jewellery and probably decorating clothes. Shells from Mediterranean species have been found at Gönnersdorf, over 1,000 kilometres from the Mediterranean coast. The higher sea levels today mean that the level and nature of coastal settlements in the Upper Paleolithic are now submerged and remain unknown.
Asia
 Cave paintings from the Indonesian island of
Cave paintings from the Indonesian island of Sulawesi
Sulawesi ( ), also known as Celebes ( ), is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the List of islands by area, world's 11th-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Min ...
, situated in the caves in the district of Maros, were dated based on Uranium–thorium dating
Uranium–thorium dating, also called thorium-230 dating, uranium-series disequilibrium dating or uranium-series dating, is a radiometric dating technique established in the 1960s which has been used since the 1970s to determine the age of calcium ...
in a 2014 study. The oldest dated image was a hand stencil, which was given a minimum age of 39,900 years. A painting of a babirusa
The babirusas, also called deer-pigs (), are a genus, ''Babyrousa'', in the Suidae, swine family found in the Indonesian islands of Sulawesi, Togian Islands, Togian, Sula Islands, Sula and Buru. All members of this genus were considered part of a ...
was dated to at least 35.4 ka, placing it among the oldest known figurative depictions worldwide.
A cave at Turobong in South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
containing human remains has been found to contain carved deer bones and depictions of deer that may be as much as 40,000 years old. Portal, p. 25 Petroglyphs of deer or reindeer found at Sokchang-ri may also date to the Upper Paleolithic. Potsherds in a style reminiscent of early Japanese work have been found at Kosan-ri on Jeju island
Jeju Island (Jeju language, Jeju/) is South Korea's largest island, covering an area of , which is 1.83% of the total area of the country. Alongside outlying islands, it is part of Jeju Province and makes up the majority of the province.
The i ...
, which, due to lower sea levels at the time, would have been accessible from Japan. Portal, p. 26
In November 2018, scientists reported the discovery of the oldest known figurative art painting, over 40,000 (perhaps as old as 52,000) years old, of an unknown animal in the cave of Lubang Jeriji Saléh on the Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
n island of Borneo
Borneo () is the List of islands by area, third-largest island in the world, with an area of , and population of 23,053,723 (2020 national censuses). Situated at the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, it is one of the Greater Sunda ...
.
Some Upper Paleolithic artifacts such as the '' Venus figurines of Mal'ta'' were found in Southern Siberia
South Central Siberia is a geographical region in North Asia, just north of the meeting point between Russia, China, Kazakhstan and Mongolia.
The Four Corners
At approximately , the borders of Russia, China, Mongolia and Kazakhstan inters ...
, Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
. These figures consist most often of ivory. The figures are about 20,000 years old and stem from the Gravettian
The Gravettian is an archaeological industry of the European Upper Paleolithic that succeeded the Aurignacian circa 33,000 years BP. It is archaeologically the last European culture many consider unified, and had mostly disappeared by ...
. Most of these statuettes show stylized clothes. Quite often the face is depicted. They were discovered at Mal'ta, at the Angara River, near Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal is a rift lake and the deepest lake in the world. It is situated in southern Siberia, Russia between the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast, Irkutsk Oblasts of Russia, Oblast to the northwest and the Repu ...
in Irkutsk Oblast
Irkutsk Oblast (; ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast), located in southeastern Siberia in the basins of the Angara River, Angara, Lena River, Lena, and Nizhnyaya Tunguska Rivers. The administrative center is ...
, Siberia.
The Bhimbetka rock shelters
The Bhimbetka rock shelters are an archaeological site in central India that spans the Paleolithic and Mesolithic periods, as well as the historic period. It exhibits the earliest traces of human life in India and evidence of the Stone Age star ...
have linear representations in green of humans dancing and hunting.
Australia

Gabarnmung
Gabarnmung (or ''Nawarla Gabarnmung'', Jawoyn language, Jawoyn for "(place of) hole in the rock")
is an archaeological site, archaeological and rock art site in south-western Arnhem Land, in the Top End of Australia’s Northern Territory. Habit ...
, or Nawarla Gabarnmung, is an Aboriginal archaeological and rock art site in south-western Arnhem Land
Arnhem Land is a historical region of the Northern Territory of Australia. It is located in the north-eastern corner of the territory and is around from the territorial capital, Darwin, Northern Territory, Darwin. In 1623, Dutch East India Compa ...
, in the Top End of Australia's Northern Territory. The rock shelter features prehistoric paintings of fish, including the barramundi, wallabies, crocodiles, people and spiritual figures. Most of the paintings are located on the shelter's ceiling, but many are found on the walls and pillars of the site.
The painting on the ceiling has been securely dated to before 27,000 years ago.
Radiocarbon dating of charcoal excavated from the base of the lowest stratigraphic layer of the floor returned a mean age of suggesting the oldest date for the earliest human habitation. Faceted and use-striated hematite crayons have been recovered from nearby locations ( Malakunanja II and Nauwalabila 1) in strata dated from 45,000 to 60,000 years old which suggests that the Gabarnmung shelter may have been decorated from its inception..
The Gwion Gwion rock paintings are a unique form of rock art found in Western Australia
Western Australia (WA) is the westernmost state of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Aust ...
. They are predominantly human figures drawn in fine detail with accurate anatomical proportioning. They have been dated at over 17,000 years old.
Near East and North Africa
Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories ...
sites of the Near East, such as the Hayonim Cave, a cave located in a limestone bluff about 250 meters above modern sea level, in the Upper Galilee
The Upper Galilee (, ''HaGalil Ha'Elyon''; , ''Al Jaleel Al A'alaa'') is a geographical region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon. Part of the larger Galilee region, it is characterized by its higher elevations and mountainous terra ...
, Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
, have wall carvings depicting symbolic shapes and animals, such as a running horse dated to the Levantine Aurignacian circa 28000 BP, and visible in the Israel Museum
The Israel Museum (, ''Muze'on Yisrael'', ) is an Art museum, art and archaeology museum in Jerusalem. It was established in 1965 as Israel's largest and foremost cultural institution, and one of the world's leading Encyclopedic museum, encyclopa ...
. This is considered as the first art object found within the context of the Levantine Upper Paleolithic.
Petroglyph
A petroglyph is an image created by removing part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, or abrading, as a form of rock art. Outside North America, scholars often use terms such as "carving", "engraving", or other descriptions ...
s of the North African Mesolithic, such as those at Tassili n'Ajjer, Algeria, are dated to about 12,000 to 10,000 years old.
Sub-Saharan Africa
 The oldest known figurative art from
The oldest known figurative art from Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the list of sovereign states and ...
are seven stone plaquettes painted with figures of animals found at the Apollo 11 Cave complex in Namibia
Namibia, officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country on the west coast of Southern Africa. Its borders include the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Angola and Zambia to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south; in the no ...
, and dated to between 27,500 and 22,500 years ago. Coulson, pp. 76–77
There is a substantial amount of rock art attributable to the Bushmen (San) found throughout Southern Africa.
Much of this art is recent (as evident from the subject matter depicted, including depictions of wagons and of European settlers wearing hats), but the oldest samples have been tentatively dated to as early as 26,000 years ago.
Matobo National Park, Zimbabwe
file:Zimbabwe, relief map.jpg, upright=1.22, Zimbabwe, relief map
Zimbabwe, officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Bots ...
, has many rock paintings. The oldest examples to 7,000 years ago, possibly as early as 13,000 years ago, while the bulk were likely produced between c. 1,700 and 1,500 years ago.
Petroglyphs in West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
, such as those of Bidzar, Cameroon, are dated to after 3,000 years ago.
Americas
Rock paintings in the Toquepala Caves in southernPeru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pac ...
are dated at ca. 11,500 years ago. Lavallée, p. 94 Some of the paintings are figurative, notably including a scene of armed men hunting guanaco
The guanaco ( ; ''Lama guanicoe'') is a camelid native to South America, closely related to the llama. Guanacos are one of two wild South American camelids; the other species is the vicuña, which lives at higher elevations.
Etymology
The gua ...
cameloids. The men are in a posture of attacking the animals with axe
An axe (; sometimes spelled ax in American English; American and British English spelling differences#Miscellaneous spelling differences, see spelling differences) is an implement that has been used for thousands of years to shape, split, a ...
, lance
The English term lance is derived, via Middle English '' launce'' and Old French '' lance'', from the Latin '' lancea'', a generic term meaning a wikt:lancea#Noun">lancea'', a generic term meaning a spear">wikt:lancea#Noun">lancea'', a generi ...
s, and spear throwers (but not including bow and arrow). The paintings are polychrome, with red made from hematite
Hematite (), also spelled as haematite, is a common iron oxide compound with the formula, Fe2O3 and is widely found in rocks and soils. Hematite crystals belong to the rhombohedral lattice system which is designated the alpha polymorph of . ...
being the dominant color.
Rock art made by the earliest inhabitants of the Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technology company
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek myth ...
region dates to between 11,800 and 12,600 years ago. The animals depicted include some now extinct, such as mastodon
A mastodon, from Ancient Greek μαστός (''mastós''), meaning "breast", and ὀδούς (''odoús'') "tooth", is a member of the genus ''Mammut'' (German for 'mammoth'), which was endemic to North America and lived from the late Miocene to ...
s and giant sloths.
Early burial sites in Peru, such as the one at Telarmachay dating from about 10 ka onward, contained evidence of ritual burial, with deposits of red ocher and bead necklaces marking the site. Lavallée, p. 115
See also
*Cave painting
In archaeology, cave paintings are a type of parietal art (which category also includes petroglyphs, or engravings), found on the wall or ceilings of caves. The term usually implies prehistoric art, prehistoric origin. These paintings were often c ...
* Cro-Magnon
Cro-Magnons or European early modern humans (EEMH) were the first early modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') to settle in Europe, migrating from western Asia, continuously occupying the continent possibly from as early as 56,800 years ago. They in ...
* Kapova Cave
Shulgan-Tash Cave (), also known as Kapova Cave (), is a limestone karst cave in the Burzyansky District of Bashkortostan, Russia. It is located in the southern Ural Mountains, approximately south-east of Ufa. Located on the Belaya River (Kama), ...
* List of Stone Age art
* Mask of la Roche-Cotard
Notes
References
* * * * * *Further reading
*External links
*EuroPreArt Database of European Prehistoric Art
Human Timeline (Interactive)
– Smithsonian,
National Museum of Natural History
The National Museum of Natural History (NMNH) is a natural history museum administered by the Smithsonian Institution, located on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., United States. It has free admission and is open 364 days a year. With 4.4 ...
(August 2016).Image Database Paleolithic art in Northern Spain
{{portal bar, Evolutionary biology
Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories ...
Upper Paleolithic