Antonov 12 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
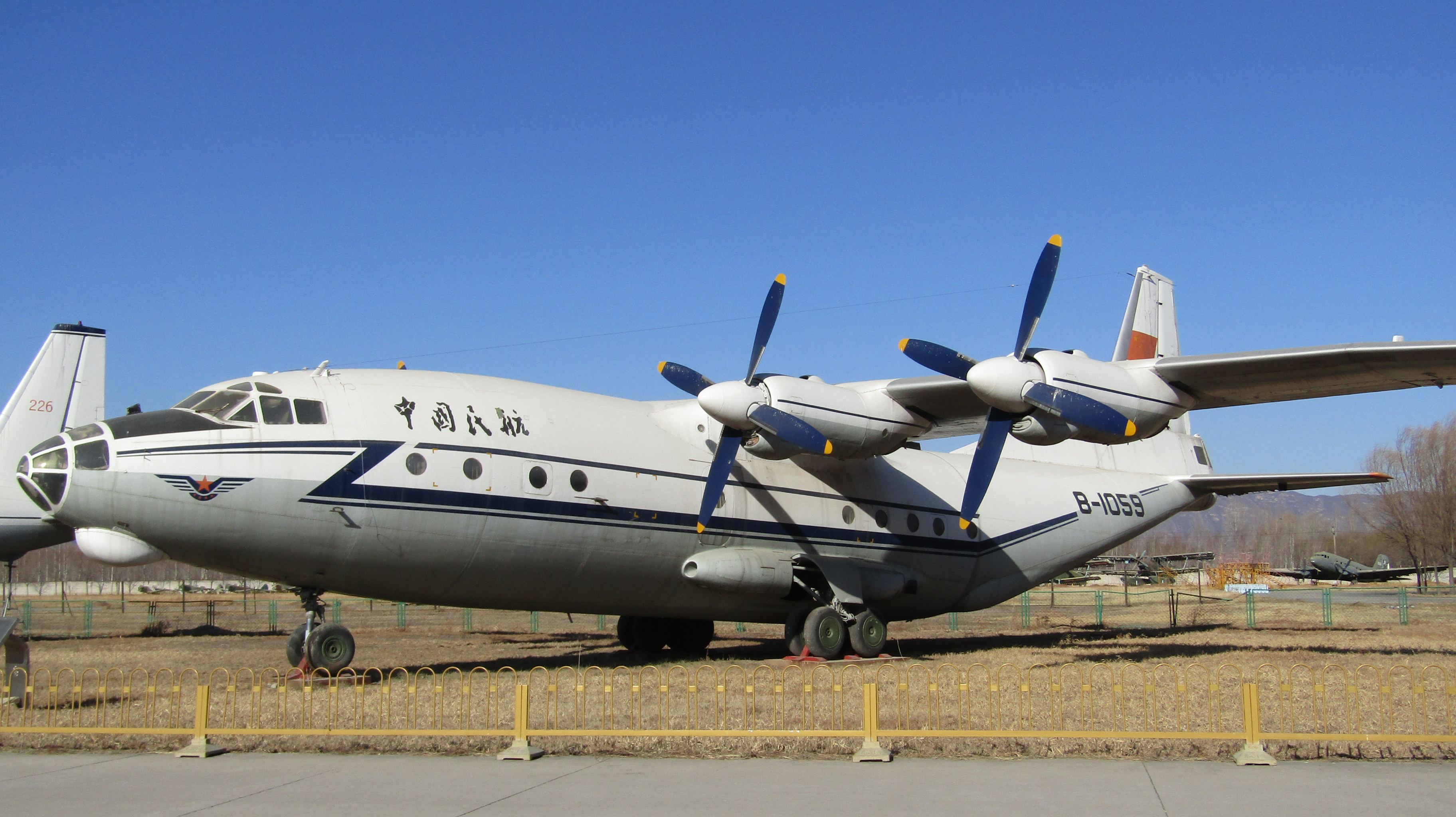
The Antonov An-12 (
 Developed from the
Developed from the

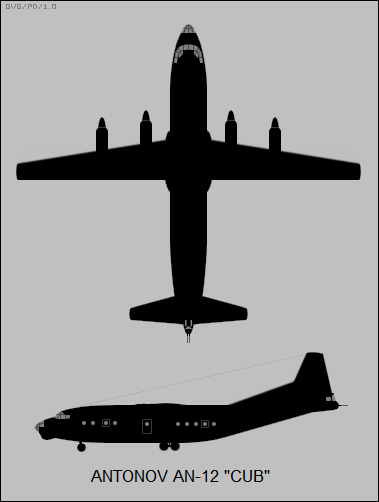
Russian
Russian(s) may refer to:
*Russians (), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*A citizen of Russia
*Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages
*''The Russians'', a b ...
: Антонов Ан-12; NATO reporting name
NATO uses a system of code names, called reporting names, to denote military aircraft and other equipment used by post-Soviet states, former Warsaw Pact countries, China, and other countries. The system assists military communications by providi ...
: Cub) is a four-engined turboprop
A turboprop is a Gas turbine, gas turbine engine that drives an aircraft Propeller (aeronautics), propeller.
A turboprop consists of an intake, reduction drive, reduction gearbox, gas compressor, compressor, combustor, turbine, and a propellin ...
transport aircraft Transport aircraft is a broad category of aircraft that includes:
* Airliners, aircraft, usually large and most often operated by airlines, intended for carrying multiple passengers or cargo in commercial service
* Cargo aircraft or freighters, fix ...
designed in the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
. It is the military version of the Antonov An-10
The Antonov An-10 Ukraina (; NATO reporting name: Cat) is a four-engined turboprop passenger transport aircraft designed in the Soviet Union.
Design and development
Development of a four-engined airliner intended for use on routes from began ...
and has many variants. For more than three decades, the An-12 was the standard medium-range cargo and paratroop transport aircraft of the Soviet air forces. A total of 1,248 aircraft were built.
Design and development
 Developed from the
Developed from the Antonov An-8
The Antonov An-8 (NATO reporting name: Camp) is a Soviet-designed twin-turboprop, high-wing light military transport aircraft.
Development
In December 1951, OKB-153 initiated the design of a twin-engined assault transport aircraft, designated D ...
, the An-12 was a military version of the An-10 passenger transport. The first prototype An-12 flew in December 1957 and entered Soviet military service in 1959. Initially, the aircraft was produced at the State Aviation Factory in Irkutsk, Siberia. From 1962, production was transferred to Tashkent
Tashkent (), also known as Toshkent, is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Uzbekistan, largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of more than 3 million people as of April 1, 2024. I ...
, where 830 were built. Later, production moved to Voronezh
Voronezh ( ; , ) is a city and the administrative centre of Voronezh Oblast in southwestern Russia straddling the Voronezh River, located from where it flows into the Don River. The city sits on the Southeastern Railway, which connects wes ...
and Kazan
Kazan; , IPA: Help:IPA/Tatar, ɑzanis the largest city and capital city, capital of Tatarstan, Russia. The city lies at the confluence of the Volga and the Kazanka (river), Kazanka Rivers, covering an area of , with a population of over 1. ...
.
In military use, the An-12 has capacity for up to 100 fully equipped paratroopers or of cargo, which is loaded through the rear loading ramp/door.
In terms of configuration, size, and capability, the aircraft is similar to the United States-built Lockheed C-130 Hercules
The Lockheed C-130 Hercules is an American four-engine turboprop military transport aircraft designed and built by Lockheed Corporation, Lockheed (now Lockheed Martin). Capable of using unprepared runways for takeoffs and landings, the C-130 w ...
. Soviet military and former-Soviet An-12s have a defensive tail gun turret.
Chinese production
In the 1960s, China purchased several An-12 aircraft from the Soviet Union, along with a license to assemble the aircraft locally. Due to theSino-Soviet split
The Sino-Soviet split was the gradual worsening of relations between the People's Republic of China (PRC) and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) during the Cold War. This was primarily caused by divergences that arose from their ...
, the Soviet Union withdrew its technical assistance. The Xi'an Aircraft Industrial Corporation, Xi'an Aircraft Company and Xi'an Aircraft Design Institute reverse-engineered the An-12 for local production, and the first flight of a Chinese-assembled An-12 was delayed until 1974 after USSR ceased production in 1973.
In 1981, the Chinese version of the An-12, designated Shaanxi Y-8, Y-8, finally entered production. Since then, the Y-8 has become one of China's most popular military and civilian transport/cargo aircraft, with many variants produced and exported. A Tu-16/Xian H-6, H-6 bomber navigator cockpit design was chosen for the Y-8 instead of the original An-12 shorter navigator cockpit design, as the H-6 bomber had been in serial production for some time. Although the An-12 is no longer in use either in Russia or in Ukraine, the Y-8 is upgraded and produced in China. The latest Y8-F600 is a joint venture between the Shaanxi Aircraft Company, Antonov Aeronautical Scientific Technical Complex (ASTC), and Pratt & Whitney Canada. The Y8-F600 has a redesigned fuselage, western avionics, Pratt & Whitney Canada PW100, PW150B turboprop engines with an R-408 propeller system, and a two-crew glass cockpit.
Operational history

Soviet Air Forces
The aircraft first took flight in 1957 and was produced in the USSR until 1973. It was used in a variety of roles from search and rescue operations to equipment transportation. Its most significant use was seen during the Soviet-Afghan War. Among Soviet soldiers, it was infamously known that the plane would take off from Afghanistan toTashkent
Tashkent (), also known as Toshkent, is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Uzbekistan, largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of more than 3 million people as of April 1, 2024. I ...
with "Cargo 200 (code name), Cargo 200" or coffins with the bodies of deceased soldiers. To this regard, the aircraft was nicknamed "Black Tulip" (Russian
Russian(s) may refer to:
*Russians (), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*A citizen of Russia
*Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages
*''The Russians'', a b ...
: «Чёрный тюльпан»); the origin of the nickname is unclear. There are quite a few monuments in Russia named to commemorate the killed during the Afghan War.
Russia
During the Russian invasion of Ukraine Russia lost one An-12 on 1 June 2025 due to Ukraine's Operation Spider's Web.Variants
In addition to its basic cargo transport role, the An-12 was adapted as a platform for a wide variety of specialist tasks and some 30 different variants were produced. Upgrades included increased take-off weights and additional fuel capacity. The upgraded variant An-12BP became the standard Airlift, tactical transport of the Soviet and other air forces. In 2019, it was announced at the military "Army-2019" Forum that Russia started working on an armed ground-attack and close air support variant of the An-12, similar to the American AC-130. In 2021, it was announced that the gunship will not be based on the An-12 after all, as it did not meet the requirements for a "flying gunner."Operators
Currently, the An-12 is popular with cargo operators, especially those in the Commonwealth of Independent States, CIS, Africa and the Indian subcontinent.Gordon, Yefim & Komissarov, Dmitry. Antonov An-12. Midland. Hinkley. 2007.Civil operators
On 8 January 2009, following numerous incidents involving the An-12 in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), the General Civil Aviation Authority (GCAA) issued a temporary ban of the An-12 from UAE airspace. On 1 March 2010, the ban was made permanent after the An-12 failed a GCAA airworthiness evaluation.Current
; * Air Armenia ; * Ruby Star (airline), Ruby Star Airways ; * Air One (Mexico) ; * ATRAN Cargo Airlines * SAT Airlines ; * Air People International ; * Aerovis Airlines * Antonov Airlines * Cavok Air * Meridian * Motor Sich Airlines * Ukraine Air Alliance * Volare Airlines (Ukraine), Volare Airlines ; * SRXFormer
; * Alada ; * Balkan Bulgarian Airlines * Air Sofia ; * CAAC Airlines; see also Shaanxi Y-8 ; * Egyptair ; * Asia Cargo Airlines *Air Mark ; * Darta ;: * Air Guinee ;: * Ghana Airways – The sole An-12 was delivered in October 1961. Withdrawn from use in 1962 and returned to the Soviet Union in 1963. ; * Iraqi Airways * Fresh Air (airline), Fresh Air ; * Interisland Airlines ; * LOT Polish Airlines ; * Avial NV, Avial Aviation ; * United International Airlines ; * Azza Transport * Badr Airlines * Juba Air CargoMilitary operators
Current
; * People's Air and Air Defence Force of AngolaHoyle ''Flight International'' 8–14 December 2015, p. 32. ; * Chadian Air Force ; * Ethiopian Air ForceHoyle ''Flight International'' 8–14 December 2015, p. 37. ;Hoyle ''Flight International'' 8–14 December 2015, p. 41. * Kazakh Air Defense Forces ; * Myanmar Air Force ; * Nigerian Air Force – 12 An-12s in service ; * Russian Aerospace ForcesHoyle ''Flight International'' 8–14 December 2015, p. 46. * Russian Naval Aviation ; * Sudanese Air ForceHoyle ''Flight International'' 8–14 December 2015, p. 48. ; * Uzbekistan Air and Air Defence ForcesHoyle ''Flight International'' 8–14 December 2015, p. 53.Former
; * Algerian Air Force ; * Armenian Air Force ; * The Afghan Air Force operated 12 from 1981 through 2001. One of their An-12s which defected to Pakistan is preserved at PAF Museum, Karachi ; * Bangladesh Air Force operated from 1973 to 1980s, now all retired ; * Cote d'Ivoire Air Force ; * Czech Air Force ; * Czechoslovak Air Force: Czechoslovakia's fleet numbering two was divided evenly between the Czech Republic and Slovak Republic upon split with Slovakia. All CzAF An-12s were phased out of active service in the 1990s. ; * Egyptian Air Force - 22 acquired ; ; * The Indian Air Force inducted the first of these aircraft in 1961, when it raised No. 44 Squadron IAF, No.44 Squadron "The Himalayan Geese". Six of these aircraft soon took part in airlifting army reinforcements to Ladakh during the Sino-Indian War of 1962. The An-12 was subsequently used to raise No. 25 Squadron IAF, No.25 Squadron. The An-12s were also used as heavy bombers during the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971. All IAF An-12s were phased out of active service in the 1990s. One of them is preserved at the Indian Air Force Museum, Palam, New Delhi. ; * Indonesian Air Force – Retired in 1970 ; * Iraqi Air Force – Retired in 2003 ; * Royal Jordanian Air Force ; * Mongolian Air Force - Retired 12 An-12 ; * Polish Air Force used two An-12B from 1966 until 1977 (crashed) and 1995 ; * Slovak Air Force received one An-12BP registered 2209 in 1993. It was sold to Moldavia in 1999 and now serves with Angolan Air Force. ; * Yemeni Air Force ; * The Soviet fleet was dispersed among many of the Soviet Union's successor states. * Soviet Air Force * Soviet Naval Aviation ; * Syrian Air Force ; * Tanzania Air Force Command ; Turkmenistan Air Forces ; * Ukrainian Air Force * Ukrainian Naval Aviation ; * SFR Yugoslav Air ForceAccidents and incidents
Specifications (An-12)

See also
References
Footnotes
Sources
* * * . * *External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Antonov An-012 Antonov aircraft, An-012 1950s Soviet cargo aircraft 1950s Soviet military transport aircraft Four-engined tractor aircraft Four-engined turboprop aircraft High-wing aircraft Aircraft first flown in 1957 Aircraft with retractable tricycle landing gear