anti-scaling agent on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Water softening is the removal of
Water softening is the removal of
 The presence of certain
The presence of certain
 Conventional water-softening appliances intended for household use depend on an
Conventional water-softening appliances intended for household use depend on an
Filtration Facts
', September 2005, U.S. Environmental Protection Administration, pp. 6-7. Accessed 6 January 2013. ion-exchange devices reduce the hardness by replacing magnesium and calcium (Mg2+ and Ca2+) with sodium or potassium ions (Na+ and K+)."
 Water softening is the removal of
Water softening is the removal of calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
, magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
, and certain other metal cation
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
s in hard water
Hard water is water that has a high mineral content (in contrast with "soft water"). Hard water is formed when water percolates through deposits of limestone, chalk or gypsum, which are largely made up of calcium and magnesium carbonates, bic ...
. The resulting soft water requires less soap
Soap is a salt (chemistry), salt of a fatty acid (sometimes other carboxylic acids) used for cleaning and lubricating products as well as other applications. In a domestic setting, soaps, specifically "toilet soaps", are surfactants usually u ...
for the same cleaning effort, as soap is not wasted bonding with calcium ions. Soft water also extends the lifetime of plumbing
Plumbing is any system that conveys fluids for a wide range of applications. Plumbing uses piping, pipes, valves, piping and plumbing fitting, plumbing fixtures, Storage tank, tanks, and other apparatuses to convey fluids. HVAC, Heating and co ...
by reducing or eliminating scale build-up in pipes and fittings. Water softening is usually achieved using lime softening
Lime softening (also known as lime buttering, lime-soda treatment, or Clark's process) is a type of water treatment used for water softening, which uses the addition of limewater (calcium hydroxide) to remove hardness (deposits of calcium and mag ...
or ion-exchange resin
An ion-exchange resin or ion-exchange polymer is a resin or polymer that acts as a medium for ion exchange, that is also known as an ionex. It is an insoluble matrix (or support structure) normally in the form of small (0.25–1.43 mm radiu ...
s, but is increasingly being accomplished using nanofiltration
Nanofiltration is a Membrane technology, membrane filtration process that uses nanometer sized pores through which particles smaller than about 1–10 nanometers pass through the membrane. Nanofiltration membranes have pore sizes of about 1–10 n ...
or reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a water purification process that uses a partially permeable membrane, semi-permeable membrane to separate water molecules from other substances. RO applies pressure to overcome osmotic pressure that favors even distribu ...
membranes.
Rationale
 The presence of certain
The presence of certain metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
ions like calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
and magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
, principally as bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula .
Bicarbonate serves a crucial bioche ...
s, chloride
The term chloride refers to a compound or molecule that contains either a chlorine anion (), which is a negatively charged chlorine atom, or a non-charged chlorine atom covalently bonded to the rest of the molecule by a single bond (). The pr ...
s, and sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ...
s, in water causes a variety of problems.
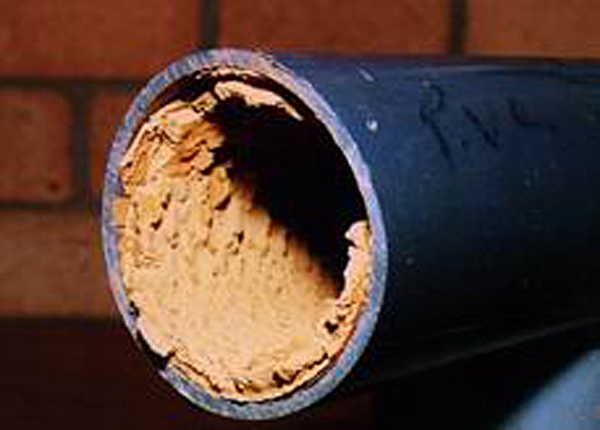
Hard water leads to the buildup of limescale
Limescale is a hard, chalky deposit, consisting mainly of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It often builds up inside kettles, boilers, and pipework, especially that for hot water. It is also often found as a similar deposit on the inner surfaces of old ...
, which can foul plumbing
Plumbing is any system that conveys fluids for a wide range of applications. Plumbing uses piping, pipes, valves, piping and plumbing fitting, plumbing fixtures, Storage tank, tanks, and other apparatuses to convey fluids. HVAC, Heating and co ...
, and promote galvanic corrosion
Galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one metal corrodes preferentially when it is in electrical contact with another, different metal, when both in the prese ...
. In industrial scale water softening plants, the effluent flow from the re-generation process can precipitate scale that can interfere with sewage systems.
The slippery feeling associated with washing in soft water is caused by the weaker attraction of the soap to the water ions when the water has been stripped of its mineral content. The surface of human skin has a light charge that the soap tends to bind with, requiring more effort and a greater volume of water to remove. Hard water contains calcium or magnesium ions that form insoluble salts
In chemistry, a salt or ionic compound is a chemical compound consisting of an assembly of positively charged ions ( cations) and negatively charged ions (anions), which results in a compound with no net electric charge (electrically neutral). ...
upon reacting with soap, leaving a coating of insoluble stearates on tub and shower surfaces, commonly called soap scum
Soap scum or lime soap is the white solid composed of calcium stearate, magnesium stearate, and similar alkaline earth metal derivatives of fatty acids. These materials result from the addition of soap and other anionic surfactants to hard water ...
.
Methods
The most common means for removing water hardness rely onion-exchange resin
An ion-exchange resin or ion-exchange polymer is a resin or polymer that acts as a medium for ion exchange, that is also known as an ionex. It is an insoluble matrix (or support structure) normally in the form of small (0.25–1.43 mm radiu ...
or reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a water purification process that uses a partially permeable membrane, semi-permeable membrane to separate water molecules from other substances. RO applies pressure to overcome osmotic pressure that favors even distribu ...
. Other approaches include precipitation methods, such as fluidized bed pellet softening, and sequestration by the addition of chelating agents. Distillation
Distillation, also classical distillation, is the process of separating the component substances of a liquid mixture of two or more chemically discrete substances; the separation process is realized by way of the selective boiling of the mixt ...
and reverse osmosis are the most widely used two non-chemical methods of water softening.
Ion-exchange resin method
 Conventional water-softening appliances intended for household use depend on an
Conventional water-softening appliances intended for household use depend on an ion-exchange resin
An ion-exchange resin or ion-exchange polymer is a resin or polymer that acts as a medium for ion exchange, that is also known as an ionex. It is an insoluble matrix (or support structure) normally in the form of small (0.25–1.43 mm radiu ...
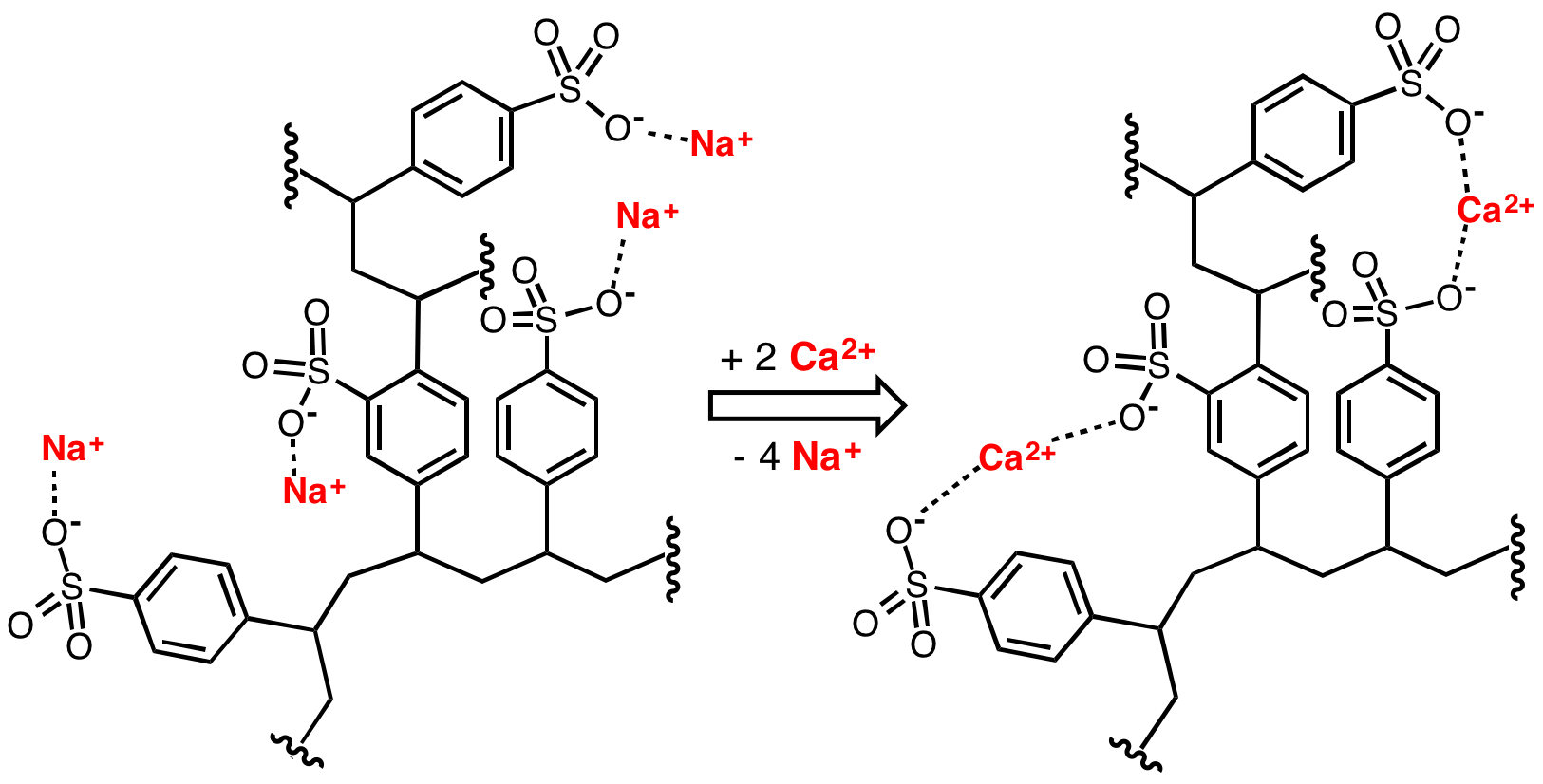
in which "hardness ions"—mainly Ca2+ and Mg2+—are exchanged for sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
ions. As described by NSF/ANSI Standard 44,Filtration Facts
', September 2005, U.S. Environmental Protection Administration, pp. 6-7. Accessed 6 January 2013. ion-exchange devices reduce the hardness by replacing magnesium and calcium (Mg2+ and Ca2+) with sodium or potassium ions (Na+ and K+)."
Ion-exchange resin
An ion-exchange resin or ion-exchange polymer is a resin or polymer that acts as a medium for ion exchange, that is also known as an ionex. It is an insoluble matrix (or support structure) normally in the form of small (0.25–1.43 mm radiu ...
s are organic polymer
A polymer () is a substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, bot ...
s containing anionic
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
functional groups to which the divalent cations (Ca2+) bind more strongly than monovalent cations (Na+). Inorganic materials called zeolite
Zeolites are a group of several microporous, crystalline aluminosilicate minerals commonly used as commercial adsorbents and catalysts. They mainly consist of silicon, aluminium, oxygen, and have the general formula ・y where is either a meta ...
s also exhibit ion-exchange properties. These minerals are widely used in laundry detergent
Laundry detergent is a type of detergent (cleaning agent) used for cleaning dirty laundry (clothes). Laundry detergent is manufactured in powder (washing powder) and liquid form.
While powdered and liquid detergents hold roughly equal share of ...
s. Resins are also available to remove the carbonate, bicarbonate, and sulfate ions that are absorbed and hydroxide ions that are released from the resin.
When all the available Na+ ions have been replaced with calcium or magnesium ions, the resin must be recharged by eluting the Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions using a solution of sodium chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as Salt#Edible salt, edible salt, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. It is transparent or translucent, brittle, hygroscopic, and occurs a ...
or sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly corrosive base (chemistry), ...
, depending on the type of resin used. For anionic resins, regeneration typically uses a solution of sodium hydroxide (lye
Lye is the common name of various alkaline solutions, including soda lye (a solution of sodium hydroxide) and potash lye (a solution of potassium hydroxide). Lyes are used as cleaning products, as ingredients in soapmaking, and in various other c ...
) or potassium hydroxide. The waste waters eluted from the ion-exchange column containing the unwanted calcium and magnesium salts are typically discharged to the sewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewerage, sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged fro ...
system.
Recharge typically takes the following steps:
* Backwash: Water is directed through the resin in the direction opposite to that of normal flow, and the output is sent to a drain for disposal. This ten-minute process flushes out solids, and expands the resin bed.
* Brine draw: Water is directed through a jet pump
An injector is a system of ducting and nozzles used to direct the flow of a high-pressure fluid in such a way that a lower pressure fluid is Entrainment (hydrodynamics), entrained in the jet and carried through a duct to a region of higher pres ...
, which pulls salt water from the brine
Brine (or briny water) is a high-concentration solution of salt (typically sodium chloride or calcium chloride) in water. In diverse contexts, ''brine'' may refer to the salt solutions ranging from about 3.5% (a typical concentration of seawat ...
tank, before the water and brine pass through the resin bed in the normal direction, if ''co-current'', or in the reverse direction, if ''counter-current''. The output of this typically thirty-minute process is discarded through the drain hose.
* Rinse: Brine draw stops, but water continues to flow from the inlet to the outlet, gradually flushing the brine out of the resin bed. The flushing water flows slowly for several minutes, then at a faster rate for as long as an hour. At some point, the brine reservoir is refilled with fresh water.
Lime softening
Lime softening is the process in which lime is added to hard water to make it softer. It has several advantages over the ion-exchange method but is mainly suited to commercial treatment applications.Chelating agents
Chelators are used inchemical analysis
Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to separate, identify, and quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute the entire analysis or be combined with another method. Separa ...
, as water softeners, and are ingredients in many commercial products such as shampoos and food preservative
A preservative is a substance or a chemical that is added to products such as food products, beverages, pharmaceutical drugs, paints, biological samples, cosmetics, wood, and many other products to prevent decomposition by microbial growth or ...
s. Citric acid
Citric acid is an organic compound with the formula . It is a Transparency and translucency, colorless Weak acid, weak organic acid. It occurs naturally in Citrus, citrus fruits. In biochemistry, it is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, ...
is used to soften water in soaps, personal care products and laundry detergent
Laundry detergent is a type of detergent (cleaning agent) used for cleaning dirty laundry (clothes). Laundry detergent is manufactured in powder (washing powder) and liquid form.
While powdered and liquid detergents hold roughly equal share of ...
s. A commonly used synthetic chelator is ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), also called EDTA acid, is an aminopolycarboxylic acid with the formula . This white, slightly water-soluble solid is widely used to bind to iron (Fe2+/Fe3+) and calcium ions (Ca2+), forming water-solubl ...
(EDTA), which may exist as a tetrasodium or disodium salt. Due to environmental and aquatic toxicity concerns regarding widespread use of EDTA in household and personal care products, alternatives such as sodium phytate/phytic acid
Phytic acid is a six-fold dihydrogenphosphate ester of inositol (specifically, of the ''myo'' isomer), also called inositol hexaphosphate, inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) or inositol polyphosphate. At physiological pH, the phosphates are partia ...
, tetrasodium glutamate diacetate and trisodium ethylenediamine disuccinate are finding more prevalent usage.
Washing soda method
In this method, water is treated with a calculated amount ofwashing soda
Sodium carbonate (also known as washing soda, soda ash, sal soda, and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield alkaline solutions in water ...
(Na2CO3), which converts the chlorides and sulphates of calcium and magnesium into their respective carbonates, which get precipitated.
Distillation and rain water
Since Ca2+ and Mg2+ exist as nonvolatile salts, they can be removed by distilling the water.Distillation
Distillation, also classical distillation, is the process of separating the component substances of a liquid mixture of two or more chemically discrete substances; the separation process is realized by way of the selective boiling of the mixt ...
is expensive and energy-inefficient compared to other methods of water softening. Rainwater is soft because it is naturally distilled during the water cycle
The water cycle (or hydrologic cycle or hydrological cycle) is a biogeochemical cycle that involves the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth across different reservoirs. The mass of water on Earth remains fai ...
of evaporation, condensation and precipitation.
Reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis uses an applied pressure gradient across asemipermeable membrane
Semipermeable membrane is a type of synthetic or biologic, polymeric membrane that allows certain molecules or ions to pass through it by osmosis. The rate of passage depends on the pressure, concentration, and temperature of the molecules o ...
to overcome osmotic pressure
Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure which needs to be applied to a Solution (chemistry), solution to prevent the inward flow of its pure solvent across a semipermeable membrane.
It is also defined as the measure of the tendency of a soluti ...
and remove water molecules from the solution with hardness ions. The membrane has pores large enough to admit water molecules for passage; hardness ions such as Ca2+ and Mg2+ will not fit through the pores. The resulting soft water supply is free of hardness ions without any other ions being added. Membranes are a type of water filter requiring regular cleaning or replacement maintenance.
Nanofiltration
Nanofiltration is a process similar to reverse osmosis in that it involves the use of a semipermeable membrane, though the filter membrane is distinct in that its pores are ≤ 10 nanometers in diameter. The process is often used in conjunction with reverse osmosis filtration, as nanofiltration on its own is not as effective and more expensive than chemical water treatment methods.Physical water treatment
Removing or replacing minerals in hard water is called water softening. An alternative water treatment is called water conditioning, in which minerals remain in the water, but are altered so they do not form scale. Although the United States has standards for measuring the minerals in water, it does not have standards for measuring scale forming ability of water. Instead, US researchers use the German DVGW-W512 protocol. Rain water contains dissolved carbon dioxide taken from the atmosphere. Some of the dissolved carbon dioxide reacts with the water to formcarbonic acid
Carbonic acid is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . The molecule rapidly converts to water and carbon dioxide in the presence of water. However, in the absence of water, it is quite stable at room temperature. The interconversion ...
, which remains in solution. Minerals containing calcium and magnesium form soluble bicarbonates when exposed to carbonic acid. Water containing these minerals is known as "hard water".
When hard water is heated in a plumbing system, carbon dioxide goes out of solution, and bicarbonates become carbonates, which are much less soluble. The carbonates bind to plumbing surfaces providing seed crystal
A seed crystal is a small piece of single crystal or polycrystal material from which a large crystal of typically the same material is grown in a laboratory. Used to replicate material, the use of seed crystal to promote growth avoids the otherwi ...
s for further crystal growth, which build up as hard scale.
Electrical water treatment
Some manufacturers claim that the electrical devices they produce can affect the interaction of minerals with water so that the minerals do not bind to surfaces. Since these systems do not work by exchanging ions, like traditional water softeners do, one benefit claimed for the user is the elimination of the need to add salt to the system. Such systems do not remove minerals from the water itself. Rather, they can only alter the downstream effects that the mineral-bearing water would otherwise have. These systems do not fall within the term "water softening" but rather "water conditioning". Electrical precipitation devices causemicroscopic
The microscopic scale () is the scale of objects and events smaller than those that can easily be seen by the naked eye, requiring a lens or microscope to see them clearly. In physics, the microscopic scale is sometimes regarded as the scale betwe ...
mineral crystals to form and remain suspended as they flow with the water, while also acting as seeds for further crystal growth. As water is heated, minerals will crystallize on these seeds, instead of the plumbing system. The dissolved minerals become insoluble solid particles in suspension, passing through the system without binding to plumbing surfaces.
Magnetic water treatment
Claims for magnetic water treatment are not considered to be valid. For instance, no reduction of scale formation was found when such a magnet device was scientifically tested.Template assisted crystallization
Cold hard water passes through a tank containing tiny polymeric beads with surfaces that allow nucleation of tiny bubbles of carbon dioxide gas. The initial nucleation of the gas bubbles can occur due to depressurization of the hard water as it flows up a water well just like when the top comes off of a beer bottle. Once carbon dioxide leaves the liquid a chemical reaction immediately drives formation of calcium carbonate crystals on the surface of the bubbles. As crystals grow on these seeds they break off in the flow while still of microscopic size. If these tiny particles travel through a water heater, further exsolution of carbon dioxide occurs due to increased temperature and new crystal growth occurs on the particles, rather than on the water heater. Once calcite occurs in the water, new calcite will prefer to form on the old calcite due to the available bonds on the crystals and the proximity and number of calcite surfaces in the water. This process is either called template assisted crystallization (TAC) or nucleation assisted crystallization (NAC). The polymeric beads arepolyphosphate
A polyphosphate is a Salt (chemistry), salt or ester of polymeric oxyanions formed from tetrahedral PO4 (phosphate) structural units linked together by sharing oxygen atoms. Polyphosphates can adopt linear or a cyclic (also called, ring) structure ...
s ranging in size from 0.5 to 2.0 μm. and some have a ceramic coating. Testing at the University of Arizona found TAC to be the most effective at reducing scale formation, followed closely by ion exchange (see chart above). They are more effective than approaches that attempt to sequester ions through application of magnetic or electric fields. The advantages of TAC tanks include simplicity, low maintenance, lack of toxic effluent (like chlorine), and the availability of calcium as a nutrient in drinking water. The disadvantages include that the calcite crystals are not avoided or removed from the water such that areas where water evaporates will still show deposits. It is claimed by manufacturers that these deposits are easier to clean since the calcite forms on seed crystals instead of on the surfaces.
Health effects
The UK's National Health Service recommends a maximum salt intake of 6g, against an actual current intake of 8.1g. The USCDC
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and is headquartered in Atlanta, ...
recommends limiting daily total sodium intake to 2,300 mg per day, though the average US American consumes 3,500 mg per day. Because the amount of sodium present in drinking water—even after softening—does not represent a significant percentage of a person's daily sodium intake, the US EPA considers sodium in drinking water to be unlikely to cause adverse health effects.
A study found the mean concentration of sodium in softened water to be 278 mg/L. In 2 liters of water—the amount of drinking water typically suggested for an average adult, this constitutes about 22% of the recommended sodium intake by the US CDC and may make a difference to those who need to significantly limit their sodium consumption. For those who are on sodium-restricted diets, the use of a reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a water purification process that uses a partially permeable membrane, semi-permeable membrane to separate water molecules from other substances. RO applies pressure to overcome osmotic pressure that favors even distribu ...
system for drinking water and cooking water will remove sodium along with any other impurities that may be present.Potassium chloride
Potassium chloride (KCl, or potassium salt) is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water, and its solutions have a sa ...
can also be used as a regenerant instead of sodium chloride, although it is more costly. For people with impaired kidney function
Assessment of kidney function occurs in different ways, using the presence of symptoms and medical sign, signs, as well as measurements using urine tests, blood tests, and medical imaging.
Renal physiology, Functions of a healthy kidney include ...
, however, elevated potassium levels, or hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia is an elevated level of potassium (K+) in the blood. Normal potassium levels are between 3.5 and 5.0 mmol/L (3.5 and 5.0 mEq/L) with levels above 5.5mmol/L defined as hyperkalemia. Typically hyperkalemia does not cause symptoms. Oc ...
, can lead to complications such as cardiac arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. Essentially, this is anything but normal sinus rhythm. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beat ...
.
High levels of water hardness in the home may also be linked to the development of atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD), also known as atopic eczema, is a long-term type of inflammation of the skin. Atopic dermatitis is also often called simply eczema but the same term is also used to refer to dermatitis, the larger group of skin conditi ...
(eczema) early in life, although the actual relationship is correlational at the present and further research is indicated to establish a causal one. However, using water softeners when atopic dermatitis is already established does not reduce the severity of the symptoms.
Environmental impact
Softened water (measured as residual sodium carbonate index) in which calcium and magnesium have been partly replaced by sodium is not suitable for irrigation use, as it tends to cause the development of alkali soils. Non-chemical devices are often used in place of traditional water softening for this application.See also
*Desalination
Desalination is a process that removes mineral components from saline water. More generally, desalination is the removal of salts and minerals from a substance. One example is Soil salinity control, soil desalination. This is important for agric ...
* Ion exchange
Ion exchange is a reversible interchange of one species of ion present in an insoluble solid with another of like charge present in a solution surrounding the solid. Ion exchange is used in softening or demineralizing of water, purification of ch ...
* Lime softening
Lime softening (also known as lime buttering, lime-soda treatment, or Clark's process) is a type of water treatment used for water softening, which uses the addition of limewater (calcium hydroxide) to remove hardness (deposits of calcium and mag ...
* Magnetic water treatment
* Purified water
Purified water is water that has been mechanically filtered or processed to remove impurities and make it suitable for use. Distilled water was, formerly, the most common form of purified water, but, in recent years, water is more frequently pu ...
* Water purification
Water purification is the process of removing undesirable chemicals, biological contaminants, suspended solids, and gases from water. The goal is to produce water that is fit for specific purposes. Most water is purified and disinfected for hu ...
References
External links
{{PlumbingSoftening
In physics and astronomy, an ''N''-body simulation is a simulation of a dynamical system of particles, usually under the influence of physical forces, such as gravity (see ''n''-body problem for other applications). ''N''-body simulations ar ...
Industrial water treatment