Anglo-Saxon Archaeology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The archaeology of
 Eventually, in the 6th and 7th centuries,
Eventually, in the 6th and 7th centuries,
 Confirmation of the use of Anglo-Saxons as ''
Confirmation of the use of Anglo-Saxons as ''
 Catherine Hills points out that it is too easy to consider Anglo-Saxon archaeology solely as a study of
Catherine Hills points out that it is too easy to consider Anglo-Saxon archaeology solely as a study of
 There are a number of difficulties in recognising early Anglo-Saxon settlements as migrant settlers. This in part is because most early rural Anglo-Saxon sites have yielded few finds other than pottery and bone. The use of aerial photography does not yield easily identifiable settlements, partly due to the dispersed nature of many of these settlements.Hamerow, Helena, David A. Hinton, and Sally Crawford, eds. The Oxford Handbook of Anglo-Saxon Archaeology. OUP Oxford, 2011. p 119–124
The distribution of known settlements also remains elusive with few settlements found in the West Midlands or North-West. Even in Kent, an area of rich early Anglo-Saxon archaeology, the number of excavated settlements is fewer than expected. However, in contrast the counties of Northamptonshire, Oxfordshire, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire are relatively rich in early settlements. These have revealed a tendency for early Anglo-Saxon settlements to be on the light soils associated with river terraces.
Many of the inland settlements are on rivers that had been major navigation routes during the Roman era. These sites, such as
There are a number of difficulties in recognising early Anglo-Saxon settlements as migrant settlers. This in part is because most early rural Anglo-Saxon sites have yielded few finds other than pottery and bone. The use of aerial photography does not yield easily identifiable settlements, partly due to the dispersed nature of many of these settlements.Hamerow, Helena, David A. Hinton, and Sally Crawford, eds. The Oxford Handbook of Anglo-Saxon Archaeology. OUP Oxford, 2011. p 119–124
The distribution of known settlements also remains elusive with few settlements found in the West Midlands or North-West. Even in Kent, an area of rich early Anglo-Saxon archaeology, the number of excavated settlements is fewer than expected. However, in contrast the counties of Northamptonshire, Oxfordshire, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire are relatively rich in early settlements. These have revealed a tendency for early Anglo-Saxon settlements to be on the light soils associated with river terraces.
Many of the inland settlements are on rivers that had been major navigation routes during the Roman era. These sites, such as
Anglo-Saxon England
Anglo-Saxon England or early medieval England covers the period from the end of Roman Empire, Roman imperial rule in Roman Britain, Britain in the 5th century until the Norman Conquest in 1066. Compared to modern England, the territory of the ...
is the study of the archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, ...
of England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
from the 5th century AD to the 11th century, when it was ruled by Germanic tribes known collectively as the Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced t ...
.
History and overview
The Anglo-Saxon period is broadly defined as the period of time from roughly 410 AD to 1066 AD. The first modern, systemic excavations of Anglo-Saxon cemeteries and settlements began in the 1920s. Since then, archaeological surveys of cemeteries and settlements have uncovered more information about the society and culture of Anglo-Saxon England. Reverend James Douglas was the first antiquarian to recognize Anglo-Saxon burials for what they were, and he described his findings in ''Nenia Britannica'' (1793). Interest in Anglo-Saxon materials increased in the 19th century, with scholars like the archaeologist Thomas Bateman and the architectThomas Rickman
Thomas Rickman (8 June 17764 January 1841) was an English architect and architectural antiquary who was a major figure in the Gothic Revival. He is particularly remembered for his ''Attempt to Discriminate the Styles of English Architecture'' ...
producing some of the earliest authoritative texts on the subject.
Architecture
Anglo-Saxon architecture is characterized by rectangular, timber buildings such as houses and halls. The construction of stone defenses and monuments became more common in the late 10th and 11th century AD, but urban buildings continued to be made of timber.Art and jewelry
Anglo-Saxon art is best known for its examples of sophisticated metalwork and jewelry, as well as carvings andilluminated manuscript
An illuminated manuscript is a formally prepared manuscript, document where the text is decorated with flourishes such as marginalia, borders and Miniature (illuminated manuscript), miniature illustrations. Often used in the Roman Catholic Churc ...
s. Anglo-Saxon art was influenced by Germanic art and Celtic art. Interactions with cultures from regions like the Mediterranean and early Christian Ireland
Early may refer to:
Places in the United States
* Early, Iowa, a city
* Early, Texas, a city
* Early Branch, a stream in Missouri
* Early County, Georgia
* Fort Early, Georgia, an early 19th century fort
Music
* Early B, stage name of Jamaican d ...
also influenced Anglo-Saxon arts.
In December 2019, Roman and Anglo-Saxon artifacts, including pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other raw materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is al ...
, jug
A jug is a type of container commonly used to hold and serve liquids, but not normally to drink from directly. It has an opening, sometimes narrow, from which to pour or drink, and has a handle, and usually a pouring lip. Jugs throughout histor ...
s, and jewelry
Jewellery (or jewelry in American English) consists of decorative items worn for personal adornment such as brooches, ring (jewellery), rings, necklaces, earrings, pendants, bracelets, and cufflinks. Jewellery may be attached to the body or the ...
, were unearthed from burial grounds by archaeologists led by Nigel Page at Baginton. The team of researchers believed that two of the graves belonged to a "high-status" rank officer and a Roman girl aged 6–12 years old. Findings from the Roman cremation burial site of a young girl included four brooch
A brooch (, ) is a decorative jewellery item designed to be attached to garments, often to fasten them together. It is usually made of metal, often silver or gold or some other material. Brooches are frequently decorated with enamel or with gem ...
es, a ring with an image of a cicada
The cicadas () are a superfamily, the Cicadoidea, of insects in the order Hemiptera (true bugs). They are in the suborder Auchenorrhyncha, along with smaller jumping bugs such as leafhoppers and froghoppers. The superfamily is divided into two ...
and a hair pin.
In August 2021, archaeologists headed by Gabor Thomas from the University of Reading
The University of Reading is a public research university in Reading, Berkshire, England. It was founded in 1892 as the University Extension College, Reading, an extension college of Christchurch College, Oxford, and became University College, ...
announced the discovery of a monastery
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of Monasticism, monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in Cenobitic monasticism, communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a ...
dated back to the reign of Queen Cynethryth
Cynethryth (''Cyneðryð''; died after AD 798) was a Queen of Mercia, wife of King Offa of Mercia and mother of King Ecgfrith of Mercia. Cynethryth is the only Anglo-Saxon queen consort in whose name coinage was definitely issued.
Biography Or ...
in the grounds of Holy Trinity Church in the village of Cookham
Cookham is a historic River Thames, Thames-side village and civil parishes in England, civil parish on the north-eastern edge of Berkshire, England, north-north-east of Maidenhead and opposite the village of Bourne End, Buckinghamshire, Bourne ...
in Berkshire. They also found items including food remains, pottery vessels used for cooking and eating, a fine bronze bracelet and a dress pin.
Burial
One of the most well-known aspects of early Anglo-Saxon society is their burial customs. Archaeological excavations at various sites includeSutton Hoo
Sutton Hoo is the site of two Anglo-Saxon cemeteries dating from the 6th to 7th centuries near Woodbridge, Suffolk, England. Archaeology, Archaeologists have been excavating the area since 1938, when an undisturbed ship burial containing a wea ...
, Spong Hill, Prittlewell
Prittlewell is an inner city area and former civil parish in Southend-on-Sea, in the ceremonial county of Essex, England. Historically, Prittlewell is the original settlement of the city, Southend being the ''south end'' of Prittlewell. The vil ...
, Snape and Walkington Wold. Around 1200 Anglo-Saxon pagan cemeteries have been discovered. There was no set form of burial amongst the pagan Anglo-Saxons, with cremation
Cremation is a method of Disposal of human corpses, final disposition of a corpse through Combustion, burning.
Cremation may serve as a funeral or post-funeral rite and as an alternative to burial. In some countries, including India, Nepal, and ...
being preferred amongst the Angles
Angles most commonly refers to:
*Angles (tribe), a Germanic-speaking people that took their name from the Angeln cultural region in Germany
*Angle, a geometric figure formed by two rays meeting at a common point
Angles may also refer to:
Places ...
in the north and inhumation
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and object ...
amongst the Saxons
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
in the south, although both forms were found throughout England, sometimes in the same cemeteries. When cremation did take place, the ashes were usually placed within an urn and then buried, sometimes along with grave goods. Free Anglo-Saxon men were buried with at least one weapon in the pagan tradition, often a seax
A ''seax'' (; also sax, sæx, sex; invariant in plural, latinized ''sachsum'') is a small sword, fighting knife or dagger typical of the Germanic peoples of the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages, especially the Saxons. The name comes f ...
, but sometimes also with a spear
A spear is a polearm consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with Fire hardening, fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable materia ...
, sword
A sword is an edged and bladed weapons, edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter ...
or shield, or a combination of these. Wealthy individuals were buried with rich grave good
Grave goods, in archaeology and anthropology, are items buried along with a corpse, body.
They are usually personal possessions, supplies to smooth the deceased's journey into an afterlife, or offerings to gods. Grave goods may be classed by re ...
s. There are also various recorded cases of animal skulls, particularly oxen but also pig, being buried in human graves, a practice that was also found in earlier Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the territory that became the Roman province of ''Britannia'' after the Roman conquest of Britain, consisting of a large part of the island of Great Britain. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410.
Julius Caes ...
.
The earliest Anglo-Saxon identifiable cemeteries appear in the early fifth century, scattered over several regions, with Kent
Kent is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Essex across the Thames Estuary to the north, the Strait of Dover to the south-east, East Sussex to the south-west, Surrey to the west, and Gr ...
as an outlier owing to notably dense settlement or perhaps an earlier and more sustained occupation. By the late fifth century, more cemeteries emerge — including along the Sussex
Sussex (Help:IPA/English, /ˈsʌsɪks/; from the Old English ''Sūþseaxe''; lit. 'South Saxons'; 'Sussex') is an area within South East England that was historically a kingdom of Sussex, kingdom and, later, a Historic counties of England, ...
coast—and some, such as Spong Hill, suggest Germanic-speaking arrivals may predate AD 450. Around ten thousand such cremations and inhumations are now known, revealing great diversity in burial styles and mortuary practice, pointing to many localized micro-cultures. Physical finds—including brooches unique to southern Britain (known as QuoitsSuzuki, Seiichi. The quoit brooch style and Anglo-Saxon settlement: a casting and recasting of cultural identity symbols. Boydell & Brewer, 2000.) - show culture was not merely transplanted from the Continent: from the start, new “Anglo-Saxon” identities were forming. Some sites yield large numbers of Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages, a group of Low Germanic languages also commonly referred to as "Frankish" varieties
* Francia, a post-Roman ...
artefacts, especially in Kent, generally interpreted as evidence of significant trade; similarly, Scandinavian elements in coastal cemeteries of East Anglia
East Anglia is an area of the East of England, often defined as including the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire, with parts of Essex sometimes also included.
The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, ...
may date to around the later fifth century., ''Mercia'', "The Archaeology of Mercia", by Martin Welch.
Skeletal analysis offers insights into how incomers and natives mixed. In some cemeteries, average male stature declines noticeably from the sixth to the eighth century, suggesting ongoing intermarriage with local Britons. The Stretton-on-Fosse II cemetery suggests that intermarriage with Romano-British women was common in some locations. Evidence for reuse of older Roman or prehistoric monuments raises the question of how such cemeteries may have drawn on preexisting identities—either genuinely inherited or claimed—and underscores the complexity of early Anglo-Saxon society, in which ethnic boundaries and burial practices often blurred.
 Eventually, in the 6th and 7th centuries,
Eventually, in the 6th and 7th centuries, burial mounds
A tumulus (: tumuli) is a mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds, mounds, howes, or in Siberia and Central Asia as ''kurgans'', and may be found throughout much of the world. ...
began to appear in Anglo-Saxon England, and in certain cases earlier burial mounds from the Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
, Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
, Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
and Romano-British
The Romano-British culture arose in Britain under the Roman Empire following the Roman conquest in AD 43 and the creation of the province of Britannia. It arose as a fusion of the imported Roman culture with that of the indigenous Britons, ...
periods were simply reused by the Anglo-Saxons. It is not known why they adopted this practice, but it may be from the practices of the native Britons. Burial mounds remained objects of veneration in early Anglo-Saxon Christianity, and numerous churches were built next to tumuli. Another form of burial was that of ship burial
A ship burial or boat grave is a burial in which a ship or boat is used either as the tomb for the dead and the grave goods, or as a part of the grave goods itself. If the ship is very small, it is called a boat grave. This style of burial was pr ...
s, which were practised by many of the Germanic peoples across northern Europe. In many cases it seems that the corpse was placed within a ship which was then either sent out to sea or left on land, but in both cases then set alight. In Suffolk
Suffolk ( ) is a ceremonial county in the East of England and East Anglia. It is bordered by Norfolk to the north, the North Sea to the east, Essex to the south, and Cambridgeshire to the west. Ipswich is the largest settlement and the county ...
however, ships were not burned, but buried, as is the case at Sutton Hoo, which is believed to have been the resting place of the king of the East Angles, Rædwald. Both ship and tumulus burials were described in the ''Beowulf'' poem, through the funerals of Scyld Scefing and Beowulf
''Beowulf'' (; ) is an Old English poetry, Old English poem, an Epic poetry, epic in the tradition of Germanic heroic legend consisting of 3,182 Alliterative verse, alliterative lines. It is one of the most important and List of translat ...
respectively.
There are also many cases where corpses have been found decapitated, for instance, at a mass grave in Thetford
Thetford is a market town and civil parishes in England, civil parish in the Breckland District of Norfolk, England. It is on the A11 road (England), A11 road between Norwich and London, just east of Thetford Forest. The civil parish, coverin ...
, Norfolk
Norfolk ( ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in England, located in East Anglia and officially part of the East of England region. It borders Lincolnshire and The Wash to the north-west, the North Sea to the north and eas ...
, fifty beheaded individuals were discovered, their heads possibly having been taken as trophies of war. In other cases of decapitation it seems possible that it was evidence of human sacrifice or execution.
In September 2020, archaeologists announced the discovery of a Sutton Hoo-era Anglo-Saxon cemetery with 17 cremations and 191 burials dating back to the 7th century in Oulton, near Lowestoft. The graves contained the remains of men, women and children, as well as artefacts including small iron knives and silver pennies, wrist clasps, strings of amber and glass beads. According to Andrew Peachey, who carried out the excavations, the skeletons had mostly vanished because of the highly acidic soil. They, fortunately, were preserved as brittle shapes and “sand silhouettes” in the sand.
In September 2021, archaeologists from LP-Archaeology led by Rachel Wood, have announced discovery of remains of St. Mary's Old Church which dates back to 1080 in Stoke Mandeville
Stoke Mandeville is a village and civil parish in the Vale of Aylesbury in Buckinghamshire, England. It is located three miles (5 km) from Aylesbury and 3.4 miles (5.5 km) from the market town of Wendover. Although a separate civil ...
. They unearthed flint walls forming a square structure, enclosed by a circular borderline and burials while working on the route of the HS2
High Speed 2 (HS2) is a high-speed railway which has been under construction in England since 2019. The line's planned route is between Handsacre – in southern Staffordshire – and London, with a branch to Birmingham. HS2 is to be Britain ...
high-speed railway.
Landscape archaeology
The Anglo-Saxons did not settle in an abandoned landscape on which they imposed new types of settlement and farming, as was once believed. By the late 4th century the English rural landscape was largely cleared and generally occupied by dispersed farms and hamlets, each surrounded by its own fields but often sharing other resources in common (called "infield-outfield cultivation"). Such fields, whether of prehistoric or Roman origin, fall into two very general types, found both separately and together: irregular layouts, in which one field after another had been added to an arable hub over many centuries; and regular rectilinear layouts, often roughly following the local topography, that had resulted from the large-scale division of considerable areas of land. Such stability was reversed within a few decades of the 5th century, as early "Anglo-Saxon" farmers, affected both by the collapse of Roman Britain and a climatic deterioration which reached its peak probably around 500, concentrated on subsistence, converting to pasture large areas of previously ploughed land. However, there is little evidence of abandoned arable land. Evidence across southern and central England increasingly shows the persistence of prehistoric and Roman field layouts into and, in some cases throughout, the Anglo-Saxon period, whether or not such fields were continuously ploughed. Landscapes atYarnton
Yarnton is a village and civil parish in Oxfordshire about southwest of Kidlington and northwest of Oxford. The 2011 Census recorded the parish's population as 2,545.
Archaeology
Early Bronze Age decorated beakers have been found in the par ...
, Oxfordshire, and Mucking
Mucking is a hamlet and former List of Church of England churches in Thurrock, Church of England parish and civil parish adjoining the Thames Estuary in the Thurrock Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area, in southern Essex, Eng ...
, Essex, remained unchanged throughout the 5th century, while at Barton Court, Oxfordshire, the 'grid of ditched paddocks or closes' of a Roman villa estate formed a general framework for the Anglo-Saxon settlement there. Similar evidence has been found at Sutton Courtenay
Sutton Courtenay is a village and civil parish in the Vale of White Horse district of Oxfordshire, England. It is situated on the south bank of the River Thames south of Abingdon-on-Thames and northwest of Didcot. The 2021 census recorded th ...
, Berkshire. The Romano-British fields at Church Down in Chalton Chalton may refer to:
* Chalton, Bedfordshire, England
* Chalton, Hampshire, England
See also
* Charlton (disambiguation)
{{place name disambiguation ...
and Catherington
Catherington is a village and former civil parish, now in the parish of Horndean, in the East Hampshire district of Hampshire, England. It is 1 mile (1.8 km) northwest of Horndean. The village is also close to Cowplain and Clanfield, Hampsh ...
, both in Hampshire, Bow Brickhill
Bow Brickhill is a village and civil parish in the unitary authority area of the City of Milton Keynes, Buckinghamshire, England. It is bounded to the north, west and east by the Milton Keynes urban area, approximately east of Fenny Stratfo ...
, Buckinghamshire, and Havering
The London Borough of Havering () in East London, England, forms part of Outer London. It has a population of 259,552 inhabitants; the principal town is Romford, while other communities include Hornchurch, Upminster, Collier Row and Rainham, Lo ...
, Essex, were all ploughed as late as the 7th century.
Susan Oosthuizen has taken this further and establishes evidence that aspects of the "collective organisation of arable cultivation appear to find an echo in fields of pre-historic and Roman Britain": in particular, the open field systems, shared between a number of cultivators but cropped individually; the link between arable holdings and rights to common pasture land; in structures of governance and the duty to pay some of the surplus to the local overlord, whether in rent or duty. Together these reveal that kinship ties and social relations were continuous across the 5th and 6th centuries, with no evidence of the uniformity or destruction, imposed by lords, the savage action of invaders or system collapse. This has implications on how later developments are considered, such as the developments in the 7th and 8th centuries.
Landscape studies draw upon a variety of topographical, archaeological and written sources. There are major problems in trying to relate Anglo-Saxon charter boundaries to those of Roman estates for which there are no written records, and by the end of the Anglo-Saxon period there had been major changes to the organisation of the landscape which can obscure earlier arrangements. Interpretation is also hindered by uncertainty about late Roman administrative arrangements. Nevertheless, studies carried out throughout the country, in "British" as well as "Anglo-Saxon" areas, have found examples of continuity of territorial boundaries where, for instance, Roman villa estate boundaries seem to have been identical with those of medieval estates, as delineated in early charters, though settlement sites within the defined territory might shift. What we see in these examples is probably continuity of the estate or territory as a unit of administration rather than one of exploitation. Although the upper level of Roman administration based on towns seems to have disappeared during the 5th century, a subsidiary system based on subdivisions of the countryside may have continued.
The basis of the internal organisation of both the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms and those of their Celtic neighbours was a large rural territory which contained a number of subsidiary settlements dependent upon a central residence which the Anglo-Saxons called a ''villa'' in Latin and a ''tūn'' in Old English. These developments suggest that the basic infrastructure of the early Anglo-Saxon local administration (or the settlement of early kings or earls) was inherited from late Roman or Sub-Roman Britain
Sub-Roman Britain, also called post-Roman Britain or Dark Age Britain, is the period of late antiquity in Great Britain between the end of Roman rule and the founding of Anglo-Saxon kingdoms. The term was originally used to describe archae ...
.
The Archaeology of the Anglo-Saxon Settlement of England
Archaeologists seeking to understand evidence for migration and/or acculturation in theAnglo-Saxon settlement of Britain
The settlement of Great Britain by Germanic peoples from continental Europe led to the development of an Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon cultural identity and a shared Germanic language—Old English—whose closest known relative is Old Frisian, s ...
must first get to grips with early Anglo-Saxon archaeology as an "Archaeology of Identity". Guarding against considering one aspect of archaeology in isolation, this concept ensures that different topics are considered together, that previously were considered separately, including gender, age, ethnicity, religion, and status.
Understanding the Roman legacy
Archaeological evidence for the emergence of both a native British identity and the appearance of a Germanic culture in Britain in the 5th and 6th centuries must consider first the period at the end of Roman rule. The collapse of Roman material culture some time in the early 5th century left a gap in the archaeological record that was quite rapidly filled by the intrusive Anglo-Saxon material culture, while the native culture became archaeologically close to invisible—although recent hoards and metal-detector finds show that coin use and imports did not stop abruptly at AD 410. The archaeology of the Roman military systems within Britain is well known but is not well understood: for example, whether theSaxon Shore
The Saxon Shore () was a military command of the Late Roman Empire, consisting of a series of fortifications on both sides of the English Channel. It was established in the late 3rd century and was led by the " Count of the Saxon Shore". In the ...
was defensive or to facilitate the passage of goods. Andrew Pearson suggests that the "Saxon Shore Forts" and other coastal installations played a more significant economic and logistical role than is often appreciated, and that the tradition of Saxon and other continental piracy, based on the name of these forts, is probably a myth.
The archaeology of late Roman (and sub-Roman) Britain has been mainly focused on the elite rather than the peasant and slave: their villas, houses, mosaics, furniture, fittings, and silver plates. This group had a strict code on how their wealth was to be displayed, and this provides a rich material culture, from which "Britons" are identified. There was a large gap between richest and poorest; the trappings of the latter have been the focus of less archaeological study. However the archaeology of the peasant from the 4th and 5th centuries is dominated by "ladder" field systems or enclosures, associated with extended families, and in the South and East of England, the extensive use of timber-built buildings and farmsteads shows a lower level of engagement with Roman building methods than is shown by the houses of the numerically much smaller elite.
Settler evidence
foederati
''Foederati'' ( ; singular: ''foederatus'' ) were peoples and cities bound by a treaty, known as ''foedus'', with Rome. During the Roman Republic, the term identified the '' socii'', but during the Roman Empire, it was used to describe foreign ...
'' or federate troops has been seen as coming from burials of Anglo-Saxons wearing military equipment of a type issued to late Roman forces, which have been found both in late Roman contexts, such as the Roman cemeteries of Winchester
Winchester (, ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in Hampshire, England. The city lies at the heart of the wider City of Winchester, a local government Districts of England, district, at the western end of the South Downs N ...
and Colchester
Colchester ( ) is a city in northeastern Essex, England. It is the second-largest settlement in the county, with a population of 130,245 at the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 Census. The demonym is ''Colcestrian''.
Colchester occupies the ...
, and in purely 'Anglo-Saxon' rural cemeteries like Mucking
Mucking is a hamlet and former List of Church of England churches in Thurrock, Church of England parish and civil parish adjoining the Thames Estuary in the Thurrock Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area, in southern Essex, Eng ...
(Essex), though this was at a settlement used by the Romano-British. The distribution of the earliest Anglo-Saxon sites and place names in close proximity to Roman settlements and roads has been interpreted as showing that initial Anglo-Saxon settlements were being controlled by the Romano-British.
Catherine Hills
Catherine Mary Hills is a British archaeologist and academic, who is a leading expert in Anglo-Saxon material culture. She is a senior research fellow at the McDonald Institute for Archaeological Research, University of Cambridge.
Education
I ...
suggests it is not necessary to see all the early settlers as federate troops, and that this interpretation has been used rather too readily by some archaeologists. A variety of relationships could have existed between Romano-British and incoming Anglo-Saxons. The broader archaeological picture suggests that no one model will explain all the Anglo-Saxon settlements in Britain and that there was considerable regional variation.Yorke, Barbara. Kings and kingdoms of early Anglo-Saxon England. Routledge, 2002. Settlement density varied within southern and eastern England. Norfolk
Norfolk ( ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in England, located in East Anglia and officially part of the East of England region. It borders Lincolnshire and The Wash to the north-west, the North Sea to the north and eas ...
has more large Anglo-Saxon cemeteries than the neighbouring East Anglian county of Suffolk
Suffolk ( ) is a ceremonial county in the East of England and East Anglia. It is bordered by Norfolk to the north, the North Sea to the east, Essex to the south, and Cambridgeshire to the west. Ipswich is the largest settlement and the county ...
; eastern Yorkshire (the nucleus of the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Deira
Deira ( ; Old Welsh/ or ; or ) was an area of Post-Roman Britain, and a later Anglian kingdom.
Etymology
The name of the kingdom is of Brythonic origin, and is derived from the Proto-Celtic , meaning 'oak' ( in modern Welsh), in which case ...
) far more than the rest of Northumbria. The settlers were not all of the same type. Some were indeed warriors who were buried equipped with their weapons, but we should not assume that all of these were invited guests who were to guard Romano-British communities. Possibly some, like the later Viking settlers, may have begun as piratical raiders who later seized land and made permanent settlements. Other settlers seem to have been much humbler people who had few if any weapons and suffered from malnutrition. These were characterised by Sonia Chadwick Hawkes
Sonia Chadwick Hawkes (5 November 1933 – 30 May 1999) was a British archaeologist specialising in early Anglo-Saxon archaeology. She led excavations on Anglo-Saxon cemeteries at Finglesham in Kent and Worthy Park in Hampshire. She was desc ...
as Germanic 'boat people', refugees from crowded settlements on the North Sea which deteriorating climatic conditions would have made untenable.
Tribal characteristics
 Catherine Hills points out that it is too easy to consider Anglo-Saxon archaeology solely as a study of
Catherine Hills points out that it is too easy to consider Anglo-Saxon archaeology solely as a study of ethnology
Ethnology (from the , meaning 'nation') is an academic field and discipline that compares and analyzes the characteristics of different peoples and the relationships between them (compare cultural, social, or sociocultural anthropology).
Sci ...
and to fail to consider that identity is "less related to an overall Anglo-Saxon ethnicity and more to membership of family or tribe, Christian or pagan, elite or peasant". "Anglo-Saxons" or "Britons" were no more homogeneous than nationalities are today, and they would have exhibited diverse characteristics: male/female, old/young, rich/poor, farmer/warrior—or even Gildas
Gildas (English pronunciation: , Breton language, Breton: ''Gweltaz''; ) — also known as Gildas Badonicus, Gildas fab Caw (in Middle Welsh texts and antiquarian works) and ''Gildas Sapiens'' (Gildas the Wise) — was a 6th-century Britons (h ...
' ''patria'' (fellow citizens), ''cives'' (indigenous people) and ''hostes'' (enemies)—as well as a diversity associated with language. Beyond these, in the early Anglo-Saxon period, identity was local: although people would have known their neighbours, it may have been important to indicate tribal loyalty with details of clothing and especially fasteners. It is sometimes hard in thinking about the period to avoid importing anachronistic 19th-century ideas of nationalism: in fact it is unlikely that people would have thought of themselves as Anglo-Saxon – instead they were part of a tribe or region, descendants of a patron or followers of a leader. It is this identity that archaeological evidence seeks to understand and determine, considering how it might support separate identity groups, or identities that were inter-connected.
Part of a well-furnished pagan-period mixed, inhumation-cremation, cemetery at Alwalton
Alwalton is a village and civil parish in Cambridgeshire, England. Alwalton lies approximately west of Peterborough city centre. Alwalton is situated within Huntingdonshire which is a non-metropolitan district of Cambridgeshire as well as being ...
near Peterborough was excavated in 1999. Twenty-eight urned and two unurned cremations dating from between the 5th and 6th centuries, and 34 inhumations, dating from between the late 5th and early 7th centuries, were uncovered. Both cremations and inhumations were provided with pyre or grave goods, and some of the burials were richly furnished. The excavation found evidence for a mixture of practices and symbolic clothing; these reflected local differences that appeared to be associated with tribal or family loyalty. This use of clothing in particular was very symbolic, and distinct differences within groups in the cemetery could be found.
Some recent scholarship has argued, however, that current approaches to the sociology of ethnicity render it extremely difficult, if not impossible, to demonstrate ethnic identity via purely archaeological means, and has thereby rejected the basis for using furnished inhumation or such clothing practices as the use of ''peplos
A peplos () is a body-length garment established as typical attire for women in ancient Greece by , during the late Archaic Greece, Archaic and Classical Greece, Classical period. It was a long, rectangular cloth with the top edge folded down ab ...
'' dress, or particular artistic styles found on artefacts such as those found at Alwalton, for evidence of pagan beliefs, or cultural memories of tribal or ethnic affiliation.
Distribution of settlements
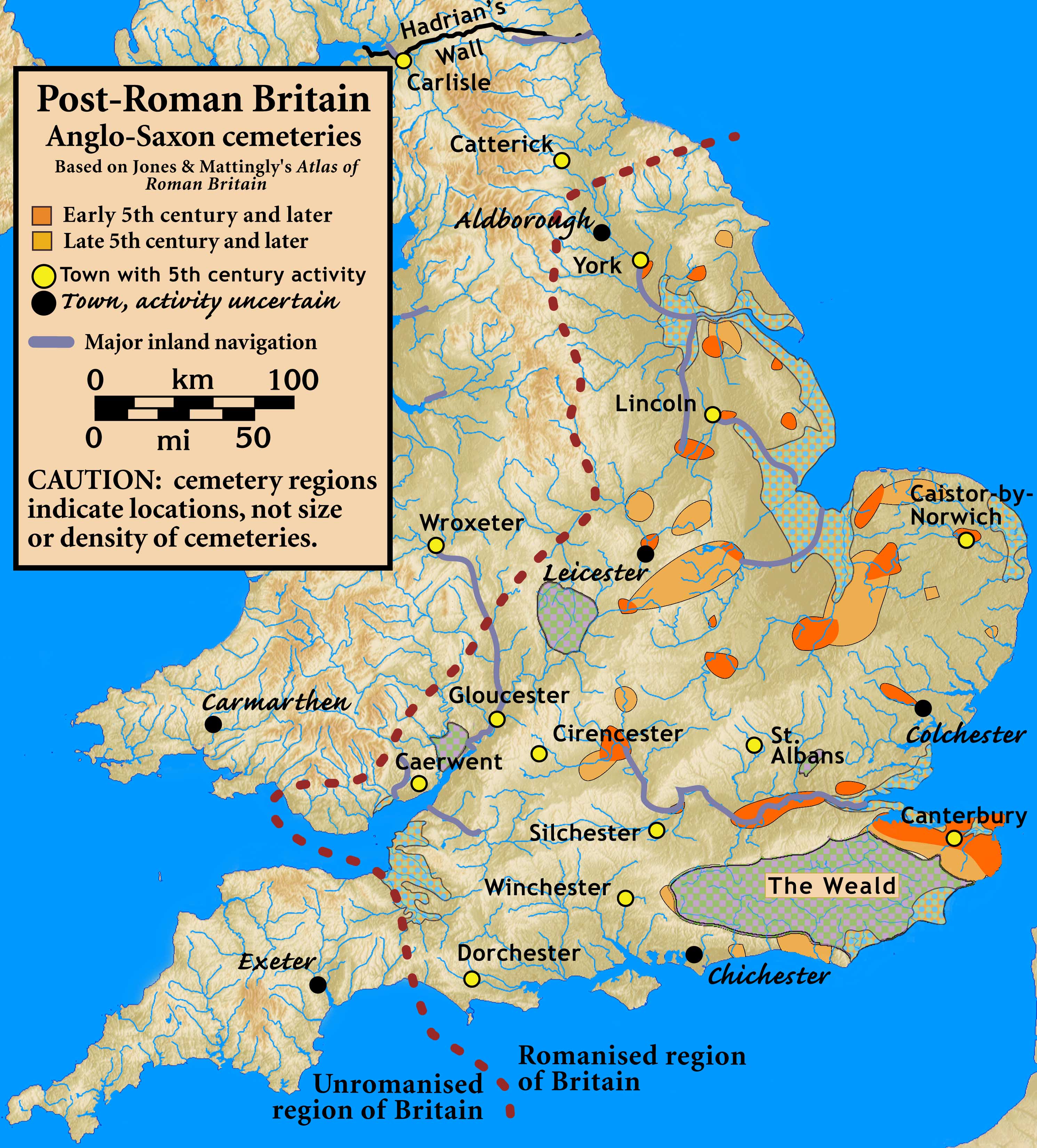
 There are a number of difficulties in recognising early Anglo-Saxon settlements as migrant settlers. This in part is because most early rural Anglo-Saxon sites have yielded few finds other than pottery and bone. The use of aerial photography does not yield easily identifiable settlements, partly due to the dispersed nature of many of these settlements.Hamerow, Helena, David A. Hinton, and Sally Crawford, eds. The Oxford Handbook of Anglo-Saxon Archaeology. OUP Oxford, 2011. p 119–124
The distribution of known settlements also remains elusive with few settlements found in the West Midlands or North-West. Even in Kent, an area of rich early Anglo-Saxon archaeology, the number of excavated settlements is fewer than expected. However, in contrast the counties of Northamptonshire, Oxfordshire, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire are relatively rich in early settlements. These have revealed a tendency for early Anglo-Saxon settlements to be on the light soils associated with river terraces.
Many of the inland settlements are on rivers that had been major navigation routes during the Roman era. These sites, such as
There are a number of difficulties in recognising early Anglo-Saxon settlements as migrant settlers. This in part is because most early rural Anglo-Saxon sites have yielded few finds other than pottery and bone. The use of aerial photography does not yield easily identifiable settlements, partly due to the dispersed nature of many of these settlements.Hamerow, Helena, David A. Hinton, and Sally Crawford, eds. The Oxford Handbook of Anglo-Saxon Archaeology. OUP Oxford, 2011. p 119–124
The distribution of known settlements also remains elusive with few settlements found in the West Midlands or North-West. Even in Kent, an area of rich early Anglo-Saxon archaeology, the number of excavated settlements is fewer than expected. However, in contrast the counties of Northamptonshire, Oxfordshire, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire are relatively rich in early settlements. These have revealed a tendency for early Anglo-Saxon settlements to be on the light soils associated with river terraces.
Many of the inland settlements are on rivers that had been major navigation routes during the Roman era. These sites, such as Dorchester on Thames
Dorchester on Thames is a historic village and civil parish in South Oxfordshire, Oxfordshire, England, located about 9 miles (14 km) southeast of Oxford at the confluence of the River Thames and River Thame.
The village has evidence of preh ...
on the upper Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after th ...
, were readily accessible by the shallow-draught, clinker-built
Clinker-built, also known as lapstrake-built, is a method of boat building in which the edges of longitudinal (lengthwise-running) hull (watercraft), hull planks overlap each other.
The technique originated in Northern Europe, with the first know ...
boats used by the Anglo-Saxons. The same is true of the settlements along the rivers Ouse
Ouse ( ) may refer to:
Places Rivers in England
* River Ouse, Yorkshire
* River Ouse, Sussex
* River Great Ouse, Northamptonshire and East Anglia
** River Little Ouse, a tributary of the River Great Ouse
Other places
* Ouse, Tasmania, a town ...
, Trent, Witham
Witham () is a town and civil parish in the Braintree district, in the county of Essex, England. In the 2011 census, it had a population of 25,353. It is twinned with the town of Waldbröl, Germany. Witham stands on the Roman road between the ...
, Nene and along the marshy lower Thames. Less well known due to a dearth of physical evidence but attested by surviving place names, there were Jutish settlements on the Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight (Help:IPA/English, /waɪt/ Help:Pronunciation respelling key, ''WYTE'') is an island off the south coast of England which, together with its surrounding uninhabited islets and Skerry, skerries, is also a ceremonial county. T ...
and the nearby southern coast of Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants.) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Berkshire to the north, Surrey and West Sussex to the east, the Isle of Wight across the Solent to the south, ...
.
A number of Anglo-Saxon settlements are located near or at Roman-era towns, but the question of simultaneous town occupation by the Romano-Britons and a nearby Anglo-Saxon settlement (i.e., suggesting a relationship) is not confirmed. At Roman Caistor-by-Norwich, for example, recent analysis suggests that the cemetery post-dates the town's virtual abandonment.
Isotope analysis
Isotope analysis
Isotope analysis is the identification of isotopic signature, abundance of certain stable isotopes of chemical elements within organic and inorganic compounds. Isotopic analysis can be used to understand the flow of energy through a food we ...
has begun to be employed to help answer the uncertainties regarding Anglo-Saxon migration; this can indicate whether an individual had always lived near his burial location. However, such studies cannot clearly distinguish ancestry. Thus, a descendant of migrants born in Britain would appear indistinguishable from somebody of native British origin.
Strontium
Strontium is a chemical element; it has symbol Sr and atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, it is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element that is highly chemically reactive. The metal forms a dark oxide layer when it is exposed to ...
data in a 5th–7th-century cemetery in West Heslerton implied the presence of two groups: one of "local" and one of "nonlocal" origin. Although the study suggested that they could not define the limits of local variation and identify immigrants with confidence, they could give a useful account of the issues. Oxygen and strontium isotope data in an early Anglo-Saxon cemetery at Wally Corner, Berinsfield
Berinsfield is an English village and civil parish in South Oxfordshire, about southeast of Oxford. The 2011 Census recorded the parish population as 2,806.
History
Palaeolithic and Roman artefacts were found during 20th century excavations ...
in the Upper Thames Valley, Oxfordshire, found only 5.3% of the sample originating from continental Europe, supporting the hypothesis of acculturation. Furthermore, they found that there was no change in this pattern over time, except amongst some females. Another isotope test, conducted in 2018 from skeletons found near Eastbourne
Eastbourne () is a town and seaside resort in East Sussex, on the south coast of England, east of Brighton and south of London. It is also a non-metropolitan district, local government district with Borough status in the United Kingdom, bor ...
in Sussex, concluded that neither the traditional invasion model nor the elite acculturation model was applicable. The study found a large number of migrants, both male and female, who seemed to be less wealthy than the natives. There was evidence of continued migration throughout the early Anglo-Saxon period.
Another isotopic method has been employed to investigate whether protein sources in human diets in the early Anglo-Saxon varied with geographic location, or with respect to age or sex. This would provide evidence for social advantage. The results suggest that protein sources varied little according to geographic location and that terrestrial foods dominated at all locations.Mays, S., and N. Beavan. "An investigation of diet in early Anglo-Saxon England using carbon and nitrogen stable isotope analysis of human bone collagen." Journal of Archaeological Science 39.4 (2012): 867–874.
Notable sites
*Sutton Hoo
Sutton Hoo is the site of two Anglo-Saxon cemeteries dating from the 6th to 7th centuries near Woodbridge, Suffolk, England. Archaeology, Archaeologists have been excavating the area since 1938, when an undisturbed ship burial containing a wea ...
* West Stow Anglo-Saxon Village
* Yeavering
Yeavering () is a hamlet in the north-east corner of the civil parish of Kirknewton in the English county of Northumberland. It is located on the River Glen at the northern edge of the Cheviot Hills. It is noteworthy as the site of a large Ang ...
* Taplow Barrow
The Taplow Barrow is an early medieval burial mound in Taplow Court, an estate in the south-eastern English county of Buckinghamshire. Constructed in the seventh century, when the region was part of an Anglo-Saxon kingdom, it contained the remains ...
* Mucking (archaeological site)
Mucking is an archaeological site near the village of Mucking in southern Essex. The site contains remains dating from the Neolithic to the Middle Ages—a period of some 3,000 years—and the Bronze Age and Anglo-Saxon features are particu ...
* Prittlewell royal Anglo-Saxon burial
The Prittlewell royal Anglo-Saxon burial or Prittlewell princely burial is a high-status Anglo-Saxon burial mounds, Anglo-Saxon burial mound which was excavated at Prittlewell, north of Southend-on-Sea, in the English county of Essex.
Artefacts ...
* Walkington Wold burials
The Walkington Wold burials in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England, comprise the skeletal remains of 13 individuals from the Anglo-Saxon period which were discovered in the late 1960s, during the excavation of a Bronze Age barrow. Subsequent e ...
* Staffordshire Hoard
The Staffordshire Hoard is the largest hoard of Anglo-Saxon gold and silver metalwork . It consists of almost 4,600 items and metal fragments, amounting to a total of of gold, of silver and some 3,500 pieces of garnet cloisonné je ...
* Canterbury-St Martin's hoard
The Canterbury-St Martin's hoard is a coin-hoard dating from the 6th century, found in the 19th century at Canterbury, Kent. The group, in the World Museum, Liverpool, consists of eight items, including three gold coins mounted with suspensio ...
* Snape
See also
* Anglo-Saxon hoards * Anglo-Saxon numismatics *Anglo-Saxon glass
Anglo-Saxon glass has been found across England during archaeological excavations of both settlement and cemetery sites. Glass in the History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon period was used in the manufacture of a range of objects including ve ...
Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{History of England