runtime environment
In computer programming, a runtime system or runtime environment is a sub-system that exists in the computer where a program is created, as well as in the computers where the program is intended to be run. The name comes from the compile time ...
used by the Android operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
. Replacing Dalvik, the process virtual machine originally used by Android, ART performs the translation of some of the application's bytecode into native instructions that are later executed by the device's runtime environment.
Overview
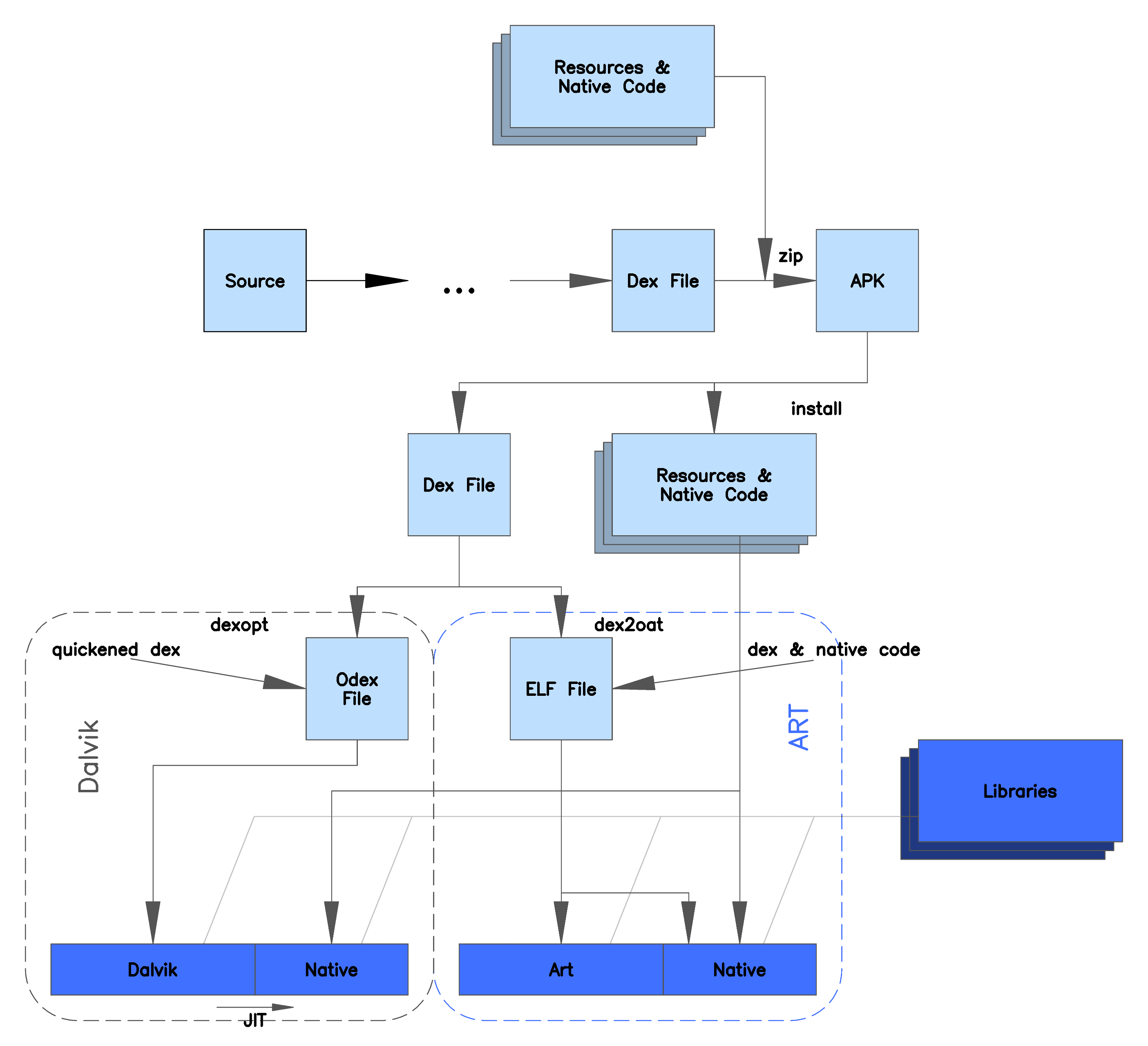 Android 2.2 "Froyo" brought trace-based just-in-time (JIT) compilation into Dalvik, optimizing the execution of applications by continually profiling applications each time they run and dynamically compiling frequently executed short segments of their bytecode into native machine code. While Dalvik interprets the rest of an application's bytecode, native execution of those short bytecode segments, called "traces", provides significant performance improvements.
Unlike Dalvik, ART introduces the use of ahead-of-time (AOT) compilation by compiling the most performance-critical parts of applications (previously, the entire app) into native machine code upon their installation. This way, ART improves the overall execution efficiency and reduces power consumption, which results in improved battery autonomy on
Android 2.2 "Froyo" brought trace-based just-in-time (JIT) compilation into Dalvik, optimizing the execution of applications by continually profiling applications each time they run and dynamically compiling frequently executed short segments of their bytecode into native machine code. While Dalvik interprets the rest of an application's bytecode, native execution of those short bytecode segments, called "traces", provides significant performance improvements.
Unlike Dalvik, ART introduces the use of ahead-of-time (AOT) compilation by compiling the most performance-critical parts of applications (previously, the entire app) into native machine code upon their installation. This way, ART improves the overall execution efficiency and reduces power consumption, which results in improved battery autonomy on mobile device
A mobile device or handheld device is a computer small enough to hold and operate in hand. Mobile devices are typically battery-powered and possess a flat-panel display and one or more built-in input devices, such as a touchscreen or keypad. ...
s. At the same time, ART brings faster execution of applications, improved memory allocation and garbage collection (GC) mechanisms, new applications debugging features, and more accurate high-level profiling of applications.
To maintain backward compatibility
In telecommunications and computing, backward compatibility (or backwards compatibility) is a property of an operating system, software, real-world product, or technology that allows for interoperability with an older legacy system, or with Input ...
, ART uses the same input bytecode as Dalvik, supplied through standard .dex files as part of APK files, while the .odex files are replaced with Executable and Linkable Format (ELF) executables. Once an application is compiled by using ART's on-device utility, it is run from the compiled ELF executable; as a result, ART eliminates various application execution overheads associated with Dalvik's interpretation and trace-based JIT compilation.
A disadvantage of ART is that additional time is required for compilation when an application is installed, and applications take up slightly more secondary storage
Computer data storage or digital data storage is a technology consisting of computer components and Data storage, recording media that are used to retain digital data. It is a core function and fundamental component of computers.
The cent ...
(usually flash memory
Flash memory is an Integrated circuit, electronic Non-volatile memory, non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for t ...
) to store the compiled code. Long AOT compilation became especially problematic when monthly security updates became the norm, locking users out of the OS for a long time after each update.
To improve on these, a hybrid approach was introduced in Android 7.0 (Nougat) which originally relies on JIT compilation, but later, when the device is idle and charging, compiles the most frequently used code as well as that on the UI thread to native code.
History
Android 4.4 "KitKat" introduced a technology preview of ART as an alternative runtime environment to Dalvik, which remained the default virtual machine. In the subsequent major Android release, Android 5.0 "Lollipop", Dalvik was entirely replaced by ART. Android 7.0 "Nougat" turned the ART from a pure AOT to a hybrid JIT/AOT solution, while switching its Java Runtime Environment from the discontinued Apache Harmony to OpenJDK, introducing a JIT compiler with code profiling. The JIT compiler complements ART's AOT compiler, helping to improve runtime performance and save storage space by identifying "hot code" (code which is frequently used, runs on the UI thread or affects startup time), which the AOT compiler compiles to machine code while the device is idle and charging. Less-frequently used code relies on JIT compilation. Android 9 "Pie" reduced the amount of storage used by APKs by using compressed bytecode files, and profiler data can be uploaded toGoogle Play
Google Play, also known as the Google Play Store, Play Store, or sometimes the Android Store (and was formerly Android Market), is a digital distribution service operated and developed by Google. It serves as the official app store for certifie ...
servers to be bundled with apps when downloaded by users with a similar device, which shortens download time from Google Play by up to 40%. Google Play cloud profiles allow apps to be optimized on installation, which helps avoid the initial performance issues present on Android 7.0 to 8.1.
In July 2021, the concept of baseline profiles was introduced. Baseline profiles are ART profiles that define methods and classes which should undergo AOT compilation from an app's first launch, and are compatible with Android 7.0 and later. They provide similar functionality to Android 9's Google Play cloud profiles when they are not available and automatically merge with cloud profiles when they are available. Baseline profiles are included with releases of AndroidX libraries and Jetpack Compose.
ART was updated with a new garbage collector (GC) utilizing the Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
userfaultfd system call in Android 13. It reduces memory pressure, compiled code size and jank, and prevents the risk of killing apps because of low memory during garbage collection. Other changes also improve app startup, reduce jank and improve performance. Because of the Mainline project, Android 12's ART will also be updated.
See also
* Android software development various concepts and software development utilities used for the creation of Android applications * Android version history a history and descriptions of Android releases, listed primarily by their official API levels * Comparison of application virtualization software various portable and scripting language virtual machines * Virtual machine an emulation of a particular computer system, with different degrees of implemented functionalityReferences
External links
* * , XDA Developers, February 12, 2014 * , Google I/O 2014, by Anwar Ghuloum, Brian Carlstrom and Ian Rogers * , Google I/O 2010, by Ben Cheng and Bill BuzbeeDelivering Highly Optimized Android Runtime (ART) and Web Runtime on Intel Architecture
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer compo ...
, August 4, 2015, by Haitao Feng and Jonathan Ding
Android 7.1 for Developers: Profile-guided JIT/AOT compilation
Android Developers, describes ART changes in Android 7.1 {{Java Virtual Machine Android (operating system) Java virtual machine Software using the Apache license