Ancient Pontus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pontus or Pontos (; ,) is a region on the southern coast of the


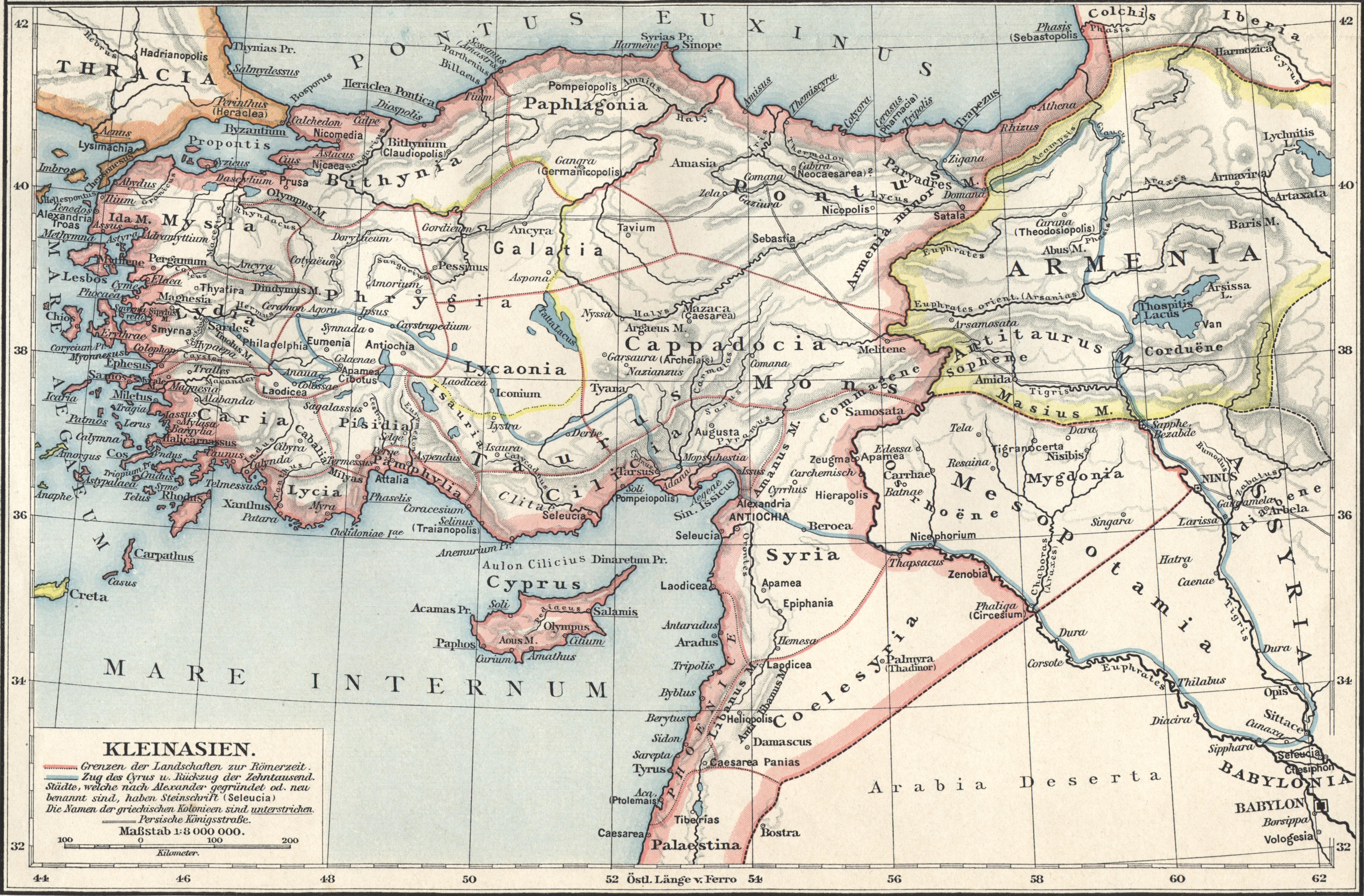 The first travels of Greek merchants and adventurers to the Pontus region occurred probably from around 1000 BC, whereas their settlements would become steady and solidified cities only by the 8th and 7th centuries BC as archaeological findings document. This fits in well with a foundation date of 731 BC as reported by
The first travels of Greek merchants and adventurers to the Pontus region occurred probably from around 1000 BC, whereas their settlements would become steady and solidified cities only by the 8th and 7th centuries BC as archaeological findings document. This fits in well with a foundation date of 731 BC as reported by

 With the reorganization of the provincial system under Diocletian (about AD 295), the Pontic districts were divided up between three smaller, independent provinces within the Dioecesis Pontica:
*Galatian Pontus, also called Diospontus, later renamed Helenopontus by
With the reorganization of the provincial system under Diocletian (about AD 295), the Pontic districts were divided up between three smaller, independent provinces within the Dioecesis Pontica:
*Galatian Pontus, also called Diospontus, later renamed Helenopontus by
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
, located in the modern-day eastern Black Sea region of Turkey. The name was applied to the coastal region and its mountainous hinterland (rising to the Pontic Alps
The Pontic Mountains or Pontic Alps (, meaning 'North Anatolian Mountains'), form a mountain range in northern Anatolia, Turkey. They are also known as the "Parhar Mountains" in the local Turkish and Pontic Greek languages. The term ''Parhar'' ...
in the east) by the Greeks who colonized the area in the Archaic period and derived from the Greek name of the Black Sea: (), 'Hospitable Sea', or simply ''Pontos'' () as early as the Aeschylean ''Persians
Persians ( ), or the Persian people (), are an Iranian ethnic group from West Asia that came from an earlier group called the Proto-Iranians, which likely split from the Indo-Iranians in 1800 BCE from either Afghanistan or Central Asia. They ...
'' (472 BC) and Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
' ''Histories
Histories or, in Latin, Historiae may refer to:
* the plural of history
* ''Histories'' (Herodotus), by Herodotus
* ''The Histories'', by Timaeus
* ''The Histories'' (Polybius), by Polybius
* ''Histories'' by Gaius Sallustius Crispus (Sallust) ...
'' ().
Having originally no specific name, the region east of the river Halys was spoken of as the country ''()'', , and hence it acquired the name of Pontus, which is first found in Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; ; 355/354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian. At the age of 30, he was elected as one of the leaders of the retreating Ancient Greek mercenaries, Greek mercenaries, the Ten Thousand, who had been ...
's ''Anabasis
Anabasis (from Greek ''ana'' = "upward", ''bainein'' = "to step or march") is an expedition from a coastline into the interior of a country. Anabase and Anabasis may also refer to:
History
* '' Anabasis Alexandri'' (''Anabasis of Alexander''), ...
'' (). The extent of the region varied through the ages but generally extended from the borders of Colchis
In classical antiquity and Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia.
Its population, the ...
(modern western Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
) until well into Paphlagonia
Paphlagonia (; , modern translit. ''Paflagonía''; ) was an ancient region on the Black Sea coast of north-central Anatolia, situated between Bithynia to the west and Pontus (region), Pontus to the east, and separated from Phrygia (later, Galatia ...
in the west, with varying amounts of hinterland
Hinterland is a German word meaning the 'land behind' a city, a port, or similar. Its use in English was first documented by the geographer George Chisholm in his ''Handbook of Commercial Geography'' (1888). Originally the term was associated wi ...
. Several states and provinces bearing the name of Pontus or variants thereof were established in the region in the Hellenistic
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
, Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
and Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
periods, culminating in the late Byzantine Empire of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond or the Trapezuntine Empire was one of the three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire that existed during the 13th through to the 15th century. The empire consisted of the Pontus, or far northeastern corner of A ...
. Pontus is sometimes considered as the original home of the Amazons
The Amazons (Ancient Greek: ', singular '; in Latin ', ') were a people in Greek mythology, portrayed in a number of ancient epic poems and legends, such as the Labours of Hercules, Labours of Heracles, the ''Argonautica'' and the ''Iliad''. ...
, in ancient Greek mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories conc ...
and historiography
Historiography is the study of the methods used by historians in developing history as an academic discipline. By extension, the term ":wikt:historiography, historiography" is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiog ...
(e.g. by Herodotus and Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
).
History

Early inhabitants
Pontus remained outside the reach of theBronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
empires, of which the closest was Great Hatti
Hatti may refer to
*Hatti (; Assyrian ) in Bronze Age Anatolia:
**the area of Hattusa, roughly delimited by the Halys bend
**the Hattians of the 3rd and 2nd millennia BC
**the Hittites of ''ca'' 1400–1200 BC
**the areas to the west of the Euphra ...
. The region went further uncontrolled by Hatti's eastern neighbors, Hurrian
The Hurrians (; ; also called Hari, Khurrites, Hourri, Churri, Hurri) were a people who inhabited the Ancient Near East during the Bronze Age. They spoke the Hurro-Urartian language, Hurrian language, and lived throughout northern Syria (region) ...
states like Azzi and (or) Hayasa. In those days, the best any outsider could hope from this region was temporary alliance with a local strongman. The Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian peoples, Anatolian Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European people who formed one of the first major civilizations of the Bronze Age in West Asia. Possibly originating from beyond the Black Sea, they settled in mo ...
called the unorganized groups on their northeastern frontier the Kaška Kashka may refer to:
* Kaskians
The Kaska (also Kaška, later Tabal (state), Tabalian Kasku and Gasga) were a loosely affiliated Bronze Age non-Indo-European tribal people, who spoke the unclassified Kaskian language and lived in mountainous East ...
. As of 2004 little had been found of them archaeologically.
In the wake of the Hittite empire's collapse, the Assyrian court noted that the "Kašku" had overrun its territory in conjunction with a hitherto unknown group whom they labeled the Muški
The Mushki (sometimes transliterated as Muški) were an Iron Age people of Anatolia who appear in sources from Assyria but not from the Hittites. Several authors have connected them with the Moschoi (Μόσχοι) of Greek sources and the Geor ...
. Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
visitors to the region, mostly Greek, noted that the hinterlands remained disunited, and they recorded the names of tribes: Moskhians (often associated with those Muški), Leucosyri
The Leuco-Syrians or literally White Syrians ( or ), also known as Syrians ( or ), and Cappadocians () were an ancient people in central Anatolia during the period of Classical Antiquity.
Name
''Leuco-Syroi'' translates literally to White-Sy ...
, Mares, Makrones, Mossynoikoi, Tibarenoi, Tzans
The Macrones ( ka, მაკრონები, ; , ''Makrōnes'') were an ancient Colchian tribe in the east of Pontus, about the Moschici Mountains (modern Yalnizçam Dağlari, Turkey). The name is allegedly derived from the name of Kromni ...
Hewsen, 43. and Chalybes
The Chalybes (; ; ka, ხალიბები, Khalibebi) and Chaldoi (; ) were peoples mentioned by classical authors as living in Pontus and Cappadocia in northern Anatolia during Classical Antiquity. Their territory was known as Chaldia, e ...
or Chaldoi.Hewsen, 46.
The Armenian language
Armenian (endonym: , , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language and the sole member of the independent branch of the Armenian language family. It is the native language of the Armenians, Armenian people and the official language of ...
went unnoted by the Hittites, the Assyrians, and all the post-Hittite nations; an ancient theory – first conjectured by Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
– is that its speakers migrated from Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; , ''Phrygía'') was a kingdom in the west-central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River.
Stories of the heroic age of Greek mythology tell of several legendary Ph ...
, past literary notice, across Pontus during the early Iron Age. The Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
, who spoke a closely related Indo-European tongue, followed them along the coast. The Greeks are the earliest long-term inhabitants of the region from whom written records survive. During the late 8th century BC, Pontus further became a base for the Cimmerians
The Cimmerians were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into W ...
, another Indo-European speaking people; however, these were defeated by the Lydians
The Lydians (Greek language, Greek: Λυδοί; known as ''Sparda'' to the Achaemenids, Old Persian cuneiform Wikt:𐎿𐎱𐎼𐎭, 𐎿𐎱𐎼𐎭) were an Anatolians, Anatolian people living in Lydia, a region in western Anatolia, who spo ...
, and became a distant memory after the campaigns of Alyattes
Alyattes ( Lydian language: ; ; reigned c. 635 – c. 585 BC), sometimes described as Alyattes I, was the fourth king of the Mermnad dynasty in Lydia, the son of Sadyattes, grandson of Ardys, and great-grandson of Gyges. He died after a r ...
.
Since there was so little literacy in northeastern Anatolia until the Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
and Hellenistic era, one can only speculate as to the other languages spoken here. Given that Kartvelian languages
The Kartvelian languages ( ; ka, ქართველური ენები, tr; also known as South Caucasian or Kartvelic languages Boeder (2002), p. 3) are a language family indigenous to the South Caucasus and spoken primarily in Geor ...
remain spoken to the east of Pontus, some are suspected to have been spoken in eastern Pontus during the Iron Age: the Tzans are usually associated with today's Laz.Ancient Greek colonization

 The first travels of Greek merchants and adventurers to the Pontus region occurred probably from around 1000 BC, whereas their settlements would become steady and solidified cities only by the 8th and 7th centuries BC as archaeological findings document. This fits in well with a foundation date of 731 BC as reported by
The first travels of Greek merchants and adventurers to the Pontus region occurred probably from around 1000 BC, whereas their settlements would become steady and solidified cities only by the 8th and 7th centuries BC as archaeological findings document. This fits in well with a foundation date of 731 BC as reported by Eusebius of Caesarea
Eusebius of Caesarea (30 May AD 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilius, was a historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christian polemicist from the Roman province of Syria Palaestina. In about AD 314 he became the bishop of Caesarea Maritima. ...
for Sinope
Sinope may refer to:
*Sinop, Turkey, a city on the Black Sea, historically known as Sinope
** Battle of Sinop, 1853 naval battle in the Sinop port
*Sinop Province
* Sinope, Leicestershire, a hamlet in the Midlands of England
* Sinope (mythology), i ...
, perhaps the most ancient of the Greek colonies in what was later to be called Pontus.Hewsen, 39 f. The epical narratives related to the travels of Jason
Jason ( ; ) was an ancient Greek mythological hero and leader of the Argonauts, whose quest for the Golden Fleece is featured in Greek literature. He was the son of Aeson, the rightful king of Iolcos. He was married to the sorceress Med ...
and the Argonauts
The Argonauts ( ; ) were a band of heroes in Greek mythology, who in the years before the Trojan War (around 1300 BC) accompanied Jason to Colchis in his quest to find the Golden Fleece. Their name comes from their ship, ''Argo'', named after it ...
to Colchis
In classical antiquity and Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia.
Its population, the ...
, the tales of Heracles
Heracles ( ; ), born Alcaeus (, ''Alkaios'') or Alcides (, ''Alkeidēs''), was a Divinity, divine hero in Greek mythology, the son of ZeusApollodorus1.9.16/ref> and Alcmene, and the foster son of Amphitryon.By his adoptive descent through ...
' navigating the Black Sea, and Odysseus
In Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology, Odysseus ( ; , ), also known by the Latin variant Ulysses ( , ; ), is a legendary Greeks, Greek king of Homeric Ithaca, Ithaca and the hero of Homer's Epic poetry, epic poem, the ''Odyssey''. Od ...
' wanderings into the land of the Cimmerians
The Cimmerians were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into W ...
, as well as the myth of Zeus
Zeus (, ) is the chief deity of the List of Greek deities, Greek pantheon. He is a sky father, sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus.
Zeus is the child ...
constraining Prometheus
In Greek mythology, Prometheus (; , , possibly meaning "forethought")Smith"Prometheus". is a Titans, Titan. He is best known for defying the Olympian gods by taking theft of fire, fire from them and giving it to humanity in the form of technol ...
to the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
mountains as a punishment for his outwitting the Gods, can all be seen as reflections of early contacts between early Greek colonists and the local, probably Caucasian, peoples. The earliest known written description of Pontus, however, is that of Scylax of Korianda, who in the 7th century BC described Greek settlements in the area.Hewsen, 39.
Persian Empire expansion
By the 6th century BC, Pontus had become officially a part of theAchaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, i ...
, which probably meant that the local Greek colonies were paying tribute to the Persians. When the Athenian commander Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; ; 355/354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian. At the age of 30, he was elected as one of the leaders of the retreating Ancient Greek mercenaries, Greek mercenaries, the Ten Thousand, who had been ...
passed through Pontus around a century later in 401-400 BC, in fact, he found no Persians in Pontus.Hewsen, 40.
The peoples of this part of northern Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
were incorporated into the third and nineteenth satrapies
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Persian (Achaemenid) Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires. A satrapy is the territory governed by a satrap.
...
of the Persian empire. Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
ian influence ran deep, illustrated most famously by the temple of the Persian deities Anaitis, Omanes, and Anadatos at Zela, founded by victorious Persian generals in the 6th century BC.
Kingdom of Pontus
TheKingdom of Pontus
Pontus ( ) was a Hellenistic kingdom centered in the historical region of Pontus in modern-day Turkey, and ruled by the Mithridatic dynasty of Persian origin, which may have been directly related to Darius the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty. ...
extended generally to the east of the Halys River. The Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
dynasty which was to found this kingdom had during the 4th century BC ruled the Greek city of Cius
Cius (; ''Kios''), later renamed Prusias on the Sea (; ) after king Prusias I of Bithynia, was an ancient Greek city bordering the Propontis (now known as the Sea of Marmara), in Bithynia and in Mysia (in modern northwestern Turkey), and had a ...
(or Kios) in Mysia
Mysia (UK , US or ; ; ; ) was a region in the northwest of ancient Asia Minor (Anatolia, Asian part of modern Turkey). It was located on the south coast of the Sea of Marmara. It was bounded by Bithynia on the east, Phrygia on the southeast, Lyd ...
, with its first known member being Ariobarzanes I of Cius and the last ruler based in the city being Mithridates II of Cius. Mithridates II's son, also called Mithridates
Mithridates or Mithradates (Old Persian 𐎷𐎡𐎰𐎼𐎭𐎠𐎫 ''Miθradāta'') is the Hellenistic period, Hellenistic form of an Iranian languages, Iranian theophoric name, meaning "given by Mithra". Its Modern Persian form is Mehrdad. It ...
, would proclaim himself later Mithridates I Ktistes of Pontus.
As the ''Encyclopaedia Iranica
An encyclopedia is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge, either general or special, in a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into articles or entries that are arranged alphabetically by artic ...
'' states, the most famous member of the family, Mithradates VI Eupator
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator (; 135–63 BC) was the ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an effective, ambitious, and r ...
, although undoubtedly presenting himself to the Greek world as a civilized philhellene and new Alexander, also paraded his Iranian
Iranian () may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Iran
** Iranian diaspora, Iranians living outside Iran
** Iranian architecture, architecture of Iran and parts of the rest of West Asia
** Iranian cuisine, cooking traditions and practic ...
background: he maintained a harem and eunuchs
A eunuch ( , ) is a male who has been castration, castrated. Throughout history, castration often served a specific social function. The earliest records for intentional castration to produce eunuchs are from the Sumerian city of Lagash in the 2 ...
in true Oriental fashion; he gave all his sons Persian names; he sacrificed spectacularly in the manner of the Persian kings at Pasargadae
Pasargadae (; ) was the capital of the Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great (559–530 BC), located just north of the town of Madar-e-Soleyman and about to the northeast of the city of Shiraz. It is one of Iran's UNESCO World Heritage Site ...
(Appian, Mith. 66, 70); and he appointed “satraps
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median kingdom, Median and Achaemenid Empire, Persian (Achaemenid) Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic period, Hellenistic empi ...
” (a Persian title) as his provincial governors. Iranica further states, and although there is only one inscription attesting it, he seems to have adopted the title “king of kings.” The very small number of Hellenistic Greek inscriptions that have been found anywhere in Pontus suggest that Greek culture
The culture of Greece has evolved over thousands of years, beginning in Minoan and later in Mycenaean Greece, continuing most notably into Classical Greece, while influencing the Roman Empire and its successor the Byzantine Empire. Other cultu ...
did not substantially penetrate beyond the coastal cities and the court.
During the troubled period following the death of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
, Mithridates Ktistes was for a time in the service of Antigonus Antigonus or Antigonos (), a Greek name meaning "comparable to his father" or "worthy of his father", may refer to:
Rulers
* Three Macedonian kings of the Antigonid dynasty that succeeded Alexander the Great:
** Antigonus I Monophthalmus (382� ...
, one of Alexander's successors, and successfully maneuvering in this unsettled time managed, shortly after 302 BC, to create the Kingdom of Pontus which would be ruled by his descendants mostly bearing the same name, until 64 BC. Thus, this Persian dynasty managed to survive and prosper in the Hellenistic
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
world while the main Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the larg ...
had fallen.
This kingdom reached its greatest height under Mithridates VI
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator (; 135–63 BC) was the ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an effective, ambitious, and r ...
or Mithridates Eupator, commonly called the Great, who for many years carried on war with the Romans. Under him, the realm of Pontus included not only Pontic Cappadocia but also the seaboard from the Bithynia
Bithynia (; ) was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor (present-day Turkey), adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwest, Paphlagonia to the northeast a ...
n frontier to Colchis
In classical antiquity and Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia.
Its population, the ...
, part of inland Paphlagonia
Paphlagonia (; , modern translit. ''Paflagonía''; ) was an ancient region on the Black Sea coast of north-central Anatolia, situated between Bithynia to the west and Pontus (region), Pontus to the east, and separated from Phrygia (later, Galatia ...
, and Lesser Armenia
Lesser Armenia (; ; ), also known as Armenia Minor and Armenia Inferior, comprised the Armenian-populated regions primarily to the west and northwest of the ancient Kingdom of Armenia (also known as Kingdom of Greater Armenia), on the western sid ...
. Despite ruling Lesser Armenia, King Mithridates VI was an ally of Armenian King Tigranes the Great
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great (''Tigran Mets'' in Armenian language, Armenian; 140–55 BC), was a king of Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Armenia. A member of the Artaxiad dynasty, he ruled from 95 BC to 55 BC. Under hi ...
, to whom he married his daughter Cleopatra. Eventually, however, the Romans defeated both King Mithridates VI and his son-in-law, Armenian King Tigranes the Great, during the Mithridatic Wars
The Mithridatic Wars were three conflicts fought by the Roman Republic against the Kingdom of Pontus and its allies between 88 and 63 BC. They are named after Mithridates VI, the King of Pontus during the course of the wars, who initiated the ho ...
, bringing Pontus under Roman rule.Hewsen, 42.
Roman province
With the subjugation of this kingdom byPompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey ( ) or Pompey the Great, was a Roman general and statesman who was prominent in the last decades of the Roman Republic. ...
in 64 BC, little changed in the daily lives of either the oligarchies that controlled the cities or for the common people there and in the hinterland, though the meaning of the name Pontus underwent a change. Part of the kingdom was now annexed to the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
, being united with Bithynia in a double province called Pontus and Bithynia: this part included only the seaboard between Heraclea (today Ereğli) and Amisus
Samsun is a List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, city on the north coast of Turkey and a major Black Sea port. The urban area recorded a population of 738,692 in 2022. The city is the capital of Samsun Province which has a population of ...
(Samsun
Samsun is a List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, city on the north coast of Turkey and a major Black Sea port. The urban area recorded a population of 738,692 in 2022. The city is the capital of Samsun Province which has a population of ...
), the ''ora Pontica''. The larger part of Pontus, however, was included in the province of Galatia.
Hereafter the simple name Pontus without qualification was regularly employed to denote the half of this dual province, especially by Romans and people speaking from the Roman point of view; it is so used almost always in the New Testament
The New Testament (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus, as well as events relating to Christianity in the 1st century, first-century Christianit ...
. The eastern half of the old kingdom was administered as a client kingdom
A client state in the context of international relations is a state that is economically, politically, and militarily subordinated to a more powerful controlling state. Alternative terms for a ''client state'' are satellite state, associated state ...
together with Colchis
In classical antiquity and Greco-Roman geography, Colchis (; ) was an exonym for the Georgian polity of Egrisi ( ka, ეგრისი) located on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, centered in present-day western Georgia.
Its population, the ...
. Its last king was Polemon II.
In AD 62, the country was constituted by Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68) was a Roman emperor and the final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 until his ...
a Roman province
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as Roman g ...
. It was divided into the three districts: Pontus Galaticus in the west, bordering on Galatia
Galatia (; , ''Galatía'') was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace (cf. Tylis), who settled here ...
; Pontus Polemoniacus in the centre, so called from its capital Polemonium
''Polemonium'', commonly called Jacob's ladders or Jacob's-ladders (the name derived from the Biblical story), is a genus of between 25 and 40 species of flowering plants in the family Polemoniaceae, native to cool temperate to arctic regions ...
; and Pontus Cappadocicus in the east, bordering on Cappadocia (Armenia Minor). Subsequently, the Roman Emperor Trajan
Trajan ( ; born Marcus Ulpius Traianus, 18 September 53) was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, remembered as the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier ...
moved Pontus into the province of Cappadocia itself in the early 2nd century AD. In response to a Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, a Germanic people
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Gothic alphabet, an alphabet used to write the Gothic language
** Gothic ( ...
raid on Trebizond in 287 AD, the Roman Emperor Diocletian
Diocletian ( ; ; ; 242/245 – 311/312), nicknamed Jovius, was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Diocles to a family of low status in the Roman province of Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia. As with other Illyri ...
decided to break up the area into smaller provinces under more localized administration.
 With the reorganization of the provincial system under Diocletian (about AD 295), the Pontic districts were divided up between three smaller, independent provinces within the Dioecesis Pontica:
*Galatian Pontus, also called Diospontus, later renamed Helenopontus by
With the reorganization of the provincial system under Diocletian (about AD 295), the Pontic districts were divided up between three smaller, independent provinces within the Dioecesis Pontica:
*Galatian Pontus, also called Diospontus, later renamed Helenopontus by Constantine the Great
Constantine I (27 February 27222 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was a Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337 and the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity. He played a Constantine the Great and Christianity, pivotal ro ...
after his mother
A mother is the female parent of a child. A woman may be considered a mother by virtue of having given birth, by raising a child who may or may not be her biological offspring, or by supplying her ovum for fertilisation in the case of ges ...
. It had its capital at Amisus
Samsun is a List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, city on the north coast of Turkey and a major Black Sea port. The urban area recorded a population of 738,692 in 2022. The city is the capital of Samsun Province which has a population of ...
, and included the cities of Sinope
Sinope may refer to:
*Sinop, Turkey, a city on the Black Sea, historically known as Sinope
** Battle of Sinop, 1853 naval battle in the Sinop port
*Sinop Province
* Sinope, Leicestershire, a hamlet in the Midlands of England
* Sinope (mythology), i ...
, Amasia
Amasia may refer:
* Amasya, a city in Northern Turkey
** Amasya Province, which contains the city
** Amasea (titular see), the former Metropolitan Archbishopric with see there, now a Latin Catholic titular see
* Amasia, Shirak, a town in Armenia
...
, Andres, Ibora, and Zela as well.
*Pontus Polemoniacus, with its capital at Polemonium (also called Side
Side or Sides may refer to:
Geometry
* Edge (geometry) of a polygon (two-dimensional shape)
* Face (geometry) of a polyhedron (three-dimensional shape)
Places
* Side, Turkey, a city in Turkey
* Side (Ainis), a town of Ainis, ancient Thessaly, ...
), and including the cities of Neocaesarea
Niksar, historically known as Neocaesarea (Νεοκαισάρεια), is a city in Tokat Province, Turkey. It is the seat of Niksar District.Argyroupolis, Comana, and Cerasus as well.
*Cappadocian Pontus, with its capital at Trebizond, and including the small ports of Athanae and Rhizaeon. This province extended all the way to Colchis.
 The Byzantine Emperor
The Byzantine Emperor

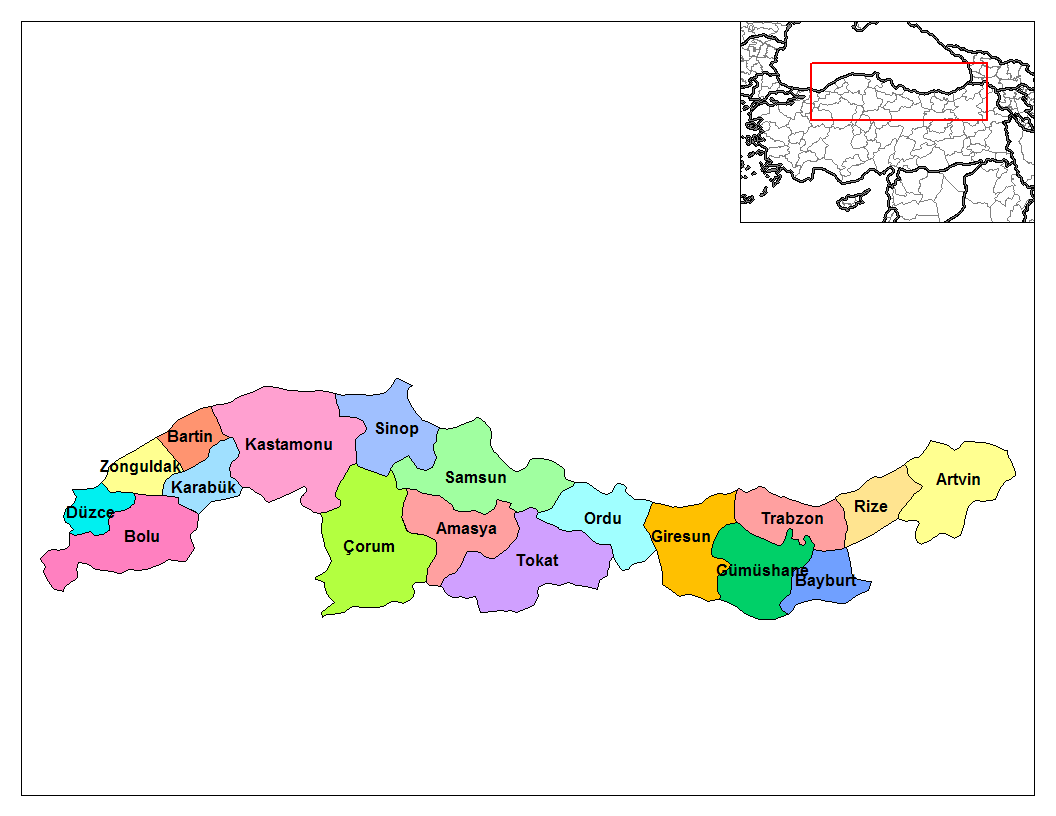 The Black Sea Region (), comprising all or parts of 22 provinces, is one of
The Black Sea Region (), comprising all or parts of 22 provinces, is one of
History of Pontus
The term Euxinus Pontus
Where East Meets West
{{Authority control Ancient Greek geography Historical regions of Anatolia History of Amasya Province History of Giresun Province History of Rize Province History of Tokat Province History of Trabzon Province
Byzantine province and theme
Justinian
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was ...
further reorganized the area in 536:
*Pontus Polemoniacus was dissolved, with the western part (Polemonium and Neocaesarea) going to Helenopontus, Comana going to the new province of Armenia II, and the rest (Trebizond and Cerasus) joining the new province of Armenia I Magna with its capital at Justinianopolis.
*Helenopontus gained Polemonium and Neocaesarea, and lost Zela to Armenia II. The provincial governor was relegated to the rank of ''moderator''.
*Paphlagonia absorbed Honorias and was put under a praetor
''Praetor'' ( , ), also ''pretor'', was the title granted by the government of ancient Rome to a man acting in one of two official capacities: (i) the commander of an army, and (ii) as an elected ''magistratus'' (magistrate), assigned to disch ...
.
By the time of the early Byzantine Empire, Trebizond became a center of culture and scientific learning. In the 7th century, an individual named Tychicus returned from Constantinople to establish a school of learning. One of his students was the early Armenian scholar Anania of Shirak.Hewsen, 47.
Under the Byzantine Empire, the Pontus came under the Armeniac Theme
The Armeniac Theme (, ''Armeniakon hema'), more properly the Theme of the Armeniacs (Greek: , ''thema Armeniakōn''), was a Byzantine theme (a military-civilian province) located in northeastern Asia Minor (modern Turkey).
History
The Armeniac ...
, with the westernmost parts (Paphlagonia) belonging to the Bucellarian Theme
The Bucellarian Theme (, ''Boukellarion thema''), more properly known as the Theme of the Bucellarians (, ''thema Boukellariōn'') was a Byzantine theme (a military-civilian province) in northern Asia Minor (modern Turkey). It was created around ...
. Progressively, these large early themes were divided into smaller ones, so that by the late 10th century, the Pontus was divided into the themes of Chaldia
Chaldia (, ''Khaldia'') was a historical region located in the mountainous interior of the eastern Black Sea, northeast Anatolia (modern Turkey). Its name was derived from a people called the ''Chaldoi'' (or '' Chalybes'') that inhabited the reg ...
, which was governed by the Gabrades family, and Koloneia. After the 8th century, the area experienced a period of prosperity, which was brought to an end only by the Seljuk Seljuk (, ''Selcuk'') or Saljuq (, ''Saljūq'') may refer to:
* Seljuk Empire (1051–1153), a medieval empire in the Middle East and central Asia
* Seljuk dynasty (c. 950–1307), the ruling dynasty of the Seljuk Empire and subsequent polities
* S ...
conquest of Asia Minor in the 1070s and 1080s. Restored to the Byzantine Empire by Alexios I Komnenos
Alexios I Komnenos (, – 15 August 1118), Latinization of names, Latinized as Alexius I Comnenus, was Byzantine Emperor, Byzantine emperor from 1081 to 1118. After usurper, usurping the throne, he was faced with a collapsing empire and ...
, the area was governed by effectively semi-autonomous rulers, like the Gabras family of Trebizond.
The region was secured militarily from the 11th through the 15th centuries with a vast network of sophisticated coastal fortresses.Robert W. Edwards, “The Garrison Forts of the Pontos: A Case for the Diffusion of the Armenian Paradigm,” ''Revue des Études Arméniennes'' 19, 1985, pp. 181-284, pls.1-51b.
Empire of Trebizond
Following Constantinople's loss of sovereignty to theFourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
in 1204, the Pontus retained independence as the Empire of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond or the Trapezuntine Empire was one of the three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire that existed during the 13th through to the 15th century. The empire consisted of the Pontus, or far northeastern corner of A ...
under the Komnenos
The House of Komnenos ( Komnenoi; , , ), Latinized as Comnenus ( Comneni), was a Byzantine Greek noble family who ruled the Byzantine Empire in the 11th and 12th centuries. The first reigning member, Isaac I Komnenos, ruled from 1057 to 1059. ...
dynasty. Through a combination of geographic remoteness and adroit diplomacy, this remnant managed to survive, until it was conquered by the Ottomans
Ottoman may refer to:
* Osman I, historically known in English as "Ottoman I", founder of the Ottoman Empire
* Osman II, historically known in English as "Ottoman II"
* Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empir ...
in 1461 after the Fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city was captured on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 55-da ...
itself. This political adroitness included becoming a vassal state at various times to both Georgia and to various inland Turkic rulers. In addition, the Empire of Trebizond became a renowned center of culture under its ruling Komnenos dynasty.Hewsen, 48 f.
Ottoman ''vilayet''
Under the subsequent Ottoman rule which began with the fall ofTrebizond
Trabzon, historically known as Trebizond, is a city on the Black Sea coast of northeastern Turkey and the capital of Trabzon Province. The city was founded in 756 BC as "Trapezous" by colonists from Miletus. It was added into the Achaemenid Em ...
, particularly starting from the 17th century, some of the region's Pontic Greeks
The Pontic Greeks (; or ; , , ), also Pontian Greeks or simply Pontians, are an ethnically Greek group indigenous to the region of Pontus, in northeastern Anatolia (modern-day Turkey). They share a common Pontic Greek culture that is di ...
became Muslim through the Devşirme
Devshirme (, usually translated as "child levy" or "blood tax", , .) was the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman practice of Conscription, forcibly recruiting soldiers and bureaucrats from among the children of their Balkan Christian subjects and raising th ...
system. But at the same time some valleys inhabited by Greeks converted voluntarily, most notably those in the Of valley. Large communities (around 25% of the population) of Christian Pontic Greeks remained throughout the area (including Trabezon and Kars in northeastern Turkey/the Russian Caucasus) until the 1920s, and in parts of Georgia and Armenia until the 1990s, preserving their own customs and dialect of Greek. One group of Islamicized Greeks were called the Kromli, but were suspected of secretly having remained Christians. They numbered between 12,000 and 15,000 and lived in villages including Krom, Imera, Livadia, Prdi, Alitinos, Mokhora, and Ligosti.Hewsen, 54. Many of the Islamized Greeks continued speaking their language, known for its unique preservation of characteristics of Ancient Greek and still today there are some in the Of valley that speak the local Ophitic dialect.
Republic of Pontus
TheRepublic of Pontus
The Republic of Pontus (, ''Dimokratía tou Póntou'') was a proposed Pontic Greek state on the southern coast of the Black Sea. Its territory would have encompassed much of historical Pontus in north-eastern Asia Minor, and today forms part of T ...
() was a proposed Pontic Greek state on the southern coast of the Black Sea. Its territory would have encompassed much of historical Pontus and today forms part of Turkey's Black Sea Region. The proposed state was discussed at the Paris Peace Conference of 1919
Paris () is the capital and largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the fourth-most populous city in the European Union and the 30th most densely popul ...
, but the Greek government of Eleftherios Venizelos
Eleftherios Kyriakou Venizelos (, ; – 18 March 1936) was a Cretan State, Cretan Greeks, Greek statesman and prominent leader of the Greek national liberation movement. As the leader of the Liberal Party (Greece), Liberal Party, Venizelos ser ...
feared the precarious position of such a state and so it was included instead in the larger proposed state of Wilsonian Armenia. Neither state came into existence and the Pontic Greek population was subjected to genocide
Genocide is violence that targets individuals because of their membership of a group and aims at the destruction of a people. Raphael Lemkin, who first coined the term, defined genocide as "the destruction of a nation or of an ethnic group" by ...
and expelled from Turkey after 1922 and resettled in the Soviet Union or in Macedonia
Macedonia (, , , ), most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a former administr ...
. This state of affairs was later formally recognized as part of the population exchange between Greece and Turkey in 1923.
Present
 The Black Sea Region (), comprising all or parts of 22 provinces, is one of
The Black Sea Region (), comprising all or parts of 22 provinces, is one of Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
's seven census-defined geographical regions. It encompasses but is larger than historic Pontus.
Religion
Mentioned thrice in the New Testament, inhabitants of Pontus were some of the first converts toChristianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
. mentions them present in Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
on the Day of Pentecost
Pentecost (also called Whit Sunday, Whitsunday or Whitsun) is a Christianity, Christian holiday which takes place on the 49th day (50th day when inclusive counting is used) after Easter Day, Easter. It commemorates the descent of the Holy Spiri ...
; Acts 18:2 mentions a Jewish tentmaker from Pontus, Aquila
Aquila may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Aquila'', a series of books by S.P. Somtow
* ''Aquila'', a 1997 book by Andrew Norriss
* ''Aquila'' (children's magazine), a UK-based children's magazine
* ''Aquila'' (journal), an orni ...
, who was then living in Corinth
Corinth ( ; , ) is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient Corinth, ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Sin ...
with his wife Priscilla
Priscilla is an English female given name adopted from Latin '' Prisca'', derived from ''priscus''. There is a theory that this biblical character was the author of the Letter to the Hebrews.
The name first appears in the New Testament either ...
, who had both converted to Christianity, and in , Peter the Apostle
Saint Peter (born Shimon Bar Yonah; 1 BC – AD 64/68), also known as Peter the Apostle, Simon Peter, Simeon, Simon, or Cephas, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus and one of the first leaders of the early Christian Church. He appears repe ...
addresses the Pontians in his letter as the "elect" and "chosen ones".
As early as the First Council of Nicea
The First Council of Nicaea ( ; ) was a council of Christian bishops convened in the Bithynian city of Nicaea (now İznik, Turkey) by the Roman Emperor Constantine I. The Council of Nicaea met from May until the end of July 325.
This ecume ...
, Trebizond had its own bishop. Subsequently, the Bishop of Trebizond was subordinated to the Metropolitan Bishop
In Christianity, Christian Christian denomination, churches with episcopal polity, the rank of metropolitan bishop, or simply metropolitan (alternative obsolete form: metropolite), is held by the diocesan bishop or archbishop of a Metropolis (reli ...
of Poti
Poti ( ka, ფოთი ; Mingrelian language, Mingrelian: ფუთი; Laz language, Laz: ჶაში/Faşi or ფაში/Paşi) is a port city in Georgia (country), Georgia, located on the eastern Black Sea coast in the mkhare, region of ...
. Then during the 9th century, Trebizond itself became the seat of the Metropolitan Bishop of Lazica
The Kingdom of Lazica (; ; ), sometimes called Lazian Empire, was a state in the territory of west Georgia in the Roman era, Georgia in the Roman period, from about the 1st century BC. Created as a result of the collapse of the kingdom of Colc ...
.
Notable Pontians
*Diogenes of Sinope
Diogenes the Cynic, also known as Diogenes of Sinope (c. 413/403–c. 324/321 BC), was an ancient Greek philosopher and one of the founders of Cynicism. Renowned for his ascetic lifestyle, biting wit, and radical critiques of social conventi ...
(c. 408–323 BC), Greek philosopher from Sinope, one of founders of Cynic philosophy
* Mithridates VI Eupator
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator (; 135–63 BC) was the ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an effective, ambitious, and ...
(c. 135 BC – 63 BC), Pontic King, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents.
* Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
(c. 64 BC – 24 AD), Greek historian, geographer, and philosopher, native from Amaseia
* Marcion of Sinope
Marcion of Sinope (; ; ) was a theologian in early Christianity. Marcion preached that God had sent Jesus Christ, who was distinct from the "vengeful" God ( Demiurge) who had created the world. He considered himself a follower of Paul the Apost ...
(c. 85 – c. 160 AD), early Christian theologian
* Evagrius Ponticus
Evagrius Ponticus (), also called Evagrius the Solitary (345–399 AD), was a Christian monk and ascetic from Heraclea, a city on the coast of Bithynia in Asia Minor. One of the most influential theologians in the late fourth-century church, ...
(345–399 AD), Greek theologian and monk
* Basilios Bessarion
Bessarion (; 2 January 1403 – 18 November 1472) was a Byzantine Greeks, Byzantine Greek Renaissance humanist, theologian, Catholic Church, Catholic Cardinal (Catholic Church), cardinal and one of the famed Greek scholars who contributed ...
(1403–1472), Greek scholar, Roman Catholic cardinal and titular Latin Patriarch of Constantinople
* Alexander Ypsilantis
Alexandros Ypsilantis (12 December 1792 – 31 January 1828) was a Greek nationalist politician who was member of a prominent Phanariot Greeks, Phanariot Greek family, a prince of the Danubian Principalities, a senior officer of the Imperial R ...
(1792–1828), Greek military commander and national hero of the 19th century
* A. I. Bezzerides
Albert Isaac "Buzz" Bezzerides ( August 9, 1908 – January 1, 2007) was an American novelist and screenwriter, best known for writing film noir, films noir and action film, motion pictures, especially several of Warners' "social conscience" film ...
(1908–2007), American novelist and screenwriter, born in Samsun
Samsun is a List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, city on the north coast of Turkey and a major Black Sea port. The urban area recorded a population of 738,692 in 2022. The city is the capital of Samsun Province which has a population of ...
* Antonis Fosteridis
Antonis Fosteridis (, also Φωστηρίδης, 1912–1979), also known by the nom de guerre of Çauş Anton (Τσαούς Αντών), was a Pontus-born Greek nationalist, anticommunist partisan during the Axis occupation of Greece, who served ...
(1912–1979), Greek nationalist, anticommunist partisan during WWII
* Stelios Kazantzidis
Stelios Kazantzidis (Greek: Στέλιος Καζαντζίδης; 29 August 1931 – 14 September 2001) was one of the most prominent Greek singers. He was of Pontian and Asia Minor roots. A top artist of Greek music, or Laïkó, he collaborat ...
(1931–2001), Greek singer of Greek popular music, or Laïkó
* Chrysanthos Theodoridis
Chrysanthos Theodoridis, or simply Chrysanthos (; 22 December 1934 – 30 March 2005) was a Greek singer and songwriter. He was born in Oinoi, Kozani to a Pontic Greek family from Kars
Kars ( or ; ; ) is a city in northeast Turkey. It is the ...
(1933–2005), singer
* Mike Lazaridis
Mihal "Mike" Lazaridis (born March 14, 1961) is a Greek Canadian businessman, investor in quantum computing technologies, and co-founder of Research In Motion, which created and manufactured the BlackBerry wireless handheld device. In November 2 ...
(b. 1961), CEO of Research in Motion
BlackBerry Limited, formerly Research In Motion (RIM), is a Canadian software company specializing in secure communications and the Internet of Things (IoT). Founded in 1984, it developed the BlackBerry brand of interactive pagers, smartpho ...
and creator of BlackBerry
BlackBerry is a discontinued brand of handheld devices and related mobile services, originally developed and maintained by the Canadian company Research In Motion (RIM, later known as BlackBerry Limited) until 2016. The first BlackBerry device ...
phones
* Melina Aslanidou
Melina Aslanidou (; born 28 August 1974) is a Greek singer.
Early life
Melina Aslanidou was born in Stuttgart, West Germany to Greek parents. Later, she moved with her family to Greece and grew up in Paralimni of Giannitsa, Greece.
Career
F ...
(1974–present), Greek singer
* Pantelis Pantelidis
Pantelis Pantelidis (; 23 November 1983 – 18 February 2016) was a Greek singer, songwriter and lyricist. He died on 18 February 2016 in a car crash.
Biography
Born on November 23, 1983, Pantelis Pantelidis grew up in Nea Ionia, a small suburb ...
(1983–2016), Greek singer
* Apolas Lermi (1986-present), Greco-Turkish folk musician
See also
* Amaseia, Ancient capital of Pontus *Ancient regions of Anatolia
The following is a list of regions of Ancient Anatolia, also known as "Asia Minor." The names reflect changes to languages, settlements and polities from the Bronze Age to conquest by Turkic peoples.
Bronze Age
* Abbawiya
* Adadura
*Adana
* ...
* Caucasus Greeks
The Caucasus Greeks ( or more commonly , ), also known as the Greeks of Transcaucasia and Russian Asia Minor, are the ethnic Greeks of the North Caucasus and Transcaucasia in what is now southwestern Russia, Georgia, and northeastern Turkey. The ...
* Greek genocide
The Greek genocide (), which included the Pontic genocide, was the systematic killing of the Christian Ottoman Greek population of Anatolia, which was carried out mainly during World War I and its aftermath (1914–1922) – including the T ...
* Lazistan
Lazistan or Lazeti (; ka, ლაზეთი, Lazeti, or ჭანეთი ''Ç'aneti''; ) is a historical and cultural region of the Caucasus and Anatolia; the term was primarily used during Ottoman rule in the region. Traditionally inhabited b ...
* Pontic Greek
Pontic Greek (, ; or ''Romeika'') is a variety of Modern Greek indigenous to the Pontus region on the southern shores of the Black Sea, northeastern Anatolia, and the Eastern Turkish and Caucasus region. An endangered Greek language variety ...
* Republic of Pontus
The Republic of Pontus (, ''Dimokratía tou Póntou'') was a proposed Pontic Greek state on the southern coast of the Black Sea. Its territory would have encompassed much of historical Pontus in north-eastern Asia Minor, and today forms part of T ...
Citations
General and cited sources
* *Ramsay MacMullen
Ramsay MacMullen (March 3, 1928 – November 28, 2022) was an American historian who was Emeritus Professor of History at Yale University, where he taught from 1967 to his retirement in 1993 as Dunham Professor of History and Classics. His scholar ...
, 2000. ''Romanization in the Time of Augustus'' (Yale University Press)
External links
History of Pontus
The term Euxinus Pontus
Where East Meets West
{{Authority control Ancient Greek geography Historical regions of Anatolia History of Amasya Province History of Giresun Province History of Rize Province History of Tokat Province History of Trabzon Province