Anchor Shipping And Foundry Company on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
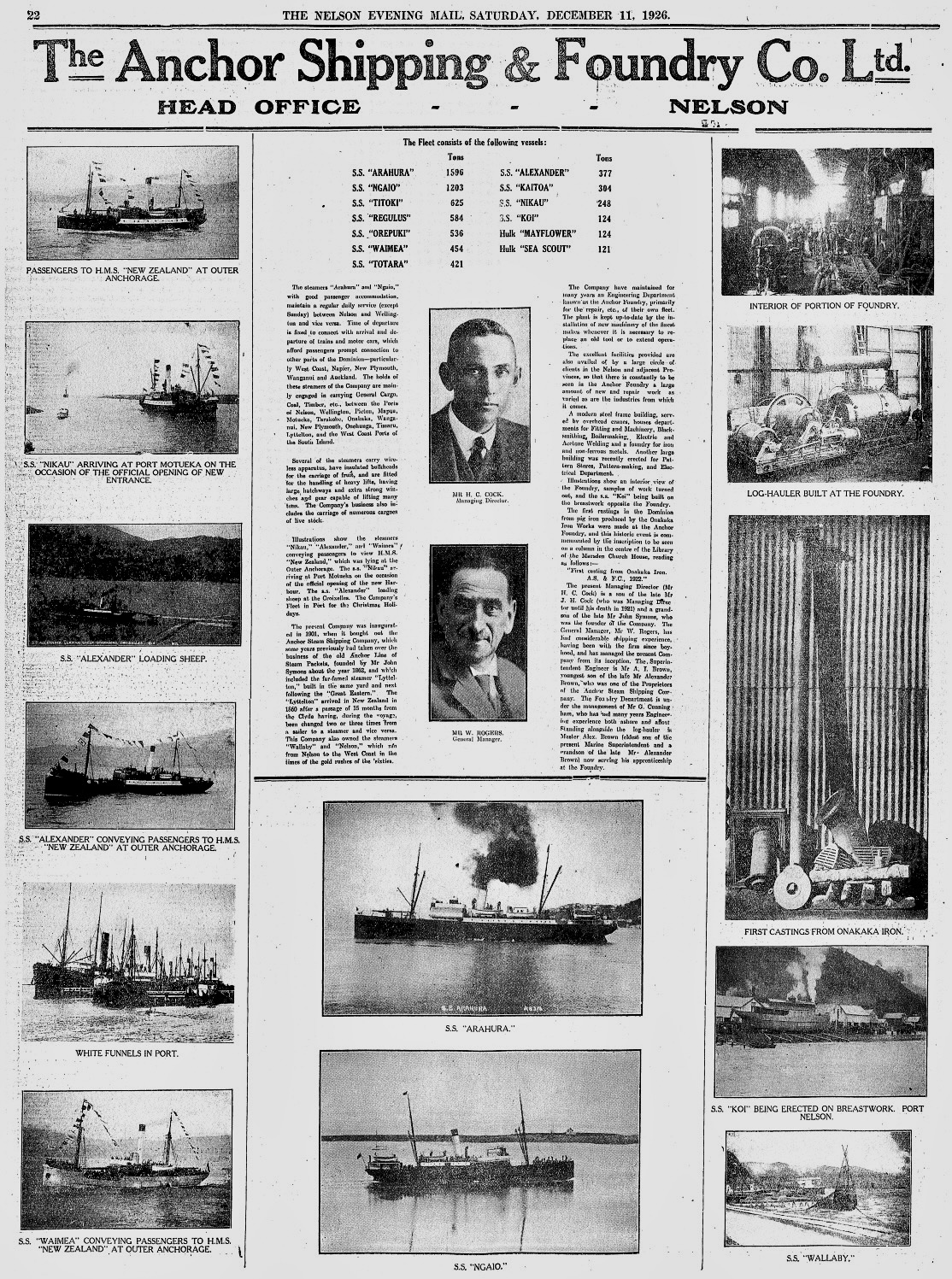 The Anchor Shipping and Foundry Company linked
The Anchor Shipping and Foundry Company linked
 The Anchor Shipping and Foundry Company linked
The Anchor Shipping and Foundry Company linked Nelson
Nelson may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Nelson'' (1918 film), a historical film directed by Maurice Elvey
* ''Nelson'' (1926 film), a historical film directed by Walter Summers
* ''Nelson'' (opera), an opera by Lennox Berkeley to a lib ...
with other parts of New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmassesŌĆöthe North Island () and the South Island ()ŌĆöand List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
from 1870 to 1974. The company's former office remains on the quay at Nelson, as do steps of their foundry, which built one of their ships, repaired their fleet and made other machinery.
Nathaniel Edwards and Company 1862ŌĆō70
Anchor had its origins on 5 February 1857, whenNathaniel Edwards Nathaniel Edwards may refer to:
* Nathaniel Edwards (politician) (1822–1880), a New Zealand MP
*Sir Nathaniel Edwards, 3rd Baronet (c. 1699–1764), of the Edwards baronets
* Nat Edwards, American baseball player
* Nathaniel Edwards (socc ...
and George Bennett formed a partnership
A partnership is an agreement where parties agree to cooperate to advance their mutual interests. The partners in a partnership may be individuals, businesses, interest-based organizations, schools, governments or combinations. Organizations ...
as Nathaniel Edwards and Company, to take over the Nelson merchants, Alfred Fell & Co. By 1860 they had become shipping agents. On 3 November 1862 another merchant, John Symons, joined N. Edwards & Co., which had just bought the paddle steamer ''Lyttelton'' in October 1862. She replaced the ''Tasmanian Maid'', when on 11 November 1862 she made her first voyage from Nelson to Blenheim, being the first steamship to reach Blenheim town wharf, on the ┼īpaoa River
The ┼īpaoa River, formerly called the Opawa River, is in the Marlborough region of the South Island of New Zealand. It begins in the Wairau valley where floodways are joined. It makes its way down the valley and flows through and looping aroun ...
. Alexander Brown, her engineer, also joined the company. ''Lyttelton'' served Tasman and Golden Bay / Mohua
Golden Bay / Mohua is a large shallow bay in New Zealand's Tasman District, near the northern tip of the South Island. An arm of the Tasman Sea, the bay lies northwest of Tasman Bay / Te Tai-o-Aorere and Cook Strait. It is protected in the nor ...
ports, with occasional trips to Wellington
Wellington is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the third-largest city in New Zealand (second largest in the North Island ...
. Paddle steamer ''Charles Edward'' was bought in 1863. In December 1864, at the start of the West Coast gold rush, Wallabi was bought from Australia, to serve Westport, Greymouth
Greymouth () (M─üori language, M─üori: ''M─üwhera'') is the largest town in the West Coast, New Zealand, West Coast List of regions in New Zealand, region in the South Island of New Zealand, and the seat of the Grey District Council. The populat ...
and Hokitika
Hokitika is a town in the West Coast region of New Zealand's South Island, south of Greymouth, and close to the mouth of the Hokitika River. It is the seat and largest town in the Westland District. The town's estimated population is as of ...
. In 1865 ''Kennedy'' also came from Australia, adding occasional trips to Taranaki
Taranaki is a regions of New Zealand, region in the west of New Zealand's North Island. It is named after its main geographical feature, the stratovolcano Mount Taranaki, Taranaki Maunga, formerly known as Mount Egmont.
The main centre is the ...
for cattle. Paddle steamer ''Nelson'' was added in 1866. In 1866 Edwards sold his shares to his partners, though he retained the shipping department. A workshop near N. Edwards & Co bulk store at Matangi Awhio/ Auckland Point was created.
Anchor Line of Steam Packets 1870ŌĆō1974
By 1870 John Symons had become the sole owner of both the merchant and shipping departments of Nathaniel Edwards & Co and, in August 1870, changed the name of the latter to Anchor Line of Steam Packets, with a new pennant, featuring an anchor, designed by artist, William Cock. Symons retired in 1878. In December 1880 a partnership was formed under the name Anchor Steam Shipping Company which purchased Anchor's 5 ships, the foundry and Albion Wharf. Forming the partnership were John H Cock & Company (Ōģō), Sclanders and Company (Ōģō), P Donald (1/6), andAlexander Brown Alexander Brown may refer to:
Sports
*Alexander Brown (cricketer) (born 1967), English cricketer
*Sandy Brown (footballer, born 1877) (Alexander Brown, 1877ŌĆō1944), Scottish footballer
*Sandy Brown (footballer, born 1939) (Alexander Dewar Brown, ...
(1/6). During the 1880s economic depression the foundry remained profitable and Anchor ships continued to serve Nelson, Wellington, New Plymouth
New Plymouth () is the major city of the Taranaki region on the west coast of the North Island of New Zealand. It is named after the English city of Plymouth, in Devon, from where the first English settlers to New Plymouth migrated. The New Pl ...
, Whanganui, Foxton, Patea
Patea ( ) is the third-largest town in South Taranaki District, New Zealand. It is on the western bank of the P─ütea River, 61 kilometres north-west of Whanganui on . H─üwera is 27 km to the north-west, and Waverley, Taranaki, Waverley 17 ...
, Onehunga and West Coast ports, with trips to Jackson Bay
Jackson Bay / Okahu () is a gently curving bay on the southern West Coast of the South Island of New Zealand. It faces the Tasman Sea to the north, and is backed by the Southern Alps. It contains the settlements of Hannahs Clearing, Waiatoto ...
and the Marlborough Sounds
The Marlborough Sounds (M─üori language, te reo M─üori: ''Te Tauihu-o-te-Waka'') are an extensive network of ria, sea-drowned valleys at the northern end of the South Island of New Zealand. The Marlborough Sounds were created by a combination ...
on occasions.
Alexander Brown and family
Alexander Brown was born atLarkhall
Larkhall (, ) is a town in South Lanarkshire, Scotland, around southeast of Glasgow. It is twinned with Seclin in northern France.
Larkhall sits on high ground between the River Clyde to the East and the Avon Water to the West. Larkhall ...
, Scotland, probably on 23 February 1830, to Ellen Graham and Thomas Brown, a blacksmith. From 1846 to 1854 he was an apprentice and then engineer at James Gray & Company shipyard. In 1855 he joined Scott Russell's shipyard at Millwall, as an engineer building the ''Great Eastern''. In 1855 he went to the Crimea as 2nd engineer of the transport ''Pioneer'', but returned to Millwall for the launch of the ''Great Eastern'' in 1858. He helped build the ''Lyttelton'' and steamed with her to New Zealand, leaving England on 18 August 1859; it was intended that he remain in the colony for a year to fit out and then work on her. The wages offered were very attractive: ┬Ż10 a month for the journey and ┬Ż20 a month while in New Zealand. On arrival Alexander Brown refitted the ''Lyttelton'' as a paddle-steamer, visiting Lyttelton and then Dunedin. During the 1861 goldrush, she took passengers from Dunedin to Taieri. N Edwards & Co purchased the ship in 1862 and used it to trade between Nelson and Blenheim. Brown joined the new owners as chief engineer. In 1866 he accepted a shore appointment in Nelson to supervise repairs and alterations to the company's ships, the start of Anchor Foundry. In 1873 the foundry moved to a new port site. He was also engineer on the ''Wallabi'' and ''Kennedy'' until 1866. In 1880 Alexander Brown became a major shareholder in the Anchor Steam Shipping Co, which purchased the shipping and foundry assets from the estate of John Symonds. Brown continued as the Anchor Foundry Manager and in 1901 was appointed a Director and Consulting Engineer to the Anchor Shipping & Foundry Company. He visited the foundry daily until a few weeks before his death. His wife, Isabella Brown, died on 9 October 1904. They married in Nelson on 3 August 1868. Although his obituaries, published on 25 January 1913, say he died the day before, following a period of ill health, his death certificate says he died on 22 January. His children were Thomas, John, Irvine, Mrs R. Ward, of Christchurch and Agnes Isabella Ambridge (died 3 July 1943).
His sons and grandsons were apprentices at the Anchor Foundry before qualifying as chief engineers. His eldest son, Thomas, was Foundry Manager from 1901 to 1921 and a company director until he died on 26 May 1943. Thomas Brown, a director of the Anchor Shipping and Foundry Co. Ltd, died at his home in Richardson street on 26 May 1943, aged 72. He was the eldest son of Alexander Brown and served his engineering apprenticeship in the Anchor foundry and then proceeded to England for further experience. For some years he was an engineer in the service of the Union Steam Ship Company, prior to succeeding his father as manager of the Anchor Company's foundry. He retired from that position in 1920 and then acted as consulting engineer to the company. In 1922 and again in 1926, in company with Mrs Brown, he visited England on the company's business. In 1922 he superintended the construction of the steamer Titoki on the Clyde, and when returning to New Zealand in 1926 he was a passenger on Aorangi on its maiden voyage. The late Mr Brown was appointed a director of Anchor when it became a limited liability company in March 1901 and he retained that position until his death. He married Helen McRitchie Simpson, who survives him.
John (Jack) Brown was an apprentice in the foundry and until he went to Glasgow for further training. He was 2nd Engineer on the Union's liner ''Moana'' on the Sydney-San Francisco service, until he returned, to Anchor as Chief Engineer for several years, including superintending construction of ''Alexander'' in 1902, the first Anchor steamer built in Britain, followed by ''Waimea'', ''Nikau'' and ''Kaitoa'' in 1909. Mr Brown on this occasion came out as Chief Engineer of the ''Kaitoa'' and on arrival here was transferred to the ''Waimea'' as Chief Engineer, continuing in that vessel until his retirement from the sea to work in the Foundry. He was a seagoing engineer and Assistant Foundry Manager from 1912 to 1915 when he retired for health reasons. John Wilson Brown, aged 59, died suddenly at 5am on 4 December 1930 at his home, Lark Hall, Richardson Street, Nelson. He was the second son of Alexander Brown and was educated as a marine engineer for Union. For a time he was a manager of Anchor. He was an invalid for several years. He left a widow and 4 daughtersŌĆöMrs W. J. Thompson, Mrs L. W. Field, Isabel and Eileen Brown. His sisters Mrs R. B. Ward, of Christchurch, and Mrs Andridge, of Rarotonga survived him.
Alexander Irvine Brown was a seagoing engineer and Superintending Engineer from 1915 until 1944. He remained a Director until his death in 1962. In 1929 their son Alex left Nelson to serve as engineer on various ships. In 1941 their second son, Ivan Graeme, married Joan Mabel Wallace, of Takapuna. In 1937 their daughter, Phyllis Maud, married Harold John Addis, of Auckland.
Thomas Alexander (Alex) Brown, the eldest son of Alexander Brown, like his father and uncles was an engineering apprentice at the Foundry, and was a seagoing engineer until his appointment as Assistant Superintending Engineer in 1938. He remained in this position until his death in 1963.
Anchor Shipping & Foundry Company 1900ŌĆō1972
In 1900 the partnership was replaced by Anchor Shipping & Foundry Company, the main shareholders being John H Cock's son, Joseph Henry Cock, Alexander Brown and his 3 sons, A H Turnbull, and David Sclanders of London. By 1907 there was demand for a nightly passenger/cargo service between Wellington Nelson-Motueka, and a number of vessels were employed, the first being the Tasman, then Nikau and Kaitoa. Union said that, due to the extension of South Island railways, it was arranged on a friendly basis that Anchor would operate the Wellington-Nelson service and Union the Wellington-Picton service. In 1908 Union bought a 50% share in Anchor, using nominees to avoid publicity. From 1921 on, there was friendly co-operation with Union. In 1916 Anchor ran 6 days a week, serving Nelson, Motueka, and Wellington with the twin-screw steamers, ''Waverley'' 157 tons, ''Koi'' 136 tons, ''Nikau'' and ''Kaitoa'' 304 tons. In 1925 the Arahura was purchased from Union for the daily service until she was replaced by an Australian built vessel ''Mourilyan'' renamed ''Matangi'' in 1929. In the 1930s and 40s ''Matangi'' left Wellington Queens Wharf No.16 at 7.30pm on Monday, Wednesday and Friday nights and Arahura on Tuesdays, Thursdays and Saturdays, a service begun in August 1909. ''Puriri'' was delivered in 1939, but, as aminesweeper
A minesweeper is a small warship designed to remove or detonate naval mines. Using various mechanisms intended to counter the threat posed by naval mines, minesweepers keep waterways clear for safe shipping.
History
The earliest known usage of ...
, struck a mine in the Hauraki Gulf
The Hauraki Gulf / T─½kapa Moana is a coastal feature of the North Island of New Zealand. It has an area of 4000 km2,M─üpua, New Zealand, M─üpua and
 The foundry built and repaired a wide range of machinery. It operated from 1866 to 1986 and was established by N. Edwards & Co. In 1866, a workshop opened near N. Edwards & Co bulk store at Matangi Awhio/Auckland Point. A January 1873 report described the newly erected workshops on the Port road, as of corrugated iron, 125 feet long, by 25 feet wide. In the centre was a 70 ft by 25 ft, general workshop, 2 forges, shortly to be added an 8 hp steam engine, to work a 5-cwt. steam hammer, lathes, and fans for the blasts of the various furnaces. A 4 hp engine driving a boring machine and 2 lathes. At the northern end is the foundry, 25 ft x 25 ft, and furnace were being erected.
A large new workshop on Wakefield Quay, named The Anchor Foundry, was in use by 1873. By then the Anchor Foundry repaired Anchor's steamers, as well as taking on outside work, such as building other steamers, making gold sluicing equipment, cast iron stoves and a locomotive for the Takaka Tramway Company. The Foundry also served local industries such as Griffin's biscuits, Samuel Kirkpatrick's jam and canning factory and Baigent Timber, offering fitting and turning, blacksmithing, moulding and casting, boiler making, electric and acetone welding, pattern making, and electrical wiring and installation. In 1883 Anchor Steam Shipping Co. was formed with the Anchor Line ships, foundry, and shipyard. It became Anchor Shipping & Foundry Co. on 31 March 1901. Anchor Foundry at Port Nelson, erected in 1907, was a long narrow building with an exterior cladding of grey corrugated iron. It extended along the waterfront from the power house building to the then Pier Hotel. When the 1907 building was opened, the overhead drive shaft extended the full length of the building, and was reputed to be the longest single overhead drive shaft in the southern hemisphere. After World War II trade declined, partly because of competition from ferries and the declining use of coal. In 1969 Anchor bought T. Dorman Engineering. Late in 1973 Anchor was wound up by Union, when it bought the remaining 12% of Anchor from the Brown families. A new company Anchor Dorman was formed to take over Union's interest in Nelson. In 1984 Anchor Dorman was sold to Perry Dines Corporation of New Plymouth, but within two years was liquidated; even the employees received no redundancy payments. The buildings were sold to Nelson Harbour Board and the plant disposed of. The Anchor Foundry buildings on Wakefield Quay were demolished in 2005 and luxury apartments built. The steps at 15 Richardson Street remain.
The foundry built and repaired a wide range of machinery. It operated from 1866 to 1986 and was established by N. Edwards & Co. In 1866, a workshop opened near N. Edwards & Co bulk store at Matangi Awhio/Auckland Point. A January 1873 report described the newly erected workshops on the Port road, as of corrugated iron, 125 feet long, by 25 feet wide. In the centre was a 70 ft by 25 ft, general workshop, 2 forges, shortly to be added an 8 hp steam engine, to work a 5-cwt. steam hammer, lathes, and fans for the blasts of the various furnaces. A 4 hp engine driving a boring machine and 2 lathes. At the northern end is the foundry, 25 ft x 25 ft, and furnace were being erected.
A large new workshop on Wakefield Quay, named The Anchor Foundry, was in use by 1873. By then the Anchor Foundry repaired Anchor's steamers, as well as taking on outside work, such as building other steamers, making gold sluicing equipment, cast iron stoves and a locomotive for the Takaka Tramway Company. The Foundry also served local industries such as Griffin's biscuits, Samuel Kirkpatrick's jam and canning factory and Baigent Timber, offering fitting and turning, blacksmithing, moulding and casting, boiler making, electric and acetone welding, pattern making, and electrical wiring and installation. In 1883 Anchor Steam Shipping Co. was formed with the Anchor Line ships, foundry, and shipyard. It became Anchor Shipping & Foundry Co. on 31 March 1901. Anchor Foundry at Port Nelson, erected in 1907, was a long narrow building with an exterior cladding of grey corrugated iron. It extended along the waterfront from the power house building to the then Pier Hotel. When the 1907 building was opened, the overhead drive shaft extended the full length of the building, and was reputed to be the longest single overhead drive shaft in the southern hemisphere. After World War II trade declined, partly because of competition from ferries and the declining use of coal. In 1969 Anchor bought T. Dorman Engineering. Late in 1973 Anchor was wound up by Union, when it bought the remaining 12% of Anchor from the Brown families. A new company Anchor Dorman was formed to take over Union's interest in Nelson. In 1984 Anchor Dorman was sold to Perry Dines Corporation of New Plymouth, but within two years was liquidated; even the employees received no redundancy payments. The buildings were sold to Nelson Harbour Board and the plant disposed of. The Anchor Foundry buildings on Wakefield Quay were demolished in 2005 and luxury apartments built. The steps at 15 Richardson Street remain.
1853 ''Nelson''
* ''Charles Edward'
at Hokitika about 1869at sea between 1889 and 1900wrecked at Castlecliff 1908
''Lady Barkly'' as a screw steamer in 1890s
* ''Koi'
ready to launchlaunchingin 1906in 1910
* ''Matangi'' as ''Mourilyan'
about 1908
at Whakatahuri breakers yard in 1956 ŌĆ
Shipping companies of New Zealand New Zealand companies established in 1870 Transport companies established in 1870 Defunct transport companies of New Zealand Nelson, New Zealand Steamships of New Zealand 1974 disestablishments in New Zealand
Motueka
Motueka is a town in the South Island of New Zealand, close to the mouth of the Motueka River on the western shore of Tasman Bay. It is the second largest in the Tasman Region, with a population of as of
The surrounding district has a numb ...
and operate the Tasman Bay-Onehunga service.
In 1949 ''Arahura'' failed her survey and was withdrawn. The 1929 ''Hualalai'' came from Honolulu in late October 1949 and was renamed ''Ngaio'', but alterations were needed and the lighthouse tender ''Matai'' ran with ''Matangi'' until May 1950, when ''Ngaio'' made her first run to Nelson. ''Matangi'' was withdrawn in 1952 and ''Ngaio'' in 1953, when the Wellington ŌĆō Nelson ferry ended, following increasing losses from 1947/48, when profit was down to ┬Ż10,051. A daily cargo run continued with Matipo and Pearl Kasper Company vessels Willomee and later Konanda. Konanda was replaced by Anchor's Towai in 1966, but in 1969 the regular service stopped, due to competition from the Cook Strait rail ferries from 1962, which also affected the Onehunga service, which was taken over by Union in 1972. ''Puriri'' was sold in 1974, ending 110 years of Anchor.
The Anchor Shipping and Foundry Company Building on Wakefield Quay
The office was built on the site of the Customhouse Hotel. The 2-storey Anchor Shipping & Foundry Co Ltd Building was designed by Arthur R. Griffin in 1927. It had a booking office, offices for managers and clerks, a strong-room, bicycle room, coke-fired central heating and steel-framed windows. The floors were covered in Rublino Tiles, a brand oflinoleum
Linoleum is a floor covering made from materials such as solidified linseed oil (linoxyn), Pine Resin, pine resin, ground Cork (material), cork dust, sawdust, and mineral fillers such as calcium carbonate, most commonly on a Hessian fabric, hes ...
. The high flat roof could be used to assess approaching weather or vessels. The Historic Places Trust
Heritage New Zealand Pouhere Taonga (initially the National Historic Places Trust and then, from 1963 to 2014, the New Zealand Historic Places Trust; in ) is a Crown entity that advocates for the protection of ancestral sites and heritage buil ...
listed the building as Category 2 on 11 November 1982. After Anchor closed, the offices were used by printers and a distillery, before being bought for $1m by Nelson City Council
Nelson City Council is the unitary local authority for Nelson in New Zealand.
History
Local governance of Nelson began with Nelson Province in 1853, which covered the entire upper South Island. The town of Nelson was managed by the Nelson ...
in September 2013. In 2014 the building was assessed as earthquake-prone, with a rating of 22% of New Building Standard. In 2021 a notice was issued requiring seismic strengthening by 23 April 2027.
Decline
Anchor gradually succumbed to air, rail and road competition. A daily freight service was maintained between the two ports in conjunction with Pearl Kasper Shipping Co's Konanda and (from 1955) Anchor's Matipo. Due to the rapid development of air transport after the War, it was decided to acquire only the ''Ngaio''. ''Matangi'' was immediately withdrawn for survey. This she failed and she was promptly laid up in Shelley Bay for disposal. Her former consort in the service, ''Arahura'', had failed her survey a year earlier. Coal from the West Coast had always figured large in Anchor's operation and in 1947 placed an order with Henry Robb Ltd. for a twin-screw motor ship which became ''Puriri'' (1,248grt). Although fitted with a full outfit of cargo gear including a jumbo derrick capable of lifting 20 tons, she was in effect a small collier. Launched on 22 July 1948, she sailed to New Zealand via Australia and arrived in Wellington on 8 January 1949 with 800 tons ofNewcastle
Newcastle usually refers to:
*Newcastle upon Tyne, a city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England, United Kingdom
*Newcastle-under-Lyme, a town in Staffordshire, England, United Kingdom
*Newcastle, New South Wales, a metropolitan area ...
coal. Much of her life was spent carrying bulk cargoes around the coast, although she did carry general cargo and timber from time to time. Her final years of service saw her engaged full time on the company's Nelson ŌĆō Onehunga route carrying general cargo and she was sold out of the fleet in 1974. to the requirements of smaller ports such as Mapua and Motueka especially in regard to length and draught. Launched on 28 July 1949 as Mamaku, she sailed from Leith on 15 October 1949 for Middlesbrough where she loaded a cargo of coke for Auckland, arriving there on 23 December. Mamaku spent most of her life in the general cargo trade between Nelson, Motueka and Onehunga, although she also shipped coal from the West Coast to North Island ports on occasion. After giving good service to the company, she was sold in 1972 for further trading.
From 1972, management of the fleet was in the hands of Union and in December 1973 the company name was changed to Anchor-Dorman Ltd. to incorporate the interests of Dorman Engineering Co. Ltd. of Nelson, which Union had acquired in 1969. In the early 1980s, Union decided that the Nelson-Onehunga trade should be containerised and the original intention was to give the new ship a traditional Anchor name and operate in their colours. This was not to be and the new ship arrived as ''Union Nelson'' in March 1982 with full Union Company colours. ''Titoki'' was withdrawn and before ''Union Nelson'' even entered service, a new crew was aboard preparing for her departure overseas. With her sale, the Anchor name disappeared forever with the shipping side of the business being renamed Union Maritime Services and the engineering interests were sold to a New Plymouth company on 31 March 1984.
Anchor had a total of 37 ships, 16 being the peak in 1930. It ran until absorbed into Union in 1972. ''Union Nelson'' ceased regular calls at Nelson in 1985, due in part to railway competition.
Foundry
 The foundry built and repaired a wide range of machinery. It operated from 1866 to 1986 and was established by N. Edwards & Co. In 1866, a workshop opened near N. Edwards & Co bulk store at Matangi Awhio/Auckland Point. A January 1873 report described the newly erected workshops on the Port road, as of corrugated iron, 125 feet long, by 25 feet wide. In the centre was a 70 ft by 25 ft, general workshop, 2 forges, shortly to be added an 8 hp steam engine, to work a 5-cwt. steam hammer, lathes, and fans for the blasts of the various furnaces. A 4 hp engine driving a boring machine and 2 lathes. At the northern end is the foundry, 25 ft x 25 ft, and furnace were being erected.
A large new workshop on Wakefield Quay, named The Anchor Foundry, was in use by 1873. By then the Anchor Foundry repaired Anchor's steamers, as well as taking on outside work, such as building other steamers, making gold sluicing equipment, cast iron stoves and a locomotive for the Takaka Tramway Company. The Foundry also served local industries such as Griffin's biscuits, Samuel Kirkpatrick's jam and canning factory and Baigent Timber, offering fitting and turning, blacksmithing, moulding and casting, boiler making, electric and acetone welding, pattern making, and electrical wiring and installation. In 1883 Anchor Steam Shipping Co. was formed with the Anchor Line ships, foundry, and shipyard. It became Anchor Shipping & Foundry Co. on 31 March 1901. Anchor Foundry at Port Nelson, erected in 1907, was a long narrow building with an exterior cladding of grey corrugated iron. It extended along the waterfront from the power house building to the then Pier Hotel. When the 1907 building was opened, the overhead drive shaft extended the full length of the building, and was reputed to be the longest single overhead drive shaft in the southern hemisphere. After World War II trade declined, partly because of competition from ferries and the declining use of coal. In 1969 Anchor bought T. Dorman Engineering. Late in 1973 Anchor was wound up by Union, when it bought the remaining 12% of Anchor from the Brown families. A new company Anchor Dorman was formed to take over Union's interest in Nelson. In 1984 Anchor Dorman was sold to Perry Dines Corporation of New Plymouth, but within two years was liquidated; even the employees received no redundancy payments. The buildings were sold to Nelson Harbour Board and the plant disposed of. The Anchor Foundry buildings on Wakefield Quay were demolished in 2005 and luxury apartments built. The steps at 15 Richardson Street remain.
The foundry built and repaired a wide range of machinery. It operated from 1866 to 1986 and was established by N. Edwards & Co. In 1866, a workshop opened near N. Edwards & Co bulk store at Matangi Awhio/Auckland Point. A January 1873 report described the newly erected workshops on the Port road, as of corrugated iron, 125 feet long, by 25 feet wide. In the centre was a 70 ft by 25 ft, general workshop, 2 forges, shortly to be added an 8 hp steam engine, to work a 5-cwt. steam hammer, lathes, and fans for the blasts of the various furnaces. A 4 hp engine driving a boring machine and 2 lathes. At the northern end is the foundry, 25 ft x 25 ft, and furnace were being erected.
A large new workshop on Wakefield Quay, named The Anchor Foundry, was in use by 1873. By then the Anchor Foundry repaired Anchor's steamers, as well as taking on outside work, such as building other steamers, making gold sluicing equipment, cast iron stoves and a locomotive for the Takaka Tramway Company. The Foundry also served local industries such as Griffin's biscuits, Samuel Kirkpatrick's jam and canning factory and Baigent Timber, offering fitting and turning, blacksmithing, moulding and casting, boiler making, electric and acetone welding, pattern making, and electrical wiring and installation. In 1883 Anchor Steam Shipping Co. was formed with the Anchor Line ships, foundry, and shipyard. It became Anchor Shipping & Foundry Co. on 31 March 1901. Anchor Foundry at Port Nelson, erected in 1907, was a long narrow building with an exterior cladding of grey corrugated iron. It extended along the waterfront from the power house building to the then Pier Hotel. When the 1907 building was opened, the overhead drive shaft extended the full length of the building, and was reputed to be the longest single overhead drive shaft in the southern hemisphere. After World War II trade declined, partly because of competition from ferries and the declining use of coal. In 1969 Anchor bought T. Dorman Engineering. Late in 1973 Anchor was wound up by Union, when it bought the remaining 12% of Anchor from the Brown families. A new company Anchor Dorman was formed to take over Union's interest in Nelson. In 1984 Anchor Dorman was sold to Perry Dines Corporation of New Plymouth, but within two years was liquidated; even the employees received no redundancy payments. The buildings were sold to Nelson Harbour Board and the plant disposed of. The Anchor Foundry buildings on Wakefield Quay were demolished in 2005 and luxury apartments built. The steps at 15 Richardson Street remain.
Fleet List
Ships were painted salmon pink to the water line, with a black hull, the super-structure finished in white and the funnel white, topped in black.{{Cite web , date=11 December 1926 , title=WHITE FUNNELS IN PORT. Nelson Evening Mail , url=https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/newspapers/NEM19261211.2.138.16.5 , access-date=4 June 2023 , website=paperspast.natlib.govt.nzReferences
External links
Illustrations ŌĆō1853 ''Nelson''
* ''Charles Edward'
at Hokitika about 1869
''Lady Barkly'' as a screw steamer in 1890s
* ''Koi'
ready to launch
* ''Matangi'' as ''Mourilyan'
about 1908
at Whakatahuri breakers yard in 1956 ŌĆ
Shipping companies of New Zealand New Zealand companies established in 1870 Transport companies established in 1870 Defunct transport companies of New Zealand Nelson, New Zealand Steamships of New Zealand 1974 disestablishments in New Zealand