Anatomical Terms Of Neuroanatomy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
This article describes
 Standard
Standard
Gray690.png, The brainstem from the front, showing a ''decussation'' of the superior pedicle and lemniscus, where nerve fibres from one side cross over to the next
Optic processing human brain.jpg, The
 Specific terms are used to represent the
Specific terms are used to represent the
anatomical terminology
Anatomical terminology is a specialized system of terms used by anatomists, zoologists, and health professionals, such as doctors, surgeons, and pharmacists, to describe the structures and functions of the body.
This terminology incorpor ...
that is used to describe the central and peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of Bilateria, bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside t ...
s - including the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
, brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is conti ...
, spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
, and nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons). Nerves have historically been considered the basic units of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the Electrochemistry, electrochemical nerv ...
s.
Anatomical terminology in neuroanatomy
Neuroanatomy
Neuroanatomy is the study of the structure and organization of the nervous system. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defi ...
, like other aspects of anatomy, uses specific terminology to describe anatomical structures. This terminology helps ensure that a structure is described accurately, with minimal ambiguity. Terms also help ensure that structures are described consistently, depending on their structure or function. Terms are often derived from Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
and Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
, and like other areas of anatomy are generally standardised based on internationally accepted lexicons such as Terminologia Anatomica
''Terminologia Anatomica'' (commonly abbreviated TA) is the international standard for human anatomy, human anatomical terminology. It is developed by the Federative International Programme on Anatomical Terminology (FIPAT) a program of the Inter ...
.
To help with consistency, humans and other species are assumed when described to be in ''standard anatomical position
The standard anatomical position, or standard anatomical model, is the scientifically agreed upon reference position for anatomical location terms. Standard anatomical positions are used to standardise the position of appendages of animals with ...
'', with the body standing erect and facing observer, arms at sides, palms forward.
Location
Anatomical terms of location
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pr ...
depend on the location and species that is being described.
To understand the terms used for anatomical localisation, consider an animal with a straight CNS, such as a fish or lizard. In such animals the terms "rostral
Rostral may refer to:
Anatomy
* Rostral (anatomical term), situated toward the oral or nasal region
* Rostral bone, in ceratopsian dinosaurs
* Rostral organ, of certain fish
* Rostral scale
The rostral scale, or rostral, in snakes and other sca ...
", " caudal", "ventral" and "dorsal" mean respectively towards the rostrum, towards the tail, towards the belly and towards the back. For a full discussion of those terms, see anatomical terms of location
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pr ...
.
For many purposes of anatomical description, positions and directions are relative to the standard anatomical planes
An anatomical plane is a hypothetical plane used to transect the body, in order to describe the location of structures or the direction of movements.
In human anatomy and non-human anatomy, four principal planes are used: the median plane, ...
and axes
Axes, plural of ''axe'' and of ''axis'', may refer to
* ''Axes'' (album), a 2005 rock album by the British band Electrelane
* a possibly still empty plot (graphics)
See also
* Axis (disambiguation)
An axis (: axes) may refer to:
Mathematics ...
. Such reference to the anatomical planes and axes is called the stereotactic
Stereotactic surgery is a minimally invasive form of surgery, surgical intervention that makes use of a three-dimensional coordinates, coordinate system to locate small targets inside the body and to perform on them some action such as ablation, ...
approach.
Standard terms used throughout anatomy include '' anterior / posterior'' for the front and back of a structure, '' superior / inferior'' for above and below, '' medial / lateral'' for structures close to and away from the midline respectively, and '' proximal / distal'' for structures close to and far away from a set point.
Some terms are used more commonly in neuroanatomy
Neuroanatomy is the study of the structure and organization of the nervous system. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defi ...
, particularly:
* ''Rostral
Rostral may refer to:
Anatomy
* Rostral (anatomical term), situated toward the oral or nasal region
* Rostral bone, in ceratopsian dinosaurs
* Rostral organ, of certain fish
* Rostral scale
The rostral scale, or rostral, in snakes and other sca ...
'' and ''caudal'': In animals with linear nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the complex system, highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its behavior, actions and sense, sensory information by transmitting action potential, signals to and from different parts of its body. Th ...
s, the term ''rostral'' (from the Latin ''rostrum'', meaning "beak") is synonymous with ''anterior'' and the term ''caudal'' (from the Latin ''cauda'', meaning "tail") is synonymous with ''posterior''. Due to human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
s having an upright posture, however, our nervous system is considered to bend about 90°. This is considered to occur at the junction of the midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum.
It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, mo ...
and diencephalon
In the human brain, the diencephalon (or interbrain) is a division of the forebrain (embryonic ''prosencephalon''). It is situated between the telencephalon and the midbrain (embryonic ''mesencephalon''). The diencephalon has also been known as t ...
(the midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum.
It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, mo ...
- diencephalic junction). Thus, the terminology changes at either side of the midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum.
It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, mo ...
- diencephalic junction. Superior to the junction, the terminology is the same as in animals with linear nervous systems; ''rostral'' is synonymous with ''anterior'' and ''caudal'' is synonymous with posterior. Inferior to the midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum.
It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, mo ...
- diencephalic junction the term ''rostral'' is synonymous with ''superior'' and ''caudal'' is synonymous with ''inferior''.
* ''Dorsal
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ‘back’) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
The fus ...
'' and ''ventral'': In animals with linear nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the complex system, highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its behavior, actions and sense, sensory information by transmitting action potential, signals to and from different parts of its body. Th ...
s, the term ''dorsal'' (from the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
dorsum, meaning "back") is synonymous with ''superior'' and the term ''ventral'' (from the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
venter, meaning "belly") is synonymous with ''inferior''. In humans, however, the terminology differs on either side of the midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum.
It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, mo ...
- diencephalic junction. Superior to the junction, the terminology is the same as in animals with linear nervous systems; ''dorsal'' is synonymous with ''superior'' and ''ventral'' is synonymous with ''inferior''. However, inferior to the midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum.
It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, mo ...
- diencephalic junction the term ''dorsal'' is synonymous with ''posterior'' and ''ventral'' is synonymous with ''anterior''.
* ''Contralateral
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
and ipsilateral
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
'' referring to a corresponding position on the opposite left or right side (the sagittal plane
The sagittal plane (; also known as the longitudinal plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into right and left sections. It is perpendicular to the transverse and coronal planes. The plane may be in the center of the body and divi ...
) and on the same side (ipsilateral) respectively.
Planes and axes
 Standard
Standard anatomical plane
An anatomical plane is a hypothetical plane used to transect the body, in order to describe the location of structures or the direction of movements.
In human anatomy and non-human anatomy, four principal planes are used: the median plane, ...
s and anatomical axes
Anatomical terminology is a specialized system of terms used by anatomists, zoologists, and health professionals, such as doctors, surgeons, and pharmacists, to describe the structures and functions of the body.
This terminology incorporat ...
are used to describe structures in animals. In humans and many other primate
Primates is an order (biology), order of mammals, which is further divided into the Strepsirrhini, strepsirrhines, which include lemurs, galagos, and Lorisidae, lorisids; and the Haplorhini, haplorhines, which include Tarsiiformes, tarsiers a ...
s the axis of the central nervous system is not straight, but bent to allow for forward vision when the body is vertical. This means that differences in terminology are needed to reflect the differences between the brains of primates and the brains of nearly all other vertebrates. For example, to describe the human brain
The human brain is the central organ (anatomy), organ of the nervous system, and with the spinal cord, comprises the central nervous system. It consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. The brain controls most of the activi ...
, "rostral" still means "towards the beak or snout (Latin ''rostrum'')", or at any rate, the interior of the cranial cavity
The cranial cavity, also known as intracranial space, is the space within the skull that accommodates the brain. The skull is also known as the cranium. The cranial cavity is formed by eight cranial bones known as the neurocranium that in human ...
just behind the face. "Caudal" means "towards the tail (Latin ''cauda''"), but not "towards the back of the cranial cavity", which is "posterior" (behind, in ordinary motion). The ''rostro-caudal'' axis of the human central nervous system (magenta in the diagram) makes a near 90° bend at the level of the midbrain and continues through the brain-stem and spinal cord. In human anatomy, the occipital lobes and the back of the head are posterior but not caudal to the frontal lobes and the face.
"Superior" and "inferior" are adjectives from human anatomy, respectively meaning towards to top of the head or the soles of the feet when standing. The brain is superior to the spinal cord in people, but in quadrupeds the brain is anterior (forward in motion) to the spinal cord.
"Dorsal" means "in the direction away from the ridge of the human back or its equivalent in other animals. In human neuroanatomy the word is somewhat distorted, becoming synonymous with "superior" in the forebrain
In the anatomy of the brain of vertebrates, the forebrain or prosencephalon is the rostral (forward-most) portion of the brain. The forebrain controls body temperature, reproductive functions, eating, sleeping, and the display of emotions.
Ve ...
, i.e. in the direction of the roof of the cranial cavity"cranial cavity and thence to the body. "Ventral" in the central nervous system also refers to the rostro-caudal axis, which changes within the head.
These three axes of the human brain match the three planes within which they lie, even though the terms for the planes have not been changed from the terms for the bodily planes. The most commonly used reference planes are:
*''Axial'' or "transverse" or "horizontal", the plane that is horizontal and parallel to the ground with the body standing in the standard anatomical position
The standard anatomical position, or standard anatomical model, is the scientifically agreed upon reference position for anatomical location terms. Standard anatomical positions are used to standardise the position of appendages of animals with ...
. It contains (and thus is defined by) the lateral and the medial axes of the brain.
*''Coronal'', a vertical plane that passes through the coronal suture of the skull (or through both ears), or any plane parallel to this. There is no term "paracoronal" comparable to the commonly used "parasagittal".
*''Sagittal'', a vertical plane that passes from between the nostrils, and between the cerebral hemispheres
The vertebrate cerebrum (brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres ...
, dividing the brain into left and right halves. "Median plane" specifically defines the midline between left and right sides of the body. It contains the dorsoventral and medial axes of the brain. A '' parasagittal'' plane is any plane parallel to the sagittal plane.
Nerves
Function
Specific terms are used for peripheral nerves that originate from, or arrive at, a specific point. An ''afferent nerve fiber
Afferent nerve fibers are axons (nerve fibers) of sensory neurons that carry sensory information from sensory receptors to the central nervous system. Many afferent projections ''arrive'' at a particular brain region.
In the peripheral nerv ...
'' is a fibre originating at the present point. For example, a striatal afferent is an afferent originating at the striatum
The striatum (: striata) or corpus striatum is a cluster of interconnected nuclei that make up the largest structure of the subcortical basal ganglia. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutamat ...
.
An ''efferent nerve fiber
Efferent nerve fibers are axons (nerve fibers) of efferent neurons that exit a particular region. These terms have a slightly different meaning in the context of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and central nervous system (CNS). The efferen ...
'' is one that arrives at the present point. For example, a cortical efferent is a fibre coming from elsewhere, and arriving to the cortex. That is the opposite of the direction in which the nerve fibre conducts signals.
Nerve fibre crossings
Specific terms are also used to describe the route of a nerve or nerve fibre: A chiasm () is used to describe different types of crossings of or withinperipheral
A peripheral device, or simply peripheral, is an auxiliary hardware device that a computer uses to transfer information externally. A peripheral is a hardware component that is accessible to and controlled by a computer but is not a core compo ...
nerve fibres between the cerebral hemispheres. The major example in the human brain is the Optic chiasm
In neuroanatomy, the optic chiasm, or optic chiasma (; , ), is the part of the brain where the optic nerves cross. It is located at the bottom of the brain immediately inferior to the hypothalamus. The optic chiasm is found in all vertebrates, ...
.
A decussation
Decussation is used in biological contexts to describe a crossing (due to the shape of the Roman numeral for ten, an uppercase 'X' (), ). In Latin anatomical terms, the form is used, e.g. .
Similarly, the anatomical term Chiasm (anatomy), chi ...
(, written as a capital X) refers to nerve fibers that cross the sagittal plane
The sagittal plane (; also known as the longitudinal plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into right and left sections. It is perpendicular to the transverse and coronal planes. The plane may be in the center of the body and divi ...
from one side of the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
to the other, and connect ''different'' brain regions. There are two kinds:
* Type 1 crosses the sagittal plane in the ''same'' brain region or spinal segment where the cell body is located. Examples are Mauthner cells in fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
and amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
s.
* Type 2 crosses the sagittal plane in a ''different'' brain region. Example: pyramidal decussations.
The first type is known also for invertebrates
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordate subphylum ...
, whereas the second type only occurs in vertebrates
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
. The second type is thought to be due to an axial twist, such that each hemisphere of the forebrain represents predominantly the contralateral side of the body.
A commissure
A commissure () is the location at which two objects wikt:abut#Verb, abut or are joined. The term is used especially in the fields of anatomy and biology.
* The most common usage of the term refers to the brain's commissures, of which there are at ...
is a bilateral connection of axons connecting the left and right side of the same brain region. For example, nerve fibre tracts that cross between the two cerebral hemispheres, are the anterior commissure
The anterior commissure (also known as the precommissure) is a white matter nerve tract, tract (a bundle of axons) connecting the two temporal lobes of the cerebral hemispheres across the midline, and placed in front of the columns of the Fornix o ...
, posterior commissure
The posterior commissure (also known as the epithalamic commissure) is a rounded band of white fibers crossing the middle line on the dorsal aspect of the rostral end of the cerebral aqueduct. It is important in the bilateral pupillary light re ...
, corpus callosum
The corpus callosum (Latin for "tough body"), also callosal commissure, is a wide, thick nerve tract, consisting of a flat bundle of commissural fibers, beneath the cerebral cortex in the brain. The corpus callosum is only found in placental ...
, hippocampal commissure, and habenular commissure
The habenular commissure is a nerve tract of commissural fibers that connects the habenular nuclei on both sides of the habenular trigone in the epithalamus.
The habenular commissure is part of the habenular trigone (a small depressed triangula ...
. The spinal cord contains a commissure as well: the anterior white commissure
The anterior white commissure (ventral white commissure) is a bundle of nerve fibers which cross the midline of the spinal cord just anterior (in front of) to the gray commissure ( Rexed lamina X). A delta fibers (Aδ fibers) and C fibers carr ...
.
A ganglion
A ganglion (: ganglia) is a group of neuron cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. In the somatic nervous system, this includes dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal ganglia among a few others. In the autonomic nervous system, there are ...
can also have the form of crossing nerves, but a ganglion always contains synapses
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that allows a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or a target effector cell. Synapses can be classified as either chemical or electrical, depending o ...
between neurons
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
as well as their cell bodies. The other kinds of nerve crossings never contain synapses of cell bodies of neurons.
The difference between a ''chiasm'' and a ''decussation'' is that the first refers to peripheral nerves whereas the latter refers to crossings inside central nervous system. A ''commissure'' connects the same brain region of each side whereas a ''decussation'' connects different brain regions.
optic chiasm
In neuroanatomy, the optic chiasm, or optic chiasma (; , ), is the part of the brain where the optic nerves cross. It is located at the bottom of the brain immediately inferior to the hypothalamus. The optic chiasm is found in all vertebrates, ...
in the human brain, showing pathways conveying information from the visual field of each eye to the contralateral visual cortex
Brain
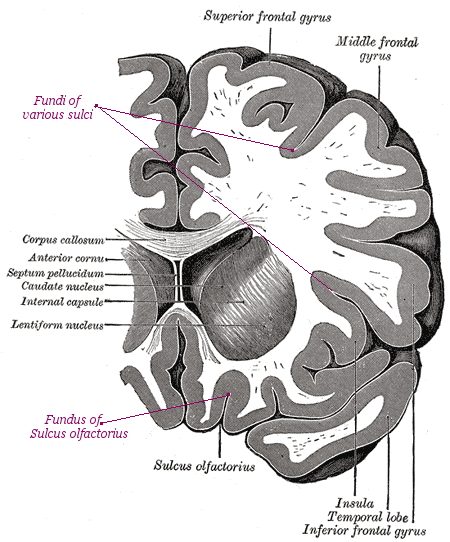
 Specific terms are used to represent the
Specific terms are used to represent the gross anatomy
Gross anatomy is the study of anatomy at the visible or macroscopic level. The counterpart to gross anatomy is the field of histology, which studies microscopic anatomy. Gross anatomy of the human body or other animals seeks to understand the ...
of the brain:
A ''gyrus
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (: gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; : sulcus). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals.
...
'' is an outward folding of the brain, for example the precentral gyrus
The precentral gyrus is a prominent gyrus on the surface of the posterior frontal lobe of the brain. It is the site of the primary motor cortex that in humans is cytoarchitecturally defined as Brodmann area 4.
Structure
The precentral gyrus li ...
. A '' sulcus'' is an inward fold, or valley in the brain's surface - for example the central sulcus
In neuroanatomy, the central sulcus (also central fissure, fissure of Rolando, or Rolandic fissure, after Luigi Rolando) is a sulcus, or groove, in the cerebral cortex in the brains of vertebrates. It is sometimes confused with the longitudinal ...
. Additional terms used to describe these may include:
* '' Annectent gyrus'', for a small gyrus hidden in the depth of a sulcus
* ''sulcal fundus'', for the bottom of a sulcus, an inward fold
A ''fissure
A fissure is a long, narrow crack opening along the surface of Earth. The term is derived from the Latin word , which means 'cleft' or 'crack'. Fissures emerge in Earth's crust, on ice sheets and glaciers, and on volcanoes.
Ground fissure
A ...
'' is used to describe:
# A deep groove produced by opercularisation. An example is the Sylvian Fissure.
# A deep groove produced by the differentiation of the telencephalic vesicles. An example is the longitudinal fissure
The longitudinal fissure (or cerebral fissure, great longitudinal fissure, median longitudinal fissure, interhemispheric fissure) is the deep groove that separates the two cerebral hemispheres of the vertebrate brain. Lying within it is a continu ...
, also known as the ''interhemispheric fissure''.
Imaging
Specific acronyms are used to represent imaging. Some common acronyms include MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
) and CT (Computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
).
See also
*Anatomical terms of muscle
Anatomical terminology is used to uniquely describe aspects of skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle such as their actions, structure, size, and location.
Types
There are three types of muscle tissue in the body: skeletal, smooth, a ...
* Anatomical terms of motion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relativ ...
References
{{ReflistNeuroanatomy
Neuroanatomy is the study of the structure and organization of the nervous system. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defi ...
Human anatomy
neuroanatomy
Neuroanatomy is the study of the structure and organization of the nervous system. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defi ...
Neuroanatomy
Neuroanatomy
Neuroanatomy is the study of the structure and organization of the nervous system. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defi ...
Wikipedia glossaries using unordered lists