Anal Phase on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The anal stage is the second stage in
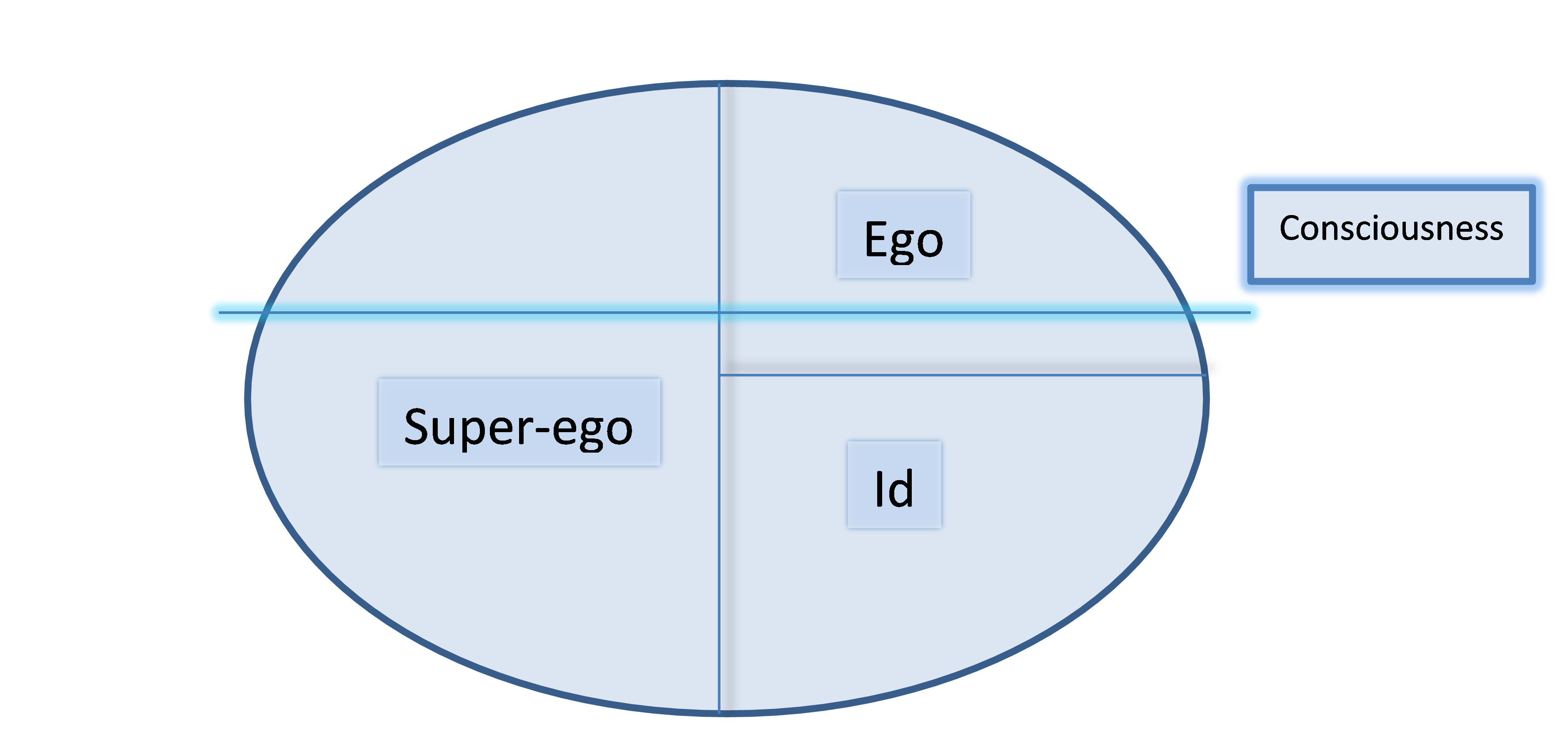
Freud's Psychosexual Stages
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Anal Stage Freudian psychology Toilet training
Sigmund Freud
Sigmund Freud ( ; ; born Sigismund Schlomo Freud; 6 May 1856 – 23 September 1939) was an Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, a clinical method for evaluating and treating psychopathology, pathologies seen as originating fro ...
's theory of psychosexual development
In psychoanalysis, psychosexual development is a central element of the sexual drive theory. According to Freud, personality develops through a series of childhood stages in which pleasure-seeking energies from the child become focused on certa ...
, taking place approximately between the ages of 18 months and three years. In this stage, the anal erogenous zone
An erogenous zone (from Greek , ''érōs'' "love"; and English ''-genous'' "producing", from Greek , ''-genḗs'' "born") is an area of the human body that has heightened Sensory processing, sensitivity, the sexual stimulation, stimulation of wh ...
becomes the primary focus of the child's libidinal energy. The main social context for the experience is the process of toilet training
Toilet training (also potty training or toilet learning) is the process of training someone, particularly a toddler or infant, to use the toilet for urination and defecation. Attitudes toward training in recent history have fluctuated substantial ...
, where anal pleasure becomes associated with the control of bowel movements
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular syste ...
.
According to Freud's theory, personality is developed through a series of stages, focused on erogenous areas, throughout childhood.
A healthy personality in adulthood is dependent upon all of these childhood stages being resolved successfully. If issues are not resolved in a stage, then fixation can occur, potentially resulting in neurotic tendencies or psychological disturbance. A fixation at this stage can result in a personality that is too rigid or one that is too disordered.
General information
The anal stage, in Freudian psychology, is the period of human development occurring at about one to three years of age. Around this age, the child begins to toilet train, which brings about the child's fascination in the erogenous zone of the anus. The erogenous zone is focused on the bowel and bladder control. Therefore, Freud believed that the libido was mainly focused on controlling the bladder and bowel movements. The anal stage coincides with the start of the child's ability to control their anal sphincter, and therefore their ability to pass or withhold feces at will. If the children during this stage can overcome the conflict it will result in a sense of accomplishment and independence.Conflict
This is the second stage of Freud's psychosexual stages. This stage represents a conflict with theid, ego, and superego
In psychoanalytic theory, the id, ego, and superego are three distinct, interacting agents in the psychic apparatus, outlined in Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche. The three agents are theoretical constructs that Freud employed t ...
. The child is approached with this conflict with the parent's demands. A successful completion of this stage depends on how the parents interact with the child while toilet training. If a parent praises the child and gives rewards for using the toilet properly and at the right times then the child will successfully go through the stage. However, if a parent ridicules and punishes a child while they are at this stage, the child can respond in negative ways.

Parents' role
As mentioned before, the ability for the children to be successful in this stage is solely dependent upon their parents and the approach they use towards toilet training. Freud believed that parents should promote the use of toilet training with praise and rewards. The use of positive reinforcement after using the toilet at the appropriate times encourages positive outcomes. This will help reinforce the feeling that the child is capable of controlling their bladder. The parents help make the outcome of this stage a positive experience which in turn will lead to a competent, productive, and creative adult. This stage is also important in the child's future relationships with authority. According to Freud's Psychosexual Theory, parents need to be very careful in how they react to their children during this sensitive stage. During this stage, children test their parents, the authority figures, on how much power they really have as opposed to how much room the child has to make his or her own decisions.Anal-retentive personality
Negative parent-child interactions in the anal stage, including early or harsh toilet training, can lead to the development of an anal-retentive personality. If the parents are too forceful or harsh in training the child to control their own bowel movements, the child may react by deliberately retaining their bowel movements in rebellion. They will form into an adult who hates mess, and is obsessively tidy, punctual, and respectful to authority. These adults can sometimes be stubborn and be very careful with their money.Anal-expulsive personality
Overly passive parent-child interactions in the anal stage lead to the development of an anal-expulsive personality. Because the child's parents were inconsistent or neglectful in teaching the child to control their own bowel movements, the child may relieve themselves at inappropriate times and soil their pants in rebellion against using the toilet. As adults, they will want to share things with their peers and give things away. They can sometimes be messy, disorganized, and rebellious. They may also be inconsiderate of others' feelings.See also
*Psychosexual development
In psychoanalysis, psychosexual development is a central element of the sexual drive theory. According to Freud, personality develops through a series of childhood stages in which pleasure-seeking energies from the child become focused on certa ...
** Oral stage
In Freudian psychoanalysis, the term oral stage denotes the first psychosexual development stage wherein the mouth of the infant is their primary erogenous zone. Spanning the life period from birth to the age of 18 months, the oral stage is the ...
** Phallic stage
In Freudian psychoanalysis, the phallic stage is the third stage of psychosexual development, spanning the ages of three to six years, wherein the infant's libido (desire) centers upon their genitalia as the erogenous zone. When children become ...
** Latency stage
The latency stage is the fourth stage of Sigmund Freud's model of a child's psychosexual development. Freud believed that the child discharges their libido (sexual energy) through a distinct body area that characterizes each stage.
The stages ...
** Genital stage
The genital stage in psychoanalysis is the term used by Sigmund Freud to describe the final stage of human psychosexual development. The individual develops a strong sexual interest in people outside of the family.
In Freud and later thinkers
Th ...
References
External links
* *Freud's Psychosexual Stages
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Anal Stage Freudian psychology Toilet training