amplitude-shift keying on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Amplitude-shift keying (ASK) is a form of
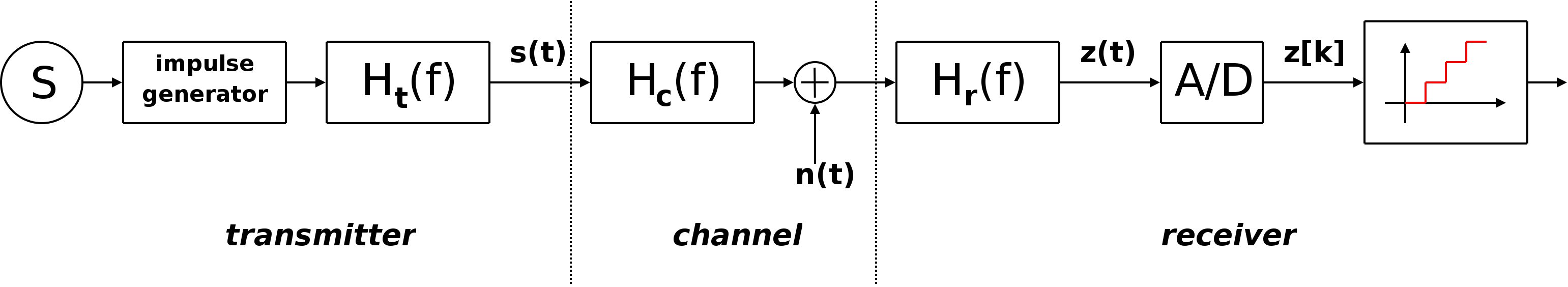 ASK system can be divided into three blocks. The first one represents the transmitter, the second one is a linear model of the effects of the channel, the third one shows the structure of the receiver. The following notation is used:
* ''ht''(f) is the carrier signal for the transmission
* ''hc''(f) is the impulse response of the channel
* ''n''(t) is the noise introduced by the channel
* ''hr''(f) is the filter at the receiver
* ''L'' is the number of levels that are used for transmission
* ''T''s is the time between the generation of two symbols
Different symbols are represented with different voltages. If the maximum allowed value for the voltage is A, then all the possible values are in the range ��A, Aand they are given by:
:
the difference between one voltage and the other is:
:
Considering the picture, the symbols v are generated randomly by the source S, then the impulse generator creates impulses with an area of v These impulses are sent to the filter ht to be sent through the channel. In other words, for each symbol a different carrier wave is sent with the relative amplitude.
Out of the transmitter, the signal s(t) can be expressed in the form:
:
In the receiver, after the filtering through hr (t) the signal is:
:
where we use the notation:
:
where * indicates the convolution between two signals. After the A/D conversion the signal z can be expressed in the form:
:
ASK system can be divided into three blocks. The first one represents the transmitter, the second one is a linear model of the effects of the channel, the third one shows the structure of the receiver. The following notation is used:
* ''ht''(f) is the carrier signal for the transmission
* ''hc''(f) is the impulse response of the channel
* ''n''(t) is the noise introduced by the channel
* ''hr''(f) is the filter at the receiver
* ''L'' is the number of levels that are used for transmission
* ''T''s is the time between the generation of two symbols
Different symbols are represented with different voltages. If the maximum allowed value for the voltage is A, then all the possible values are in the range ��A, Aand they are given by:
:
the difference between one voltage and the other is:
:
Considering the picture, the symbols v are generated randomly by the source S, then the impulse generator creates impulses with an area of v These impulses are sent to the filter ht to be sent through the channel. In other words, for each symbol a different carrier wave is sent with the relative amplitude.
Out of the transmitter, the signal s(t) can be expressed in the form:
:
In the receiver, after the filtering through hr (t) the signal is:
:
where we use the notation:
:
where * indicates the convolution between two signals. After the A/D conversion the signal z can be expressed in the form:
:
amplitude modulation
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a signal modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the instantaneous amplitude of the wave is varied in proportion t ...
that represents digital data
Digital data, in information theory and information systems, is information represented as a string of Discrete mathematics, discrete symbols, each of which can take on one of only a finite number of values from some alphabet (formal languages ...
as variations in the amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of am ...
of a carrier wave
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a periodic waveform (usually sinusoidal) that conveys information through a process called ''modulation''. One or more of the wave's properties, such as amplitude or freq ...
. In an ASK system, a symbol
A symbol is a mark, Sign (semiotics), sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, physical object, object, or wikt:relationship, relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by cr ...
, representing one or more bit
The bit is the most basic unit of information in computing and digital communication. The name is a portmanteau of binary digit. The bit represents a logical state with one of two possible values. These values are most commonly represented as ...
s, is sent by transmitting a fixed-amplitude carrier wave at a fixed frequency for a specific time duration. For example, if each symbol represents a single bit, then the carrier signal could be transmitted at nominal amplitude when the input value is 1, but transmitted at reduced amplitude or not at all when the input value is 0.
Method
Any digital modulation scheme uses afinite
Finite may refer to:
* Finite set, a set whose cardinality (number of elements) is some natural number
* Finite verb, a verb form that has a subject, usually being inflected or marked for person and/or tense or aspect
* "Finite", a song by Sara Gr ...
number of distinct signals to represent digital data. ASK uses a finite number of amplitudes, each assigned a unique pattern of binary digit
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two values (0 and 1) for each digit
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical o ...
s. Usually, each amplitude encodes an equal number of bits. Each pattern of bits forms the symbol
A symbol is a mark, Sign (semiotics), sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, physical object, object, or wikt:relationship, relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by cr ...
that is represented by the particular amplitude. The demodulator
Demodulation is the process of extracting the original information-bearing signal from a carrier wave. A demodulator is an electronic circuit (or computer program in a software-defined radio) that is used to recover the information content from ...
, which is designed specifically for the symbol-set used by the modulator, determines the amplitude of the received signal and maps it back to the symbol it represents, thus recovering the original data. Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
and phase
Phase or phases may refer to:
Science
*State of matter, or phase, one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist
*Phase (matter), a region of space throughout which all physical properties are essentially uniform
*Phase space, a mathematica ...
of the carrier are kept constant.
Like AM, an ASK is also linear and sensitive to atmospheric noise, distortions, propagation conditions on different routes in PSTN
The public switched telephone network (PSTN) is the aggregate of the world's telephone networks that are operated by national, regional, or local telephony operators. It provides infrastructure and services for public telephony. The PSTN consists ...
, etc. Both ASK modulation and demodulation processes are relatively inexpensive. The ASK technique is also commonly used to transmit digital data
Digital data, in information theory and information systems, is information represented as a string of Discrete mathematics, discrete symbols, each of which can take on one of only a finite number of values from some alphabet (formal languages ...
over optical fiber. For LED transmitters, binary 1 is represented by a short pulse of light and binary 0 by the absence of light. Laser transmitters normally have a fixed "bias" current that causes the device to emit a low light level. This low level represents binary 0, while a higher-amplitude lightwave represents binary 1.
The simplest and most common form of ASK operates as a switch, using the presence of a carrier wave to indicate a binary one and its absence to indicate a binary zero. This type of modulation is called on-off keying On-off or Onoff may refer to:
* On-off control, a type of feedback controller
* On-off keying, a type of line modulation
* On-off relationship, a form of personal relationship
* On-Off Singles, a type of tennis game
* On-off switch, a type of e ...
(OOK), and is used at radio frequencies to transmit Morse code (referred to as continuous wave operation),
More sophisticated encoding schemes have been developed which represent data in groups using additional amplitude levels. For instance, a four-level encoding scheme can represent two bits with each shift in amplitude; an eight-level scheme can represent three bits; and so on. These forms of amplitude-shift keying require a high signal-to-noise ratio for their recovery, as by their nature much of the signal is transmitted at reduced power.
 ASK system can be divided into three blocks. The first one represents the transmitter, the second one is a linear model of the effects of the channel, the third one shows the structure of the receiver. The following notation is used:
* ''ht''(f) is the carrier signal for the transmission
* ''hc''(f) is the impulse response of the channel
* ''n''(t) is the noise introduced by the channel
* ''hr''(f) is the filter at the receiver
* ''L'' is the number of levels that are used for transmission
* ''T''s is the time between the generation of two symbols
Different symbols are represented with different voltages. If the maximum allowed value for the voltage is A, then all the possible values are in the range ��A, Aand they are given by:
:
the difference between one voltage and the other is:
:
Considering the picture, the symbols v are generated randomly by the source S, then the impulse generator creates impulses with an area of v These impulses are sent to the filter ht to be sent through the channel. In other words, for each symbol a different carrier wave is sent with the relative amplitude.
Out of the transmitter, the signal s(t) can be expressed in the form:
:
In the receiver, after the filtering through hr (t) the signal is:
:
where we use the notation:
:
where * indicates the convolution between two signals. After the A/D conversion the signal z can be expressed in the form:
:
ASK system can be divided into three blocks. The first one represents the transmitter, the second one is a linear model of the effects of the channel, the third one shows the structure of the receiver. The following notation is used:
* ''ht''(f) is the carrier signal for the transmission
* ''hc''(f) is the impulse response of the channel
* ''n''(t) is the noise introduced by the channel
* ''hr''(f) is the filter at the receiver
* ''L'' is the number of levels that are used for transmission
* ''T''s is the time between the generation of two symbols
Different symbols are represented with different voltages. If the maximum allowed value for the voltage is A, then all the possible values are in the range ��A, Aand they are given by:
:
the difference between one voltage and the other is:
:
Considering the picture, the symbols v are generated randomly by the source S, then the impulse generator creates impulses with an area of v These impulses are sent to the filter ht to be sent through the channel. In other words, for each symbol a different carrier wave is sent with the relative amplitude.
Out of the transmitter, the signal s(t) can be expressed in the form:
:
In the receiver, after the filtering through hr (t) the signal is:
:
where we use the notation:
:
where * indicates the convolution between two signals. After the A/D conversion the signal z can be expressed in the form:
: