Amorites on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Amorites () were an ancient

 There are also sparse mentions about Amorites (often as MAR-DUki) in tablets from the
There are also sparse mentions about Amorites (often as MAR-DUki) in tablets from the
Northwest Semitic
Northwest Semitic is a division of the Semitic languages comprising the indigenous languages of the Levant. It emerged from Proto-Semitic language, Proto-Semitic in the Early Bronze Age. It is first attested in proper names identified as Amorite l ...
-speaking Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
people from the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
. Initially appearing in Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
ian records c. 2500 BC, they expanded and ruled most of the Levant, Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
and parts of Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
from the 21st century BC to the late 17th century BC.
The Amorites established several prominent city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world throughout history, including cities such as Rome, ...
s in various locations, such as Isin
Isin (, modern Arabic language, Arabic: Ishan al-Bahriyat) is an archaeological site in Al-Qādisiyyah Governorate, Iraq which was the location of the Ancient Near East city of Isin, occupied from the late 4th millennium Uruk period up until at ...
, Kurda, Larsa
Larsa (, read ''Larsamki''), also referred to as Larancha/Laranchon (Gk. Λαραγχων) by Berossus, Berossos and connected with the biblical Arioch, Ellasar, was an important city-state of ancient Sumer, the center of the Cult (religious pra ...
, Mari, and Ebla
Ebla (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', , modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a Tell (archaeology), tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was ...
, and later founded Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
and the Old Babylonian Empire
The Old Babylonian Empire, or First Babylonian Empire, is dated to , and comes after the end of Sumerian power with the destruction of the Third Dynasty of Ur, and the subsequent Isin-Larsa period. The chronology of the first dynasty of Babylon ...
. They also founded the Fourteenth Dynasty of Egypt during the fragmented era of the Second Intermediate Period in the Nile Delta
The Nile Delta (, or simply , ) is the River delta, delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's larger deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the eas ...
, which was characterized by rulers bearing Amorite names such as Yakbim Sekhaenre, and were likely part of the later Hyksos
The Hyksos (; Egyptian language, Egyptian ''wikt:ḥqꜣ, ḥqꜣ(w)-wikt:ḫꜣst, ḫꜣswt'', Egyptological pronunciation: ''heqau khasut'', "ruler(s) of foreign lands"), in modern Egyptology, are the kings of the Fifteenth Dynasty of Egypt ( ...
.
The term in Akkadian and Sumerian texts refers to the Amorites, their principal deity, and an Amorite kingdom. The Amorites are mentioned in the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
. '' Canaan CanaanThe current scholarly edition of the Septuagint, Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus Testamentum graece iuxta LXX interprets. 2. ed. / recogn. et emendavit Robert Hanhart. Stuttgart : D ...
both before and after the conquest of the land under . '' Canaan CanaanThe current scholarly edition of the Septuagint, Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus Testamentum graece iuxta LXX interprets. 2. ed. / recogn. et emendavit Robert Hanhart. Stuttgart : D ...
Joshua
Joshua ( ), also known as Yehoshua ( ''Yəhōšuaʿ'', Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: ''Yŏhōšuaʿ,'' Literal translation, lit. 'Yahweh is salvation'), Jehoshua, or Josue, functioned as Moses' assistant in the books of Book of Exodus, Exodus and ...
.van Seters, John, "The Terms 'Amorite' and 'Hittite' in the Old Testament", Vetus Testamentum, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 64–81, 1972
History

Third millennium BC
It is thought that terms like were used to represent what we now call the Amorites: In two Sumerian literary compositions written long afterward in the Old Babylonian period, ''Enmerkar and the Lord of Aratta
''Enmerkar and the Lord of Aratta'' is a legendary Sumerian language, Sumerian account, preserved in early post-Sumerian copies, composed in the Neo-Sumerian period (ca. 21st century BC).
It is one of a series of accounts describing the conflicts ...
'' and ''Lugalbanda and the Anzu Bird
''Lugalbanda and the Anzu Bird'' (or ''Lugalbanda II'', ''The Return of Lugalbanda'', ''Lugalbanda and the Anzu Bird'') is a Sumerian mythological account. The story is the second of two about the hero Lugalbanda. The first story is known as '' ...
'', the Early Dynastic ruler of Uruk Enmerkar
Enmerkar () was an ancient Sumerian ruler to whom the construction of the city of Uruk and a 420-year reign was attributed. According to literary sources, he led various campaigns against the land of Aratta.
He is credited in Sumerian legend as ...
(listed in the Sumerian King List
The ''Sumerian King List'' (abbreviated ''SKL'') or ''Chronicle of the One Monarchy'' is an ancient Composition (language), literary composition written in Sumerian language, Sumerian that was likely created and redacted to legitimize the claims ...
) mentions "the land of the ". It is not known to what extent these reflect historical facts.
 There are also sparse mentions about Amorites (often as MAR-DUki) in tablets from the
There are also sparse mentions about Amorites (often as MAR-DUki) in tablets from the East Semitic
The East Semitic languages are one of three divisions of the Semitic languages. The East Semitic group is attested by three distinct languages, Akkadian, Eblaite and possibly Kishite, all of which have been long extinct. They were influenced ...
-speaking kingdom of Ebla
Ebla (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', , modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a Tell (archaeology), tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was ...
, dating from 2500 BC to the destruction of the city in BC. From the perspective of the Eblaites, the Amorites were a rural group living in the narrow basin of the middle and upper Euphrates in northern Syria. The Eblaites used the term MAR.TU in an early time for a state and people east to Ebla (around Emar and Tuttul
Tuttul (Akkadian language, Akkadian: tu-ut-tu-ulki, Ugaritic: 𐎚𐎚𐎍 – ) was an ancient Near East city. Tuttul is identified with the archaeological site of Tell Bi'a (also Tall Bi'a) in Raqqa Governorate, Syria. Tell Bi'a is located near t ...
), which means the name Amurru for the west is later than the name for the state or the people.Streck, Michael P., ''Das amurritische Onomastikon der altbabylonischen Zeit. Band 1: Die Amurriter, die onomastische Forschung, Orthographie und Phonologie, Nominalmorphologie'', Ugarit-Verlag, 2000, p. 26
For the Akkadian emperors of central Mesopotamia, was one of the "Four Quarters" surrounding Akkad, along with Subartu (north), Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
(south), and Elam
Elam () was an ancient civilization centered in the far west and southwest of Iran, stretching from the lowlands of what is now Khuzestan and Ilam Province as well as a small part of modern-day southern Iraq. The modern name ''Elam'' stems fr ...
(east). Naram-Sin of Akkad
Naram-Sin, also transcribed Narām-Sîn or Naram-Suen (: '' DNa-ra-am D Sîn'', meaning "Beloved of the Moon God Sîn", the "𒀭" a determinative marking the name of a god; died 2218 BC), was a ruler of the Akkadian Empire, who reigned –22 ...
records in a royal inscription defeating a coalition of Sumerian cities and Amorites near Jebel Bishri in northern Syria BC. His successor, Shar-Kali-Sharri, recorded in one of his year names "In the year in which Szarkaliszarri was victorious over Amurru in the ebel Bishri.
By the time of the last days of the Third Dynasty of Ur
The Third Dynasty of Ur or Ur III was a Sumerian dynasty based in the city of Ur in the 22nd and 21st centuries BC ( middle chronology). For a short period they were the preeminent power in Mesopotamia and their realm is sometimes referred to by ...
, the immigrating Amorites had become such a force that kings such as Shu-Sin were obliged to construct a wall from the Tigris
The Tigris ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the eastern of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian Desert, Syrian and Arabia ...
to the Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originati ...
to hold them off. The Amorites are depicted in contemporary records as nomadic tribes under chiefs, who forced themselves into lands they needed to graze their herds. Some of the Akkadian literature of this era speaks disparagingly of the Amorites and implies that the Akkadian- and Sumerian-speakers of Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
viewed their nomadic and primitive way of life with disgust and contempt. In the Sumerian myth "Marriage of Martu", written early in the 2nd millennium BC
File:2nd millennium BC montage.jpg, 400x400px, From top left clockwise: Hammurabi, Babylonian king, best known for his Code of Hammurabi, code of laws; The gold Mask of Tutankhamun, funerary mask of Tutankhamun has become a symbol of ancient Egypt ...
, a goddess considering marriage to the god of the Amorites is warned:
As the centralized structure of the Third Dynasty of Ur slowly collapsed, the city-states of the south such as Isin, Larsa and Eshnunna, began to reassert their former independence, and the areas in southern Mesopotamia with Amorites were no exception. Elsewhere, the armies of Elam
Elam () was an ancient civilization centered in the far west and southwest of Iran, stretching from the lowlands of what is now Khuzestan and Ilam Province as well as a small part of modern-day southern Iraq. The modern name ''Elam'' stems fr ...
were attacking and weakening the empire, making it vulnerable. Ur was eventually occupied by the Elamites. They remained until they were rejected by the Isin ruler Ishbi-Erra
Ishbi-Erra ( Akkadian: d''iš-bi-ir₃-ra'') was the founder of the dynasty of Isin, reigning from c. 2017— 1986 BC ( MC). Ishbi-Erra was preceded by Ibbi-Sin of the third dynasty of Ur in ancient Lower Mesopotamia, and then succeeded by � ...
, which marked the beginning of the Isin-Larsa period.
2nd millennium BC
After the decline of Ur III, Amorite rulers gained power in a number of Mesopotamian city-states beginning in the Isin-Larsa period and peaking in the Old Babylonian period. In the north, the Amorite ruler of Ekallatum,Shamshi-Adad I
Shamshi-Adad (; Amorite: ''Shamshi-Addu''), ruled 1813–1776 BC, was an Amorite warlord and conqueror who had conquered lands across much of Syria, Anatolia, and Upper Mesopotamia.Some of the Mari letters addressed to Shamsi-Adad by his son ca ...
conquered Assur
Aššur (; AN.ŠAR2KI, Assyrian cuneiform: ''Aš-šurKI'', "City of God Aššur"; ''Āšūr''; ''Aθur'', ''Āšūr''; ', ), also known as Ashur and Qal'at Sherqat, was the capital of the Old Assyrian city-state (2025–1364 BC), the Midd ...
and formed the large, though short-lived Kingdom of Upper Mesopotamia. In the south, Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
became the major power under the Amorite ruler Sumu-la-El and his successors, including the notable Hammurabi
Hammurabi (; ; ), also spelled Hammurapi, was the sixth Amorite king of the Old Babylonian Empire, reigning from to BC. He was preceded by his father, Sin-Muballit, who abdicated due to failing health. During his reign, he conquered the ci ...
. Higher up the Euphrates, to the northwest, the Amorite kingdom of Mari arose, later to be destroyed by Hammurabi. Babylon itself would later be sacked by the Hittites, with its empire assumed by the Kassites
The Kassites () were a people of the ancient Near East. They controlled Babylonia after the fall of the Old Babylonian Empire from until (short chronology).
The Kassites gained control of Babylonia after the Hittite sack of Babylon in 1531 B ...
. West of Mari, Yamhad
Yamhad (Yamḫad) was an ancient Semitic languages, Semitic-speaking kingdom centered on Ḥalab (Aleppo) in Syria (region), Syria. The kingdom emerged at the end of the 19th century BC and was ruled by the Yamhad dynasty, who counted on both mi ...
ruled from its capital Halab, today's Aleppo, until it was destroyed by the Hittites in 16th century BC. The city of Ebla
Ebla (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', , modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a Tell (archaeology), tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was ...
, under the control of Yamhad in this period, also had Amorite rulership.
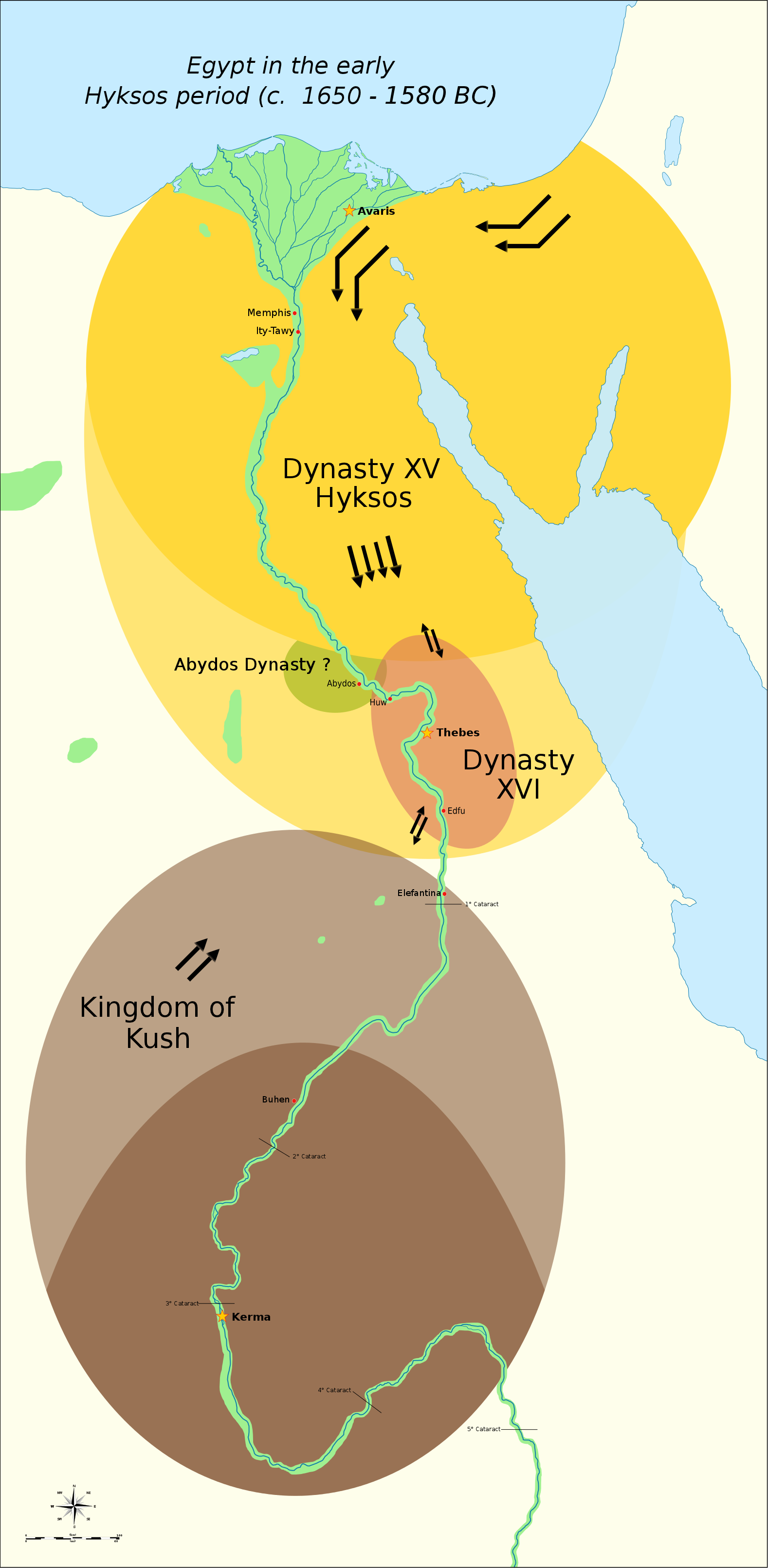
There is thought to have been an Amorite presence in Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
from the 19th century BC. The Fourteenth Dynasty of Egypt, centred in the Nile Delta
The Nile Delta (, or simply , ) is the River delta, delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's larger deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the eas ...
, had rulers bearing Amorite names such as Yakbim. Furthermore, increasing evidence suggests that the succeeding Hyksos
The Hyksos (; Egyptian language, Egyptian ''wikt:ḥqꜣ, ḥqꜣ(w)-wikt:ḫꜣst, ḫꜣswt'', Egyptological pronunciation: ''heqau khasut'', "ruler(s) of foreign lands"), in modern Egyptology, are the kings of the Fifteenth Dynasty of Egypt ( ...
of Egypt were an amalgam of peoples from Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
of which the Amorites were also part. Based on temple architecture, Manfred Bietak argues for strong parallels between the religious practices of the Hyksos at Avaris
Avaris (Egyptian: ḥw.t wꜥr.t, sometimes ''hut-waret''; ; ; ) was the Hyksos capital of Egypt located at the modern site of Tell el-Dab'a in the northeastern region of the Nile Delta. As the main course of the Nile migrated eastward, its po ...
with those of the area around Byblos
Byblos ( ; ), also known as Jebeil, Jbeil or Jubayl (, Lebanese Arabic, locally ), is an ancient city in the Keserwan-Jbeil Governorate of Lebanon. The area is believed to have been first settled between 8800 and 7000BC and continuously inhabited ...
, Ugarit
Ugarit (; , ''ủgrt'' /ʾUgarītu/) was an ancient port city in northern Syria about 10 kilometers north of modern Latakia. At its height it ruled an area roughly equivalent to the modern Latakia Governorate. It was discovered by accident in 19 ...
, Alalakh
Alalakh (''Tell Atchana''; Hittite: Alalaḫ) is an ancient archaeological site approximately northeast of Antakya (historic Antioch) in what is now Turkey's Hatay Province. It flourished as an urban settlement in the Middle and Late Bronze Age ...
and Tell Brak and defines the "spiritual home" of the Hyksos as "in northernmost Syria and northern Mesopotamia", areas typically associated with Amorites at the time.
In 1650 BC, the Hyksos established the Fifteenth Dynasty of Egypt
The Fifteenth Dynasty was a foreign dynasty of ancient Egypt. It was founded by Salitis, a Hyksos from West Asia whose people had invaded the country and conquered Lower Egypt. The 15th, 16th, and 17th Dynasties of ancient Egypt are often comb ...
and ruled most of Lower
Lower may refer to:
* ''Lower'' (album), 2025 album by Benjamin Booker
*Lower (surname)
*Lower Township, New Jersey
*Lower Receiver (firearms)
*Lower Wick
Lower Wick is a small hamlet located in the county of Gloucestershire, England. It is sit ...
and Middle Egypt contemporaneously with the Sixteenth and Seventeenth dynasties of Thebes during the chaotic Second Intermediate Period
The Second Intermediate Period dates from 1700 to 1550 BC. It marks a period when ancient Egypt was divided into smaller dynasties for a second time, between the end of the Middle Kingdom and the start of the New Kingdom. The concept of a Secon ...
.
Fall
In the 16th century BC, the Amorite era ended in Mesopotamia with the decline and fall of Babylon and other Amorite-ruled cities. TheKassites
The Kassites () were a people of the ancient Near East. They controlled Babylonia after the fall of the Old Babylonian Empire from until (short chronology).
The Kassites gained control of Babylonia after the Hittite sack of Babylon in 1531 B ...
occupied Babylon and reconstituted it under the Kassite dynasty under the name of Karduniaš around 1595 BC. In far southern Mesopotamia, the native First Sealand dynasty had reigned over the Mesopotamian Marshes region until the Kassites brought the region under their control. In northern Mesopotamia
Upper Mesopotamia constitutes the uplands and great outwash plain of northwestern Iraq, northeastern Syria and southeastern Turkey, in the northern Middle East. Since the early Muslim conquests of the mid-7th century, the region has been known by ...
, the power vacuum left by the Amorites brought the rise of the Mitanni
Mitanni (–1260 BC), earlier called Ḫabigalbat in old Babylonian texts, ; Hanigalbat or Hani-Rabbat in Assyrian records, or in Ancient Egypt, Egyptian texts, was a Hurrian language, Hurrian-speaking state in northern Syria (region), Syria an ...
(Ḫanigalbat) c. 1600 BC.
From the 15th century BC onward, the term ''Amurru'' is usually applied to the region extending north of Canaan as far as Kadesh on the Orontes River
The Orontes (; from Ancient Greek , ) or Nahr al-ʿĀṣī, or simply Asi (, ; ) is a long river in Western Asia that begins in Lebanon, flowing northwards through Syria before entering the Mediterranean Sea near Samandağ in Hatay Province, Turk ...
in northern Syria.Lawson Younger, K., "The Late Bronze Age / Iron Age Transition and the Origins of the Arameans", Ugarit at Seventy-Five, edited by K. Lawson Younger Jr., University Park, US: Penn State University Press, pp. 131–174, 2007
After the mid-2nd millennium BC, Syrian Amorites came under the domination of first the Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian peoples, Anatolian Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European people who formed one of the first major civilizations of the Bronze Age in West Asia. Possibly originating from beyond the Black Sea, they settled in mo ...
and, from the 14th century BC, the Middle Assyrian Empire
The Middle Assyrian Empire was the third stage of Assyrian history, covering the history of Assyria from the accession of Ashur-uballit I 1363 BC and the rise of Assyria as a territorial kingdom to the death of Ashur-dan II in 912 BC. ...
. They then appear to have been displaced or absorbed by other semi-nomadic West Semitic-speaking peoples, known collectively as the Ahlamu during the Late Bronze Age collapse
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a period of societal collapse in the Mediterranean basin during the 12th century BC. It is thought to have affected much of the Eastern Mediterranean and Near East, in particular Egypt, Anatolia, the Aegea ...
. The Arameans
The Arameans, or Aramaeans (; ; , ), were a tribal Semitic people in the ancient Near East, first documented in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. Their homeland, often referred to as the land of Aram, originally covered c ...
rose to be the prominent group amongst the Ahlamu. From c. 1200 BC onward, the Amorites disappeared from the pages of history, but the name reappeared in the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
. '' Canaanite,
The Ancient Languages of Syria-Palestine and Arabia
' (2008) (pp. 5–6). Roger D. Woodard, editor. Cambridge University Press, (262 pages).
 There are a wide range of views regarding the Amorite homeland. One extreme is the view that /''māt amurrim'' covered the whole area between the
There are a wide range of views regarding the Amorite homeland. One extreme is the view that /''māt amurrim'' covered the whole area between the
Hans Jonas, "Chamberlain and the Jews",
Entanglement, the Amorite koine, and the Amorite Cultures in the Levant
, Aram Society for the Syro-Mesopotamian Studies 26, pp. 357–373, 2014 * Burke, Aaron A., "Amorites and Canaanites: Memory, Tradition, and Legacy in Ancient Israel and Judah", The Ancient Israelite World. Routledge, pp. 523–536, 2022 * George, Andrew, and Manfred Krebernik, "Two Remarkable Vocabularies: Amorite-Akkadian Bilinguals!", Revue d'assyriologie et d'archéologie orientale 116.1, pp. 113–166, 2022 * Højlund, Flemming,
The Formation Of The Dilmun State And The Amorite Tribes
, Proceedings of the Seminar for Arabian Studies, vol. 19, pp. 45–59, 1989 * Homsher, R. and Cradic, M., "The Amorite Problem: Resolving a Historical Dilemma", Levant 49, pp. 259–283, 2018
Howard, J. Caleb, "Amorite Names through Time and Space", Journal of Semitic Studies, 2023 * Streck, Michael P., ''Das amurritische Onomastikon der altbabylonischen Zeit. Band 1: Die Amurriter, die onomastische Forschung, Orthographie und Phonologie, Nominalmorphologie'', Ugarit-Verlag, 2000 * Torczyner, H. Tur-Sinai, "The Amorite and the Amurrû of the Inscriptions", The Jewish Quarterly Review, vol. 39, no. 3, pp. 249–258, 1949 * Vidal, Jordi,
Prestige Weapons in an Amorite Context
, Journal of Near Eastern Studies, vol. 70, no. 2, pp. 247–52, 2011 * Wallis, Louis,
Amorite Influence in the Religion of the Bible
, The Biblical World, vol. 45, no. 4, pp. 216–23, 1915 * Wasserman, Nathan, and Yigal Bloch, "The Amorites: A Political History of Mesopotamia in the Early Second Millennium BCE", The Amorites, Brill, 2023 * Zeynivand, Mohsen,
A Cylinder Seal With An Amorite Name From Tepe Musiyan, Deh Luran Plain
, Journal of Cuneiform Studies, vol. 71, pp. 77–83, 2019
Cryptic lost Canaanite language decoded on 'Rosetta Stone'-like tablets – LiveScience – Tom Metcalfe – 30 January 2023
Two 3,800-year-old Cuneiform Tablets Found in Iraq Give First Glimpse of Hebrew Precursor – Haaretz – Jan 20, 2023
Amorites
in the ''Jewish Encyclopedia'' {{Use dmy dates, date=April 2017 Amorites, Ancient Levant Ancient Syria States and territories established in the 3rd millennium BC States and territories disestablished in the 18th century BC States and territories disestablished in the 16th century BC Canaan Hebrew Bible nations Semitic-speaking peoples Ancient peoples of the Near East 21st-century BC establishments Giants in the Hebrew Bible
. '' Canaanite,
Aramaic
Aramaic (; ) is a Northwest Semitic language that originated in the ancient region of Syria and quickly spread to Mesopotamia, the southern Levant, Sinai, southeastern Anatolia, and Eastern Arabia, where it has been continually written a ...
and Sam'alian languages. In the 18th century BC at Mari Amorite scribes wrote in an Eshnunna dialect of the East Semitic
The East Semitic languages are one of three divisions of the Semitic languages. The East Semitic group is attested by three distinct languages, Akkadian, Eblaite and possibly Kishite, all of which have been long extinct. They were influenced ...
Akkadian language
Akkadian ( ; )John Huehnergard & Christopher Woods, "Akkadian and Eblaite", ''The Cambridge Encyclopedia of the World's Ancient Languages''. Ed. Roger D. Woodard (2004, Cambridge) Pages 218–280 was an East Semitic language that is attested ...
. Since the texts contain Northwest Semitic
Northwest Semitic is a division of the Semitic languages comprising the indigenous languages of the Levant. It emerged from Proto-Semitic language, Proto-Semitic in the Early Bronze Age. It is first attested in proper names identified as Amorite l ...
forms, words and constructions, the Amorite language
Amorite is an extinct early Semitic language, formerly spoken during the Bronze Age by the Amorite tribes prominent in ancient Near Eastern history. It is known from Ugaritic, which is classed by some as its westernmost dialect, and from non- Akk ...
is thought to be a Northwest Semitic language. The main sources for the extremely limited extant knowledge of the Amorite language are the proper names and loanwords, not Akkadian in style, that are preserved in such texts.Michalowski, Piotr, "Chapter 5. The Amorites in Ur III Times", The Correspondence of the Kings of Ur: An Epistolary History of an Ancient Mesopotamian Kingdom, University Park, US: Penn State University Press, pp. 82–121, 2011 Amorite proper names were found throughout Mesopotamia in the Old Babylonian period, as well as places as far afield as Alalakh
Alalakh (''Tell Atchana''; Hittite: Alalaḫ) is an ancient archaeological site approximately northeast of Antakya (historic Antioch) in what is now Turkey's Hatay Province. It flourished as an urban settlement in the Middle and Late Bronze Age ...
in Turkey and modern day Bahrain ( Dilmun). They are also found in Egyptian records.
Ugaritic
Ugaritic () is an extinct Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language known through the Ugaritic texts discovered by French archaeology, archaeologists in 1928 at Ugarit, including several major literary texts, notably the Baal cycl ...
is also a Northwest Semitic language and is possibly an Amorite dialect.Pardee, Dennis. "Ugaritic", in The Ancient Languages of Syria-Palestine and Arabia
' (2008) (pp. 5–6). Roger D. Woodard, editor. Cambridge University Press, (262 pages).
Religion
A bilingual list of the names of ten Amorite deities alongside Akkadian counterparts from the Old Babylonian period was translated in 2022. These deities are as follows: * Dagan, who is identified withEnlil
Enlil, later known as Elil and Ellil, is an List of Mesopotamian deities, ancient Mesopotamian god associated with wind, air, earth, and storms. He is first attested as the chief deity of the Sumerian pantheon, but he was later worshipped by t ...
. Dagan was the supreme god in many cities in the Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originati ...
region of Upper Mesopotamia
Upper Mesopotamia constitutes the Upland and lowland, uplands and great outwash plain of northwestern Iraq, northeastern Syria and southeastern Turkey, in the northern Middle East. Since the early Muslim conquests of the mid-7th century, the regio ...
, especially at sites such as Mari, Tuttul
Tuttul (Akkadian language, Akkadian: tu-ut-tu-ulki, Ugaritic: 𐎚𐎚𐎍 – ) was an ancient Near East city. Tuttul is identified with the archaeological site of Tell Bi'a (also Tall Bi'a) in Raqqa Governorate, Syria. Tell Bi'a is located near t ...
, and Terqa
Terqa is an ancient city discovered at the site of Tell Ashara on the banks of the middle Euphrates in Deir ez-Zor Governorate, Syria, approximately from the modern border with Iraq and north of the ancient site of Mari, Syria. Its name had b ...
. Babylonian texts refer to the chief god of the Amorites as Amurru (, read as " ilu Amurru"), corresponding to their name for the ethnic group. They also identify his consort as the goddess Ašratum.
* Kamiš, an otherwise poorly attested deity largely known from Akkadian and Amorite theophoric name
A theophoric name (from Greek: , ''theophoros'', literally "bearing or carrying a god") embeds the word equivalent of 'god' or a god's name in a person's name, reflecting something about the character of the person so named in relation to that d ...
s. He was significant at Ebla
Ebla (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', , modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a Tell (archaeology), tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was ...
, where a month was named after him. The bilingual identifies him with the god Ea though other god lists identify him with Nergal
Nergal ( Sumerian: d''KIŠ.UNU'' or ; ; Aramaic: ܢܸܪܓܲܠ; ) was a Mesopotamian god worshiped through all periods of Mesopotamian history, from Early Dynastic to Neo-Babylonian times, with a few attestations indicating that his cult surv ...
.
* Ašratum, whose name is cognate with Asherah
Asherah (; ; ; ; Qatabanian language, Qatabanian: ') was a goddess in ancient Semitic religions. She also appears in Hittites, Hittite writings as ''Ašerdu(š)'' or ''Ašertu(š)'' (), and as Athirat in Ugarit. Some scholars hold that Ashera ...
and is identified with Belet-ili.
* Yaraḫum, the moon god, who is named Yarikh
Yarikh (Ugaritic: , , "moon"), or Yaraḫum, was a moon god worshiped in the Ancient Near East. He is best attested in sources from the Amorite city of Ugarit in the north of modern Syria, where he was one of the principal deities. His primary cul ...
at Ugarit
Ugarit (; , ''ủgrt'' /ʾUgarītu/) was an ancient port city in northern Syria about 10 kilometers north of modern Latakia. At its height it ruled an area roughly equivalent to the modern Latakia Governorate. It was discovered by accident in 19 ...
. He is identified with the god Sīn.
* Rašapum, equated with Nergal
Nergal ( Sumerian: d''KIŠ.UNU'' or ; ; Aramaic: ܢܸܪܓܲܠ; ) was a Mesopotamian god worshiped through all periods of Mesopotamian history, from Early Dynastic to Neo-Babylonian times, with a few attestations indicating that his cult surv ...
and also known from Ebla.
* A god with an incompletely reconstructed name (possibly ''/ʔārum/'') who is identified with Išum.
* Ḫalamu, identified with Šubula, a deity in the netherworld god's circle.
* Ḫanatum, who is here identified with Ištar
Inanna is the ancient Mesopotamian goddess of war, love, and fertility. She is also associated with political power, divine law, sensuality, and procreation. Originally worshipped in Sumer, she was known by the Akkadians, Babylonians, and As ...
.
* Pidray, previously known only from the Late Bronze Age Ugaritic texts and later. In the bilingual list she is identified with Nanaya.
* ''Aštiulḫālti'', who is identified with Ištaran, the tutelary deity of the city of Der.
This list is not thought to represent a full Amorite pantheon, as it does not include important members such as the sun and weather deities.
Biblical Amorites
The term ''Amorites'' is used in theBible
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) originally writt ...
to refers to certain highlanders who inhabited the land of Canaan
CanaanThe current scholarly edition of the Septuagint, Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus Testamentum graece iuxta LXX interprets. 2. ed. / recogn. et emendavit Robert Hanhart. Stuttgart : D ...
, described in Genesis as descendants of Canaan, the son of Ham (). This aligns with Akkadian and Babylonian traditions that equate Syro-Palestine with the "land of the Amorites". They are described as a powerful people of great stature "like the height of the cedars" () who had occupied the land east and west of the Jordan
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian ter ...
. The height and strength mentioned in Amos 2:9 has led some Christian scholars, including Orville J. Nave, who wrote the Nave's Topical Bible, to refer to the Amorites as "giants". In Deuteronomy
Deuteronomy (; ) is the fifth book of the Torah (in Judaism), where it is called () which makes it the fifth book of the Hebrew Bible and Christian Old Testament.
Chapters 1–30 of the book consist of three sermons or speeches delivered to ...
, the Amorite king Og is described as the last "of the remnant of the Rephaim
In the Hebrew Bible, as well as non-Jews, Jewish ancient texts from the region, the Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic term Rephaite or Repha'im (cf. the plural word in ; , ) refers either to a people of greater-than-average height and ...
" (). The terms Amorite and Canaanite seem to be used more or less interchangeably, but sometimes Amorite refers to a specific tribe living in Canaan.
The Biblical Amorites seem to have originally occupied the region stretching from the heights west of the Dead Sea
The Dead Sea (; or ; ), also known by #Names, other names, is a landlocked salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east, the Israeli-occupied West Bank to the west and Israel to the southwest. It lies in the endorheic basin of the Jordan Rift Valle ...
() to Hebron
Hebron (; , or ; , ) is a Palestinian city in the southern West Bank, south of Jerusalem. Hebron is capital of the Hebron Governorate, the largest Governorates of Palestine, governorate in the West Bank. With a population of 201,063 in ...
(), embracing "all Gilead
Gilead or Gilad (, ; ''Gilʿāḏ'', , ''Jalʻād'') is the ancient, historic, biblical name of the mountainous northern part of the region of Transjordan.''Easton's Bible Dictionary'Galeed''/ref> The region is bounded in the west by the J ...
and all Bashan
Bashan (; ; or ''Basanitis'') is the ancient, biblical name used for the northernmost region of Transjordan during the Iron Age. It is situated in modern-day Jordan and Syria. Its western part, nowadays known as the Golan Heights, was occupied b ...
" (), with the Jordan Valley on the east of the river (), the land of the "two kings of the Amorites", Sihon
Sihon was an Amorite king mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, king of Ashtaroth, who refused to let the Israelites pass through his country. Chronicled in Numbers, he was defeated by Moses and the Israelites at the battle of Jahaz. He and Og were said ...
and Og ( and ). Sihon
Sihon was an Amorite king mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, king of Ashtaroth, who refused to let the Israelites pass through his country. Chronicled in Numbers, he was defeated by Moses and the Israelites at the battle of Jahaz. He and Og were said ...
and Og were independent kings whose people were displaced from their land in battle with the Israelites ()—though in the case of the war led by Og/Bashan it appears none of them survived, and the land became part of Israel (). The Amorites seem to have been linked to the Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
region, and the Jebusites
The Jebusites (; ) were, according to the Book of Joshua and Books of Samuel from the Hebrew Bible, a Canaanite tribe that inhabited Jerusalem, called Jebus () before the conquest initiated by Joshua (, ) and completed by David (). According to s ...
may have been a subgroup of them (). The southern slopes of the mountains of Judea
Judea or Judaea (; ; , ; ) is a mountainous region of the Levant. Traditionally dominated by the city of Jerusalem, it is now part of Palestine and Israel. The name's usage is historic, having been used in antiquity and still into the pres ...
are called the "mount of the Amorites" ().
The Book of Joshua
The Book of Joshua is the sixth book in the Hebrew Bible and the Old Testament, and is the first book of the Deuteronomistic history, the story of Israel from the conquest of Canaan to the Babylonian captivity, Babylonian exile. It tells of the ...
states the five kings of the Amorites were first defeated with great slaughter by Joshua
Joshua ( ), also known as Yehoshua ( ''Yəhōšuaʿ'', Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: ''Yŏhōšuaʿ,'' Literal translation, lit. 'Yahweh is salvation'), Jehoshua, or Josue, functioned as Moses' assistant in the books of Book of Exodus, Exodus and ...
(). Then, more Amorite kings were defeated at the waters of Merom by Joshua (). It is mentioned that in the days of Samuel
Samuel is a figure who, in the narratives of the Hebrew Bible, plays a key role in the transition from the biblical judges to the United Kingdom of Israel under Saul, and again in the monarchy's transition from Saul to David. He is venera ...
, there was peace between them and the Israelites (). The Gibeonites were said to be their descendants, being an offshoot of the Amorites who made a covenant with the Hebrews (). When Saul
Saul (; , ; , ; ) was a monarch of ancient Israel and Judah and, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament, the first king of the United Monarchy, a polity of uncertain historicity. His reign, traditionally placed in the late eleventh c ...
later broke that vow and killed some of the Gibeonites, God is said to have sent a famine to Israel ().
In 2017, Philippe Bohstrom of ''Haaretz
''Haaretz'' (; originally ''Ḥadshot Haaretz'' – , , ) is an List of newspapers in Israel, Israeli newspaper. It was founded in 1918, making it the longest running newspaper currently in print in Israel. The paper is published in Hebrew lan ...
'' observed similarities between the Amorites and modern-day Jews, since both may have originated from a single spot, spread around their regions and managed to stay distantly connected kinshipwise. He believes possibly either that Abraham
Abraham (originally Abram) is the common Hebrews, Hebrew Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father who began the Covenant (biblical), covenanta ...
was among the Amorites who migrated to Land of Israel
The Land of Israel () is the traditional Jewish name for an area of the Southern Levant. Related biblical, religious and historical English terms include the Land of Canaan, the Promised Land, the Holy Land, and Palestine. The definition ...
, around the same time of the destruction of the Sumerian capital Ur by Elamites in 1750 BCE, or suggests continuity between "the bible’s portrait of Israel’s tribal organization and mobile herding background" and that of the Amorites. Nonetheless, the Biblical writers only applied the Amorite ethnonym to Canaanite nations existing pre-Israelite conquest. According to biblical scholar Daniel E. Fleming, reasons for Biblical appearances include a polemical desire to use the stereotypes present in the Sumerian myth ''Marriage of Martu'' and explaining the acquisition of current territory, caveating both that the lack of evidence of Biblical writers having access to contemporaneous texts describing the historical past of Amorites may result in only historical interest from their use of the ethnonym.
Origin
 There are a wide range of views regarding the Amorite homeland. One extreme is the view that /''māt amurrim'' covered the whole area between the
There are a wide range of views regarding the Amorite homeland. One extreme is the view that /''māt amurrim'' covered the whole area between the Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originati ...
and the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
, the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
included. The most common view is that the "homeland" of the Amorites was a limited area in central Syria identified with the mountainous region of Jebel Bishri. The Amorites are regarded as one of the ancient Semitic-speaking peoples
Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples or Proto-Semitic people were speakers of Semitic languages who lived throughout the ancient Near East and North Africa, including the Levant, Mesopotamia, the Arabian Peninsula and Carthage from the 3rd millenniu ...
.
Ancient DNA analysis on 28 human remains dating to the Middle and Late Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
from ancient Alalakh
Alalakh (''Tell Atchana''; Hittite: Alalaḫ) is an ancient archaeological site approximately northeast of Antakya (historic Antioch) in what is now Turkey's Hatay Province. It flourished as an urban settlement in the Middle and Late Bronze Age ...
, an Amorite city with a Hurrian
The Hurrians (; ; also called Hari, Khurrites, Hourri, Churri, Hurri) were a people who inhabited the Ancient Near East during the Bronze Age. They spoke the Hurro-Urartian language, Hurrian language, and lived throughout northern Syria (region) ...
minority, found that the inhabitants of Alalakh were a mixture of Copper age
The Chalcolithic ( ) (also called the Copper Age and Eneolithic) was an archaeological period characterized by the increasing use of smelted copper. It followed the Neolithic and preceded the Bronze Age. It occurred at different periods in dif ...
Levantines and Mesopotamians, and were genetically similar to contemporaneous Levantines.
The view that Amorites were fierce and tall nomads led to an anachronistic theory among some racialist writers in the 19th century that they were a tribe of "Aryan
''Aryan'' (), or ''Arya'' (borrowed from Sanskrit ''ārya''), Oxford English Dictionary Online 2024, s.v. ''Aryan'' (adj. & n.); ''Arya'' (n.)''.'' is a term originating from the ethno-cultural self-designation of the Indo-Iranians. It stood ...
" warriors, who at one point dominated the Israelites. This belief, which originated with Felix von Luschan, fit models of Indo-European migrations
The Indo-European migrations are hypothesized migrations of Proto-Indo-Europeans, peoples who spoke Proto-Indo-European language, Proto-Indo-European (PIE) and the derived Indo-European languages, which took place from around 4000 to 1000 BCE, ...
posited during his time, but Luschan later abandoned that theory. Houston Stewart Chamberlain
Houston Stewart Chamberlain (; 9 September 1855 – 9 January 1927) was a British-German-French philosopher who wrote works about political philosophy and natural science. His writing promoted German ethnonationalism, antisemitism, scientific r ...
claims that King David
David (; , "beloved one") was a king of ancient Israel and Judah and the third king of the United Monarchy, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament.
The Tel Dan stele, an Aramaic-inscribed stone erected by a king of Aram-Dam ...
and Jesus
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Chris ...
were both Aryans of Amorite extraction. The argument was repeated by the Nazi
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During H ...
ideologue Alfred Rosenberg.Hans Jonas, "Chamberlain and the Jews",
New York Review of Books
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
** "New" (Paul McCartney song), 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, 1995
* "New" (Daya song), 2017
* "New" (No Doubt song), 1 ...
, 5 June 1981Amorite states
In the Levant: *Amurru kingdom
Amurru ( Sumerian: 𒈥𒌅𒆠 ''MAR.TUKI''; Akkadian: 𒀀𒈬𒌨𒊏 ''Amûrra'', 𒀀𒈬𒊑 ''Amuri'', 𒀀𒄯𒊑 ''Amurri'') The Ammuru Kingdom was an ancient kingdom located in the Middle East region, known for its role in early Bronze ...
* Ebla's Third Dynasty
* Emar
* Mukish
* Shaddai
* Qatna
Qatna (modern: , Tell al-Mishrifeh; also Tell Misrife or Tell Mishrifeh) was an ancient city located in Homs Governorate, Syria. Its remains constitute a tell situated about northeast of Homs near the village of al-Mishrifeh. The city was an ...
* Ugarit
Ugarit (; , ''ủgrt'' /ʾUgarītu/) was an ancient port city in northern Syria about 10 kilometers north of modern Latakia. At its height it ruled an area roughly equivalent to the modern Latakia Governorate. It was discovered by accident in 19 ...
* Yamhad
Yamhad (Yamḫad) was an ancient Semitic languages, Semitic-speaking kingdom centered on Ḥalab (Aleppo) in Syria (region), Syria. The kingdom emerged at the end of the 19th century BC and was ruled by the Yamhad dynasty, who counted on both mi ...
* Zahiran
In Mesopotamia:
* Andarig
* Apum
* First Babylonian Dynasty
The Old Babylonian Empire, or First Babylonian Empire, is dated to , and comes after the end of Sumerian power with the destruction of the Third Dynasty of Ur, and the subsequent Isin-Larsa period. The Chronology of the Ancient Near East, chrono ...
* Ekallatum
* Mari's Lim Dynasty
* Ṭābetu
* Kingdom of Upper Mesopotamia
In Egypt:
* Fourteenth Dynasty of Egypt
* Fifteenth Dynasty of Egypt
The Fifteenth Dynasty was a foreign dynasty of ancient Egypt. It was founded by Salitis, a Hyksos from West Asia whose people had invaded the country and conquered Lower Egypt. The 15th, 16th, and 17th Dynasties of ancient Egypt are often comb ...
?
Notes
References
Further reading
* Albright, W. F., "The Amorite Form of the Name Ḫammurabi", The American Journal of Semitic Languages and Literatures, vol. 38, no. 2, pp. 140–41, 1922 * Bailey, Lloyd R, "Israelite 'Ēl Šadday and Amorite Bêl Šadê", Journal of Biblical Literature, vol. 87, no. 4, pp. 434–38, 1968 * Burke, S.,Entanglement, the Amorite koine, and the Amorite Cultures in the Levant
, Aram Society for the Syro-Mesopotamian Studies 26, pp. 357–373, 2014 * Burke, Aaron A., "Amorites and Canaanites: Memory, Tradition, and Legacy in Ancient Israel and Judah", The Ancient Israelite World. Routledge, pp. 523–536, 2022 * George, Andrew, and Manfred Krebernik, "Two Remarkable Vocabularies: Amorite-Akkadian Bilinguals!", Revue d'assyriologie et d'archéologie orientale 116.1, pp. 113–166, 2022 * Højlund, Flemming,
The Formation Of The Dilmun State And The Amorite Tribes
, Proceedings of the Seminar for Arabian Studies, vol. 19, pp. 45–59, 1989 * Homsher, R. and Cradic, M., "The Amorite Problem: Resolving a Historical Dilemma", Levant 49, pp. 259–283, 2018
Howard, J. Caleb, "Amorite Names through Time and Space", Journal of Semitic Studies, 2023 * Streck, Michael P., ''Das amurritische Onomastikon der altbabylonischen Zeit. Band 1: Die Amurriter, die onomastische Forschung, Orthographie und Phonologie, Nominalmorphologie'', Ugarit-Verlag, 2000 * Torczyner, H. Tur-Sinai, "The Amorite and the Amurrû of the Inscriptions", The Jewish Quarterly Review, vol. 39, no. 3, pp. 249–258, 1949 * Vidal, Jordi,
Prestige Weapons in an Amorite Context
, Journal of Near Eastern Studies, vol. 70, no. 2, pp. 247–52, 2011 * Wallis, Louis,
Amorite Influence in the Religion of the Bible
, The Biblical World, vol. 45, no. 4, pp. 216–23, 1915 * Wasserman, Nathan, and Yigal Bloch, "The Amorites: A Political History of Mesopotamia in the Early Second Millennium BCE", The Amorites, Brill, 2023 * Zeynivand, Mohsen,
A Cylinder Seal With An Amorite Name From Tepe Musiyan, Deh Luran Plain
, Journal of Cuneiform Studies, vol. 71, pp. 77–83, 2019
External links
Cryptic lost Canaanite language decoded on 'Rosetta Stone'-like tablets – LiveScience – Tom Metcalfe – 30 January 2023
Two 3,800-year-old Cuneiform Tablets Found in Iraq Give First Glimpse of Hebrew Precursor – Haaretz – Jan 20, 2023
Amorites
in the ''Jewish Encyclopedia'' {{Use dmy dates, date=April 2017 Amorites, Ancient Levant Ancient Syria States and territories established in the 3rd millennium BC States and territories disestablished in the 18th century BC States and territories disestablished in the 16th century BC Canaan Hebrew Bible nations Semitic-speaking peoples Ancient peoples of the Near East 21st-century BC establishments Giants in the Hebrew Bible