American Steam Carriage Company on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Norris Locomotive Works was a
 The company was started in 1832 as the American Steam Carriage Company by William Norris (1802–1867) and Major Stephen H. Long (1784–1864), a military topographical engineer and explorer. The two men had experimented with steam engine building for years and, as early as 1829, designed a locomotive to burn
The company was started in 1832 as the American Steam Carriage Company by William Norris (1802–1867) and Major Stephen H. Long (1784–1864), a military topographical engineer and explorer. The two men had experimented with steam engine building for years and, as early as 1829, designed a locomotive to burn
 One of the most historic events in railroading history occurred on July 10, 1836, when the Norris Brothers ran a test of a 4-2-0 locomotive on the Belmont Inclined Plane of the Philadelphia and Columbia Railroad The two-track incline ran from the
One of the most historic events in railroading history occurred on July 10, 1836, when the Norris Brothers ran a test of a 4-2-0 locomotive on the Belmont Inclined Plane of the Philadelphia and Columbia Railroad The two-track incline ran from the  The Norris Locomotive Works sold many locomotives overseas, as noted above. This company was the first American exporter of locomotives—and perhaps of large mechanical devices generally. As early as 1840, thirty percent of the firm's production until then had been for foreign markets. Norris machines operated in
The Norris Locomotive Works sold many locomotives overseas, as noted above. This company was the first American exporter of locomotives—and perhaps of large mechanical devices generally. As early as 1840, thirty percent of the firm's production until then had been for foreign markets. Norris machines operated in
"Locomotive Steam Engine of William Norris, Philadelphia"
(1838), a tri-lingual pamphlet produced by Norris with accounts of the ''George Washington'' trials (at the Internet Archive) {{Authority control 1832 establishments in Pennsylvania American companies established in 1832 Defunct locomotive manufacturers of the United States Industrial buildings and structures in Pennsylvania Industrial buildings completed in 1832 Manufacturing companies established in 1832
steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, Fuel oil, oil or, rarely, Wood fuel, wood) to heat ...
manufacturing company based in Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
, that produced nearly one thousand railroad engines between 1832 and 1866. It was the dominant American locomotive producer during most of that period and the first major exporter of American locomotives, selling its popular 4-2-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, two powered driving wheels on one axle and no trailing wheels. This type of locomotive is often called a ...
engines to railways in Europe and building the first locomotive used in South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
.
History
Origin
 The company was started in 1832 as the American Steam Carriage Company by William Norris (1802–1867) and Major Stephen H. Long (1784–1864), a military topographical engineer and explorer. The two men had experimented with steam engine building for years and, as early as 1829, designed a locomotive to burn
The company was started in 1832 as the American Steam Carriage Company by William Norris (1802–1867) and Major Stephen H. Long (1784–1864), a military topographical engineer and explorer. The two men had experimented with steam engine building for years and, as early as 1829, designed a locomotive to burn anthracite coal
Anthracite, also known as hard coal and black coal, is a hard, compact variety of coal that has a submetallic lustre. It has the highest carbon content, the fewest impurities, and the highest energy density of all types of coal and is the highe ...
. Norris and Long also built an engine called the ''Black Hawk'', which performed with partial success on the Boston and Providence Railroad
The Boston and Providence Railroad was a railroad company in the states of Massachusetts and Rhode Island which connected its namesake cities. It opened in two sections in 1834 and 1835 - one of the Rail transportation in the United States, fir ...
and the Philadelphia and Columbia Railroad
Philadelphia and Columbia Railroad (P&CR) (1834) was one of the earliest commercial railroads in the United States, running from Philadelphia to Columbia, Pennsylvania, Columbia, Pennsylvania, it was built by the Pennsylvania Canal Commission in l ...
in the early 1830s. Long later left the firm and William Norris was joined by his brother Septimus, who patented several locomotive-related inventions. The two brothers reformed the enterprise into the Norris Locomotive Works.
Growth and success

 One of the most historic events in railroading history occurred on July 10, 1836, when the Norris Brothers ran a test of a 4-2-0 locomotive on the Belmont Inclined Plane of the Philadelphia and Columbia Railroad The two-track incline ran from the
One of the most historic events in railroading history occurred on July 10, 1836, when the Norris Brothers ran a test of a 4-2-0 locomotive on the Belmont Inclined Plane of the Philadelphia and Columbia Railroad The two-track incline ran from the Schuylkill River
The Schuylkill River ( , ) is a river in eastern Pennsylvania. It flows for U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map(). accessed April 1, 2011. from Pottsville, Pennsylvania, Pottsville ...
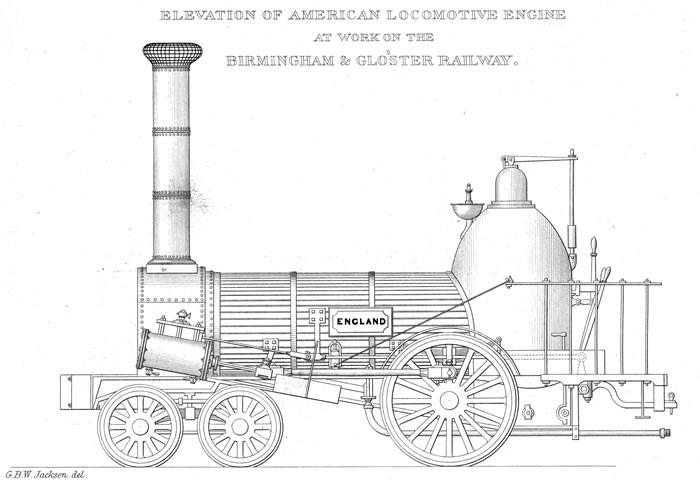
for towards present-day Belmont Avenue, rising one foot in 15 for a total of . Named ''George Washington'', the engine hauled a load of , including 24 people riding on the tender and a freight car up the grade at . This engine, the first in the world to ascend a hill by its own power, proved that a steam locomotive could climb a grade while pulling a load. So notable was this accomplishment that reports published in engineering journals emphatically doubted its occurrence. A second, more formal trial with an even greater load proved the engine's capabilities on July 19, 1836. Norris 4-2-0s were exported to England for the Lickey Incline
The Lickey Incline, south of Birmingham, is the steepest sustained main-line railway incline in Great Britain. The climb is a gradient of 1 in 37.7 (2.65% or 26.5‰ or 1.52°) for a continuous distance of two miles (3.2 km). Constructed o ...
about 1842, English manufacturers having declined to supply.
Norris built the ''Lafayette'' for the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was the oldest railroads in North America, oldest railroad in the United States and the first steam engine, steam-operated common carrier. Construction of the line began in 1828, and it operated as B&O from 1830 ...
the following year based on plans of the ''George Washington''. Named after the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
hero Marquis de Lafayette
Marie-Joseph Paul Yves Roch Gilbert du Motier de La Fayette, Marquis de La Fayette (; 6 September 1757 – 20 May 1834), known in the United States as Lafayette (), was a French military officer and politician who volunteered to join the Conti ...
, this new 4-2-0 engine was the B&O's first locomotive to feature a leading truck and may have been the first standardized production model locomotive in the entire world. Innovations included positioning of cylinder
A cylinder () has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infinite ...
s outside and adjacent to the smokebox
A smokebox is one of the major basic parts of a steam locomotive exhaust system. Smoke and hot gases pass from the firebox through tubes where they pass heat to the surrounding water in the boiler. The smoke then enters the smokebox, and is ...
with pistons connecting to the face of the drive wheels instead of a crank axle, the four-wheel swiveling pilot truck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport freight, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame construct ...
, inside bar frame
A locomotive frame is the structure that forms the backbone of the railway locomotive, giving it strength and supporting the superstructure elements such as a Cab (locomotive), cab, locomotive boiler, boiler or bodywork. The vast majority of loc ...
support, and placement of the two drivers ahead of the firebox (this supposedly offered greater power output as more of the locomotive's weight rested on the drivers and therefore increased tractive effort). The ''Lafayette'' established the configuration that American steam locomotives would follow until the end of the steam era.
In 1847, the Norris Works built the first ten-wheel locomotive in America: the ''Chesapeake''. Operated by the Philadelphia and Reading Railroad
The Reading Company ( ) was a Philadelphia-headquartered railroad that provided passenger and freight transport in eastern Pennsylvania and neighboring states from 1924 until its acquisition by Conrail in 1976.
Commonly called the Reading Railro ...
, this was also the world's first 4-6-0
A 4-6-0 steam locomotive, under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, has four leading wheels on two axles in a leading bogie and six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles with the abs ...
locomotive. It weighed and had cylinders and diameter driving wheel
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons (or turbine, in the case of a steam turbine locomotive). On a conventional, non-articulated locomotive, the driving wheels are all coupled t ...
s. Initially a wood-burning locomotive, the ''Chesapeake'' was converted to burn anthracite coal in 1862, and ran for about another fifteen years. Some authorities claim that Septimus Norris came up with the design, but other sources attribute it to master builder John Brandt of the Erie Railway.
There were nine Norris brothers altogether, six of them had been involved in locomotive building at some point. William Norris' enterprise was renamed Norris Brothers when brothers Richard and Octavius joined it in 1844 during a period of financial distress and reorganization that included William's gradual departure from the business. The firm later became Richard Norris and Son. Other locomotive factories, operated independently (and unsuccessfully) by various Norris brothers later opened in Lancaster, Pennsylvania
Lancaster ( ) is a city in Lancaster County, Pennsylvania, United States, and its county seat. With a population of 58,039 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, eighth-most populous ci ...
, and Schenectady, New York
Schenectady ( ) is a City (New York), city in Schenectady County, New York, United States, of which it is the county seat. As of the United States Census 2020, 2020 census, the city's population of 67,047 made it the state's ninth-most populo ...
.
England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
, France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, the states of the German Confederation
The German Confederation ( ) was an association of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states in Central Europe. It was created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as a replacement of the former Holy Roman Empire, which had been dissolved ...
(including Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
, Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
and Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ...
), Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
, Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, Cuba
Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island country, comprising the island of Cuba (largest island), Isla de la Juventud, and List of islands of Cuba, 4,195 islands, islets and cays surrounding the main island. It is located where the ...
and South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
('' The Copiapó'', built in 1850 for Chilean Railroad, was the first locomotive in all of South America). These engines influenced contemporary and subsequent locomotive design in many of these countries.
William Norris had several large-scale operating models constructed as presentation pieces to rulers of several nations. Such sovereigns included Tsar Nicholas I
Nicholas I, group=pron (Russian language, Russian: Николай I Павлович; – ) was Emperor of Russia, List of rulers of Partitioned Poland#Kings of the Kingdom of Poland, King of Congress Poland, and Grand Duke of Finland from 18 ...
of Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
and King Louis Philippe I
Louis Philippe I (6 October 1773 – 26 August 1850), nicknamed the Citizen King, was King of the French from 1830 to 1848, the penultimate monarch of France, and the last French monarch to bear the title "King". He abdicated from his throne ...
of France, who was so pleased with his model that he gave Norris a gold medal and a gold box. A quarter-sized 4-4-0
4-4-0, in the Whyte notation, denotes a steam locomotive with a wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles (usually in a leading bogie), four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and no trailing wheels.
First built in the ...
locomotive and tender were built for Commodore Matthew C. Perry
Matthew Calbraith Perry (April 10, 1794 – March 4, 1858) was a United States Navy officer who commanded ships in several wars, including the War of 1812 and the Mexican–American War. He led the Perry Expedition that Bakumatsu, ended Japan' ...
to deliver as a gift on his second expedition to Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
in 1854. A small circular railway - which also included a miniature passenger car made by another manufacturer and a mile of track — was set up near Yokohama
is the List of cities in Japan, second-largest city in Japan by population as well as by area, and the country's most populous Municipalities of Japan, municipality. It is the capital and most populous city in Kanagawa Prefecture, with a popu ...
, making it the first railway built in the Far East
The Far East is the geographical region that encompasses the easternmost portion of the Asian continent, including North Asia, North, East Asia, East and Southeast Asia. South Asia is sometimes also included in the definition of the term. In mod ...
.
Demise
Richard Norris and Son was the largest locomotive maker in the United States, if not the world, during the 1850s. Employing many hundreds of men, the factory consisted of some ten buildings spread over several city blocks at what is now the campus of theCommunity College of Philadelphia
The Community College of Philadelphia (CCP) is a public community college with campuses throughout Philadelphia. The college was founded in 1965 and is accredited by the Middle States Commission on Higher Education. It offers over 100 associate ...
. The firm reached its peak in 1857–58, after which time, the Norris family seems to have lost interest in the business. Manufacturing quality and output fell during the Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
and the plant closed in 1866, although deliveries continued for a year or two.
The firm's factory complex was located in the area around 17th and Hamilton Streets in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
, on several acres of what had once been the famous Bush Hill estate of Andrew Hamilton, used as a hospital during the 1793 Philadelphia yellow fever epidemic
During the 1793 yellow fever epidemic in Philadelphia, 5,000 or more people were listed in the register of deaths between August 1st and November 9th. The vast majority of them died of yellow fever, making the epidemic in the city of 50,000 peo ...
. The site was near the right-of-way of the Philadelphia and Columbia Railroad
Philadelphia and Columbia Railroad (P&CR) (1834) was one of the earliest commercial railroads in the United States, running from Philadelphia to Columbia, Pennsylvania, Columbia, Pennsylvania, it was built by the Pennsylvania Canal Commission in l ...
, which crossed through Philadelphia just north of Callowhill Street. This route was later owned by the Reading Railroad
The Reading Company ( ) was a Philadelphia-headquartered railroad that provided passenger and freight transport in eastern Pennsylvania and neighboring states from 1924 until its acquisition by Conrail in 1976.
Commonly called the Reading Railr ...
.
The property lay idle until the adjacent Baldwin Locomotive Works
The Baldwin Locomotive Works (BLW) was an American manufacturer of railway locomotives from 1825 to 1951. Originally located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, it moved to nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania, Eddystone in the early 20th century. The com ...
, which had surpassed Norris as the largest locomotive builder in the U.S., acquired the site in 1873. The Norris buildings stood until 1896, when part of the property was cleared for construction of the third United States Mint
The United States Mint is a bureau of the United States Department of the Treasury, Department of the Treasury responsible for producing coinage for the United States to conduct its trade and commerce, as well as controlling the movement of bull ...
in Philadelphia. Still standing, that building has been adapted as part of the Community College of Philadelphia. No trace of either the Norris or Baldwin factories remains in that part of Philadelphia.
Notes
References
* Brian Reed, ''The Norris Locomotives'', LOCO Profile 11, Volume 1 (Windsor, Berkshire, England: Profile Publications Ltd., 1971) * John H. White, Jr., ''Once the Greatest of Builders: The Norris Locomotive Works'', Bulletin 150 (Westford, MA: Railway & Locomotive Hist. Soc., Spring 1984).External links
"Locomotive Steam Engine of William Norris, Philadelphia"
(1838), a tri-lingual pamphlet produced by Norris with accounts of the ''George Washington'' trials (at the Internet Archive) {{Authority control 1832 establishments in Pennsylvania American companies established in 1832 Defunct locomotive manufacturers of the United States Industrial buildings and structures in Pennsylvania Industrial buildings completed in 1832 Manufacturing companies established in 1832