Ambrym Island on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ambrym is a
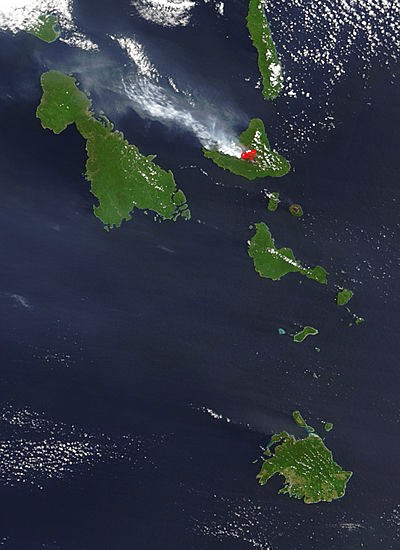 Ambrym is a large
Ambrym is a large

volcanic
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often fo ...
island
An island or isle is a piece of land, distinct from a continent, completely surrounded by water. There are continental islands, which were formed by being split from a continent by plate tectonics, and oceanic islands, which have never been ...
in Malampa Province
Malampa is one of the six provinces of Vanuatu, located in the center of the country. It consists of three main islands: Malakula, Ambrym and Paama, and takes its name from the first syllable of their names. It includes a number of other islands � ...
in the archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands. An archipelago may be in an ocean, a sea, or a smaller body of water. Example archipelagos include the Aegean Islands (the o ...
of Vanuatu
Vanuatu ( or ; ), officially the Republic of Vanuatu (; ), is an island country in Melanesia located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is east of northern Australia, northeast of New Caledonia, east o ...
. Volcanic activity on the island includes lava lake
Lava lakes are large volumes of molten lava, usually basaltic, contained in a volcanic vent, crater, or broad depression. The term is used to describe both lava lakes that are wholly or partly molten and those that are solidified (sometim ...
s in two craters near the summit.
Etymology
Ambrym (also known as ''Ambrin'', ''"ham rim"'' in the Ranon language) was allegedly named byCaptain Cook
Captain James Cook (7 November 1728 – 14 February 1779) was a British Royal Navy officer, explorer, and cartographer famous for his three voyages of exploration to the Pacific and Southern Oceans, conducted between 1768 and 1779. He complet ...
, who is said to have anchored off there in 1774. In fact, his expedition never touched Ambrym.
Geography
Located near the center of theVanuatu
Vanuatu ( or ; ), officially the Republic of Vanuatu (; ), is an island country in Melanesia located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is east of northern Australia, northeast of New Caledonia, east o ...
an archipelago, Ambrym is roughly triangular in shape, about wide. With of surface area, it is the fifth largest island in the country. The summit at the centre of the island is dominated by a desert-like caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcanic eruption. An eruption that ejects large volumes of magma over a short period of time can cause significant detriment to the str ...
, which covers an area of . With the exception of human settlements, the rest of the island is covered by a dense jungle.
Important Bird Area
The western part of the island, comprising 17,605 ha of forest, together with gardens around habitation, has been recognised as anImportant Bird Area
An Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) is an area identified using an internationally agreed set of criteria as being globally important for the conservation of bird populations.
IBA was developed and sites are identified by BirdLife Int ...
(IBA) by BirdLife International
BirdLife International is a global partnership of non-governmental organizations that strives to conserve birds and their habitats. BirdLife International's priorities include preventing extinction of bird species, identifying and safeguarding i ...
because it supports populations of Vanuatu megapode
The Vanuatu megapode or Vanuatu scrubfowl (''Megapodius layardi'') is a species of bird in the family Megapodiidae. It was formerly known as the New Hebrides scrubfowl. It is found only in Vanuatu. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical ...
s, Tanna fruit dove
The Tanna fruit dove (''Ptilinopus tannensis'') is a species of bird in the family Columbidae. It is endemic to Vanuatu.
Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forest, subtropical or tropical moist montane forest, and hea ...
s, red-bellied fruit doves, grey-eared honeyeaters, cardinal myzomela
The cardinal myzomela is a species of passerine bird in the honeyeater family Meliphagidae. It is named for the scarlet color of the male. It is found in New Caledonia, Solomon Islands, and Vanuatu. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropica ...
s, fan-tailed gerygone
The fan-tailed gerygone (''Gerygone flavolateralis'') is a species of bird in the family Acanthizidae. It is found in New Caledonia and Vanuatu. The Rennell gerygone (''G. citrina'') of the Solomon Islands was formerly considered conspecific, b ...
s, long-tailed trillers, streaked fantails, Melanesian flycatcher
The Melanesian flycatcher (''Myiagra caledonica'') is a species of bird in the monarch-flycatcher family Monarchidae. The species is found on islands in Melanesia.
Taxonomy and systematics
It is closely related to the Vanikoro flycatcher. Alter ...
s, buff-bellied monarchs and Vanuatu white-eyes.
Volcanology
 Ambrym is a large
Ambrym is a large basaltic
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron ( mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% ...
volcano with a 12-km-wide caldera, and is one of the most active volcanoes of the New Hebrides
New Hebrides, officially the New Hebrides Condominium () and named after the Hebrides in Scotland, was the colonial name for the island group in the South Pacific Ocean that is now Vanuatu. Native people had inhabited the islands for three th ...
volcanic arc. The caldera is the result of a huge Plinian eruption
Plinian eruptions or Vesuvian eruptions are volcanic eruptions characterized by their similarity to the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD, which destroyed the ancient Roman cities of Herculaneum and Pompeii. The eruption was described in a le ...
, which took place around AD 50
__NOTOC__
AD 50 ( L) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time it was known in Europe as the Year of the Consulship of Vetus and Nerullinus (or, less frequently, year 803 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denominati ...
. Its explosive force is rated 6, the third highest in the Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums, Education center, education and Research institute, research centers, created by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. government "for the increase a ...
's Volcanic Explosivity Index
The volcanic explosivity index (VEI) is a scale used to measure the size of explosive volcanic eruptions. It was devised by Christopher G. Newhall of the United States Geological Survey and Stephen Self in 1982.
Volume of products, eruption c ...
ranks of the largest volcanic explosions in recent geological history.
While at higher elevations cinder cones predominate, the western tip of the island is characterized by a series of basaltic
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron ( mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% ...
tuff
Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock co ...
rings, of which the largest is about in diameter. These were produced by phreatic eruptions
A phreatic eruption, also called a phreatic explosion, ultravulcanian eruption or steam-blast eruption, occurs when magma heats ground water or surface water. The extreme temperature of the magma (anywhere from ) causes near-instantaneous evap ...
when magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma (sometimes colloquially but incorrectly referred to as ''lava'') is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also ...
contacted the water table
The water table is the upper surface of the phreatic zone or zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is where the pores and fractures of the ground are saturated with groundwater, which may be fresh, saline, or brackish, depending on the loc ...
and water-saturated sediments along the coast. The massive, 1900-year-old, × caldera is the site of two active volcanic cones, Benbow and Marum (also spelled Maroum). Mount Benbow was named after English Admiral John Benbow
Vice-Admiral John Benbow (10 March 16534 November 1702) was an English Royal Navy officer. He joined the Navy in 1678, seeing action against Barbary pirates before leaving to join the Merchant Navy in which Benbow served until the 1688 Glorio ...
(1653–1702) by Captain Cook.
Several times a century, Ambrym volcano has destructive eruptions. Mount Benbow last erupted explosively in 1913, destroying the mission hospital at Dip Point. Volcanic gas emissions from this volcano are measured by a Multi-Component Gas Analyzer System
A multi-component gas analyzer system (Multi-GAS) is an instrument package used to take real-time high-resolution measurements of volcanic gases. A Multi-GAS package includes an infrared spectrometer for carbon dioxide, CO2, two electrochemical sen ...
, which detects pre-eruptive degassing of rising magmas, improving prediction of volcanic activity
Prediction of volcanic activity, and volcanic eruption forecasting, is an interdisciplinary monitoring and research effort to predict the time and severity of a volcano's eruption. Of particular importance is the prediction of hazardous eruptions ...
.
In March 2017, Google added Marum crater with its lava lakes to Google Streetview. Since the last fissure eruption on 16 Dec 2018, the lava lake has disappeared.
Demographics
With the neighbouring island ofMalakula
Malakula, also spelled Malekula, is the second-largest island in the nation of Vanuatu, formerly the New Hebrides, in Melanesia, a region of the Pacific Ocean.
Location
Malakula is separated from the islands of Espiritu Santo and Malo Island, Ma ...
and a few smaller islands, Ambrym forms Malampa Province
Malampa is one of the six provinces of Vanuatu, located in the center of the country. It consists of three main islands: Malakula, Ambrym and Paama, and takes its name from the first syllable of their names. It includes a number of other islands � ...
. The population of 7,275 inhabitants lives mainly off coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (biology), family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, ...
plantations
Plantations are farms specializing in cash crops, usually mainly planting a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Plantations, centered on a plantation house, grow crops including cotton, cannabis, tobacco ...
in the three corners of the island.

Languages
Like many islands in Vanuatu, Ambrym has its ownAustronesian languages
The Austronesian languages ( ) are a language family widely spoken throughout Maritime Southeast Asia, parts of Mainland Southeast Asia, Madagascar, the islands of the Pacific Ocean and Taiwan (by Taiwanese indigenous peoples). They are spoken ...
.
In the north:
* Fanbyak
* North Ambrym language
In the southeast:
* Vatlongos ( Southeast Ambrym language)
In the southwest:
* Daakie
* Daakaka
* Dalkalaen
* Lonwolwol
* Raljago
Towns and villages
Southwest
* Fali, Craig Cove, Baiap, Sesivi, Port Vato, Bwele, Lalinda, Tow, Yaotilie, Sanesup, Emiotungan, Maranata and PelibetakeverSoutheast
* Maat, Paamal, Toak, Uléi, Utas, Tavéak, Asé, Pawé, Saméo, Endu, Pahakol and BeneboNorth
* Ranuetlam, Ranon, Olal, Fanla, Linboul, Wilit, Lonwara, Fona, Nebul and MeghamTourism
Tourists are attracted by Ambrym's active volcanoes, tropical vegetation, and the customs of the local villagers. They stay in traditional bungalows, as there are no hotels on the island.Transportation
The island is served by two airports, Ulei Airport in the southeast and Craig Cove Airport in the southwest.Popular culture
Ambrym is featured in the 2016Werner Herzog
Werner Herzog (; né Stipetić; born 5 September 1942) is a German filmmaker, actor, opera director, and author. Regarded as a pioneer of New German Cinema, his films often feature ambitious protagonists with impossible dreams, people with unusu ...
documentary, '' Into the Inferno''.
Episode two of the BBC documentary "Into the Volcano" hosted by Kate Humble
Katherine Mary Humble (born 12 December 1968) is an English television presenter and narrator, mainly working for the BBC, specialising in wildlife and science programmes. Humble served as president of the Royal Society for the Protection of Bir ...
was filmed on Ambrym in 2014.
References
External links
* * * * {{Authority control Islands of Vanuatu Malampa Province Shield volcanoes of Vanuatu Mountains of Vanuatu Subduction volcanoes Active volcanoes VEI-6 volcanoes Calderas of Oceania Pyroclastic shields Lava lakes Important Bird Areas of Vanuatu